Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 24-26 | Checkpoint Exam: ARP, DNS, DHCP and the Transport Layer Answers Full 100% 2025
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 24-26 | Checkpoint Exam: ARP, DNS, DHCP and the Transport Layer Answers Full 100% 2025
This Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 24-26 section for Checkpoint Exam: ARP, DNS, DHCP and the Transport Layer Answers which is provided with the correct answers to 100% of the questions. This module 24-26 exam answer is used for the Cisco SkillsForAll platform which is the latest version just released in 2025. Review all the questions and answers here, then you will meet randomly 21 questions from all here.
-
What statement describes the function of the Address Resolution Protocol? *
- ARP is used to discover the IP address of any host on a diccerent network.
- ARP is used to discover the IP address of any host on the local network.
- ARP is used to discover the MAC address of any host on the local network.
- ARP is used to discover the MAC address of any host on a diccerent network.
Explanation: When a PC wants to send data on the network, it always knows the IP address of the destination. However, it also needs to discover the MAC address of the destination. ARP is the protocol that is used to discover the MAC address of a host that belongs to the same network.
-
A user sends an HTTP request to a web server on a remote network. During encapsulation for this request, what information is added to the address field of a frame to indicate the destination?
- the IP address of the default gateway
- the MAC address of the default gateway
- the MAC address of the destination host
- the network domain of the destination host
Explanation: A frame is encapsulated with source and destination MAC addresses. The source device will not know the MAC address of the remote host. An ARP request will be sent by the source and will be responded to by the router. The router will respond with the MAC address of its interface, the one which is connected to the same network as the source.
-
Refer to the exhibit. PC1 issues an ARP request because it needs to send a packet to PC3. In this scenario, what will happen next?
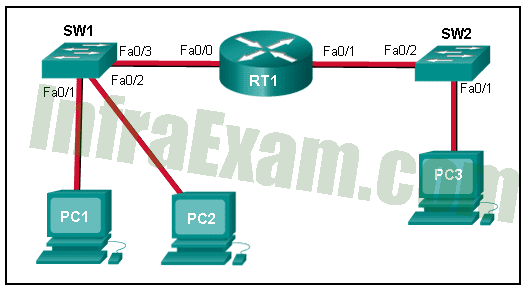
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 24-26 Checkpoint Exam ARP, DNS, DHCP and the Transport Layer Answers 03 - RT1 will send an ARP reply with its own Fa0/0 MAC address.
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with its own Fa0/1 MAC address.
- RT1 will forward the ARP request to PC3.
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with the PC3 MAC address.
- SW1 will send an ARP reply with its Fa0/1 MAC address.
Explanation: When a network device has to communicate with a device on another network, it broadcasts an ARP request asking for the default gateway MAC address. The default gateway (RT1) unicasts an ARP reply with the Fa0/0 MAC address.
-
Refer to the exhibit.
What does R1 use as the MAC address of the destination when constructing the frame that will go from R1 to Server B?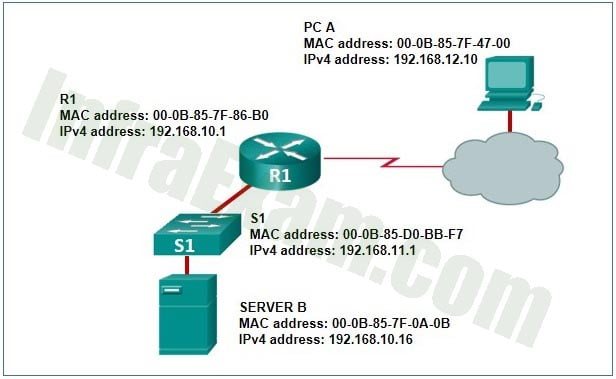
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 24-26 Checkpoint Exam ARP, DNS, DHCP and the Transport Layer Answers 02 - The packet is encapsulated into a PPP frame, and R1 adds the PPP destination address to the frame.
