DA-100 : Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI : Part 03
DA-100 : Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI : Part 03
-
HOTSPOT
You have a Power BI report.
You need to create a calculated table to return the 100 highest spending customers.
How should you complete the DAX expression? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q01 053 Question 
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q01 053 Answer Explanation:Box 1: TOPN
TOPN returns the top N rows of the specified table.Box 2: SUMMARIZE
SUMMARIZE returns a summary table for the requested totals over a set of groups.Box 3: DESC
Sort in descending order.It is last in the TOPN command.
TOPN syntax:
TOPN(<n_value>, <table>, <orderBy_expression>, [<order>[, <orderBy_expression>, [<order>]]…]) -
HOTSPOT
You have two tables named Customers and Invoice in a Power BI model. The Customers table contains the following fields:
– CustomerID
– Customer City
– Customer State
– Customer Name
– Customer Address 1
– Customer Address 2
– Customer Postal CodeThe Invoice table contains the following fields:
– Order ID
– Invoice ID
– Invoice Date
– Customer ID
– Total Amount
– Total Item CountThe Customers table is related to the Invoice table through the Customer ID columns. A customer can have many invoices within one month.
The Power BI model must provide the following information:
– The number of customers invoiced in each state last month
– The average invoice amount per customer in each postal codeYou need to define the relationship from the Customers table to the Invoice table. The solution must optimize query performance.
What should you configure? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q02 054 Question 
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q02 054 Answer Explanation:Box 1: One-to-many
A customer can have many invoices within one month.Box 2: Single
For One-to-many relationships, the cross filter direction is always from the “one” side, and optionally from the “many” side (bi-directional). ForSingle cross filter direction means “single direction”, and Both means “both directions”. A relationship that filters in both directions is commonly described as bi-directional.
-
You have a Microsoft Power BI data model that contains three tables named Orders, Date, and City. There is a one-to-many relationship between Date and Orders and between City and Orders.
The model contains two row-level security (RLS) roles named Role1 and Role2. Role1 contains the following filter.
City[State Province] = "Kentucky"
Role2 contains the following filter.
Date[Calendar Year] = 2020
If a user is a member of both Role1 and Role2, what data will they see in a report that uses the model?
- The user will see data for which the State Province value is Kentucky and the Calendar Year is 2020.
- The user will see data for which the State Province value is Kentucky or the Calendar Year is 2020.
- The user will see only data for which the State Province value is Kentucky.
- The user will receive an error and will not be able to see the data in the report.
Explanation: When a report user is assigned to multiple roles, RLS filters become additive. It means report users can see table rows that represent the union of those filters. -
HOTSPOT
Your company has affiliates who help the company acquire customers.
You build a report for the affiliate managers at the company to assist them in understanding affiliate performance.
The managers request a visual showing the total sales value of the latest 50 transactions for each affiliate. You have a data model that contains the following tables.

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q04 055 The Affiliate table has a one-to-many relationship to the Transactions table based on the AffiliateID column.
You need to develop a measure to support the visual.
How should you complete the DAX expression? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
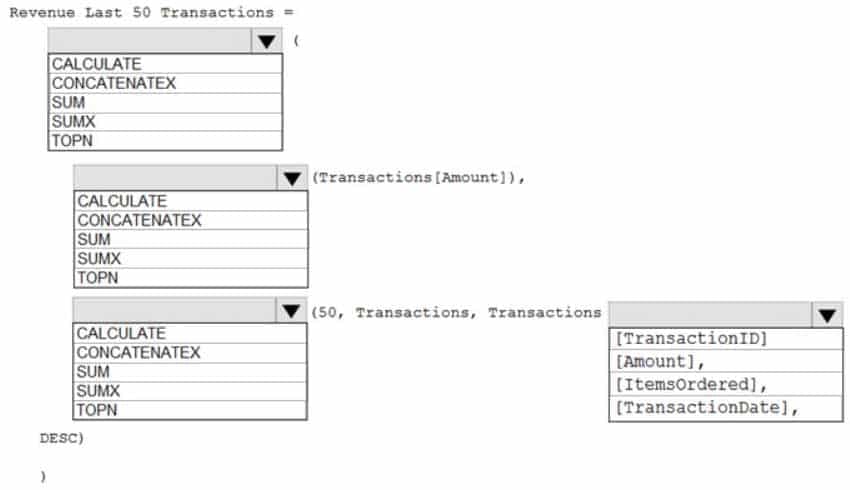
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q04 056 Question 
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q04 056 Answer Explanation:Box 1: CALCULATE
Start with CALCULATE and use a SUMX.CALCULATE evaluates an expression in a modified filter context.
Box 2: SUMX
SUMX returns the sum of an expression evaluated for each row in a table.The following sample creates a measure with the sales of the top 10 sold products.
= SUMX(TOPN(10, SUMMARIZE(Product, [ProductKey], “TotalSales”, SUMX(RELATED(InternetSales_USD[SalesAmount_USD]), InternetSales_USD[SalesAmount_USD]) + SUMX(RELATED(ResellerSales_USD[SalesAmount_USD]), ResellerSales_USD[SalesAmount_USD]))
Box 3: TOPN
TOPN returns the top N rows of the specified table.Box 4: [TransactionDate]
TOPN Syntax: TOPN(<n_value>, <table>, <orderBy_expression>, [<order>[, <orderBy_expression>, [<order>]]…])The orderBy_expression: Any DAX expression where the result value is used to sort the table and it is evaluated for each row of table.
