98-366 : Networking Fundamentals : Part 08
98-366 : Networking Fundamentals : Part 08
-
What are two advantages of using star topology rather than ring topology in a computer lab workgroup? (Choose two.)
- Failure of a central connectivity device does not bring down the entire network.
- A central connection point allows for flexibility and scalability.
- Data travels on redundant paths, so one cable cannot stop its transmission.
- A cable problem within the group affects two nodes, at most.
-
What are three characteristics of Ethernet network topology? (Choose three.)
- It uses tokens to avoid collisions on the network.
- It can use coaxial, twisted pair, and fiber optic media.
- It comprises the largest share of the networks in place today.
- It is a non-switching protocol.
- It can negotiate different transmission speeds.
Explanation:B: Ethernet networks can use coax, twisted-pair, or fibre optic cabling.
C: Ethernet is the most widely used network topology.
E: Speed can be negotiated on Ethernet network.Incorrect:
not A: Tokes is used in ring topologies. The two possible topologies for Ethernet are bus and star.
Not D: A network topology is not a protocol. Switching can be performed on Ethernet networks. -
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
Plain old telephone service (POTS), most ISDN lines, and switched T1 lines are all examples of “Message Switching”.
Select the correct answer if the underlined text does not make the statement correct. Select ‘No change is needed” if the underlined text makes the statement correct.
- Circuit Switching
- Packet Switching
- FDDI Switching
- No change is needed
Explanation:* Examples of circuit-switched networks
Public switched telephone network (PSTN)
ISDN B-channel* You can get a circuit-switched T1, while frames clouds on T1s are usually packet-switched.
-
HOTSPOT
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-366 Part 08 Q04 040 Question 
98-366 Part 08 Q04 040 Answer Explanation:
NO. No. YES.In computer security, a DMZ or demilitarized zone (sometimes referred to as a perimeter network) is a physical or logical subnetwork that contains and exposes an organization’s external-facing services to a larger and untrusted network, usually the Internet. The purpose of a DMZ is to add an additional layer of security to an organization’s local area network (LAN); an external network node only has direct access to equipment in the DMZ, rather than any other part of the network.
-
HOTSPOT
You are an intern for Contoso Ltd. Your supervisor asks you to configure the security zones for three new PCs so that they are able to connect to two web servers.The servers connect to the three new PCs as shown in the following image:
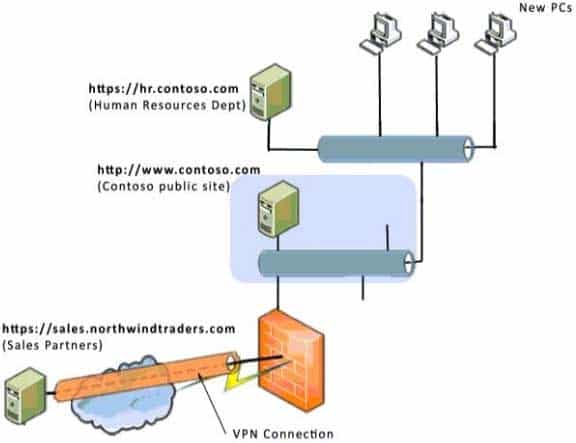
98-366 Part 08 Q05 041 Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement. Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-366 Part 08 Q05 042 Question 
98-366 Part 08 Q05 042 Answer Explanation:* Trusted sites
The level of security set for Trusted sites is applied to sites that you have specifically indicated to be ones that you trust not to damage your computer or information.* Local intranet
The level of security set for the Local intranet zone is applied to websites and content that is stored on a corporate or business network. -
Your home computer is having problems accessing the Internet.
You suspect that your Internet router’s DHCP service is not functioning, so you check your computer’s IP address.
Which address indicates that your router’s DHCP service is NOT functioning?
- 169.254.1.15
- 172.16.1.15
- 192.168.1.15
- 10.19.1.15
Explanation:169.254.1.15 is an APIPA address. An APIPA address is used when the DHCP server is not available.
