Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 8-11 | Checkpoint Exam: The Internet Protocol Answers Full 100%
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 8-11 | Checkpoint Exam: The Internet Protocol Answers Full 100% 2023 2024
This Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 8-11 section for Checkpoint Exam: The Internet Protocol Answers which is provided with the correct answers to 100% of the questions. This module 8-11 exam answer is used for the Cisco SkillsForAll platform which is the latest version just released in 2023 2024. Review all the questions and answers here, then you will meet randomly 20 questions from all here.
-
True or False?
Every device on a network needs an IP address to identify itself and communicate on the network.
- true
- false
Explanation:
All network devices must have an IP address to communicate on the network. The IP address is used to uniquely identify each device on the network.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The IP address settings of a host are shown. What is the host number of the IP address?
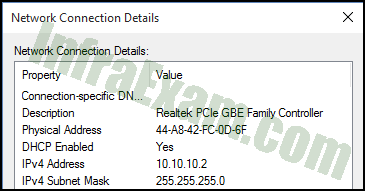
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 8-11 Checkpoint Exam The Internet Protocol Answers 01 - 10
- 1
- 2
- 255
Explanation:
An IP address consists of two parts. The first part is the network number and the second part is the host number. The length of the network number is defined by the subnet mask. For each 255 in the subnet mask, that much of the IP address represents the network part. For each 0 on the right part of the subnet mask, that part of the IP address identifies the host number. In this example the subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 means that 10.10.10.0 is the network number and 2 is the host number.
-
How many bits make up an IPv4 address?
- 128
- 32
- 64
- 48
Explanation:
An IPv4 address is a 32-bit logical address.
-
When IPv4 is configured for a computer on a network, what does the subnet mask identify?
- the part of the IP address that identifies the network
- the device that the computer uses to access another network
- the pool of addresses assigned within the network
- the dynamic subnetwork configuration
Explanation:
The IP addressing system is a hierarchical addressing system. An IP address is made up of two parts: the network address and the host address. For IPv4, the subnet mask is used to identify which portion of an IPv4 address is the network address and which portion is the host address.
-
Refer to the exhibit. What is the network number of the LAN that is shown?
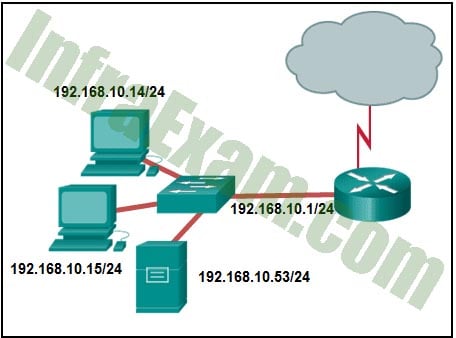
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 8-11 Checkpoint Exam The Internet Protocol Answers 02 - 192.168.10.1
- 192.168.0.0
- 192.168.10.0
- 255.255.255.0
Explanation:
All of the hosts have IP addresses with 192.168.10.__/24 in common. The last digit can be any number in the range from 0 to 255. The first number of the range represents the network number and the last number in the range represents the broadcast address. Hosts can be assigned any number from 1 to 254. The network number in this case is 192.168.10.0
-
A student is helping a friend with a home computer that can no longer access the Internet. Upon investigation, the student discovers that the computer has been assigned the IP address 169.254.100.88. What could cause a computer to get such an IP address?
- interference from surrounding devices
- static IP addressing with incomplete information
- unreachable DHCP server
- reduced computer power supply output
Explanation:
When a PC does not have a static IP address or cannot pick one up from a DHCP server, Windows will automatically assign the PC an IP address using APIPA, that uses the range of addresses 169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255.
-
What is the purpose of the subnet mask in conjunction with an IP address?
- to mask the IP address to outsiders
- to determine the subnet to which the host belongs
- to identify whether the address is public or private
- to uniquely identify a host on a network
Explanation:
With the IPv4 address, a subnet mask is also necessary. A subnet mask is a special type of IPv4 address that coupled with the IP address determines the subnet of which the device is a member.
-
What are the three ranges of IP addresses that are reserved for internal private use? (Choose three.)
