98-366 : Networking Fundamentals : Part 04
98-366 : Networking Fundamentals : Part 04
-
You need to divide a network into three subnets.
Which device should you use?
- Hub
- Bridge
- Router
- Segmenter
Explanation:You can use a router to divide your network into subnets.
-
The type of connector used on a 100BaseT Ethernet cable is:
- RJ-11
- RJ-45.
- TNC.
- BNC.
-
In addition to switching, multilayer switches also:
- Provide Layer 3 routing functions.
- Interface with CAT3, CATS, CAT5e, and fiber optics.
- Support 10 MB, 100 MB, and 1 GB local area network (LAN) ports.
- Operate by using only Layer 1 and 2 protocols.
-
One reason to replace an unmanaged switch with a managed switch is to:
- Manage the routing tables.
- Support multiple VLANS.
- Reduce collision domains.
- Route between networks,
Explanation:A multilayer switch (MLS) is a computer networking device that switches on OSI layer 2 like an ordinary network switch and provides extra functions on higher OSI layers.
The major difference between the packet switching operation of a router and that of a Layer 3 switch is the physical implementation. In general-purpose routers, packet switching takes place using software that runs on a microprocessor, whereas a Layer 3 switch performs this using dedicated application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) hardware.
-
To directly connect the Ethernet network interface cards (NICs) of two computers, you should use a:
- Crossover cable
- Straight cable
- Rollover cable
- Coaxial cable
Explanation:An Ethernet crossover cable is a type of Ethernet cable used to connect computing devices together directly. Normal straight through cables were used to connect from a host network interface controller (a computer or similar device) to a network switch, hub or router.
-
The function of a router is to:
- Provide IP subnet masks for hosts.
- Forward traffic to other networks.
- Broadcast routing tables to clients.
- Store tables for name resolution.
Explanation:A router is a device that forwards data packets along networks. A router is connected to at least two networks, commonly two LANs or WANs or a LAN and its ISP’s network. Routers are located at gateways, the places where two or more networks connect.
-
If a router cannot determine the next hop for a packet, the router will:
- Forward the packet to the default route.
- Send the packet back to the packet’s source.
- Broadcast the packet.
- Store the packet in the memory buffer.
Explanation:If there is no next hop, the packets are not policy routed.
A default route of a computer that is participating in computer networking is the packet forwarding rule (route) taking effect when no other route can be determined for a given Internet Protocol (IP) destination address.
-
In which physical network topology is each computer connected to a central point?
- Star
- Mesh
- Ring
- Bus
Explanation:In local area networks with a star topology, each network host is connected to a central hub with a point-to-point connection.
-
Which two of the following are connectivity options for wide area networks (WANs)? (Choose two.)
- Token ring
- Ethernet
- Dial-up
- Leased line
Explanation:Token ring and Ethernet are used in LANs.
-
A private network that allows members of an organization to exchange data is an:
- Extranet
- Ethernet
- Intranet
- Internet
Explanation:An intranet is a computer network that uses Internet Protocol technology to share information, operational systems, or computing services within an organization. This term is used in contrast to extranet, a network between organizations, and instead refers to a network within an organization.
-
Security is a concern on wireless networks due to:
- The radio broadcast access method.
- Spread spectrum issues.
- Frequency modulation issues.
- The potential for cross-talk.
-
A characteristic of the mesh topology is that it:
- Uses a central hub.
- Cannot use wired connections.
- Uses redundant paths.
- Cannot use wireless connections.
Explanation:Mesh network topology is one of the key network architectures in which devices are connected with many redundant interconnections between network nodes such as routers and switches. In a mesh topology, if any cable or node fails, there are many other ways for two nodes to communicate.
-
To protect a network when it is connected to the Internet, you should use a:
- Bridge
- Firewall
- Switch
- Router
Explanation:A firewall is software or hardware that checks information coming from the Internet or a network, and then either blocks it or allows it to pass through to your computer, depending on your firewall settings.
-
One purpose of a perimeter network is to:
- Make resources available to the intranet.
- Link campus area networks (CANs).
- Link local area networks (LANs).
- Make resources available to the Internet.
Explanation:In computer security, a DMZ or demilitarized zone (sometimes referred to as a perimeter network) is a physical or logical subnetwork that contains and exposes an organization’s external-facing services to a larger and untrusted network, usually the Internet. The purpose of a DMZ is to add an additional layer of security to an organization’s local area network (LAN); an external network node only has direct access to equipment in the DMZ, rather than any other part of the network.
-
Which protocol can be used to encrypt packets on the Internet?
- SNMP
- HTTPS
- TFTP
- HTTP
Explanation:HTTPS, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, makes it more difficult for hackers, the NSA, and others to track users. The protocol makes sure the data isn’t being transmitted in plain-text format, which is much easier to eavesdrop on.
-
The service that resolves fully qualified domain names (FQDN) to IP addresses is:
- Windows Internet Name Service (WINS).
- Domain Name Service (DNS).
- Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP).
Explanation:The DNS translates Internet domain and host names to IP addresses. DNS automatically converts the names we type in our Web browser address bar to the IP addresses of Web servers hosting those sites.
-
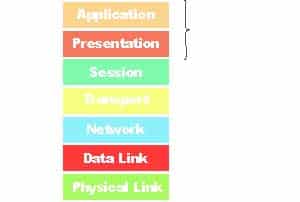
DRAG DROP
Order the layers of the OSI model:
98-366 Part 04 Q17 004 Question 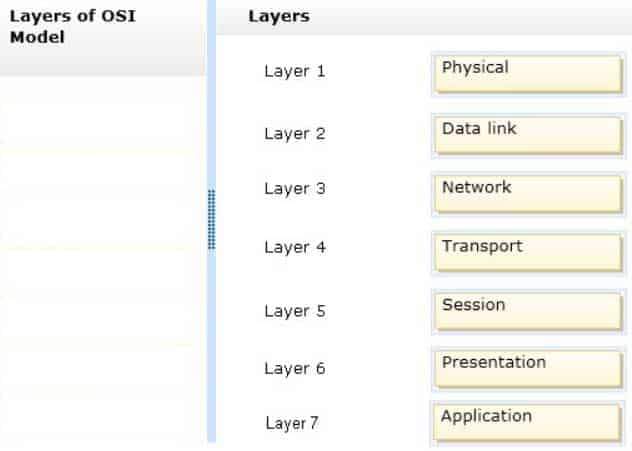
98-366 Part 04 Q17 004 Answer -
If a router is installed so that it separates a DHCP server from its clients, the clients will:
- Immediately lose connectivity to all segments.
- Be unable to obtain their leases from the server.
- Immediately lose connectivity to the local segment.
- Receive an immediate renewal of their lease.
-
Which of the following services masks internal IP addresses from outside the network?
- DHCP
- WINS
- NAT
- DNS
Explanation:The majority of NATs map multiple private hosts to one publicly exposed IP address. In a typical configuration, a local network uses one of the designated “private” IP address subnets (RFC 1918). A router on that network has a private address in that address space. The router is also connected to the Internet with a “public” address assigned by an Internet service provider.
-
The query protocol used to locate resources on a network is:
- User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
- Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
- Tracert
- Telnet.
Explanation:The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is an open, vendor-neutral, industry standard application protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an Internet Protocol (IP) network.
Directory services play an important role in developing intranet and Internet applications by allowing the sharing of information about users, systems, networks, services, and applications throughout the network.