-
Which of these is a public address space?
- 192.168.0.0/16
- 197.16.0.0/12
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 172.16.0.0/12
Explanation:Incorrect:
The private address space specified in RFC 1918 is defined by the following three address blocks:
not A: 192.168.0.0/16
The 192.168.0.0/16 private network can be interpreted either as a block of 256 class C network IDs or as a 16-bit assignable address space (16 host bits) that can be used for any subnetting scheme within the private organization. The 192.168.0.0/16 private network allows the following range of valid IP addresses: 192.168.0.1 to 192.168.255.254.Not C:
10.0.0.0/8
The 10.0.0.0/8 private network is a class A network ID that allows the following range of valid IP addresses: 10.0.0.1 to 10.255.255.254. The 10.0.0.0/8 private network has 24 host bits that can be used for any subnetting scheme within the private organization.Not D:
172.16.0.0/12
The 172.16.0.0/12 private network can be interpreted either as a block of 16 class B network IDs or as a 20-bit assignable address space (20 host bits) that can be used for any subnetting scheme within the private organization. The 172.16.0.0/12 private network allows the following range of valid IP addresses: 172.16.0.1 to 172.31.255.254. -
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
In a wireless network that requires an SSL certificate, “WEP” handles the SSL certificate.
Select the correct answer if the underlined text does not make the statement correct. Select ‘No change is needed” if the underlined text makes the statement correct.
- 802.1X
- WPA2-PSK
- WPA-PSK
- No change is needed
Explanation:802.1x
This deployment scenario requires server certificates for each NPS server that performs 802.1X authentication. -
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
To set lower security settings in Internet Explorer for an extranet site, add the site’s URL to the “Local Intranet “zone.
Select the correct answer if the underlined text does not make the statement correct. Select ‘No change is needed” if the underlined text makes the statement correct.
- Internet
- Trusted Sites
- Extranet Sites
- No change is needed
Explanation:Trusted sites
The level of security set for Trusted sites is applied to sites that you have specifically indicated to be ones that you trust not to damage your computer or information. -
You are helping a friend set up a public-facing web server for a home office.
Your friend wants to protect the internal network from intrusion.
What should you do?
- Set the web server in a perimeter network.
- Set the web server to block access on ports 80 and 443.
- Configure the firewall to block access on ports 80 and 443.
- Set the IP address of the web server to be within the LAN.
Explanation:In computer security, a DMZ or demilitarized zone (sometimes referred to as a perimeter network) is a physical or logical subnetwork that contains and exposes an organization’s external-facing services to a larger and untrusted network, usually the Internet. The purpose of a DMZ is to add an additional layer of security to an organization’s local area network (LAN); an external network node only has direct access to equipment in the DMZ, rather than any other part of the network.
-
HOTSPOT
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-366 Part 08 Q11 043 Question 
98-366 Part 08 Q11 043 Answer Explanation:* No.
Network bridging is the action taken by network equipment to create an aggregate network from
either two or more communication networks, or two or more network segments. If one or more segments of the bridged network are wireless, it is known as wireless bridging.* Yes.
In Wi-Fi, repeater mode is a variation on bridging. Rather than join multiple LANs, repeater mode is intended mainly to increase the range of a single wireless LAN by extending the same wireless signal.* No.
In Wi-Fi networking, bridging mode allows two or more wireless access points (APs) to communicate with each for the purpose of joining multiple LANs. -
What are two characteristics of the CSMA/CD access method? (Choose two.)
- It checks to see if a collision has been detected.
- It does a round robin search for requests to transmit from all nodes on the network.
- It signals its intent to transmit on the network.
- It waits until the transmission medium is idle.
Explanation:– Main procedure for the CSMA/CD:
– Is my frame ready for transmission? If yes, it goes on to the next point.
– Is medium idle? If not, wait until it becomes ready
– Start transmitting.
– Did a collision occur? If so, go to collision detected procedure.
