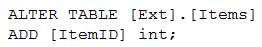DP-203 : Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure : Part 01
DP-203 : Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure : Part 01
-
Case study
This is a case study. Case studies are not timed separately. You can use as much exam time as you would like to complete each case. However, there may be additional case studies and sections on this exam. You must manage your time to ensure that you are able to complete all questions included on this exam in the time provided.
To answer the questions included in a case study, you will need to reference information that is provided in the case study. Case studies might contain exhibits and other resources that provide more information about the scenario that is described in the case study. Each question is independent of the other questions in this case study.
At the end of this case study, a review screen will appear. This screen allows you to review your answers and to make changes before you move to the next section of the exam. After you begin a new section, you cannot return to this section.
To start the case study
To display the first question in this case study, click the Next button. Use the buttons in the left pane to explore the content of the case study before you answer the questions. Clicking these buttons displays information such as business requirements, existing environment, and problem statements. If the case study has an All Information tab, note that the information displayed is identical to the information displayed on the subsequent tabs. When you are ready to answer a question, click the Question button to return to the question.Overview
Contoso, Ltd. is a clothing retailer based in Seattle. The company has 2,000 retail stores across the United States and an emerging online presence.
The network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. The forest it integrated with an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named contoso.com. Contoso has an Azure subscription associated to the contoso.com Azure AD tenant.
Existing Environment
Transactional Data
Contoso has three years of customer, transactional, operational, sourcing, and supplier data comprised of 10 billion records stored across multiple on-premises Microsoft SQL Server servers. The SQL Server instances contain data from various operational systems. The data is loaded into the instances by using SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) packages.
You estimate that combining all product sales transactions into a company-wide sales transactions dataset will result in a single table that contains 5 billion rows, with one row per transaction.
Most queries targeting the sales transactions data will be used to identify which products were sold in retail stores and which products were sold online during different time periods. Sales transaction data that is older than three years will be removed monthly.
You plan to create a retail store table that will contain the address of each retail store. The table will be approximately 2 MB. Queries for retail store sales will include the retail store addresses.
You plan to create a promotional table that will contain a promotion ID. The promotion ID will be associated to a specific product. The product will be identified by a product ID. The table will be approximately 5 GB.
Streaming Twitter Data
The ecommerce department at Contoso develops an Azure logic app that captures trending Twitter feeds referencing the company’s products and pushes the products to Azure Event Hubs.
Planned Changes and Requirements
Planned Changes
Contoso plans to implement the following changes:
– Load the sales transaction dataset to Azure Synapse Analytics.
– Integrate on-premises data stores with Azure Synapse Analytics by using SSIS packages.
– Use Azure Synapse Analytics to analyze Twitter feeds to assess customer sentiments about products.Sales Transaction Dataset Requirements
Contoso identifies the following requirements for the sales transaction dataset:
– Partition data that contains sales transaction records. Partitions must be designed to provide efficient loads by month. Boundary values must belong to the partition on the right.
– Ensure that queries joining and filtering sales transaction records based on product ID complete as quickly as possible.
– Implement a surrogate key to account for changes to the retail store addresses.
– Ensure that data storage costs and performance are predictable.
– Minimize how long it takes to remove old records.Customer Sentiment Analytics Requirements
Contoso identifies the following requirements for customer sentiment analytics:
– Allow Contoso users to use PolyBase in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool to query the content of the data records that host the Twitter feeds. Data must be protected by using row-level security (RLS). The users must be authenticated by using their own Azure AD credentials.
– Maximize the throughput of ingesting Twitter feeds from Event Hubs to Azure Storage without purchasing additional throughput or capacity units.
– Store Twitter feeds in Azure Storage by using Event Hubs Capture. The feeds will be converted into Parquet files.
– Ensure that the data store supports Azure AD-based access control down to the object level.
– Minimize administrative effort to maintain the Twitter feed data records.
– Purge Twitter feed data records that are older than two years.Data Integration Requirements
Contoso identifies the following requirements for data integration:
– Use an Azure service that leverages the existing SSIS packages to ingest on-premises data into datasets stored in a dedicated SQL pool of Azure Synapse Analytics and transform the data.
– Identify a process to ensure that changes to the ingestion and transformation activities can be version-controlled and developed independently by multiple data engineers.-
DRAG DROP
You need to ensure that the Twitter feed data can be analyzed in the dedicated SQL pool. The solution must meet the customer sentiment analytic requirements.
Which three Transact-SQL DDL commands should you run in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate commands from the list of commands to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
NOTE: More than one order of answer choices is correct. You will receive credit for any of the correct orders you select.

DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q01 001 Question 
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q01 001 Answer Explanation:Scenario: Allow Contoso users to use PolyBase in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool to query the content of the data records that host the Twitter feeds. Data must be protected by using row-level security (RLS). The users must be authenticated by using their own Azure AD credentials.
