24.1.3 Lab – Implement SNMP and Syslog Answers
| CCNP ENCOR v8 & 8.01 | |
| Final Exam Answers | |
| This Chapters 22 - 24 | |
| Chapters 22 - 24 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Chapters 22 - 24 Quizzes Answers | Online Test |
| Next Chapters 25 - 26 | |
| Chapters 25 - 26 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Chapters 25 - 26 Quizzes Answers | Online Test |
| CCNP ENCOR Packet Tracer Activity Files Answers | |
| 24.2.1 Packet Tracer – Configure Syslog and NTP Answers | |
| 24.2.2 Packet Tracer – Logging from Multiple Sources Answers | |
| CCNP ENCOR Student Lab Source Files Answers | |
| 24.1.2 Lab – Use Connectivity Tests and Debug for Network Assurance Answers | |
| 24.1.3 Lab – Implement SNMP and Syslog Answers | |
| 24.1.4 Lab – Implement Flexible Netflow Answers | |
| 24.1.5 Lab – Implement SPAN Technologies Answers | |
| 24.1.6 Lab – Implement IP SLA Answers | |
Lab – Implement SNMP and Syslog (Answers Version)
Answers Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
Topology

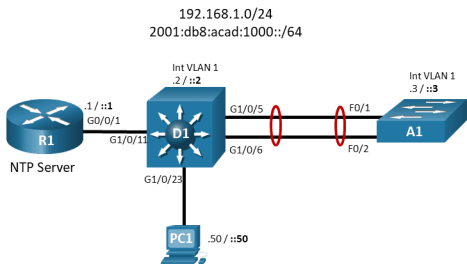
Addressing Table
|
Device |
Interface |
IP Address |
3IPv6 Address |
IPv6 Link Local |
|
R1 |
G0/0/1 |
192.168.1.1/24 |
2001:db8:acad:1000::1/64 |
fe80::1:1 |
|
D1 |
VLAN 1 |
192.168.1.2/24 |
2001:db8:acad:1000::2/64 |
fe80::d1:1 |
|
A1 |
VLAN 1 |
192.168.1.3/24 |
2001:db8:acad:1000::3/64 |
fe80::a1:1 |
|
PC1 |
NIC |
192.168.1.50/24 |
2001:db8:acad:1000::50/64 |
EUI-64 |
Objectives
Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings and Interface Addressing
Part 2: Configure and Verify SNMP
Part 3: Configure and Verify Syslog
Background / Scenario
Network Monitoring is critical to security and troubleshooting tasks. As your network grows and evolves, centralized monitoring becomes even more important. SNMP is a protocol that allows you to remotely monitor a wide range of settings and counters, be alerted when there are changes, and even remotely make configuration changes. Syslog is the log collector protocol. All of your devices should use Syslog to report device activity to a central location for correlation and records keeping. In this lab, you will configure both of these extremely important protocols.
Note: This lab is an exercise in configuring options available for SNMP and Syslog and does not necessarily reflect network troubleshooting best practices.
Note: The routers used with CCNP hands-on labs are Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 (universalk9 image). The switches used in the labs are Cisco Catalyst 3650s with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 (universalk9 image) and Cisco Catalyst 2960s with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) (lanbasek9 image). Other routers, switches, and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and the output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of the lab for the correct interface identifiers.
Note: Make sure that the switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure, contact your instructor.
Note: The default Switch Database Manager (SDM) template on a Catalyst 2960 does not support IPv6. You must change the default SDM template to the dual-ipv4-and-ipv6 default template using the sdm prefer dual-ipv4-and-ipv6 default global configuration command. Changing the template will require a reboot.
Answers Note: Refer to the Answers Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices.
Required Resources
- 1 Router (Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
- 1 Switch (Cisco 3650 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
- 1 Switch (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
- 1 PC (Choice of operating system with a terminal emulation program and packet capture utility installed)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Part 1:Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings and Interface Addressing
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings and interface addressing on routers.
Step 1:Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Attach the devices as shown in the topology diagram, and cable as necessary.
Step 2:Configure basic settings for each device.
- Console into each device, enter global configuration mode, and apply the basic settings. The startup configurations for each device are provided below.
