Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 5-7 | Checkpoint Exam: Network Access Answers Full 100% 2023 2024
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 5-7 | Checkpoint Exam: Network Access Answers Full 100% 2023 2024
This Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 5-7 section for Checkpoint Exam: Build a Small Network Answers which is provided with the correct answers to 100% of the questions. This module 5-7 exam answer is used for the Cisco SkillsForAll platform which is the latest version just released in 2023 2024. Review all the questions and answers here, then you will meet randomly 21 questions from all here.
-
Which three acronyms/initialisms represent standards organizations? (Choose three.)
- IANA
- IEEE
- MAC
- IETF
- TCP/IP
- OSI
Explanation and Hint:
The application layer of the TCP/IP model maps to the top three layers of the OSI model, which are the application, presentation, and session layers.
-
Which statement is true about the TCP/IP and OSI models?
- The OSI Layer 7 and the TCP/IP application layer provide identical functions.
- The TCP/IP network access layer has similar functions to the OSI network layer.
- The first three OSI layers describe general services that are also provided by the TCP/IP internet layer.
- The TCP/IP transport layer and OSI Layer 4 provide similar services and functions.
Explanation and Hint:
The TCP/IP internet layer provides the same function as the OSI network layer. The transport layer of both the TCP/IP and OSI models provides the same function. The TCP/IP application layer includes the same functions as OSI Layers 5, 6, and 7.
-
Match the TCP/IP model layer to the function.
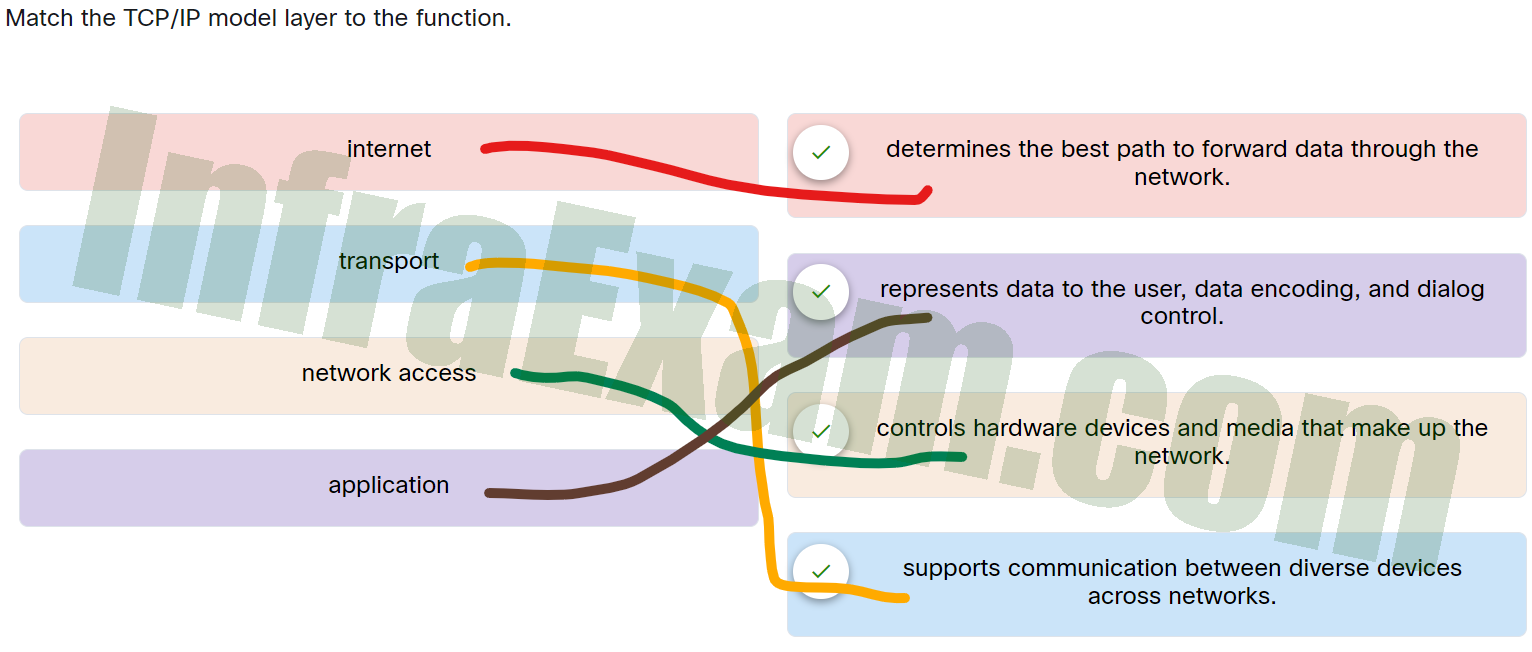
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 5 – 7 Checkpoint Exam Answers 001 - application —> represents data to the user, data encoding, and dialog control.
