CSSLP : Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional : Part 04
CSSLP : Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional : Part 04
-
SIMULATION
Fill in the blank with an appropriate phrase. is used to provide security mechanisms for the storage, processing, and transfer of data.
Data classification
Explanation:
Data classification is used to protect the data based on its sensitivity, secrecy, and confidentiality. It provides security mechanisms for storage, processing, and transfer of data. Data classification also helps to verify the effort, funds, and resources allocated to save the data, and controls access to it.
-
System Authorization is the risk management process. System Authorization Plan (SAP) is a comprehensive and uniform approach to the System Authorization Process. What are the different phases of System Authorization Plan? Each correct answer represents a part of the solution. Choose all that apply.
- Post-certification
- Post-Authorization
- Authorization
- Pre-certification
- Certification
Explanation:The creation of System Authorization Plan (SAP) is mandated by System Authorization. System Authorization Plan (SAP) is a comprehensive and uniform approach to the System Authorization Process. It consists of four phases: Phase 1 – Pre-certification Phase 2 – Certification Phase 3 – Authorization Phase 4 – Post-Authorization -
Mark works as a Network Administrator for NetTech Inc. The company has a Windows 2000 domain-based network. Users report that they are unable to log on to the network. Mark finds that accounts are locked out due to multiple incorrect log on attempts. What is the most likely cause of the account lockouts?
- Spoofing
- Brute force attack
- SYN attack
- PING attack
Explanation:Brute force attack is the most likely cause of the account lockouts. In a brute force attack, unauthorized users attempt to log on to a network or a computer by using multiple possible user names and passwords. Windows 2000 and other network operating systems have a security feature that locks a user account if the number of failed logon attempts occur within a specified period of time, based on the security policy lockout settings. Answer: A is incorrect. Spoofing is a technique that makes a transmission appear to have come from an authentic source by forging the IP address, email address, caller ID, etc. In IP spoofing, a hacker modifies packet headers by using someone else’s IP address to hide his identity. However, spoofing cannot be used while surfing the Internet, chatting on-line, etc. because forging the source IP address causes the responses to be misdirected. Answer: C is incorrect. A SYN attack affects computers running on the TCP/IP protocol. It is a protocol-level attack that can render a computer’s network services unavailable. A SYN attack is also known as SYN flooding. Answer: D is incorrect. When a computer repeatedly sends ICMP echo requests to another computer, it is known as a PING attack. -
Which of the following scanning techniques helps to ensure that the standard software configuration is currently with the latest security patches and software, and helps to locate uncontrolled or unauthorized software?
- Port Scanning
- Discovery Scanning
- Server Scanning
- Workstation Scanning
Explanation:Workstation scanning provides help to ensure that the standard software configuration exists with the most recent security patches and software. It helps to locate uncontrolled or unauthorized software. A full workstation vulnerability scan of the standard corporate desktop configuration must be implemented on a regularly basis. Answer: B is incorrect. The discovery scanning technique is used to gather adequate information regarding each network device to identify what type of device it is, its operating system, and if it is running any externally vulnerable services, like Web services, FTP, or email. Answer: C is incorrect. A full server vulnerability scan helps to determine if the server OS has been configured to the corporate standards and identify if applications have been updated with the latest security patches and software versions. Answer: A is incorrect. Port scanning technique describes the process of sending a data packet to a port to gather information about the state of the port. -
Which of the following tiers addresses risks from an information system perspective?
- Tier 0
- Tier 3
- Tier 2
- Tier 1
Explanation:The information system level is the tier 3. It addresses risks from an information system perspective, and is guided by the risk decisions at tiers 1 and 2. Risk decisions at tiers 1 and 2 impact the ultimate selection and deployment of requisite safeguards. This also has an impact on the countermeasures at the information system level. The RMF primarily operates at tier3 but it can also have interactions at tiers 1 and 2. Answer: A is incorrect. It is an invalid Tier description. Answer: D is incorrect. The Organization Level is the Tier 1, and it addresses risks from an organizational perspective. Answer: C is incorrect. The mission and business process level is the Tier 2, and it addresses risks from the mission and business process perspective. -
Which of the following is the most secure method of authentication?