- If the destination MAC address that corresponds to the IPv4 address is not in the ARP cache, R1 sends an ARP request.
- R1 leaves the field blank and forwards the data to the PC.
- R1 uses the destination MAC address of S1.
Explanation: Communication inside a local network uses Address Resolution Protocol to obtain a MAC address from a known IPv4 address. A MAC address is needed to construct the frame in which the packet is encapsulated.
-
What are two problems that can be caused by a large number of ARP request and reply messages?
(Choose two.)- A large number of ARP request and reply messages may slow down the switching process, leading the switch to make many changes in its MAC table.
- The network may become overloaded because ARP reply messages have a very large payload due to the 48-bit MAC address and 32-bit IP address that they contain.
- Switches become overloaded because they concentrate all the traccic from the attached subnets.
- All ARP request messages must be processed by all nodes on the local network.
- The ARP request is sent as a broadcast, and will flood the entire subnet.
Explanation: ARP requests are sent as broadcasts:
(1) All nodes will receive them, and they will be processed by software, interrupting the CPU.
(2) The switch forwards (floods) Layer 2 broadcasts to all ports.A switch does not change its MAC table based on ARP request or reply messages. The switch populates the MAC table using the source MAC address of all frames. The ARP payload is very small and does not overload the switch.
-
Refer to the exhibit. When PC1 wants to send a packet to PC3, the IP address of the device that will respond to the ARP request is
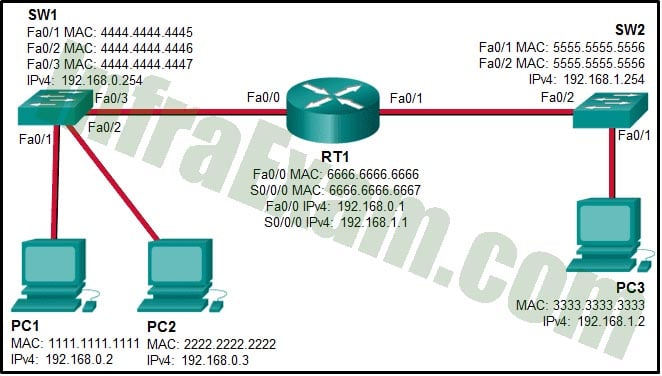
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 24-26 Checkpoint Exam ARP, DNS, DHCP and the Transport Layer Answers 04 - 192.168.1.1
- 192.168.0.1
- 192.168.0.2
- 192.168.0.254
- 192.168.1.2
- 192.168.0.3
- 192.168.1.254
Explanation: When a network device has to communicate with a device on another network, it broadcasts an ARP request asking for the default gateway MAC address. The default gateway (RT1) unicasts an ARP reply with the Fa0/0 MAC address.
-
What is the protocol that is used to discover a physical address from a known logical address and what message type does it use?
- DNS, unicast
- PING, broadcast
- ARP, broadcast
- ARP, multicast
- PING, multicast
- DNS, broadcast
Explanation: An ARP request is broadcast to all devices on a LAN segment which seek the MAC address for a known IP address. Pings are used to verify connectivity between two devices, and DNS resolves URLs to IP addresses.
-
Which DHCP IPv4 message contains the following information?
Destination address: 255.255.255.255
Client IPv4 address: 0.0.0.0
Default gateway address: 0.0.0.0
Subnet mask: 0.0.0.0- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOccER
- DHCPACK
Explanation: A client will first send the DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message to find DHCPv4 servers on the network. This message will have the limited broadcast address, 255.255.255.255, as the destination address. The client IPv4 address, the default gateway address, and subnet fields will all be 0.0.0.0 because these have not yet been configured on the client. When the DHCPv4 server receives a DHCPDISCOVER message, it reserves an available IPv4 address to lease to the client and sends the unicast DHCPOccER message to the requesting client. When the client receives the DHCPOccER from the server, it sends back a DHCPREQUEST broadcast message. On receiving the DHCPREQUEST message, the server replies with a unicast DHCPACK message.
