CSSLP : Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional : Part 07
CSSLP : Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional : Part 07
-
Which of the following components of configuration management involves periodic checks to determine the consistency and completeness of accounting information and to verify that all configuration management policies are being followed?
- Configuration Identification
- Configuration Auditing
- Configuration Control
- Configuration Status Accounting
Explanation:
Configuration auditing is a component of configuration management, which involves periodic checks to establish the consistency and completeness of accounting information and to confirm that all configuration management policies are being followed. Configuration audits are broken into functional and physical configuration audits. They occur either at delivery or at the moment of effecting the change. A functional configuration audit ensures that functional and performance attributes of a configuration item are achieved, while a physical configuration audit ensures that a configuration item is installed in accordance with the requirements of its detailed design documentation. Answer: D is incorrect. The configuration status accounting procedure is the ability to record and report on the configuration baselines associated with each configuration item at any moment of time. It supports the functional and physical attributes of software at various points in time, and performs systematic control of accounting to the identified attributes for the purpose of maintaining software integrity and traceability throughout the software development life cycle. Answer: C is incorrect. Configuration control is a procedure of the Configuration management. Configuration control is a set of processes and approval stages required to change a configuration item’s attributes and to re-baseline them. It supports the change of the functional and physical attributes of software at various points in time, and performs systematic control of changes to the identified attributes. Answer: A is incorrect. Configuration identification is the process of identifying the attributes that define every aspect of a configuration item. A configuration item is a product (hardware and/or software) that has an end-user purpose. These attributes are recorded in configuration documentation and baselined. Baselining an attribute forces formal configuration change control processes to be effected in the event that these attributes are changed.
-
The NIST ITL Cloud Research Team defines some primary and secondary technologies as the fundamental elements of cloud computing in its “Effectively and Securely Using the Cloud Computing Paradigm” presentation. Which of the following technologies are included in the primary technologies? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Web application framework
- Free and open source software
- SOA
- Virtualization
Explanation:The primary technologies defined by the NIST ITL Cloud Research Team in its “Effectively and Securely Using the Cloud Computing Paradigm” presentation are as follows: Virtualization Grid technology SOA (Service Oriented Architecture) Distributed computing Broadband network Browser as a platform Free and open source software Answer: A is incorrect. It is defined as the secondary technology. -
A service provider guarantees for end-to-end network traffic performance to a customer. Which of the following types of agreement is this?
- SLA
- VPN
- NDA
- LA
Explanation:This is a type of service-level agreement. A service-level agreement (SLA) is a negotiated agreement between two parties where one is the customer and the other is the service provider. It records a common understanding about services, priorities, responsibilities, guarantees, and warranties. Each area of service scope should have the ‘level of service’ defined. The SLA may specify the levels of availability, serviceability, performance, operation, or other attributes of the service, such as billing. Answer: C is incorrect. Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are often used to protect the confidentiality of an invention as it is being evaluated by potential licensees. Answer: D is incorrect. License agreements (LA) describe the rights and responsibilities of a party related to the use and exploitation of intellectual property. Answer: B is incorrect. There is no such type of agreement as VPN. -
According to the NIST SAMATE, dynamic analysis tools operate by generating runtime vulnerability scenario using some functions. Which of the following are functions that are used by the dynamic analysis tools and are summarized in the NIST SAMATE? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Implementation attack
- Source code security
- File corruption
- Network fault injection
Explanation:According to the NIST SAMATE, dynamic analysis tools operate by generating runtime vulnerability scenario using the following functions: Resource fault injection Network fault injection System fault injection User interface fault injection Design attack Implementation attack File corruption Answer: B is incorrect. This function is summarized for static analysis tools. -
Which of the following is a formula, practice, process, design, instrument, pattern, or compilation of information which is not generally known, but by which a business can obtain an economic advantage over its competitors?
