CyberOps Associate (200-201) Certification Practice Exam Answers Full 100% 2023 2024
CyberOps Associate (200-201) Certification Practice Exam Answers Full 100% 2023 2024
These are both versions of NetAcad Cisco CA 1.02 and CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate (200-201) Certification Practice Exam Full 100% in 2023 and 2024 verified by experts with explanations and hints.
| CyberOps - Associate 1.0 & 1.01 | |
| Final Exam | |
| Practice Final Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Final Exam Answers | Online Test |
| 200-201 Certification Practice | Online Test |
-
At the request of investors, a company is proceeding with cyber attribution with a particular attack that was conducted from an external source. Which security term is used to describe the person or device responsible for the attack?
- fragmenter
- skeleton
- threat actor
- tunneler
Explanation & Hint:
Some people may use the common word of “hacker” to describe a threat actor. A threat actor is an entity that is involved with an incident that impacts or has the potential to impact an organization in such a way that it is considered a security risk or threat.
-
Which term describes a threat actor who has advanced skills and pursues a social agenda?
- script kiddie
- organized crime
- corporate/industrial spies
- hacktivist
Explanation & Hint:
Threat actors who have advanced hacking abilities and pursue a social or political agenda are known as hacktivists.
-
What are two motivating factors for nation-state sponsored threat actors? (Choose two.)
- financial gain
- social or personal causes
- industrial espionage
- disruption of trade or infrastructure
- showing off their hacking skill
Explanation & Hint:
Nation-state threat actors are not typically interested or motivated by financial gain. They are primarily involved in corporate espionage or disrupting international trade or critical infrastructure.
-
Match the definition to the Microsoft Windows term. (Not all options are used.)
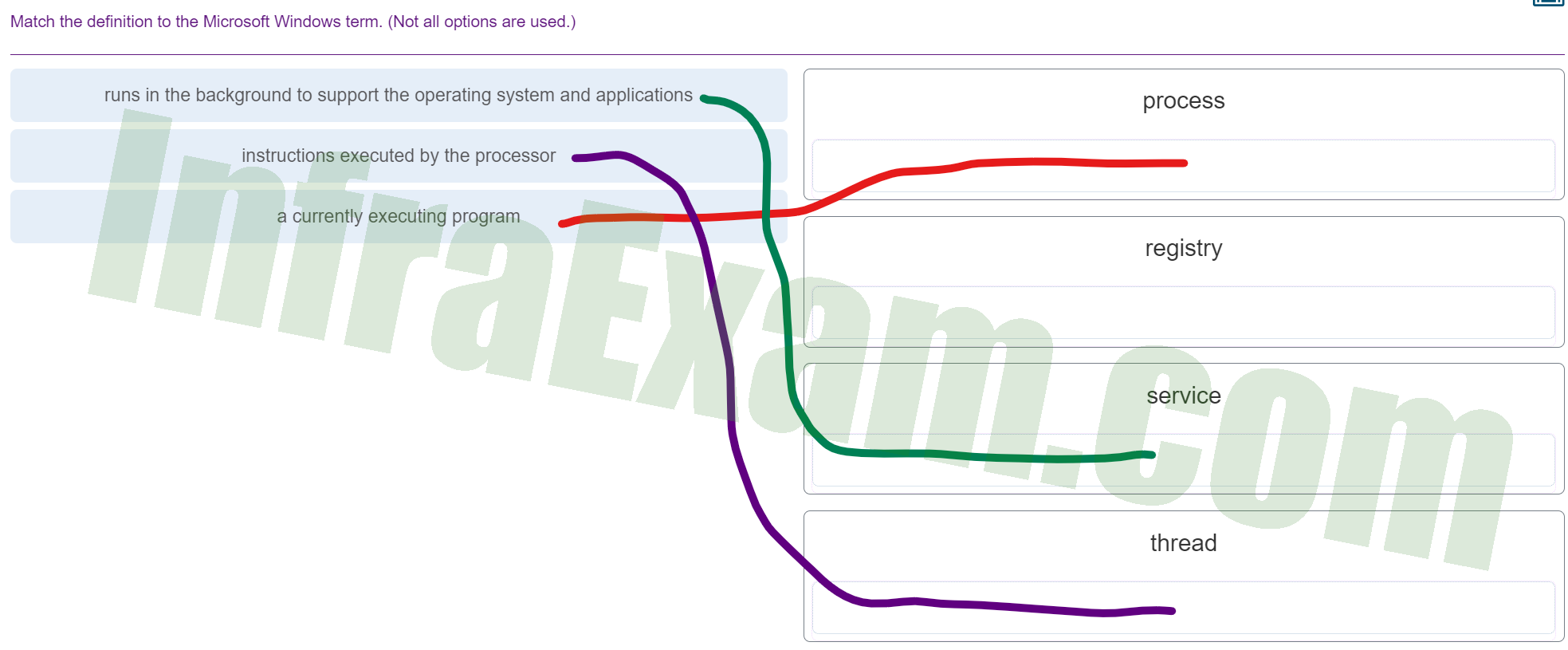
Match the definition to the Microsoft Windows term 01 - runs in the background to support the operating system and applications ==> service
- instructions executed by the processor ==> thread
- a currently executing program ==> process
Explanation & Hint:
- Process: A process in Windows is an instance of a computer program that is being executed. It contains the program code and its current activity. Depending on the operating system (OS), a process may be made up of multiple threads of execution that execute instructions concurrently.
- Registry: The Windows Registry is a hierarchical database that stores low-level settings for the Microsoft Windows operating system and for applications that opt to use the Registry. The kernel, device drivers, services, Security Accounts Manager, and user interface can all use the Registry. The Registry also allows access to counters for profiling system performance.
- Service: In Windows, a service is a computer program that operates in the background and provides support to other programs, particularly at the OS level. Services often provide core operating system features, such as web serving, event logging, or file serving. Services can be configured to start automatically at boot, can be paused and restarted, and do not show any user interface.
- Thread: A thread is the smallest sequence of programmed instructions that can be managed independently by a scheduler, which is typically a part of the operating system. Multiple threads can exist within the same process and share resources such as memory, while different processes do not share these resources. In particular, threads of a process share its executable code and the values of its variables at any given time.
-
Match the definition to the Microsoft Windows term. (Not all options are used.)
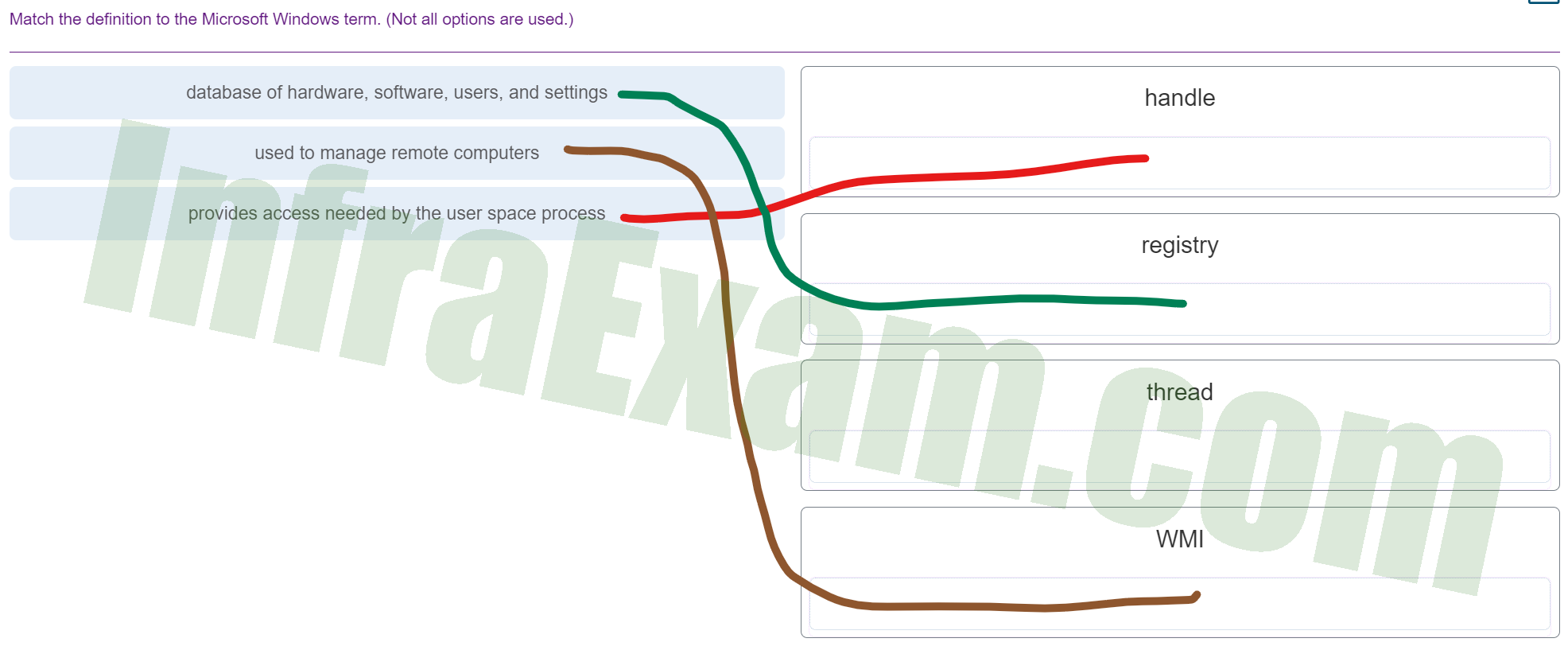
Match the definition to the Microsoft Windows term 02 - database of hardware, software, users, and settings ==> registry
- used to manage remote computers ==> WMI
- provides access needed by the user space process ==> handle
Explanation & Hint:
- Database of hardware, software, users, and settings: This likely refers to the Windows Registry, which is a centralized database that Windows uses to store information about the system’s configuration. It keeps track of settings for the operating system, installed software, the system hardware, and user profiles.
- Used to manage remote computers: This might refer to Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), which is a set of specifications from Microsoft for consolidating the management of devices and applications in a network from Windows computing systems.
- Provides access needed by the user space process: This is probably referring to a Handle. In Windows, a handle is an abstract reference or pointer to a resource that is used by the operating system to track resources like files, windows, sockets, or any other system resource. Handles are used by programs to access these resources. They are granted by the operating system to the program and are used by the program to refer to the resources.
- Thread: A thread in computing is the smallest sequence of programmed instructions that can be managed independently by the operating system scheduler. In Windows, a thread is part of a process, and multiple threads can be executing concurrently within the same process.
- WMI: Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) is the infrastructure for management data and operations on Windows-based operating systems. WMI is used for accessing management information in an enterprise environment.
-
Match the Windows term to the description.
