AZ-104 : Microsoft Azure Administrator : Part 04
AZ-104 : Microsoft Azure Administrator : Part 04
-
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure File sync group that has the endpoints shown in the following table.
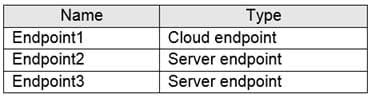
AZ-104 Part 04 Q01 057 Cloud tiering is enabled for Endpoint3.
You add a file named File1 to Endpoint1 and a file named File2 to Endpoint2.
On which endpoints will File1 and File2 be available within 24 hours of adding the files? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

AZ-104 Part 04 Q01 058 Question 
AZ-104 Part 04 Q01 058 Answer Explanation:
File1: Endpoint3 only
Cloud Tiering: A switch to enable or disable cloud tiering. When enabled, cloud tiering will tier files to your Azure file shares. This converts on-premises file shares into a cache, rather than a complete copy of the dataset, to help you manage space efficiency on your server. With cloud tiering, infrequently used or accessed files can be tiered to Azure Files.File2: Endpoint1, Endpoint2, and Endpoint3
-
HOTSPOT
You have several Azure virtual machines on a virtual network named VNet1.
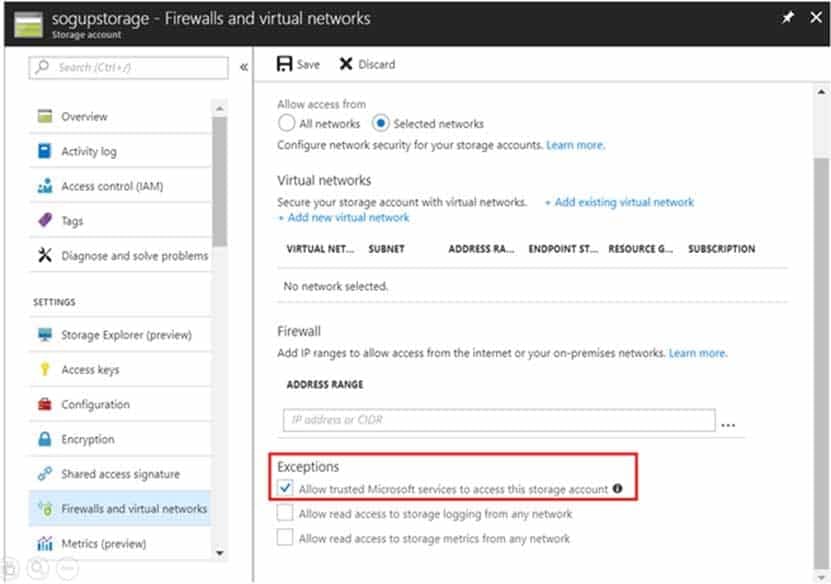
You configure an Azure Storage account as shown in the following exhibit.
AZ-104 Part 04 Q02 059 Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

AZ-104 Part 04 Q02 060 Question 
AZ-104 Part 04 Q02 060 Answer Explanation:
Box 1: never
The 10.2.9.0/24 subnet is not whitelisted.Box 2: never
After you configure firewall and virtual network settings for your storage account, select Allow trusted Microsoft services to access this storage account as an exception to enable Azure Backup service to access the network restricted storage account. -
HOTSPOT
You have a sync group named Sync1 that has a cloud endpoint. The cloud endpoint includes a file named File1.txt.
Your on-premises network contains servers that run Windows Server 2016. The servers are configured as shown in the following table.
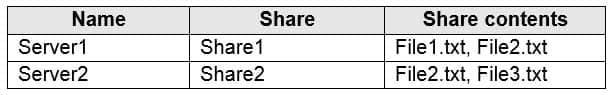
AZ-104 Part 04 Q03 062 You add Share1 as an endpoint for Sync1. One hour later, you add Share2 as an endpoint for Sync1.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

AZ-104 Part 04 Q03 063 Question 
AZ-104 Part 04 Q03 063 Answer Explanation:
Box 1: Yes
If you add an Azure file share that has an existing set of files as a cloud endpoint to a sync group, the existing files are merged with any other files that are already on other endpoints in the sync group.Box 2: No
Box 3: Yes
-
You have an Azure subscription that contains the storage accounts shown in the following table.
