98-366 : Networking Fundamentals : Part 03
98-366 : Networking Fundamentals : Part 03
-
Which of the following determines the media access method that is used in a network?
- Number of hosts connected to the network
- Number of domain servers on the segment
- Maximum speed of the media
- Topology and protocols
-
Which wireless authentication method provides the highest level of security?
- Wired Equivalency Privacy (WEP)
- IEEE 802.lln
- WI-FI Protected Access (WPA)
- IEEE 802.11a
Explanation:WPA aims to provide stronger wireless data encryption than WEP.
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a security protocol and security certification program developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance to secure wireless computer networks.
-
The topology of a local area network (LAN) is defined by the:
- Number of devices to connect.
- Physical and logical characteristics.
- Distance between workstations.
- Type of cable being used.
Explanation:Network topology is the arrangement of the various elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a computer network. Essentially, it is the topological structure of a network and may be depicted physically or logically.
-
The maximum throughput of an 802.llg network is:
- 2.4 GHz.
- 54 GHz.
- 2.4 Mbps
- 54 Mbps.
Explanation:The 802.11g standard for wireless networking supports a maximum bandwidth of 54 Mbps.
-
A node within a local area network (LAN) must have a network interface device and a:
- Network account
- Table of all network nodes
- Host address
- Resource to share
Explanation:In network addressing, the host address, or the host ID portion of an IP address, is the portion of the address used to identify hosts (any device requiring a Network Interface Card, such as a PC or networked printer) on the network.
-
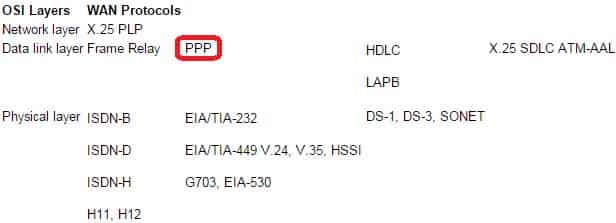
Which of the following is a Layer 2 WAN protocol?
- Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
- Internet Protocol (IP)
Explanation:WAN Protocols and Their Corresponding OSI Layers
-
Which type of port is used to support VLAN traffic between two switches?
- Virtual port
- WAN port
- Trunk port
- LAN port
Explanation:Trunk links are required to pass VLAN information between switches.
-
The protocol that maps IP addresses to a Media Access Control (MAC) address is:
- Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP).
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
- Routing Information Protocol (RIP).
- User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP).
Explanation:Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol for mapping an Internet Protocol address (IP address) to a physical machine address (MAC address) that is recognized in the local network.
-
A user reports that she cannot connect to network resources from a computer on the company network. The user was able to connect to the network resources yesterday.
You verify that the user’s computer is properly physically connected to the network. You discover that the computer’s IP address is 169.254.48.97.
You need to restore access to network resources.
What should you do next?
- Flush the cache on the DNS server.
- Reset the user’s password on the server.
- Check your router’s current routing tables.
- Verify that the DHCP service is available.
Explanation:169.254.48.97 is an APIPA address. An APIPA address is used when the DHCP server is not available.
-
The host name of the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) mail.exchange.corp.nwtraders.com is:
- corp
- com
- nwtraders
- exchange
Explanation:Hostnames are composed of series of labels concatenated with dots, as are all domain names. For example, let’s break mail.google.com into its component parts:
mail is the host or local hostname; and
google.com is the domain or parent domain name. -
To which IP configuration does the CIDR notation 192.168.1.1/25 refer?
- 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.64
- 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.1
- 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.32
- 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.256
- 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.128
-
Which command is used to verify that a server is connected to the network?
- IPCONFIG
- ROUTE
- PING
- CHECK
Explanation:Ping is a computer network administration software utility used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network and to measure the round-trip time for messages sent from the originating host to a destination computer.
-
Which of these represents the Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) loopback address?
- 127.0.0.1
- 192.168.0.1
- FEC0:A8C0::AA01
- ::1
Explanation:The localhost (loopback) address, 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, and the IPv6 unspecified address, 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0, are reduced to ::1 and ::, respectively.
-
Which of these addresses is a multicast address?
- 127.0.0.1
- 169.254.0.1
- 192.168.0.1
- 224.0.0.1
Explanation:The full range of multicast addresses is from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255.
-
Which of the following uses pointer records and A records?
- IDS
- DNS Server
- NAT Server
- IPS
Explanation:DNS records include:
* A
Address record
* PTR
Pointer record -
The ipconfig command will:
- Configure routers
- Display a client’s address
- Display a client’s broadcast mode
- Configure DHCP clients
Explanation:ipconfig
Displays all current TCP/IP network configuration values and refreshes Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings. Used without parameters, ipconfig displays the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway for all adapters. -
One reason to incorporate VLANs in a network is to:
- Increase the number of available IP addresses.
- Increase the number of available Media Access Control (MAC) addresses.
- Reduce the number of broadcast domains.
- Reduce the number of nodes in a broadcast domain.
Explanation:VLANs provide the following advantages:
* VLANs enable logical grouping of end-stations that are physically dispersed on a network. …
* VLANs reduce the need to have routers deployed on a network to contain broadcast traffic. …
* Confinement of broadcast domains on a network significantly reduces traffic.
By confining the broadcast domains, end-stations on a VLAN are prevented from listening to or receiving broadcasts not intended for them. Moreover, if a router is not connected between the VLANs, the end-stations of a VLAN cannot communicate with the end-stations of the other VLANs. -
Which of these is an application layer protocol?
- TCP
- FTP
- IP
- UDP
Explanation:FTP is an application layer protocol.
-
The top-level domain of www.adventureworks.com is:
- www
- adventureworks
- adventureworks.com
- com
Explanation:A top-level domain (TLD) is one of the domains at the highest level in the hierarchical Domain Name System of the Internet.
-
At what layer in the OSI model are hardware addresses referenced?
- Network
- Application
- Data link
- Physical