CCSK Module 2 Unit 5 Answers – Securing Compute Workloads Knowledge Check Quiz
CCSK Module 2 Unit 5 Answers – Securing Compute Workloads Knowledge Check Quiz Full 100% 2023 2024
This is CCSK Module 2 Unit 5 Answers – Securing Compute Workloads Knowledge Check Quiz. Our expert team has verified questions and answers with clear explanations to get a full score of 100%. You can review all these questions before taking the exam.
-
Which of the following are cloud workloads? Select all that apply:
- Host servers
- Virtual machines
- Containers
- Serverless/Function as a Service
-
Answers Explanation & Hint:
All of the following are considered cloud workloads:
- Virtual machines: These are instances of operating systems that run on a physical server but are abstracted from the underlying hardware, allowing for better resource utilization and flexibility.
- Containers: Containers provide a lightweight and portable way to package and run applications along with their dependencies. They enable consistent deployment across different environments.
- Serverless/Function as a Service (FaaS): Serverless computing involves running individual functions or pieces of code in response to events without the need to manage underlying infrastructure. It abstracts the server management aspect from the developer.
Host servers, while integral to the cloud infrastructure, are not typically referred to as cloud workloads themselves. They provide the foundation on which virtual machines, containers, and serverless functions run.
-
Click on the pipeline component that executed security tests and builds images:
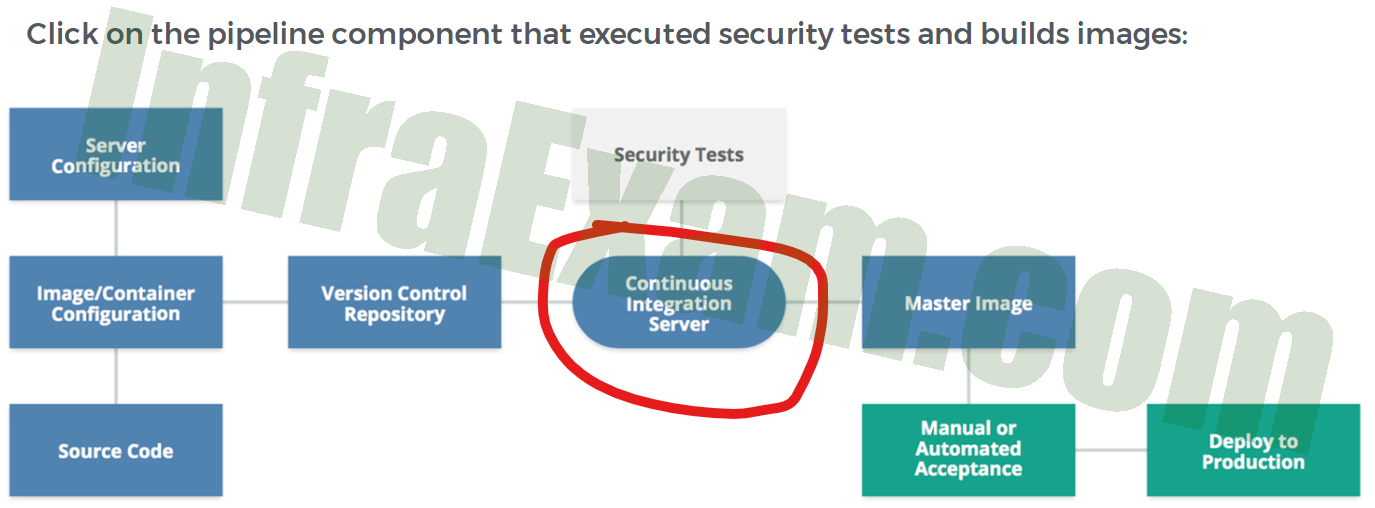
CCSK Module 2 Unit 5 Answers – Securing Compute Workloads Knowledge Check Quiz 01 -
Which of the following *most* impacts traditional workload security controls when applied to cloud deployments?
- Serverless
- Hypervisors
- Low resiliency
- High volatility/rates of change
- Security groups
-
Answers Explanation & Hint:
“High volatility/rates of change” is likely the option that most impacts traditional workload security controls when applied to cloud deployments.