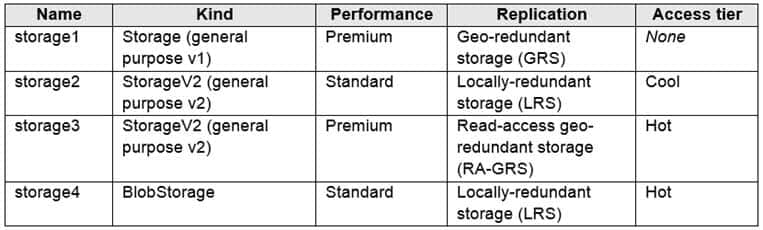
AZ-104 Part 04 Q04 064 You need to identify which storage account can be converted to zone-redundant storage (ZRS) replication by requesting a live migration from Azure support.
What should you identify?
- storage1
- storage2
- storage3
- storage4
Explanation:
ZRS currently supports standard general-purpose v2, FileStorage and BlockBlobStorage storage account types.Incorrect Answers:
A, not C: Live migration is supported only for storage accounts that use LRS replication. If your account uses GRS or RA-GRS, then you need to first change your account’s replication type to LRS before proceeding. This intermediary step removes the secondary endpoint provided by GRS/RA-GRS.Also, only standard storage account types support live migration. Premium storage accounts must be migrated manually.
D: ZRS currently supports standard general-purpose v2, FileStorage and BlockBlobStorage storage account types.
-
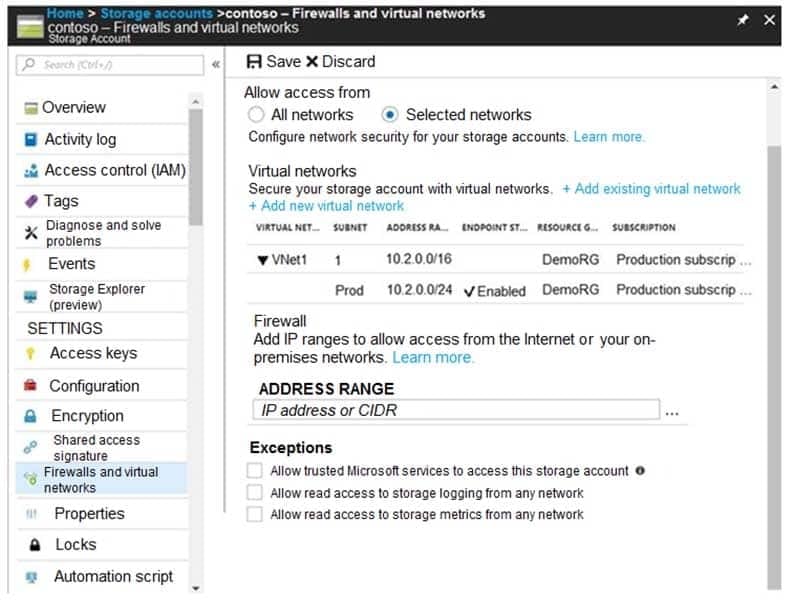
You have an Azure subscription that contains a storage account named account1.
You plan to upload the disk files of a virtual machine to account1 from your on-premises network. The on-premises network uses a public IP address space of 131.107.1.0/24.
You plan to use the disk files to provision an Azure virtual machine named VM1. VM1 will be attached to a virtual network named VNet1. VNet1 uses an IP address space of 192.168.0.0/24.
You need to configure account1 to meet the following requirements:
– Ensure that you can upload the disk files to account1.
– Ensure that you can attach the disks to VM1.
– Prevent all other access to account1.Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- From the Firewalls and virtual networks blade of account1, select Selected networks.
- From the Firewalls and virtual networks blade of account1, select Allow trusted Microsoft services to access this storage account.
- From the Firewalls and virtual networks blade of account1, add the 131.107.1.0/24 IP address range.
- From the Firewalls and virtual networks blade of account1, add VNet1.
- From the Service endpoints blade of VNet1, add a service endpoint.
Explanation:
A: By default, storage accounts accept connections from clients on any network. To limit access to selected networks, you must first change the default action.
Azure portal
1. Navigate to the storage account you want to secure.
2. Click on the settings menu called Firewalls and virtual networks.
3. To deny access by default, choose to allow access from ‘Selected networks’. To allow traffic from all networks, choose to allow access from ‘All networks’.
