CCNA 2 v7 SRWE v7.02 – Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essentials (Version 7.00) – Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 2023 2024 Full 100%
CCNA 2 v7 SRWE v7.02 – Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essentials (Version 7.00) – Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 2023 2024 Full 100%
This is NetAcad Cisco CCNA 2 v7 SRWE v7.02 Modules 7 – 9 Exam Answers 2023 2024 and Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essentials ( Version 7.00) – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers Full 100%. All answers have been verified by experts.
Cisco Netacad SRWE Version 7.00 CCNA 2 v7 & v7.02 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 2023 2024 – Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essential
-
Match each DHCP message type with its description. (Not all options are used.)
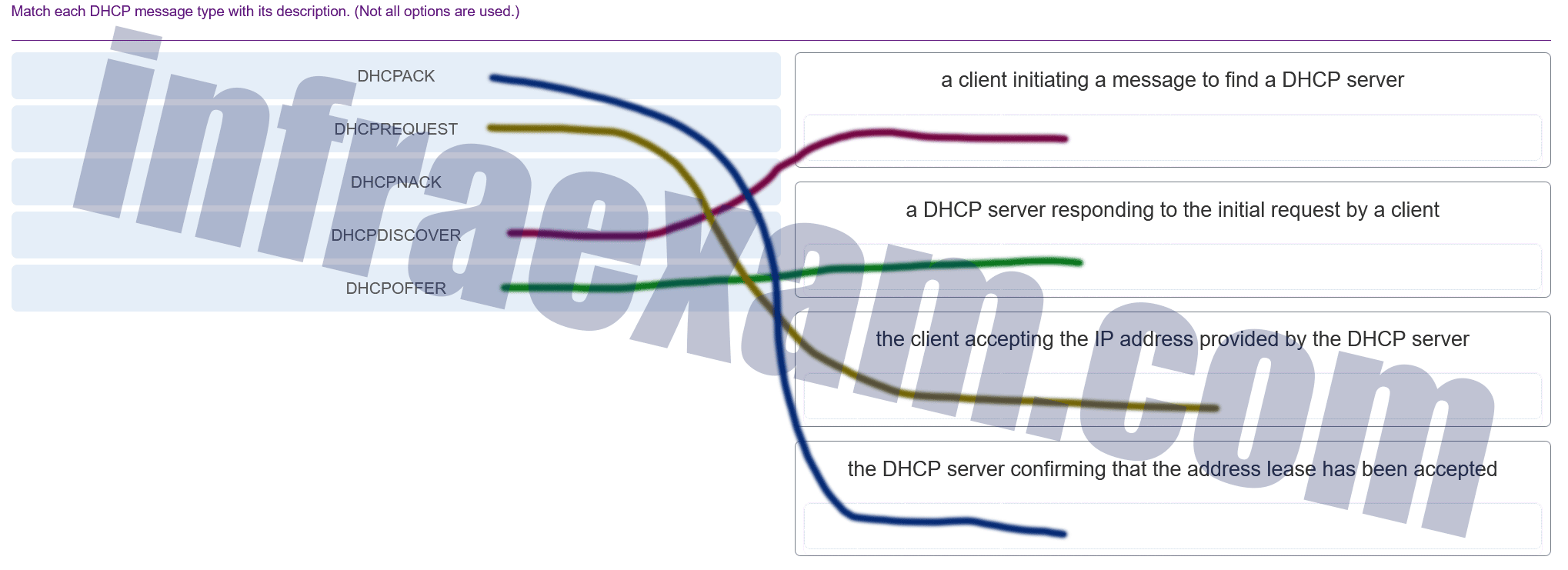
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 001 Answers Explanation & Hints: Place the options in the following order:
- a client initiating a message to find a DHCP server – DHCPDISCOVER
- a DHCP server responding to the initial request by a client – DHCPOFFER
- the client accepting the IP address provided by the DHCP server – DHCPREQUEST
- the DHCP server confirming that the lease has been accepted – DHCPACK
-
Which protocol automates assignment of IP addresses on a network, and which port number does it use? (Choose two.)
- DHCP
- DNS
- SMB
- 53
- 67
- 80
Answers Explanation & Hints: DNS uses port 53 and translates URLs to IP addresses. SMB provides shared access to files and printers and uses port 445. Port 80 is used by HTTP. HTTP is a protocol used to communicate between a web browser and a server.
-
Refer to the exhibit. PC1 is configured to obtain a dynamic IP address from the DHCP server. PC1 has been shut down for two weeks. When PC1 boots and tries to request an available IP address, which destination IP address will PC1 place in the IP header?
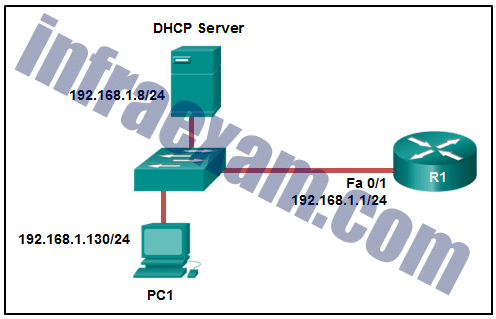
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 01 - 192.168.1.1
- 192.168.1.8
- 192.168.1.255
- 255.255.255.255
Answers Explanation & Hints: When a host boots and has been configured for dynamic IP addressing, the device tries to obtain a valid IP address. It sends a DHCPDISCOVER message. This is a broadcast message because the DHCP server address is unknown (by design). The destination IP address in the IP header is 255.255.255.255 and the destination MAC address is FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF.
-
A company uses DHCP servers to dynamically assign IPv4 addresses to employee workstations. The address lease duration is set as 5 days. An employee returns to the office after an absence of one week. When the employee boots the workstation, it sends a message to obtain an IP address. Which Layer 2 and Layer 3 destination addresses will the message contain?
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and 255.255.255.255
- both MAC and IPv4 addresses of the DHCP server
- MAC address of the DHCP server and 255.255.255.255
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and IPv4 address of the DHCP server
Answers Explanation & Hints: When the lease of a dynamically assigned IPv4 address has expired, a workstation will send a DHCPDISCOVER message to start the process of obtaining a valid IP address. Because the workstation does not know the addresses of DHCP servers, it sends the message via broadcast, with destination addresses of FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and 255.255.255.255.
-
Which command will allow a network administrator to check the IP address that is assigned to a particular MAC address?
- Router# show ip dhcp binding
- Router# show ip dhcp pool
- Router# show ip dhcp server statistics
- Router# show running-config I section_dhcp
Answers Explanation & Hints: The show ip dhcp binding command will show the leases, including IP addresses, MAC addresses, lease expiration, type of lease, client ID, and user name.
-
Which message does an IPv4 host use to reply when it receives a DHCPOFFER message from a DHCP server?
- DHCPACK
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPREQUEST
Answers Explanation & Hints: When the client receives the DHCPOFFER from the server, it sends back a DHCPREQUEST broadcast message. On receiving the DHCPREQUEST message, the server replies with a unicast DHCPACK message.
-
Which command, when issued in the interface configuration mode of a router, enables the interface to acquire an IPv4 address automatically from an ISP, when that link to the ISP is enabled?
- ip dhcp pool
- ip address dhcp
- service dhcp
- ip helper-address
Answers Explanation & Hints: The ip address dhcp interface configuration command configures an Ethernet interface as a DHCP client. The service dhcp global configuration command enables the DHCPv4 server process on the router. The ip helper-address command is issued to enable DHCP relay on the router. The ip dhcp pool command creates the name of a pool of addresses that the server can assign to hosts.
-
Which set of commands will configure a router as a DHCP server that will assign IPv4 addresses to the 192.168.100.0/23 LAN while reserving the first 10 and the last addresses for static assignment?
- ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.10
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.254
ip dhcp pool LAN-POOL-100
network 192.168.100.0 255.255.255.0
ip default-gateway 192.168.100.1 - ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.10
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.101.254
ip dhcp pool LAN-POOL-100
network 192.168.100.0 255.255.254.0
default-router 192.168.100.1 - dhcp pool LAN-POOL-100
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.9
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.254
network 192.168.100.0 255.255.254.0
default-router 192.168.101.1 - ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.9
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.101.254
ip dhcp pool LAN-POOL-100
ip network 192.168.100.0 255.255.254.0
ip default-gateway 192.168.100.1Answers Explanation & Hints: The /23 prefix is equivalent to a network mask of 255.255.254.0. The network usable IPv4 address range is 192.168.100.1 to 192.168.101.254 inclusive. The commands dhcp pool , ip default-gateway , and ip network are not valid DHCP configuration commands.
- ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.10
-
Which kind of message is sent by a DHCP client when its IP address lease is about to expire?
- a DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message
- a DHCPREQUEST broadcast message
- a DHCPREQUEST unicast message
- a DHCPDISCOVER unicast message
Answers Explanation & Hints: When the IP address lease time of the DHCP client expires, it sends a DHCPREQUEST unicast message directly to the DHCPv4 server that originally offered the IPv4 address.
-
A host PC is attempting to lease an address through DHCP. What message is sent by the server to let the client know it is able to use the provided IP information?
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPACK
- DHCPNACK
Answers Explanation & Hints: When a host uses DHCP to automatically configure an IP address, the typically sends two messages: the DHCPDISCOVER message and the DHCPREQUEST message. These two messages are usually sent as broadcasts to ensure that all DHCP servers receive them. The servers respond to these messages using DHCPOFFER, DHCPACK, and DHCPNACK messages, depending on the circumstance.
-
What is a result when the DHCP servers are not operational in a network?
- Workstations are assigned with the IP address 0.0.0.0.
- Workstations are assigned with the IP address 127.0.0.1.
- Workstations are assigned with IP addresses in the 10.0.0.0/8 network.
- Workstations are assigned with IP addresses in the 169.254.0.0/16 network.
Answers Explanation & Hints: When workstations are configured with obtaining IP address automatically but DHCP servers are not available to respond to the requests, a workstation can assign itself an IP addresses from the 169.254.0.0/16 network.