- network access —> controls hardware devices and media that make up the network.
- transport —> supports communication between diverse devices across networks.
- internet —> determines the best path to forward data through the network.
Explanation and Hint:
Place the options in the following order:
Internet Determines the best path to forward data through the network. Application Represents data to the user, data encoding, and dialog control. Network access Controls hardware devices and media that make up the network. Transport Supports communication between diverse devices across networks.
-
Which statement defines a data communications protocol?
- a set of product standards for types of network devices
- a set of rules that govern the communication process
- an exchange agreement of network devices among vendors
- an alliance of network device manufacturers
Explanation and Hint:
A data communication protocol is a set of rules that govern the communication process.
-
Which three elements do all communication methods have in common? (Choose three.)
- message destination
- transmission medium
- message priority
- message source
- message type
- message data
Explanation and Hint:
All communication methods include a message source, destination, and a transmission medium.
-
Match the protocol function to the description while taking into consideration that a network client is visiting a web site.
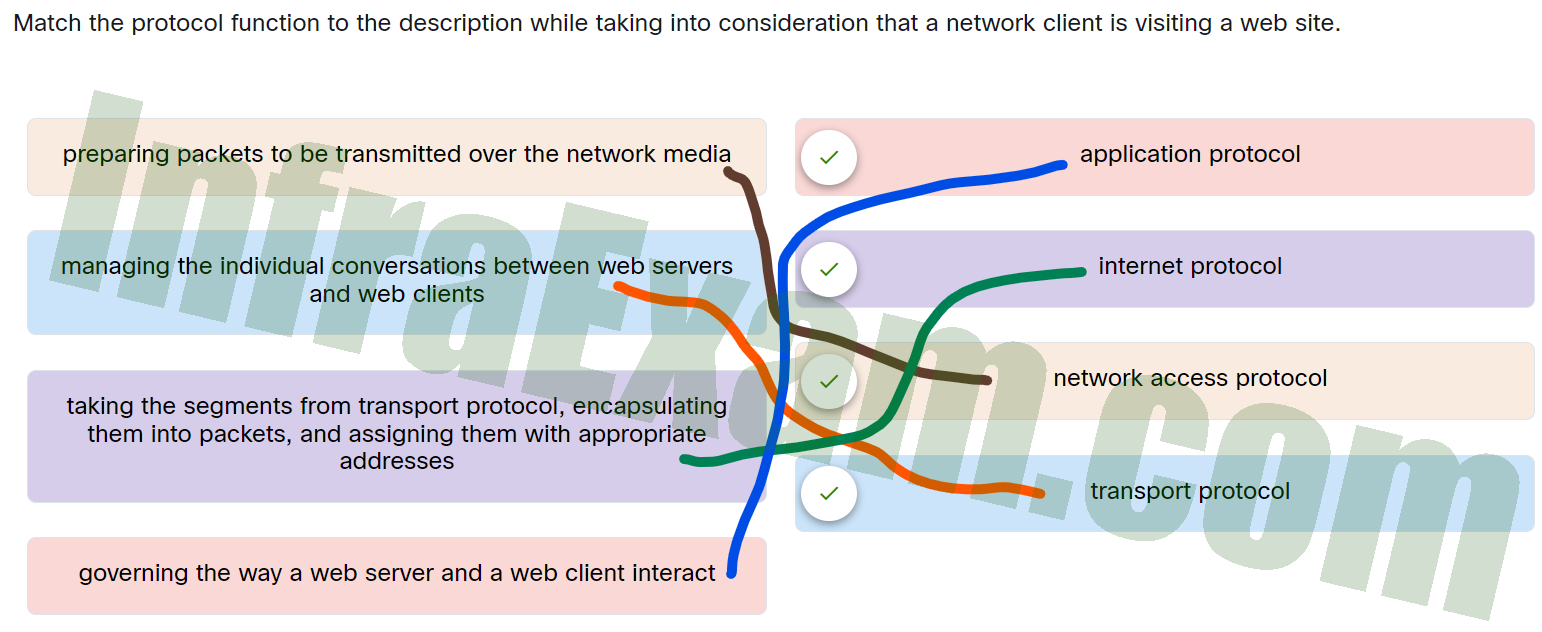
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 5 – 7 Checkpoint Exam Answers 002 - taking the segments from transport protocol, encapsulating them into packets, and assigning them with appropriate addresses —> internet protocol
- preparing packets to be transmitted over the network media —> network access protocol
- managing the individual conversations between web servers and web clients —> transport protocol
- governing the way a web server and a web client interact —> application protocol
Explanation and Hint:
Place the options in the following order:
Governing the way a web server and a web client interact. Application protocol Taking the segments from transport protocol, encapsulating them into packets, and assigning them with appropriate addresses. Internet protocol Preparing packets to be transmitted over the network media. Network access protocol Managing the individual conversations between web servers and web clients. Transport protocol
-
Which two OSI model layers have the same functionality as two layers of the TCP/IP model? (Choose two.)