In a traditional on-premises environment, security controls are often designed to work in a relatively stable and controlled setting. However, cloud deployments, especially those that involve rapidly changing resources and configurations, can introduce challenges for traditional security approaches. The high volatility and frequent changes in cloud environments can make it harder to maintain consistent security configurations and apply traditional security controls effectively.
While all the options listed can have an impact on security controls, the fast-paced changes and high volatility of cloud resources can lead to difficulties in ensuring consistent security configurations, timely updates, and accurate threat detection and response. This can make it necessary to adapt security practices and tools to suit the dynamic nature of cloud deployments.
-
How can immutable workloads improve security?
- They eliminate error-prone manual management
- They better support use of traditional security tools
- They better meet performance requirements
- They scale for DDoS
-
Answers Explanation & Hint:
Immutable workloads can improve security primarily by eliminating error-prone manual management. Immutable workloads refer to applications or components that, once deployed, cannot be modified. This approach has several security benefits:
- Elimination of Manual Management Errors: Immutable workloads prevent unauthorized or accidental changes, reducing the risk of misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, or unintended modifications that could compromise security.
- Reduced Attack Surface: Since immutable workloads cannot be altered after deployment, potential attack vectors are minimized, making it harder for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities.
- Consistency: Immutable workloads ensure that the deployed environment remains consistent over time, which can lead to more predictable and manageable security outcomes.
The other options mentioned are not directly related to the advantages of immutable workloads:
- Better support for traditional security tools: Immutable workloads may not necessarily improve support for traditional security tools, as these tools might need to be adapted or replaced to work effectively with immutable environments.
- Better meeting performance requirements: Immutable workloads are not inherently designed to better meet performance requirements. Performance depends on various factors, and immutability itself may not directly address this aspect.
- Scaling for DDoS: Scalability for Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks is not a specific advantage of immutable workloads. DDoS protection typically involves network and application-level solutions that can be applied irrespective of the workload’s immutability.
-
Select the cloud workload security option that can most improve overall security and reduce attack surface:
- Store logs external to instances
- Select cloud aware host security agents
- Use immutable as much as possible
- Leverage existing/traditional vulnerability assessment tools.
-
Answers Explanation & Hint:
The option that can most improve overall security and reduce the attack surface is:
Use immutable as much as possible
Using immutable workloads can significantly improve security by reducing the attack surface. Immutable workloads, once deployed, cannot be modified, which helps prevent unauthorized changes, misconfigurations, and potential vulnerabilities. This approach minimizes the potential points of entry that attackers could exploit, leading to a more secure environment.
The other options have their own benefits but might not directly contribute to reducing the attack surface as effectively as the use of immutable workloads:
- Store logs external to instances: Storing logs externally can aid in incident response and forensic analysis, but it doesn’t directly reduce the attack surface.
- Select cloud-aware host security agents: While these agents can enhance security by providing real-time threat detection and response, they don’t inherently reduce the attack surface.
- Leverage existing/traditional vulnerability assessment tools: While vulnerability assessment tools are important, they focus on identifying vulnerabilities rather than directly reducing the attack surface. They are part of a comprehensive security strategy but may not have the same impact on attack surface reduction as using immutable workloads.
-
Which of the following is primarily a cloud consumer workload security responsibility?
- Hypervisor security
- Underlying infrastructure security
- Volatile memory security
- Monitoring and logging
-
Answers Explanation & Hint:
“Monitoring and logging” is primarily a cloud consumer workload security responsibility.
While all aspects of security are important, monitoring and logging are tasks that the cloud consumer (i.e., the organization using the cloud services) has a significant responsibility for. Monitoring involves actively observing the behavior of your workloads, applications, and resources to detect any unusual or potentially malicious activities. Logging involves generating and storing records of events and actions within your environment.
Here’s a breakdown of the other options:
- Hypervisor security: This is more related to the cloud provider’s responsibility, as the hypervisor is part of the underlying infrastructure that hosts virtual machines.
- Underlying infrastructure security: This is primarily the responsibility of the cloud provider. They are responsible for securing the physical infrastructure, network, and hypervisor layers.
- Volatile memory security: While securing volatile memory is important for overall security, it’s often a responsibility shared between the cloud consumer and provider, depending on the specific cloud service and deployment model being used. The cloud provider is responsible for securing the underlying hardware and infrastructure, while the cloud consumer is responsible for securing the operating system, applications, and data within their virtualized environment.