5.2.5 Lab – Configure Administrative Roles Answers
Lab – Configure Administrative Roles (Answers Version)
Answers Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
Topology
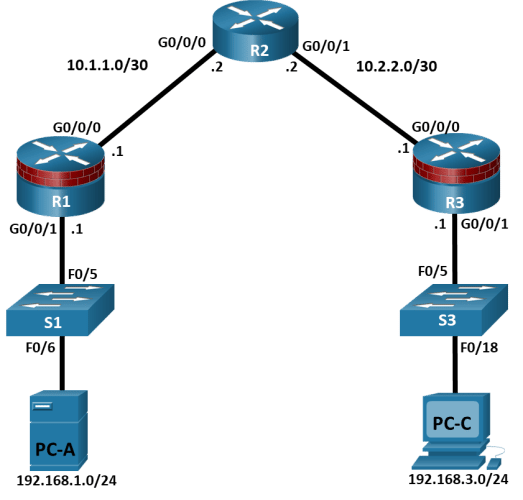
IP Addressing Table
|
Device |
Interface |
IP Address |
Subnet Mask |
Default Gateway |
Switch Port |
|
R1 |
G0/1 |
192.168.1.1 |
255.255.255.0 |
N/A |
S1 F0/5 |
|
R1 |
S0/0/0 (DCE) |
10.1.1.1 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
N/A |
|
R2 |
S0/0/0 |
10.1.1.2 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
N/A |
|
R2 |
S0/0/1 (DCE) |
10.2.2.2 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
N/A |
|
R3 |
G0/1 |
192.168.3.1 |
255.255.255.0 |
N/A |
S3 F0/5 |
|
R3 |
S0/0/1 |
10.2.2.1 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
N/A |
|
PC-A |
NIC |
192.168.1.3 |
255.255.255.0 |
192.168.1.1 |
S1 F0/6 |
|
PC-C |
NIC |
192.168.3.3 |
255.255.255.0 |
192.168.3.1 |
S3 F0/18 |
Blank Line, No additional information
Objectives
Part 1: Configure Basic Device Settings
Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Configure basic IP addressing for routers and PCs.
Configure OSPF routing.
Configure PC hosts.
Verify connectivity between hosts and routers.
Part 2: Configure Administrative Roles
Create multiple role views and grant varying privileges.
Verify and contrast views.
Background / Scenario
The router is a critical component in any network. It controls the movement of data into and out of the network and between devices within the network. It is particularly important to protect network routers because the failure of a routing device could make sections of the network, or the entire network, inaccessible. Controlling access to routers and enabling reporting on routers is critical to network security and should be part of a comprehensive security policy.
In this lab, you will build a multi–router network and configure the routers and hosts. You will configure administrative roles with different privilege levels.
Note: The routers used with hands-on labs are Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.6 (universalk9 image). The switches used in the labs are Cisco Catalyst 2960+ with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(7) (lanbasek9 image). Other routers, switches, and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and the output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of the lab for the correct interface identifiers.
Note: Before you begin, ensure that the routers and the switches have been erased and have no startup configurations.
Required Resources
3 Routers (Cisco 4221 with Cisco XE Release 16.9.6 universal image or comparable with a Security Technology Package license)
2 Switches (Cisco 2960+ with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(7) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
2 PCs (Windows OS with a terminal emulation program, such as PuTTY or Tera Term installed)
Console cables to configure Cisco networking devices
Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Instructions
Part 1:Configure Basic Device Settings
In this part, set up the network topology and configure basic settings, such as interface IP addresses.
Step 1:Cable the network.
Attach the devices, as shown in the topology diagram, and cable as necessary.
Step 2:Configure basic settings for each router.
Open configuration window
Console into the router and enable privileged EXEC mode.
Router> enable
Router# configure terminal
Configure host names as shown in the topology.
R1(config)# hostname R1
Configure interface IP addresses as shown in the IP Addressing Table.
R1(config)# interface g0/0/0
R1(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R1(config)# interface g0/0/1
R1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
- To prevent the router from attempting to translate incorrectly entered commands as though they were host names, disable DNS lookup. R1 is shown here as an example.
R1(config)# no ip domain-lookup
Step 3:Configure OSPF routing on the routers.
- Use the router ospf command in global configuration mode to enable OSPF on R1.
R1(config)# router ospf 1
- Configure the network statements for the networks on R1. Use an area ID of 0.
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
R1(config-router)# network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
- Configure OSPF on R2 and R3.