Router R1
hostname R1
no ip domain lookup
ipv6 unicast-routing
banner motd # R1, Implement SNMP and Syslog #
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
exit
line vty 0 4
privilege level 15
exec-timeout 0 0
password cisco123
login
exit
interface g0/0/1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address fe80::1:1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:1000::1/64
no shutdown
exit
ntp master 3
end
Switch D1
hostname D1
no ip domain lookup
ipv6 unicast-routing
banner motd # D1, Implement SNMP and Syslog #
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
exit
line vty 0 4
privilege level 15
exec-timeout 0 0
password cisco123
login
exit
interface vlan 1
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address fe80::d1:1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:1000::2/64
no shutdown
exit
ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1
interface g1/0/23
spanning-tree portfast
switchport mode access
no shutdown
exit
interface g1/0/11
spanning-tree portfast
switchport mode access
no shutdown
exit
interface range g1/0/5-6
switchport mode trunk
channel-group 1 mode active
no shutdown
exit
interface range g1/0/1-4, g1/0/7-10, g1/0/12-22, g1/0/24, g1/1/1-4
shutdown
exit
ntp server 192.168.1.1
end
Switch A1
hostname A1
no ip domain lookup
ipv6 unicast-routing
banner motd # A1, Implement SNMP and Syslog #
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
exit
line vty 0 4
privilege level 15
exec-timeout 0 0
password cisco123
login
exit
interface vlan 1
ip address 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address fe80::a1:1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:1000::3/64
no shutdown
exit
ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1
interface range f0/1-2
switchport mode trunk
channel-group 1 mode active
no shutdown
exit
interface range f0/3-24, g0/1-2
shutdown
exit
ntp server 192.168.1.1
end
- Set the clock on each device to UTC time.
- Save the running configuration to startup-config.
- Configure IPv4 and IPv6 addresses on host PC1 as shown in the addressing table.
- Verify that R1, D1, and A1 can successfully ping 192.168.1.50.
Part 2:Configure and Verify SNMP
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange of management information between an agent and a management server. SNMP enables network administrators to monitor and manage network performance, find and solve network problems, and plan for network growth. SNMP management workstations can ask (get) for the value of a specific object identifier (OID) from the management information base (MIB) maintained by SNMP agents. The Manager can also configure (set) specific variable values in an OID. Additionally, the agent can send notifications (traps or informs) when an event occurs, or threshold is reached (an inform is a trap that must be acknowledged by the manager). Like any powerful tool, SNMP can be dangerous if not used properly, and securing the protocol and its uses are critical.
There are three SNMP versions. SNMPv3 is considered the most secure because it offers authentication and encryption, where SNMP versions 1 and 2 offer neither. SNMP access can also be limited using an access control list. SNMPv3 is rather complex to configure, and adoption is not universal. For this lab, we will configure SNMPv2c.
Step 1:Configure access-lists for SNMP.
Configure an access list on each device. This ACL will be used to specify exactly where SNMP get and set messages should be coming from.In this lab, the 192.168.1.0/24 network is the management network, and the SNMP manager is located at 192.168.1.50. Configure this ACL on all three devices:
R1(config)# ip access-list standard NMS-SERVER
R1(config-std-nacl)# permit host 192.168.1.50
R1(config-std-nacl)# exit
Step 2:Configure general SNMP information.
Configure general values to identify the device, its location, and a point of contact. Configure this with appropriate values on all three devices:
D1(config)# snmp-server location D1 Rack 1
D1(config)# snmp-server contact Student 555-1213
D1(config)# snmp-server chassis-id Cisco Device D1
Step 3:Configure SNMP community string.
SNMPv2c using a community string–based authentication. Access can be limited further by using an access list. Create a read-only community named CCNPv8 that is limited by the NMS-SERVER ACL. Configure this on all three devices:
R1(config)# snmp-server community CCNPv8 ro NMS-SERVER
R1(config)# snmp-server community CCNPv8 rw NMS-SERVER
Step 4:Configure SNMP trap receiver.
Configure the NMS server that traps will be sent to. As a part of this command, specific traps or sets of traps to send can be specified. If no traps are specified, this receiver will be forwarded to all traps that are enabled. This particular configuration needs to be coordinated with the network management system and network monitoring requirements for the organization.
Configure 192.168.1.50 as a trap receiver using SNMPv2c and the community CCNPv8. Configure this on all three devices:
A1(config)# snmp-server host 192.168.1.50 version 2c CCNPv8
Step 5:Configure interface index persistence.
Network monitoring systems record throughput and other interface statistics using SNMP polling. Each interface is referenced by its unique index number, which is dynamically assigned by the IOS during bootup. The index of each interface can be determined with the command show snmp mib ifmib ifindex. The dynamic assignment aspect of this can be problematic for documentation. Therefore, it is a good idea to instruct the system to keep a persistent list of interfaces, rather than a dynamic one.The use of this command creates a file stored in NVRAM. Configure this on all three devices:
A1(config)# snmp-server ifindex persist
Step 6:Run Wireshark on PC1.
Before enabling traps to be sent, run Wireshark or another packet capture utility on PC1 and filter the output to display only SNMP packets. This ensures that the packets are actually getting to the SNMP management server.
