CSSLP : Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional : Part 06
CSSLP : Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional : Part 06
-
The mission and business process level is the Tier 2. What are the various Tier 2 activities? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Defining the types of information that the organization needs, to successfully execute the stated missions and business processes
- Defining the types of information that the organization needs, to successfully execute the stated missions and business processes
- Specifying the degree of autonomy for the subordinate organizations
- Defining the core missions and business processes for the organization
- Prioritizing missions and business processes with respect to the goals and objectives of the organization
Explanation:
The mission and business process level is the Tier 2. It addresses risks from the mission and business process perspective. It is guided by the risk decisions at Tier 1. The various Tier 2 activities are as follows: It defines the core missions and business processes for the organization. It also prioritizes missions and business processes, with respect to the goals and objectives of the organization. It defines the types of information that an organization requires, to successfully execute the stated missions and business processes. It helps in developing an organization-wide information protection strategy and incorporating high-level information security requirements. It specifies the degree of autonomy for the subordinate organizations.
-
Numerous information security standards promote good security practices and define frameworks or systems to structure the analysis and design for managing information security controls. Which of the following are the U.S. Federal Government information security standards? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- IR Incident Response
- Information systems acquisition, development, and maintenance
- SA System and Services Acquisition
- CA Certification, Accreditation, and Security Assessments
Explanation:Following are the various U.S. Federal Government information security standards: AC Access Control AT Awareness and Training AU Audit and Accountability CA Certification, Accreditation, and Security Assessments CM Configuration Management CP Contingency Planning IA Identification and Authentication IR Incident Response MA Maintenance MP Media Protection PE Physical and Environmental Protection PL Planning PS Personnel Security RA Risk Assessment SA System and Services Acquisition SC System and Communications Protection SI System and Information Integrity Answer: B is incorrect. Information systems acquisition, development, and maintenance is an International information security standard. -
Which of the following phases of NIST SP 800-37 C&A methodology examines the residual risk for acceptability, and prepares the final security accreditation package?
- Security Accreditation
- Initiation
- Continuous Monitoring
- Security Certification
Explanation:The various phases of NIST SP 800-37 C&A are as follows: Phase 1: Initiation- This phase includes preparation, notification and resource identification. It performs the security plan analysis, update, and acceptance. Phase 2: Security Certification- The Security certification phase evaluates the controls and documentation. Phase 3: Security Accreditation- The security accreditation phase examines the residual risk for acceptability, and prepares the final security accreditation package. Phase 4: Continuous Monitoring-This phase monitors the configuration management and control, ongoing security control verification, and status reporting and documentation. -
John works as a security manager for SoftTech Inc. He is working with his team on the disaster recovery management plan. One of his team members has a doubt related to the most cost effective DRP testing plan. According to you, which of the following disaster recovery testing plans is the most cost-effective and efficient way to identify areas of overlap in the plan before conducting more demanding training exercises?
- Full-scale exercise
- Walk-through drill
- Structured walk-through test
- Evacuation drill
Explanation:The structured walk-through test is also known as the table-top exercise. In structured walk-through test, the team members walkthrough the plan to identify and correct weaknesses and how they will respond to the emergency scenarios by stepping in the course of the plan. It is the most effective and competent way to identify the areas of overlap in the plan before conducting more challenging training exercises. Answer: A is incorrect. In full-scale exercise, the critical systems run at an alternate site. Answer: B is incorrect. The emergency management group and response teams actually perform their emergency response functions by walking through the test, without actually initiating recovery procedures. But it is not much cost effective. Answer: D is incorrect. It is a test performed when personnel walks through the evacuation route to a designated area where procedures for accounting for the personnel are tested. -
DRAG DROP
A number of security design patterns are developed for software assurance in general. Drag and drop the appropriate security design patterns in front of their respective descriptions.

