22.1.3 Lab – Troubleshoot uRPF Answers
Lab – Troubleshoot uRPF (Answers Version)
Answers Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
Topology
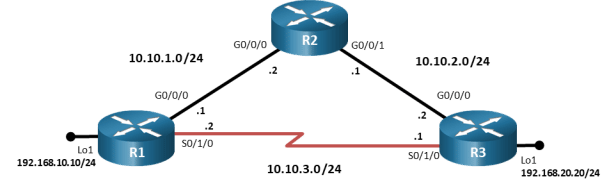
Addressing Table
|
Device |
Interface |
IP Address |
Subnet Mask |
|
|
R1 |
G0/0/0 |
10.10.1.1 |
255.255.255.0 |
|
|
R1 |
S0/1/0 |
10.10.3.2 |
255.255.255.0 |
|
|
R1 |
Lo1 |
192.168.10.10 |
255.255.255.0 |
|
|
R2 |
G0/0/0 |
10.10.1.2 |
255.255.255.0 |
|
|
R2 |
G0/0/1 |
10.10.2.1 |
255.255.255.0 |
|
|
R3 |
G0/0/0 |
10.10.2.2 |
255.255.255.0 |
|
|
R3 |
S0/1/0 |
10.10.3.1 |
255.255.255.0 |
|
|
R3 |
Lo1 |
192.168.20.20 |
255.255.255.0 |
|
Objectives
Troubleshoot issues related to the configuration and operation of uRPF.
Background / Scenario
uRPF is a security feature that helps limit or even eliminate spoofed IP packets on a network. In this lab, you will be loading configurations with intentional errors onto the network. Your tasks are to FIND the error(s), document your findings and the command(s) or method(s) used to fix them, FIX the issue(s) presented here, and then test the network to ensure both of the following conditions are met:
1)The trouble ticket has been resolved
2)The network is fully functioning
Note: The routers used with CCNP hands-on labs are Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 (universalk9 image). Other routers and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and the output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of the lab for the correct interface identifiers.
Note: Make sure that the devices have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure, contact your instructor.
Answers Note: Refer to the Answers Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices.
Required Resources
- 3 Routers (Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- 1 PC (Choice of operating system with a terminal emulation program installed)
- Ethernet and serial cables as shown in the topology
Instructions
Part 1:Trouble Ticket 22.1.3.1
Scenario:
As a security measure, uRPF was implemented on router R1 to ensure a malicious actor could not circumvent access control restrictions using a spoofed IP address. A fellow colleague was tasked with configuring uRPF on R1 to ensure that any spoofed IP packets received are dropped. However, after the implementation, R3’s loopback address has lost connectivity to the 192.168.10.0/24 network.
Step 1:Cable the network as shown in the topology.
- Attach the devices as shown in the topology diagram, and cable as necessary.
- Use the commands listed below to load the configuration files for this trouble ticket:
Answers Note: Commands for uploading the configuration are provided at the end of this document.
|
Device |
Command |
|
R1 |
copy flash:/enarsi/22.1.3.1-r1-config.txt run |
|
R2 |
copy flash:/enarsi/22.1.3.1–r2-config.txt run |
|
R3 |
copy flash:/enarsi/22.1.3.1–r3-config.txt run |
Note: Passwords on all devices are cisco12345.
Step 2:Troubleshoot Ticket.
Troubleshoot and repair the issue. All devices, including loopback addresses, should be able to ping each other.
Step 3:Complete the Ticket.
- After you have fixed the ticket, change the MOTD on Router R1 using the following command:
banner motd # This is $(hostname) FIXED from ticket <ticket number> #
- Verify that uRPF is enabled, configured correctly and all devices, including loopback addresses, can ping each other. Then save the configuration by issuing the wri command.
- Inform your instructor that you are have completed the ticket.
- After the instructor approves your solution for this ticket, issue the reset.now privileged EXEC command on each device. This script will clear your configurations and reload the devices.