-
You are configuring a Microsoft Power BI data model to enable users to ask natural language questions by using Q&A.
You have a table named Customer that has the following measure.
Customer Count = DISTINCTCOUNT(Customer[CustomerID])
Users frequently refer to customers as subscribers.
You need to ensure that the users can get a useful result for “subscriber count” by using Q&A. The solution must minimize the size of the model.
What should you do?
- Set Summarize By to None for the CustomerID column.
- Add a synonym of “subscriber” to the Customer table.
- Add a synonym of “subscriberID” to the CustomerID column.
- Add a description of “subscriber count” to the Customer Count measure.
Explanation:You can add synonyms to tables and columns.
Note: This step applies specifically to Q&A (and not to Power BI reports in general). Users often have a variety of terms they use to refer to the same thing, such as total sales, net sales, total net sales. You can add these synonyms to tables and columns in the Power BI model.
This step applies specifically to Q&A (and not to Power BI reports in general). Users often have a variety of terms they use to refer to the same thing, such as total sales, net sales, total net sales. You can add these synonyms to tables and columns in the Power BI model.
-
HOTSPOT
You are creating a Microsoft Power BI data model that has the tables shown in the following table.

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q06 057 The Products table is related to the ProductCategory table through the ProductCategoryID column.
You need to ensure that you can analyze sales by product category.
How should you configure the relationships from ProductCategory to Products? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q06 058 Question 
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q06 058 Answer Explanation:Box 1: One-to-many
Each ProductCategory can have many Products, while each Product belongs to exactly one ProductCategory.Box 2: Both
For One-to-many relationships, the cross filter direction is always from the “one” side, and optionally from the “many” side (bi-directional).Note:

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q06 059 -
HOTSPOT
You are creating an analytics report that will consume data from the tables shown in the following table.
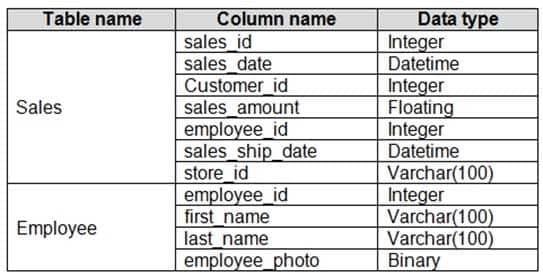
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q07 060 There is a relationship between the tables.
There are no reporting requirements on employee_id and employee_photo.
You need to optimize the data model.
What should you configure for employee_id and employee_photo? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
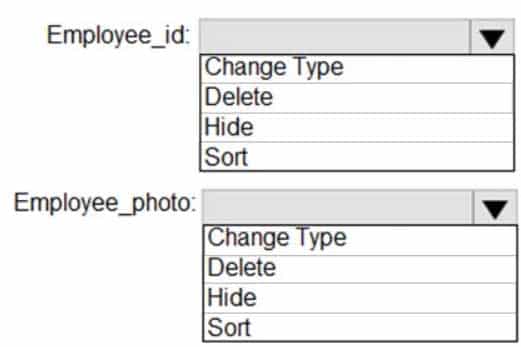
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q07 061 Question 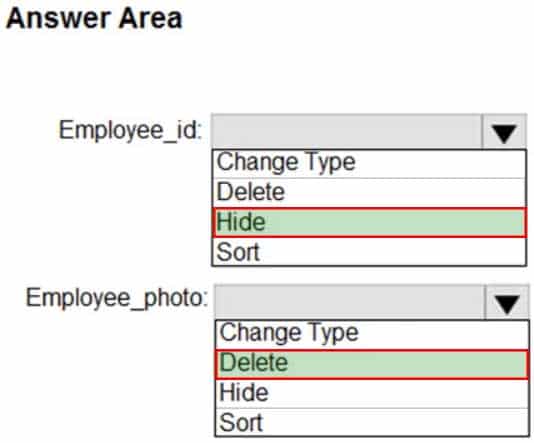
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q07 061 Answer Explanation:Box 1: Hide
Optimize data by hiding fields and sorting visualization dataBox 2: Delete
The fastest way to optimize your Power BI report is to limit the number of columns to only the ones you need in your data model. Go through your tables in Power Query and determine what fields are being used. Delete these columns if they are not being used in any of your reports or calculations. -
HOTSPOT
You are creating a Microsoft Power BI model that has two tables named CityData and Sales.
CityData contains only the data shown in the following table.
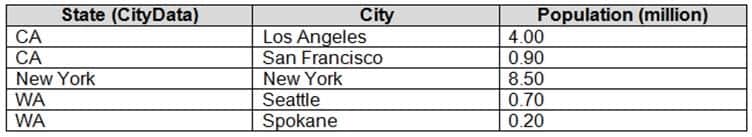
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q08 062 Sales contains only the data shown in the following table.

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q08 063 CityData and Sales are related using a many-to-many relationship based upon the State column in each table.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q08 064 Question 
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q08 064 Answer Explanation:Box 1: Yes
The Related function returns a related value from another table.The RELATED function requires that a relationship exists between the current table and the table with related information. You specify the column that contains the data that you want, and the function follows an existing many-to-one relationship to fetch the value from the specified column in the related table. If a relationship does not exist, you must create a relationship.