-
What is one indication that a Windows computer did not receive an IPv4 address from a DHCP server?
- The computer cannot ping 127.0.0.1.
- Windows displays a DHCP timeout message.
- The computer receives an IP address that starts with 169.254.
- The computer cannot ping other devices on the same network with IP addresses in the 169.254.0.0/16 range.
Answers Explanation & Hints: When a Windows PC cannot communicate with an IPv4 DHCP server, the computer automatically assigns an IP address in the 169.254.0.0/16 range. Any other device on the same network that receives an address in the same range is reachable.
-
Which DHCPv4 message will a client send to accept an IPv4 address that is offered by a DHCP server?
- unicast DHCPACK
- broadcast DHCPACK
- unicast DHCPREQUEST
- broadcast DHCPREQUEST
Answers Explanation & Hints: When a DHCP client receives DHCPOFFER messages, it will send a broadcast DHCPREQUEST message for two purposes. First, it indicates to the offering DHCP server that it would like to accept the offer and bind the IP address. Second, it notifies any other responding DHCP servers that their offers are declined.
-
A small coffee shop is offering free Wi-Fi to customers. The network includes a wireless router and a DSL modem that is connected to the local phone company. What method is typically used to configure the connection to the phone company?
- Set the WAN connection in the wireless router as a DHCP client.
- Set the DSL modem as a DHCP client to get a public IP address from the wireless router.
- Set the connection between the wireless router and the DSL modem as a private IP network.
- Set the DSL modem as a DHCP client to the phone company and a DHCP server for the internal connection.
Answers Explanation & Hints: In a SOHO environment, a wireless router connects to an ISP via a DSL or cable modem. The IP address between the wireless router and ISP site is typically assigned by the ISP through DHCP. The DSL modem does not manage IP address allocation.
-
What is the reason that an ISP commonly assigns a DHCP address to a wireless router in a SOHO environment?
- better connectivity
- better network performance
- easy IP address management
- easy configuration on ISP firewall
Answers Explanation & Hints: In a SOHO environment, a wireless router connects to the ISP via a DSL or cable modem. The IP address between the wireless router and ISP site is typically assigned by the ISP through DHCP. This method facilitates the IP addressing management in that IP addresses for clients are dynamically assigned so that if a client is dropped, the assigned IP address can be easily reassigned to another client.
-
A company uses DHCP to manage IP address deployment for employee workstations. The IT department deploys multiple DHCP servers in the data center and uses DHCP relay agents to facilitate the DHCP requests from workstations. Which two UDP ports are used to forward DHCP traffic? (Choose two.)
- 23
- 53
- 67
- 68
- 80
Answers Explanation & Hints: The DHCP protocol operates with 2 UDP ports. UDP port 67 is the destination port for DHCP servers, and DHCP clients use UDP port 68.
-
What information can be verified through the show ip dhcp binding command?
- the number of IP addresses remaining in the DHCP pool
- the IPv4 addresses that have been excluded from the DHCPv4 pool
- that DHCPv4 discover messages are still being received by the DHCP server
- the IPv4 addresses that are assigned to hosts by the DHCP server
Answers Explanation & Hints: The show ip dhcp binding command shows a list of IPv4 addresses and the MAC addresses of the hosts to which they are assigned. Using this information an administrator can determine which host interfaces have been assigned to specific hosts.
-
A client device on an Ethernet segment needs an IP address in order to communicate on the network. A DHCP server with IP address 192.168.1.1 has been configured and enabled on the network. How will a client device obtain a usable IP address for this network?
- Send a DHCPREQUEST packet to IP address 255.255.255.255.
- Send a DHCPACK packet to the default gateway address.
- Send a DHCPDISCOVER message to physical address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF.
- Use a statically configured IP address from the pool of IP addresses that is offered by the DHCP server.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Like IP addressing, there is also a special MAC address for broadcast purposes: FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF. When a DHCP client needs to send a DHCP Discover message in order to seek DHCP servers, the client will use this MAC address as the destination MAC address in the Ethernet frame. It does this because it has no knowledge of the IP and MAC addresses of DHCP servers.
-
What is the result of a network technician issuing the command ip dhcp excluded-address 10.0.15.1 10.0.15.15 on a Cisco router?
- The Cisco router will exclude 15 IP addresses from being leased to DHCP clients.
- The Cisco router will allow only the specified IP addresses to be leased to clients.
- The Cisco router will exclude only the 10.0.15.1 and 10.0.15.15 IP addresses from being leased to DHCP clients.
- The Cisco router will automatically create a DHCP pool using a /28 mask.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The ip dhcp excluded-address command is followed by the first and the last addresses to be excluded from being leased to DHCP clients.
-
What is an advantage of configuring a Cisco router as a relay agent?
- It will allow DHCPDISCOVER messages to pass without alteration.
- It can forward both broadcast and multicast messages on behalf of clients.
- It can provide relay services for multiple UDP services.
- It reduces the response time from a DHCP server.
Answers Explanation & Hints: By default, the ip helper-address command forwards the following eight UDP services:Port 37: Time
Port 49: TACACS
Port 53: DNS
Port 67: DHCP/BOOTP client
Port 68: DHCP/BOOTP server
Port 69: TFTP
Port 137: NetBIOS name service
Port 138: NetBIOS datagram service
-
Which statement is true about DHCP operation?
- If the client receives several DHCPOFFER messages from different servers, it sends a unicast DHCPREQUEST message to the server from which it chooses to obtain the IP information.
- A client must wait for lease expiration before it sends another DHCPREQUEST message.
- When a device that is configured to use DHCP boots, the client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to identify any available DHCP servers on the network.
- The DHCPDISCOVER message contains the IP address and subnet mask to be assigned, the IP address of the DNS server, and the IP address of the default gateway.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to identify any available DHCP servers on the network. A DHCP server replies with a DHCPOFFER message. This message offers to the client a lease that contains such information as the IP address and subnet mask to be assigned, the IP address of the DNS server, and the IP address of the default gateway. After the client receives the lease, the received information must be renewed through another DHCPREQUEST message prior to the lease expiration.
-
Match the purpose with its DHCP message type. (Not all options are used.)
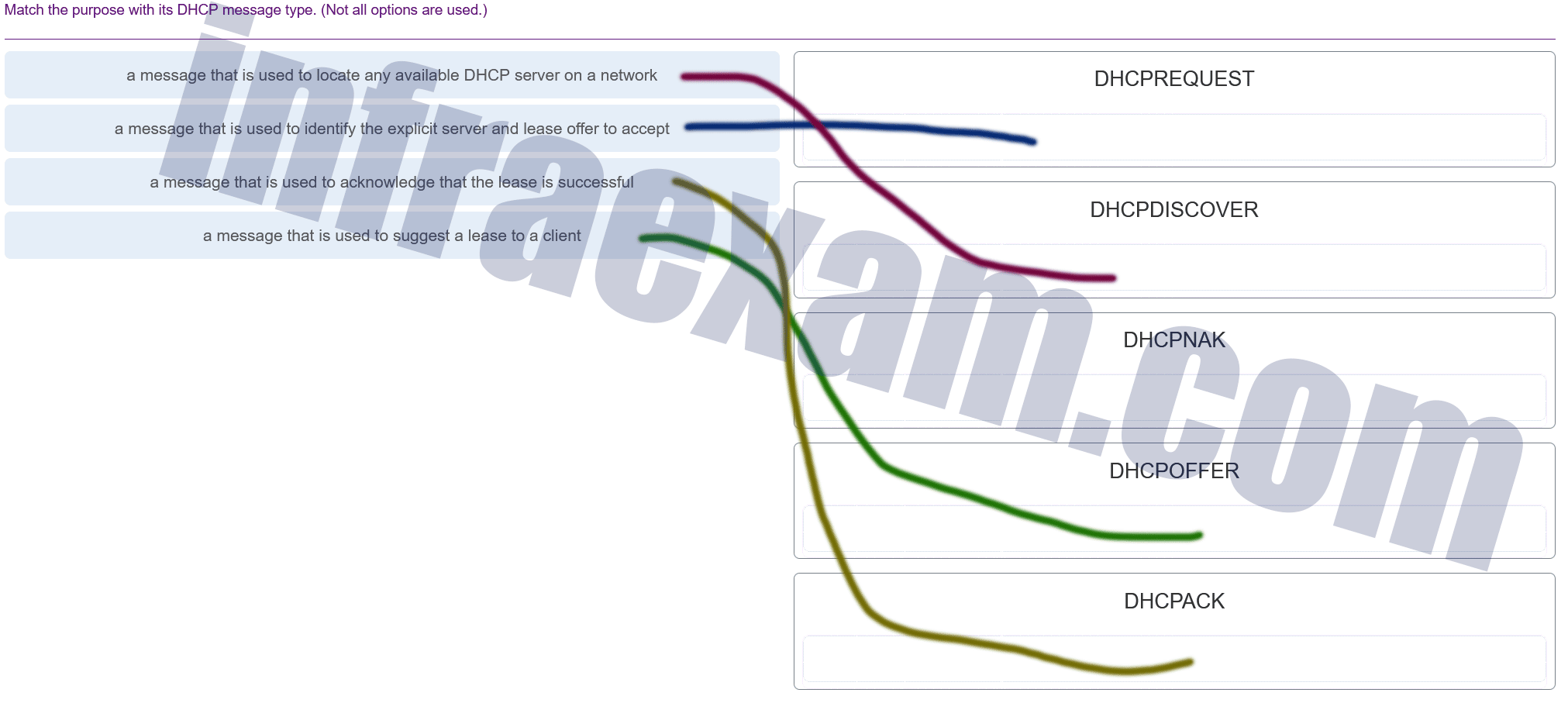
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 002 Answers Explanation & Hints: The DHCPDISCOVER message is used to identify any DHCP servers on a network. The DHCPOFFER message is used by a server to offer a lease to a client. The DHCPREQUEST message is used to identify both the specific DHCP server and the lease that the client is accepting.