Box 1: CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE
External data sources are used to connect to storage accounts.Box 2: CREATE EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT
CREATE EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT creates an external file format object that defines external data stored in Azure Blob Storage or Azure Data Lake Storage. Creating an external file format is a prerequisite for creating an external table.Box 3: CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE AS SELECT
When used in conjunction with the CREATE TABLE AS SELECT statement, selecting from an external table imports data into a table within the SQL pool. In addition to the COPY statement, external tables are useful for loading data.
Incorrect Answers:
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE
The CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE command creates an external table for Synapse SQL to access data stored in Azure Blob Storage or Azure Data Lake Storage. -
HOTSPOT
You need to design the partitions for the product sales transactions. The solution must meet the sales transaction dataset requirements.
What should you include in the solution? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q01 002 Question 
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q01 002 Answer Explanation:Box 1: Sales date
Scenario: Contoso requirements for data integration include:
– Partition data that contains sales transaction records. Partitions must be designed to provide efficient loads by month. Boundary values must belong to the partition on the right.Box 2: An Azure Synapse Analytics Dedicated SQL pool
Scenario: Contoso requirements for data integration include:
– Ensure that data storage costs and performance are predictable.The size of a dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) is determined by Data Warehousing Units (DWU).
Dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) stores data in relational tables with columnar storage. This format significantly reduces the data storage costs, and improves query performance.
Synapse analytics dedicated sql pool -
You need to implement the surrogate key for the retail store table. The solution must meet the sales transaction dataset requirements.
What should you create?
- a table that has an IDENTITY property
- a system-versioned temporal table
- a user-defined SEQUENCE object
- a table that has a FOREIGN KEY constraint
Explanation:Scenario: Implement a surrogate key to account for changes to the retail store addresses.
A surrogate key on a table is a column with a unique identifier for each row. The key is not generated from the table data. Data modelers like to create surrogate keys on their tables when they design data warehouse models. You can use the IDENTITY property to achieve this goal simply and effectively without affecting load performance.
-
HOTSPOT
You need to design an analytical storage solution for the transactional data. The solution must meet the sales transaction dataset requirements.
What should you include in the solution? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Explanation:Box 1: Round-robin
Round-robin tables are useful for improving loading speed.Scenario: Partition data that contains sales transaction records. Partitions must be designed to provide efficient loads by month.
Box 2: Hash
Hash-distributed tables improve query performance on large fact tables.Scenario:
– You plan to create a promotional table that will contain a promotion ID. The promotion ID will be associated to a specific product. The product will be identified by a product ID. The table will be approximately 5 GB.
– Ensure that queries joining and filtering sales transaction records based on product ID complete as quickly as possible.
-
-
HOTSPOT
You are creating dimensions for a data warehouse in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool.
You create a table by using the Transact-SQL statement shown in the following exhibit.

DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q02 003 Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
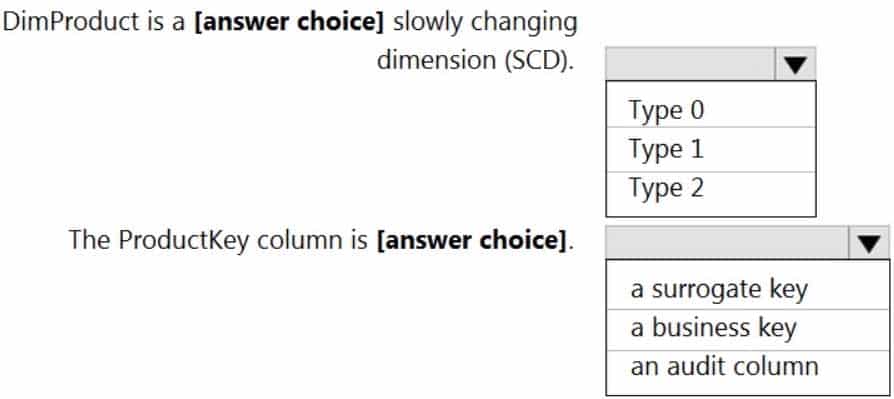
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q02 004 Question 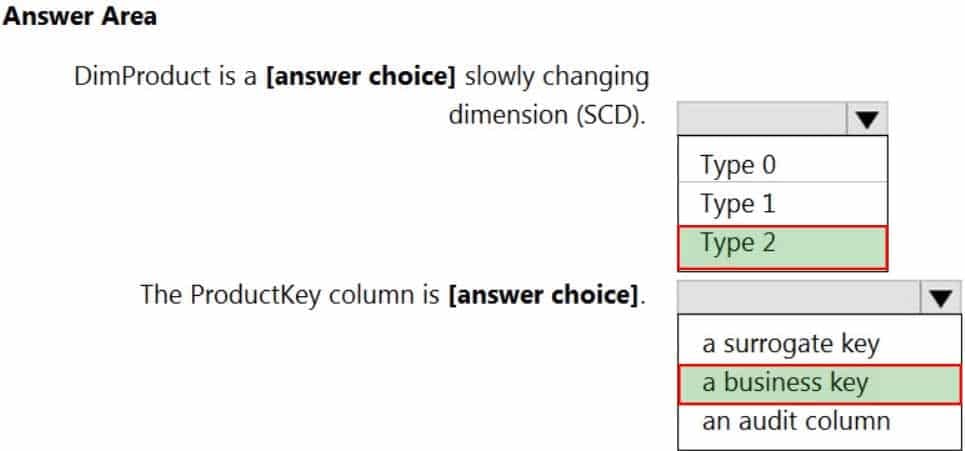
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q02 004 Answer Explanation:Box 1: Type 2
A Type 2 SCD supports versioning of dimension members. Often the source system doesn’t store versions, so the data warehouse load process detects and manages changes in a dimension table. In this case, the dimension table must use a surrogate key to provide a unique reference to a version of the dimension member. It also includes columns that define the date range validity of the version (for example, StartDate and EndDate) and possibly a flag column (for example, IsCurrent) to easily filter by current dimension members.Incorrect Answers:
A Type 1 SCD always reflects the latest values, and when changes in source data are detected, the dimension table data is overwritten.Box 2: a business key
A business key or natural key is an index which identifies uniqueness of a row based on columns that exist naturally in a table according to business rules. For example business keys are customer code in a customer table, composite of sales order header number and sales order item line number within a sales order details table. -
You are designing a fact table named FactPurchase in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool. The table contains purchases from suppliers for a retail store. FactPurchase will contain the following columns.