4. Click Save to apply your changes.E: Grant access from a Virtual Network
Storage accounts can be configured to allow access only from specific Azure Virtual Networks.By enabling a Service Endpoint for Azure Storage within the Virtual Network, traffic is ensured an optimal route to the Azure Storage service. The identities of the virtual network and the subnet are also transmitted with each request.
-
DRAG DROP
You have an on-premises file server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2016.
You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure file share.
You deploy an Azure File Sync Storage Sync Service, and you create a sync group.
You need to synchronize files from Server1 to Azure.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
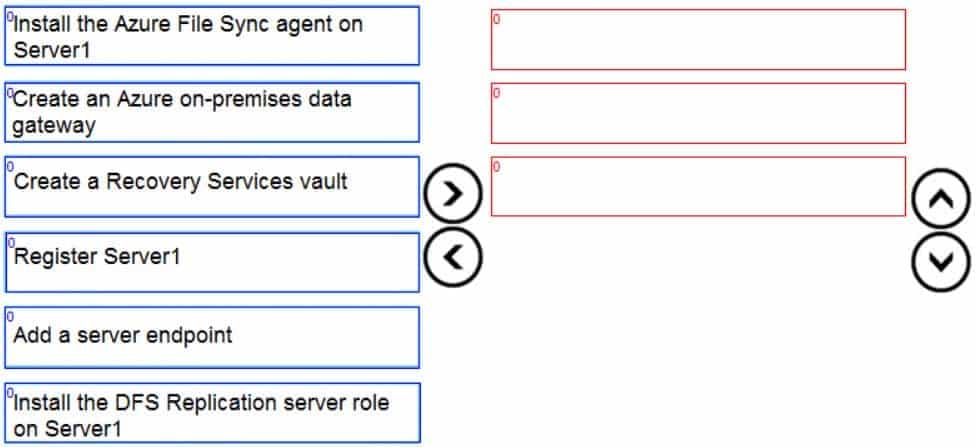
AZ-104 Part 04 Q06 065 Question 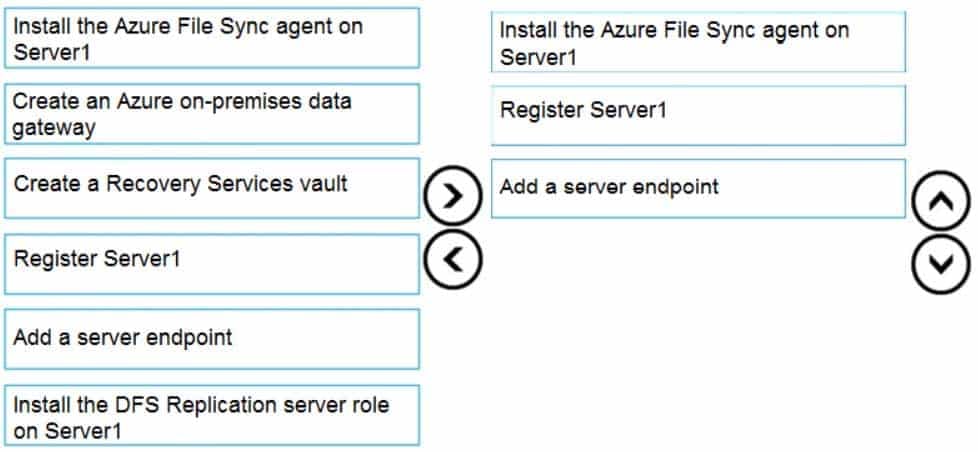
AZ-104 Part 04 Q06 065 Answer Explanation:
Step 1: Install the Azure File Sync agent on Server1
The Azure File Sync agent is a downloadable package that enables Windows Server to be synced with an Azure file shareStep 2: Register Server1.
Register Windows Server with Storage Sync Service
Registering your Windows Server with a Storage Sync Service establishes a trust relationship between your server (or cluster) and the Storage Sync Service.Step 3: Add a server endpoint
Create a sync group and a cloud endpoint.
A sync group defines the sync topology for a set of files. Endpoints within a sync group are kept in sync with each other. A sync group must contain one cloud endpoint, which represents an Azure file share and one or more server endpoints. A server endpoint represents a path on registered server. -
HOTSPOT
You plan to create an Azure Storage account in the Azure region of East US 2.
You need to create a storage account that meets the following requirements:
– Replicates synchronously.
