CSSLP : Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional : Part 10
CSSLP : Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional : Part 10
-
There are seven risks responses that a project manager can choose from. Which risk response is appropriate for both positive and negative risk events?
- Acceptance
- Transference
- Sharing
- Mitigation
Explanation:
Only acceptance is appropriate for both positive and negative risk events. Often sharing is used for low probability and low impact risk events regardless of the positive or negative effects the risk event may bring the project. Acceptance response is a part of Risk Response planning process. Acceptance response delineates that the project plan will not be changed to deal with the risk. Management may develop a contingency plan if the risk does occur. Acceptance response to a risk event is a strategy that can be used for risks that pose either threats or opportunities. Acceptance response can be of two types: Passive acceptance: It is a strategy in which no plans are made to try or avoid or mitigate the risk. Active acceptance: Such responses include developing contingency reserves to deal with risks, in case they occur. Acceptance is the only response for both threats and opportunities. Answer: C is incorrect. Sharing is a positive risk response that shares an opportunity for all parties involved in the risk event. Answer: B is incorrect. Transference is a negative risk event that transfers the risk ownership to a third party, such as vendor, through a contractual relationship. Answer: D is incorrect. Mitigation is a negative risk event that seeks to lower the probability and/or impact of a risk event.
-
You work as a Security Manager for Tech Perfect Inc. In the organization, Syslog is used for computer system management and security auditing, as well as for generalized informational, analysis, and debugging messages. You want to prevent a denial of service (DoS) for the Syslog server and the loss of Syslog messages from other sources. What will you do to accomplish the task?
- Use a different message format other than Syslog in order to accept data.
- Enable the storage of log entries in both traditional Syslog files and a database.
- Limit the number of Syslog messages or TCP connections from a specific source for a certain time period.
- Encrypt rotated log files automatically using third-party or OS mechanisms.
Explanation:In order to accomplish the task, you should limit the number of Syslog messages or TCP connections from a specific source for a certain time period. This will prevent a denial of service (DoS) for the Syslog server and the loss of Syslog messages from other sources. Answer: D is incorrect. You can encrypt rotated log files automatically using third-party or OS mechanisms to protect data confidentiality. Answer: A is incorrect. You can use a different message format other than Syslog in order to accept data for aggregating data from hosts that do not support Syslog. Answer: B is incorrect. You can enable the storage of log entries in both traditional Syslog files and a database for creating a database storage for logs. -
A Web-based credit card company had collected financial and personal details of Mark before issuing him a credit card. The company has now provided Mark’s financial and personal details to another company. Which of the following Internet laws has the credit card issuing company violated?
- Trademark law
- Security law
- Privacy law
- Copyright law
Explanation:The credit card issuing company has violated the Privacy law. According to the Internet Privacy law, a company cannot provide their customer’s financial and personal details to other companies. Answer: A is incorrect. Trademark laws facilitate the protection of trademarks around the world. Answer: B is incorrect. There is no law such as Security law. Answer: D is incorrect. The Copyright law protects original works or creations of authorship including literary, dramatic, musical, artistic, and certain other intellectual works. -
Which of the following statements is true about residual risks?
- It is the probabilistic risk after implementing all security measures.
- It can be considered as an indicator of threats coupled with vulnerability.
- It is a weakness or lack of safeguard that can be exploited by a threat.
- It is the probabilistic risk before implementing all security measures.
