98-366 : Networking Fundamentals : Part 09
98-366 : Networking Fundamentals : Part 09
-
HOTSPOT
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-366 Part 09 Q01 046 Question 
98-366 Part 09 Q01 046 Answer Explanation:* Yes.
QoS traffic control: Regulate data flows by classifying, scheduling, and marking packets based on priority and by shaping traffic (smoothing bursts of traffic by limiting the rate of flow). Traffic control mechanisms segregate traffic into service classes and control delivery to the network. The service class assigned to a traffic flow determines the QoS treatment the traffic receives.* Yes.
The goal of QoS is to provide preferential delivery service for the applications that need it by ensuring sufficient bandwidth, controlling latency and jitter, and reducing data loss.* No
-
Which of these cable types transmits data the greatest distance?
- Multi-mode fiber
- Single-mode fiber
- Cat5e
- Cat6
Explanation:When working with distances up to 2 km, use multimode optical-fiber cable.
Like multi-mode optical fibers, single mode fibers do exhibit modal dispersion resulting from multiple spatial modes but with narrower modal dispersion. Single mode fibers are therefore better at retaining the fidelity of each light pulse over longer distances than multi-mode fibers.Incorrect:
Cat5e and Cat6 max cable length is 100 metres. -
What is a similarity between Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches?
- Both provide a high level of security to the network.
- Both use logical addressing to forward transmissions.
- Both forward packets onto the network.
- Both allow the implementation of VLANs.
Explanation:A single layer-2 network may be partitioned to create multiple distinct broadcast domains, which are mutually isolated so that packets can only pass between them via one or more routers; such a domain is referred to as a virtual local area network, virtual LAN or VLAN.
LANs are layer 2 constructs, so they can be supported by both Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches.Incorrect:
Not A: Layer 2 switches do not provide high level of security.
Not B: Another name for logical address is IP address. Only Layer 3 switches uses IP address. Layer 2 switches uses MAC addresses.
Not C: only Layer 3 switches forward packets on the network (like routers). -
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
“Dynamic routing” is fault tolerant.
Select the correct answer if the underlined text does not make the statement correct. Select ‘No change is needed” if the underlined text makes the statement correct.
- Static routing
- Default route
- Least cost routing
- No change is needed
Explanation:
Dynamic routing protocols can be fault tolerant. -
You need to run four Ethernet network drops. Each drop is approximately 125 feet/46.33 meters.
An interference exists along the path of each drop.
You need to ensure that interference is reduced.
Which cable type should you use?
- STP Cat5e
- UTPCat5e
- Cat3
- UTPCat6
Explanation:Shielded cable, here STP Cat5e, would reduce interference.
-
What is an example of a Layer 3 device that connects multiple computers and networks?
- Packet
- Repeater
- Switch
- Router
Explanation:A router is a layer 3 device, although some newer switches also perform layer 3 functions.
-
Which metric does Routing Information Protocol (RIP) use to determine the least costly route?
- Delay
- Host ID
- Hop count
- Interface
Explanation:RIP uses a single routing metric (hop count) to measure the distance between the source and a destination network.
-
What are two differences between switches and hubs? (Choose two.)
- Switches are slower than hubs because of the extra addressing functions that switches perform.
- Switches send data to all of the computers that are connected to them for efficiency.
- Switches are capable of sending and receiving data at the same time.
- Switches identify the intended destination of the data that they receive.
Explanation:Hubs repeat everything they receive and can be used to extend the network.
Switches control the flow of network traffic based on the address information in each packet. A switch learns which devices are connected to its ports (by monitoring the packets it receives), and then forwards on packets to the appropriate port only. This allows simultaneous communication across the switch, improving bandwidth. -
What is the DNS record type that specifies an alias name of another address record?
- MX
- CNAME
- NS
- SOA
Explanation:CNAME stands for Canonical Name. CNAME records can be used to alias one name to another.
-
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
Each IPv4 address consists of a “MAC address and data-link laver address”.
Select the correct answer if the underlined text does not make the statement correct. Select “No change is needed” if the underlined text makes the statement correct.
- Network ID and a host ID
- DNS record and a default route
- 64-bit binary number divided into octets
- No change is needed
Explanation:Each IP address is separated internally into two parts–a network ID and a host ID.
-
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
The “NTP” value in a resource record indicates a length of time that other DNS servers use to determine how long to cache information for a record before expiring and discarding it.