The DHCPACK message is used by a server to finalize a successful lease with a client.
The DHCPNAK message is used when an offered lease is no longer valid. -
A company uses the method SLAAC to configure IPv6 addresses for the workstations of the employees. A network administrator configured the IPv6 address on the LAN interface of the router. The interface status is UP. However, the workstations on the LAN segment did not obtain the correct prefix and prefix length. What else should be configured on the router that is attached to the LAN segment for the workstations to obtain the information?
- R1(config-if)# ipv6 enable
- R1(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
- R1(config-if)# ipv6 nd other-config-flag
- R1(config)# ipv6 dhcp pool < name of the pool >
Answers Explanation & Hints: A PC that is configured to use the SLAAC method obtains the IPv6 prefix and prefix length from a router. When the PC boots, it sends an RS message to inform the routers that it needs the information. A router sends an RA message that includes the required information. For a router to be able to send RA messages, it must be enabled as an IPv6 router by the unicast ipv6-routing command in global configuration mode. The other options are not used to enable IPv6 routing on a router.
-
A network administrator configures a router to send RA messages with M flag as 0 and O flag as 1. Which statement describes the effect of this configuration when a PC tries to configure its IPv6 address?
- It should contact a DHCPv6 server for all the information that it needs.
- It should use the information that is contained in the RA message exclusively.
- It should use the information that is contained in the RA message and contact a DHCPv6 server for additional information.
- It should contact a DHCPv6 server for the prefix, the prefix-length information, and an interface ID that is both random and unique.
Answers Explanation & Hints: ICMPv6 RA messages contain two flags to indicate whether a workstation should use SLAAC, a DHCPv6 server, or a combination to configure its IPv6 address. These two flags are M flag and O flag. When both flags are 0 (by default), a client must only use the information in the RA message. When M flag is 0 and O flag is 1, a client should use the information in the RA message and look for the other configuration parameters (such as DNS server addresses) on DHCPv6 servers.
-
Refer to the exhibit. What should be done to allow PC-A to receive an IPv6 address from the DHCPv6 server?
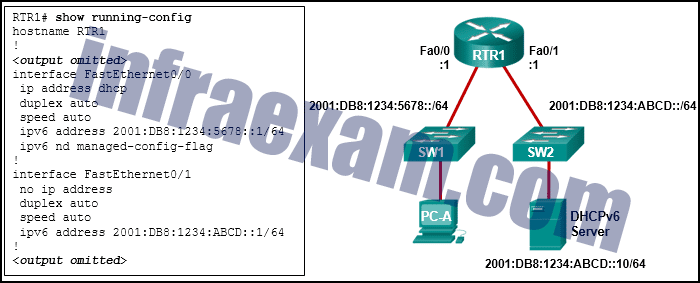
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 04 - Add the ipv6 dhcp relay command to interface Fa0/0.
- Configure the ipv6 nd managed-config-flag command on interface Fa0/1.
- Change the ipv6 nd managed-config-flag command to ipv6 nd other-config-flag .
- Add the IPv6 address 2001:DB8:1234:5678::10/64 to the interface configuration of the DHCPv6 server.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Client DHCPv6 messages are sent to a multicast address with link-local scope, which means that the messages will not be forwarded by routers. Because the client and server are on different subnets on different interfaces, the message will not reach the server. The router can be configured to relay the DHCPv6 messages from the client to the server by configuring the ipv6 dhcp relay command on the interface that is connected to the client.
-
Refer to the exhibit. PC-A is unable to receive an IPv6 address from the stateful DHCPv6 server. What is the problem?
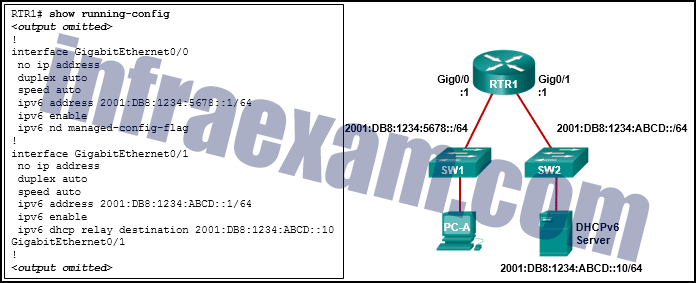
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 05 - The ipv6 dhcp relay command should be applied to interface Gig0/0.
- The ipv6 nd managed-config-flag should be applied to interface Gig0/1.
- The ipv6 nd managed-config-flag command should be ipv6 nd other-config-flag .
- The ipv6 dhcp relay command should use the link-local address of the DHCP server.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The ipv6 dhcp relay command must be applied to the interface where the clients are located. The ipv6 dhcp relay command can use either the link-local or global unicast address of the DHCPv6 server, or even a multicast address. The ipv6 nd managed-config-flag indicates to the clients that they should use stateful DHCPv6 and is also applied to the interface where the clients are located.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is implementing the stateless DHCPv6 operation for the company. Clients are configuring IPv6 addresses as expected. However, the clients are not getting the DNS server address and the domain name information configured in the DHCP pool. What could be the cause of the problem?
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 08 - The GigabitEthernet interface is not activated.
- The router is configured for SLAAC operation.
- The DNS server address is not on the same network as the clients are on.
- The clients cannot communicate with the DHCPv6 server, evidenced by the number of active clients being 0.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The router is configured for SLAAC operation because there is no configuration command to change the RA M and O flag value. By default, both M and O flags are set to 0. In order to permint stateless DHCPv6 operation, the interface command ipv6 nd other-config-flag should be issued. The GigabitEthernet interface is in working condition because clients can get RA messages and configure their IPv6 addresses as expected. Also, the fact that R1 is the DHCPv6 server and clients are getting RA messages indicates that clients can communicate with the DHCP server. The number of active clients is 0 because the DHCPv6 server does not maintain the state of clients IPv6 addresses (it is not configured for stateful DHCPv6 operation). The DNS server address issue is not relevant to the problem.
-
Match the DHCP message types to the order of the stateful DHCPv6 process when a client first connects to an IPv6 network. (Not all options are used.)
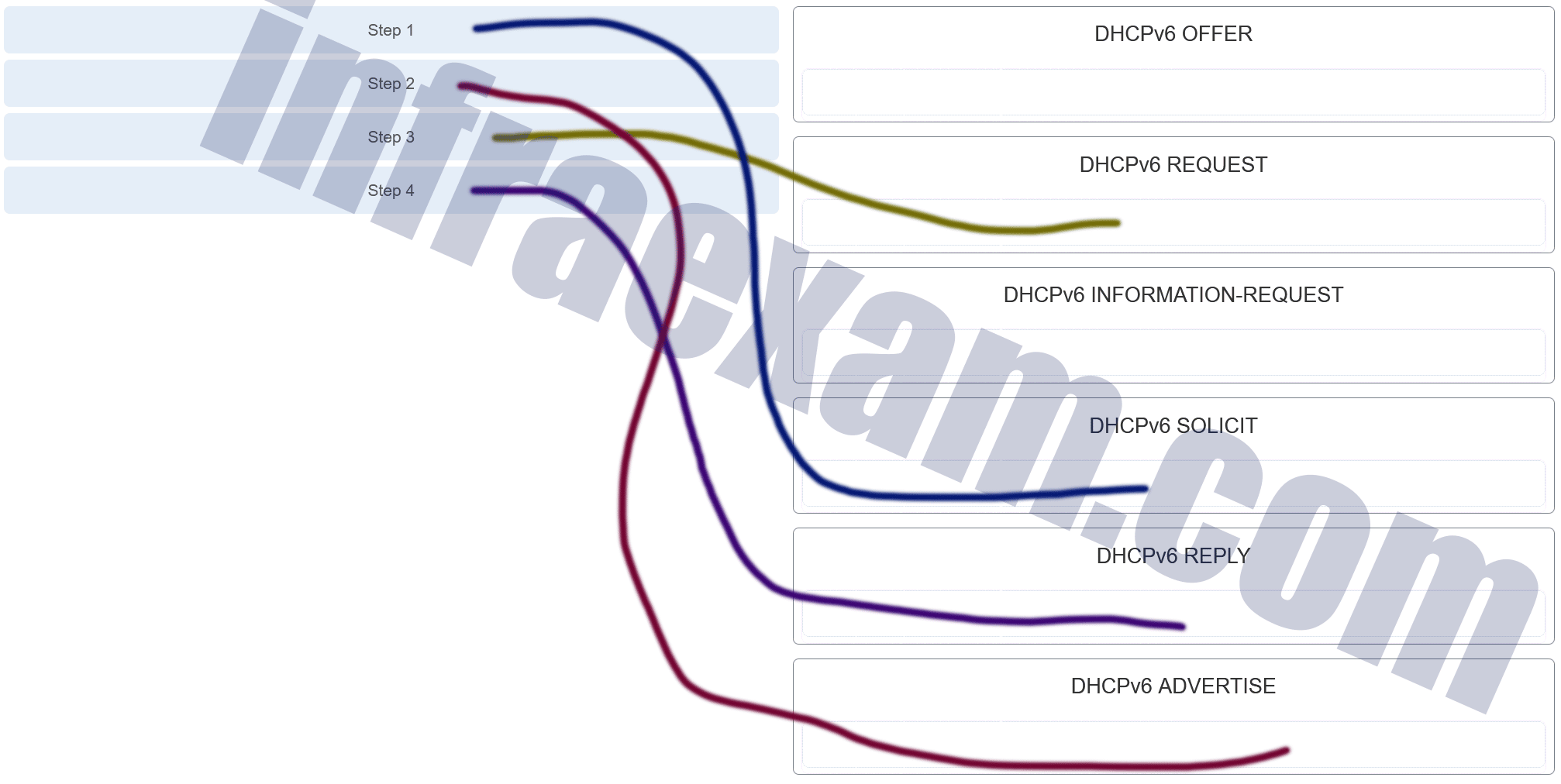
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 003 Answers Explanation & Hints: A stateless DHCPv6 client would send a DHCPv6 INFORMATION-REQUEST message as step 3 in the process.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring a router as a DHCPv6 server. The administrator issues a show ipv6 dhcp pool command to verify the configuration. Which statement explains the reason that the number of active clients is 0?