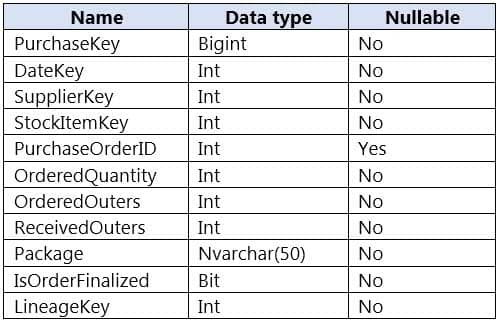
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q03 005 FactPurchase will have 1 million rows of data added daily and will contain three years of data.
Transact-SQL queries similar to the following query will be executed daily.
SELECT SupplierKey, StockItemKey, COUNT(*) FROM FactPurchase WHERE DateKey >= 20210101 AND DateKey <= 20210131 GROUP By SupplierKey, StockItemKey
Which table distribution will minimize query times?
- replicated
- hash-distributed on PurchaseKey
- round-robin
- hash-distributed on DateKey
Explanation:Hash-distributed tables improve query performance on large fact tables, and are the focus of this article. Round-robin tables are useful for improving loading speed.
Incorrect:
Not D: Do not use a date column. . All data for the same date lands in the same distribution. If several users are all filtering on the same date, then only 1 of the 60 distributions do all the processing work. -
You have a table in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool. The table was created by using the following Transact-SQL statement.

DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q04 006 You need to alter the table to meet the following requirements:
– Ensure that users can identify the current manager of employees.
– Support creating an employee reporting hierarchy for your entire company.
– Provide fast lookup of the managers’ attributes such as name and job title.Which column should you add to the table?
-
[ManagerEmployeeID] [int] NULL -
[ManagerEmployeeID] [smallint] NULL
-
[ManagerEmployeeKey] [int] NULL
-
[ManagerName] [varchar](200) NULL
Explanation:
Use the same definition as the EmployeeID column. -
-
You have an Azure Synapse workspace named MyWorkspace that contains an Apache Spark database named mytestdb.
You run the following command in an Azure Synapse Analytics Spark pool in MyWorkspace.
CREATE TABLE mytestdb.myParquetTable( EmployeeID int, EmployeeName string, EmployeeStartDate date) USING Parquet
You then use Spark to insert a row into mytestdb.myParquetTable. The row contains the following data.

DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q05 007 One minute later, you execute the following query from a serverless SQL pool in MyWorkspace.
SELECT EmployeeID FROM mytestdb.dbo.myParquetTable WHERE name = 'Alice';
What will be returned by the query?
- 24
- an error
- a null value
Explanation:Once a database has been created by a Spark job, you can create tables in it with Spark that use Parquet as the storage format. Table names will be converted to lower case and need to be queried using the lower case name. These tables will immediately become available for querying by any of the Azure Synapse workspace Spark pools. They can also be used from any of the Spark jobs subject to permissions.
Note: For external tables, since they are synchronized to serverless SQL pool asynchronously, there will be a delay until they appear.
-
DRAG DROP
You have a table named SalesFact in an enterprise data warehouse in Azure Synapse Analytics. SalesFact contains sales data from the past 36 months and has the following characteristics:
– Is partitioned by month
– Contains one billion rows
– Has clustered columnstore indexesAt the beginning of each month, you need to remove data from SalesFact that is older than 36 months as quickly as possible.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence in a stored procedure? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.

DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q06 008 Question 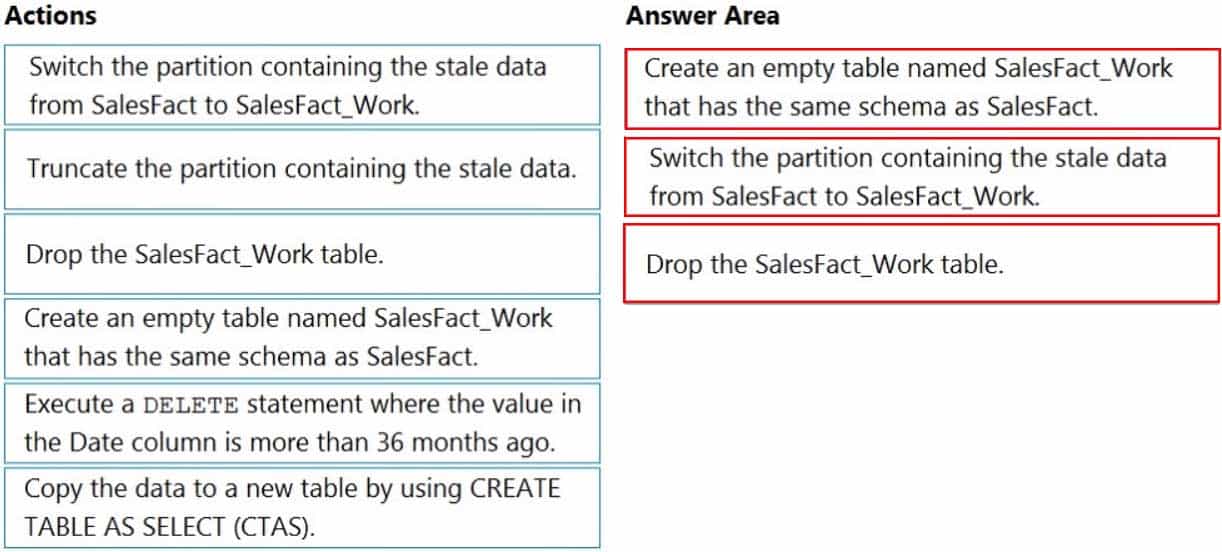
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q06 008 Answer Explanation:Step 1: Create an empty table named SalesFact_work that has the same schema as SalesFact.
Step 2: Switch the partition containing the stale data from SalesFact to SalesFact_Work.
SQL Data Warehouse supports partition splitting, merging, and switching. To switch partitions between two tables, you must ensure that the partitions align on their respective boundaries and that the table definitions match.Loading data into partitions with partition switching is a convenient way stage new data in a table that is not visible to users the switch in the new data.
Step 3: Drop the SalesFact_Work table.
-
You have files and folders in Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 for an Azure Synapse workspace as shown in the following exhibit.
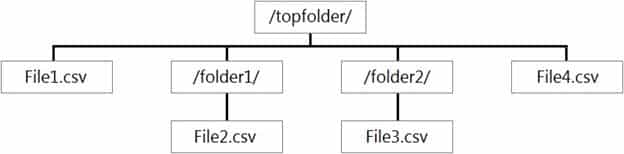
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q07 009 You create an external table named ExtTable that has LOCATION=’/topfolder/’.
When you query ExtTable by using an Azure Synapse Analytics serverless SQL pool, which files are returned?
- File2.csv and File3.csv only
- File1.csv and File4.csv only
- File1.csv, File2.csv, File3.csv, and File4.csv
- File1.csv only
Explanation:To run a T-SQL query over a set of files within a folder or set of folders while treating them as a single entity or rowset, provide a path to a folder or a pattern (using wildcards) over a set of files or folders.
-
HOTSPOT
You are planning the deployment of Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2.
You have the following two reports that will access the data lake:
– Report1: Reads three columns from a file that contains 50 columns.
– Report2: Queries a single record based on a timestamp.You need to recommend in which format to store the data in the data lake to support the reports. The solution must minimize read times.
What should you recommend for each report? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
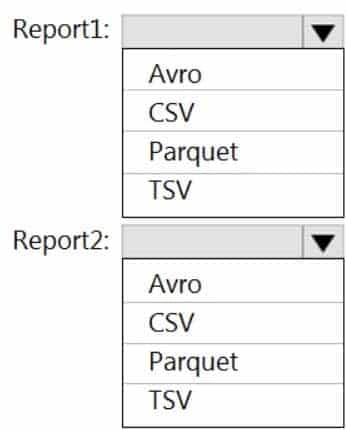
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q08 010 Question 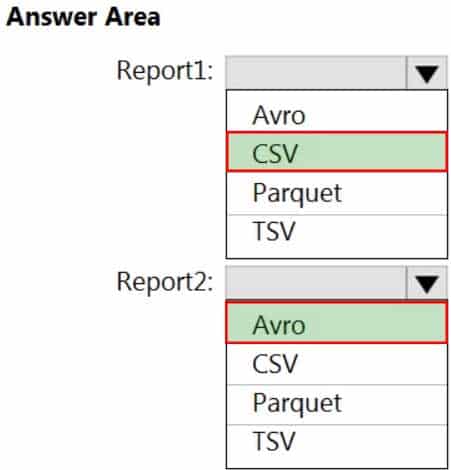
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q08 010 Answer Explanation:Report1: CSV
CSV: The destination writes records as delimited data.Report2: AVRO
AVRO supports timestamps.