Step 7:Enable SNMP trap sending.
This final command actually enables the forwarding of traps to the configured trap receivers. As a part of this command, traps can be limited (as they can be in the snmp-server host command). Coordinate this with the network management system and network monitoring requirements for the organization. For this lab, you will simply enable all traps to be sent. Configure this on all three devices:
R1(config)# snmp-server enable traps
Step 8:Verify SNMP configuration.
- To verify that traps are being sent, issue the command debug snmp packets and then enter and exit configuration mode on each device. You should see debug output indicating that a packet was sent each time. It might take a few minutes for each device to start sending traps.
R1# config t
Enter configuration commands, one per line.End with CNTL/Z.
R1(config)#
*Jan 30 16:48:07.628: SNMP: Queuing packet to 192.168.1.50
*Jan 30 16:48:07.628: SNMP: V2 Trap, reqid 1, errstat 0, erridx 0
sysUpTime.0 = 139363
snmpTrapOID.0 = ccmCLIRunningConfigChanged
ccmHistoryRunningLastChanged.0 = 135133
ccmHistoryEventTerminalType.2 = 3
*Jan 30 16:48:07.633: SNMP: Queuing packet to 192.168.1.50
*Jan 30 16:48:07.633: SNMP: V2 Trap, reqid 2, errstat 0, erridx 0
sysUpTime.0 = 139364
snmpTrapOID.0 = ciscoConfigManEvent
ccmHistoryEventCommandSource.3 = 1
ccmHistoryEventConfigSource.3 = 2
ccmHistoryEventConfigDestination.3 = 3
*Jan 30 16:48:07.640: SNMP: Queuing packet to 192.168.1.50
*Jan 30 16:48:07.640: SNMP: V2 Trap
R1(config)#, reqid 3, errstat 0, erridx 0
sysUpTime.0 = 139364
snmpTrapOID.0 = ccmCLIRunningConfigChanged
ccmHistoryRunningLastChanged.0 = 136364
ccmHistoryEventTerminalType.3 = 3
*Jan 30 16:48:07.645: SNMP: Queuing packet to 192.168.1.50
*Jan 30 16:48:07.645: SNMP: V2 Trap, reqid 4, errstat 0, erridx 0
sysUpTime.0 = 139365
snmpTrapOID.0 = ciscoConfigManEvent
ccmHistoryEventCommandSource.4 = 1
ccmHistoryEventConfigSource.4 = 2
ccmHistoryEventConfigDestination.4 = 3
*Jan 30 16:48:07.879: SNMP: Packet sent via UDP to 192.168.1.50
*Jan 30 16:48:08.129: SNMP: Packet sent via UDP to 192.168.1.50
*Jan 30 16:48:08.380: SNMP: Packet sent via UDP to 192.168.1.50
R1(config)#
*Jan 30 16:48:08.631: SNMP: Packet sent via UDP to 192.168.1.50
R1(config)# exit
- Check the Wireshark output on PC1 and you should see the received SNMP messages in the packet capture.
- Issue the undebug all command on each device to turn off the debugs.
Part 3:Configure and Verify Syslog
For a multitude of reasons, logging is a critical part of your network management plan. Cisco devices log to three general facilities: the console, the logging buffer, and a syslog server, if configured. All three of these can be controlled and configured so that the type of log message they record is specific. You have already experienced console logging simply by viewing the messages the device shows you when something happens. The logging buffer has also been collecting that same information. Both of these are local to the device. What you have not done yet is customize those facilities, nor have you configured and used a centralized syslog server, which would collect log messages from each of your devices and keep them so that you can examine and correlate events between different devices.
Before configuring logging, it is important that your devices have synchronized with an NTP server, so that they are all on the same time. This makes sorting and correlating events possible.
You also must have some kind of plan of how to separate and manage the log messages. Your plan must answer the questions “What do we do with all these logs?” and “What messages go where?”.
Syslog messages are separated into eight different severity levels, numbered 0 through 7. The lower numbers indicate a more critical message. The severity levels also have keywords:
|
Severity Level |
Keyword |
Meaning |
|
0 |
emergencies |
System is unusable |
|
1 |
alerts |
Immediate action required |
|
2 |
critical |
Critical conditions |
|
3 |
errors |
Error conditions |
|
4 |
warnings |
Warning conditions |
|
5 |
notifications |
Normal but significant condition |
|
6 |
informational |
Informational messages |
|
7 |
debugging |
Debugging messages |
Note: When you designate a particular severity number as the specific message you want to log, you get that and anything with a smaller severity number. For example, if you set the level to 4, or use the keyword warnings, you capture messages with severity levels 4, 3, 2, 1, and 0.