- 192.168.0.0/16
- 127.16.0.0/12
- 64.100.0.0/14
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 192.31.7.0/24
- 172.16.0.0/12
Explanation:
The private IP address blocks that are used inside companies are as follows:
- 10.0.0.0 /8 (any address that starts with 10 in the first octet)
- 172.16.0.0 /12 (any address that starts with 172.16 in the first two octets through 172.31.255.255)
- 192.168.0.0 /16 (any address that starts with 192.168 in the first two octets)
-
Match each description with an appropriate IP address.
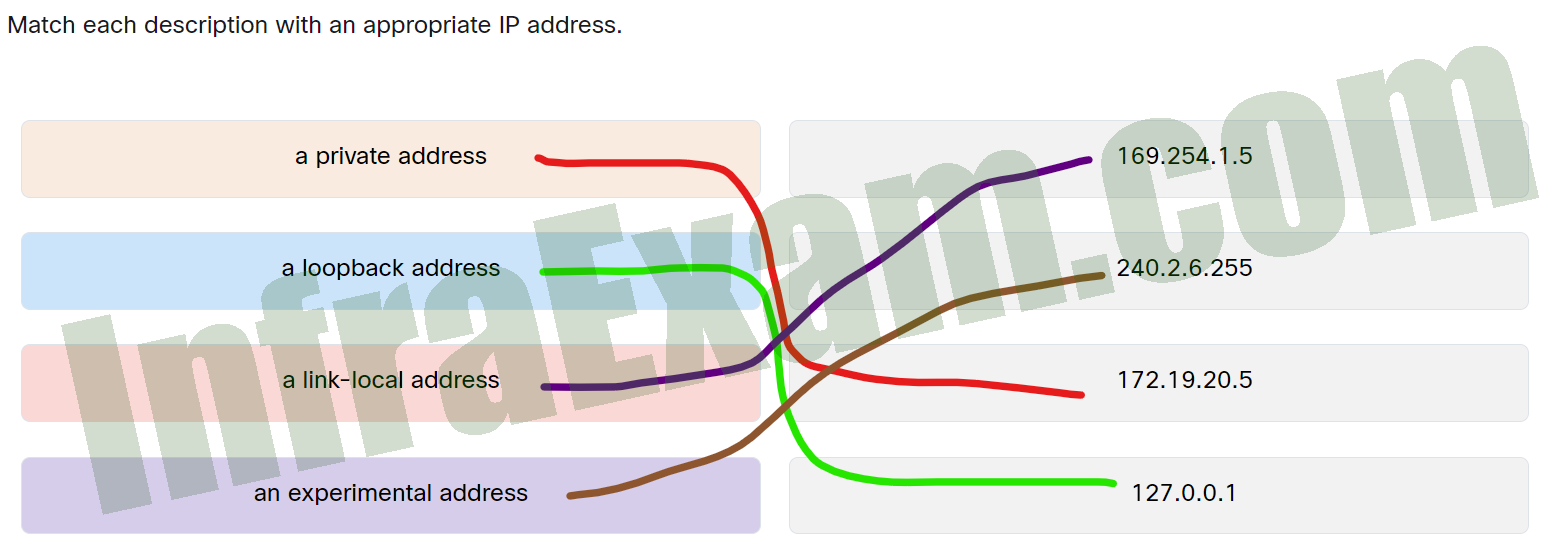
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 8-11 Checkpoint Exam The Internet Protocol Answers 001 - a private address —> 172.19.20.5
- a loopback address —> 127.0.0.1
- a link-local address —> 169.254.1.5
- an experimental address —> 240.2.6.255
Explanation:
Place the options in the following order:
A link-local address 169.254.1.5 An experimental address 240.2.6.255 A private address 172.19.20.5 A loopback address 127.0.0.1
-
What are two reasons a network administrator might want to create subnets? (Choose two.)
- simplifies network design
- improves network performance
- reduction in number of routers needed
- reduction in number of switches needed
- easier to implement security policies
Explanation:
Two reasons for creating subnets include reduction of overall network traffic and improvement of network performance. Subnets also allow an administrator to implement subnet-based security policies. The number of routers or switches is not affected. Subnets do not simplify network design.
-
What is one factor increasing the adoption of IPv6 network addresses?
- IoT adds millions of network-ready sensors that need IP addresses.
- IPv4 addresses cannot coexist with IPv6 addresses on the internet.
- Devices communicate faster using IPv6 addresses than when using IPv4.
- IPv4 will no longer be supported on mobile devices.
Explanation:
Factors that are driving an increase in IPv6 adoption are an increasing internet population, a limited IPv4 address space, issues with NAT and the large number of internet-ready IoT devices.