- Biometrics
- Username and password
- Anonymous
- Smart card
Explanation:Biometrics is a method of authentication that uses physical characteristics, such as fingerprints, scars, retinal patterns, and other forms of biophysical qualities to identify a user. Nowadays, the usage of biometric devices such as hand scanners and retinal scanners is becoming more common in the business environment. It is the most secure method of authentication. Answer: B is incorrect. Username and password is the least secure method of authentication in comparison of smart card and biometrics authentication. Username and password can be intercepted. Answer: D is incorrect. Smart card authentication is not as reliable as biometrics authentication. Answer: C is incorrect. Anonymous authentication does not provide security as a user can log on to the system anonymously and he is not prompted for credentials. -
Penetration tests are sometimes called white hat attacks because in a pen test, the good guys are attempting to break in. What are the different categories of penetration testing? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Open-box
- Closed-box
- Zero-knowledge test
- Full-box
- Full-knowledge test
- Partial-knowledge test
Explanation:The different categories of penetration testing are as follows: Open-box: In this category of penetration testing, testers have access to internal system code. This mode is basically suited for Unix or Linux. Closed-box: In this category of penetration testing, testers do not have access to closed systems. This method is good for closed systems. Zero-knowledge test: In this category of penetration testing, testers have to acquire information from scratch and they are not supplied with information concerning the IT system. Partial-knowledge test: In this category of penetration testing, testers have knowledge that may be applicable to a specific type of attack and associated vulnerabilities. Full-knowledge test: In this category of penetration testing, testers have massive knowledge concerning the information system to be evaluated. Answer: D is incorrect. There is no such category of penetration testing. -
Shoulder surfing is a type of in-person attack in which the attacker gathers information about the premises of an organization. This attack is often performed by looking surreptitiously at the keyboard of an employee’s computer while he is typing in his password at any access point such as a terminal/Web site. Which of the following is violated in a shoulder surfing attack?
- Integrity
- Availability
- Confidentiality
- Authenticity
Explanation:Confidentiality is violated in a shoulder surfing attack. The CIA triad provides the following three tenets for which security practices are measured: Confidentiality: It is the property of preventing disclosure of information to unauthorized individuals or systems. Breaches of confidentiality take many forms. Permitting someone to look over your shoulder at your computer screen while you have confidential data displayed on it could be a breach of confidentiality. If a laptop computer containing sensitive information about a company’s employees is stolen or sold, it could result in a breach of confidentiality. Integrity: It means that data cannot be modified without authorization. Integrity is violated when an employee accidentally or with malicious intent deletes important data files, when a computer virus infects a computer, when an employee is able to modify his own salary in a payroll database, when an unauthorized user vandalizes a web site, when someone is able to cast a very large number of votes in an online poll, and so on. Availability: It means that data must be available at every time when it is needed. Answer: D is incorrect. Authenticity is not a tenet of the CIA triad. -
John works as a professional Ethical Hacker. He has been assigned the project of testing the security of www.we-are-secure.com. He finds that the We-are-secure server is vulnerable to attacks. As a countermeasure, he suggests that the Network Administrator should remove the IPP printing capability from the server. He is suggesting this as a countermeasure against __________.
- SNMP enumeration
- IIS buffer overflow
- NetBIOS NULL session
- DNS zone transfer
Explanation:Removing the IPP printing capability from a server is a good countermeasure against an IIS buffer overflow attack. A Network Administrator should take the following steps to prevent a Web server from IIS buffer overflow attacks: Conduct frequent scans for server vulnerabilities. Install the upgrades of Microsoft service packs.