Before we start configuring logging, let’s look at how logging is configured by default.
R1# show run all | include logging
no logging discriminator
logging exception 4096
no logging count
no logging message-counter log
no logging message-counter debug
logging message-counter syslog
no logging snmp-authfail
no logging userinfo
logging buginf
logging queue-limit 1024
logging queue-limit esm 0
logging queue-limit trap 1024
logging buffered 4096 debugging
logging reload message-limit 1000 notifications
no logging persistent
logging rate-limit console 40 except errors
no logging console guaranteed
logging console debugging
logging monitor debugging
logging cns-events informational
logging on
ethernet cfm logging alarm ieee
ethernet cfm logging alarm cisco
ethernet cfm logging ais
ethernet cfm logging lck
no ipv6 snooping logging packet drop
no ipv6 snooping logging theft
no ipv6 snooping logging resolution-veto
no authentication logging verbose
no mab logging verbose
no cts logging verbose
no dot1x logging verbose
netconf-yang cisco-ia logging ciaauthd-log-level error
netconf-yang cisco-ia logging confd-log-level error
netconf-yang cisco-ia logging nes-log-level error
netconf-yang cisco-ia logging onep-log-level error
netconf-yang cisco-ia logging sync-log-level error
logging esm config
logging history size 1
logging history warnings
no logging alarm
logging trap informational
logging delimiter tcp
no logging origin-id
logging facility local7
no logging source-interface
logging server-arp
Focusing on the lines in the output that are highlighted, we see that the router is configured to send debugging (or level 7) messages to the console, monitor, and buffer. We further see that logging is turned on, and that the trap logging level is informational (or level 6), and that the logging facility is number 7. The logging trap and logging facility commands have to deal with what messages are sent to an external server and how the server routes the log messages when they are received (Log facility 7 indicates one of several custom logging facilities, which are typically tied to a specific file).
Step 1:Modify buffered logging.
The logging buffer is set to hold 4096 bytes in a circular buffer and keep log messages at the debugging level and below. 4096 bytes is not quite enough space for a busy system, so you need to change the log buffer size to something larger. We will not be sending debugging messages to the syslog server, so the buffer is the only place those messages are stored. We will leave the logging buffer level at debugging for now and set the size of the buffer to 16384 bytes. Configure this on all three devices:
R1(config)# logging buffered 16384
Step 2:Modify the logging trap level.
The default logging trap level is 7 (keyword: debugging), and we do not really want debug messages in the logs that we will have to archive, so we need to change the logging trap level to 6 (keyword: informational). Configure this on all three devices:
R1(config)# logging trap informational
Step 3:Configure the Syslog server.
Next you need to configure the host address for the syslog server. In this lab, the Syslog server is 192.168.1.50. You should get a message saying logging to 192.168.1.50 has started. Configure this on all three devices:
R1(config)# logging host 192.168.1.50
R1(config)#
*Jan 30 19:35:58.039: %SYS-6-LOGGINGHOST_STARTSTOP: Logging to host 192.168.1.50 port 514 started – CLI initiated
Step 4:Verify the device configuration.
Check the device configuration by issuing the command show logging at the privileged exec prompt.
R1# show logging
Syslog logging: enabled (0 messages dropped, 2 messages rate-limited, 0 flushes, 0 overruns, xml disabled, filtering disabled)
No Active Message Discriminator.
No Inactive Message Discriminator.
Console logging: level debugging, 63 messages logged, xml disabled,
filtering disabled
Monitor logging: level debugging, 0 messages logged, xml disabled,
filtering disabled
Buffer logging:level debugging, 5 messages logged, xml disabled,
filtering disabled
Exception Logging: size (4096 bytes)
Count and timestamp logging messages: disabled
Persistent logging: disabled
No active filter modules.
Trap logging: level informational, 68 message lines logged
Logging to 192.168.1.50(udp port 514, audit disabled,
link up),
3 message lines logged,
0 message lines rate-limited,
0 message lines dropped-by-MD,
xml disabled, sequence number disabled
filtering disabled
Logging Source-Interface:VRF Name:
Log Buffer (16384 bytes):
*Jan 30 19:25:12.331: %SYS-5-LOG_CONFIG_CHANGE: Buffer logging: level debugging, xml disabled, filtering disabled, size (16384)
*Jan 30 19:35:57.038: %SYS-6-LOGGINGHOST_STARTSTOP: Logging to host 192.168.1.50 port 0 CLI Request Triggered
*Jan 30 19:35:58.039: %SYS-6-LOGGINGHOST_STARTSTOP: Logging to host 192.168.1.50 port 514 started – CLI initiated
Jan 30 19:36:49.443: %PKI-6-AUTHORITATIVE_CLOCK: The system clock has been set.
