98-366 : Networking Fundamentals : Part 10
98-366 : Networking Fundamentals : Part 10
-
Which utility would you use to determine if your Domain Name System (DNS) server is properly resolving fully qualified domain names (FQDNs) as IP addresses?
- netstat
- nslookup
- nbtstat
- ipconfig
-
What type of DNS resource record maps an IP address to a fully qualified domain name (FQDN)?
- CNAME
- PTR
- AAAA
- A
-
Your network is reconfigured as multiple subnets. Your company needs to support legacy NetBIOS applications across subnet boundaries.
Which should you use for name resolution?
- DNS server
- Client HOSTS file
- WINS server
- NetBIOS broadcasts
-
HOTSPOT
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-366 Part 10 Q04 053 Question 
98-366 Part 10 Q04 053 Answer Explanation:
The Application layer supplies network services to end-user applications. Network services are typically protocols that work with user’s data. For example, in a Web browser application, the Application layer protocol HTTP packages the data needed to send and receive Web page content. This Layer 7 provides data to (and obtains data from) the Presentation layer.
The Transport Layer delivers data across network connections. TCP is the most common example of a Transport Layer 4 network protocol. Different transport protocols may support a range of optional capabilities including error recovery, flow control, and support for re-transmission.
The Transport Layer delivers data across network connections. TCP is the most common example of a Transport Layer 4 network protocol. Different transport protocols may support a range of optional capabilities including error recovery, flow control, and support for re-transmission.
The Network layer adds the concept of routing above the Data Link layer. When data arrives at the Network layer, the source and destination addresses contained inside each frame are examined to determine if the data has reached its final destination. If the data has reached the final destination, this Layer 3 formats the data into packets delivered up to the Transport layer. Otherwise, the Network layer updates the destination address and pushes the frame back down to the lower layers. -
A Layer 2 device that connects multiple computers within a network is:
- an access point
- a switch
- a router
- a bridge
-
What are two characteristics of switches? (Choose two.)
- Switches identify the intended destination of the data that they receive
- Switches cause more data collisions than hubs
- Switches are capable of sending and receiving data at the same time
- Switches send each packet to all of the computer that are connected to them
-
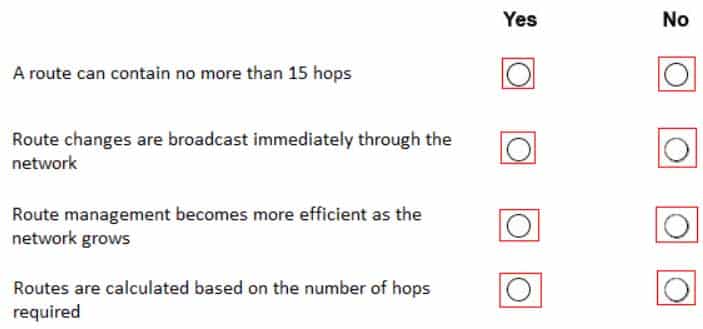
HOT SPOT
Your network uses routers configured with the RIP router protocol.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
98-366 Part 10 Q07 054 Question 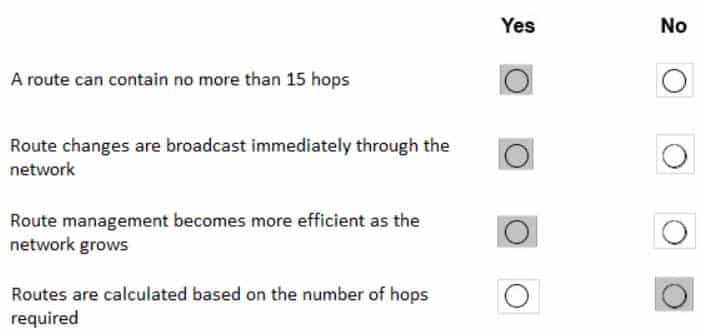
98-366 Part 10 Q07 054 Answer Explanation:
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) uses hop count as the metric to rate the value of different routes. The hop count is the number of devices that can be traversed in a route. A directly connected network has a metric of zero; an unreachable network has a metric of 16. This limited metric range makes RIP unsuitable for large networks.