Not Parquet, TSV: Not options for Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2. -
You are designing the folder structure for an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 container.
Users will query data by using a variety of services including Azure Databricks and Azure Synapse Analytics serverless SQL pools. The data will be secured by subject area. Most queries will include data from the current year or current month.
Which folder structure should you recommend to support fast queries and simplified folder security?
-
/{SubjectArea}/{DataSource}/{DD}/{MM}/{YYYY}/{FileData}_{YYYY}_{MM}_{DD}.csv -
/{DD}/{MM}/{YYYY}/{SubjectArea}/{DataSource}/{FileData}_{YYYY}_{MM}_{DD}.csv -
/{YYYY}/{MM}/{DD}/{SubjectArea}/{DataSource}/{FileData}_{YYYY}_{MM}_{DD}.csv -
/{SubjectArea}/{DataSource}/{YYYY}/{MM}/{DD}/{FileData}_{YYYY}_{MM}_{DD}.csv
Explanation:There’s an important reason to put the date at the end of the directory structure. If you want to lock down certain regions or subject matters to users/groups, then you can easily do so with the POSIX permissions. Otherwise, if there was a need to restrict a certain security group to viewing just the UK data or certain planes, with the date structure in front a separate permission would be required for numerous directories under every hour directory. Additionally, having the date structure in front would exponentially increase the number of directories as time went on.
Note: In IoT workloads, there can be a great deal of data being landed in the data store that spans across numerous products, devices, organizations, and customers. It’s important to pre-plan the directory layout for organization, security, and efficient processing of the data for down-stream consumers. A general template to consider might be the following layout:
{Region}/{SubjectMatter(s)}/{yyyy}/{mm}/{dd}/{hh}/
-
-
HOTSPOT
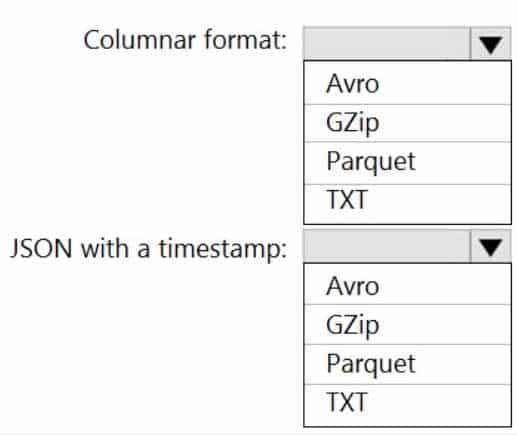
You need to output files from Azure Data Factory.
Which file format should you use for each type of output? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q10 011 Question 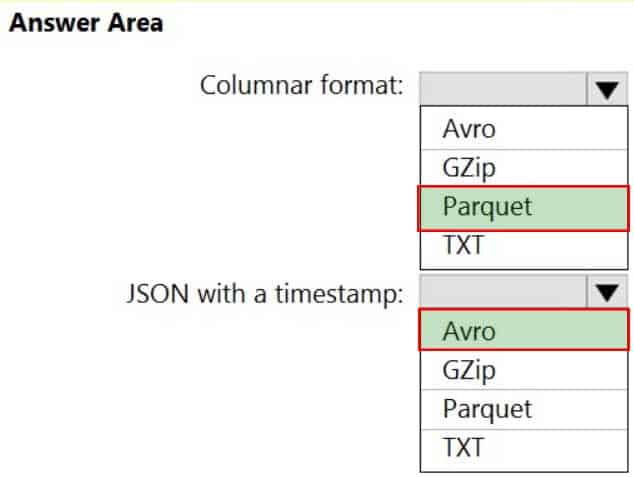
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q10 011 Answer Explanation:Box 1: Parquet
Parquet stores data in columns, while Avro stores data in a row-based format. By their very nature, column-oriented data stores are optimized for read-heavy analytical workloads, while row-based databases are best for write-heavy transactional workloads.Box 2: Avro
An Avro schema is created using JSON format.
AVRO supports timestamps.Note: Azure Data Factory supports the following file formats (not GZip or TXT).
– Avro format
– Binary format
– Delimited text format
– Excel format
– JSON format
– ORC format
– Parquet format
– XML format -
HOTSPOT
You use Azure Data Factory to prepare data to be queried by Azure Synapse Analytics serverless SQL pools.