- session
- physical
- transport
- data link
- network
Explanation and Hint:
The OSI transport layer is functionally equivalent to the TCP/IP transport layer, and the OSI network layer is equivalent to the TCP/IP internet layer. The OSI data link and physical layers together are equivalent to the TCP/IP network access layer. The OSI session layer (with the presentation layer) is included within the TCP/IP application layer.
-
Which three layers of the OSI model map to the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- application
- presentation
- network
- data link
- transport
- session
Explanation and Hint:
The application layer of the TCP/IP model maps to the top three layers of the OSI model, which are the application, presentation, and session layers.
-
Which type of network cable is commonly used in backbone networks and telephone companies?
- fiber-optic cable
- shielded twisted-pair cable
- twisted-pair cable
- coaxial cable
Explanation and Hint:
Fiber-optic cables can carry very large amounts of data and are used extensively by telephone companies and in backbone networks.
-
Refer to the graphic. What type of cabling is shown?

Network Basics Module 5 – 7 Checkpoint Exam Answers 03 - coaxial
- plastic fiber-optic
- glass fiber-optic
- twisted-pair
Explanation and Hint:
Network cabling includes different types of cables:
Twisted-pair Ethernet cables consist of four pairs of color-coded wires that have been twisted together and then encased in a flexible plastic sheath.
Coaxial cables use a copper conductor and a layer of flexible plastic insulation that surrounds the copper conductor.
Fiber-optic cables are flexible, extremely thin, transparent strands of glass surrounded by plastic insulation.
-
A network technician is researching the use of fiber optic cabling in a new technology center. Which two issues should be considered before implementing fiber optic media? (Choose two.)
- Fiber optic cabling requires specific grounding to be immune to EMI.
- Fiber optic cabling is susceptible to loss of signal due to RFI.
- Fiber optic cable is able to withstand rough handling.
- Fiber optic provides higher data capacity but is more expensive than copper cabling.
- Fiber optic cabling requires different termination and splicing expertise from what copper cabling requires.
Explanation and Hint:
Fiber optic media is more expensive than copper cabling used over the same distance. Fiber optic cables use light instead of an electrical signal, so EMI and RFI are not issues. However, fiber optic does require different skills to terminate and splice.
-
Which two applications are suitable for deploying coaxial cables? (Choose two.)
- to connect a TV set to the wall plug at home
- to connect various components in a satellite communication system
- to connect data centers with high bandwidth requirements over long distances
- to connect PC computers in an office
- to connect network devices in backbone networks
Explanation and Hint:
Coaxial cable is the kind of copper cable used by cable TV companies. It is used to connect TV sets to the wall jacks that are connected to a cable TV company. It is also used for connecting the various components which make up satellite communication systems.
-
What two characteristics describe an Ethernet cable? (Choose two.)
- 4 pairs of twisted cables
- color coded pairs of cables
- single copper core surrounded by a layer of insulation
- plastic core surrounded by multiple layers for isolation and protection
- glass core surrounded by multiple layers for isolation and protection
Explanation and Hint:
In twisted-pair cables, wires are grouped in pairs and twisted together to reduce interference. The pairs of wires are colored so that the same wire at each end can be easily identified.
-
Which criterion can be used to select the appropriate type of network media for a network?
- the cost of the end devices that are used in the network
- the environment where the selected medium is to be installed
- the types of data that need to be prioritized
- the number of intermediary devices that are installed in the network
Explanation and Hint:
Criteria for choosing a network medium are the distance across which the selected medium can successfully carry a signal, the environment in which the selected medium is to be installed, the amount of data and the speed at which the data must be transmitted, and the cost of the medium and its installation.
-
Which data encoding technology is used in fiber-optic cables?
- electrical pulses
- modulation of specific frequencies of electromagnetic waves
- modulation of electrical voltage
- pulses of light
Explanation and Hint:
Data is transmitted across a network on media. Modern networks primarily use three types of media to interconnect devices:
Metal wires within cables (copper cable, such as twisted-pair and coaxial cable) – Data is encoded into electrical impulses.
Glass or plastic fibers within cables (fiber-optic cable) – Data is encoded into pulses of light.
Wireless transmission – Data is encoded via modulation of specific frequencies of electromagnetic waves.
-
What are two actions performed by a Cisco switch? (Choose two.)