Implement effective firewalls. Apply URLScan and IISLockdown utilities. Remove the IPP printing capability. Answer: D is incorrect. The following are the DNS zone transfer countermeasures: Do not allow DNS zone transfer using the DNS property sheet: a.Open DNS. b.Right-click a DNS zone and click Properties. c.On the Zone Transfer tab, clear the Allow zone transfers check box. Configure the master DNS server to allow zone transfers only from secondary DNS servers: a.Open DNS. b.Right-click a DNS zone and click Properties. c.On the zone transfer tab, select the Allow zone transfers check box, and then do one of the following: To allow zone transfers only to the DNS servers listed on the name servers tab, click on the Only to the servers listed on the Name Server tab. To allow zone transfers only to specific DNS servers, click Only to the following servers, and add the IP address of one or more servers. Deny all unauthorized inbound connections to TCP port 53. Implement DNS keys and encrypted DNS payloads. Answer: A is incorrect. The following are the countermeasures against SNMP enumeration: 1.Removing the SNMP agent or disabling the SNMP service 2.Changing the default PUBLIC community name when ‘shutting off SNMP’ is not an option 3.Implementing the Group Policy security option called Additional restrictions for anonymous connections 4.Restricting access to NULL session pipes and NULL session shares 5.Upgrading SNMP Version 1 with the latest version 6.Implementing Access control list filtering to allow only access to the read-write community from approved stations or subnets Answer: C is incorrect. NetBIOS NULL session vulnerabilities are hard to prevent, especially if NetBIOS is needed as part of the infrastructure. One or more of the following steps can be taken to limit NetBIOS NULL session vulnerabilities: 1.Null sessions require access to the TCP 139 or TCP 445 port, which can be disabled by a Network Administrator. 2.A Network Administrator can also disable SMB services entirely on individual hosts by unbinding WINS Client TCP/IP from the interface. 3.A Network Administrator can also restrict the anonymous user by editing the registry values: a.Open regedit32, and go to HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\LSA. b.Choose edit > add value. Value name: RestrictAnonymous Data Type: REG_WORD Value: 2 -
Mark is the project manager of the NHQ project in StarTech Inc. The project has an asset valued at $195,000 and is subjected to an exposure factor of 35 percent. What will be the Single Loss Expectancy of the project?
- $68,250
- $92,600
- $72,650
- $67,250
Explanation:The Single Loss Expectancy (SLE) of this project will be $68,250. Single Loss Expectancy is a term related to Risk Management and Risk Assessment. It can be defined as the monetary value expected from the occurrence of a risk on an asset. It is mathematically expressed as follows: Single Loss Expectancy (SLE) = Asset Value (AV) * Exposure Factor (EF) where the Exposure Factor is represented in the impact of the risk over the asset, or percentage of asset lost. As an example, if the Asset Value is reduced two thirds, the exposure factor value is .66. If the asset is completely lost, the Exposure Factor is 1.0. The result is a monetary value in the same unit as the Single Loss Expectancy is expressed. Here, it is as follows:
SLE = Asset Value * Exposure Factor
= 195,000 * 0.35
= $68,250
Answer: B, C, and D are incorrect. These are not valid SLE’s for this project. -
FIPS 199 defines the three levels of potential impact on organizations: low, moderate, and high. Which of the following are the effects of loss of confidentiality, integrity, or availability in a high level potential impact?
- The loss of confidentiality, integrity, or availability might result in a major damage to organizational assets.
- The loss of confidentiality, integrity, or availability might result in severe damages like life threatening injuries or loss of life.
- The loss of confidentiality, integrity, or availability might result in major financial losses.
- The loss of confidentiality, integrity, or availability might cause severe degradation in or loss of mission capability to an extent.
Explanation:The following are the effects of loss of confidentiality, integrity, or availability in a high level potential impact: It might cause a severe degradation in or loss of mission capability to an extent. It might result in a major damage to organizational assets. It might result in a major financial loss. It might result in severe harms such as serious life threatening injuries or loss of life. -
Which of the following concepts represent the three fundamental principles of information security? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose three.