Box 2: Yes
Box 3: No
TX only occurs in the Sales table, but not in the CityData table. -
DRAG DROP
You build a report about warehouse inventory data. The dataset has more than 10 million product records from 200 warehouses worldwide.
You have a table named Products that contains the columns shown in the following table.
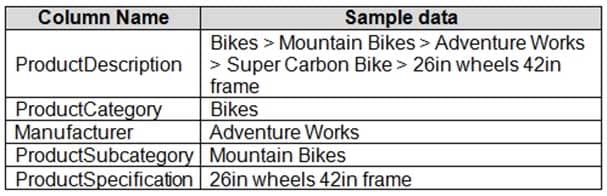
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q09 065 Warehouse managers report that it is difficult to use the report because the report uses only the product name in tables and visuals. The product name is contained within the ProductDescription column and is always the fourth value.
You need to modify the report to support the warehouse managers requirement to explore inventory levels at different levels of the product hierarchy. The solution must minimize the model size.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q09 066 Question 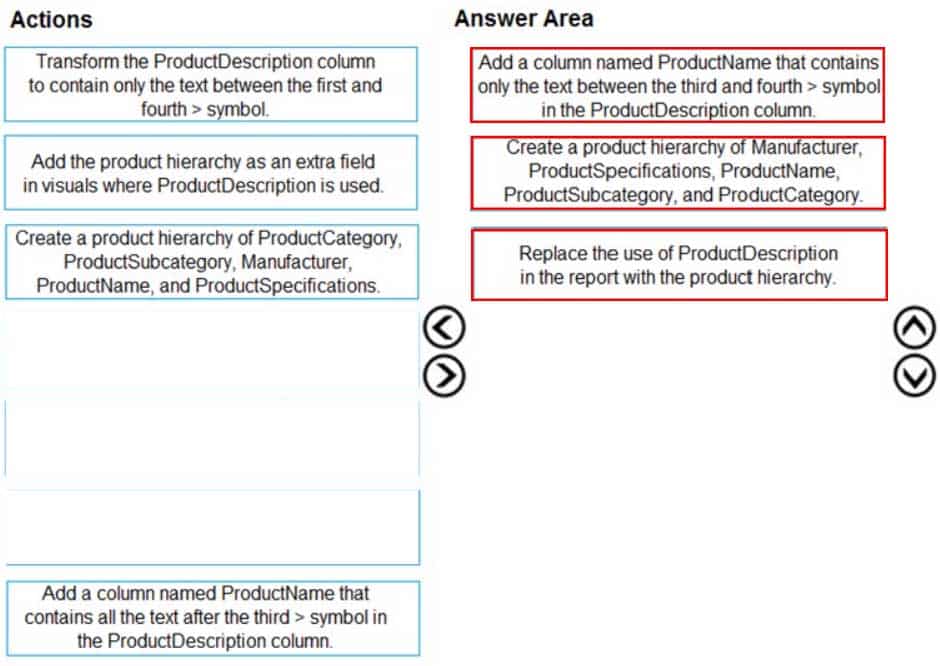
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q09 066 Answer Explanation: Power BI Desktop supports the use of inline hierarchy labels. With inline hierarchy labels, you can see hierarchy labels as you expand visuals using the Expand All feature. -
You have a query that returns the data shown in the following exhibit.

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q10 067 You need to configure the query to display the data shown in the following exhibit.
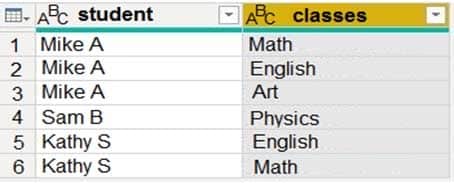
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q10 068 Which step should you use in the query?
-
= Table.SplitColumn(Source, "classes", Splitter.SplitTextByDelimiter(",", QuoteStyle.None), {"classes.1"}) -
= Table.Unpivot(Source, {"classes"}, "Attribute", "Value") -
= Table.SplitColumn(Source, "classes", Splitter.SplitTextByPositions({10}), {"classes.1"}) -
= Table.ExpandListColumn(Table.TransformColumns(Source, {{"classes", Splitter.SplitTextByDelimiter(",", QuoteStyle.None), let itemType = (type nullable text) meta [Serialized.Text = true] in type {itemType}}}), "classes")
Explanation:Power Query Unpivot columns: You might want to unpivot data, sometimes called flattening the data, to put it in a matrix format so that all similar values are in one column. This is necessary, for example, to create a chart or a report.
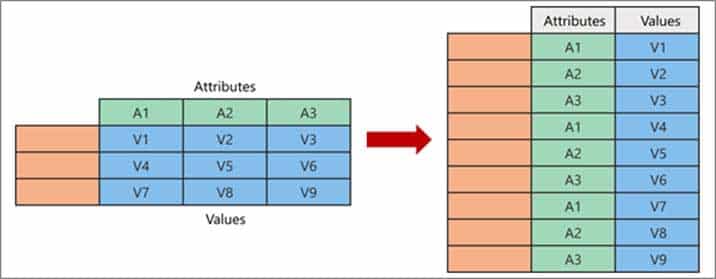
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q10 069 Note:
Syntax: Table.Unpivot(table as table, pivotColumns as list, attributeColumn as text, valueColumn as text) as tableTable.Unpivot translates a set of columns in a table into attribute-value pairs, combined with the rest of the values in each row.