- examining the destination MAC address to add new entries to the MAC address table
- utilizing the MAC address table to forward frames via the destination MAC address
- forwarding frames with unknown destination IP addresses to the default gateway
- using the source MAC addresses of frames to build and maintain a MAC address table
- building a routing table that is based on the first IP address in the frame header
Explanation and Hint:
Important actions that a switch performs are as follows:
When a frame comes in, the switch examines the Layer 2 source address to build and maintain the Layer 2 MAC address table.
It examines the Layer 2 destination address to determine how to forward the frame. When the destination address is in the MAC address table, then the frame is sent out a particular port. When the address is unknown, the frame is sent to all ports that have devices connected to that network.
-
Which information does a switch use to populate the MAC address table?
- the source and destination MAC addresses and the incoming port
- the destination MAC address and the incoming port
- the source MAC address and the outgoing port
- the destination MAC address and the outgoing port
- the source and destination MAC addresses and the outgoing port
- the source MAC address and the incoming port
Explanation and Hint:
To maintain the MAC address table, the switch uses the source MAC address of the incoming packets and the port that the packets enter. The destination address is used to select the outgoing port.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A PC with the MAC address of 0800.069d.3841 attached to port Fa0/8 is sending data to a device that has the MAC address of 6400.6a5a.6821. What will the switch do first to handle the data transfer?
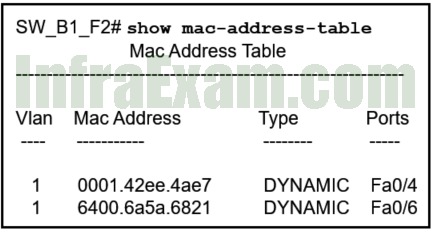
Network Basics Module 5 – 7 Checkpoint Exam Answers 02 - The switch will flood the frame out all ports except port Fa0/8.
- The switch will add the address 0800.069d.3841 to the MAC address table.
- The switch will send the frame to port Fa0/6.
- The switch will add the address 6400.6151.6821 to the MAC address table.
- The switch will send the frame to ports Fa0/4 and Fa0/6.
Explanation and Hint:
A switches performs two functions when it receives a frame:
The switch examines the source MAC address and adds it to the MAC address table if it is not already in the table.
The switch examines the destination MAC address. If the MAC address is in the MAC address table, the frame is sent to the appropriate port. If the MAC address is not in the MAC address table, the frame is sent to all ports that have devices attached except the port the frame came in on.
-
Refer to the exhibit. How is a frame sent from PCA forwarded to PCC if the MAC address table on switch SW1 is empty?
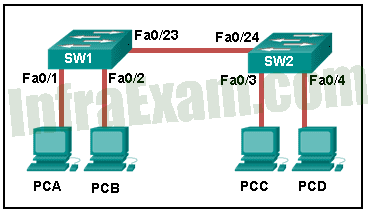
Network Basics Module 5 – 7 Checkpoint Exam Answers 01 - SW1 forwards the frame directly to SW2. SW2 floods the frame to all ports connected to SW2, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 drops the frame because it does not know the destination MAC address.
- SW1 floods the frame on all ports on SW1, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 floods the frame on all ports on the switch, excluding the interconnected port to switch SW2 and the port through which the frame entered the switch.
Explanation and Hint:
When a switch powers on, the MAC address table is empty. The switch builds the MAC address table by examining the source MAC address of incoming frames. The switch forwards based on the destination MAC address found in the frame header. If a switch has no entries in the MAC address table or if the destination MAC address is not in the switch table, the switch will forward the frame out all ports except the port that brought the frame into the switch.
-
How much data can be encapsulated into a normal sized Ethernet frame before it is sent over the network?
- 0 to 1024 bytes
- 46 to 1500 bytes
- 32 to 1500 bytes
- 64 to 1518 bytes
Explanation and Hint:
According to the Ethernet standards, each Ethernet frame can carry 46 to 1500 bytes of user data. During the encapsulation process, other fields are added, such as destination MAC address, source MAC address, and FCS. The size of Ethernet frames is normally limited to a maximum of 1518 bytes and a minimum of 64 bytes.
-
Which type of address does a switch use to build the MAC address table?
- destination IP address
- destination MAC address
- source MAC address
- source IP address
Explanation and Hint:
When a switch receives a frame with a source MAC address that is not in the MAC address table, the switch will add that MAC address to the table and map that address to a specific port. Switches do not use IP addressing in the MAC address table.
-
Which term refers to the process of placing one message format inside another message format?
- segmenting
- encapsulation
- encoding
- manipulation
Explanation and Hint:
Encapsulation is the process of placing one type of message format into another. On computer networks this process is known as encapsulation. Once a message is encapsulated, it is called a frame.