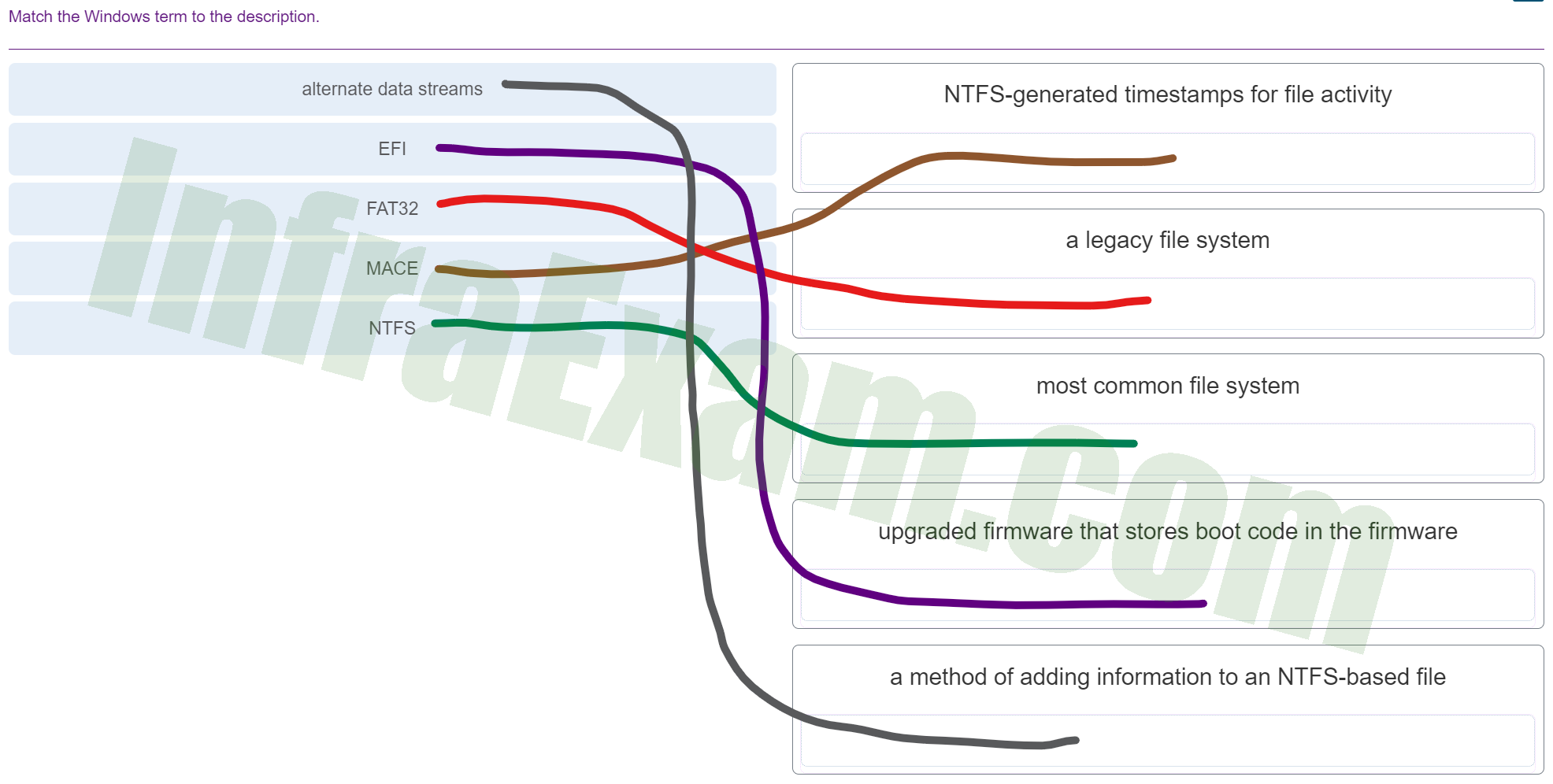
Match the Windows term to the description - alternate data streams ==> a method of adding information to an NTFS-based file
- EFI ==> upgraded firmware that stores boot code in the firmware
- FAT32 ==> a legacy file system
- MACE ==> NTFS-generated timestamps for file activity
- NTFS ==> most common file system
Explanation & Hint:
- Alternate Data Streams (ADS): This is a feature of the NTFS file system that allows more than one data stream to be associated with a filename, which is a method of adding information to an NTFS-based file without affecting the main file stream.
- EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface): This is a specification that defines a software interface between an operating system and platform firmware. EFI is the upgraded firmware that stores boot code in the firmware.
- FAT32 (File Allocation Table 32): This is a legacy file system that was popular for its simplicity and compatibility with a wide array of operating systems and devices.
- MACE (Modification, Access, Creation, Entry): These are NTFS-generated timestamps for file activity. Each file or directory is tagged with the time when it was last modified (M), accessed (A), created (C), and when the entry to the file was changed (E).
- NTFS (New Technology File System): This is the most common file system used by Windows operating systems today. It has several improvements over previous file systems, such as support for metadata, advanced data structures to improve performance, reliability, and disk space utilization, as well as additional extensions, such as security access control lists (ACL) and file system journaling.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A security specialist is checking if files in the directory contain ADS data. Which switch should be used to show that a file has ADS attached?

CyberOps Associate (200-201) Certification Practice Exam Answers 03 - /a
- /d
- /r
- /s
Explanation & Hint:
By using NTFS, Alternate Data Streams (ADSs) can be connected to a file as an attribute called $DATA. The command dir /r can be used to see if a file contains ADS data.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Approximately what percentage of the physical memory is still available on this Windows system?
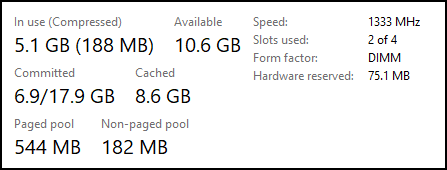
CyberOps Associate (200-201) Certification Practice Exam Answers 05 - 32%
- 53%
- 68%
- 90%
Explanation & Hint:
The graphic shows that there is 5.1 GB (187 MB) of memory in use with 10.6 GB still available. Together this adds up to 16 GB of total physical memory. 5 GB is approximately 32% of 16 GB leaving 68% still available.
-
Which Windows application is commonly used by a cybersecurity analyst to view Microsoft IIS access logs?
- Event Viewer
- Notepad
- SIEM
- Word
Explanation & Hint:
Event Viewer is an application on a Windows-based device used to view event logs including IIS access logs.
-
Which Windows tool can be used by a cybersecurity administrator to secure stand-alone computers that are not part of an active directory domain?
- Local Security Policy
- Windows Defender
- Windows Firewall
- PowerShell
Explanation & Hint:
Windows systems that are not part of an Active Directory Domain can use the Windows Local Security Policy to enforce security settings on each stand-alone system.
-
What are three benefits of using symbolic links over hard links in Linux? (Choose three.)
- Symbolic links can be exported.
- They can be encrypted.
- They can be compressed.
- They can link to a directory.
- They can show the location of the original file.
- They can link to a file in a different file system.
Explanation & Hint:
In Linux, a hard link is another file that points to the same location as the original file. A soft link (also called a symbolic link or a symlink) is a link to another file system name. Hard links are limited to the file system in which they are created and they cannot link to a directory; soft links are not limited to the same file system and they can link to a directory. To see the location of the original file for a symbolic link use the ls –l command.
-
Match the description to the Linux term. (Not all options are used.)
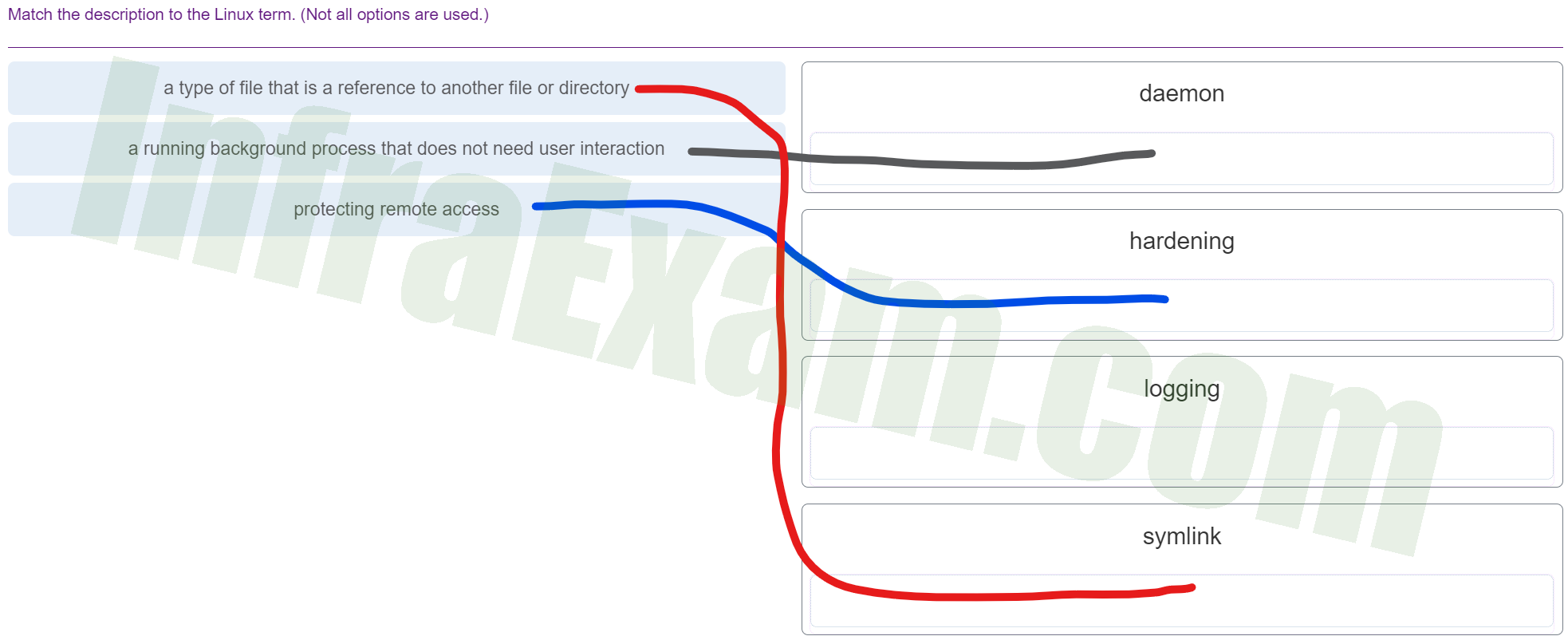
Match the description to the Linux term 01 - a type of file that is a reference to another file or directory ==> symlink
- a running background process that does not need user interaction ==> daemon
- protecting remote access ==> hardening
Explanation & Hint:
- Daemon: A daemon is a type of program on Unix-like operating systems that runs unobtrusively in the background, rather than under the direct control of a user. Daemons typically start at boot time and serve the function of responding to network requests, hardware activity, or other programs by performing some task. Daemons are often used to provide background services, and they do not need user interaction.
- Hardening: This is the process of securing a system by reducing its surface of vulnerability. Hardening involves various techniques to protect remote access, system access, and other vectors that could be exploited by attackers. This can include configuring system and network components to eliminate unnecessary functions and services, applying security patches, and setting up firewalls and other security measures.
- Logging: In the context of computing, logging refers to the recording of events in a computer system. Logs can track various kinds of data, such as system events, network traffic, user operations, and errors. Logging is critical for system management, security monitoring, and debugging purposes.
- Symlink (Symbolic Link): A symlink is a term used in Linux that refers to a symbolic path indicating the abstract location of another file. A symbolic link is a type of file that contains a reference to another file or directory in the form of an absolute or relative path and that affects pathname resolution.