- Copyright
- Utility model
- Trade secret
- Cookie
Explanation:
A trade secret is a formula, practice, process, design, instrument, pattern, or compilation of information which is not generally known. It helps a business to obtain an economic advantage over its competitors or customers. In some jurisdictions, such secrets are referred to as confidential information or classified information. Answer: A is incorrect. A copyright is a form of intellectual property, which secures to its holder the exclusive right to produce copies of his or her works of original expression, such as a literary work, movie, musical work or sound recording, painting, photograph, computer program, or industrial design, for a defined, yet extendable, period of time. It does not cover ideas or facts. Copyright laws protect intellectual property from misuse by other individuals. Answer: B is incorrect. A utility model is an intellectual property right to protect inventions. Answer: D is incorrect. A cookie is a small bit of text that accompanies requests and pages as they move between Web servers and browsers. It contains information that is read by a Web application, whenever a user visits a site. Cookies are stored in the memory or hard disk of client computers. A Web site stores information, such as user preferences and settings in a cookie. This information helps in providing customized services to users. There is absolutely no way a Web server can access any private information about a user or his computer through cookies, unless a user provides the information. A Web server cannot access cookies created by other Web servers. -
Which of the following statements about a host-based intrusion prevention system (HIPS) are true? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose two.
- It can detect events scattered over the network.
- It is a technique that allows multiple computers to share one or more IP addresses.
- It can handle encrypted and unencrypted traffic equally.
- It cannot detect events scattered over the network.
Explanation:A host-based intrusion prevention system (HIPS) is an application usually employed on a single computer. It complements traditional finger- print-based and heuristic antivirus detection methods, since it does not need continuous updates to stay ahead of new malware. When a malicious code needs to modify the system or other software residing on the machine, a HIPS system will notice some of the resulting changes and prevent the action by default or notify the user for permission. It can handle encrypted and unencrypted traffic equally and cannot detect events scattered over the network. Answer: B is incorrect. Network address translation (NAT) is a technique that allows multiple computers to share one or more IP addresses. NAT is configured at the server between a private network and the Internet. It allows the computers in a private network to share a global, ISP assigned address. NAT modifies the headers of packets traversing the server. For packets outbound to the Internet, it translates the source addresses from private to public, whereas for packets inbound from the Internet, it translates the destination addresses from public to private. Answer: A is incorrect. Network intrusion prevention system (NIPS) is a hardware/software platform that is designed to analyze, detect, and report on security related events. NIPS is designed to inspect traffic and based on its configuration or security policy, it can drop malicious traffic. NIPS is able to detect events scattered over the network and can react. -
Who amongst the following makes the final accreditation decision?
- ISSE
- CRO
- DAA
- ISSO
Explanation:The DAA, also known as Authorizing Official, makes the final accreditation decision. The Designated Approving Authority (DAA), in the United States Department of Defense, is the official with the authority to formally assume responsibility for operating a system at an acceptable level of risk. The DAA is responsible for implementing system security. The DAA can grant the accreditation and can determine that the system’s risks are not at an acceptable level and the system is not ready to be operational. Answer: D is incorrect. An Information System Security Officer (ISSO) plays the role of a supporter. The responsibilities of an Information System Security Officer (ISSO) are as follows: Manages the security of the information system that is slated for Certification & Accreditation (C&A). Insures the information systems configuration with the agency’s information security policy. Supports the information system owner/information owner for the completion of security-related responsibilities. Takes part in the formal configuration management process. Prepares Certification & Accreditation (C&A) packages. Answer: A is incorrect. An Information System Security Engineer (ISSE) plays the role of an advisor. The responsibilities of an Information System Security Engineer are as follows: Provides view on the continuous monitoring of the information system. Provides advice on the impacts of system changes. Takes part in the configuration management process. Takes part in the development activities that are required to implement system changes. Follows approved system changes. Answer: B is incorrect. A Chief Risk Officer (CRO) is also known as Chief Risk Management Officer (CRMO). The Chief Risk Officer or Chief Risk Management Officer of a corporation is the executive accountable for enabling the efficient and effective governance of significant risks, and related opportunities, to a business and its various segments. Risks are commonly categorized as strategic, reputational, operational, financial, or compliance-related. CRO’s are accountable to the Executive Committee and The Board for enabling the business to balance risk and reward. In more complex organizations, they are generally responsible for coordinating the organization’s Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) approach. -
In which of the following deployment models of cloud is the cloud infrastructure administered by the organizations or a third party? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose two.
- Private cloud
- Public cloud
- Hybrid cloud
- Community cloud
Explanation:In private cloud, the cloud infrastructure is operated exclusively for an organization. The private cloud infrastructure is administered by the organization or a third party, and exists on premise and off premise. In community cloud, the cloud infrastructure is shared by a number of organizations and supports a particular community. The community cloud infrastructure is administered by the organizations or a third party and exists on premise or off premise. Answer: B is incorrect. In public cloud, the cloud infrastructure is administered by an organization that sells cloud services. Answer: C is incorrect. In hybrid cloud, the cloud infrastructure is administered by both, i.e., an organization and a third party. -
Which of the following disaster recovery tests includes the operations that shut down at the primary site, and are shifted to the recovery site according to the disaster recovery plan?