-
Which shortened address is an accurate representation of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:ab00:0000:0000:0000?
- 2001:db8:0:0:ab::
- 2001:db8::ab00::
- 2001:db8:0:ab00:0
- 2001:db8:0:0:ab00::
Explanation:
There are two rules to help reduce the notation of IPv6 addresses. The first one is to omit any leading 0s (zeros) in any hextet. The second one is that a double colon (::) can replace any single, contiguous string of one or more 16-bit hextets consisting of all zeros, but the double colon (::) can only be used once within an address. If an address has more than one contiguous string of all-0 hextets, the best practice is to use the double colon (::) on the longest string. So, applying the first rule in the IPv6 address we have 2001:db8:0:0:ab00:0:0:0, and applying the second rule results in 2001:db8:0:0:ab00::
-
How many binary bits exist within an IPv6 address?
- 48
- 128
- 32
- 64
- 256
Explanation:
IPv4 addressing space is exhausted by the rapid growth of the Internet and the devices connected to the Internet. IPv6 expands the IP addressing space by increasing the address length from 32 bits to 128 bits.
-
What is the valid most compressed format possible of the IPv6 address 2001:0DB8:0000:AB00:0000:0000:0000:1234?
- 2001:DB8:0:AB00::1234
- 2001:DB8:0:AB:0:1234
- 2001:DB8:0:AB::1234
- 2001:DB8::AB00::1234
Explanation:
There are two rules defining how an IPv6 address can be compressed. The first rule states that leading zeros in a hextet can be eliminated. The second rule states that a single :: can be used to represent one or more contiguous all zero hextets. There can be one and only one :: in an IPv6 address.
-
Three methods allow IPv6 and IPv4 to co-exist. Match each method with its description.
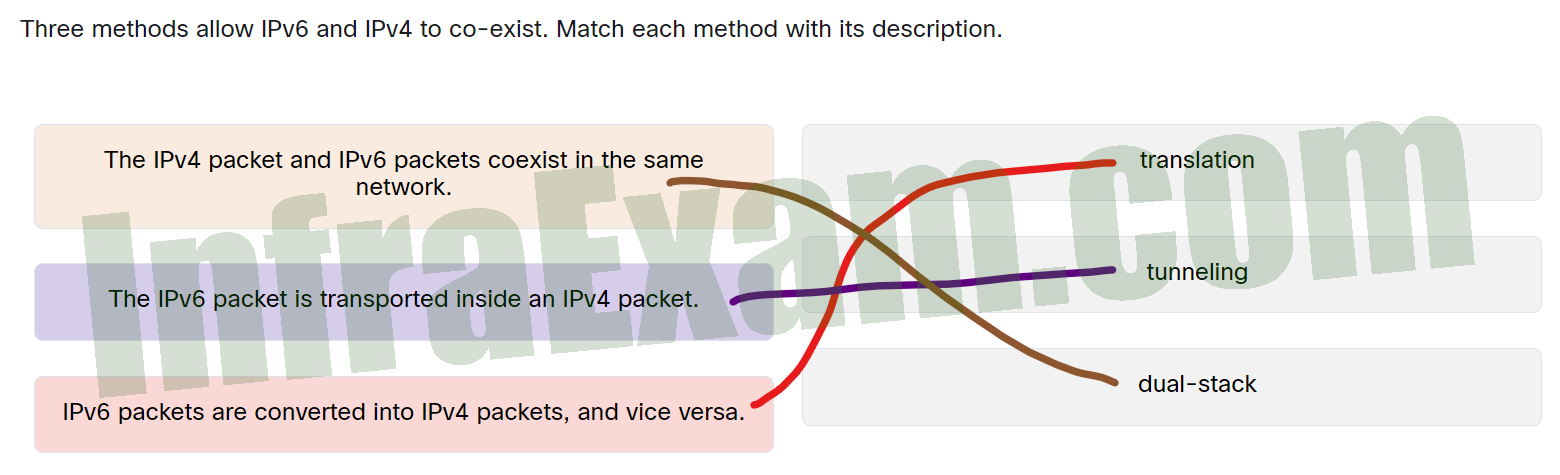
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 8-11 Checkpoint Exam The Internet Protocol Answers 002 - IPv6 packets are converted into IPv4 packets, and vice versa. —> translation
- The IPv6 packet is transported inside an IPv4 packet. —> tunneling
- The IPv4 packet and IPv6 packets coexist in the same network. —> dual-stack
Explanation:
Place the options in the following order:
IPv6 packets are converted into IPv4 packets, and vice versa. Translation The IPv6 packet is transported inside an IPv4 packet. Tunneling The IPv4 packet and IPv6 packets coexist in the same network. Dual-stack
-
A DHCP-enabled client PC has just booted. During which two steps will the client PC use broadcast messages when communicating with a DHCP server? (Choose two.)