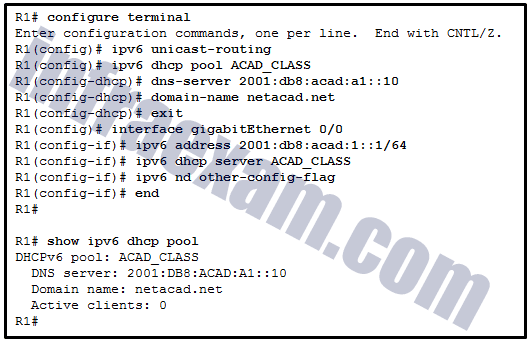
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 10 - The default gateway address is not provided in the pool.
- No clients have communicated with the DHCPv6 server yet.
- The IPv6 DHCP pool configuration has no IPv6 address range specified.
- The state is not maintained by the DHCPv6 server under stateless DHCPv6 operation.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Under the stateless DHCPv6 configuration, indicated by the command ipv6 nd other-config-flag , the DHCPv6 server does not maintain the state information, because client IPv6 addresses are not managed by the DHCP server. Because the clients will configure their IPv6 addresses by combining the prefix/prefix-length and a self-generated interface ID, the ipv6 dhcp pool configuration does not need to specify the valid IPv6 address range. And because clients will use the link-local address of the router interface as the default gateway address, the default gateway address is not necessary .
-
A company uses the SLAAC method to configure IPv6 addresses for the employee workstations. Which address will a client use as its default gateway?
- the all-routers multicast address
- the link-local address of the router interface that is attached to the network
- the unique local address of the router interface that is attached to the network
- the global unicast address of the router interface that is attached to the network
Answers Explanation & Hints: When a PC is configured to use the SLAAC method for configuring IPv6 addresses, it will use the prefix and prefix-length information that is contained in the RA message, combined with a 64-bit interface ID (obtained by using the EUI-64 process or by using a random number that is generated by the client operating system), to form an IPv6 address. It uses the link-local address of the router interface that is attached to the LAN segment as its IPv6 default gateway address.
-
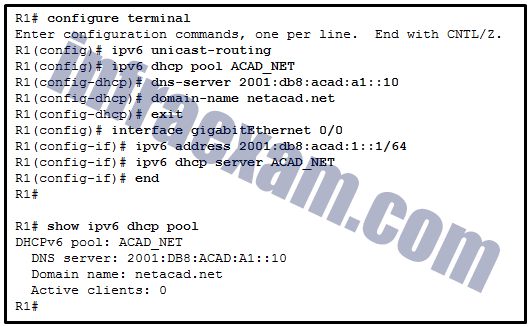
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring a router for DHCPv6 operation. Which conclusion can be drawn based on the commands?
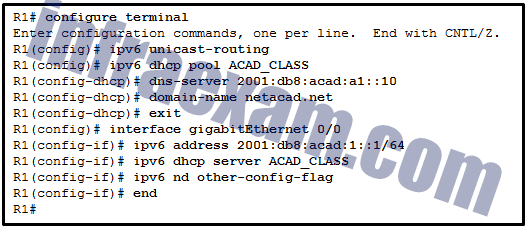
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 02 - The DHCPv6 server name is ACAD_CLASS.
- The router is configured for stateless DHCPv6 operation.
- Clients would configure the interface IDs above 0010.
- The router is configured for stateful DHCPv6 operation, but the DHCP pool configuration is incomplete.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The DHCPv6 is for the stateless DHCPv6 operation that is indicated by changing the O flag to 1 and leaving the M flag as default, which is 0. Therefore, it is not configured for stateful DHCPv6 operation. Although the DNS server has the interface ID 0010, clients in stateless DHCPv6 operation will configure their interface IDs either by EUI-64 or a random number. The ACAD_CLASS is the name of the DHCP pool, not the DHCP server name.
-
Match the descriptions to the corresponding DHCPv6 server type. (Not all options are used.)
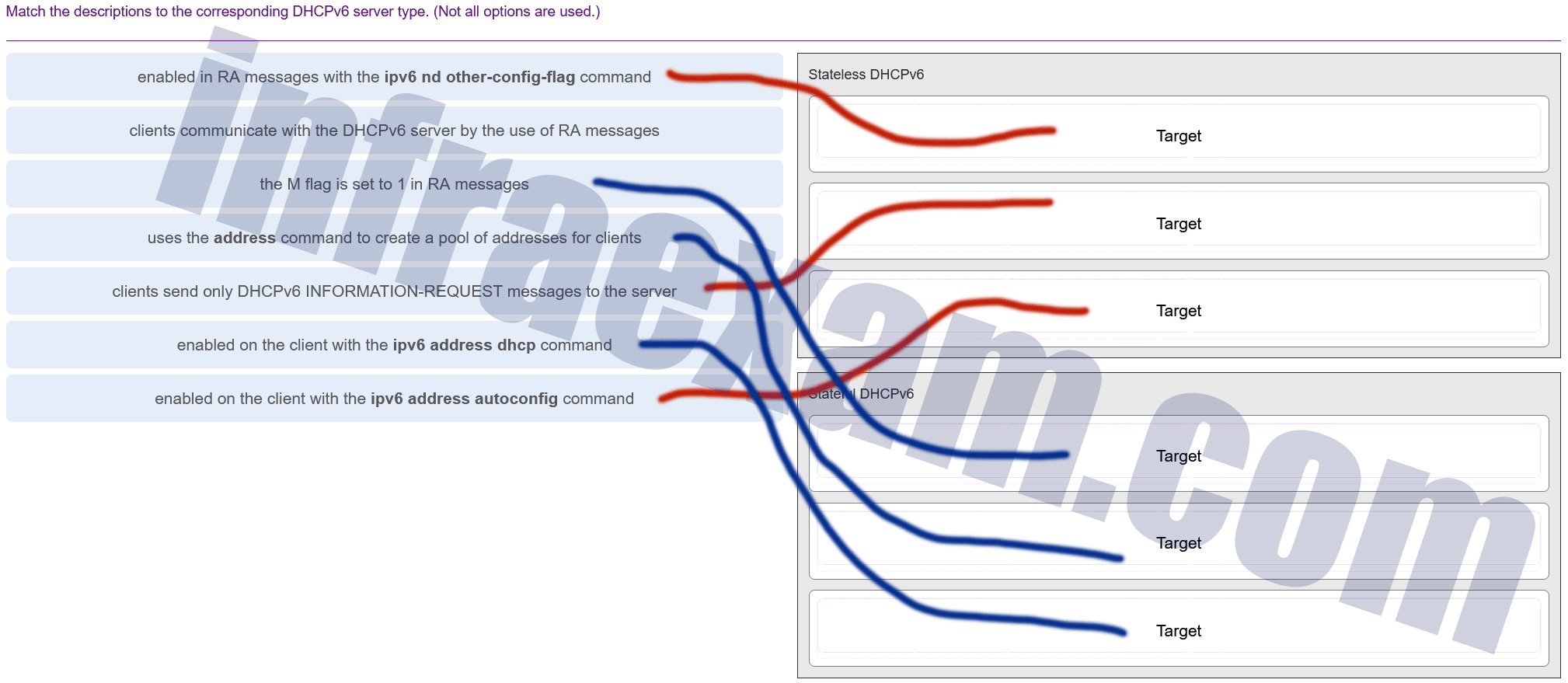
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 004 -
Explanation & Hint: - Stateless DHCPv6: This configuration does not assign IP addresses to clients. Instead, it provides other configuration details such as DNS server information. It usually works with SLAAC (Stateless Address Autoconfiguration), where the client auto-configures its own IP address based on the Router Advertisement (RA) messages and then contacts the DHCPv6 server for additional information if needed.
- Stateful DHCPv6: This is when the DHCPv6 server assigns the IP address to the client in addition to other configuration details. The server keeps track of the IP addresses that it has assigned to prevent two clients from getting the same IP address.
- Router Advertisement (RA) messages: These are sent by routers to advertise their presence along with various link and Internet parameters. The M flag (Managed address configuration flag) and O flag (Other configuration flag) in these messages inform the client of whether to use stateful (M flag) or stateless (O flag) DHCPv6 services.
-
-
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output that is shown, what kind of IPv6 addressing is being configured?
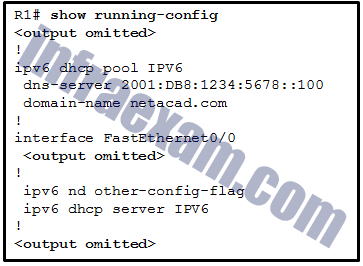
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 03 - SLAAC
- stateful DHCPv6
- stateless DHCPv6
- static link-local
Answers Explanation & Hints: Stateful DHCPv6 pools are configured with address prefixes for hosts via the address command, whereas stateless DHCPv6 pools typically only contain information such as DNS server addresses and the domain name. RA messages that are sent from routers that are configured as stateful DHCPv6 servers have the M flag set to 1 with the command ipv6 nd managed-config-flag , whereas stateless DHCPv6 servers are indicated by setting the O flag to 1 with the ipv6 nd other-config-flag command.
-
A network administrator is analyzing the features that are supported by different first-hop router redundancy protocols. Which statement describes a feature that is associated with HSRP?
- HSRP uses active and standby routers.
- It uses ICMP messages in order to assign the default gateway to hosts.
- It allows load balancing between a group of redundant routers.
- HSRP is nonproprietary.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The HSRP first-hop router redundancy protocol is Cisco proprietary and supports standby and active devices. VRRPv2 and VRRPv3 are nonproprietary. GLBP is Cisco proprietary and supports load balancing between a group of redundant routers.