Jan 30 19:37:58.857: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
<output omitted>
Now go to PC1 and reset Wireshark (if you have not already) and change the filter from snmp to syslog. Go into and out of configuration mode on each device, and you should see syslog messages in Wireshark:

Note: The Destination Unreachable messages are host 192.168.1.50, telling the devices that there is not actually a Syslog server running at this IP address.
Router Interface Summary Table
|
Router Model |
Ethernet Interface #1 |
Ethernet Interface #2 |
Serial Interface #1 |
Serial Interface #2 |
|
1800 |
Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) |
Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) |
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
|
1900 |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) |
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
|
2801 |
Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) |
Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) |
Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) |
Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
|
2811 |
Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) |
Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) |
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
|
2900 |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) |
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
|
4221 |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) |
Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) |
Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
|
4300 |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) |
Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) |
Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface.
End of document
Device Configs – Final
Router R1
R1# show run
Building configuration…
Current configuration : 9146 bytes
!
! Last configuration change at 19:58:02 UTC Thu Jan 30 2020
!
version 16.9
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
platform qfp utilization monitor load 80
no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core
!
hostname R1
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
logging buffered 16384
!
no aaa new-model
!
no ip domain lookup
!
!
login on-success log
!
!
subscriber templating
!
!
ipv6 unicast-routing
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
!
crypto pki trustpoint TP-self-signed-3903873913
enrollment selfsigned
subject-name cn=IOS-Self-Signed-Certificate-3903873913
revocation-check none
rsakeypair TP-self-signed-3903873913
!
!
crypto pki certificate chain TP-self-signed-3903873913
certificate self-signed 01
<output omitted>
quit
!
license udi pid ISR4221/K9 sn FGL23313183
no license smart enable
diagnostic bootup level minimal
!
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
!
redundancy
mode none
!
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
no ip address
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
negotiation auto
ipv6 address FE80::1:1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:1000::1/64
!
interface Serial0/1/0
no ip address
shutdown
!
interface Serial0/1/1
no ip address
shutdown
!
ip forward-protocol nd
no ip http server
ip http secure-server
!
!
ip access-list standard NMS-SERVER
permit 192.168.1.50
logging host 192.168.1.50
!
!
snmp-server community CCNPv8 RW NMS-SERVER
snmp-server location R1 Rack 1
snmp-server contact Student 555-1213
snmp-server chassis-id Cisco Device R1
snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkdown linkup coldstart warmstart
snmp-server enable traps vrrp
snmp-server enable traps pfr
snmp-server enable traps flowmon
snmp-server enable traps ds1
snmp-server enable traps entity-perf throughput-notif
snmp-server enable traps ds3
snmp-server enable traps call-home message-send-fail server-fail
snmp-server enable traps tty
snmp-server enable traps eigrp
snmp-server enable traps casa
snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change
snmp-server enable traps ospf errors
snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit
snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific state-change nssa-trans-change
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific state-change shamlink interface
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific state-change shamlink neighbor
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific retransmit
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa
snmp-server enable traps license
snmp-server enable traps smart-license
snmp-server enable traps cef resource-failure peer-state-change peer-fib-state-change inconsistency
snmp-server enable traps memory bufferpeak
snmp-server enable traps config-copy
snmp-server enable traps config
snmp-server enable traps config-ctid
snmp-server enable traps fru-ctrl
snmp-server enable traps entity
snmp-server enable traps event-manager
snmp-server enable traps frame-relay
snmp-server enable traps frame-relay subif
snmp-server enable traps hsrp
snmp-server enable traps ip local pool
snmp-server enable traps pppoe
snmp-server enable traps cpu threshold
snmp-server enable traps syslog
snmp-server enable traps l2tun session
snmp-server enable traps l2tun pseudowire status
snmp-server enable traps atm subif
snmp-server enable traps pki
snmp-server enable traps ethernet evc status create delete
snmp-server enable traps ether-oam
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up mep-down cross-connect loop config
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck mep-missing mep-unknown service-up
snmp-server enable traps entity-state
snmp-server enable traps entity-qfp mem-res-thresh throughput-notif
snmp-server enable traps adslline
snmp-server enable traps vdsl2line
snmp-server enable traps entity-sensor
snmp-server enable traps flash insertion removal lowspace