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPACK
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPNAK
Explanation:
All DHCP messages between a DHCP-enabled client and a DHCP server are using broadcast messages until after the DHCPACK message. The DHCPDISCOVER and DHCPREQUEST messages are the only messages that are sent by a DHCP-enabled client. All DHCP messages between a DHCP-enabled client and a DHCP server use broadcast messages when the client is obtaining a lease for the first time.
-
Which DHCPv4 message will a client send to accept an IPv4 address that is offered by a DHCP server?
- broadcast DHCPACK
- unicast DHCPREQUEST
- unicast DHCPACK
- broadcast DHCPREQUEST
Explanation:
When a DHCP client receives DHCPOFFER messages, it will send a broadcast DHCPREQUEST message for two purposes. First, it indicates to the offering DHCP server that it would like to accept the offer and bind the IP address. Second, it notifies any other responding DHCP servers that their offers are declined.
-
What is the destination IP address when an IPv4 host sends a DHCPDISCOVER message?
- 224.0.0.1
- 255.255.255.255
- 192.168.1.1
- 0.0.0.0
Explanation:
Because a DHCP client does not have a valid IPv4 address, it must use a broadcast IP address of 255.255.255.255 as the destination address to communicate with the DHCP server. The DHCPDISCOVER message sent by the client is the first message sent in order to make initial contact with a DHCP server.
-
Which statement is true about DHCP operation?
- A client must wait for lease expiration before it sends another DHCPREQUEST message.
- When a device that is configured to use DHCP boots, the client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to identify any available DHCP servers on the network.
- The DHCPDISCOVER message contains the IP address and subnet mask to be assigned, the IP address of the DNS server, and the IP address of the default gateway.
- If the client receives several DHCPOFFER messages from different servers, it sends a unicast DHCPREQUEST message to the server from which it chooses to obtain the IP information.
Explanation:
The client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to identify any available DHCP servers on the network. A DHCP server replies with a DHCPOFFER message. This message offers to the client a lease that contains such information as the IP address and subnet mask to be assigned, the IP address of the DNS server, and the IP address of the default gateway. After the client receives the lease, the received information must be renewed through another DHCPREQUEST message prior to the lease expiration.
-
If more than one DHCP server is available on the local network, in which order will DHCP messages be sent between a host and a DHCP server?
- request, discover, offer, acknowledgment
- discover, offer, request, acknowledgment
- acknowledgment, request, offer, discover
- request, acknowledgment, discover, offer
Explanation:
A DHCP host broadcasts a DHCP discover message to locate available servers. If more than one DHCP server is available, each server will respond to the host with a unicast DHCP offer message, which offers a lease to the client. The client then broadcasts a DHCP request message that identifies the specific server and offer that the client will accept. The identified server will unicast a DHCP acknowledgment message to finalize the offer.
-
Consider the group of five IPv4 addresses with the subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. Select three of them that belong to the same logical network.
- 172.16.45.35
- 172.16.45.12
- 172.16.35.45
- 172.16.45.56
- 173.16.45.18
Explanation & Hint:
-
When the IETF began development of IPv6, what was the goal of implementing this technology?
- to increase the limiting 128 bits available in IPv4 to facilitate the growing Internet
- to provide more address space in the Internet Names Registry
- to relieve IPv4 address depletion
- to make reading a 32-bit address easier
Explanation & Hint:
IPv6 is designed to be the successor to IPv4. IPv6 has a larger 128 bit address space to provide many more addresses than IPv4.
-
Which two types of devices are typically assigned static IP addresses? (Choose two.)
- web servers
- hubs
- printers
- laptops
- workstations
Explanation & Hint:
Servers and peripherals are often accessed by an IP address, so these devices need predictable IP addresses. End-user devices often have dynamic addresses that are assigned. Hubs do not require IPv4 addresses to operate as intermediary devices.