– Remains available if a single data center in the region fails.How should you configure the storage account? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
AZ-104 Part 04 Q07 066 Question 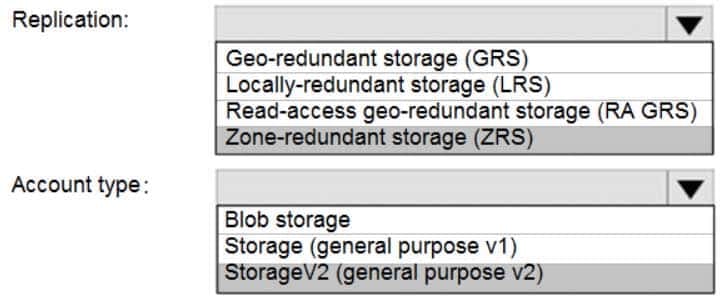
AZ-104 Part 04 Q07 066 Answer Explanation:
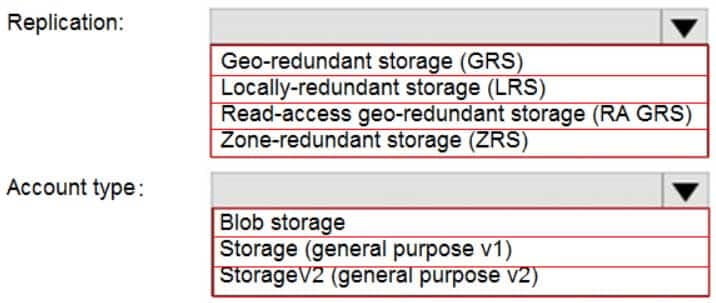
Box 1: Zone-redundant storage (ZRS)
Zone-redundant storage (ZRS) replicates your data synchronously across three storage clusters in a single region.LRS would not remain available if a data center in the region fails
GRS and RA GRS use asynchronous replication.Box 2: StorageV2 (general purpose V2)
ZRS only support GPv2. -
You plan to use the Azure Import/Export service to copy files to a storage account.
Which two files should you create before you prepare the drives for the import job? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- an XML manifest file
- a dataset CSV file
- a JSON configuration file
- a PowerShell PS1 file
- a driveset CSV file
Explanation:
B: Modify the dataset.csv file in the root folder where the tool resides. Depending on whether you want to import a file or folder or both, add entries in the dataset.csv fileE: Modify the driveset.csv file in the root folder where the tool resides.
-
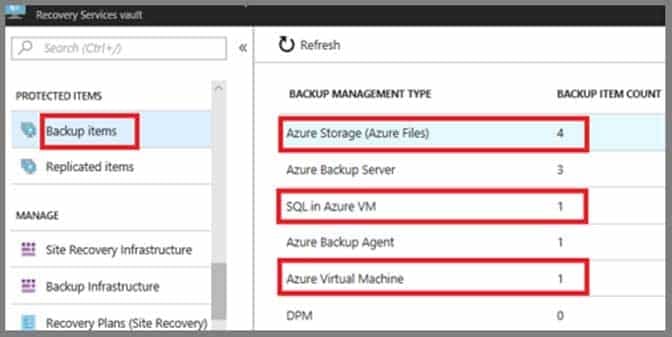
You have a Recovery Service vault that you use to test backups. The test backups contain two protected virtual machines.
You need to delete the Recovery Services vault.
What should you do first?
- From the Recovery Service vault, delete the backup data.
- Modify the disaster recovery properties of each virtual machine.
- Modify the locks of each virtual machine.
- From the Recovery Service vault, stop the backup of each backup item.
Explanation:
You can’t delete a Recovery Services vault if it is registered to a server and holds backup data. If you try to delete a vault, but can’t, the vault is still configured to receive backup data.Remove vault dependencies and delete vault
In the vault dashboard menu, scroll down to the Protected Items section, and click Backup Items. In this menu, you can stop and delete Azure File Servers, SQL Servers in Azure VM, and Azure virtual machines. -
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that contains the resources shown in the following table.
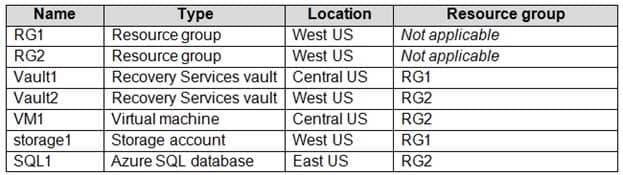
AZ-104 Part 04 Q10 068 In storage1, you create a blob container named blob1 and a file share named share1.