-
Refer to the exhibit. What protocol can be configured on gateway routers R1 and R2 that will allow traffic from the internal LAN to be load balanced across the two gateways to the Internet?
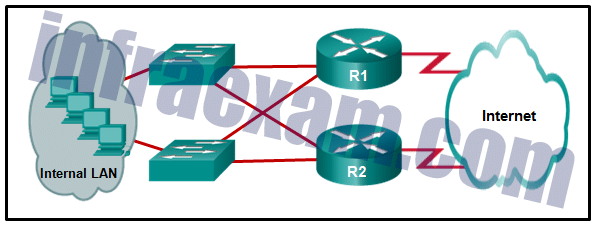
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 07 - STP
- PVST
- PVST+
- GLBP
Answers Explanation & Hints: GLBP, or Group Load Balancing Protocol, allows multiple routers to act as a single default gateway for hosts. GLBP load balances the traffic across the individual routers on a per host basis.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer is troubleshooting host connectivity on a LAN that uses a first hop redundancy protocol. Which IPv4 gateway address should be configured on the host?
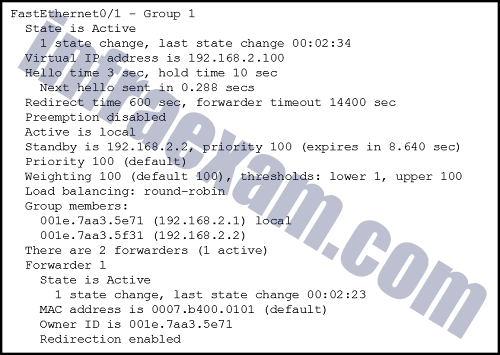
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 06 - 192.168.2.0
- 192.168.2.1
- 192.168.2.2
- 192.168.2.100
Answers Explanation & Hints: The host default gateway address should be the FHRP (in this case GLBP) virtual IP address.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which destination MAC address is used when frames are sent from the workstation to the default gateway?
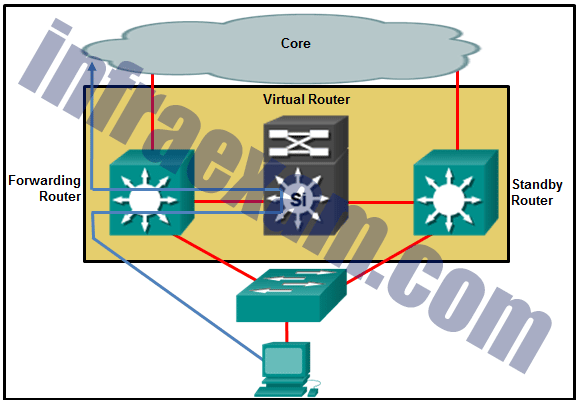
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 09 - MAC address of the forwarding router
- MAC addresses of both the forwarding and standby routers
- MAC address of the standby router
- MAC address of the virtual router
Answers Explanation & Hints: The IP address of the virtual router acts as the default gateway for all the workstations. Therefore, the MAC address that is returned by the Address Resolution Protocol to the workstation will be the MAC address of the virtual router.
-
Match the step number to the sequence of stages that occur during the HSRP failover process. (Not all options are used.)
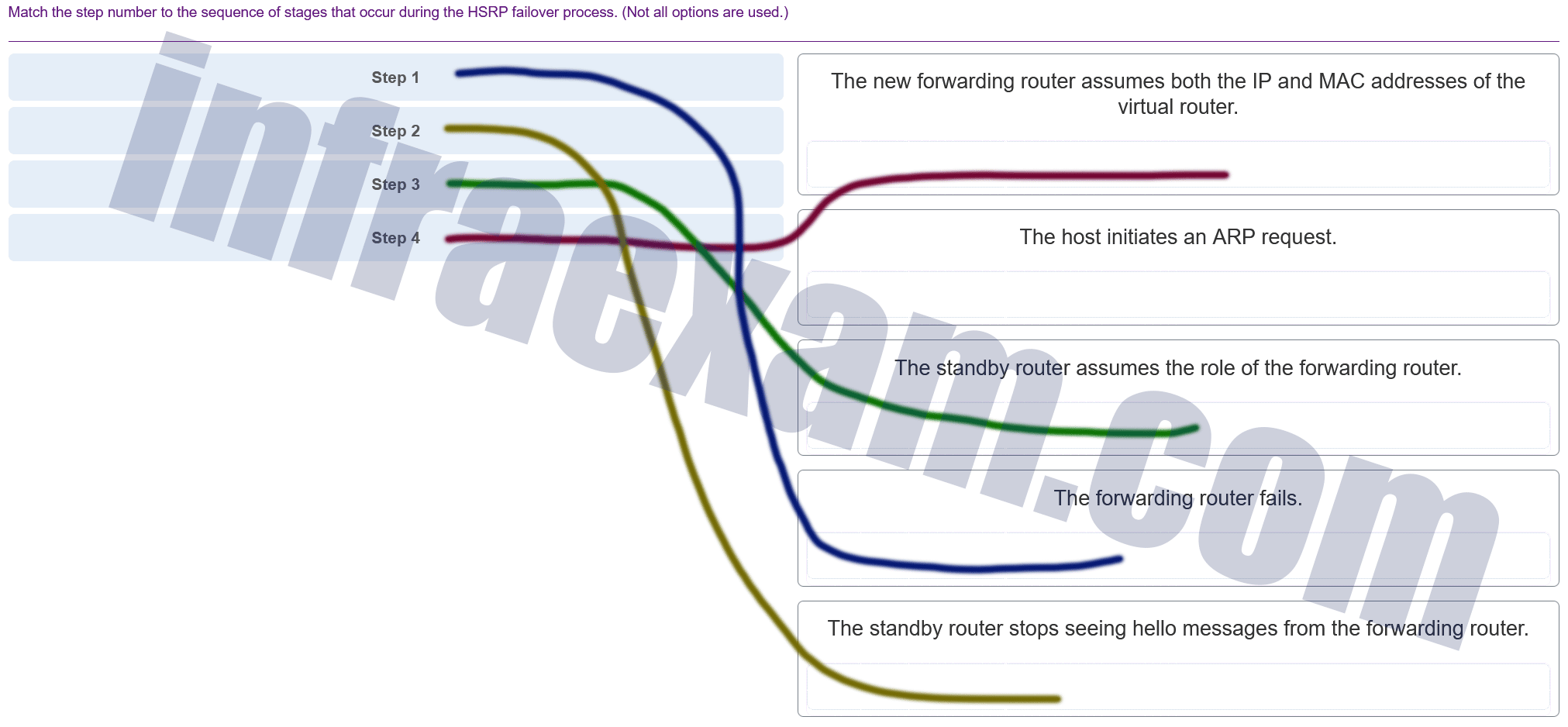
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 005 Answers Explanation & Hints: Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that is designed to allow for transparent failover of a first-hop IPv4 device.
-
Match the FHRP protocols to the appropriate description. (Not all options are used.)
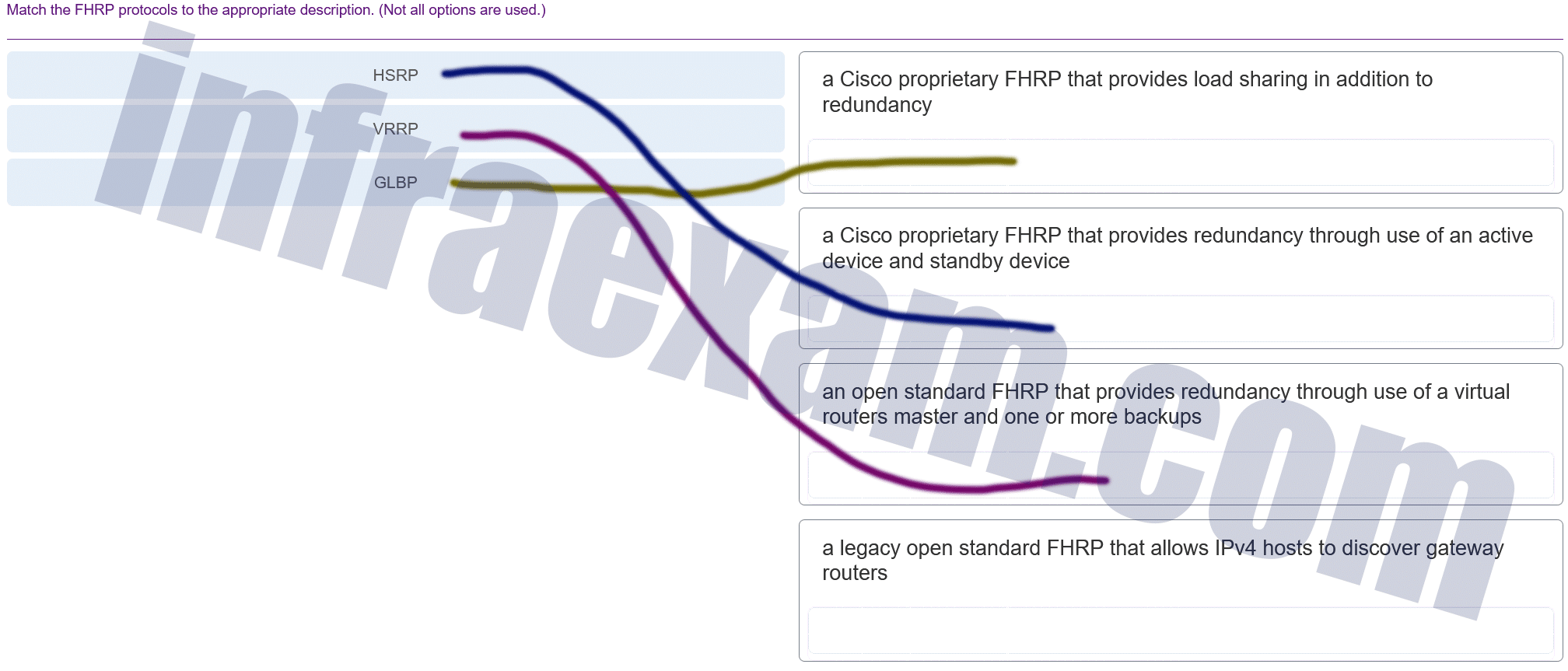
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 006 Answers Explanation & Hints: GLBP, A Cisco proprietary FHRP that provides load sharing in addition to redundancy. HSRP A Cisco proprietary FHRP that provides redundancy through use of an active device and standby device. VRRP, An open standard FHRP that provides redundancy through use of a virtual routers master and one or more backups. Distractor, A legacy open standard FHRP that allows IPv4 hosts to discover gateway routers.