-
-
You have files sales regions. Each region is assigned a single salesperson.
You have an imported dataset that has a dynamic row-level security (RLS) role named Sales. The Sales role filters sales transaction data by salesperson.
Salespeople must see only the data from their region.
You publish the dataset to powerbi.com, set RLS role membership, and distribute the dataset and related reports to the salespeople.
A salesperson reports that she believes she should see more data.
You need to verify what data the salesperson currently sees.
What should you do?
- Use the Test as role option to view data as the salesperson’s user account.
- Instruct the salesperson to open the report in Microsoft Power BI Desktop.
- Filter the data in the reports to match the intended logic in the filter on the sales transaction table.
- Use the Test as role option to view data as the Sales role.
Explanation:Validate the roles within Power BI Desktop
1. After you’ve created your roles, test the results of the roles within Power BI Desktop.From the Modeling tab, select View as.

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q11 070 The View as roles window appears, where you see the roles you’ve created.
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q11 071 2. Select a role you created, and then select OK to apply that role.
3. The report renders the data relevant for that role.
You can also select Other user and supply a given user.

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q11 072 4. Select OK.
The report renders based on what that user can see.
-
HOTSPOT
You are creating a quick measure as shown in the following exhibit.
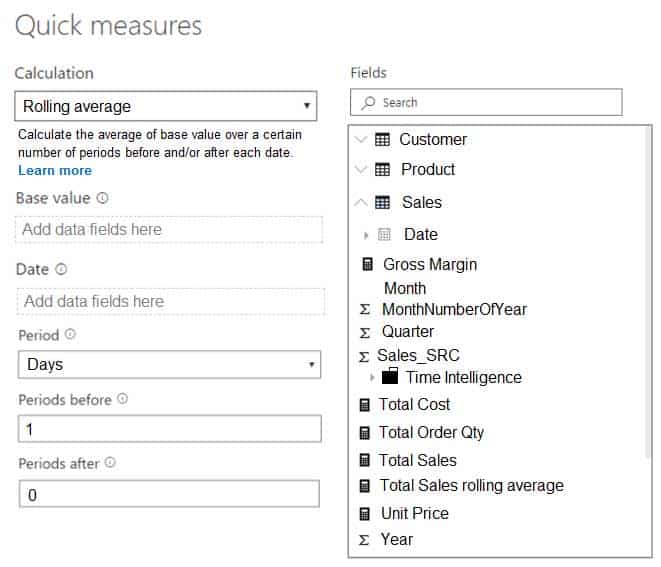
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q12 073 You need to create a monthly rolling average measure for Sales over time.
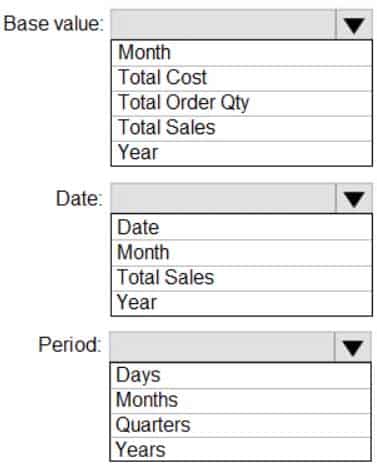
How should you configure the quick measure calculation? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q12 074 Question 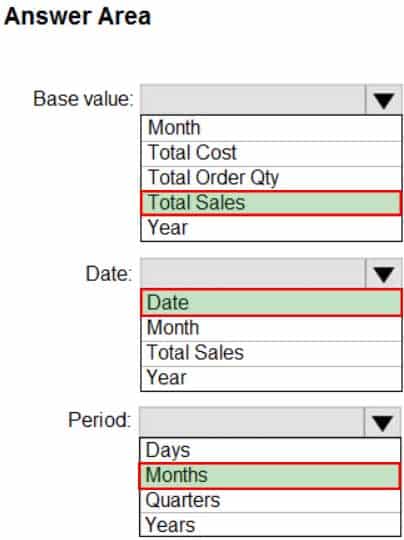
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q12 074 Answer Explanation:Box 1: Total Sales
We select the field Total SalesBox 2: Date
Select a date field.Box 3: Month
Monthly periods. -
You have four sales regions. Each region has multiple sales managers.
You implement row-level security (RLS) in a data model. You assign the relevant mail-enabled security group to each role.
You have sales reports that enable analysis by region. The sales managers can view the sales records of their region. The sales managers are prevented from viewing records from other regions.
A sales manager changes to a different region.
You need to ensure that the sales manager can see the correct sales data.
What should you do?
- Change the Microsoft Power BI license type of the sales manager.
- From Microsoft Power BI Desktop, edit the Row-Level Security setting for the reports.
- Request that the sales manager be added to the correct Azure Active Directory group.
- Manage the permissions of the underlying dataset.
Explanation:Using AD Security Groups, you no longer need to maintain a long list of users.
All that you will need to do is to put in the AD Security group with the required permissions and Power BI will do the REST! This means a small and simple security file with the permissions and AD Security group.
Note: Configure role mappings
Once published to Power BI, you must map members to dataset roles.
Members can be user accounts or security groups. Whenever possible, we recommend you map security groups to dataset roles. It involves managing security group memberships in Azure Active Directory. Possibly, it delegates the task to your network administrators. -
DRAG DROP
You have a Microsoft Power BI data model that contains three tables named Sales, Product, and Date.