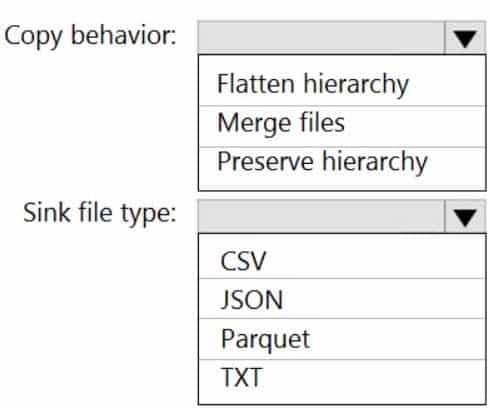
Files are initially ingested into an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account as 10 small JSON files. Each file contains the same data attributes and data from a subsidiary of your company.
You need to move the files to a different folder and transform the data to meet the following requirements:
– Provide the fastest possible query times.
– Automatically infer the schema from the underlying files.How should you configure the Data Factory copy activity? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q11 012 Question 
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q11 012 Answer Explanation:Box 1: Preserver herarchy
Compared to the flat namespace on Blob storage, the hierarchical namespace greatly improves the performance of directory management operations, which improves overall job performance.Box 2: Parquet
Azure Data Factory parquet format is supported for Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2.
Parquet supports the schema property. -
HOTSPOT
You have a data model that you plan to implement in a data warehouse in Azure Synapse Analytics as shown in the following exhibit.
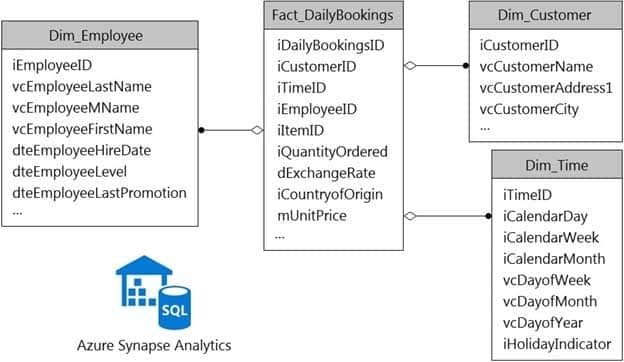
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q12 013 All the dimension tables will be less than 2 GB after compression, and the fact table will be approximately 6 TB. The dimension tables will be relatively static with very few data inserts and updates.
Which type of table should you use for each table? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
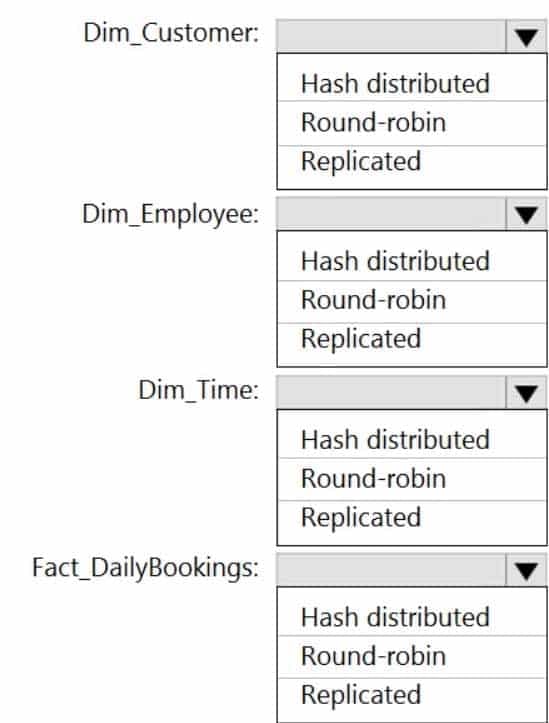
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q12 014 Question 
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q12 014 Answer Explanation:Box 1: Replicated
Replicated tables are ideal for small star-schema dimension tables, because the fact table is often distributed on a column that is not compatible with the connected dimension tables. If this case applies to your schema, consider changing small dimension tables currently implemented as round-robin to replicated.Box 2: Replicated
Box 3: Replicated
Box 4: Hash-distributed
For Fact tables use hash-distribution with clustered columnstore index. Performance improves when two hash tables are joined on the same distribution column. -
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 container.
Data is ingested into the container, and then transformed by a data integration application. The data is NOT modified after that. Users can read files in the container but cannot modify the files.
You need to design a data archiving solution that meets the following requirements:
– New data is accessed frequently and must be available as quickly as possible.
– Data that is older than five years is accessed infrequently but must be available within one second when requested.
– Data that is older than seven years is NOT accessed. After seven years, the data must be persisted at the lowest cost possible.