Explanation:The residual risk is the risk or danger of an action or an event, a method or a (technical) process that still conceives these dangers even if all theoretically possible safety measures would be applied. The formula to calculate residual risk is (inherent risk) x (control risk) where inherent risk is (threats vulnerability). Answer: B is incorrect. In information security, security risks are considered as an indicator of threats coupled with vulnerability. In other words, security risk is a probabilistic function of a given threat agent exercising a particular vulnerability and the impact of that risk on the organization. Security risks can be mitigated by reviewing and taking responsible actions based on possible risks. Answer: C is incorrect. Vulnerability is a weakness or lack of safeguard that can be exploited by a threat, thus causing harm to the information systems or networks. It can exist in hardware , operating systems, firmware, applications, and configuration files. Vulnerability has been variously defined in the current context as follows: 1.A security weakness in a Target of Evaluation due to failures in analysis, design, implementation, or operation and such. 2.Weakness in an information system or components (e.g. system security procedures, hardware design, or internal controls that could be exploited to produce an information-related misfortune.) 3.The existence of a weakness, design, or implementation error that can lead to an unexpected, undesirable event compromising the security of the system, network, application, or protocol involved. -
To help review or design security controls, they can be classified by several criteria . One of these criteria is based on their nature. According to this criterion, which of the following controls consists of incident response processes, management oversight, security awareness, and training?
- Compliance control
- Physical control
- Procedural control
- Technical control
Explanation:Procedural controls include incident response processes, management oversight, security awareness, and training. Answer: B is incorrect. Physical controls include fences, doors, locks, and fire extinguishers. Answer: D is incorrect. Technical controls include user authentication (login) and logical access controls, antivirus software, and firewalls. Answer: A is incorrect. The legal and regulatory, or compliance controls, include privacy laws, policies, and clauses. -
Which of the following NIST Special Publication documents provides a guideline on network security testing?
- NIST SP 800-42
- NIST SP 800-53A
- NIST SP 800-60
- NIST SP 800-53
- NIST SP 800-37
- NIST SP 800-59
Explanation:NIST SP 800-42 provides a guideline on network security testing. Answer: E, D, B, F, and C are incorrect. NIST has developed a suite of documents for conducting Certification & Accreditation (C&A). These documents are as follows: NIST Special Publication 800-37: This document is a guide for the security certification and accreditation of Federal Information Systems. NIST Special Publication 800-53: This document provides a guideline for security controls for Federal Information Systems. NIST Special Publication 800-53A. This document consists of techniques and procedures for verifying the effectiveness of security controls in Federal Information System. NIST Special Publication 800-59: This document is a guideline for identifying an information system as a National Security System. NIST Special Publication 800-60: This document is a guide for mapping types of information and information systems to security objectives and risk levels. -
The organization level is the Tier 1 and it addresses risks from an organizational perspective. What are the various Tier 1 activities? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- The organization plans to use the degree and type of oversight, to ensure that the risk management strategy is being effectively carried out.
- The level of risk tolerance.
- The techniques and methodologies an organization plans to employ, to evaluate information system-related security risks.
- The RMF primarily operates at Tier 1.
Explanation:The Organization Level is the Tier 1, and it addresses risks from an organizational perspective. It includes the following points: The techniques and methodologies an organization plans to employ, to evaluate information system-related security risks. During risk assessment, the methods and procedures the organization plans to use, to evaluate the significance of the risks identified. The types and extent of risk mitigation measures the organization plans to employ, to address identified risks. The level of risk tolerance. According to the environment of operation, how the organization plans to monitor risks on an ongoing basis, given the inevitable changes to organizational information system.
The organization plans to use the degree and type of oversight, in order to ensure that the risk management strategy is being effectively carried out. Answer: D is incorrect. The RMF primarily operates at Tier 3. -
An asset with a value of $600,000 is subject to a successful malicious attack threat twice a year. The asset has an exposure of 30 percent to the threat. What will be the annualized loss expectancy?
- $360,000
- $180,000
- $280,000
- $540,000
Explanation:The annualized loss expectancy will be $360,000. Annualized loss expectancy (ALE) is the annually expected financial loss to an organization from a threat. The annualized loss expectancy (ALE) is the product of the annual rate of occurrence (ARO) and the single loss expectancy (SLE). It is mathematically expressed as follows:
ALE = Single Loss Expectancy (SLE) * Annualized Rate of Occurrence (ARO)
Here, it is as follows:
SLE = Asset value * EF (Exposure factor)
= 600,000 * (30/100)
= 600,000 * 0.30
= 180,000
ALE = SLE * ARO
= 180,000 * 2
= 360,000
Answer: C, B, and D are incorrect. These are not valid answers. -
Which of the following is a variant with regard to Configuration Management?