snmp-server enable traps srp
snmp-server enable traps entity-diag boot-up-fail hm-test-recover hm-thresh-reached scheduled-test-fail
snmp-server enable traps isdn call-information
snmp-server enable traps isdn layer2
snmp-server enable traps isdn chan-not-avail
snmp-server enable traps isdn ietf
snmp-server enable traps cnpd
snmp-server enable traps bfd
snmp-server enable traps ipsla
snmp-server enable traps stpx inconsistency root-inconsistency loop-inconsistency
snmp-server enable traps c3g
snmp-server enable traps LTE
snmp-server enable traps vtp
snmp-server enable traps vlancreate
snmp-server enable traps vlandelete
snmp-server enable traps port-security
snmp-server enable traps firewall serverstatus
snmp-server enable traps aaa_server
snmp-server enable traps dhcp
snmp-server enable traps auth-framework sec-violation
snmp-server enable traps rsvp
snmp-server enable traps ipmulticast
snmp-server enable traps msdp
snmp-server enable traps pim neighbor-change rp-mapping-change invalid-pim-message
snmp-server enable traps mvpn
snmp-server enable traps pimstdmib neighbor-loss invalid-register invalid-join-prune rp-mapping-change interface-election
snmp-server enable traps isis
snmp-server enable traps bgp cbgp2
snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 state-change
snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 errors
snmp-server enable traps nhrp nhs
snmp-server enable traps nhrp nhc
snmp-server enable traps nhrp nhp
snmp-server enable traps nhrp quota-exceeded
snmp-server enable traps ike policy add
snmp-server enable traps ike policy delete
snmp-server enable traps ike tunnel start
snmp-server enable traps ike tunnel stop
snmp-server enable traps ipsec cryptomap add
snmp-server enable traps ipsec cryptomap delete
snmp-server enable traps ipsec cryptomap attach
snmp-server enable traps ipsec cryptomap detach
snmp-server enable traps ipsec tunnel start
snmp-server enable traps ipsec tunnel stop
snmp-server enable traps ipsec too-many-sas
snmp-server enable traps gdoi gm-start-registration
snmp-server enable traps gdoi gm-registration-complete
snmp-server enable traps gdoi gm-re-register
snmp-server enable traps gdoi gm-rekey-rcvd
snmp-server enable traps gdoi gm-rekey-fail
snmp-server enable traps gdoi ks-rekey-pushed
snmp-server enable traps gdoi gm-incomplete-cfg
snmp-server enable traps gdoi ks-no-rsa-keys
snmp-server enable traps gdoi ks-new-registration
snmp-server enable traps gdoi ks-reg-complete
snmp-server enable traps gdoi ks-role-change
snmp-server enable traps gdoi ks-gm-deleted
snmp-server enable traps gdoi ks-peer-reachable
snmp-server enable traps gdoi ks-peer-unreachable
snmp-server enable traps bulkstat collection transfer
snmp-server enable traps alarms informational
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm alarm
snmp-server enable traps rf
snmp-server enable traps transceiver all
snmp-server enable traps vrfmib vrf-up vrf-down vnet-trunk-up vnet-trunk-down
snmp-server host 192.168.1.50 version 2c CCNPv8
snmp ifmib ifindex persist
!
!
control-plane
!
banner motd ^C R1, Implement SNMP and Syslog ^C
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
transport input none
stopbits 1
line aux 0
stopbits 1
line vty 0 4
exec-timeout 0 0
privilege level 15
password cisco123
login
!
ntp master 3
!
!
end
R1#
Switch D1
D1# show run
Building configuration…
Current configuration : 8608 bytes
!
! Last configuration change at 19:58:57 UTC Thu Jan 30 2020
!
version 16.9
no service pad
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core
!
hostname D1
!
!
vrf definition Mgmt-vrf
!
address-family ipv4
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv6
exit-address-family
!
logging buffered 16384
!
no aaa new-model
switch 1 provision ws-c3650-24ps
!
!
no ip domain lookup
!
!
login on-success log
ipv6 unicast-routing
!
!
license boot level ipservicesk9
!
!
diagnostic bootup level minimal
!
spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
!
redundancy
mode sso
!
!
transceiver type all
monitoring
!
!
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-topology-control
description Topology control
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sw-forward
description Sw forwarding, L2 LVX data, LOGGING
class-map match-any system-cpp-default
description Inter FED, EWLC control, EWLC data
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sys-data
description Learning cache ovfl, High Rate App, Exception, EGR Exception, NFLSAMPLED DATA, RPF Failed
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-punt-webauth
description Punt Webauth
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2lvx-control
description L2 LVX control packets
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-forus
description Forus Address resolution and Forus traffic
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast-end-station
description MCAST END STATION
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast
description Transit Traffic and MCAST Data
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2-control
description L2 control
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dot1x-auth
description DOT1X Auth
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-data
description ICMP redirect, ICMP_GEN and BROADCAST
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-stackwise–virt-control
description Stackwise Virtual
class-map match-any non-client-nrt-class
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-routing-control
description Routing control and Low Latency
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-protocol-snooping
description Protocol snooping
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dhcp-snooping
description DHCP snooping
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-system-critical
description System Critical and Gold Pkt
!
policy-map system-cpp-policy
!