– Costs must be minimized while maintaining the required availability.How should you manage the data? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point
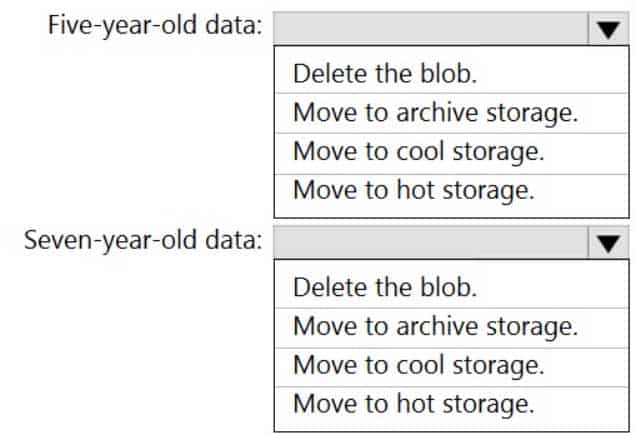
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q13 015 Question 
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q13 015 Answer Explanation:Box 1: Move to cool storage
Box 2: Move to archive storage
Archive – Optimized for storing data that is rarely accessed and stored for at least 180 days with flexible latency requirements, on the order of hours.The following table shows a comparison of premium performance block blob storage, and the hot, cool, and archive access tiers.

DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q13 016 -
DRAG DROP
You need to create a partitioned table in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool.
How should you complete the Transact-SQL statement? To answer, drag the appropriate values to the correct targets. Each value may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q14 017 Question 
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q14 017 Answer Explanation:Box 1: DISTRIBUTION
Table distribution options include DISTRIBUTION = HASH ( distribution_column_name ), assigns each row to one distribution by hashing the value stored in distribution_column_name.Box 2: PARTITION
Table partition options. Syntax:
PARTITION ( partition_column_name RANGE [ LEFT | RIGHT ] FOR VALUES ( [ boundary_value [,…n] ] )) -
You need to design an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool that meets the following requirements:
– Can return an employee record from a given point in time.
– Maintains the latest employee information.
– Minimizes query complexity.How should you model the employee data?
- as a temporal table
- as a SQL graph table
- as a degenerate dimension table
- as a Type 2 slowly changing dimension (SCD) table
Explanation:A Type 2 SCD supports versioning of dimension members. Often the source system doesn’t store versions, so the data warehouse load process detects and manages changes in a dimension table. In this case, the dimension table must use a surrogate key to provide a unique reference to a version of the dimension member. It also includes columns that define the date range validity of the version (for example, StartDate and EndDate) and possibly a flag column (for example, IsCurrent) to easily filter by current dimension members. -
You have an enterprise-wide Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account. The data lake is accessible only through an Azure virtual network named VNET1.
You are building a SQL pool in Azure Synapse that will use data from the data lake.
Your company has a sales team. All the members of the sales team are in an Azure Active Directory group named Sales. POSIX controls are used to assign the Sales group access to the files in the data lake.
You plan to load data to the SQL pool every hour.
You need to ensure that the SQL pool can load the sales data from the data lake.
Which three actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each area selection is worth one point.
- Add the managed identity to the Sales group.
- Use the managed identity as the credentials for the data load process.
- Create a shared access signature (SAS).
- Add your Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) account to the Sales group.
- Use the shared access signature (SAS) as the credentials for the data load process.
- Create a managed identity.
Explanation:The managed identity grants permissions to the dedicated SQL pools in the workspace.
Note: Managed identity for Azure resources is a feature of Azure Active Directory. The feature provides Azure services with an automatically managed identity in Azure AD
-
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool that contains the users shown in the following table.
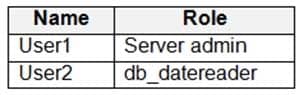
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q17 018 User1 executes a query on the database, and the query returns the results shown in the following exhibit.

DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q17 019 User1 is the only user who has access to the unmasked data.
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q17 020 Question 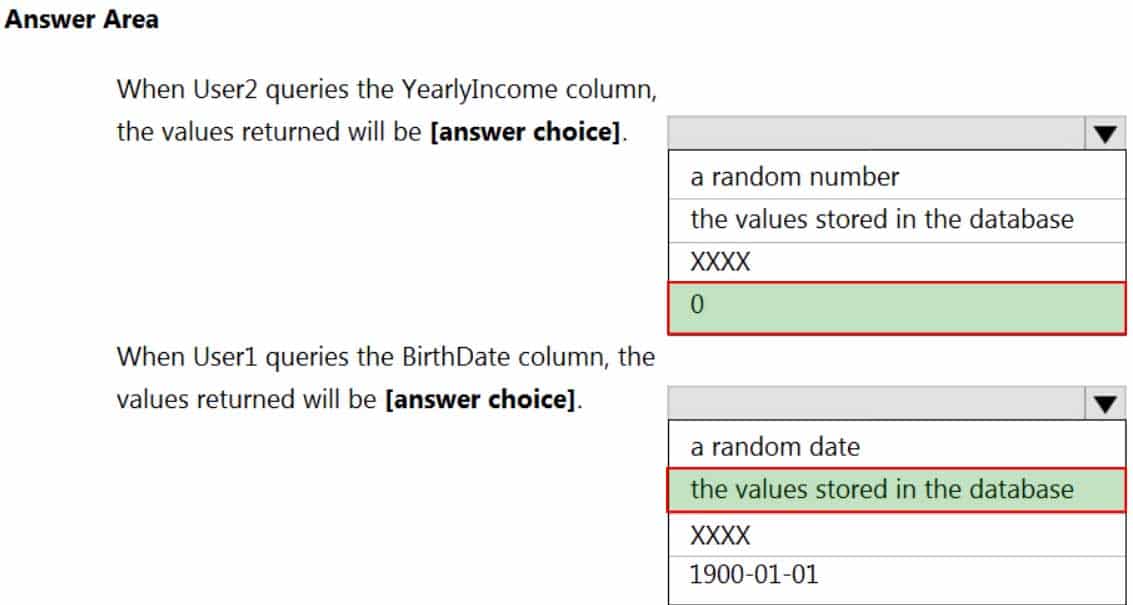
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q17 020 Answer Explanation:Box 1: 0
The YearlyIncome column is of the money data type.