-
Which FHRP implementation is a nonproprietary IPv4-only election protocol with limited scalability?
- VRRPv2
- GLBP for IPv6
- GLBP
- IRDP
Explanation & Hint: The First Hop Redundancy Protocol (FHRP) implementation that is a nonproprietary IPv4-only election protocol with limited scalability is VRRPv2 (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol version 2).
Here’s a brief overview of the protocols mentioned:
- VRRPv2: This is a nonproprietary election protocol used for IPv4. VRRPv3 supports IPv6, but VRRPv2 is limited to IPv4. VRRP allows for automatic assignment of available IP routers to participating hosts. This version has some scalability limitations due to the restricted number of virtual routers that can be supported.
- GLBP (Gateway Load Balancing Protocol): GLBP is a Cisco proprietary FHRP that provides redundancy for IPv4 and load balancing over multiple routers (gateways). It is more scalable and offers load balancing, unlike VRRP which does not.
- GLBP for IPv6: This would be the GLBP version that supports IPv6, offering the same features as GLBP but for IPv6 networks.
- IRDP (ICMP Router Discovery Protocol): This is an older, less commonly used protocol for router discovery which can provide some level of redundancy but it’s not an election protocol like VRRP or GLBP.
Therefore, the answer to your question is VRRPv2.
-
Which FHRP implementation is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that suppports IPv6 load balancing?
- GLBP for IPv6
- GLBP
- VRRPv3
- IRDP
-
Explanation & Hint: The First Hop Redundancy Protocol (FHRP) implementation that is a Cisco-proprietary protocol supporting IPv6 load balancing is GLBP for IPv6.
Here’s why:
- GLBP (Gateway Load Balancing Protocol): This Cisco proprietary protocol provides redundancy and automatic load balancing between multiple routers (gateways), but the original GLBP is specific to IPv4.
- GLBP for IPv6: This is an extension of the original GLBP to support IPv6. It inherits the same features of GLBP but is designed for IPv6 networks, providing both redundancy and load balancing.
- VRRPv3 (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol version 3): Although VRRPv3 does support IPv6, it is not a Cisco proprietary protocol and does not inherently provide load balancing like GLBP does. VRRP is an election protocol that allows for router redundancy, ensuring that user traffic immediately and transparently recovers from first hop router failures, where the “virtual router” described by a VRRP configuration is a master/backup relationship of multiple routers.
- IRDP (ICMP Router Discovery Protocol): IRDP is neither proprietary to Cisco nor does it support load balancing. It is an older protocol used for router discovery and is not considered an FHRP.
Based on this information, the correct answer is GLBP for IPv6.
-
Which FHRP implementation is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that suppports IPv6 load balancing?
- GLBP for IPv6
- VRRPv3
- GLBP
- VRRPv2
-
Explanation & Hint: The FHRP (First Hop Redundancy Protocol) implementation that is a Cisco-proprietary protocol and supports IPv6 load balancing is GLBP (Gateway Load Balancing Protocol). Although traditionally associated with IPv4, Cisco has extended GLBP to support IPv6 environments as well.
Here’s a breakdown of the options you’ve listed:
- GLBP for IPv6: This is the version of GLBP that has been extended to support IPv6. It is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that allows for both redundancy and load balancing over multiple routers.
- VRRPv3 (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol version 3): While VRRPv3 does support IPv6, it is not a Cisco-proprietary protocol and it does not provide load balancing functionality; it is primarily for router redundancy.
- GLBP: This is the correct answer as it is Cisco-proprietary and provides IPv6 load balancing when extended to support IPv6.
- VRRPv2: This is an earlier version of VRRP that supports IPv4 only and is not Cisco-proprietary. It also does not provide load balancing functionality.
Therefore, the correct answer remains GLBP (assuming the context includes its IPv6 support).
-
Which FHRP implementation is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that suppports IPv4 load sharing?
- GLBP
- VRRPv3
- GLBP for IPv6
- VRRPv2
-
Explanation & Hint: - GLBP: Gateway Load Balancing Protocol is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that supports load balancing and redundancy for IPv4 networks. GLBP allows multiple routers to share the load of traffic for a single IP address, providing both redundancy and efficient utilization of network resources on IPv4 networks. It is the only protocol among the options provided that supports both redundancy and load sharing for IPv4 and is Cisco-specific.
- VRRPv3: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol version 3 is not proprietary to Cisco; it is an open standard. VRRPv3 adds support for IPv6 in addition to IPv4. However, its primary function is to provide redundancy rather than load sharing. VRRPv3 enables one router to automatically take over if the other fails, with the master router handling all traffic for the virtual router IP address and the backup router taking over if necessary.
- GLBP for IPv6: This would be the version of GLBP that supports IPv6. Like its IPv4 counterpart, it would be Cisco-proprietary and capable of load balancing. However, this option specifically references IPv6 support, and the question asks about IPv4 load sharing, making this option less relevant to the question.
- VRRPv2: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol version 2 is also not proprietary to Cisco; it is an open standard and it only supports IPv4. Similar to VRRPv3, VRRPv2’s primary role is to provide redundancy rather than load sharing. In a VRRP setup, one router is elected as the master, and the rest are backups in case the master router fails.
In summary, for IPv4 load sharing with a Cisco-proprietary protocol, the correct answer is GLBP.
-
Which FHRP implementation is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that suppports IPv4 load sharing?
- GLBP
- IRDP
- GLBP for IPv6
- VRRPv3
-
Explanation & Hint: Among the options provided, the FHRP implementation that is a Cisco-proprietary protocol and supports IPv4 load sharing is:
- GLBP: Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) is a Cisco-proprietary protocol designed to manage the process of backing up routers for LAN hosts and also allows for load balancing of traffic across multiple routers (gateways). GLBP is unique among FHRPs because it can not only provide redundancy but also load balancing, which is not a feature offered by VRRP or HSRP.
Here’s an analysis for the other options for clarity:
- IRDP: ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP) is not an FHRP, but rather a protocol that allows hosts on an IPv4 network to discover the addresses of routers that they can use as a default gateway. IRDP is based on ICMP messages and is not proprietary to Cisco, nor does it provide load balancing capabilities.
- GLBP for IPv6: This would be the IPv6 version of GLBP, which, like the IPv4 version, is Cisco-proprietary and supports load balancing. However, since the question specifies IPv4, this option is not applicable.
- VRRPv3: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol version 3 (VRRPv3) is an open standard, not Cisco-proprietary, and while it does support both IPv4 and IPv6, it does not inherently provide load sharing functionality; it is designed for router redundancy.
Therefore, the Cisco-proprietary protocol that supports IPv4 load sharing is GLBP.
-
Which FHRP implementation is a nonproprietary protocol which relies on ICMP to provide IPv4 redundancy?
- IRDP
- GLBP for IPv6
- GLBP
- VRRPv3
-
Explanation & Hint: The FHRP (First Hop Redundancy Protocol) implementation that is a nonproprietary protocol and relies on ICMP to provide IPv4 redundancy is:
- IRDP: ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP) uses ICMP messages to allow IPv4 hosts to discover the IP addresses of active routers, providing basic redundancy in that hosts can learn about more than one router they can use as a default gateway. IRDP does not facilitate load balancing or active/active router redundancy like other FHRPs but does allow for router discovery which can provide redundancy.
Here’s an analysis for the other options:
- GLBP for IPv6: Gateway Load Balancing Protocol for IPv6 is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that provides load balancing and redundancy for IPv6 networks. It does not rely on ICMP for redundancy and is not designed for IPv4 networks.
- GLBP: Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that provides load balancing and redundancy, but it does not rely on ICMP for operation and is specifically for IPv4.
- VRRPv3: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol version 3 (VRRPv3) is an election protocol that allows for the creation of virtual routers for IPv4 and IPv6 redundancy. It is an open standard protocol and does not rely on ICMP messages for its operation.
In summary, IRDP is the correct answer to the question as it is nonproprietary and uses ICMP for providing IPv4 redundancy.
-
Which FHRP implementation is a nonproprietary protocol which relies on ICMP to provide IPv4 redundancy?
- IRDP
- HSRP for IPv6
- VRRPv2
- VRRPv3
-
Explanation & Hint: The FHRP implementation that is a nonproprietary protocol and relies on ICMP to provide IPv4 redundancy is:
- IRDP: ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP) uses ICMP messages to enable IPv4 hosts to discover routers that are available as default gateways. It is a simple protocol that uses ICMP for communication, which is inherent to the IP protocol suite, and is nonproprietary.
Here’s an analysis for the other options for clarity:
- HSRP for IPv6: Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is a Cisco-proprietary redundancy protocol for establishing a fault-tolerant default gateway, and it does not rely on ICMP for operation. Moreover, HSRP for IPv6 is, as the name implies, for IPv6 networks, and the question specifies IPv4 redundancy.
- VRRPv2: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol version 2 (VRRPv2) is an election protocol that allows multiple routers to share a virtual IP address for redundancy purposes. It is designed for IPv4 and is an open standard, but it does not use ICMP for its redundancy capabilities.