The Sales table has an existing measure named [Total Sales] that sums the total sales from the Sales table.
You need to write a calculation that returns the percentage of total sales that a selected Product Category Name value represents. The calculation must respect any slicers on Product Category Name and must show the percentage of visible total sales. For example, if there are four Product Category Name values, and a user filters one out, a table showing Product Category Name and the calculation must sum up to 100 percent.
How should you complete the calculation? To answer, drag the appropriate values to the correct targets. Each value may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q14 075 Question 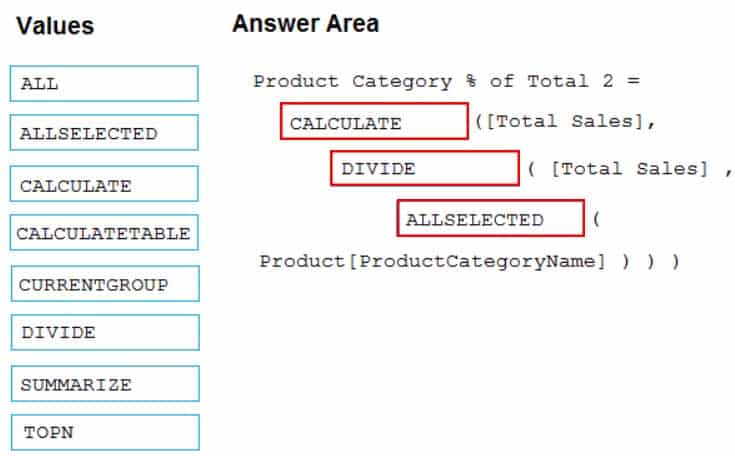
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q14 075 Answer Explanation:Box 1: CALCULATE
CALCULATE rvaluates an expression in a modified filter context.Box 2: DIVIDE
As a data modeler, when you write a DAX expression to divide a numerator by a denominator, you can choose to use the DIVIDE function or the divide operator (/ – forward slash).When using the DIVIDE function, you must pass in numerator and denominator expressions.
Box 3: ALLSELECTED
ALLSELECTED removes context filters from columns and rows in the current query, while retaining all other context filters or explicit filters.The ALLSELECTED function gets the context that represents all rows and columns in the query, while keeping explicit filters and contexts other than row and column filters. This function can be used to obtain visual totals in queries.
Example:
measure ‘Reseller Sales'[Reseller Visual Total]=calculate(sum(‘Reseller Sales'[Sales Amount]), ALLSELECTED()) -
You have sales data in a star schema that contains four tables named Sales, Customer, Date, and Product. The Sales table contains purchase and ship dates.
Most often, you will use the purchase date to analyze the data, but you will analyze the data by both dates independently and together.
You need to design an imported dataset to support the analysis. The solution must minimize the model size and the number of queries against the data source.
Which data modeling design should you use?
- Use the Auto Date/Time functionality in Microsoft Power BI and do NOT import the Date table.
- Duplicate the Date query in Power Query and create active relationships between Sales and both Date tables in the modeling view.
- On the Date table, use a reference query in Power Query and create active relationships between Sales and both Date tables in the modeling view.
- Import the Date table twice in Power Query and create active relationships between Sales and both Date tables in the modeling view.
Explanation:Microsoft recommends defining active relationships whenever possible. They widen the scope and potential of how your model can be used by report authors, and users working with Q&A.
Refactoring methodology (example): Here’s a methodology to refactor a model from a single role-playing dimension-type table, to a design with one table per role.
1. Remove any inactive relationships.
2. Consider renaming the role-playing dimension-type table to better describe its role. In the example, the Airport table is related to the ArrivalAirport column of the Flight table, so it’s renamed as Arrival Airport.
3. Create a copy of the role-playing table, providing it with a name that reflects its role. If it’s an Import table, we recommend defining a calculated table. If it’s a Direct Query table, you can duplicate the Power Query query.Only one relationship can be active.
Note: If you query two or more tables at the same time, when the data is loaded, Power BI Desktop attempts to find and create relationships for you. The relationship options Cardinality, Cross filter direction, and Make this relationship active are automatically set.
-
You have a sales system that contains the tables shown in the following table.

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q16 076 The Date table is marked as a date table. DateID is the date data type.
You need to create an annual sales growth percentage measure.
Which DAX expression should you use?
-
SUM(sales[sales_amount]) - CALCULATE(SUM(sales[sales_amount]), SAMEPERIODLASTYEAR('Date'[DateID]) -
(SUM(‘Sales’[sales_amount]) - CALCULATE(SUM(‘Sales’[sales_amount]), SAMEPERIODLASTYEAR(‘Date’[DateID]))) / CALCULATE(SUM(‘Sales’[sales_amount]), SAMEPERIODLASTYEAR(‘Date’[DateID])) -
CALCULATE(SUM(sales[sales_amount]), DATESYTD(‘Date’[DateID]))
-
CALCULATE(SUM(sales[sales_amount]), SAMEPERIODLASTYEAR(‘Date’[DateID]))
Explanation:SAMEPERIODLASTYEAR returns a table that contains a column of dates shifted one year back in time from the dates in the specified dates column, in the current context. -
-
In Power BI Desktop, you are building a sales report that contains two tables. Both tables have row-level security (RLS) configured.
You need to create a relationship between the tables. The solution must ensure that bidirectional cross-filtering honors the RLS settings.