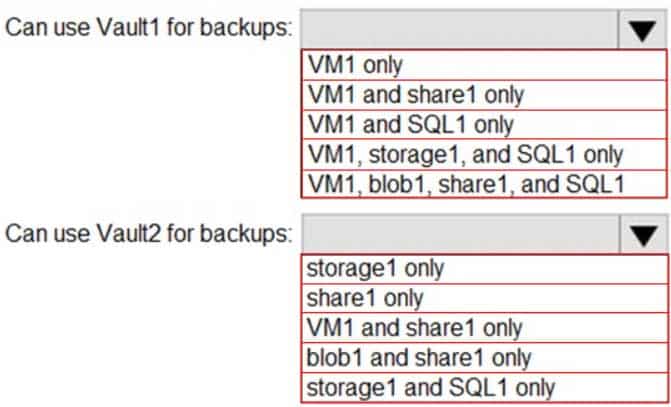
Which resources can be backed up to Vault1 and Vault2? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
AZ-104 Part 04 Q10 069 Question 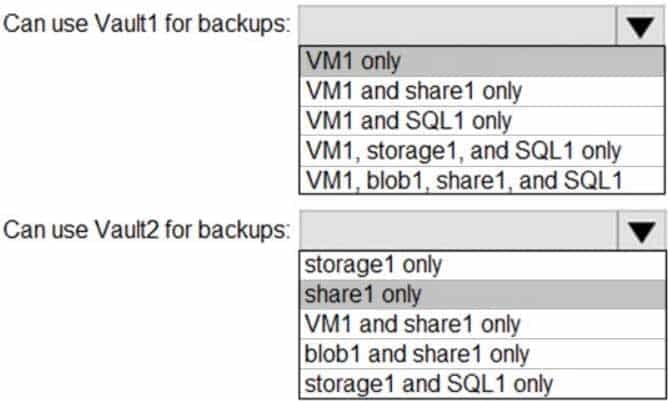
AZ-104 Part 04 Q10 069 Answer Explanation:
Box 1: VM1 only
VM1 is in the same region as Vault1.
File1 is not in the same region as Vautl1.
SQL is not in the same region as Vault1.
Blobs cannot be backup up to service vaults.Note: To create a vault to protect virtual machines, the vault must be in the same region as the virtual machines.
Box 2: Share1 only.
Storage1 is in the same region (West USA) as Vault2. Share1 is in Storage1.Note: After you select Backup, the Backup pane opens and prompts you to select a storage account from a list of discovered supported storage accounts. They’re either associated with this vault or present in the same region as the vault, but not yet associated to any Recovery Services vault.
-
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1.
You have 5 TB of data that you need to transfer to Subscription1.
You plan to use an Azure Import/Export job.
What can you use as the destination of the imported data?
- a virtual machine
- an Azure Cosmos DB database
- Azure File Storage
- the Azure File Sync Storage Sync Service
Explanation:
Azure Import/Export service is used to securely import large amounts of data to Azure Blob storage and Azure Files by shipping disk drives to an Azure datacenter.The maximum size of an Azure Files Resource of a file share is 5 TB.
Note:
There are several versions of this question in the exam. The question has two correct answers:
1. Azure File Storage
2. Azure Blob StorageThe question can have other incorrect answer options, including the following:
– Azure Data Lake Store
– Azure SQL Database
– Azure Data Factory -
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure subscription.
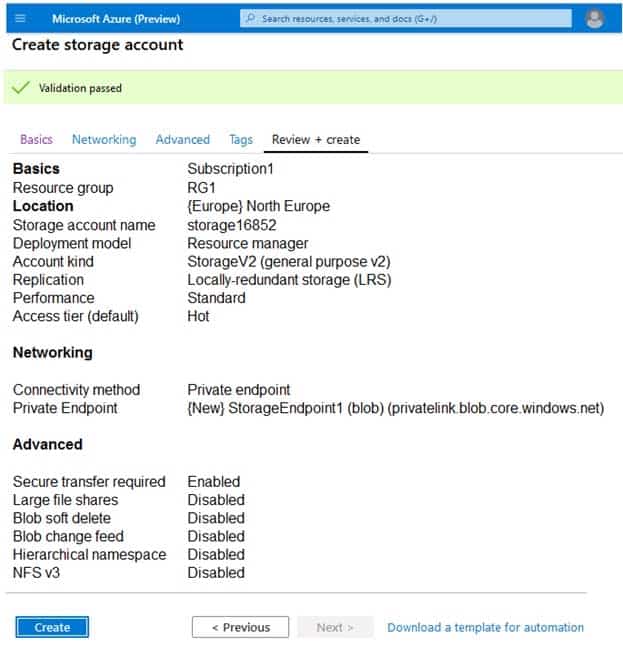
You create the Azure Storage account shown in the following exhibit.