- VRRPv3: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol version 3 (VRRPv3) is similar to VRRPv2 but adds support for IPv6 in addition to IPv4. Like VRRPv2, it is an open standard and does not rely on ICMP for providing redundancy.
The only protocol in the list that uses ICMP to provide redundancy and is nonproprietary is IRDP.
-
Which FHRP implementation is a nonproprietary IPv4-only election protocol which has one master router per group?
- VRRPv2
- HSRP for IPv6
- VRRPv3
- GLBP
-
Explanation & Hint: The FHRP (First Hop Redundancy Protocol) implementation that is a nonproprietary IPv4-only election protocol with one master router per group is:
- VRRPv2: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol version 2 (VRRPv2) is an open standard, nonproprietary election protocol used for creating a virtual router among multiple physical routers in an IPv4 network. In a VRRPv2 group, one router is elected as the master router, while the others serve as backups. If the master router fails, one of the backup routers takes over as the master, ensuring continued availability of the network gateway.
Here’s an analysis for the other options:
- HSRP for IPv6: Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is a Cisco-proprietary redundancy protocol. The version for IPv6, as indicated, is designed for IPv6 networks, not IPv4. Additionally, HSRP is not an open standard.
- VRRPv3: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol version 3 (VRRPv3) is an evolution of VRRPv2 that supports both IPv4 and IPv6. Like VRRPv2, it is an open standard and allows for the election of a master router. However, it is not limited to IPv4 only.
- GLBP: Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that provides redundancy and load balancing. Unlike VRRPv2, GLBP allows for multiple routers to be active in forwarding traffic, not just a single master router.
Therefore, VRRPv2 is the correct answer as it is a nonproprietary, IPv4-only protocol with a single master router in each group.
-
Which FHRP implementation is a nonproprietary IPv4-only election protocol which has one master router per group?
- VRRPv2
- HSRP
- HSRP for IPv6
- VRRPv3
-
Explanation & Hint: The FHRP (First Hop Redundancy Protocol) implementation that is a nonproprietary, IPv4-only election protocol with one master router per group is:
- VRRPv2: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol version 2 (VRRPv2) fits this description accurately. It is an open standard and nonproprietary, designed specifically for IPv4 networks. In a VRRPv2 setup, one router is elected as the master router, and the others serve as backups. If the master router fails, one of the backup routers takes over as the master, ensuring continuous availability of the network gateway.
Here’s a brief analysis of the other options:
- HSRP: Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is a Cisco-proprietary redundancy protocol and not a nonproprietary one. It also establishes one active (master) router and one or more standby routers for IPv4 networks.
- HSRP for IPv6: This is the IPv6 version of HSRP, a Cisco-proprietary protocol. As it is specifically for IPv6, it does not fit the requirement of being an IPv4-only protocol.
- VRRPv3: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol version 3 (VRRPv3) supports both IPv4 and IPv6. Though it is an open standard like VRRPv2, its support for both IPv4 and IPv6 disqualifies it as an IPv4-only protocol.
Thus, the protocol that best matches the description of a nonproprietary, IPv4-only election protocol with one master router per group is VRRPv2.
-
Which FHRP implementation is Cisco-proprietary and permits only one router in a group to forward IPv6 packets?
- HSRP for IPv6
- HSRP
- VRRPv2
- VRRPv3
-
Explanation & Hint: The FHRP (First Hop Redundancy Protocol) implementation that is Cisco-proprietary and permits only one router in a group to forward IPv6 packets is:
- HSRP for IPv6: Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) for IPv6 is the correct answer. It is a Cisco-proprietary protocol designed to allow for network redundancy. HSRP works by creating a virtual router (represented by a virtual IP address) among a group of routers. In an HSRP setup, only one router is actively forwarding packets at any given time (the “active” router), while the other router(s) remain in standby mode, ready to take over if the active router fails. The specific version for IPv6 supports these functions on IPv6 networks.
Here’s an analysis of the other options:
- HSRP: The original Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is a Cisco-proprietary redundancy protocol, but it is primarily associated with IPv4 networks.
- VRRPv2: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol version 2 (VRRPv2) is an open standard, not Cisco-proprietary, and is designed for IPv4 networks, not IPv6.
- VRRPv3: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol version 3 (VRRPv3) is also an open standard and supports both IPv4 and IPv6. However, it is not a Cisco-proprietary protocol.
Therefore, HSRP for IPv6 is the correct answer as it is specifically a Cisco-proprietary protocol for IPv6 that allows only one router in a group to actively forward packets.
-
The address pool of a DHCP server is configured with 10.19.44.0/24. The network administrator reserves 6 IP addresses for servers. How many IP addresses are left in the pool to be assigned to other hosts?
- 248
- 246
- 238
- 252
- 249
Answers Explanation & Hints: Calculate the maximum number of hosts available for the slash value and subtract the required static IP addresses required for the devices.
/24 = 254 hosts
/25 = 126 hosts
/26 = 62 hosts
/27 = 30 hosts
/28 = 14 hosts
-
The address pool of a DHCP server is configured with 10.19.44.0/24. The network administrator reserves 3 IP addresses for servers. How many IP addresses are left in the pool to be assigned to other hosts?
- 251
- 249
- 241
- 255
- 252
Answers Explanation & Hints: Calculate the maximum number of hosts available for the slash value and subtract the required static IP addresses required for the devices.
/24 = 254 hosts
/25 = 126 hosts
/26 = 62 hosts
/27 = 30 hosts
/28 = 14 hosts
-
The address pool of a DHCP server is configured with 10.3.2.0/24. The network administrator reserves 3 IP addresses for printers. How many IP addresses are left in the pool to be assigned to other hosts?
- 251
- 249
- 241
- 255
- 252
Answers Explanation & Hints: Calculate the maximum number of hosts available for the slash value and subtract the required static IP addresses required for the devices.
/24 = 254 hosts
/25 = 126 hosts
/26 = 62 hosts
/27 = 30 hosts
/28 = 14 hosts
-
The address pool of a DHCP server is configured with 172.18.93.0/25. The network administrator reserves 10 IP addresses for web servers. How many IP addresses are left in the pool to be assigned to other hosts?
- 116
- 114
- 106
- 120
- 117
Answers Explanation & Hints: Calculate the maximum number of hosts available for the slash value and subtract the required static IP addresses required for the devices.
/24 = 254 hosts
/25 = 126 hosts
/26 = 62 hosts
/27 = 30 hosts
/28 = 14 hosts
-
The address pool of a DHCP server is configured with 192.168.184.0/26. The network administrator reserves 18 IP addresses for access points. How many IP addresses are left in the pool to be assigned to other hosts?
- 44
- 46
- 57
- 54
- 36
Answers Explanation & Hints: Calculate the maximum number of hosts available for the slash value and subtract the required static IP addresses required for the devices.
/24 = 254 hosts
/25 = 126 hosts
/26 = 62 hosts
/27 = 30 hosts
/28 = 14 hosts
-
The address pool of a DHCP server is configured with 172.23.143.0/26. The network administrator reserves 14 IP addresses for file servers. How many IP addresses are left in the pool to be assigned to other hosts?
- 48
- 50
- 61
- 58
- 40
Answers Explanation & Hints: Calculate the maximum number of hosts available for the slash value and subtract the required static IP addresses required for the devices.
/24 = 254 hosts
/25 = 126 hosts
/26 = 62 hosts
/27 = 30 hosts
/28 = 14 hosts
-
The address pool of a DHCP server is configured with 192.168.234.0/27. The network administrator reserves 22 IP addresses for IP phones. How many IP addresses are left in the pool to be assigned to other hosts?
- 8
- 10
- 21
- 18
- 0
Answers Explanation & Hints: Calculate the maximum number of hosts available for the slash value and subtract the required static IP addresses required for the devices.
/24 = 254 hosts
/25 = 126 hosts
/26 = 62 hosts
/27 = 30 hosts
/28 = 14 hosts
-
The address pool of a DHCP server is configured with 10.92.71.0/25. The network administrator reserves 8 IP addresses for servers. How many IP addresses are left in the pool to be assigned to other hosts?
- 118
- 116
- 108
- 122
- 119
Answers Explanation & Hints: Calculate the maximum number of hosts available for the slash value and subtract the required static IP addresses required for the devices.
/24 = 254 hosts
/25 = 126 hosts
/26 = 62 hosts
/27 = 30 hosts
/28 = 14 hosts
-
The address pool of a DHCP server is configured with 10.7.30.0/24. The network administrator reserves 5 IP addresses for printers. How many IP addresses are left in the pool to be assigned to other hosts?
- 249
- 247
- 239
- 253
- 250
Answers Explanation & Hints: Calculate the maximum number of hosts available for the slash value and subtract the required static IP addresses required for the devices.
/24 = 254 hosts
/25 = 126 hosts
/26 = 62 hosts
/27 = 30 hosts
/28 = 14 hosts
-
The address pool of a DHCP server is configured with 172.21.121.0/25. The network administrator reserves 12 IP addresses for web servers. How many IP addresses are left in the pool to be assigned to other hosts?
- 114
- 112
- 104
- 118
- 115
Answers Explanation & Hints: Calculate the maximum number of hosts available for the slash value and subtract the required static IP addresses required for the devices.
/24 = 254 hosts
/25 = 126 hosts
/26 = 62 hosts
/27 = 30 hosts
/28 = 14 hosts
-
Match the DHCP message types to the order of the DHCPv4 process. (Not all options are used.)