-
When attempting to improve system performance for Linux computers with a limited amount of memory, why is increasing the size of the swap file system not considered the best solution?
- A swap file system only supports the ex2 file system.
- A swap file system does not have a specific file system.
- A swap file system cannot be mounted on an MBR partition.
- A swap file system uses hard disk space to store inactive RAM content.
Explanation & Hint:
The swap file system is used by Linux when it runs out of physical memory. When needed, the kernel moves inactive RAM content to the swap partition on the hard disk. Storing and retrieving content in the swap partition is much slower than RAM is, and therefore using the swap partition should not be considered the best solution to improving system performance.
-
Match the description to the Linux term. (Not all options are used.)
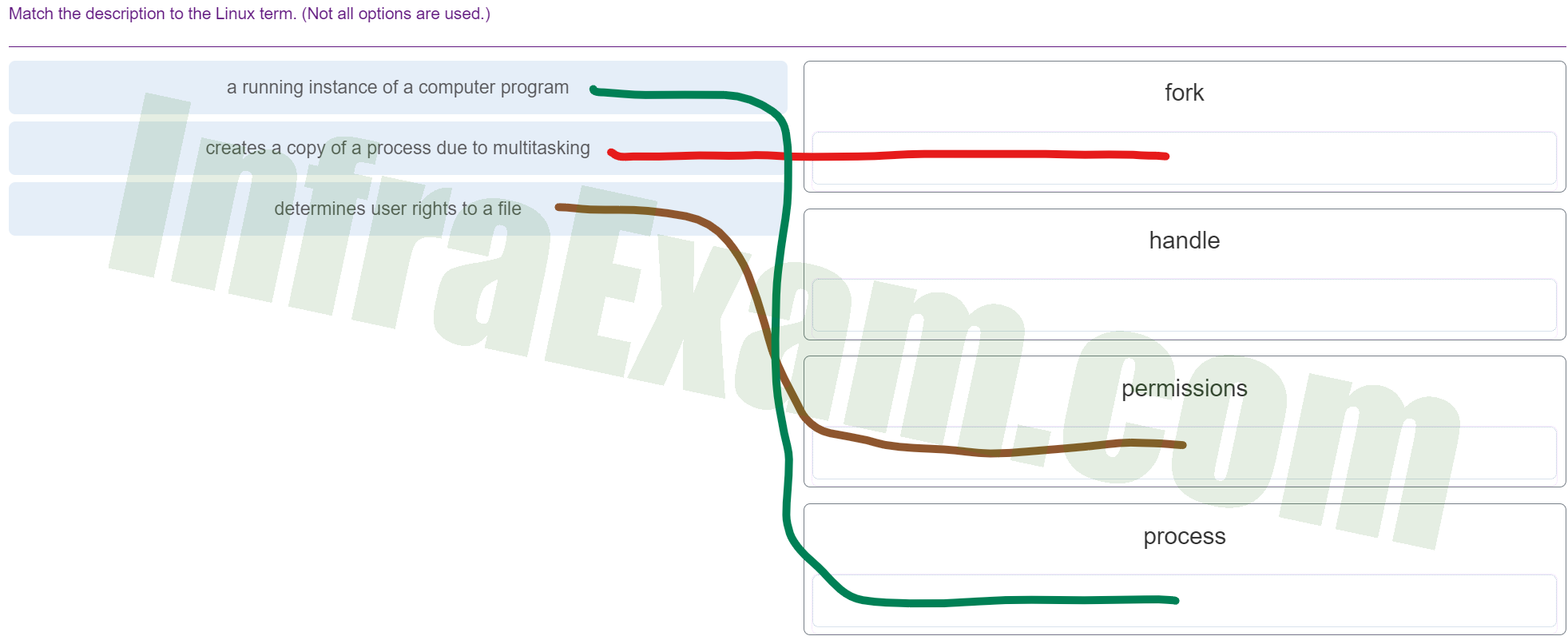
Match the description to the Linux term 02 - a running instance of a computer program ==> process
- creates a copy of a process due to multitasking ==> fork
- determines user rights to a file ==> permissions
Explanation & Hint:
- Process: This is a running instance of a computer program. In Linux, when a program is running, it is called a process. Each process is provided with its own set of virtual memory and system resources.
- Fork: This creates a copy of a process due to multitasking. The
fork()system call is used in Unix/Linux to create a new process, which is called a child process, from an existing process, which is the parent process. - Permissions: This determines user rights to a file. In Linux, permissions control the actions that users can perform on files and directories. There are three types of permissions: read, write, and execute, and they can be set for the file owner, the owner’s group, and others.
- Handle: This term is not as commonly used in Linux in the same way as in some other systems. In general computing, a handle can refer to a reference to a resource, such as a file or a window. In Linux, these are usually referred to more specifically, such as file descriptors or pointers to data structures.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A security analyst is reviewing the logs of an Apache web server. Which action should the analyst take based on the output shown?
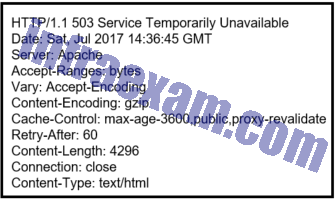
CyberOps Associate (200-201) Certification Practice Exam Answers 01 - Ignore the message.
- Notify the server administrator.
- Restart the server.
- Notify the appropriate security administration for the country.
Explanation & Hint:
An Apache web server is an open source server that delivers web pages. Security access logs for an Apache web server include a 3-digit HTTP code that represents the status of the web request. A code that begins with 2 indicates access success. A code that begins with 3 represents redirection. A code that begins with 4 represents a client error and a code that begins with 5 represents a server error. The server administrator should be alerted if a server error such as the 503 code occurs.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which technology would contain information similar to the data shown for infrastructure devices within a company?
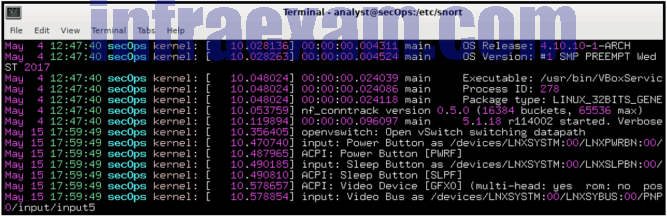
CyberOps Associate (200-201) Certification Practice Exam Answers 02 - Apache server
- firewall
- HIDS
- syslog server
Explanation & Hint:
A syslog server consolidates and maintains messages from infrastructure devices that have been configured to send logging information. Data from the syslog server can be analyzed to detect anomalies..
-
Which two algorithms use a hashing function to ensure message integrity? (Choose two.)
- SEAL
- AES
- 3DES
- MD5
- SHA
Explanation & Hint:
Hashing algorithms are used to provide data integrity, which ensures that the data has not changed during transmission. MD5 and SHA are commonly used hashing algorithms.
-
Match the antimalware approach to the description.
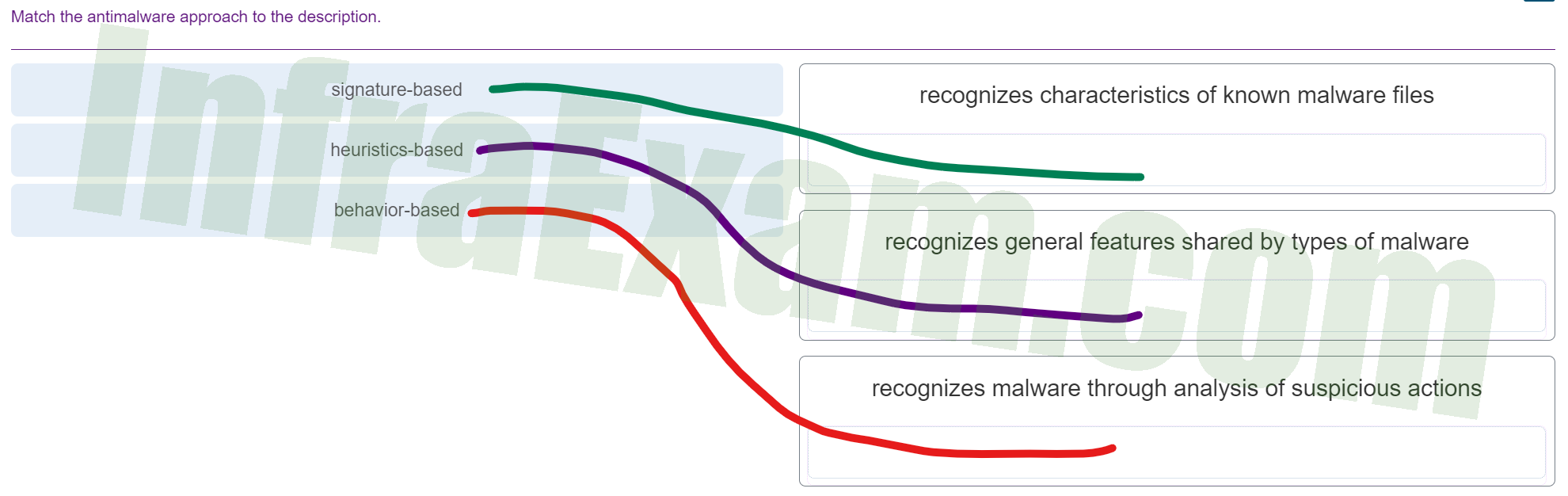
Match the antimalware approach to the description - signature-based ==> recognizes characteristics of known malware files
- heuristics-based ==> recognizes general features shared by types of malware
- behavior-based ==> recognizes malware through analysis of suspicious actions
Explanation & Hint:
- Signature-based: This antimalware approach involves recognizing characteristics of known malware files. Signature-based detection is one of the most common methods. It uses specific patterns of data or “signatures” that are characteristic of malware and compares them to files and programs to identify potential threats.
- Heuristics-based: This approach recognizes general features shared by types of malware. Heuristics-based detection looks at broader patterns and behaviors that are often found in malicious code. This allows it to detect new, previously unseen viruses or variants of existing viruses that have changed some aspects of their code.
- Behavior-based: This approach recognizes malware through the analysis of suspicious actions. Behavior-based detection monitors the behavior of programs in real-time. If a piece of code acts similarly to known malware after it has been executed, this can trigger a response from the antimalware system.
-
A security professional is making recommendations to a company for enhancing endpoint security. Which security endpoint technology would be recommended as an agent-based system to protect hosts against malware?
- baselining
- block listing
- HIDS
- IPS
Explanation & Hint:
A host-based intrusion detection systems (HIDS) is a comprehensive security application that provides antimalware applications, a firewall, and monitoring and reporting.
-
Which security endpoint setting would be used by a security analyst to determine if a computer has been configured to prevent a particular application from running?
- baselining
- block listing
- services
- whitelisting
Explanation & Hint:
Blacklisting can be used on a local system or updated on security devices such as a firewall. Blacklists can be manually entered or obtained from a centralized security system. Blacklists are applications that are prevented from executing because they pose a security risk to the individual system and potentially the company.
-
Which technique could be used by security personnel to analyze a suspicious file in a safe environment?
- baselining
- block listing
- sandboxing
- whitelisting
Explanation & Hint:
Sandboxing allows suspicious files to be executed and analyzed in a safe environment. There are free public sandboxes that allow for malware samples to be uploaded or submitted and analyzed.