AZ-104 Part 04 Q12 070 Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
AZ-104 Part 04 Q12 071 Question 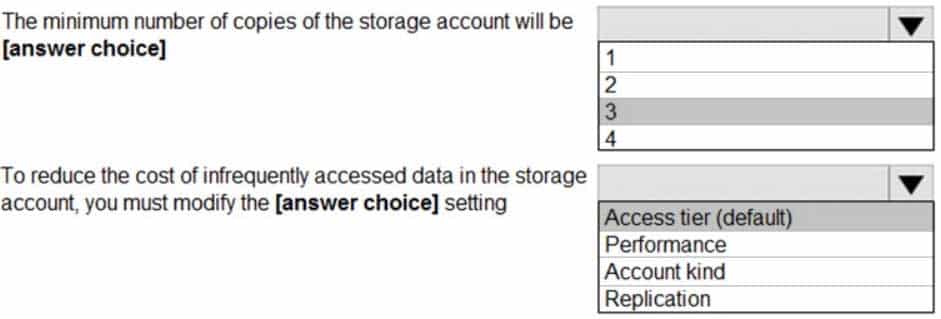
AZ-104 Part 04 Q12 071 Answer Explanation:
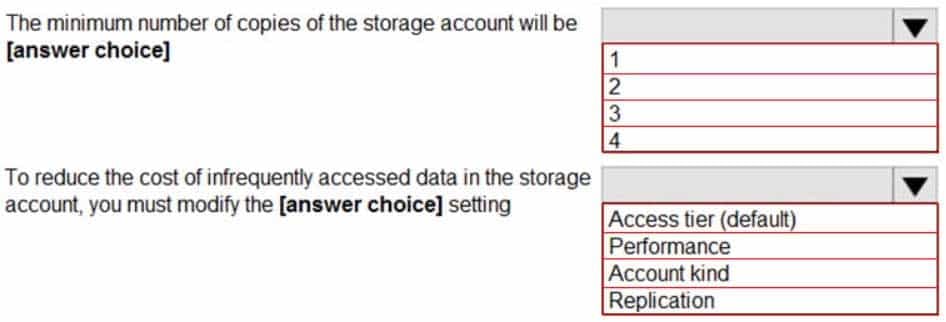
Box 1: 3
Locally Redundant Storage (LRS) provides highly durable and available storage within a single location (sub region). We maintain an equivalent of 3 copies (replicas) of your data within the primary location as described in our SOSP paper; this ensures that we can recover from common failures (disk, node, rack) without impacting your storage account’s availability and durability.Box 2: Access tier
Change the access tier from Hot to Cool.Note: Azure storage offers different access tiers, which allow you to store blob object data in the most cost-effective manner. The available access tiers include:
Hot – Optimized for storing data that is accessed frequently.
Cool – Optimized for storing data that is infrequently accessed and stored for at least 30 days.
Archive – Optimized for storing data that is rarely accessed and stored for at least 180 days with flexible latency requirements (on the order of hours). -
You have an Azure Storage account named storage1.
You plan to use AzCopy to copy data to storage1.
You need to identify the storage services in storage1 to which you can copy the data.
What should you identify?
- blob, file, table, and queue
- blob and file only
- file and table only
- file only
- blob, table, and queue only
Explanation:
AzCopy is a command-line utility that you can use to copy blobs or files to or from a storage account.Incorrect Answers:
A, C, E: AzCopy does not support table and queue storage services.D: AzCopy supports file storage services, as well as blob storage services.
-
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure Storage account named storage1 that uses Azure Blob storage and Azure File storage.
You need to use AzCopy to copy data to the blob storage and file storage in storage1.