- Structured walk-through test
- Full-interruption test
- Parallel test
- Simulation test
Explanation:A full-interruption test includes the operations that shut down at the primary site and are shifted to the recovery site according to the disaster recovery plan. It operates just like a parallel test. The full-interruption test is very expensive and difficult to arrange. Sometimes, it causes a major disruption of operations if the test fails. Answer: A is incorrect. The structured walk-through test is also known as the table-top exercise. In structured walk-through test, the team members walkthrough the plan to identify and correct weaknesses and how they will respond to the emergency scenarios by stepping in the course of the plan. It is the most effective and competent way to identify the areas of overlap in the plan before conducting more challenging training exercises. Answer: C is incorrect. A parallel test includes the next level in the testing procedure, and relocates the employees to an alternate recovery site and implements site activation procedures. These employees present with their disaster recovery responsibilities as they would for an actual disaster. The disaster recovery sites have full responsibilities to conduct the day-to-day organization’s business. Answer: D is incorrect. A simulation test is a method used to test the disaster recovery plans. It operates just like a structured walk- through test. In the simulation test, the members of a disaster recovery team present with a disaster scenario and then, discuss on appropriate responses. These suggested responses are measured and some of them are taken by the team. The range of the simulation test should be defined carefully for avoiding excessive disruption of normal business activities. -
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the various SSE-CMM levels at the appropriate places.
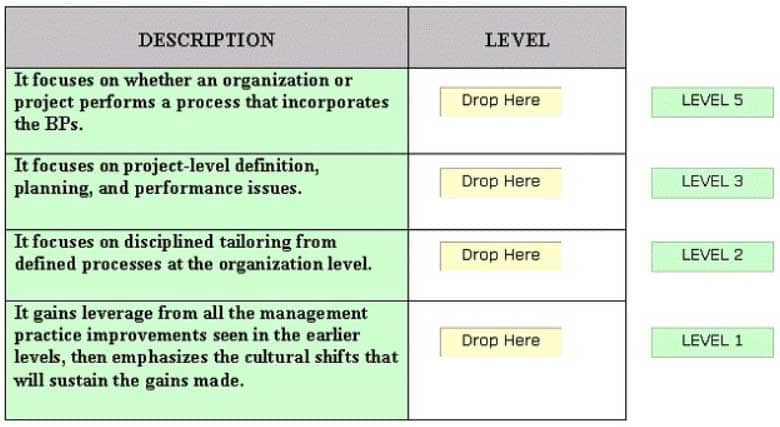
CSSLP Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional Part 07 Q10 007 Question 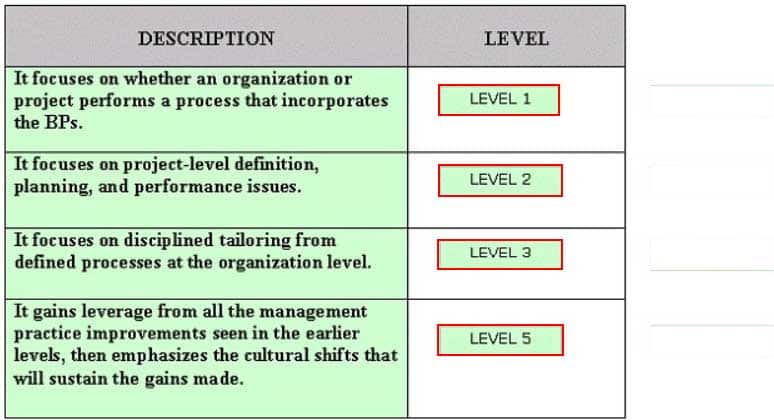
CSSLP Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional Part 07 Q10 007 Answer -
John works as a professional Ethical Hacker. He is assigned a project to test the security of www.we-are-secure.com. You have searched all open ports of the we-are-secure server. Now, you want to perform the next information-gathering step, i.e., passive OS fingerprinting. Which of the following tools can you use to accomplish the task?