- Privacy
- Availability
- Integrity
- Confidentiality
Explanation:The following concepts represent the three fundamental principles of information security: 1.Confidentiality 2.Integrity 3.Availability Answer: B is incorrect. Privacy, authentication, accountability, authorization and identification are also concepts related to information security, but they do not represent the fundamental principles of information security. -
DRAG DROP
RCA (root cause analysis) is an iterative and reactive method that identifies the root cause of various incidents, and the actions required to prevent these incidents from reoccurring. RCA is classified in various categories. Choose appropriate categories and drop them in front of their respective functions.

CSSLP Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional Part 04 Q13 004 Question 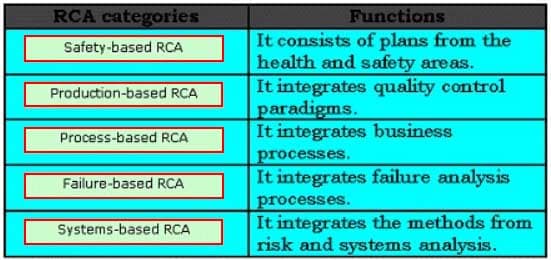
CSSLP Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional Part 04 Q13 004 Answer Explanation:The various categories of root cause analysis (RCA) are as follows: Safety-based RC A. It consists of plans from the health and safety areas. Production-based RCA. It integrates quality control paradigms. Process-based RCA. It integrates business processes. Failure-based RCA. It integrates failure analysis processes as employed in engineering and maintenance. Systems-based RCA. It integrates the methods from risk and systems analysis. -
The service-oriented modeling framework (SOMF) introduces five major life cycle modeling activities that drive a service evolution during design-time and run-time. Which of the following activities integrates SOA software assets and establishes SOA logical environment dependencies?
- Service-oriented discovery and analysis modeling
- Service-oriented business integration modeling
- Service-oriented logical architecture modeling
- Service-oriented logical design modeling
Explanation:The service-oriented logical architecture modeling integrates SOA software assets and establishes SOA logical environment dependencies. It also offers foster service reuse, loose coupling and consolidation. Answer: A is incorrect. The service-oriented discovery and analysis modeling discovers and analyzes services for granularity, reusability, interoperability, loose-coupling, and identifies consolidation opportunities. Answer: B is incorrect. The service-oriented business integration modeling identifies service integration and alignment opportunities with business domains’ processes. Answer: D is incorrect. The service-oriented logical design modeling establishes service relationships and message exchange paths. -
Which of the following statements reflect the ‘Code of Ethics Canons’ in the ‘(ISC)2 Code of Ethics’? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Act honorably, honestly, justly, responsibly, and legally.
- Give guidance for resolving good versus good and bad versus bad dilemmas.
- Provide diligent and competent service to principals.
- Protect society, the commonwealth, and the infrastructure.
Explanation:The Code of Ethics Canons in (ISC)2 code of ethics are as follows: Protect society, the commonwealth, and the infrastructure. Act honorably, honestly, justly, responsibly, and legally. Provide diligent and competent service to principals. Advance and protect the profession. -
The Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is the process of creating or altering the systems; and the models and methodologies that people use to develop these systems. Which of the following are the different phases of system development life cycle? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Testing
- Implementation
- Operation/maintenance
- Development/acquisition
- Disposal
- Initiation
Explanation:The Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC), or Software Development Life Cycle in systems engineering, information systems, and software engineering, is the process of creating or altering the systems; and the models and methodologies that people use to develop these systems. The concept generally refers to computers or information systems. The following are the five phases in a generic System Development Life Cycle: 1.Initiation 2.Development/acquisition 3.Implementation 4.Operation/maintenance 5.Disposal -
Rob is the project manager of the IDLK Project for his company. This project has a budget of $5,600,000 and is expected to last 18 months. Rob has learned that a new law may affect how the project is allowed to proceed – even though the organization has already invested over $750,000 in the project. What risk response is the most appropriate for this instance?