Select the correct answer if the underlined text does not make the statement correct. Select “No change is needed” if the underlined text makes the statement correct.
- TTL
- GPS
- SOA RR
- No change is needed
Explanation:Time to live (TTL) is what dictates how long it will be until your computer refreshes its DNS related information.
-
HOTSPOT
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-366 Part 09 Q12 047 Question 
98-366 Part 09 Q12 047 Answer Explanation:
* Yes.
Layer 7 TCP/IP protocols include:
HTTP, Hypertext Transfer Protocol
Telnet, a remote terminal access protocol
SMTP, Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
TFTP, Trivial File Transfer Protocol, a simple file transfer protocol
* No.
The session layer (layer 5) controls the dialogues (connections) between computers.
The transport layer provides the functional and procedural means of transferring variable-length data sequences from a source to a destination host via one or more networks, while maintaining the quality of service functions.
* Yes.
The network layer provides the functional and procedural means of transferring variable length data sequences (called datagrams) from one node to another connected to the same network. It translates logical network address into physical machine address. A network is a medium to which many nodes can be connected, on which every node has an address and which permits nodes connected to it to transfer messages to other nodes connected to it by merely providing the content of a message and the address of the destination node and letting the network find the way to deliver (“route”) the message to the destination node. -
HOTSPOT
You are studying for finals in the student lounge. When your laptop is connected to the wireless network, access to the Internet is slow. When you plug your laptop into a wall jack, you can no longer access the Internet at all.
You run the ipconfig /all command. The results are shown in the following image:
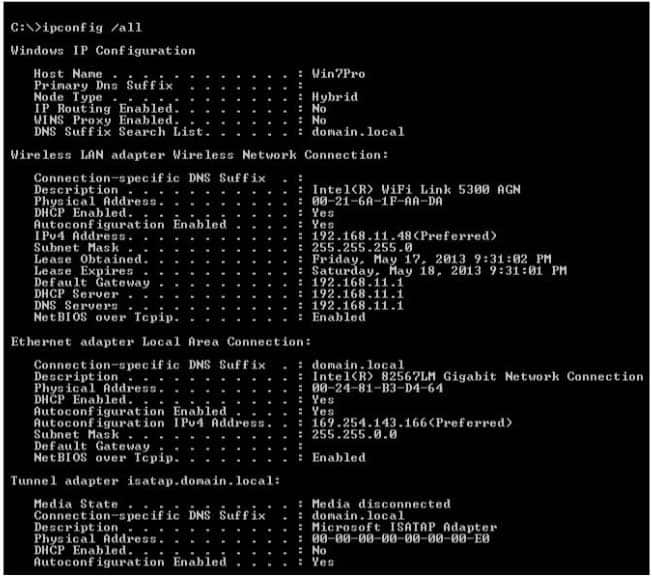
98-366 Part 09 Q13 048 Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement. Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-366 Part 09 Q13 049 Question 
98-366 Part 09 Q13 049 Answer Explanation:
The wireless adapter is DHCP enabled and has a normal IP address of 192.168.11.1.The Ethernet adapter is also DHCP enabled but has an APIPA IP address of 169.254.143.166.
-
HOTSPOT
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-366 Part 09 Q14 050 Question 
98-366 Part 09 Q14 050 Answer Explanation:* No. IPv6 addresses are 128 bit in length.
* No.No.
IPv6 addresses are written in eight groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons, such as 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334. -
HOTSPOT
Where in the diagram is a T3 connection possible? (To answer, select the appropriate connection in the diagram in the answer area.)