-
Which type of evidence cannot prove an IT security fact on its own?
- best
- corroborative
- hearsay
- indirect
Explanation & Hint:
Indirect evidence cannot prove a fact on its own, but direct evidence can. Corroborative evidence is supporting information. Best evidence is most reliable because it is something concrete such as a signed contract.
-
A cybersecurity analyst has been called to a crime scene that contains several technology items including a computer. Which technique will be used so that the information found on the computer can be used in court?
- log collection
- rootkit
- Tor
- unaltered disk image
Explanation & Hint:
A normal file copy does not recover all data on a storage device so an unaltered disk image is commonly made. An unaltered disk image preserves the original evidence, thus preventing inadvertent alteration during the discovery phase. It also allows recreation of the original evidence.
-
Which SOC technology automates security responses by using predefined playbooks which require a minimum amount of human intervention?
- SOAR
- SIEM
- NetFlow
- Wireshark
- syslog
Explanation & Hint:
SOAR technology goes a step further than SIEM by integrating threat intelligence and automating incident investigation and response workflows based on playbooks developed by the security team.
-
The SOC manager is reviewing the metrics for the previous calendar quarter and discovers that the MTTD for a breach of password security perpetrated through the Internet was forty days. What does the MTTD metric represent within the SOC?
- the average time that it takes to stop and remediate a security incident
- the average time that it takes to identify valid security incidents that have occurred
- the time required to stop the incident from causing further damage to systems or data
- window of time required to stop the spread of malware in the network
Explanation & Hint:
Cisco defines MTTD as the average time that it takes for the SOC personnel to identify that valid security incidents have occurred in the network.
-
Match the file system term used in Linux to the function.
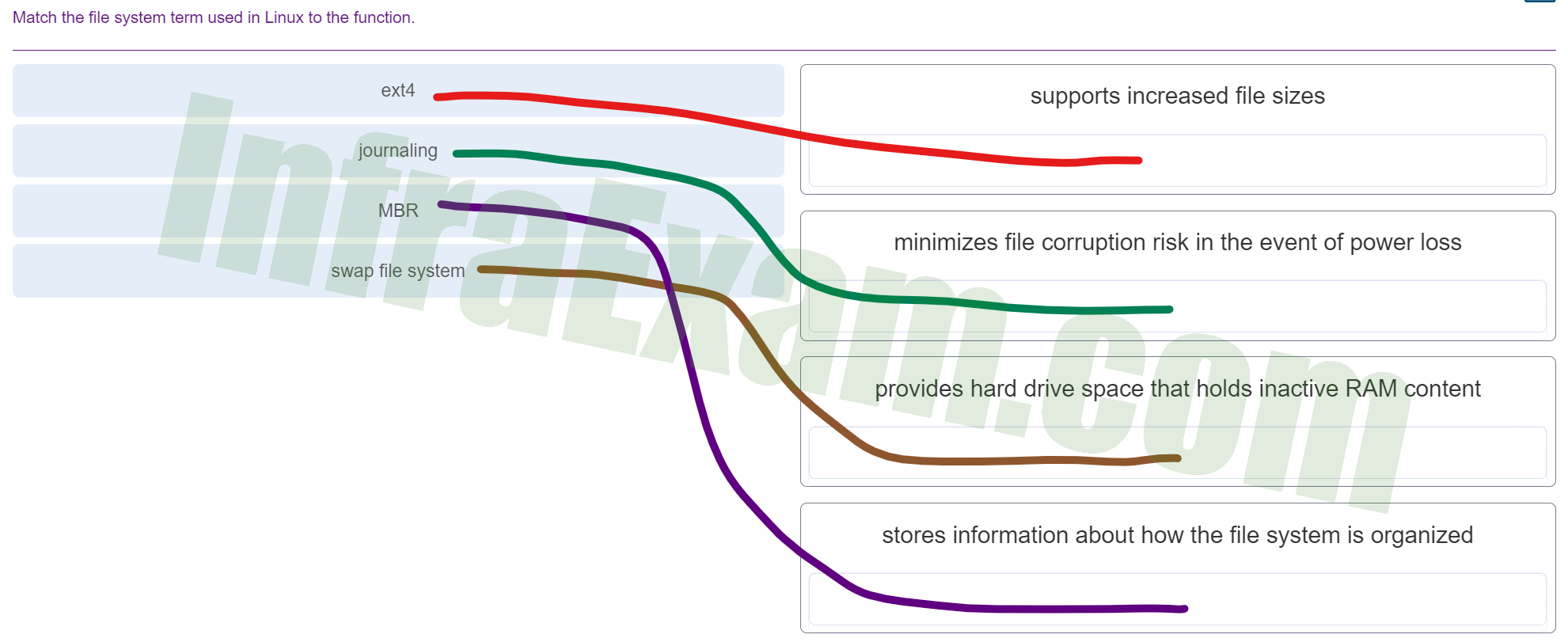
Match the file system term used in Linux to the function - ext4 ==> supports increased file sizes
- journaling ==> minimizes file corruption risk in the event of power loss
- MBR ==> stores information about how the file system is organized
- swap file system ==> provides hard drive space that holds inactive RAM content
Explanation & Hint:
- ext4: This is a widely-used journaling file system in Linux. It supports increased file sizes and has better performance and scalability than its predecessor ext3.
- Journaling: This is a feature used by file systems like ext3 and ext4 to minimize file corruption risk in the event of power loss or system crash. Journaling file systems record changes in a dedicated space on the disk before committing them to the main file system, which can help in recovering from an unexpected interruption.
- Swap file system: This doesn’t refer to a specific file system type but a space on a disk that a Linux system uses as virtual memory. It provides hard drive space to hold inactive RAM content. When the system runs out of physical RAM, less frequently used data can be ‘swapped’ out to the swap space on the disk.
- MBR (Master Boot Record): This is not a file system but a type of boot sector at the beginning of the storage device that contains information about how the logical partitions, containing file systems, are organized on that medium. The MBR also contains executable code to function as a loader for the installed operating system—typically by passing control to the loader’s second stage, or in conjunction with each partition’s Volume Boot Record.
-
What is the first line of defense when an organization is using a defense-in-depth approach to network security?
- IPS
- edge router
- firewall
- proxy server
Explanation & Hint:
A defense-in-depth approach uses layers of security measures starting at the network edge, working through the network, and finally ending at the network endpoints. Routers at the network edge are the first line of defense and forward traffic intended for the internal network to the firewall.
-
What is the benefit of a defense-in-depth approach?
- The effectiveness of other security measures is not impacted when a security mechanism fails.
- The need for firewalls is eliminated.
- All network vulnerabilities are mitigated.
- Only a single layer of security at the network core is required.
Explanation & Hint:
The benefit of the defense-in-depth approach is that network defenses are implemented in layers so that failure of any single security mechanism does not impact other secuirty measures.
-
Match the security concept to the description.

Match the security concept to the description - threat ==> a potential danger to an asset
- vulnerability ==> a weakness in a system
- exploit ==> a mechanism used to compromise an asset
- risk ==> the likelihood of undesireable consequences
Explanation & Hint:
- Threat: A potential danger to an asset. In cybersecurity, a threat is any circumstance or event that has the potential to cause harm to a data network or system in the form of unauthorized access, destruction, disclosure, modification of data, and denial of service.
- Vulnerability: A weakness in a system. Vulnerabilities are flaws or weaknesses in a system’s design, implementation, or operation and management that could be exploited to violate the system’s security policy.
- Exploit: A mechanism used to compromise an asset. An exploit is a piece of software, a chunk of data, or a sequence of commands that take advantage of a bug or vulnerability in order to cause unintended or unanticipated behavior to occur on computer software, hardware, or something electronic (usually computerized).
- Risk: The likelihood of undesirable consequences. Risk in the context of cybersecurity is often quantified as the potential that a given threat will exploit a particular vulnerability of the system and cause harm to assets.
-
Which access control model allows users to control access to data as an owner of that data?
- mandatory access control
- nondiscretionary access control
- discretionary access control
- attribute-based access control
Explanation & Hint:
In the discretionary access control (DAC) model, users can control access to data as owners of the data.
-
What is the principle behind the nondiscretionary access control model?
- It applies the strictest access control possible.
- It allows access decisions to be based on roles and responsibilities of a user within the organization.
- It allows users to control access to their data as owners of that data.
- It allows access based on attributes of the object be to accessed.
Explanation & Hint:
The nondiscretionary access control model used the roles and responsibilities of the user as the basis for access decisions.
-
What is an example of privilege escalation attack?
- A threat actor sends an email to an IT manager to request the root access.
- A threat actor performs an access attack and gains the administrator password.
- A DDoS attack is launched against a government server and causes the server to crash.
- A port scanning attack finds that the FTP service is running on a server that allows anonymous access.
Explanation & Hint:
With the privilege escalation exploit, vulnerabilities in servers or access control systems are exploited to grant an unauthorized user, or software process, higher levels of privilege than either should have. After the higher privilege is granted, the threat actor can access sensitive information or take control of a system.
-
Which access control model applies the strictest access control and is often used in military and mission critical applications?
- discretionary
- mandatory
- nondiscretionary
- attribute-based
Explanation & Hint:
Military and mission critical applications typically use mandatory access control which applies the strictest access control to protect network resources.
-
Match the information security component with the description.

Match the information security component with the description - availability ==> Authorized users must have uninterrupted access to important resources and data.
- confidentiality ==> Only authorized individuals, entities, or processes can access sensitive information.
- integrity ==> Data is protected from unauthorized alteration.
Explanation & Hint:
- Confidentiality: Only authorized individuals, entities, or processes can access sensitive information. Confidentiality measures are designed to prevent the unauthorized disclosure of information.
- Integrity: Data is protected from unauthorized alteration. Integrity measures ensure that data is accurate and reliable and has not been tampered with or altered by unauthorized individuals.
- Availability: Authorized users must have uninterrupted access to important resources and data. Availability ensures that data and resources are available to authorized users when needed.
-
Which information security component is compromised in a DDoS attack?
- confidentiality
- accountability
- integrity
- availability
Explanation & Hint:
Confidentiality, integrity, and availability are the elements contained in the CIA triad. Availability means that all authorized users have uninterrupted access to important resources and data. In a DDoS attack, servers and services are overloaded and applications are no longer available to users.
-
Which access control model assigns security privileges based on the position, responsibilities, or job classification of an individual or group within an organization?
- discretionary
- role-based
- mandatory
- rule-based
Explanation & Hint:
Role-based access control models assign privileges based on position, responsibilities, or job classification. Users and groups with the same responsibilities or job classification share the same assigned privileges. This type of access control is also referred to as nondiscretionary access control.
-
Which component is a pillar of the zero trust security approach that focuses on the secure access of devices, such as servers, printers, and other endpoints, including devices attached to IoT?
- workforce
- workflows
- workloads
- workplace
Explanation & Hint:
The workplace pillar focuses on secure access for any and all devices, including devices on the internet of things (IoT), which connect to enterprise networks, such as user endpoints, physical and virtual servers, printers, cameras, HVAC systems, kiosks, infusion pumps, industrial control systems, and more.