The Routing Information Protocol (RIP) sends routing-update messages at regular intervals and when the network topology changes. When a device receives a RIP routing update that includes changes to an entry, the device updates its routing table to reflect the new route. The metric value for the path is increased by 1, and the sender is indicated as the next hop. RIP devices maintain only the best route (the route with the lowest metric value) to a destination. After updating its routing table, the device immediately begins transmitting RIP routing updates to inform other network devices of the change. These updates are sent independently of the regularly scheduled updates that RIP devices send.
Summarizing routes in RIP Version 2 improves scalability and efficiency in large networks. Summarizing IP addresses means that there is no entry for child routes (routes that are created for any combination of the individual IP addresses contained within a summary address) in the RIP routing table, reducing the size of the table and allowing the router to handle more routes.
It is a stable protocol that uses a distance-vector algorithm to calculate routes. -
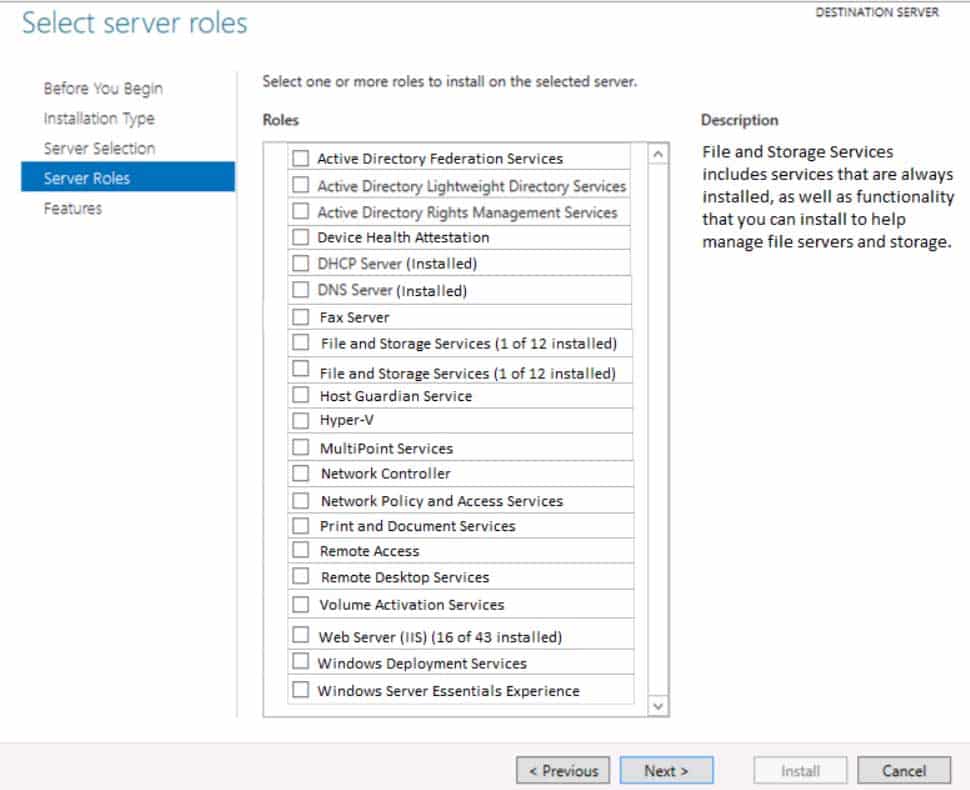
HOTSPOT
You deploy a computer running Windows Server 2016 in your perimeter network. You want to use this computer to route traffic between the Internet and your network.
Which role do you need to configure?
To answer, select the appropriate role in the answer area.