Which authentication method should you use for each type of storage? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

AZ-104 Part 04 Q14 072 Question 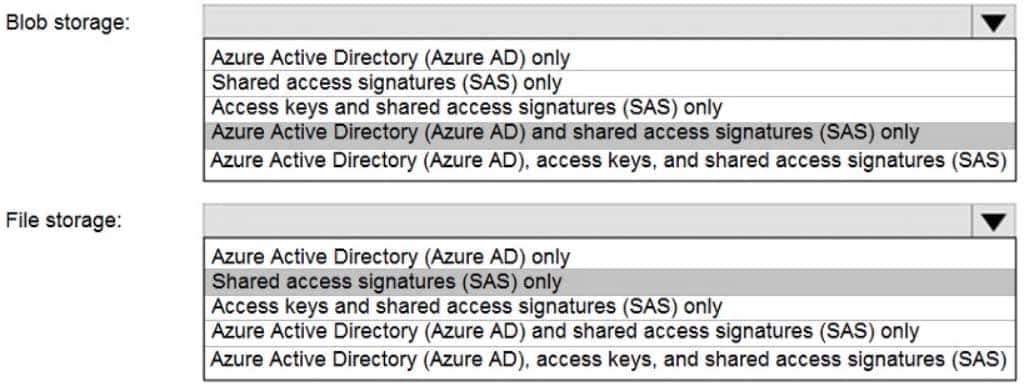
AZ-104 Part 04 Q14 072 Answer Explanation:
You can provide authorization credentials by using Azure Active Directory (AD), or by using a Shared Access Signature (SAS) token.
Box 1:
Both Azure Active Directory (AD) and Shared Access Signature (SAS) token are supported for Blob storage.Box 2:
Only Shared Access Signature (SAS) token is supported for File storage. -
You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Storage account.
You plan to create an Azure container instance named container1 that will use a Docker image named Image1. Image1 contains a Microsoft SQL Server instance that requires persistent storage.
You need to configure a storage service for Container1.
What should you use?
- Azure Files
- Azure Blob storage
- Azure Queue storage
- Azure Table storage
-
You have an app named App1 that runs on two Azure virtual machines named VM1 and VM2.
You plan to implement an Azure Availability Set for App1. The solution must ensure that App1 is available during planned maintenance of the hardware hosting VM1 and VM2.
What should you include in the Availability Set?
- one update domain
- two fault domains
- one fault domain
- two update domains
Explanation:
Microsoft updates, which Microsoft refers to as planned maintenance events, sometimes require that VMs be rebooted to complete the update. To reduce the impact on VMs, the Azure fabric is divided into update domains to ensure that not all VMs are rebooted at the same time.Incorrect Answers:
A: An update domain is a group of VMs and underlying physical hardware that can be rebooted at the same time.B, C: A fault domain shares common storage as well as a common power source and network switch. It is used to protect against unplanned system failure.
-
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1.
You have 5 TB of data that you need to transfer to Subscription1.
You plan to use an Azure Import/Export job.
What can you use as the destination of the imported data?
- an Azure Cosmos DB database
- Azure Blob storage
- Azure Data Lake Store
- the Azure File Sync Storage Sync Service
Explanation:
Azure Import/Export service is used to securely import large amounts of data to Azure Blob storage and Azure Files by shipping disk drives to an Azure datacenter.Note:
There are several versions of this question in the exam. The question has two correct answers:
1. Azure File Storage
2. Azure Blob StorageThe question can have other incorrect answer options, including the following:
– a virtual machine
– Azure SQL Database
– Azure Data Factory -
DRAG DROP
You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure file share.
You have an on-premises server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2016.
You plan to set up Azure File Sync between Server1 and the Azure file share.
You need to prepare the subscription for the planned Azure File Sync.