-
Which two tasks can be performed by a local DNS server? (Choose two.)
- mapping name-to-IP addresses for internal hosts
- providing IP addresses to local hosts
- forwarding name resolution requests between servers
- retrieving email messages
- allowing data transfer between two network devices
Explanation: Two important functions of DNS are to (1) provide IP addresses for domain names such as www.cisco.com, and (2) forward requests that cannot be resolved to other servers in order to provide domain name to IP address translation. DHCP provides IP addressing information to local devices. A file transfer protocol such as FTP, SFTP, or TFTP provides file sharing services. IMAP or POP can be used to retrieve an email message from a server.
-
Which three statements describe a DHCP Discover message? (Choose three.)
- All hosts receive the message, but only a DHCP server replies.
- Only the DHCP server receives the message.
- The message comes from a client seeking an IP address.
- The destination IP address is 255.255.255.255.
- The source MAC address is 48 ones (cc-cc-cc-cc-cc-cc).
- The message comes from a server occering an IP address.
Explanation: When a host configured to use DHCP powers up on a network it sends a DHCPDISCOVER message. cc-cc-cc-cc-cc-cc is the L2 broadcast address. A DHCP server replies with a unicast DHCPOccER message back to the host.
-
What IPv4-related DNS record type is used by a DNS server in response to a host requesting for a web server address via the URL?
- MX record
- A record
- AAAA record
- NS record
Explanation: A DNS server uses an A record type for an IPv4 end device address. The AAAA record is for an IPv6 end device address. The MX record is used to map the domain name to mail exchange servers. The NS record indicates the authoritative name server.
-
A DHCP configured PC boots up. What is the order of the messages that are sent and received by this PC in order to obtain an appropriate IP address?
- DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPOccER, DHCPACK
- DHCPREQUEST, DHCPOccER, DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPACK
- DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPOccER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPACK
- DHCPOccER, DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPACK
Explanation: During the boot process, the PC starts by broadcasting a DHCPDISCOVER message to request an available IP address. A DHCP server replies with a DHCPOccER message, which occers a lease to the device. This message contains the IP address and other information. The PC may receive multiple DHCPOccER messages if there is more than one DHCP server. In this case, the PC must choose one of the server DHCP occerings. The PC broadcasts a DHCPREQUEST message that identifies the explicit server and lease occer that the PC is accepting. Then the server will return a DHCPACK message that acknowledges to the PC that the lease is finalized.
-
A user reports that the corporate web server cannot be accessed. A technician verifies that the web server can be accessed by its IP address. What are two possible causes of the problem? (Choose two.)
- The web server is misconfigured.
- The network connection is down.
- The default gateway address is misconfigured on the workstation.
- The DNS server address is misconfigured on the workstation.
- The web server information is misconfigured on the DNS server.
Explanation: The fact that the web server can be accessed by its IP address indicates that the web server is working and there is connectivity between the workstation and the web server. However, the web server domain name is not resolving correctly to its IP address. This could be caused by a misconfiguration of the DNS server IP address on the workstation or the wrong entry of the web server in the DNS server.
-
Which two commands could be used to check if DNS name resolution is working properly on a Windows PC? (Choose two.)
- ipconfig /flushdns
- nbtstat cisco.com
- nslookup cisco.com
- net cisco.com
- ping cisco.com
Explanation: The ping command tests the connection between two hosts. When ping uses a host domain name to test the connection, the resolver on the PC will first perform the name resolution to query the DNS server for the IP address of the host. If the ping command is unable to resolve the domain name to an IP address, an error will result.
Nslookup is a tool for testing and troubleshooting DNS servers.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Host A and the file server have established a TCP session to exchange data. What acknowledgement number will the file server send to host A to acknowledge receipt of the first three segments of data?