CSSLP Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional Part 06 Q05 006 Question 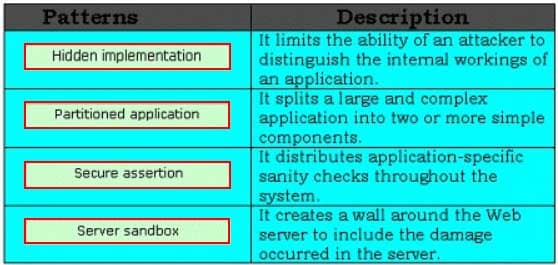
CSSLP Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional Part 06 Q05 006 Answer Explanation:The various patterns applicable to software assurance in general are as follows: Hidden implementation: It limits the ability of an attacker to distinguish the internal workings of an application. Partitioned application: It splits a large and complex application into two or more simple components. Secure assertion: It distributes application-specific sanity checks throughout the system. Server sandbox: It creates a wall around the Web server to include the damage that occurs because of an undetected fault in the server or an exploited vulnerability. -
ISO 27003 is an information security standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Which of the following elements does this standard contain? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Inter-Organization Co-operation
- Information Security Risk Treatment
- CSFs (Critical success factors)
- ystem requirements for certification bodies Managements
- Terms and Definitions
- Guidance on process approach
Explanation:ISO 27003 is an information security standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). It is entitled as “Information Technology – Security techniques – Information security management system implementation guidance”. The ISO 27003 standard provides guidelines for implementing an ISMS (Information Security Management System). It mainly focuses upon the PDCA method along with establishing, implementing, reviewing, and improving the ISMS itself. The ISO 27003 standard contains the following elements: Introduction Scope Terms and Definitions CSFs (Critical success factors) Guidance on process approach Guidance on using PDCA Guidance on Plan Processes Guidance on Do Processes Guidance on Check Processes Guidance on Act Processes Inter-Organization Co-operation Answer: B is incorrect. This element is included in the ISO 27005 standard. Answer: D is incorrect. This element is included in the ISO 27006 standard. -
Certification and Accreditation (C&A or CnA) is a process for implementing information security. Which of the following is the correct order of C&A phases in a DITSCAP assessment?
- Verification, Definition, Validation, and Post Accreditation
- Definition, Validation, Verification, and Post Accreditation
- Definition, Verification, Validation, and Post Accreditation
- Verification, Validation, Definition, and Post Accreditation
Explanation:C&A consists of four phases in a DITSCAP assessment. These phases are the same as NIACAP phases. The order of these phases is as follows: 1.Definition: The definition phase is focused on understanding the IS business case, the mission, environment, and architecture. This phase determines the security requirements and level of effort necessary to achieve Certification & Accreditation (C&A). 2.Verification: The second phase confirms the evolving or modified system’s compliance with the information. The verification phase ensures that the fully integrated system will be ready for certification testing. 3.Validation: The third phase confirms abidance of the fully integrated system with the security policy. This phase follows the requirements slated in the SSAA. The objective of the validation phase is to show the required evidence to support the DAA in accreditation process. 4.Post Accreditation: The Post Accreditation is the final phase of DITSCAP assessment and it starts after the system has been certified and accredited for operations. This phase ensures secure system management, operation, and maintenance to save an acceptable level of residual risk. -
Which of the following is NOT a responsibility of a data owner?
- Approving access requests
- Ensuring that the necessary security controls are in place
- Delegating responsibility of the day-to-day maintenance of the data protection mechanisms to the data custodian
- Maintaining and protecting data
Explanation:It is not a responsibility of a data owner. The data custodian (information custodian) is responsible for maintaining and protecting the data.
