MS-203 : Microsoft 365 Messaging : Part 01
MS-203 : Microsoft 365 Messaging : Part 01
-
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have a Microsoft Exchange Server 2019 organization that contains 200 mailboxes.
You need to add a second email address to each mailbox. The address must have a syntax that uses the first letter of each user’s last name, followed by the user’s first name, and then @fabrikam.com.
Solution: You convert all the mailboxes to shared mailboxes, and then you run the
Set-Mailbox cmdlet and specify the -EmailAddressPolicyEnabled $false parameter.Does this meet the goal?
- Yes
- No
Explanation:Email address policies define the rules that create email addresses for recipients in your Exchange organization.
The basic components of an email address policy are:
– Email address templates: Define the email address format for the recipients (for example <firstname>@contoso.com or <lastname>.<firstname>@contoso.com).
– Recipient filter: Specifies the recipients whose email addresses are configured by the policy.
– Priority: Specifies the order to apply the email address policies (important if a recipient is identified by more than one policy).The EmailAddressPolicyEnabled parameter specifies whether to apply email address policies to this recipient. Valid values are:
– $true: Email address policies are applied to this recipient. This is the default value.
– $false: Email address policies aren’t applied to this recipient. -
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have a Microsoft Exchange Server 2019 organization that contains 200 mailboxes.
You need to add a second email address to each mailbox. The address must have a syntax that uses the first letter of each user’s last name, followed by the user’s first name, and then @fabrikam.com.
Solution: You create an email address policy that uses the %1s%g@fabrikam.com email address format.
Does this meet the goal?
- Yes
- No
-
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have a Microsoft Exchange Server 2019 organization that contains 200 mailboxes.
You need to add a second email address to each mailbox. The address must have a syntax that uses the first letter of each user’s last name, followed by the user’s first name, and then @fabrikam.com.
Solution: You convert all the mailboxes to shared mailboxes, and then you run the
Set-Mailbox cmdlet and specify the -EmailAddressPolicyEnabled $true parameter.Does this meet the goal?
- Yes
- No
Explanation:Email address policies define the rules that create email addresses for recipients in your Exchange organization.
The basic components of an email address policy are:
– Email address templates: Define the email address format for the recipients (for example <firstname>@contoso.com or <lastname>.<firstname>@contoso.com).
– Recipient filter: Specifies the recipients whose email addresses are configured by the policy.
– Priority: Specifies the order to apply the email address policies (important if a recipient is identified by more than one policy).The EmailAddressPolicyEnabled parameter specifies whether to apply email address policies to this recipient. Valid values are:
– $true: Email address policies are applied to this recipient. This is the default value.
– $false: Email address policies aren’t applied to this recipient. -
HOTSPOT
You have a Microsoft Exchange Online subscription.
You run the following command.
Set-ActiveSyncOrganizationSettings –DefaultAccessLevel Block
You run Get-ActiveSyncDeviceAccessRule | fl Identity,AccessLevel,Characteristic,QueryString, and you receive the following output.

MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q04 001 For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q04 002 Question 
MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q04 002 Answer -
DRAG DROP
You have a Microsoft Exchange Online tenant.
You enable hierarchical address books (HABs).
You create a new distribution group named Contoso.
You need to configure the Contoso group as the root of the hierarchy. The members of the group must appear in the hierarchy.
How should you complete the PowerShell commands? To answer, drag the appropriate cmdlets to the correct targets. Each cmdlet may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q05 003 Question 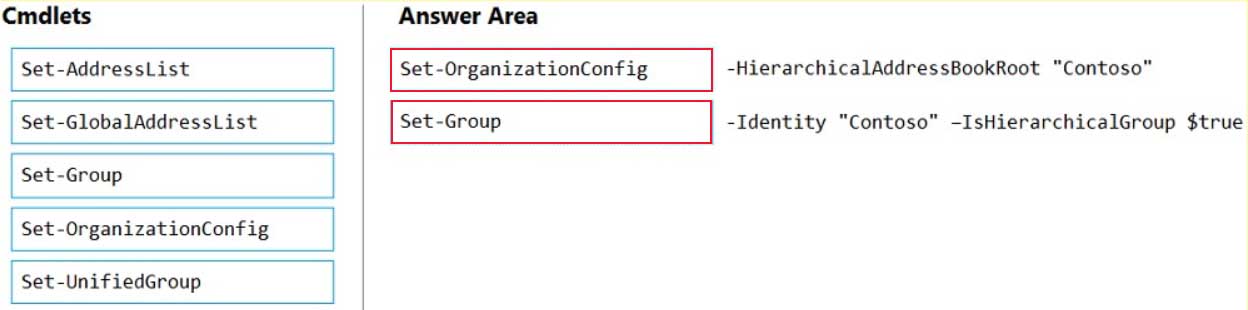
MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q05 003 Answer -
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription.
Several users report today that they cannot access email from their mobile device. They successfully accessed their email from the same device yesterday.
You need to identify which mobile device access rule applies to the devices.
Which cmdlet should you run?
-
Get-ActiveSyncDeviceClass
-
Get-ActiveSyncOrganizationSettings
-
Get-MobileDevice -
Get-MobileDeviceMailboxPolicy
Explanation:The Get-MobileDevice cmdlet returns identification, configuration, and status information for each mobile device.
Note: The Get-MobileDeviceStatistics cmdlet can also be used.
-
-
You have a Microsoft Exchange Online tenant.
All users are assigned only an Office 365 Enterprise E3 license.
You need to ensure that the users can use only Microsoft Outlook to connect to their Microsoft 365 mailbox when they connect from an Android device.
What should you create?
- a conditional access policy in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD)
- a data loss prevention (DLP) policy
- an app protection policy Microsoft Endpoint Manager
- a connection filter policy in Exchange Online Protection (EOP)
Explanation:Use the ApprovedApplicationList with the New-MobileDeviceMailboxPolicy cmdlet. This option is only available in PowerShell and not in the Exchange Admin Console.
Not A. Conditional Access Policy requires Azure Premium P1 which is not included in an Office 365 Enterprise E3 license.
-
You manage a hybrid deployment between Microsoft Exchange Online and on-premises Exchange Server 2019. The deployment contains a primary SMTP domain named contoso.com.
Users have email addresses that use a syntax of firstname.lastname@contoso.com.
A user named Ben Smith receives a new client computer. You configure the computer to access Ben Smith’s mailbox. Ben Smith reports that he cannot connect to his mailbox from the new computer.
You verify that other users can connect successfully to their mailbox and that new users can discover their mailboxes by using Autodiscover.
You need to ensure that Ben Smith can connect to his mailbox from the new computer.
What should you do?
- Modify the primarySmtpAddress property fox the mailbox of Ben Smith.
- Modify the RemoteRoutingAddress parameter for the mailbox of Ben Smith.
- Modify the email address of Ben Smith to use a syntax of lastname.firstname@contoso.com.
- Modify the email address of Ben Smith to use a syntax of firstname.lastname@contoso.onmicrosoft.com.
-
You have a Microsoft Exchange Online tenant that contains 1,000 user mailboxes and 10 mail-enabled users. The mail-enabled users have email addresses in two SMTP domains named fabrikam.com and contoso.com.
You need to convert the mail-enabled users into user mailboxes.
What should you do first?
- Remove the remote domains of fabrikam.com and contoso.com.
- Assign a license to each user.
- Add the users to an Office 365 group.
- Modify the email forwarding settings of each user.
Explanation:
You need to remove the remote domains first then assign a license to the user account. -
You have two mailboxes named Mailbox1 and Mailbox2 that have the ProhibitSendReceiveQuota parameter set to 50 GB.
From a Microsoft Exchange Online tenant, you run the following PowerShell command.

MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q10 004 You review the license status of each mailbox and discover the configurations shown in the following table.

MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q10 005 You need to increase the quota for Mailbox1 and Mailbox2.
What should you do first?
- Enable an archive for each mailbox.
- Assign a license to each mailbox.
- Place both mailboxes on retention hold.
- Convert each mailbox into an equipment mailbox.
Explanation:
Shared and resource mailboxes don’t require a license. However, without a license, these mailboxes are limited to 50 GB. To increase the mailbox size, an E3 or E5 license must be assigned. This will increase the mailbox to 100 GB. -
You have 1,000 user accounts that are each licensed for Microsoft 365. Each user account has a Microsoft Exchange Online mailbox.
Ten of the user accounts are configured as service accounts for applications. The applications send event notifications to the mailboxes of the service accounts by using SMTP. The developers of each application have delegated access to the mailbox of their respective application.
You need to ensure that all the event notifications sent by the applications are retained in the service account mailboxes so that new developers can review older notifications. The developers must be able to view only the notifications for their respective application. The solution must minimize licensing costs.
What should you do?
- Replace the service account mailboxes with a single user mailbox that contains journal rules.
- Replace the service account mailboxes with a mail-enabled group.
- Convert the service account mailboxes into shared mailboxes.
- Convert the service account mailboxes into mail-enabled users.
-
All the users in your company have Microsoft 365 mailboxes.
Each user connects to Microsoft Exchange Online and OneDrive for Business from a personal computer that runs Windows 10.
You need to ensure that the users can save attachments to OneDrive for Business only when they connect to their mailbox from Outlook on the web.
What should you create?
- an Exchange ActiveSync device access rule
- an app protection policy in Microsoft Endpoint Manager
- an Outlook Web App policy in Exchange Online
- a device compliance policy in Microsoft Endpoint Manager
-
HOTSPOT
You have a Microsoft Exchange Server 2019 organization.
You have the Address Book Policies (ABP) and address lists in the following table.
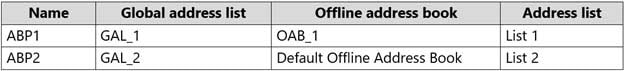
MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q13 006 You have the users in the following table.

MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q13 007 You assign ABP1 to User1 and User2.
User3 is NOT assigned to an Address Book Policy.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q13 008 Question 
MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q13 008 Answer -
You have a Microsoft Exchange Server 2019 organization.
A compliance manager plans to create retention policies for the mailboxes of executive users. The policies will move specific emails to an archive mailbox.
You need to create an archive mailbox for each executive user.
What should you do?
- Run the Set-Mailbox cmdlet.
- Enable In-Place Archiving for each mailbox.
- Enable mailbox journaling.
- Run the New-Mailbox cmdlet.
-
HOTSPOT
You need to create an address list that contains all the users who have a title of Director.
How should you complete the command? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q15 009 Question 
MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q15 009 Answer -
HOTSPOT
You have an address book policy named Contoso-US that contains an address list named Contoso-Finance.
You need to add an address list named Contoso-Marketing to Contoso-US without removing Contoso-Finance.
How should you complete the command? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
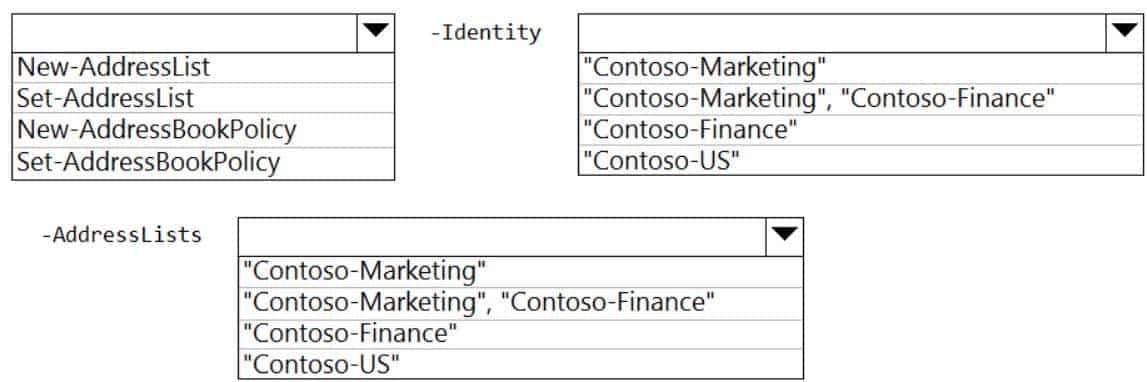
MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q16 010 Question 
MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q16 010 Answer -
HOTSPOT
Your company named ADatum Corporation has a Microsoft Exchange Online subscription that contains the sharing policies shown in the following table.

MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q17 011 The subscription contains the mailboxes shown in the following table.
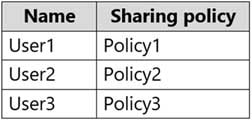
MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q17 012 ADatum does business with the partner companies shown in the following table.

MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q17 013 For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q17 014 Question 
MS-203 Microsoft 365 Messaging Part 01 Q17 014 Answer -
You have a Microsoft Exchange Server 2019 hybrid deployment.
You need to change the free/busy data access sharing level between the on-premises organization and Exchange Online.
What should you do?
- Modify the organization relationship.
- Create an individual sharing policy.
- Run the Hybrid Configuration wizard.
- Create an organization sharing policy.
-
You have a Microsoft Exchange Server 2019 organization.
You purchase a Microsoft Office 365 E5 subscription.
You plan to implement Exchange Modern Hybrid and free/busy sharing.
Which two components should you configure for the planned implementation? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- a sharing policy
- a federation trust
- an organization relationship
- a relying party trust
- Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS)
-
You have a Microsoft Exchange Online tenant that uses an email domain named @contoso.com.
You recently purchased an email domain named fabrikam.com.
You need to ensure that all the users in the tenant can receive email messages by using the @fabrikam.com email domain. The solution must ensure that the users can continue to receive email by using the @contoso.com email domain.
Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- From the Microsoft 365 admin center, add the fabrikam.com email domain.
- From the Exchange admin center, add an accepted domain for fabrikam.com.
- From the Microsoft 365 admin center, modify the organization profile.
- From the Exchange admin center, add a remote domain for fabrikam.com.
- From the Exchange Management Shell, create a script that runs the Set-Mailbox cmdlet.
Explanation:
A: the first step is to add the Fabrikam.com domain to Microsoft 365. You would also need to verify the domain (verify that you own the domain).
E: create a script that runs the Set-Mailbox cmdlet to add an @fabrikam.com email address to each mailbox.