What should you do?
- Create an active relationship between the tables and select Assume referential integrity.
- Create an inactive relationship between the tables and select Assume referential integrity.
- Create an inactive relationship between the tables and select Apply security filter in both directions.
- Create an active relationship between the tables and select Apply security filter in both directions.
Explanation:By default, row-level security filtering uses single-directional filters, whether the relationships are set to single direction or bi-directional. You can manually enable bi-directional cross-filtering with row-level security by selecting the relationship and checking the Apply security filter in both directions checkbox. Select this option when you’ve also implemented dynamic row-level security at the server level, where row-level security is based on username or login ID.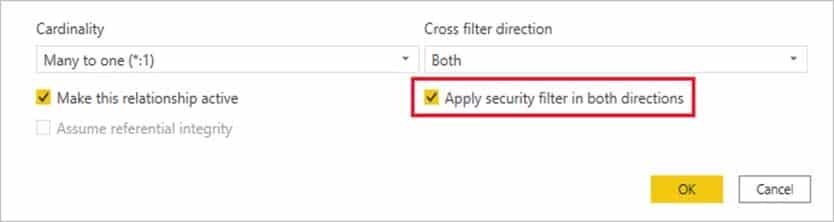
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q17 077 -
You have a Power BI dataset that contains a table named Temperature Readings. Temperature Readings contains the columns shown in the following table.
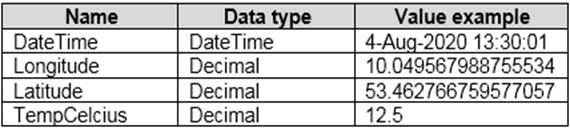
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q18 078 The table has 12 million rows. All the columns are needed for analysis.
You need to optimize the dataset to decrease the model size. The solution must not affect the precision of the data.
What should you do?
- Split the DateTime column into separate date and time columns.
- Change the data type of the DateTime column to Date.
- Change the data type of the Latitude column to Fixed Decimal.
- Disable the Power Query load.
Explanation:Disable Power Query query load.
Power Query queries that are intended support data integration with other queries should not be loaded to the model. To avoid loading the query to the model, take care to ensure that you disable query load in these instances. -
Case Study
This is a case study. Case studies are not timed separately. You can use as much exam time as you would like to complete each case. However, there may be additional case studies and sections on this exam. You must manage your time to ensure that you are able to complete all questions included on this exam in the time provided.
To answer the questions included in a case study, you will need to reference information that is provided in the case study. Case studies might contain exhibits and other resources that provide more information about the scenario that is described in the case study. Each question is independent of the other question on this case study.
At the end of this case study, a review screen will appear. This screen allows you to review your answers and to make changes before you move to the next section of the exam. After you begin a new section, you cannot return to this section.
To start the case study
To display the first question on this case study, click the Next button. Use the buttons in the left pane to explore the content of the case study before you answer the questions. Clicking these buttons displays information such as business requirements, existing environment, and problem statements. If the case study has an All Information tab, note that the information displayed is identical to the information displayed on the subsequent tabs. When you are ready to answer a question, click the Question button to return to the question.Overview
Litware, Inc. is an online retailer that uses Microsoft Power BI dashboards and reports.
The company plans to leverage data from Microsoft SQL Server databases, Microsoft Excel files, text files, and several other data sources.
Litware uses Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) to authenticate users.
Existing Environment
Sales Data
Litware has online sales data that has the SQL schema shown in the following table.

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q19 079 In the Date table, the date_id column has a format of yyyymmdd and the month column has a format of yyyymm.
The week column in the Date table and the week_id column in the Weekly_Returns table have a format of yyyyww.
The sales_id column in the Sales table represents a unique transaction.
The region_id column can be managed by only one sales manager.
Data Concerns
You are concerned with the quality and completeness of the sales data. You plan to verify the sales data for negative sales amounts.
Reporting Requirements
Litware identifies the following technical requirements:
– Executives require a visual that shows sales by region.
– Regional managers require a visual to analyze weekly sales and returns.
– Sales managers must be able to see the sales data of their respective region only.
– The sales managers require a visual to analyze sales performance versus sales targets.
– The sale department requires reports that contain the number of sales transactions.
– Users must be able to see the month in reports as shown in the following example: Feb 2020.
– The customer service department requires a visual that can be filtered by both sales month and ship month independently.-
HOTSPOT
You need to create a visualization to meet the reporting requirements of the sales managers.
How should you create the visualization? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
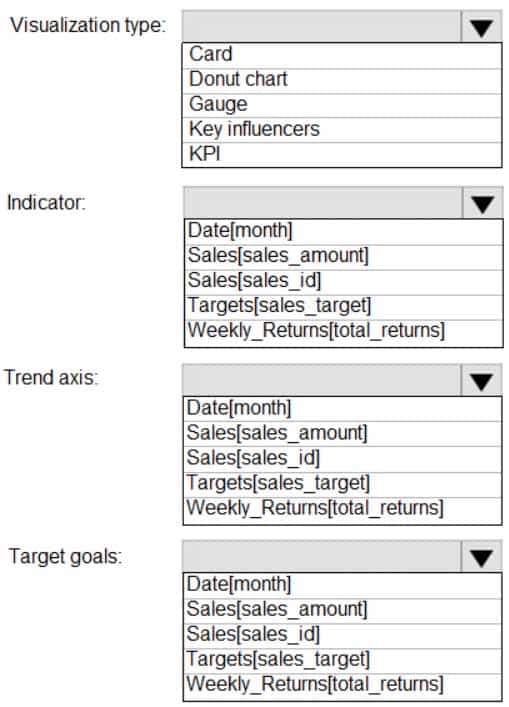
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q19 080 Question 
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q19 080 Answer Explanation:Scenario: The sales managers require a visual to analyze sales performance versus sales targets.