- Superscan
- NBTscan
- Nmap
- P0f
Explanation:According to the scenario, you have searched all open ports of the we-are-secure server. Now you want to perform the next information-gathering step, i.e., passive OS fingerprinting. For this, you will use the P0f tool to accomplish the task. P0f is a passive OS fingerprinting tool that is used to identify the operating system of a target host simply by examining captured packets even when the device is behind a packet firewall. It does not generate any additional direct or indirect network traffic. P0f can also be used to gather various information, such as firewall presence, NAT use (for policy enforcement), existence of a load balancer setup, the distance to the remote system and its uptime, etc. Answer: C is incorrect. Nmap is used for active OS fingerprinting. Nmap is a free open-source utility for network exploration and security auditing. It is used to discover computers and services on a computer network, thus creating a “map” of the network. Just like many simple port scanners, Nmap is capable of discovering passive services. In addition, Nmap may be able to determine various details about the remote computers. These include operating system, device type, uptime, software product used to run a service, exact version number of that product, presence of some firewall techniques and, on a local area network, even vendor of the remote network card. Nmap runs on Linux, Microsoft Windows etc.Answer: A is incorrect. SuperScan is a TCP/UDP port scanner. It also works as a ping sweeper and hostname resolver. It can ping a given range of IP addresses and resolve the host name of the remote system.The features of SuperScan are as follows: It scans any port range from a built-in list or any given range. It performs ping scans and port scans using any IP range. It modifies the port list and port descriptions using the built in editor. It connects to any discovered open port using user-specified “helper” applications. It has the transmission speed control utility.
Answer: B is incorrect. NBTscan is a scanner that scans IP networks for NetBIOS name information. It sends a NetBIOS status query to each address in a supplied range and lists received information in human readable form. It displays IP address, NetBIOS computer name, logged-in user name and MAC address of each responded host. NBTscan works in the same manner as nbtstat, but it operates on a range of addresses instead of just one. -
Which of the following fields of management focuses on establishing and maintaining consistency of a system’s or product’s performance and its functional and physical attributes with its requirements, design, and operational information throughout its life?
- Configuration management
- Risk management
- Change management
- Procurement management
Explanation:Configuration management is a field of management that focuses on establishing and maintaining consistency of a system’s or product’s performance and its functional and physical attributes with its requirements, design, and operational information throughout its life. Configuration Management System is a subsystem of the overall project management system. It is a collection of formal documented procedures used to identify and document the functional and physical characteristics of a product, result, service, or component of the project. It also controls any changes to such characteristics, and records and reports each change and its implementation status. It includes the documentation, tracking systems, and defined approval levels necessary for authorizing and controlling changes. Audits are performed as part of configuration management to determine if the requirements have been met. Answer: D is incorrect. The procurement management plan defines more than just the procurement of team members, if needed. It defines how procurements will be planned and executed, and how the organization and the vendor will fulfill the terms of the contract. Answer: B is incorrect. Risk Management is used to identify, assess, and control risks. It includes analyzing the value of assets to the business, identifying threats to those assets, and evaluating how vulnerable each asset is to those threats. Answer: C is incorrect. Change Management is used to ensure that standardized methods and procedures are used for efficient handling of all changes. -
Which of the following US Acts emphasized a “risk-based policy for cost-effective security” and makes mandatory for agency program officials, chief information officers, and inspectors general (IGs) to conduct annual reviews of the agency’s information security program and report the results to Office of Management and Budget?
- Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002 (FISMA)
- The Electronic Communications Privacy Act of 1986 (ECPA)
- The Equal Credit Opportunity Act (ECOA)
- The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)
Explanation:The Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002 (“FISMA”, 44 U.S.C. 3541, et seq.) is a United States federal law enacted in 2002 as Title III of the E-Government Act of 2002 (Pub.L. 107-347, 116 Stat. 2899). The act recognized the importance of information security to the economic and national security interests of the United States. The act requires each federal agency to develop, document, and implement an agency-wide program to provide information security for the information and information systems that support the operations and assets of the agency, including those provided or managed by another agency, contractor, or other source. FISMA has brought attention within the federal government to cybersecurity and explicitly emphasized a “risk-based policy for cost-effective security”. FISMA requires agency program officials, chief information officers, and inspectors general (IGs) to conduct annual reviews of the agency’s information security program and report the results to Office of Management and Budget (OMB). OMB uses this data to assist in its oversight responsibilities and to prepare this annual report to Congress on agency compliance with the act. Answer: C is incorrect. The Equal Credit Opportunity Act (ECOA) is a United States law (codified at 15 U.S.C. 1691 et seq.), enacted in 1974, that makes it unlawful for any creditor to discriminate against any applicant, with respect to any aspect of a credit transaction, on the basis of race, color, religion, national origin, sex, marital status, or age; to the fact that all or part of the applicant’s income derives from a public assistance program; or to the fact that the applicant has in good faith exercised any right under the Consumer Credit Protection Act. The law applies to any person who, in the ordinary course of business, regularly participates in a credit decision, including banks, retailers, bankcard companies, finance companies, and credit unions. Answer: B is incorrect. The Electronic Communications Privacy Act of 1986 (ECPA Pub. L. 99-508, Oct. 21, 1986, 100 Stat. 1848, 18 U.S.C. 2510) was enacted by the United States Congress to extend government restrictions on wire taps from telephone calls to include transmissions of electronic data by computer. Specifically, ECPA was an amendment to Title III of the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act of 1968 (the Wiretap Statute), which was primarily designed to prevent unauthorized government access to private electronic communications. The ECPA also added new provisions prohibiting access to stored electronic communications, i.e., the Stored Communications Act,18 U.S.C. 2701-2712. Answer: D is incorrect. The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is an American federal law (codified at 15 U.S.C. 1681 et seq.) that regulates the collection, dissemination, and use of consumer information, including consumer credit information. Along with the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA), it forms the base of consumer credit rights in the United States. It was originally passed in 1970, and is enforced by the US Federal Trade Commission. -
Which of the following allows multiple operating systems (guests) to run concurrently on a host computer?
- Emulator
- Hypervisor
- Grid computing
- CP/CMS
Explanation:A hypervisor is a virtualization technique that allows multiple operating systems (guests) to run concurrently on a host computer. It is also called the virtual machine monitor (VMM). The hypervisor provides a virtual operating platform to the guest operating systems and checks their execution process. It provides isolation to the host’s resources. The hypervisor is installed on server hardware. Answer: A is incorrect. Emulator duplicates the functions of one system using a different system, so that the second system behaves like the first system. Answer: D is incorrect. CP/CMS is a time-sharing operating system of the late 60s and early 70s, and it is known for its excellent performance and advanced features. Answer: C is incorrect. Grid computing refers to the combination of computer resources from multiple administrative domains to achieve a common goal. -
Frank is the project manager of the NHH Project. He is working with the project team to create a plan to document the procedures to manage risks throughout the project. This document will define how risks will be identified and quantified. It will also define how contingency plans will be implemented by the project team. What document is Frank and the NHH Project team creating in this scenario?
- Risk management plan
- Project plan
- Project management plan
- Resource management plan
Explanation:The risk management plan, part of the comprehensive management plan, defines how risks will be identified, analyzed, monitored and controlled, and even responded to. A Risk management plan is a document arranged by a project manager to estimate the effectiveness, predict risks, and build response plans to mitigate them. It also consists of the risk assessment matrix. Risks are built in with any project, and project managers evaluate risks repeatedly and build plans to address them. The risk management plan consists of analysis of possible risks with both high and low impacts, and the mitigation strategies to facilitate the project and avoid being derailed through which the common problems arise. Risk management plans should be timely reviewed by the project team in order to avoid having the analysis become stale and not reflective of actual potential project risks. Most critically, risk management plans include a risk strategy for project execution. Answer: C is incorrect. The project management plan is a comprehensive plan that communicates the intent of the project for all project management knowledge areas. Answer: B is incorrect. The project plan is not an official PMBOK project management plan. Answer: D is incorrect. The resource management plan defines the management of project resources, such as project team members, facilities, equipment, and contractors. -
Which of the following security related areas are used to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of federal information systems and information processed by those systems?
- Personnel security
- Access control
- Configuration management
- Media protection
- Risk assessment
Explanation:The minimum security requirements cover seventeen security related areas to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of federal information systems and information processed by those systems. They are as follows: Access control Awareness and training Audit and accountability Certification, accreditation, and security assessment Configuration management Contingency planning Identification and authentication Incident response Maintenance Media protection Physical and environmental protection Planning Personnel security Risk assessment Systems and services acquisition System and communications protection System and information integrity -
What are the various benefits of a software interface according to the “Enhancing the Development Life Cycle to Produce Secure Software” document? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose three.
- It modifies the implementation of a component without affecting the specifications of the interface.
- It controls the accessing of a component.
- It displays the implementation details of a component.
- It provides a programmatic way of communication between the components that are working with different programming languages.