Answers Notes:
This trouble ticket contains one intentional error:
Static route on R3 is routing traffic for 192.168.10.0/24 from its Lo1 via S0/1/0 instead of G0/0/0. This is triggering uRPF to drop packets because the packets are being received on an unexpected interface.
The command to fix these errors should be:
R3(config)# no ip route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 s0/1/0
Router Interface Summary Table
|
Router Model |
Ethernet Interface #1 |
Ethernet Interface #2 |
Serial Interface #1 |
Serial Interface #2 |
|
1800 |
Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) |
Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) |
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
|
1900 |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) |
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
|
2801 |
Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) |
Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) |
Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) |
Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
|
2811 |
Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) |
Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) |
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
|
2900 |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) |
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
|
4221 |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) |
Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) |
Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
|
4300 |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) |
Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) |
Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface.
End of document
Uploading Configuration Files
Use the commands below to create the configuration files on the lab devices for each trouble ticket in this lab. The TCL script commands help create and copy the configurations. However, the configuration commands could also be copied and pasted directly into global config mode on each device. Simply remove the TCL script commands, enter the enable and configure t commands on the device, and copy and paste the configuration commands.
Important: The device requires a folder in flash named enarsi. Use the dir command to verify. If the folder is missing, then create it using the mkdir flash:/enarsi privileged EXEC command. For all switches, make sure the vlan.dat file is set to the default. Use the delete vlan.dat privileged EXEC command, if necessary.
Reset scripts
These TCL scripts will completely clear and reload the device in preparation for the next ticket. Copy and paste the appropriate script to the appropriate device.
Router Reset Script
tclsh
puts [ open “flash:/enarsi/reset.tcl” w+ ] {
typeahead “\n”
copy running-config startup-config
typeahead “\n”
erase startup-config
puts “Reloading the router”
typeahead “\n”
reload
}
tclquit
R1 Configuration File Scripts
!R1 – Trouble Ticket #1
tclsh
puts [ open “flash:/enarsi/22.1.3.1-r1-config.txt” w+ ] {
hostname R1
enable secret cisco12345
no ip domain lookup
banner motd # R1 Trouble ticket 22.1.3.1 #
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
exit
interface g0/0/0
ip address 10.10.1.1 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
ip verify unicast source reachable-via rx
exit
interface s0/1/0
ip address 10.10.3.2 255.255.255.0
ip verify unicast source reachable-via rx
exit
interface lo1
ip address 192.168.10.10 255.255.255.0
exit
router eigrp 1
network 10.10.1.0 255.255.255.0
network 10.10.3.0 255.255.255.0
network 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0
exit
alias exec reset.now tclsh flash:/enarsi/reset.tcl
end
}
tclquit
R2 Configuration File Scripts
!R2 – Trouble Ticket #1
tclsh
puts [ open “flash:/enarsi/22.1.3.1-r2-config.txt” w+ ] {
hostname R2
enable secret cisco12345
no ip domain lookup
banner motd # R2 Trouble ticket 22.1.3.1 #
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
exit
interface g0/0/0
ip address 10.10.1.2 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
exit
interface g0/0/1
ip address 10.10.2.1 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
exit
router eigrp 1
network 10.10.1.0 255.255.255.0
network 10.10.2.0 255.255.255.0
exit
alias exec reset.now tclsh flash:/enarsi/reset.tcl
end
}
tclquit
R3 Configuration File Scripts
!R3 – Trouble Ticket #1
tclsh
puts [ open “flash:/enarsi/22.1.3.1-r3-config.txt” w+ ] {
hostname R3
enable secret cisco12345
no ip domain lookup
banner motd # R3 Trouble ticket 22.1.3.1 #
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
exit
interface g0/0/0
ip address 10.10.2.2 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
exit
interface s0/1/0
ip address 10.10.3.1 255.255.255.0
exit
interface lo1
ip address 192.168.20.20 255.255.255.0
exit
router eigrp 1
network 10.10.2.0 255.255.255.0
network 10.10.3.0 255.255.255.0
network 192.168.20.0 255.255.255.0
exit
ip route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 s0/1/0
alias exec reset.now tclsh flash:/enarsi/reset.tcl
end
}
tclquit