- A CI that has the same name as another CI but shares no relationship.
- A CI that particularly refers to a software version.
- A CI that has the same essential functionality as another CI but a bit different in some small manner.
- A CI that particularly refers to a hardware specification.
Explanation:A CI that has the same essential functionality as another CI but a bit different in some small manner, and therefore, might be required to be analyzed along with its generic group. A Configuration item (CI) is an IT asset or a combination of IT assets that may depend and have relationships with other IT processes. A CI will have attributes which may be hierarchical and relationships that will be assigned by the configuration manager in the CM database. The Configuration Item (CI) attributes are as follows: 1.Technical: It is data that describes the CI’s capabilities which include software version and model numbers, hardware and manufacturer specifications, and other technical details like networking speeds, and data storage size. Keyboards, mice and cables are considered consumables. 2.Ownership: It is part of financial asset management, ownership attributes, warranty, location, and responsible person for the CI. 3.Relationship: It is the relationship among hardware items, software, and users. Answer: B, D, and A are incorrect. These are incorrect definitions of a variant with regard to Configuration Management. -
Bill is the project manager of the JKH Project. He and the project team have identified a risk event in the project with a high probability of occurrence and the risk event has a high cost impact on the project. Bill discusses the risk event with Virginia, the primary project customer, and she decides that the requirements surrounding the risk event should be removed from the project. The removal of the requirements does affect the project scope, but it can release the project from the high risk exposure. What risk response has been enacted in this project?
- Mitigation
- Transference
- Acceptance
- Avoidance
Explanation:This is an example of the avoidance risk response. Because the project plan has been changed to avoid the risk event, so it is considered the avoidance risk response. Risk avoidance is a technique used for threats. It creates changes to the project management plan that are meant to either eliminate the risk completely or to protect the project objectives from its impact. Risk avoidance removes the risk event entirely either by adding additional steps to avoid the event or reducing the project scope requirements. It may seem the answer to all possible risks, but avoiding risks also means losing out on the potential gains that accepting (retaining) the risk might have allowed. Answer: C is incorrect. Acceptance is when the stakeholders acknowledge the risk event and they accept that the event could happen and could have an impact on the project. Acceptance is usually used for risk events that have low risk exposure or risk events in which the project has no control, such as a pending law or weather threats. Answer: A is incorrect. Mitigation is involved with the actions to reduce an included risk’s probability and/or impact on the project’s objectives. As the risk was removed from the project, this scenario describes avoidance, not mitigation. Answer: B is incorrect. Transference is when the risk is still within the project, but the ownership and management of the risk event is transferred to a third party – usually for a fee. -
Martha registers a domain named Microsoft.in. She tries to sell it to Microsoft Corporation. The infringement of which of the following has she made?
- Copyright
- Trademark
- Patent
- Intellectual property
Explanation:According to the Lanham Act, domain names fall under trademarks law. A new section 43(d) of the Trademark Act (Lanham Act) states that anyone who in bad faith registers, traffics in, or uses a domain name that infringes or dilutes another’s trademark has committed trademark infringement. Factors involved in assessing bad faith focus on activities typically associated with cyberpiracy or cybersquatting, such as whether the registrant has offered to sell the domain name to the trademark holder for financial gain without having used or intended to use it for a bona fide business; whether the domain-name registrant registered multiple domain names that are confusingly similar to the trademarks of others; and whether the trademark incorporated in the domain name is distinctive and famous. Other factors are whether the domain name consists of the legal name or common handle of the domain-name registrant and whether the domain-name registrant previously used the mark in connection with a bona fide business. -
Certification and Accreditation (C&A or CnA) is a process for implementing information security. It is a systematic procedure for evaluating, describing, testing, and authorizing systems prior to or after a system is in operation. Which of the following statements are true about Certification and Accreditation? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose two.