Answer: B, A, and C are incorrect. All of these are responsibilities of a data owner. The roles and responsibilities of a data owner are as follows: The data owner (information owner) is usually a member of management, in charge of a specific business unit, and is ultimately responsible for the protection and use of a specific subset of information. The data owner decides upon the classification of the data that he is responsible for and alters that classification if the business needs arise. This person is also responsible for ensuring that the necessary security controls are in place, ensuring that proper access rights are being used, defining security requirements per classification and backup requirements, approving any disclosure activities, and defining user access criteria. The data owner approves access requests or may choose to delegate this function to business unit managers. And it is the data owner who will deal with security violations pertaining to the data he is responsible for protecting. The data owner, who obviously has enough on his plate, delegates responsibility of the day-to-day maintenance of the data protection mechanisms to the data custodian. -
Which of the following are examples of passive attacks? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Dumpster diving
- Placing a backdoor
- Eavesdropping
- Shoulder surfing
Explanation:In eavesdropping, dumpster diving, and shoulder surfing, the attacker violates the confidentiality of a system without affecting its state. Hence, they are considered passive attacks. -
SIMULATION
Fill in the blank with an appropriate phrase The is a formal state transition system of computer security policy that describes a set of access control rules designed to ensure data integrity.
Biba model
Explanation:The Biba model is a formal state transition system of computer security policy that describes a set of access control rules designed to ensure data integrity. Data and subjects are grouped into ordered levels of integrity. The model is designed so that subjects may not corrupt data in a level ranked higher than the subject, or be corrupted by data from a lower level than the subject. -
Which of the following elements of the BCP process emphasizes on creating the scope and the additional elements required to define the parameters of the plan?
- Business continuity plan development
- Plan approval and implementation
- Business impact analysis
- Scope and plan initiation
Explanation:The scope and plan initiation process in BCP symbolizes the beginning of the BCP process. It emphasizes on creating the scope and the additional elements required to define the parameters of the plan. The scope and plan initiation phase embodies a check of the company’s operations and support services. The scope activities include creating a detailed account of the work required, listing the resources to be used, and defining the management practices to be employed. Answer: C is incorrect. The business impact assessment is a method used to facilitate business units to understand the impact of a disruptive event. This phase includes the execution of a vulnerability assessment. This process makes out the mission-critical areas and business processes that are important for the survival of business. It is similar to the risk assessment process. The function of a business impact assessment process is to create a document, which is used to help and understand what impact a disruptive event would have on the business.
Answer: A is incorrect. The business continuity plan development refers to the utilization of the information collected in the Business Impact Analysis (BIA) for the creation of the recovery strategy plan to support the critical business functions. The information gathered from the BIA is mapped out to make a strategy for creating a continuity plan. The business continuity plan development process includes the areas of plan implementation, plan testing, and ongoing plan maintenance. This phase also consists of defining and documenting the continuity strategy. Answer: B is incorrect. The plan approval and implementation process involves creating enterprise-wide awareness of the plan, getting the final senior management signoff, and implementing a maintenance procedure for updating the plan as required. -
Which of the following are the phases of the Certification and Accreditation (C&A) process? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose two.
- Continuous Monitoring
- Auditing
- Detection
- Initiation
Explanation:The Certification and Accreditation (C&A) process consists of four distinct phases: 1.Initiation 2.Security Certification 3.Security Accreditation 4.Continuous Monitoring The C&A activities can be applied to an information system at appropriate phases in the system development life cycle by selectively tailoring the various tasks and subtasks. Answer: B and C are incorrect. Auditing and detection are not phases of the Certification and Accreditation process. -
You work as a project manager for BlueWell Inc. You are preparing to plan risk responses for your project with your team. How many risk response types are available for a negative risk event in the project?
- Three
- Seven
- One
- Four
Explanation:There are four risk responses available for a negative risk event. The risk response strategies for negative risks are: Avoid: It involves altering the project management plan to remove the threats completely. Transfer: It requires shifting some or all of the negative effects of a threat including the ownership of response, to a third party. Mitigate: It implies a drop in the probability and impact of an unfavorable risk event to be within suitable threshold limits. Accept: It delineates that the project plan will not be changed to deal with the risk. Management may develop a contingency plan if the risk occurs. It is used for both negative and positive risks. Answer: C is incorrect. There are four responses for negative risk events. Answer: A is incorrect. There are four, not three, responses for negative risk events. Do not forget that acceptance can be used for negative risk events. Answer: B is incorrect. There are seven total risk responses, four of which can be used for negative risk events. -
You work as an analyst for Tech Perfect Inc. You want to prevent information flow that may cause a conflict of interest in your organization representing competing clients. Which of the following security models will you use?