Explanation:The benefits of a software interface are as follows: It provides a programmatic way of communication between the components that are working with different programming languages. It prevents direct communication between components. It modifies the implementation of a component without affecting the specifications of the interface. It hides the implementation details of a component. It controls the accessing of a component. Answer: C is incorrect. A software interface hides the implementation details of the component. -
Elizabeth is a project manager for her organization and she finds risk management to be very difficult for her to manage. She asks you, a lead project manager, at what stage in the project will risk management become easier. What answer best resolves the difficulty of risk management practices and the effort required?
- Risk management only becomes easier when the project moves into project execution.
- Risk management only becomes easier when the project is closed.
- Risk management is an iterative process and never becomes easier.
- Risk management only becomes easier the more often it is practiced.
Explanation:According to the PMBOK, “Like many things in project management, the more it is done the easier the practice becomes.” Answer: B is incorrect. This answer is not the best choice for the project. Answer: A is incorrect. Risk management likely becomes more difficult in project execution that in other stages of the project. Answer: C is incorrect. Risk management does become easier the more often it is done. -
You work as a Network Administrator for uCertify Inc. You need to secure web services of your company in order to have secure transactions. Which of the following will you recommend for providing security?
- SSL
- VPN
- S/MIME
- HTTP
Explanation:The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a commonly-used protocol for managing the security of a message transmission on the Internet. SSL has recently been succeeded by Transport Layer Security (TLS), which is based on SSL. SSL uses a program layer located between the Internet’s Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and Transport Control Protocol (TCP) layers. SSL is included as part of both the Microsoft and Netscape browsers and most Web server products. URLs that require an SSL connection start with https: instead of http:. Answer: C is incorrect. S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) is a standard for public key encryption and signing of e- mail encapsulated in MIME. S/MIME provides the following cryptographic security services for electronic messaging applications: authentication, message integrity, non-repudiation of origin (using digital signatures), privacy, and data security (using encryption). Answer: D is incorrect. Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is a client/server TCP/IP protocol used on the World Wide Web (WWW) to display Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) pages. HTTP defines how messages are formatted and transmitted, and what actions Web servers and browsers should take in response to various commands. For example, when a client application or browser sends a request to the server using HTTP commands, the server responds with a message containing the protocol version, success or failure code, server information, and body content, depending on the request. HTTP uses TCP port 80 as the default port. Answer: B is incorrect. A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a computer network that is implemented in an additional software layer (overlay) on top of an existing larger network for the purpose of creating a private scope of computer communications or providing a secure extension of a private network into an insecure network such as the Internet. The links between nodes of a Virtual Private Network are formed over logical connections or virtual circuits between hosts of the larger network. The Link Layer protocols of the virtual network are said to be tunneled through the underlying transport network. -
Which of the following security models focuses on data confidentiality and controlled access to classified information?
- Clark-Wilson model
- Biba model
- Take-Grant model
- Bell-La Padula model
Explanation:The Bell-La Padula Model is a state machine model used for enforcing access control in government and military applications. The model is a formal state transition model of computer security policy that describes a set of access control rules which use security labels on objects and clearances for subjects. Security labels range from the most sensitive (e.g.,”Top Secret”), down to the least sensitive (e.g., “Unclassified” or “Public”).
The Bell-La Padula model focuses on data confidentiality and controlled access to classified information, in contrast to the Biba Integrity Model which describes rules for the protection of data integrity. Answer: B is incorrect. The Biba model is a formal state transition system of computer security policy that describes a set of access control rules designed to ensure data integrity. Data and subjects are grouped into ordered levels of integrity. The model is designed so that subjects may not corrupt data in a level ranked higher than the subject, or be corrupted by data from a lower level than the subject. Answer: A is incorrect. The Clark-Wilson model provides a foundation for specifying and analyzing an integrity policy for a computing system. The model is primarily concerned with formalizing the notion of information integrity. Information integrity is maintained by preventing corruption of data items in a system due to either error or malicious intent. The model’s enforcement and certification rules define data items and processes that provide the basis for an integrity policy. The core of the model is based on the notion of a transaction. Answer: C is incorrect. The take-grant protection model is a formal model used in the field of computer security to establish or disprove the safety of a given computer system that follows specific rules. It shows that for specific systems the question of safety is decidable in linear time, which is in general undecidable. The model represents a system as directed graph, where vertices are either subjects or objects. The edges between them are labeled and the label indicates the rights that the source of the edge has over the destination. Two rights occur in every instance of the model: take and grant. They play a special role in the graph rewriting rules describing admissible changes of the graph.