Box 1: KPI
A Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a visual cue that communicates the amount of progress made toward a measurable goal.Box 2: Sales[sales_amount]
Box 3: Date[month]
Time > FiscalMonth. This value will represent the trend.Box 4: Targets[sales_target]
-
HOTSPOT
You need to create a KPI visualization to meet the reporting requirements of the sales managers.
How should you create the visualization? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
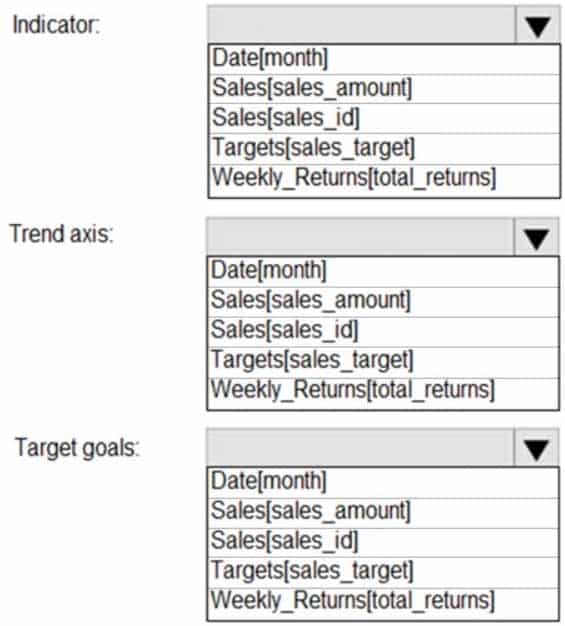
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q19 081 Question 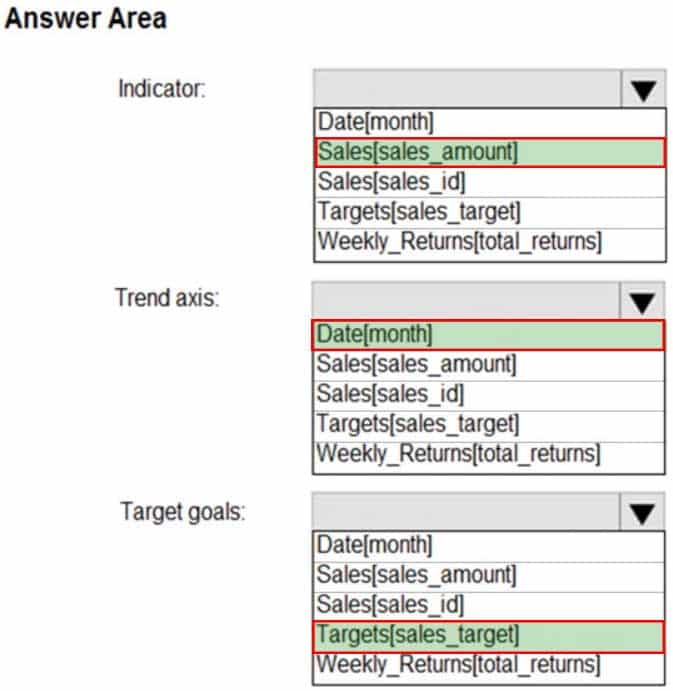
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q19 081 Answer Explanation:Scenario: The sales managers require a visual to analyze sales performance versus sales targets.
Box 1: Sales[sales_amount]
Box 2: Date[month]
Time > FiscalMonth. This value will represent the trend.Box 3: Targets[sales_target]
-
-
Case Study
This is a case study. Case studies are not timed separately. You can use as much exam time as you would like to complete each case. However, there may be additional case studies and sections on this exam. You must manage your time to ensure that you are able to complete all questions included on this exam in the time provided.
To answer the questions included in a case study, you will need to reference information that is provided in the case study. Case studies might contain exhibits and other resources that provide more information about the scenario that is described in the case study. Each question is independent of the other question on this case study.
At the end of this case study, a review screen will appear. This screen allows you to review your answers and to make changes before you move to the next section of the exam. After you begin a new section, you cannot return to this section.
To start the case study
To display the first question on this case study, click the Next button. Use the buttons in the left pane to explore the content of the case study before you answer the questions. Clicking these buttons displays information such as business requirements, existing environment, and problem statements. If the case study has an All Information tab, note that the information displayed is identical to the information displayed on the subsequent tabs. When you are ready to answer a question, click the Question button to return to the question.Overview
Contoso, Ltd. is a manufacturing company that produces outdoor equipment. Contoso has quarterly board meetings for which financial analysts manually prepare Microsoft Excel reports, including profit and loss statements for each of the company’s four business units, a company balance sheet, and net income projections for the next quarter.
Existing Environment
Data and Sources
Data for the reports comes from three sources. Detailed revenue, cost, and expense data comes from an Azure SQL database. Summary balance sheet data comes from Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central. The balance sheet data is not related to the profit and loss results, other than they both relate to dates.