-
Which type of evaluation includes the assessment of the likelihood of an attack, the type of threat actor likely to perpetrate such an attack, and what the consequences could be to the organization if the exploit is successful?
- risk analysis
- vulnerability identification
- penetration testing
- server profiling
Explanation & Hint:
When evaluating a cyber security risk, the analyst takes into account the likelihood of an attack occurring, who the potential threat actors might be, as well as the consequences that might occur if the exploit is successful.
-
Which metric in the CVSS Base Metric Group is used with an attack vector?
- the proximity of the threat actor to the vulnerability
- the determination whether the initial authority changes to a second authority during the exploit
- the presence or absence of the requirement for user interaction in order for an exploit to be successful
- the number of components, software, hardware, or networks, that are beyond the control of the attacker and that must be present in order for a vulnerability to
- be successfully exploited
Explanation & Hint:
The attack vector is one of several metrics defined in the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) Base Metric Group Exploitability metrics. The attack vector is how close the threat actor is to the vulnerable component. The farther away the threat actor is to the component, the higher the severity because threat actors close to the network are easier to detect and mitigate.
-
A cybersecurity analyst is performing a CVSS assessment on an attack where a web link was sent to several employees. Once clicked, an internal attack was launched. Which CVSS Base Metric Group Exploitability metric is used to document that the user had to click on the link in order for the attack to occur?
- availability requirement
- integrity requirement
- scope
- user interaction
Explanation & Hint:
The CVSS Base Metric Group has the following metrics: attack vector, attack complexity, privileges required, user interaction, and scope. The user interaction metric expresses the presence or absence of the requirement for user interaction in order for an exploit to be successful.
-
A security analyst is investigating a cyber attack that began by compromising one file system through a vulnerability in a custom software application. The attack now appears to be affecting additional file systems under the control of another security authority. Which CVSS v3.0 base exploitability metric score is increased by this attack characteristic?
- scope
- attack complexity
- user interaction
- privileges required
Explanation & Hint:
The scope metric is impacted by an exploited vulnerability that can affect resources beyond the authorized privileges of the vulnerable component or that are managed by a different security authority.
-
What are the three impact metrics contained in the CVSS 3.0 Base Metric Group? (Choose three.)
- attack vector
- availability
- confidentiality
- exploit
- integrity
- remediation level
Explanation & Hint:
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a vendor-neutral, industry standard, open framework for weighing the risks of a vulnerability using a variety of metrics. CVSS uses three groups of metrics to assess vulnerability, the Base Metric Group, Temporal Metric Group, and Environmental Metric Group. The Base Metric Group has two classes of metrics (exploitability and impact). The impact metrics are rooted in the following areas: confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
-
A threat hunter is concerned about a significant increase in TCP traffic sourced from port 53. It is suspected that malicious file transfer traffic is being tunneled out using the TCP DNS port. Which deep packet inspection tool can detect the type of application originating the suspicious traffic?
- Wireshark
- NetFlow
- NBAR2
- syslog analyzer
- IDS/IPS
Explanation & Hint:
NBAR2 is used to discover the applications that are responsible for network traffic. NBAR is a classification engine that can recognize a wide variety of applications, including web-based applications and client/server applications.
-
A security analyst is reviewing information contained in a Wireshark capture created during an attempted intrusion. The analyst wants to correlate the Wireshark information with the log files from two servers that may have been compromised. What type of information can be used to correlate the events found in these multiple data sets?
- logged-in user account
- ISP geolocation data
- IP five-tuples
- ownership metadata
Explanation & Hint:
The source and destination IP address, ports, and protocol (the IP five-tuples) can be used to correlate different data sets when analyzing an intrusion.
-
Which type of analysis relies on predefined conditions and can analyze applications that only use well-known fixed ports?
- probabilistic
- deterministic
- statistical
- log
Explanation & Hint:
Deterministic analysis uses predefined conditions to analyze applications that conform to specification standards, such as performing a port-based analysis.
-
Which type of analysis relies on different methods to establish the likelihood that a security event has happened or will happen?
- deterministic
- log
- statistical
- probabilistic
Explanation & Hint:
Probabilistic methods use powerful tools to create a probabilistic answer as a result of analyzing applications.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A security specialist is using Wireshark to review a PCAP file generated by tcpdump . When the client initiated a file download request, which source socket pair was used?
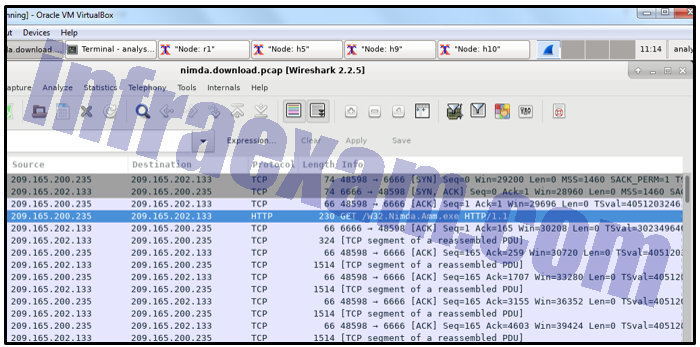
CyberOps Associate (200-201) Certification Practice Exam Answers 07 - 209.165.202.133:6666
- 209.165.200.235:6666
- 209.165.202.133:48598
- 209.165.200.235:48598
Explanation & Hint:
The combination of the source IP address and source port number, or the destination IP address and destination port number, is known as a socket. A socket is shown as the IP address and associated port number with a colon in between the two (IP_address:port_number).
-
Which three fields are found in both the TCP and UDP headers? (Choose three.)
- options
- source port
- destination port
- checksum
- sequence number
- window
Explanation & Hint:
The UPD header has four fields. Three of these fields are in common with the TCP header. These three fields are the source port, destination port, and checksum.
-
What is a feature of an IPS?
- It can stop malicious packets.
- It has no impact on latency.
- It is deployed in offline mode.
- It is primarily focused on identifying possible incidents.
Explanation & Hint:
An advantage of an intrusion prevention systems (IPS) is that it can identify and stop malicious packets. However, because an IPS is deployed inline, it can add latency to the network.
-
Match the security service with the description.
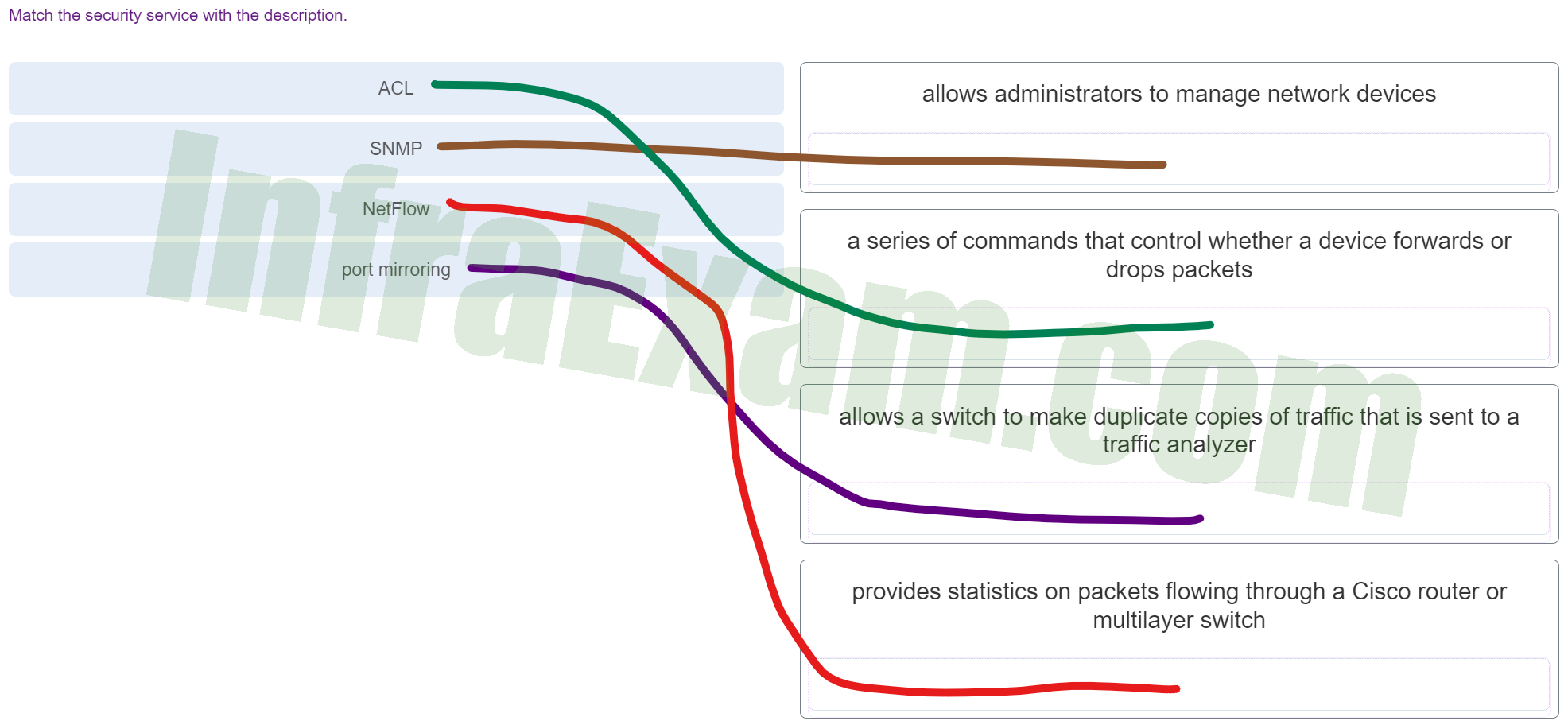
Match the security service with the description - ACL ==> a series of commands that control whether a device forwards or drops packets
- SNMP ==> allows administrators to manage network devices
- NetFlow ==> provides statistics on packets flowing through a Cisco router or multilayer switch
- port mirroring ==> allows a switch to make duplicate copies of traffic that is sent to a traffic analyzer
Explanation & Hint:
- ACL (Access Control List): This is a series of commands that control whether a device forwards or drops packets. ACLs are used to filter traffic based on a set of rules defined by the network administrator to increase security by restricting the flow of packets allowed to enter or exit network interfaces.
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol): This allows administrators to manage network devices. SNMP is used for collecting information from, and configuring, network devices, such as servers, printers, hubs, switches, and routers on an Internet Protocol (IP) network.
- NetFlow: This provides statistics on packets flowing through a Cisco router or multilayer switch. NetFlow is a network protocol developed by Cisco for collecting IP traffic information and monitoring network traffic.
- Port Mirroring: This allows a switch to make duplicate copies of traffic that is sent to a traffic analyzer. Port mirroring is used on a network switch to send a copy of network packets seen on one switch port (or an entire VLAN) to a network monitoring connection on another switch port.
-
Which field in the IPv6 header points to optional network layer information that is carried in the IPv6 packet?
- flow label
- version
- traffic class
- next header
Explanation & Hint:
Optional Layer 3 information about fragmentation, security, and mobility is carried inside of extension headers in an IPv6 packet. The next header field of the IPv6 header acts as a pointer to these optional extension headers if they are present.
-
Which three IPv4 header fields have no equivalent in an IPv6 header? (Choose three.)