- Transference
- Enhance
- Mitigation
- Acceptance
Explanation:At this point all that Rob can likely do is accepting the risk event. Because this is an external risk, there is little that Rob can do other than document the risk and share the new with management and the project stakeholders. If the law is passed then Rob can choose the most appropriate way for the project to continue. Acceptance response is a part of Risk Response planning process. Acceptance response delineates that the project plan will not be changed to deal with the risk. Management may develop a contingency plan if the risk does occur. Acceptance response to a risk event is a strategy that can be used for risks that pose either threats or opportunities. Acceptance response can be of two types: Passive acceptance: It is a strategy in which no plans are made to try or avoid or mitigate the risk. Active acceptance: Such responses include developing contingency reserves to deal with risks, in case they occur. Acceptance is the only response for both threats and opportunities. Answer: B is incorrect. Mitigation aims to lower the probability and/or impact of the risk event. Answer: C is incorrect. Transference transfers the ownership of the risk event to a third party, usually through a contractual agreement. Answer: D is incorrect. Enhance is a risk response that tries to increase the probability and/or impact of the positive risk event. -
Which of the following methods is a means of ensuring that system changes are approved before being implemented, only the proposed and approved changes are implemented, and the implementation is complete and accurate?
- Configuration control
- Documentation control
- Configuration identification
- Configuration auditing
Explanation:Documentation control is a method of ensuring that system changes should be agreed upon before being implemented, only the proposed and approved changes are implemented, and the implementation is complete and accurate. Documentation control is involved in the strict events for proposing, monitoring, and approving system changes and their implementation. It helps the change process by supporting the person who synchronizes the analytical task, approves system changes, reviews the implementation of changes, and oversees other tasks such as documenting the controls. Answer: D is incorrect. Configuration auditing is the quality assurance element of configuration management. It is occupied in the process of periodic checks to establish the consistency and completeness of accounting information and to validate that all configuration management policies are being followed. Configuration audits are broken into functional and physical configuration audits. They occur either at delivery or at the moment of effecting the change. A functional configuration audit ensures that functional and performance attributes of a configuration item are achieved, while a physical configuration audit ensures that a configuration item is installed in accordance with the requirements of its detailed design documentation. Answer: A is incorrect. Configuration control is a procedure of the Configuration management. Configuration control is a set of processes and approval stages required to change a configuration item’s attributes and to re-baseline them. It supports the change of the functional and physical attributes of software at various points in time, and performs systematic control of changes to the identified attributes. Answer: C is incorrect. Configuration identification is the process of identifying the attributes that define every aspect of a configuration item. A configuration item is a product (hardware and/or software) that has an end-user purpose. These attributes are recorded in configuration documentation and baselined. Baselining an attribute forces formal configuration change control processes to be effected in the event that these attributes are changed. -
Information Security management is a process of defining the security controls in order to protect information assets. The first action of a management program to implement information security is to have a security program in place. What are the objectives of a security program? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Security education
- Security organization
- System classification
- Information classification
Explanation:The first action of a management program to implement information security is to have a security program in place. The objectives of a security program are as follows: Protect the company and its assets Manage risks by identifying assets, discovering threats, and estimating the risk Provide direction for security activities by framing of information security policies, procedures, standards, guidelines and baselines Information classification Security organization Security education Answer: C is incorrect. System classification is not one of the objectives of a security program. -
The Phase 3 of DITSCAP C&A is known as Validation. The goal of Phase 3 is to validate that the preceding work has produced an IS that operates in a specified computing environment. What are the process activities of this phase? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Certification and accreditation decision
- Continue to review and refine the SSAA
- Perform certification evaluation of the integrated system
- System development
- Develop recommendation to the DAA
Explanation:The Phase 3 of DITSCAP C&A is known as Validation. The goal of Phase 3 is to validate that the preceding work has produced an IS that operates in a specified computing environment. The process activities of this phase are as follows: Continue to review and refine the SSAA Perform certification evaluation of the integrated system Develop recommendation to the DAA Certification and accreditation decision Answer: D is incorrect. System development is a Phase 2 activity.