– Reset retransmission counters and end frame transmission.Note:
Carrier Sense Multiple Access With Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) is a media access control method used most notably in local area networking using early Ethernet technology. It uses a carrier sensing scheme in which a transmitting data station detects other signals while transmitting a frame, and stops transmitting that frame, transmits a jam signal, and then waits for a random time interval before trying to resend the frame. -
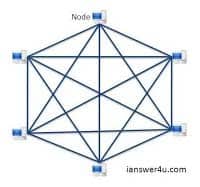
What are two characteristics of a mesh network topology? (Choose two.)
- It is fault tolerant because of redundant connections.
- Every node connects to every other node on the network.
- It works best for networks with a large number of nodes.
- It requires less cabling than either a star or ring topology.
Explanation:In a (full) mesh network topology, each of the network node, computer and other devices, are interconnected with one another. Every node not only sends its own signals but also relays data from other nodes. In fact a true mesh topology is the one where every node is connected to every other node in the network. This type of topology is very expensive as there are many redundant connections, thus it is not mostly used in computer networks. It is commonly used in wireless networks.
Illustration:
-
Which protocol is responsible for automatically assigning IP addresses?
- HTTP
- DHCP
- DNS
- WINS
Explanation:Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network protocol that enables a server to automatically assign an IP address to a computer from a defined range of numbers (i.e., a scope) configured for a given network.
-
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
According to the OSI model, encryption takes place on the “transport layer”.
Select the correct answer if the underlined text does not make the statement correct. Select ‘No change is needed” if the underlined text makes the statement correct.
- Presentation
- Network
- Application
- No change is needed
Explanation:SSL or TLS encryption takes place at the presentation layer, Layer 6 of the OSI model.
-
HOTSPOT
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-366 Part 08 Q16 045 Question 
98-366 Part 08 Q16 045 Answer Explanation:* No.
IPv4 uses a 32-bit address scheme.* Yes.
IPv4 addresses may be written in any notation expressing a 32-bit integer value, but for human convenience, they are most often written in the dot-decimal notation, which consists of four octets of the address expressed individually in decimal and separated by periods.* No.
Each octet has a value between 0 and 255. -
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
IPSec policies for two machines on a LAN can be modified by using the “IPSec policy snap-in” on Windows 7.
Select the correct answer if the underlined text does not make the statement correct. Select ‘No change is needed” if the underlined text makes the statement correct.
- Windows Firewall with Advanced Security snap-in
- LAN adapter properties
- Remote Access snap-in
- No change is needed
Explanation:Windows Firewall with Advanced Security is an advanced interface for IT professionals to use to configure both Windows Firewall and Internet Protocol security (IPsec) settings for the computers on their networks.
Applies To: Windows 7, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Vista
-
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
An Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table is used to associate IP addresses with “host names”.
Select the correct answer if the underlined text does not make the statement correct. Select ‘No change is needed” if the underlined text makes the statement correct.
- MAC addresses
- HomeGroup membership
- Preferred routers
- No change is needed
Explanation:Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol for mapping an Internet Protocol address (IP address) to a physical machine address (MAC address) that is recognized in the local network.
-
Which network device interconnects computers in a workgroup, is able to be remotely configured, and provides the best throughput?
- Unmanaged switch
- Hub
- Router
- Managed switch
Explanation:Managed switches – these switches have one or more methods to modify the operation of the switch. Common management methods include: a command-line interface (CLI) accessed via serial console, telnet or Secure Shell, an embedded Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) agent allowing management from a remote console or management station, or a web interface for management from a web browser.
Incorrect:
not A: Unmanaged switches are basic plug-and-play switches with no remote configuration, management, or monitoring options, although many can be locally monitored and configured via LED indicators and DIP switches.
Not B: Hubs cannot be managed.
Not C: Switches are faster than routers. -
What is the maximum cable length for a single Cat5 UTP cable run?
- 285 feet/86.87 meters
- 328 feet/99.97 meters
- 432 feet/131.67 meters
- 600 feet/182.88 meters
ExplanationCat5/5e/6 Ethernet Copper Cabling has a Maximum Segment Length of 100 Meters.