- fragment offset
- flag
- identification
- version
- protocol
- TTL
Explanation & Hint:
Unlike IPv4, IPv6 routers do not perform fragmentation. Therefore, all three fields supporting fragmentation in the IPv4 header are removed and have no equivalent in the IPv6 header. These three fields are fragment offset, flag, and identification. IPv6 does support host packet fragmentation through the use of extension headers, which are not part of the IPv6 header.
-
Which data security component is provided by hashing algorithms?
- key exchange
- confidentiality
- integrity
- authentication
Explanation & Hint:
Hashing algorithms are used to provide message integrity, which ensures that data in transit has not changed or been altered.
-
What is a key difference between the data captured by NetFlow and data captured by Wireshark?
- NetFlow provides transaction data whereas Wireshark provides session data.
- NetFlow data is analyzed by tcpdump whereas Wireshark data is analyzed by nfdump .
- NetFlow collects metadata from a network flow whereas Wireshark captures full data packets.
- NetFlow data shows network flow contents whereas Wireshark data shows network flow statistics.
Explanation & Hint:
Wireshark captures the entire contents of a packet. NetFlow does not. Instead, NetFlow collects metadata, or data about the flow.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which technology generated the event log?
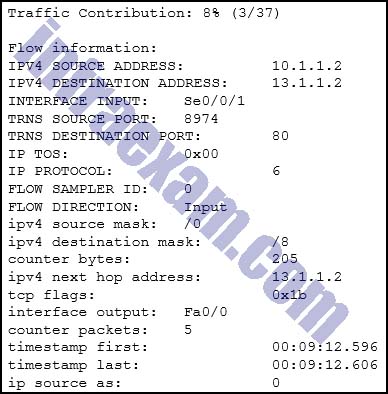
CyberOps Associate (200-201) Certification Practice Exam Answers 04 - Wireshark
- web proxy
- syslog
- Netflow
Explanation & Hint:
The source of the output is Netflow.
-
Match the IPS alarm with the description.

Match the IPS alarm with the description - false positive ==> normal traffic is incorrectly identified as a threat
- false negative ==> malicious traffic is not correctly identified as a threat
- true positive ==> malicious traffic is correctly identified as a threat
- true negative ==> normal traffic is correctly not identified as a threat
Explanation & Hint:
- True Positive: This is when malicious traffic is correctly identified as a threat by the IPS. The system correctly detects and potentially stops an actual attack.
- True Negative: This is when normal traffic is correctly not identified as a threat. The IPS allows legitimate traffic to pass without any alert.
- False Positive: This is when normal traffic is incorrectly identified as a threat. The system mistakenly perceives normal activity as malicious, which can lead to unnecessary or disruptive actions.
- False Negative: This is when malicious traffic is not correctly identified as a threat. The system fails to detect an actual attack, which allows the malicious activity to proceed unchecked.
-
What classification is used for an alert that correctly identifies that an exploit has occurred?
- true positive
- false positive
- true negative
- false negative
Explanation & Hint:
A true positive occurs when an IDS and IPS signature is correctly fired and an alarm is generated when offending traffic is detected.
-
What will match the regular expression ^83?
- any string that begins with 83
- any string that ends with 83
- any string that includes 83
- any string with values greater than 83
Explanation & Hint:
The expression ^83 indicates any string that begins with 83 will be matched.
-
Which regular expression would match any string that contains 4 consecutive zeros?
- [0-4]
- 0{4}
- {0-4}
- ^0000
Explanation & Hint:
The regular expression 0{4} matches any string that contains 4 repetitions of zero or 4 consecutive zeros.
-
Using Tcpdump and Wireshark, a security analyst extracts a downloaded file from a pcap file. The analyst suspects that the file is a virus and wants to know the file type for further examination. Which Linux command can be used to determine the file type?
- tail
- file
- ls -l
- nano
Explanation & Hint:
The Linux file command can be used to determine a file type, such as whether it is executable, ASCII text, or zip.
-
Which attack surface, defined by the SANS Institute, is delivered through the exploitation of vulnerabilities in web, cloud, or host-based applications?
- host
- human
- network
- software
Explanation & Hint:
The SANS Institute describes three components of the attack surface:
Network Attack Surface – exploits vulnerabilities in networks
Software Attack Surface – delivered through the exploitation of vulnerabilities in web, cloud, or host-based software applications
Human Attack Surface – exploits weaknesses in user behavior
-
What is an example of a local exploit?
- Port scanning is used to determine if the Telnet service is running on a remote server.
- A threat actor performs a brute force attack on an enterprise edge router to gain illegal access.
- A buffer overflow attack is launched against an online shopping website and causes the server crash.
- A threat actor tries to gain the user password of a remote host by using a keyboard capture software installed on it by a Trojan.
Explanation & Hint:
Vulnerability exploits may be remote or local. In a local exploit, the threat actor has some type of user access to the end system, either physically or through remote access. The exploitation activity is within the local network.
-
Which type of cyber attack is a form of MiTM in which the perpetrator copies IP packets off the network without modifying them?
- IP spoofing
- denial-of-service
- eavesdropping
- compromised key
Explanation & Hint:
An eavesdropping attack is a form of man-in-the-middle in which the perpetrator just reads or copies IP packets off the network but does not alter them.
-
Which is an example of social engineering?
- a computer displaying unauthorized pop-ups and adware
- the infection of a computer by a virus carried by a Trojan
- an anonymous programmer directing a DDoS attack on a data center
- an unidentified person claiming to be a technician collecting user information from employees
Explanation & Hint:
A social engineer attempts to gain the confidence of an employee and convince that person to divulge confidential and sensitive information, such as usernames and passwords. DDoS attacks, pop-ups, and viruses are all examples of software based security threats, not social engineering.
-
To which category of security attacks does man-in-the-middle belong?
- DoS
- access
- reconnaissance
- social engineering
Explanation & Hint:
With a man-in-the-middle attack, a threat actor is positioned in between two legitimate entities in order to read, modify, or redirect the data that passes between the two parties.
-
Which evasion method describes the situation that after gaining access to the administrator password on a compromised host, a threat actor is attempting to login to another host using the same credentials?
- pivoting
- traffic substitution
- resource exhaustion
- protocol-level misinterpretation
Explanation & Hint:
Pivoting is an evasion method that assumes the threat actor has compromised an inside host and the actor wants to expand the access further into the compromised network.
-
What is the main goal of using different evasion techniques by threat actors?
- to launch DDoS attacks on targets
- to identify vulnerabilities of target systems
- to gain the trust of a corporate employee in an effort to obtain credentials
- to prevent detection by network and host defenses
Explanation & Hint:
Many threat actors use stealthy evasion techniques to disguise an attack payload because the malware and attack methods are most effective if they are undetected. The goal is to prevent detection by network and host defenses.
-
What are two examples of DoS attacks? (Choose two.)
- phishing
- ping of death
- SQL injection
- port scanning
- buffer overflow
Explanation & Hint:
The buffer overflow and ping of death DoS attacks exploit system memory-related flaws on a server by sending an unexpected amount of data or malformed data to the server.
-
Which attack is integrated with the lowest levels of the operating system of a host and attempts to completely hide the activities of the threat actor on the local system?
- rootkit
- traffic insertion
- traffic substitution
- encryption and tunneling
Explanation & Hint:
A rootkit is a complex attack tool and it integrates with the lowest levels of the operating system. The goal of the rootkit is to completely hide the activities of the threat actor on the local system.
-
Which type of evasion technique splits malicious payloads into smaller packets in order to bypass security sensors that do not reassemble the payloads before scanning them?
- traffic insertion
- protocol-level misinterpretation
- pivoting
- traffic fragmentation
Explanation & Hint:
In order to keep the malicious payload from being recognized by security sensors, such as IPS or IDS, perpetrators fragment the data into smaller packets.These fragments can be passed by sensors that do not reassemble the data before scanning.
-
Which two attacks target web servers through exploiting possible vulnerabilities of input functions used by an application? (Choose two.)
- SQL injection
- port scanning
- port redirection
- trust exploitation
- cross-site scripting
Explanation & Hint:
When a web application uses input fields to collect data from clients, threat actors may exploit possible vulnerabilities for entering malicious commands. The malicious commands that are executed through the web application might affect the OS on the web server. SQL injection and cross-site scripting are two different types of command injection attacks.
-
Which security function is provided by encryption algorithms?
- key management
- authorization
- integrity
- confidentiality
Explanation & Hint:
Encryption algorithms are used to provide data confidentiality, which ensures that if data is intercepted in transit, it cannot be read.
-
Which type of attack is carried out by threat actors against a network to determine which IP addresses, protocols, and ports are allowed by ACLs?
- phishing
- reconnaissance
- denial of service
- social engineering
Explanation & Hint:
Packet filtering ACLs use rules to filter incoming and outgoing traffic. These rules are defined by specifying IP addresses, port numbers, and protocols to be matched. Threat actors can use a reconnaissance attack involving port scanning or penetration testing to determine which IP addresses, protocols, and ports are allowed by ACLs.
-
How can NAT/PAT complicate network security monitoring if NetFlow is being used?
- It changes the source and destination MAC addresses.
- It conceals the contents of a packet by encrypting the data payload.
- It disguises the application initiated by a user by manipulating port numbers.
- It hides internal IP addresses by allowing them to share one or a few outside IP addresses.
Explanation & Hint:
NAT/PAT maps multiple internal IP addresses with only a single or a few outside IP addresses breaking end-to-end flows. The result makes it difficult to log the inside device that is requesting and receiving the traffic. This is especially a problem with a NetFlow application because NetFlow flows are unidirectional and are defined by the addresses and ports that they share.
-
Which statement describes the function provided by the Tor network?
- It distributes user packets through load balancing.
- It allows users to browse the Internet anonymously.
- It conceals packet contents by establishing end-to-end tunnels.
- It manipulates packets by mapping IP addresses between two networks.
Explanation & Hint:
Tor is a software platform and network of P2P hosts that function as Internet routers on the Tor network. The Tor network allows users to browse the Internet anonymously.
-
Which type of data is used by Cisco Cognitive Intelligence to find malicious activity that has bypassed security controls, or entered through unmonitored channels, and is operating inside an enterprise network?
- alert
- session
- statistical
- transaction
Explanation & Hint:
Cisco Cognitive Intelligence utilizes statistical data for statistical analysis in order to find malicious activity that has bypassed security controls, or entered through unmonitored channels (including removable media), and is operating inside the network of an organization.
-
Which tool captures full data packets with a command-line interface only?
- nfdump
- NBAR2
- tcpdump
- Wireshark
Explanation & Hint:
The command-line tool tcpdump is a packet analyzer. Wireshark is a packet analyzer with a GUI interface.
-
Which Cisco appliance can be used to filter network traffic contents to report and deny traffic based on the web server reputation?
- ASA
- AVC
- ESA
- WSA
Explanation & Hint:
The Cisco Web Security Appliance (WSA) acts as a web proxy for an enterprise network. WSA can provide many types of logs related to web traffic security including ACL decision logs, malware scan logs, and web reputation filtering logs. The Cisco Email Security Appliance (ESA) is a tool to monitor most aspects of email delivery, system functioning, antivirus, antispam operations, and blacklist and whitelist decisions. The Cisco ASA is a firewall appliance. The Cisco Application Visibility and Control (AVC) system combines multiple technologies to recognize, analyze, and control over 1000 applications.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A security analyst is reviewing an alert message generated by Snort. What does the number 2100498 in the message indicate?