Which two actions should you perform in the Azure subscription? To answer, drag the appropriate actions to the correct targets. Each action may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
AZ-104 Part 04 Q18 073 Question 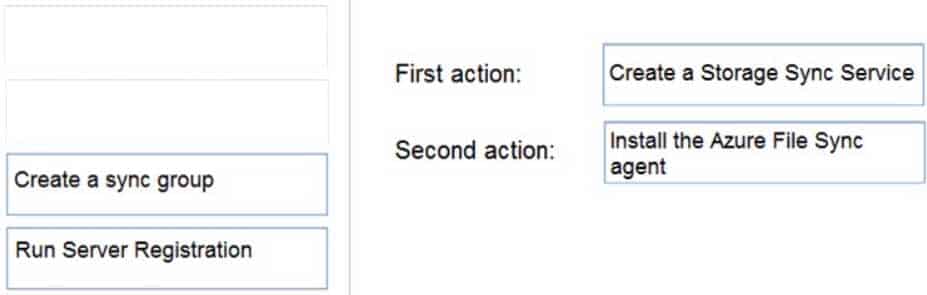
AZ-104 Part 04 Q18 073 Answer Explanation:
First action: Create a Storage Sync Service
The deployment of Azure File Sync starts with placing a Storage Sync Service resource into a resource group of your selected subscription.Second action: Install the Azure File Sync agent
The Azure File Sync agent is a downloadable package that enables Windows Server to be synced with an Azure file share. -
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure subscription that contains the file shares shown in the following table.
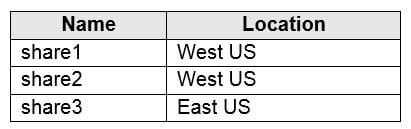
AZ-104 Part 04 Q19 074 You have the on-premises file shares shown in the following table.
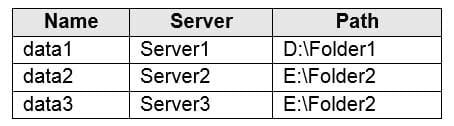
AZ-104 Part 04 Q19 075 You create an Azure file sync group named Sync1 and perform the following actions:
– Add share1 as the cloud endpoint for Sync1.
– Add data1 as a server endpoint for Sync1.
– Register Server1 and Server2 to Sync1.For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

AZ-104 Part 04 Q19 076 Question 
AZ-104 Part 04 Q19 076 Answer Explanation:
Box 1: No
A sync group must contain one cloud endpoint, which represents an Azure file share and one or more server endpoints.Box 2: Yes
Data2 is located on Server2 which is registered to Sync1.Box 3: No
Data3 is located on Server3 which is not registered to Sync1. -
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that contains the resources shown in the following table:
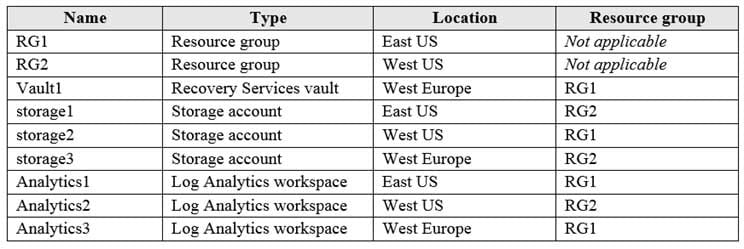
AZ-104 Part 04 Q20 077 You plan to configure Azure Backup reports for Vault1.
You are configuring the Diagnostics settings for the AzureBackupReports log.
Which storage accounts and which Log Analytics workspaces can you use for the Azure Backup reports of Vault1? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
AZ-104 Part 04 Q20 078 Question 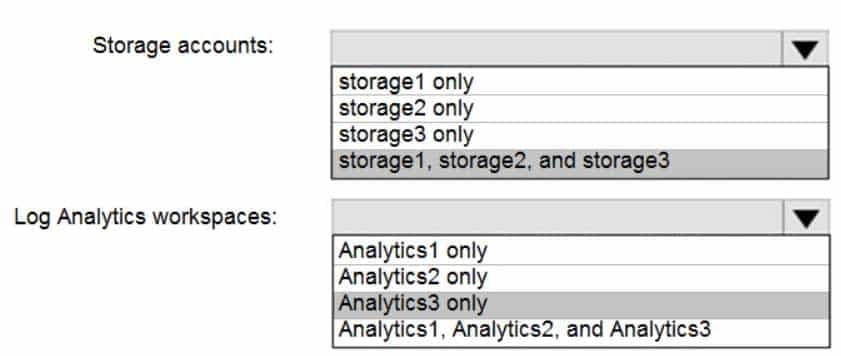
AZ-104 Part 04 Q20 078 Answer Explanation:
Box 1: storage1, storage2, and storage3
The location and subscription where this Log Analytics workspace can be created is independent of the location and subscription where your vaults exist.Box 2: Analytics3
Vault1 and Analytics3 are both in West Europe.