- Certification is a comprehensive assessment of the management, operational, and technical security controls in an information system.
- Accreditation is a comprehensive assessment of the management, operational, and technical security controls in an information system.
- Accreditation is the official management decision given by a senior agency official to authorize operation of an information system.
- Certification is the official management decision given by a senior agency official to authorize operation of an information system.
Explanation:Certification and Accreditation (C&A or CnA) is a process for implementing information security. It is a systematic procedure for evaluating, describing, testing, and authorizing systems prior to or after a system is in operation. The C&A process is used extensively in the U.S. Federal Government. Some C&A processes include FISMA, NIACAP, DIACAP, and DCID 6/3. Certification is a comprehensive assessment of the management, operational, and technical security controls in an information system, made in support of security accreditation, to determine the extent to which the controls are implemented correctly, operating as intended, and producing the desired outcome with respect to meeting the security requirements for the system. Accreditation is the official management decision given by a senior agency official to authorize operation of an information system and to explicitly accept the risk to agency operations (including mission, functions, image, or reputation), agency assets, or individuals, based on the implementation of an agreed-upon set of security controls. -
The Phase 1 of DITSCAP C&A is known as Definition Phase. The goal of this phase is to define the C&A level of effort, identify the main C&A roles and responsibilities, and create an agreement on the method for implementing the security requirements. What are the process activities of this phase? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Negotiation
- Registration
- Document mission need
- Initial Certification Analysis
Explanation:The Phase 1 of DITSCAP C&A is known as Definition Phase. The goal of this phase is to define the C&A level of effort, identify the main C&A roles and responsibilities, and create an agreement on the method for implementing the security requirements. The Phase 1 starts with the input of the mission need. This phase comprises three process activities: Document mission need Registration Negotiation Answer: D is incorrect. Initial Certification Analysis is a Phase 2 activity. -
You have a storage media with some data and you make efforts to remove this data. After performing this, you analyze that the data remains present on the media. Which of the following refers to the above mentioned condition?
- Object reuse
- Degaussing
- Residual
- Data remanence
Explanation:Data remanence refers to the data that remains even after the efforts have been made for removing or erasing the data. This event occurs because of data being left intact by an insignificant file deletion operation, by storage media reformatting, or through physical properties of the storage medium. Data remanence can make unintentional disclosure of sensitive information possible. So, it is required that the storage media is released into an uncontrolled environment. Answer: C and B are incorrect. These are the made-up disasters. Answer: A is incorrect. Object reuse refers to reassigning some other object of a storage media that has one or more objects. -
Which of the following are the common roles with regard to data in an information classification program? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Editor
- Custodian
- Owner
- User
- Security auditor
Explanation:The following are the common roles with regard to data in an information classification program: Owner Custodian User Security auditor The following are the responsibilities of the owner with regard to data in an information classification program: Determining what level of classification the information requires. Reviewing the classification assignments at regular time intervals and making changes as the business needs change. Delegating the responsibility of the data protection duties to the custodian. The following are the responsibilities of the custodian with regard to data in an information classification program: Running regular backups and routinely testing the validity of the backup data Performing data restoration from the backups when necessary Controlling access, adding and removing privileges for individual users The users must comply with the requirements laid out in policies and procedures. They must also exercise due care. A security auditor examines an organization’s security procedures and mechanisms. -
Which of the following life cycle modeling activities establishes service relationships and message exchange paths?
- Service-oriented logical design modeling
- Service-oriented conceptual architecture modeling
- Service-oriented discovery and analysis modeling
- Service-oriented business integration modeling
Explanation:The service-oriented logical design modeling establishes service relationships and message exchange paths. It also addresses service visibility and crafts service logical compositions. -
You work as a project manager for a company. The company has started a new security software project. The software configuration management will be used throughout the lifecycle of the project. You are tasked to modify the functional features and the basic logic of the software and then make them compatible to the initial design of the project. Which of the following procedures of the configuration management will you follow to accomplish the task?