CyberOps Associate (200-201) Certification Practice Exam Answers 03 - the message length in bits
- the Snort rule that is triggered
- the session number of the message
- the id of the user that triggers the alert
Explanation & Hint:
The sid field in a Snort alert message indicates the Snort security rule that is triggered.
-
When establishing a network profile for an organization, which element describes the time between the establishment of a data flow and its termination?
- total throughput
- session duration
- routing protocol convergence
- bandwidth of the Internet connection
Explanation & Hint:
A network profile should include some important elements, such as the following:
Total throughput – the amount of data passing from a given source to a given destination in a given period of time
Session duration – the time between the establishment of a data flow and its termination
Ports used – a list of TCP or UDP processes that are available to accept data
Critical asset address space – the IP addresses or the logical location of essential systems or data
-
A network administrator is creating a network profile to generate a network baseline. What is included in the critical asset address space element?
- the list of TCP or UDP processes that are available to accept data
- the IP addresses or the logical location of essential systems or data
- the time between the establishment of a data flow and its termination
- the TCP and UDP daemons and ports that are allowed to be open on the server
Explanation & Hint:
A network profile should include some important elements, such as the following:
Total throughput – the amount of data passing from a given source to a given destination in a given period of time
Session duration – the time between the establishment of a data flow and its termination
Ports used – a list of TCP or UDP processes that are available to accept data
Critical asset address space – the IP addresses or the logical location of essential systems or data
-
When establishing a server profile for an organization, which element describes the type of service that an application is allowed to run on the server?
- user account
- listening port
- service account
- software environment
Explanation & Hint:
A server profile should contain some important elements including these:
Listening ports – the TCP and UDP daemons and ports that are allowed to be open on the server
User accounts – the parameters defining user access and behavior
Service accounts – the definitions of the type of service that an application is allowed to run on a server
Software environment – the tasks, processes, and applications that are permitted to run on the server
-
When a server profile for an organization is being established, which element describes the TCP and UDP daemons and ports that are allowed to be open on the server?
- listening ports
- service accounts
- software environment
- critical asset address space
Explanation & Hint:
A server profile will often contain the following:
Listening ports – the TCP and UDP daemons and ports that are allowed to be open on the server
User accounts – the parameters defining user access and behavior
Service accounts – the definitions of the type of service that an application is allowed to run on a server
Software environment – the tasks, processes, and applications that are permitted to run on the server
-
According to the Cyber Kill Chain model, after a weapon is delivered to a targeted system, what is the next step that a threat actor would take?
- installation
- exploitation
- weaponization
- action on objectives
Explanation & Hint:
The Cyber Kill Chain specifies seven steps (or phases) and sequences that a threat actor must complete to accomplish an attack:
Reconnaissance – The threat actor performs research, gathers intelligence, and selects targets.
Weaponization – The threat actor uses the information from the reconnaissance phase to develop a weapon against specific targeted systems.
Delivery – The weapon is transmitted to the target using a delivery vector.
Exploitation – The threat actor uses the weapon delivered to break the vulnerability and gain control of the target.
Installation – The threat actor establishes a back door into the system to allow for continued access to the target.
Command and Control (CnC) – The threat actor establishes command and control (CnC) with the target system.
Action on Objectives – The threat actor is able to take action on the target system, thus achieving the original objective.
-
What will a threat actor do to create a back door on a compromised target according to the Cyber Kill Chain model?
- Collect and exfiltrate data.
- Add services and autorun keys.
- Obtain an automated tool to deliver the malware payload.
- Open a two-way communications channel to the CnC infrastructure.
Explanation & Hint:
Once a target system is compromised, the threat actor will establish a back door into the system to allow for continued access to the target. Adding services and autorun keys is a way to create a point of persistent access.
-
Which three things will a threat actor do to prepare a DDoS attack against a target system on the Internet? (Choose three.)
- Collect and exfiltrate data.
- Install attack software on zombies.
- Install a black door on the target system.
- Compromise many hosts on the Internet.
- Obtain an automated tool to deliver the malware payload.
- Establish two-way communications channels to the CnC infrastructure with zombies.
Explanation & Hint:
To prepare for launching a DDoS attack, a threat actor will compromise many hosts on the Internet, called zombies. The threat actor will then install attack software on zombies and establish a two-way communications channel to CnC infrastructure with zombies. The threat actor will issue the command to zombies through the CnC to launch a DDoS attack against a target system.
-
Place the seven steps defined in the Cyber Kill Chain in the correct order.
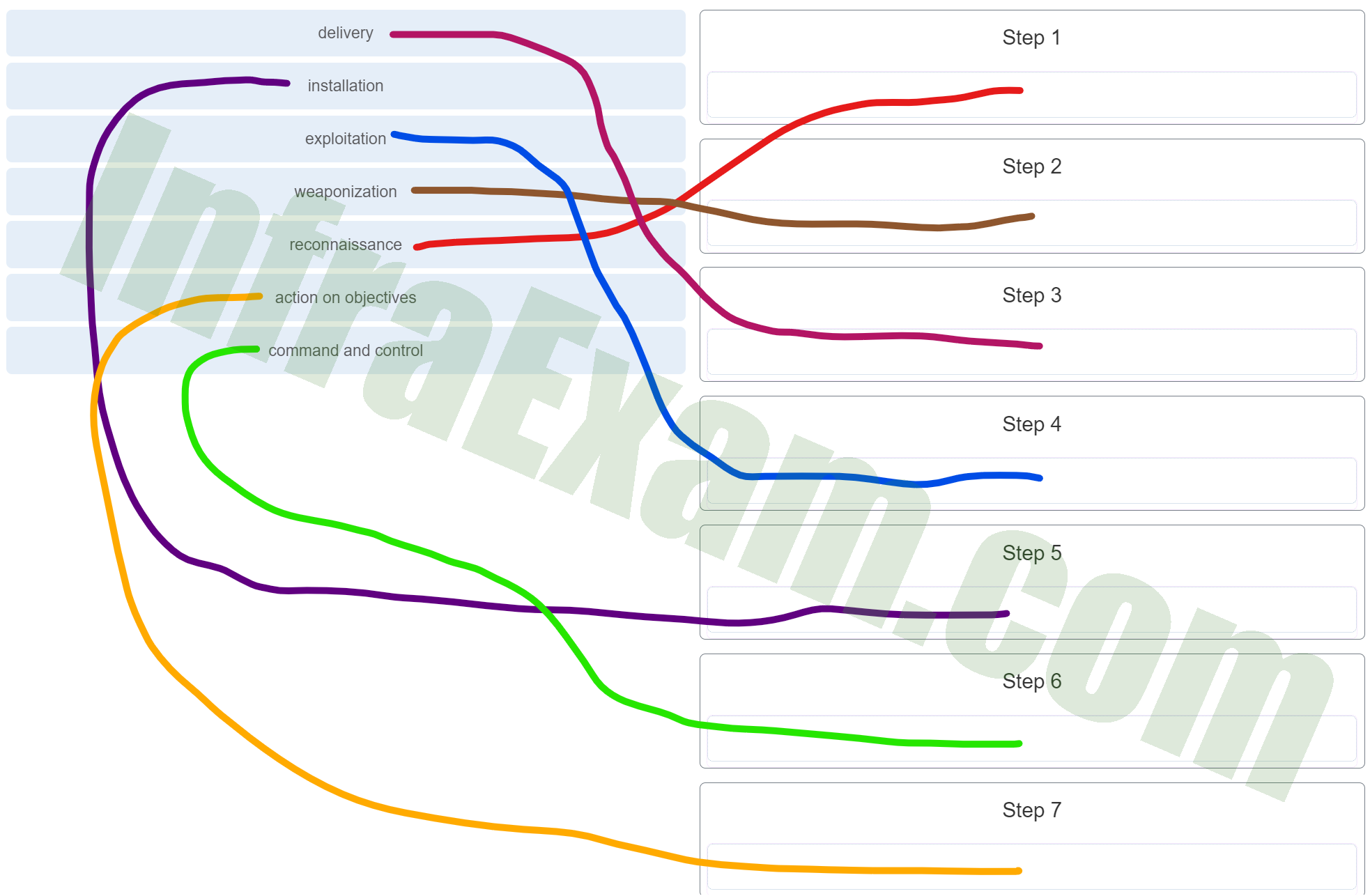
Place the seven steps defined in the Cyber Kill Chain in the correct order - delivery ==> Step 3
- installation ==> Step 5
- exploitation ==> Step 4
- weaponization ==> Step 2
- reconnaissance ==> Step 1
- action on objectives ==> Step 7
- command and control ==> Step 6
Explanation & Hint:
- Reconnaissance: The attacker gathers information on the target before launching an attack.
- Weaponization: The attacker creates malware designed to exploit the vulnerabilities of the target’s system.
- Delivery: The attacker transmits the weaponized bundle to the victim via email, USB, etc.
- Exploitation: The attacker’s code exploits a vulnerability in the victim’s system.
- Installation: The malware is installed on the victim’s system, allowing the attacker to maintain presence.
- Command and Control (C2): The attacker establishes a command and control channel to remotely manipulate the compromised system.
- Actions on Objectives: The attacker accomplishes their end goal, which could be data exfiltration, destruction of data, or any other malicious outcome.
-
Which two actions should be taken during the preparation phase of the incident response life cycle defined by NIST? (Choose two.)
- Fully analyze the incident.
- Create and train the CSIRT.
- Detect all the incidents that occurred.
- Acquire and deploy the tools that are needed to investigate incidents.
- Meet with all involved parties to discuss the incident that took place.
Explanation & Hint:
According to the guideline defined in the NIST Incident Response Life Cycle, several actions should be taken during the preparation phase including (1) creating and training the CSIRT and (2) acquiring and deploying the tools needed by the team to investigate incidents.
-
During the detection and analysis phase of the NIST incident response process life cycle, which sign category is used to describe that an incident might occur in the future?
- attrition
- indicator
- precursor
- impersonation
Explanation & Hint:
There are two categories for the signs of an incident:
Precursor – a sign that an incident might occur in the future
Indicator – a sign that an incident might already have occurred or is currently occurring
-
A company is applying the NIST.SP800-61 r2 incident handling process to security events. What are two examples of incidents that are in the category of precursor? (Choose two.)
- an IDS alert message being sent
- multiple failed logins from an unknown source
- log entries that show a response to a port scan
- a host that has been verified as infected with malware
- a newly-discovered vulnerability in Apache web servers
Explanation & Hint:
As an incident category, the precursor is a sign that an incident might occur in the future. Examples of precursors are log entries that show a response to a port scan or a newly-discovered vulnerability in web servers using Apache.
-
Match the NIST incident response life cycle phase with the description.