R2(config)# router ospf 1
R2(config-router)# network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
R2(config-router)# network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
R3(config)# router ospf 1
R3(config-router)# network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
R3(config-router)# network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
- Issue the passive-interface command to change the G0/0/1 interface on R1 and R3 to passive.
R1(config)# router ospf 1
R1(config-router)# passive-interface g0/0/1
R3(config)# router ospf 1
R3(config-router)# passive-interface g0/0/1
Step 2:Verify OSPF neighbors and routing information.
- Issue the show ip ospf neighbor command to verify that each router lists the other routers in the network as neighbors.
R1# show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor IDPriStateDead TimeAddressInterface
10.2.2.21FULL/BDR00:00:3710.1.1.2GigabitEthernet0/0/0
- Issue the show ip route command to verify that all networks display in the routing table on all routers.
R1# show ip route
Codes: L – local, C – connected, S – static, R – RIP, M – mobile, B – BGP
D – EIGRP, EX – EIGRP external, O – OSPF, IA – OSPF inter area
N1 – OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 – OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 – OSPF external type 1, E2 – OSPF external type 2
i – IS-IS, su – IS-IS summary, L1 – IS-IS level-1, L2 – IS-IS level-2
ia – IS-IS inter area, * – candidate default, U – per-user static route
o – ODR, P – periodic downloaded static route, H – NHRP, l – LISP
a – application route
+ – replicated route, % – next hop override, p – overrides from PfR
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
C10.1.1.0/30 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
L10.1.1.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
O10.2.2.0/30 [110/2] via 10.1.1.2, 00:01:11, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
L192.168.1.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
O192.168.3.0/24 [110/3] via 10.1.1.2, 00:01:07, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
Step 3:Configure PC host IP settings.
Configure a static IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway for PC-A and PC-C as shown in the IP Addressing Table.
Step 4:Verify connectivity between PC-A and PC-C.
- Ping from R1 to R3.
If the pings are not successful, troubleshoot the basic device configurations before continuing.
- Ping from PC-A, on the R1 LAN, to PC-C, on the R3 LAN.
If the pings are not successful, troubleshoot the basic device configurations before continuing.
Note: If you can ping from PC-A to PC-C you have demonstrated that OSPF routing is configured and functioning correctly. If you cannot ping but the device interfaces are up and IP addresses are correct, use the show run, show ip ospf neighbor, and show ip route commands to help identify routing protocol-related problems.
Step 5:Save the basic running configuration for each router.
Save the basic running configuration for the routers as text files on your PC. These text files can be used to restore configurations later in the lab.
Close configuration window
Part 2:Configure Administrative Roles
In this part of lab, you will:
Create multiple administrative roles, or views, on routers R1 and R3.
Grant each view varying privileges.
Verify and contrast the views.
The role-based CLI access feature allows the network administrator to define views, which are a set of operational commands and configuration capabilities that provide selective or partial access to Cisco IOS EXEC and configuration (config) mode commands. Views restrict user access to the Cisco IOS CLI and configuration information. A view can define which commands are accepted and what configuration information is visible.
Note: Perform all tasks on both R1 and R3. The procedures and output for R1 are shown here.
If an administrator wants to configure another view to the system, the system must be in root view. When a system is in root view, the user has the same access privileges as a user who has level–15 privileges, but the root view user can also configure a new view and add or remove commands from the view. When you are in a CLI view, you have access only to the commands that have been added to that view by the root view user.
Step 1:Enable AAA on router R1.
Open configuration window
To define views, enable AAA on the router.
R1# configure terminal
R1(config)# aaa new-model
Step 2:Configure privileged EXEC mode password.
A privileged EXEC mode password is required to access the root view. The password cisco12345 is used in this example.
R1(config)# enable secret cisco12345
R1# exit
Step 3:Enable the root view.
Use the command enable view to enable the root view.
R1# enable view
Password: cisco12345
Step 4:Create the admin1 view, establish a password, and assign privileges.
- The admin1 user is the top-level user below root that is allowed to access this router. It has the most authority. The admin1 user can use all show, config, and debug commands. Use the following command to create the admin1 view while in the root view.
R1# configure terminal
R1(config)# parser view admin1
R1(config-view)#
Note: To delete a view, use the command no parser view viewname.
- Associate the admin1 view with an encrypted password.
R1(config-view)# secret admin1pass
R1(config-view)#
- Review the commands that can be configured in the admin1 view. Use the commands ? command to see available commands. The following is a partial listing of the available commands.