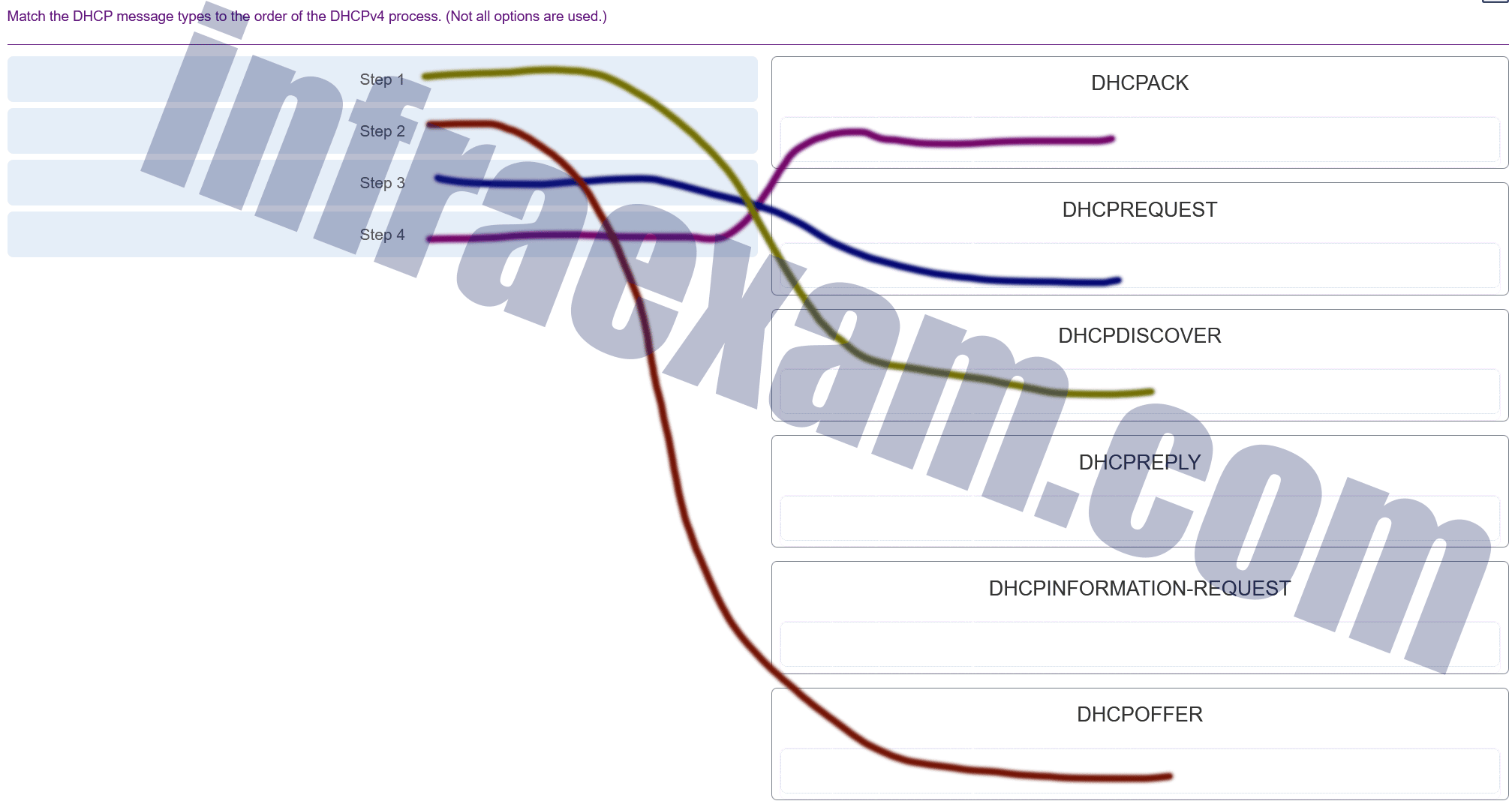
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers 007 Answers Explanation & Hints: The broadcast DHCPDISCOVER message finds DHCPv4 servers on the network. When the DHCPv4 server receives a DHCPDISCOVER message, it reserves an available IPv4 address to lease to the client and sends the unicast DHCPOFFER message to the requesting client. When the client receives the DHCPOFFER from the server, it sends back a DHCPREQUEST. On receiving the DHCPREQUEST message the server replies with a unicast DHCPACK message. DHCPREPLY and DHCPINFORMATION-REQUEST are DHCPv6 messages.
-
After a host has generated an IPv6 address by using the DHCPv6 or SLAAC process, how does the host verify that the address is unique and therefore usable?
- The host sends an ICMPv6 echo request message to the DHCPv6 or SLAAC-learned address and if no reply is returned, the address is considered unique.
- The host sends an ICMPv6 neighbor solicitation message to the DHCP or SLAAC-learned address and if no neighbor advertisement is returned, the address is considered unique.
- The host checks the local neighbor cache for the learned address and if the address is not cached, it it considered unique.
- The host sends an ARP broadcast to the local link and if no hosts send a reply, the address is considered unique.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Before a host can actually configure and use an IPv6 address learned through SLAAC or DHCP, the host must verify that no other host is already using that address. To verify that the address is indeed unique, the host sends an ICMPv6 neighbor solicitation to the address. If no neighbor advertisement is returned, the host considers the address to be unique and configures it on the interface.
-
Which statement describes HSRP?
- If the virtual router master fails, one router is elected as the virtual router master with the other routers acting as backups.
- It is an open standard protocol.
- It uses ICMP to allow IPv4 hosts to locate routers that provide IPv4 connectivity to remote IP networks.
- It is used within a group of routers for selecting an active device and a standby device to provide gateway services to a LAN.
Answers Explanation & Hints: It is VRRP that elects one router as the virtual router master, with the other routers acting as backups in case the virtual router master fails. HSRP is a Cisco-proprietary protocol. IRDP uses ICMP messages to allow IPv4 hosts to locate routers that provide IPv4 connectivity to other (nonlocal) IP networks. HSRP selects active and standby routers to provide gateway services to hosts on a LAN.
-
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.

CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers PT 001A 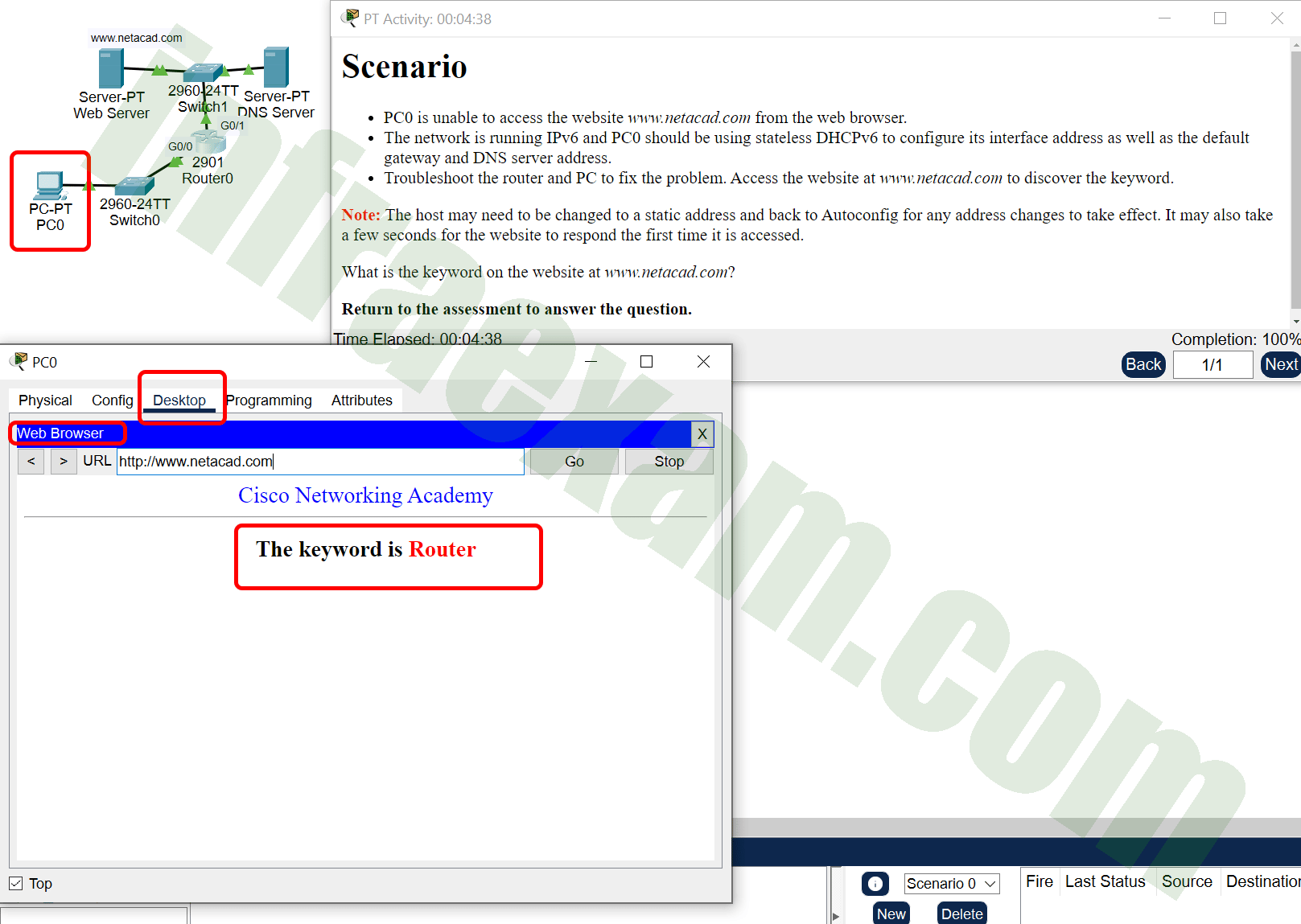
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 7 – 9 – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers PT 001B What is the keyword that is displayed on www.netacad.com?
- DHCP
- IPv6
- Cisco
- Router
- switch
- networking
Answers Explanation & Hints: In order for the host to receive the address of the DNS server, the host must use stateless DHCPv6. The router is configured with the correct DHCPv6 pool, but is missing the command ipv6 nd other-config-flag that signals to the host that it should use DHCPv6 to get additional address information. This command should be added to the interface Gigabit0/0 configuration on the router.