The Default masking function: Full masking according to the data types of the designated fields
– Use a zero value for numeric data types (bigint, bit, decimal, int, money, numeric, smallint, smallmoney, tinyint, float, real).Box 2: the values stored in the database
Users with administrator privileges are always excluded from masking, and see the original data without any mask. -
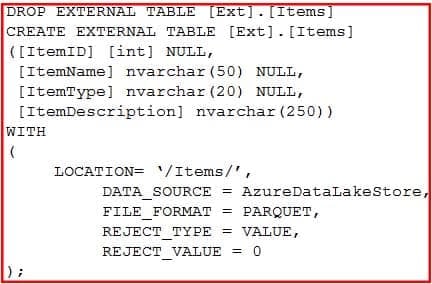
You have an enterprise data warehouse in Azure Synapse Analytics.
Using PolyBase, you create an external table named [Ext].[Items] to query Parquet files stored in Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 without importing the data to the data warehouse.
The external table has three columns.
You discover that the Parquet files have a fourth column named ItemID.
Which command should you run to add the ItemID column to the external table?
Explanation:Incorrect Answers:
A, D: Only these Data Definition Language (DDL) statements are allowed on external tables:– CREATE TABLE and DROP TABLE
– CREATE STATISTICS and DROP STATISTICS
– CREATE VIEW and DROP VIEW -
HOTSPOT
You have two Azure Storage accounts named Storage1 and Storage2. Each account holds one container and has the hierarchical namespace enabled. The system has files that contain data stored in the Apache Parquet format.
You need to copy folders and files from Storage1 to Storage2 by using a Data Factory copy activity. The solution must meet the following requirements:
– No transformations must be performed.
– The original folder structure must be retained.
– Minimize time required to perform the copy activity.How should you configure the copy activity? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
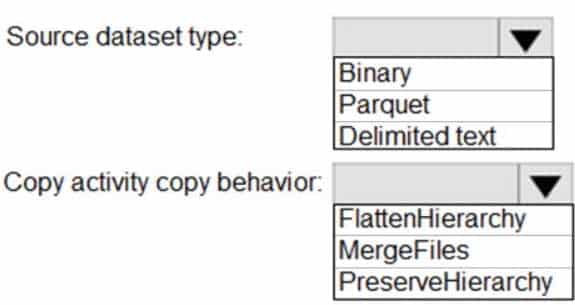
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q19 025 Question 
DP-203 Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure Part 01 Q19 025 Answer Explanation:Box 1: Parquet
For Parquet datasets, the type property of the copy activity source must be set to Parquet Source.Box 2: Preserve Hierarchy
Preserve Hierarchy (default): Preserves the file hierarchy in the target folder. The relative path of the source file to the source folder is identical to the relative path of the target file to the target folder.Incorrect Answers:
– Flatten Hierarchy: All files from the source folder are in the first level of the target folder. The target files have autogenerated names.
– Merge Files: Merges all files from the source folder to one file. If the file name is specified, the merged file name is the specified name. Otherwise, it’s an autogenerated file name. -
You have an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 container that contains 100 TB of data.
You need to ensure that the data in the container is available for read workloads in a secondary region if an outage occurs in the primary region. The solution must minimize costs.
Which type of data redundancy should you use?
- geo-redundant storage (GRS)
- read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS)
- zone-redundant storage (ZRS)
- locally-redundant storage (LRS)
Explanation:Geo-redundant storage (with GRS or GZRS) replicates your data to another physical location in the secondary region to protect against regional outages. However, that data is available to be read only if the customer or Microsoft initiates a failover from the primary to secondary region. When you enable read access to the secondary region, your data is available to be read at all times, including in a situation where the primary region becomes unavailable.
Incorrect Answers:
A: While Geo-redundant storage (GRS) is cheaper than Read-Access Geo-Redundant Storage (RA-GRS), GRS does NOT initiate automatic failover.
C, D: Locally redundant storage (LRS) and Zone-redundant storage (ZRS) provides redundancy within a single region.