- Bell-LaPadula model
- Chinese Wall model
- Clark-Wilson model
- Biba model
Explanation:The Chinese Wall Model is the basic security model developed by Brewer and Nash. This model prevents information flow that may cause a conflict of interest in an organization representing competing clients. The Chinese Wall Model provides both privacy and integrity for data. Answer: D is incorrect. The Biba model is a formal state transition system of computer security policy that describes a set of access control rules designed to ensure data integrity. Data and subjects are grouped into ordered levels of integrity. The model is designed so that subjects may not corrupt data in a level ranked higher than the subject, or be corrupted by data from a lower level than the subject. Answer: C is incorrect. The Clark-Wilson model provides a foundation for specifying and analyzing an integrity policy for a computing system. The model is primarily concerned with formalizing the notion of information integrity. Information integrity is maintained by preventing corruption of data items in a system due to either error or malicious intent. The model’s enforcement and certification rules define data items and processes that provide the basis for an integrity policy. The core of the model is based on the notion of a transaction. Answer: A is incorrect. The Bell-La Padula Model is a state machine model used for enforcing access control in government and military applications. The model is a formal state transition model of computer security policy that describes a set of access control rules which use security labels on objects and clearances for subjects. Security labels range from the most sensitive (e.g.,”Top Secret”), down to the least sensitive (e.g., “Unclassified” or “Public”). The Bell-La Padula model focuses on data confidentiality and controlled access to classified information, in contrast to the Biba Integrity Model which describes rules for the protection of data integrity. -
Copyright holders, content providers, and manufacturers use digital rights management (DRM) in order to limit usage of digital media and devices. Which of the following security challenges does DRM include? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- OTA provisioning
- Access control
- Key hiding
- Device fingerprinting
Explanation:The security challenges for DRM are as follows: Key hiding: It prevents tampering attacks that target the secret keys. In the key hiding process, secret keys are used for authentication, encryption, and node-locking. Device fingerprinting: It prevents fraud and provides secure authentication. Device fingerprinting includes the summary of hardware and software characteristics in order to uniquely identify a device. OTA provisioning: It provides end-to-end encryption or other secure ways for delivery of copyrighted software to mobile devices. Answer: B is incorrect. Access control is not a security challenge for DRM. -
Which of the following describes the acceptable amount of data loss measured in time?
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
- Recovery Consistency Objective (RCO)
- Recovery Time Actual (RTA)
Explanation:The Recovery Point Objective (RPO) describes the acceptable amount of data loss measured in time. It is the point in time to which data must be recovered as defined by the organization. The RPO is generally a definition of what an organization determines is an “acceptable loss” in a disaster situation. If the RPO of a company is 2 hours and the time it takes to get the data back into production is 5 hours, the RPO is still 2 hours. Based on this RPO the data must be restored to within 2 hours of the disaster. Answer: B is incorrect. The Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the duration of time and a service level within which a business process must be restored after a disaster or disruption in order to avoid unacceptable consequences associated with a break in business continuity. It includes the time for trying to fix the problem without a recovery, the recovery itself, tests and the communication to the users. Decision time for user representative is not included. The business continuity timeline usually runs parallel with an incident management timeline and may start at the same, or different, points. In accepted business continuity planning methodology, the RTO is established during the Business Impact Analysis (BIA) by the owner of a process (usually in conjunction with the Business Continuity planner). The RTOs are then presented to senior management for acceptance. The RTO attaches to the business process and not the resources required to support the process. Answer: D is incorrect. The Recovery Time Actual (RTA) is established during an exercise, actual event, or predetermined based on recovery methodology the technology support team develops. This is the time frame the technology support takes to deliver the recovered infrastructure to the business. Answer: C is incorrect. The Recovery Consistency Objective (RCO) is used in Business Continuity Planning in addition to Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO). It applies data consistency objectives to Continuous Data Protection services. -
Which of the following terms refers to the protection of data against unauthorized access?