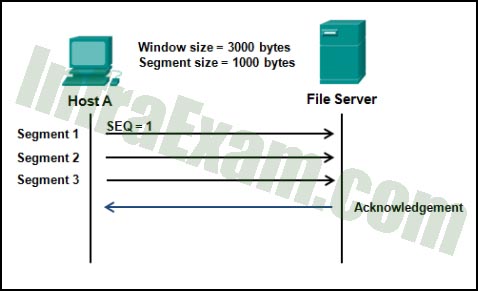
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 24-26 Checkpoint Exam ARP, DNS, DHCP and the Transport Layer Answers 01 - 3001
- 1000
- 3000
- 1002
- 4000
Explanation: The file server will send back an acknowledgement number of 3001 to host A after receiving the first three segments. The starting sequence number was 1. 1000 bytes were sent in each of the three segments for a total of 3000 bytes. Because the initial sequence number was 1, the last byte sent was byte number 3000. The file server will now expect to receive byte number 3001 and above. Therefore, it communicates to host A through the acknowledgement number of 3001.
-
What is a socket?
- the combination of the source and destination sequence numbers and port numbers
- the combination of the source and destination sequence and acknowledgment numbers
- the combination of the source and destination IP address and source and destination Ethernet address
- the combination of a source IP address and port number or a destination IP address and port number
Explanation: A socket is a combination of the source IP address and source port or the destination IP address and the destination port number.
-
A client is establishing a TCP session with a server. How is the acknowledgment number in the response segment to the client determined?
- The acknowledgment number field uses a random source port number in response to the client.
- The acknowledgment number is set to 1 to signify an acknowledgment packet back to the client.
- The acknowledgment number is set to 11 to signify an acknowledgment packet and synchronization packet back to the client.
- The acknowledgment number field is modified by adding 1 to the randomly chosen initial sequence number in response to the client.
Explanation: To establish a session with the client, the TCP server will acknowledge the receipt of the SYN segment from the client. The server sends a segment back to the client with the ACK flag set indicating that the acknowledgment number is significant.The value of the acknowledgment number field is equal to the randomly chosen initial sequence number (ISN) plus 1.
-
A host device needs to send a large video file across the network while providing data communication to other users. Which feature will allow diccerent communication streams to occur at the same time, without having a single data stream using all available bandwidth?
- multiplexing
- window size
- acknowledgments
- port numbers
Explanation: Multiplexing is useful for interleaving multiple communication streams. Window size is used to slow down the rate of data communication. Port numbers are used to pass data streams to their proper applications. Acknowledgments are used to notify a sending device that a stream of data packets has or has not been received.
-
What TCP mechanism is used to enhance performance by allowing a device to continuously send a steady stream of segments as long as the device is also receiving necessary acknowledgements?
- three-way handshake
- socket pair
- two-way handshake
- sliding window
Explanation: TCP uses windows to attempt to manage the rate of transmission to the maximum flow that the network and destination device can support while minimizing loss and retransmissions. When overwhelmed with data, the destination can send a request to reduce the of the window. The process of the destination sending acknowledgments as it processes bytes received and the continual adjustment of the source send window is known as sliding windows.
-
What does a client application select for a TCP or UDP source port number?
- a random value in the range of the registered ports
- a predefined value in the well-known port range
- a predefined value in the range of the registered ports
- a random value in the well-known port range
Explanation: The client randomly selects an available source port in the range of the registered ports.
-
Which two TCP header fields are used to confirm receipt of data? (Choose two.)
- FCS
- sequence number
- acknowledgment number
- preamble
- checksum
Explanation: Together the TCP sequence number and acknowledgment number fields are used by the receiver to inform the sender of the bytes of data that the receiver has accepted.
-
When a computer is pinging another computer for the first time, what type of message does it place on the network to determine the MAC address of the other device?
- a multicast to any Layer 3 devices that are connected to the local network
- an RFI (Request for Information) message
- an ARP request
- an ICMP ping
Explanation: An ARP request is used to determine any unknown MAC address when the destination IP address is known. In an IPv4-based network, this request is sent as a Layer 2 broadcast.