R1(config-view)# commands ?
RITE-profileRouter IP traffic export profile command mode
RMI Node ConfigResource Policy Node Config mode
RMI Resource GroupResource Group Config mode
RMI Resource ManagerResource Manager Config mode
RMI Resource PolicyResource Policy Config mode
SASL-profileSASL profile configuration mode
aaa-attr-listAAA attribute list config mode
aaa-userAAA user definition
accept-dialinVPDN group accept dialin configuration mode
accept-dialoutVPDN group accept dialout configuration mode
address-familyAddress Family configuration mode
<output omitted>
- Add all config, show, and debug commands to the admin1 view and then exit from view configuration mode.
R1(config-view)# commands exec include all show
R1(config-view)# commands exec include all config terminal
R1(config-view)# commands exec include all debug
R1(config-view)# end
- Verify the admin1 view.
R1# enable view admin1
Password: admin1pass
R1# show parser view
Current view is ‘admin1’
- Examine the commands available in the admin1 view.
R1# ?
Exec commands:
<0-0>/<0-4>Enter card slot/sublot number
configureEnter configuration mode
debugDebugging functions (see also ‘undebug’)
do-execMode-independent “do-exec” prefix support
enableTurn on privileged commands
exitExit from the EXEC
showShow running system
Note: There may be more EXEC commands available than are displayed. This depends on your device and the IOS image used.
- Examine the show commands available in the admin1 view.
R1# show ?
aaaShow AAA values
access-expressionList access expression
access-listsList access lists
acircuitAccess circuit info
adjacencyAdjacent nodes
aliasesDisplay alias commands
alignmentShow alignment information
appfwApplication Firewall information
archiveArchive functions
arpARP table
<output omitted>
Step 5:Create the admin2 view, establish a password, and assign privileges.
- The admin2 user is a junior administrator in training who is allowed to view all configurations but is not allowed to configure the routers or use debug commands.
- Use the enable view command to enable the root view, and enter the enable secret password cisco12345.
R1# enable view
Password: cisco12345
- Use the following command to create the admin2 view.
R1# configure terminal
R1(config)# parser view admin2
- Associate the admin2 view with a password.
R1(config-view)# secret admin2pass
- Add all show commands to the view, and then exit from view configuration mode.
R1(config-view)# commands exec include all show
R1(config-view)# end
- Verify the admin2 view.
R1# enable view admin2
Password: admin2pass
R1# show parser view
Current view is ‘admin2’
- Examine the commands available in the admin2 view.
R1# ?
Exec commands:
<0-0>/<0-4>Enter card slot/sublot number
do-execMode-independent “do-exec” prefix support
enableTurn on privileged commands
exitExit from the EXEC
showShow running system information
Note: There may be more EXEC commands available than are displayed. This depends on your device and the IOS image used.
Question:
What is missing from the list of admin2 commands that is present in the admin1 commands?
Type your answers here.
configure and debug
Step 6:Create the tech view, establish a password, and assign privileges.
- The tech user typically installs end-user devices and cabling. Tech users are only allowed to use selected show commands.
- Use the enable view command to enable the root view, and enter the enable secret password cisco12345.
R1# enable view
Password: cisco12345
- Use the following command to create the tech view.
R1(config)# parser view tech
- Associate the tech view with a password.
R1(config-view)# secret techpasswd
- Add the following show commands to the view and then exit from view configuration mode.
R1(config-view)# commands exec include show version
R1(config-view)# commands exec include show interfaces
R1(config-view)# commands exec include show ip interface brief
R1(config-view)# commands exec include show parser view
R1(config-view)# end
- Verify the tech view.
R1# enable view tech
Password: techpasswd
R1# show parser view
Current view is ‘tech’
- Examine the commands available in the tech view.
R1# ?
Exec commands:
<0-0>/<0-4>Enter card slot/sublot number
do-execMode-independent “do-exec” prefix support
enableTurn on privileged commands
exitExit from the EXEC
showShow running system information
Note: There may be more EXEC commands available than are displayed. This depends on your device and the IOS image used.
- Examine the show commands available in the tech view.
R1# show ?
bannerDisplay banner information
flash0:display information about flash0: file system
flash1:display information about flash1: file system
flash:display information about flash: file system
interfacesInterface status and configuration
ipIP information
parserDisplay parser information
usbflash0:display information about usbflash0: file system
versionSystem hardware and software status
Note: There may be more EXEC commands available than are displayed. This depends on your device and the IOS image used.