!
interface Port-channel1
switchport mode trunk
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
vrf forwarding Mgmt-vrf
no ip address
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
switchport mode trunk
channel-group 1 mode active
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6
switchport mode trunk
channel-group 1 mode active
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/7
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/8
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/9
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/10
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/11
switchport mode access
spanning-tree portfast
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/12
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/13
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/15
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/16
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/17
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/18
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/19
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/20
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/21
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/22
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/23
switchport mode access
spanning-tree portfast
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/24
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/1/1
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/1/2
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/1/3
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/1/4
shutdown
!
interface Vlan1
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address FE80::D1:1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:1000::2/64
!
ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1
ip forward-protocol nd
ip http server
ip http secure-server
!
!
ip access-list standard NMS-SERVER
permit 192.168.1.50
!
!
logging host 192.168.1.50
!
!
snmp-server community CCNPv8 RW NMS-SERVER
snmp-server location D1 Rack 1
snmp-server contact Student 555-1213
snmp-server chassis-id Cisco Device D1
snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkdown linkup coldstart warmstart
snmp-server enable traps flowmon
snmp-server enable traps entity-perf throughput-notif
snmp-server enable traps call-home message-send-fail server-fail
snmp-server enable traps tty
snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change
snmp-server enable traps ospf errors
snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit
snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific state-change nssa-trans-change
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific state-change shamlink interface
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific state-change shamlink neighbor
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific retransmit
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa
snmp-server enable traps eigrp
snmp-server enable traps auth-framework sec-violation
snmp-server enable traps rep
snmp-server enable traps vtp
snmp-server enable traps vlancreate
snmp-server enable traps vlandelete
snmp-server enable traps port-security
snmp-server enable traps license
snmp-server enable traps smart-license
snmp-server enable traps cpu threshold
snmp-server enable traps memory bufferpeak
snmp-server enable traps stackwise
snmp-server enable traps fru-ctrl
snmp-server enable traps flash insertion removal lowspace
snmp-server enable traps energywise
snmp-server enable traps power-ethernet group 1 threshold 80
snmp-server enable traps power-ethernet police
snmp-server enable traps entity
snmp-server enable traps envmon
snmp-server enable traps cef resource-failure peer-state-change peer-fib-state-change inconsistency
snmp-server enable traps lisp
snmp-server enable traps isis
snmp-server enable traps ipsla
snmp-server enable traps entity-diag boot-up-fail hm-test-recover hm-thresh-reached scheduled-test-fail
snmp-server enable traps bfd
snmp-server enable traps ike policy add
snmp-server enable traps ike policy delete
snmp-server enable traps ike tunnel start
snmp-server enable traps ike tunnel stop
snmp-server enable traps ipsec cryptomap add
snmp-server enable traps ipsec cryptomap delete
snmp-server enable traps ipsec cryptomap attach
snmp-server enable traps ipsec cryptomap detach
snmp-server enable traps ipsec tunnel start
snmp-server enable traps ipsec tunnel stop
snmp-server enable traps ipsec too-many-sas
snmp-server enable traps config-copy
snmp-server enable traps config
snmp-server enable traps config-ctid
snmp-server enable traps dhcp
snmp-server enable traps event-manager
snmp-server enable traps hsrp
snmp-server enable traps ipmulticast
snmp-server enable traps msdp
snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 state-change
snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 errors
snmp-server enable traps pim neighbor-change rp-mapping-change invalid-pim-message
snmp-server enable traps bridge newroot topologychange
snmp-server enable traps stpx inconsistency root-inconsistency loop-inconsistency
snmp-server enable traps syslog
snmp-server enable traps bgp cbgp2
snmp-server enable traps nhrp nhs
snmp-server enable traps nhrp nhc
snmp-server enable traps nhrp nhp
snmp-server enable traps nhrp quota-exceeded
snmp-server enable traps mpls rfc ldp
snmp-server enable traps mpls ldp
snmp-server enable traps mpls rfc traffic-eng
snmp-server enable traps mpls traffic-eng
snmp-server enable traps mpls fast-reroute protected
snmp-server enable traps local-auth
snmp-server enable traps vlan-membership
snmp-server enable traps errdisable
snmp-server enable traps rf
snmp-server enable traps transceiver all
snmp-server enable traps bulkstat collection transfer
snmp-server enable traps mac-notification change move threshold
snmp-server enable traps vrfmib vrf-up vrf-down vnet-trunk-up vnet-trunk-down
snmp-server enable traps mpls vpn
snmp-server enable traps mpls rfc vpn
snmp-server host 192.168.1.50 version 2c CCNPv8
snmp ifmib ifindex persist
!
control-plane
service-policy input system-cpp-policy
!
banner motd ^C D1, Implement SNMP and Syslog ^C
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
stopbits 1
line aux 0
stopbits 1
line vty 0 4
exec-timeout 0 0
privilege level 15
password cisco123
login
line vty 5 15
login
!
ntp server 192.168.1.1
!