- Configuration status accounting
- Configuration control
- Configuration audits
- Configuration identification
Explanation:Configuration control is a procedure of the Configuration management. Configuration control is a set of processes and approval stages required to change a configuration item’s attributes and to re-baseline them. It supports the change of the functional and physical attributes of software at various points in time, and performs systematic control of changes to the identified attributes. Answer: C is incorrect. Configuration audits confirm that the configuration identification for a configured item is accurate, complete, and will meet specified program needs. Configuration audits are broken into functional and physical configuration audits. They occur either at delivery or at the moment of effecting the change. A functional configuration audit ensures that functional and performance attributes of a configuration item are achieved, while a physical configuration audit ensures that a configuration item is installed in accordance with the requirements of its detailed design documentation. Answer: D is incorrect. Configuration identification is the process of identifying the attributes that define every aspect of a configuration item. A configuration item is a product (hardware and/or software) that has an end-user purpose. These attributes are recorded in configuration documentation and baselined. Baselining an attribute forces formal configuration change control processes to be effected in the event that these attributes are changed. Answer: A is incorrect. The configuration status accounting procedure is the ability to record and report on the configuration baselines associated with each configuration item at any moment of time. It supports the functional and physical attributes of software at various points in time, and performs systematic control of accounting to the identified attributes for the purpose of maintaining software integrity and traceability throughout the software development life cycle. -
Which of the following software review processes increases the software security by removing the common vulnerabilities, such as format string exploits, race conditions, memory leaks, and buffer overflows?
- Management review
- Code review
- Peer review
- Software audit review
Explanation:A code review is a systematic examination of computer source code, which searches and resolves issues occurred in the initial development phase. It increases the software security by removing common vulnerabilities, such as format string exploits, race conditions, memory leaks, and buffer overflows. A code review is performed in the following forms: Pair programming Informal walkthrough Formal inspection Answer: C is incorrect. A peer review is an examination process in which author and one or more colleagues examine a work product, such as document, code, etc., and evaluate technical content and quality. According to the Capability Maturity Model, peer review offers a systematic engineering practice in order to detect and resolve issues occurring in the software artifacts, and stops the leakage into field operations. Answer: A is incorrect. Management review is a management study into a project’s status and allocation of resources. Answer: D is incorrect. In software audit review one or more auditors, who are not members of the software development organization, perform an independent examination of a software product, software process, or a set of software processes for assessing compliance with specifications, standards, contractual agreements, or other specifications. -
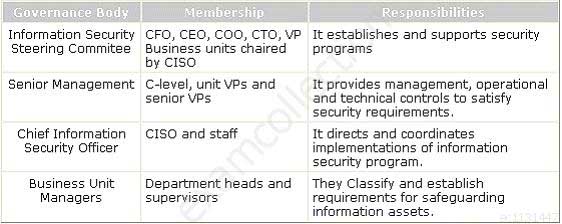
Which of the following governance bodies directs and coordinates implementations of the information security program?
- Chief Information Security Officer
- Information Security Steering Committee
- Business Unit Manager
- Senior Management
-
Which of the following secure coding principles and practices defines the appearance of code listing so that a code reviewer and maintainer who have not written that code can easily understand it?
- Make code forward and backward traceable
- Review code during and after coding
- Use a consistent coding style
- Keep code simple and small
Explanation:Use a consistent coding style is one of the principles and practices that contribute to defensive coding. This principle defines the appearance of code listing so that a code reviewer and maintainer who have not written that code can easily understand it. For this purpose, all programmers of a team must follow the same guidelines. Answer: D is incorrect. Keep code simple and small defines that it is easy to verify the software security when a programmer uses small and simple code base. Answer: A is incorrect. Make code forward and backward traceable defines that traceability is necessary in order to validate requirements, prevent defects, and find and solve inconsistencies among all objects generated in the SDLC phases. Answer: B is incorrect. Review code during and after coding defines that code must be examined in order to identify coding errors in modules.