98-366 Part 10 Q08 055 Question 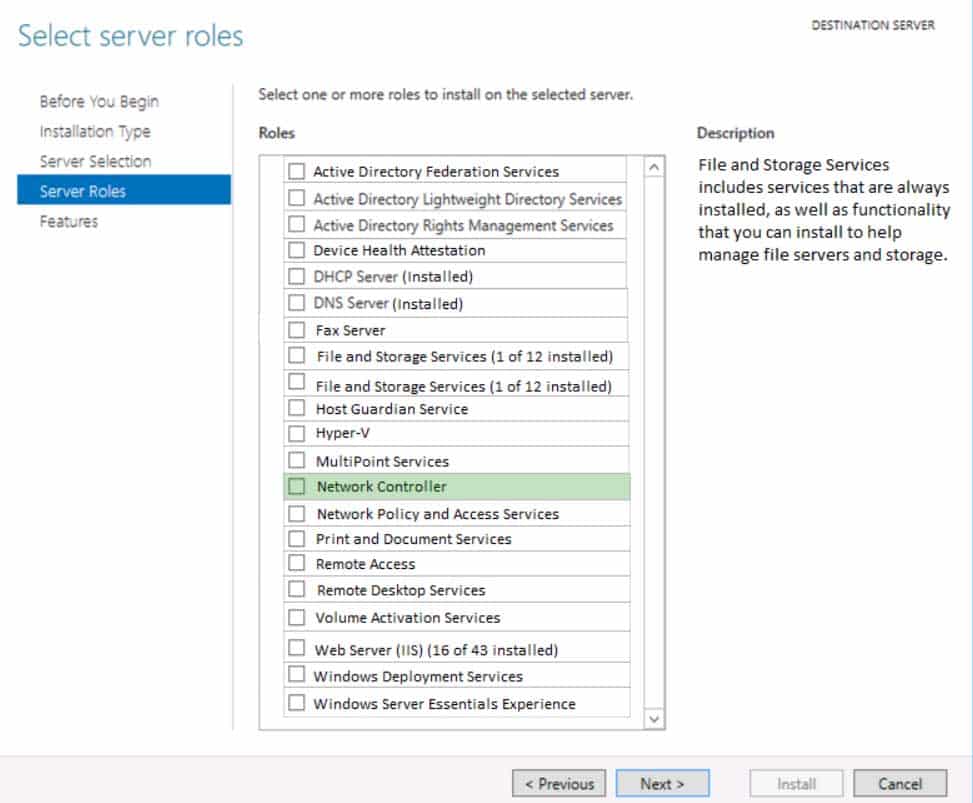
98-366 Part 10 Q08 055 Answer Explanation:
Network Controller is a highly available and scalable server role, and provides one application programming interface (API) that allows Network Controller to communicate with the network, and a second API that allows you to communicate with Network Controller.
-
At Ethernet 1000BaseT network is wired as a physical star using switches.
What is the logical topology?
- mesh
- ring
- bus
- star
-
Which access method is used in a physical ring topology?
- collision
- token passing
- avoidance
- polling
-
What are two characteristics of wired Ethernet network topology? (Choose two.)
- It uses network adapters physically encoded with an IP address
- It uses tokens to avoid collisions on the network
- It is typically employed using twisted pair of fiber optic media
- It can negotiate different transmission speeds
-
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
All devices on your company network connect to the same network switch. This is an example of a physical star topology.
Review the underlined text. If it makes the statement correct, select “No change is needed.” If the statement is incorrect, select the answer choice that makes the statement correct.
- ring
- bus
- mesh
- No change is needed
-
What is the primary purpose of a perimeter network?
- to act as a hidden location to deploy network clients
- to act as a secure location for deploying highly sensitive network servers
- to provide a buffer area between a private intranet and the public Internet
- to monitor traffic between routed subnets in a private LAN
-
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
The 802.11n wireless standard specifies a maximum data rate of 54 Mbps.
Review the underlined text. If it makes the statement correct, select “No change is needed.” If the statement is incorrect, select the answer choice that makes the statement correct.
- 10 Mbps
- 11-128 Mbps
- 300-600 Mbps
- No change is needed
-
What is the purpose of a Media Access Control (MAC) address?
- identify a network device to the Internet
- uniquely identify a physical network device
- manage permissions for shared network resources
- provide a routing address on a local area network (LAN)
-
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
A network that separates an organization’s private network from a public network is an extranet.
Review the underlined text. If it makes the statement correct, select “No change is needed.” If the statement is incorrect, select the answer choice that makes the statement correct.
- a perimeter
- an intranet
- the Internet
- No change is needed
-
Which connectivity option for wide area networks (WANs) is most readily available in most geographic areas?
- Leased line
- ISDN
- T1
- Dial-up