Monthly revenue and expense projections for the next quarter come from a Microsoft SharePoint Online list. Quarterly projections relate to the profit and loss results by using the following shared dimensions: date, business unit, department, and product category.
Net Income Projection Data
Net income projection data is stored in a SharePoint Online list named Projections in the format shown in the following table.
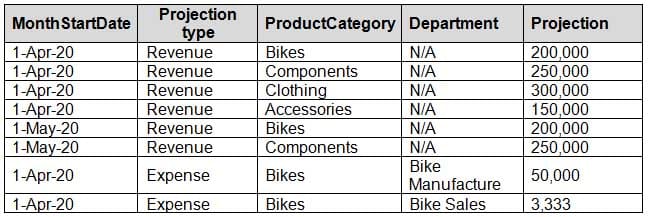
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q20 082 Revenue projections are set at the monthly level and summed to show projections for the quarter.
Balance Sheet Data
The balance sheet data is imported with final balances for each account per month in the format shown in the following table.

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q20 083 There is always a row for each account for each month in the balance sheet data.
Dynamics 365 Business Central Data
Business Central contains a product catalog that shows how products roll up to product categories, which roll up to business units.
Revenue data is provided at the date and product level. Expense data is provided at the date and department level.
Business Issues
Historically, it has taken two analysts a week to prepare the reports for the quarterly board meetings. Also, there is usually at least one issue each quarter where a value in a report is wrong because of a bad cell reference in an Excel formula. On occasion, there are conflicting results in the reports because the products and departments that roll up to each business unit are not defined consistently.
Requirements
Planned Changes
Contoso plans to automate and standardize the quarterly reporting process by using Microsoft Power BI. The company wants to how long it takes to populate reports to less than two days. The company wants to create common logic for business units, products, and departments to be used across all reports, including, but not limited, to the quarterly reporting for the board.
Technical Requirements
Contoso wants the reports and datasets refreshed with minimal manual effort.
The company wants to provide a single package of reports to the board that contains custom navigation and links to supplementary information.
Maintenance, including manually updating data and access, must be minimized as much as possible.
Security Requirements
The reports must be made available to the board from powerbi.com. An Azure Active Directory group will be used to share information with the board.
The analysts responsible for each business unit must see all the data the board sees, except the profit and loss data, which must be restricted to only their business unit’s data. The analysts must be able to build new reports from the dataset that contains the profit and loss data, but any reports that the analysts build must not be included in the quarterly reports for the board. The analysts must not be able to share the quarterly reports with anyone.
Report Requirements
You plan to relate the balance sheet to a standard date table in Power BI in a many-to-one relationship based on the last day of the month. At least one of the balance sheet reports in the quarterly reporting package must show the ending balances for the quarter, as well as for the previous quarter.
Projections must contain a column named Revenue Projection that contains the revenue projection amounts. A relationship must be created from Projections to a table named Date that contains the columns shown in the following table.
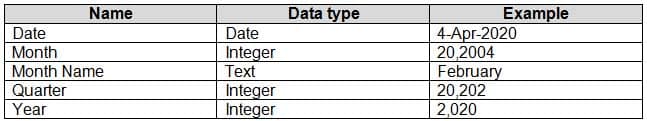
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q20 084 The definitions and attributes of products, departments, and business units must be consistent across all reports.
The board must be able to get the following information from the quarterly reports:
– Revenue trends over time
– Ending balances for each account
– A comparison of expenses versus projections by quarter
– Changes in long-term liabilities from the previous quarter
– A comparison of quarterly revenue versus the same quarter during the prior year-
DRAG DROP
You need to create a DAX measure in the data model that only allows users to see projections at the appropriate level of granularity.
How should you complete the measure? To answer, drag the appropriate values to the correct targets. Each value may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q20 085 Question 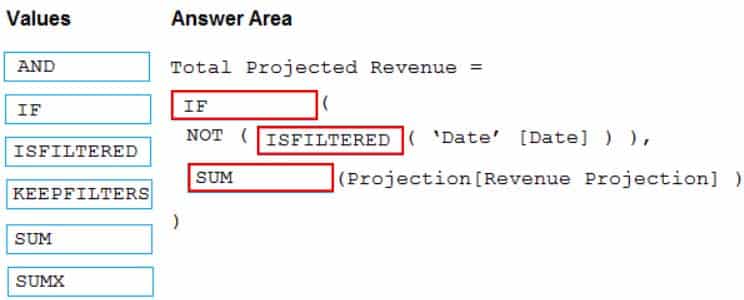
DA-100 Analyzing Data with Microsoft Power BI Part 03 Q20 085 Answer Explanation:Scenario: Revenue projections are set at the monthly level and summed to show projections for the quarter.
Box 1: IF
Box 2: ISFILTERED
ISFILTERED returns TRUE when column Name is being filtered directly. If there is no filter on the column or if the filtering happens because a different column in the same table or in a related table is being filtered then the function returns FALSE.Box 3: SUM
-
Which two types of visualizations can be used in the balance sheet reports to meet the reporting goals? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- a line chart that shows balances by quarter filtered to account categories that are long-term liabilities.
- a clustered column chart that shows balances by date (x-axis) and account category (legend) without filters.
- a clustered column chart that shows balances by quarter filtered to account categories that are long-term liabilities.
- a pie chart that shows balances by account category without filters.
- a ribbon chart that shows balances by quarter and accounts in the legend.
-