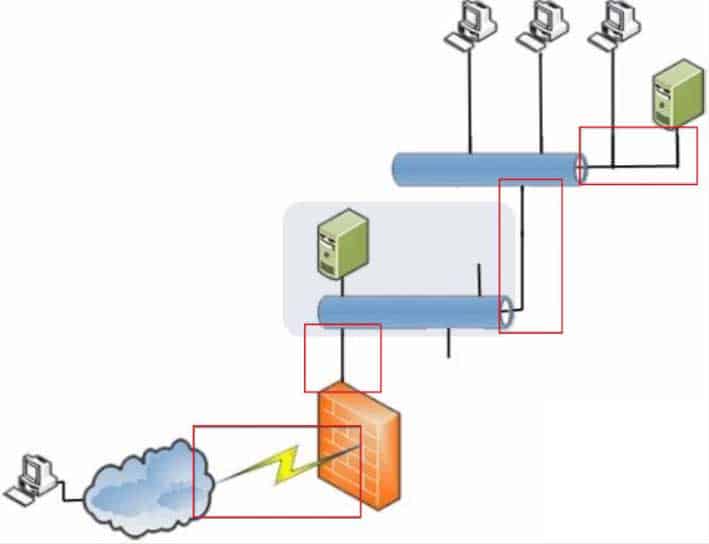
98-366 Part 09 Q15 051 Question 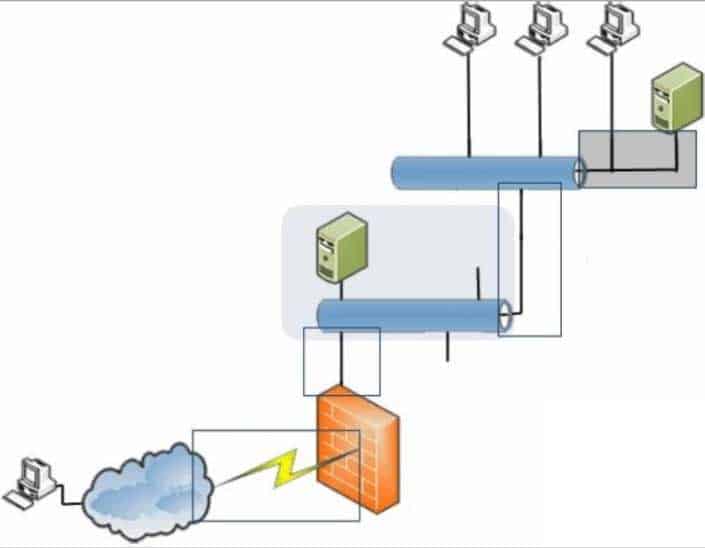
98-366 Part 09 Q15 051 Answer Explanation:T3 lines are a common aggregation of 28 T1 circuits that yields 44.736 Mbps total network bandwidth . Besides being used for long-distance traffic, T3 lines are also often used to build the core of a business network at its headquarters
-
What happens when an 802.11a node broadcasts within the range of an 802.11g access point?
- The access point transmits, but the node is unable to receive.
- A connection occurs.
- Both the node and the access point are unable to transmit.
- The node transmits, but the access point is unable to receive.
Explanation:Because 802.11a and 802.11b utilize different frequencies, the two technologies are incompatible with each other.
A huge problem with 802.11a is that it’s not directly compatible with 802.11b or 802.11g networks. In other words, a user equipped with an 802.11b or 802.11g radio card will not be able to interface directly to an 802.11a access point. -
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
An ICMP ping message is sent at the application layer of the OSI model.
Review the underlined text. If it makes the statement correct, select “No change is needed.” If the statement is incorrect, select the answer choice that makes the statement correct.
- network
- transport
- data-link
- No change is needed
-
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
The query protocol used to locate resources on a network is User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
Review the underlined text. If it makes the statement correct, select “No change is needed.” If the statement is incorrect, select the answer choice that makes the statement correct.
- Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
- Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
- Network File System (NFS)
- No change is needed
-
HOTSPOT
Network client computers running Windows 8.1 and Windows 10 are configured to receive IPv4 addresses through DHCP. The DHCP server fails.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.

98-366 Part 09 Q19 052 Question 
98-366 Part 09 Q19 052 Answer Explanation:The IpReleaseAddress and IpRenewAddress functions are used to release and renew the current Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) lease. The IpReleaseAddress function releases an IPv4 address previously obtained through DHCP. The IpRenewAddress function renews a lease on an IPv4 address previously obtained through DHCP. It is common to use these two functions together, first releasing the lease with a call to IpReleaseAddress, and then renewing the lease with a call to the IpRenewAddress function.
When a DHCP client has previously obtained a DHCP lease and IpReleaseAddress is not called before the IpRenewAddress function, the DHCP client request is sent to the DHCP server that issued the initial DHCP lease. This DHCP server may not available or the DHCP request may fail. When a host has previously obtained a DHCP lease and IpReleaseAddress is called before the IpRenewAddress function, the DHCP client first releases the IP address obtained and sends a DHCP client request for a response from any available DHCP server. -
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
The protocol that maps IP addresses to a Media Access Control (MAC) address is Domain Name Systems (DNS).
Review the underlined text. If it makes the statement correct, select “No change is needed.” If the statement is incorrect, select the answer choice that makes the statement correct.
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
- Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
- No change is needed