- Integrity
- Recovery
- Auditing
- Confidentiality
Explanation:Confidentiality is a term that refers to the protection of data against unauthorized access. Administrators can provide confidentiality by encrypting data. Symmetric encryption is a relatively fast encryption method. Hence, this method of encryption is best suited for encrypting large amounts of data such as files on a computer. Answer: A is incorrect. Integrity ensures that no intentional or unintentional unauthorized modification is made to data. Answer: C is incorrect. Auditing is used to track user accounts for file and object access, logon attempts, system shutdown etc. This enhances the security of the network. Before enabling auditing, the type of event to be audited should be specified in the Audit Policy in User Manager for Domains. -
Which of the following DoD directives defines DITSCAP as the standard C&A process for the Department of Defense?
- DoD 8910.1
- DoD 5200.22-M
- DoD 8000.1
- DoD 5200.40
Explanation:DITSCAP stands for DoD Information Technology Security Certification and Accreditation Process. The DoD Directive 5200.40 (DoD Information Technology Security Certification and Accreditation Process) established the DITSCAP as the standard C&A process for the Department of Defense. The Department of Defense Information Assurance Certification and Accreditation Process (DIACAP) is a process defined by the United States Department of Defense (DoD) for managing risk. DIACAP replaced the former process, known as DITSCAP, in 2006. Answer: B is incorrect. This DoD Directive is known as National Industrial Security Program Operating Manual. Answer: C is incorrect. This DoD Directive is known as Defense Information Management (IM) Program. Answer: A is incorrect. This DoD Directive is known as Management and Control of Information Requirements. -
Which of the following are the responsibilities of a custodian with regard to data in an information classification program? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose three.
- Performing data restoration from the backups when necessary
- Running regular backups and routinely testing the validity of the backup data
- Determining what level of classification the information requires
- Controlling access, adding and removing privileges for individual users
Explanation:The owner of information delegates the responsibility of protecting that information to a custodian. The following are the responsibilities of a custodian with regard to data in an information classification program: Running regular backups and routinely testing the validity of the backup data Performing data restoration from the backups when necessary Controlling access, adding and removing privileges for individual users Answer: C is incorrect. Determining what level of classification the information requires is the responsibility of the owner. -
You are the project manager of the GHY project for your organization. You are about to start the qualitative risk analysis process for the project and you need to determine the roles and responsibilities for conducting risk management. Where can you find this information?
- Risk register
- Staffing management plan
- Risk management plan
- Enterprise environmental factors
Explanation:The risk management plan defines the roles and responsibilities for conducting risk management. A Risk management plan is a document arranged by a project manager to estimate the effectiveness, predict risks, and build response plans to mitigate them. It also consists of the risk assessment matrix. Risks are built in with any project, and project managers evaluate risks repeatedly and build plans to address them. The risk management plan consists of analysis of possible risks with both high and low impacts, and the mitigation strategies to facilitate the project and avoid being derailed through which the common problems arise. Risk management plans should be timely reviewed by the project team in order to avoid having the analysis become stale and not reflective of actual potential project risks. Most critically, risk management plans include a risk strategy for project execution. Answer: A is incorrect. The risk register does not define the risk management roles and responsibilities. Answer: D is incorrect. Enterprise environmental factors may define the roles that risk management officials or departments play in the project, but the best answer for all projects is the risk management plan. Answer: B is incorrect. The staffing management plan does not define the risk management roles and responsibilities.