!
end
D1#
Switch A1
A1# show run
Building configuration…
Current configuration : 3857 bytes
!
! Last configuration change at 19:58:27 UTC Thu Jan 30 2020
!
version 15.2
no service pad
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname A1
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
logging buffered 16384
!
no aaa new-model
system mtu routing 1500
!
!
no ip domain-lookup
ipv6 unicast-routing
!
!
spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
vlan internal allocation policy ascending
!
!
interface Port-channel1
switchport mode trunk
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
switchport mode trunk
channel-group 1 mode active
!
interface FastEthernet0/2
switchport mode trunk
channel-group 1 mode active
!
interface FastEthernet0/3
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/4
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/5
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/6
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/7
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/8
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/9
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/10
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/11
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/12
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/13
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/14
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/15
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/16
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/17
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/18
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/19
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/20
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/21
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/22
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/23
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/24
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
shutdown
!
interface Vlan1
ip address 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address FE80::A1:1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:1000::3/64
!
ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1
ip http server
ip http secure-server
!
ip access-list standard NMS-SERVER
permit 192.168.1.50
!
logging host 192.168.1.50
!
snmp-server community CCNPv8 RW NMS-SERVER
snmp-server location A1 Rack 1
snmp-server contact Student 555-1213
snmp-server chassis-id Cisco Device A1
snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkdown linkup coldstart warmstart
snmp-server enable traps transceiver all
snmp-server enable traps call-home message-send-fail server-fail
snmp-server enable traps tty
snmp-server enable traps entity
snmp-server enable traps cpu threshold
snmp-server enable traps vtp
snmp-server enable traps vlancreate
snmp-server enable traps vlandelete
snmp-server enable traps flash insertion removal
snmp-server enable traps port-security
snmp-server enable traps auth-framework sec-violation
snmp-server enable traps envmon fan shutdown supply temperature status
snmp-server enable traps energywise
snmp-server enable traps power-ethernet group 1
snmp-server enable traps power-ethernet police
snmp-server enable traps fru-ctrl
snmp-server enable traps event-manager
snmp-server enable traps trustsec-sxp conn-srcaddr-err msg-parse-err conn-config-err binding-err conn-up conn-down binding-expn-fail oper–nodeid-change binding-conflict
snmp-server enable traps config-copy
snmp-server enable traps config
snmp-server enable traps config-ctid
snmp-server enable traps bridge newroot topologychange
snmp-server enable traps stpx inconsistency root-inconsistency loop-inconsistency
snmp-server enable traps syslog
snmp-server enable traps pki
snmp-server enable traps mac-notification change move threshold
snmp-server enable traps vlan-membership
snmp-server enable traps errdisable
snmp-server enable traps bulkstat collection transfer
snmp-server host 192.168.1.50 version 2c CCNPv8
snmp ifmib ifindex persist
banner motd ^C A1, Implement SNMP and Syslog ^C
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
line vty 0 4
exec-timeout 0 0
privilege level 15
password cisco123
login
line vty 5 15
login
!
ntp server 192.168.1.1
end
A1#
| CCNP ENCOR v8 & 8.01 | |
| Final Exam Answers | |
| This Chapters 22 - 24 | |
| Chapters 22 - 24 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Chapters 22 - 24 Quizzes Answers | Online Test |
| Next Chapters 25 - 26 | |
| Chapters 25 - 26 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Chapters 25 - 26 Quizzes Answers | Online Test |
| CCNP ENCOR Packet Tracer Activity Files Answers | |
| 24.2.1 Packet Tracer – Configure Syslog and NTP Answers | |
| 24.2.2 Packet Tracer – Logging from Multiple Sources Answers | |
| CCNP ENCOR Student Lab Source Files Answers | |
| 24.1.2 Lab – Use Connectivity Tests and Debug for Network Assurance Answers | |
| 24.1.3 Lab – Implement SNMP and Syslog Answers | |
| 24.1.4 Lab – Implement Flexible Netflow Answers | |
| 24.1.5 Lab – Implement SPAN Technologies Answers | |
| 24.1.6 Lab – Implement IP SLA Answers | |