- Issue the show ip interface brief command.
Question:
Were you able to do it as the tech user? Explain.
Type your answers here.
Yes. It is one of the allowed commands.
- Issue the show ip route command.
Question:
Were you able to do it as the tech user?
Type your answers here.
No. It is not one of the allowed commands.
R1# show ip route
^
% Invalid input detected at ‘^’ marker.
- Return to root view with the enable view command.
R1# enable view
Password: cisco12345
- Issue the show run command to see the views you created.
Question:
For tech view, why are the show and show ip commands listed as well as show ip interface and show ip interface brief?
Type your answers here.
All parts of the command must be listed for the more specific parameters to work.
- Configure the same administrative roles on router R3.
Step 7:Save the configuration on routers R1 and R3.
Save the running configuration to the startup configuration from the privileged EXEC prompt.
Close configuration window
Router Interface Summary Table
|
Router Model |
Ethernet Interface #1 |
Ethernet Interface #2 |
Serial Interface #1 |
Serial Interface #2 |
|
1900 |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) |
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
|
2900 |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) |
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
|
4221 |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) |
Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) |
Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
|
4300 |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) |
Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) |
Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
Blank Line, No additional information
Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface.
Device Configs
Router R1
R1# show run
Building configuration…
Current configuration : 4283 bytes
!
version 16.9
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
platform qfp utilization monitor load 80
platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core
!
hostname R1
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
enable secret 5 $1$rbvn$rvn7uAGEnICrnFbOCy7EJ/
!
aaa new-model
!
aaa session-id common
!
no ip domain lookup
!
login on-success log
!
subscriber templating
!
!multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
redundancy
mode none
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
negotiation auto
!
router ospf 1
passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
ip forward-protocol nd
ip http server
ip http authentication local
ip http secure-server
!
control-plane
!
parser view admin1
secret 5 $1$yJFu$69HoDt.mlTmw19x.yywF20
commands exec include all configure terminal
commands exec include configure
commands exec include all show
commands exec include all debug
!
parser view admin2
secret 5 $1$AaDz$Qq/xDc4PBtAk1.6mNXl9o.
commands exec include all show
!
parser view tech
secret 5 $1$qw41$fcbJH6sBfk4jH2caDnEsS/
commands exec include show ip interface brief
commands exec include show ip interface
commands exec include show ip
commands exec include show version
commands exec include show parser view
commands exec include show parser
commands exec include show interfaces
commands exec include show
!
line con 0
transport input none
stopbits 1
line aux 0
stopbits 1
line vty 0 4
!
end
Router R2
R2# show run
Building configuration…
Current configuration : 3347 bytes
!
version 16.9
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
platform qfp utilization monitor load 80
platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core
!
hostname R2
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
no aaa new-model
!
no ip domain lookup
!
login on-success log
!
subscriber templating
!
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
redundancy
mode none
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.252
negotiation auto
!
router ospf 1
network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
!
ip forward-protocol nd
ip http server
ip http authentication local
ip http secure-server
!
control-plane
!
line con 0
transport input none
stopbits 1
line aux 0
stopbits 1
line vty 0 4
login
!
end
Router R3
R3# show run
Building configuration…
Current configuration : 4258 bytes
!
version 16.9
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
platform qfp utilization monitor load 80
platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core
!
hostname R3
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
enable secret 5 $1$8sRN$RJ0AjzOhohjYyJPQKhsLt0
!
aaa new-model
!
aaa session-id common
!
no ip domain lookup
!
login on-success log
!
subscriber templating
!
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
redundancy
mode none
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.252
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
negotiation auto
!
router ospf 1
passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
ip forward-protocol nd
ip http server
ip http authentication local
ip http secure-server
!
control-plane
!
parser view admin1
secret 5 $1$rGTd$aNno9FgtvQ3.jQwzJGC1P.
commands exec include all configure terminal
commands exec include configure
commands exec include all show
commands exec include all debug
!
parser view admin2
secret 5 $1$Hf3l$aZCOieWbTU0TPuX3tBy1H1
commands exec include all show
!
parser view tech
secret 5 $1$mb5M$wZOZggPSgQnrqMTtaKDXm/
commands exec include show ip interface brief
commands exec include show ip interface
commands exec include show ip
commands exec include show version
commands exec include show parser view
commands exec include show parser
commands exec include show interfaces
commands exec include show
!
line con 0
transport input none
stopbits 1
line aux 0
stopbits 1
line vty 0 4
!
end