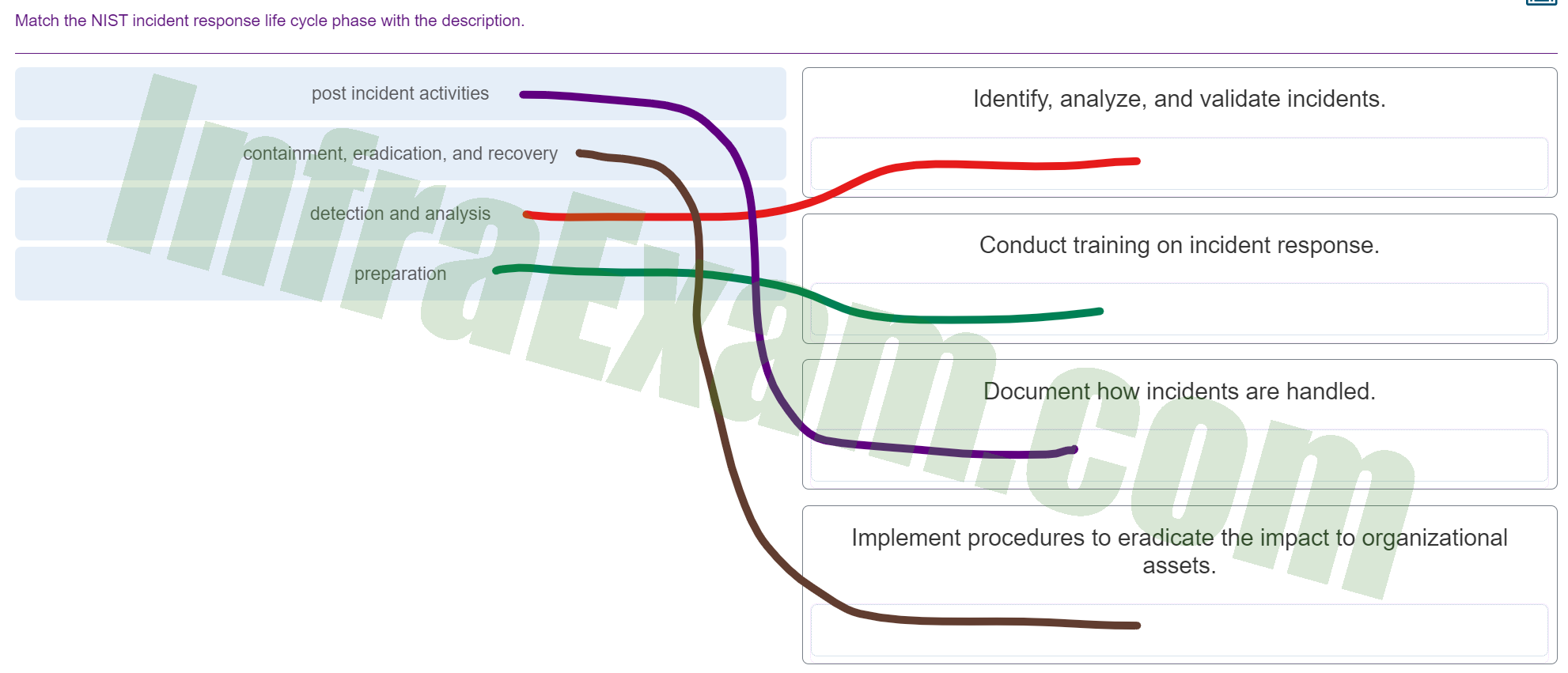
Match the NIST incident response life cycle phase with the description - post incident activities ==> Document how incidents are handled.
- containment, eradication, and recovery ==> Implement procedures to eradicate the impact to organizational assets.
- detection and analysis ==> Identify, analyze, and validate incidents.
- preparation ==> Conduct training on incident response.
Explanation & Hint:
- Preparation: This phase involves establishing and training the incident response team, creating incident response policies and procedures, and setting up communication plans. The description “Conduct training on incident response” matches this phase.
- Detection and Analysis: This phase is about monitoring for, detecting, and analyzing potential security incidents. The description “Identify, analyze, and validate incidents” matches this phase.
- Containment, Eradication, and Recovery: Once an incident is confirmed, the next steps are to contain the threat, eradicate it from the system, and recover any affected systems to a secure state. The description “Implement procedures to eradicate the impact to organizational assets” matches this phase.
- Post-Incident Activities: After an incident has been dealt with, the organization should review what happened, document the lessons learned, and update the incident response plan accordingly. The description “Document how incidents are handled” matches this phase.
-
What is defined in the policy element of the NIST incident response plan?
- how to handle incidents based on the mission and functions of an organization
- how the incident response team of an organization will communicate with organization stakeholders
- the metrics used for measuring incident response capability in an organization
- a roadmap for updating the incident response capability
Explanation & Hint:
The policy element of the NIST incident response plan details how incidents should be handled based on the mission and function of the organization.
-
What is specified in the plan element of the NIST incident response plan?
- metrics for measuring the incident response capability and effectiveness
- organizational structure and the definition of roles, responsibilities, and levels of authority
- priority and severity ratings of incidents
- incident handling based on the mission of the organization
Explanation & Hint:
NIST recommends creating policies, plans, and procedures for establishing and maintaining a CSIRC. One component of the plan element is to develop metrics for measuring the incident response capability and its effectiveness.
-
Match the NIST incident response stakeholder with the role.
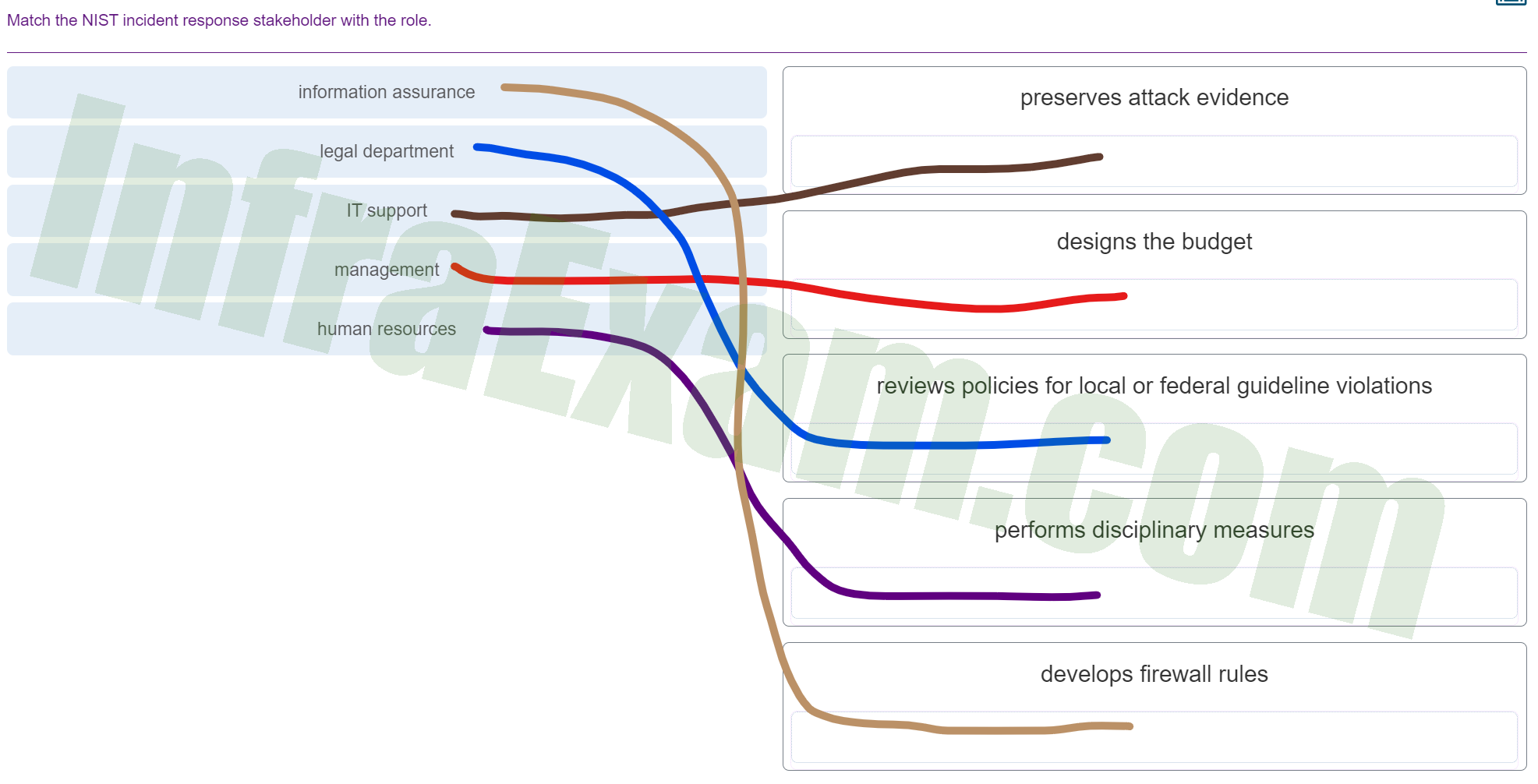
Match the NIST incident response stakeholder with the role - information assurance ==> develops firewall rules
- legal department ==> reviews policies for local or federal guideline violations
- IT support ==> preserves attack evidence
- management ==> designs the budget
- human resources ==> performs disciplinary measures
Explanation & Hint:
- Information Assurance: This role typically involves preserving attack evidence. They ensure that the information remains secure during and after an incident, which includes maintaining the integrity of the evidence.
- Legal Department: They would be involved in reviewing policies for local or federal guideline violations. The legal team would also be involved in any legal actions that need to be taken as a result of the incident.
- IT Support: This role would likely develop firewall rules as part of their duties in maintaining the security infrastructure.
- Management: Management would be responsible for designing the budget. They oversee and approve the funding for cybersecurity measures and incident response activities.
- Human Resources: HR may be involved in performing disciplinary measures if the incident involves internal staff or violations of company policy.
-
Which NIST-defined incident response stakeholder is responsible for coordinating incident response with other stakeholders and minimizing the damage of an incident?
- IT support
- the legal department
- management
- human resources
Explanation & Hint:
The management team creates the policies, designs the budget, and is in charge of staffing all departments. Management is also responsible for coordinating the incident response with other stakeholders and minimizing the damage of an incident.
-
What is the responsibility of the IT support group when handing an incident as defined by NIST?
- reviews the incident policies, plans, and procedures for local or federal guideline violations
- performs actions to minimize the effectiveness of the attack and preserve evidence
- coordinates the incident response with other stakeholders and minimizes the damage of an incident
- performs disciplinary measures if an incident is caused by an employee
Explanation & Hint:
IT support best understands the technology used in the organization and can perform the correct actions to minimize the effectiveness of the attack and preserve evidence.
-
What is the responsibility of the human resources department when handing a security incident as defined by NIST?
- Coordinate the incident response with other stakeholders and minimize the damage of an incident.
- Review the incident policies, plans, and procedures for local or federal guideline violations.
- Perform actions to minimize the effectiveness of the attack and preserve evidence.
- Perform disciplinary actions if an incident is caused by an employee.
Explanation & Hint:
The human resources department may be called upon to perform disciplinary measures if an incident is caused by an employee.
| CyberOps - Associate 1.0 & 1.01 | |
| Final Exam | |
| Practice Final Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Final Exam Answers | Online Test |
| 200-201 Certification Practice | Online Test |