CAPM : Certified Associate in Project Management (PMI-100) : Part 32
CAPM : Certified Associate in Project Management (PMI-100) : Part 32
-
Projects are separated into phases or subprojects; these phases include:
- feasibility study, concept development, design, and prototype.
- initiate, plan, execute, and monitor.
- Develop Charter, Define Activities, Manage Stakeholder Expectations, and Report Performance.
- Identify Stakeholders, develop concept, build, and test.
-
In which type of contract are the performance targets established at the onset and the final contract price determined after completion of all work based on the sellers performance?
- Firm-Fixed-Price (FFP)
- Fixed Price with Economic Price Adjustments (FP-EPA)
- Fixed-Price-Incentive-Fee (FPIF)
- Cost Plus Fixed Fee (CPFF)
-
Which of the following is an input to the Develop Project Charter process?
- Work performance information
- Project management plan
- Business case
- Change requests
Explanation:
Process: 4.1. Develop Project Charter
Definition: The process of developing a document that formally authorizes the existence of a project and provides the project manager with the authority to apply organizational resources to project activities.
Key Benefit: The key benefit of this process is a well-defined project start and project boundaries, creation of a formal record of the project, and a direct way for senior management to formally accept and commit to the project.Inputs
1. Project statement of work
2. Business case
3. Agreements
4. Enterprise environmental factors
5. Organizational process assets
Tools & Techniques
1. Expert judgment
2. Facilitation techniques
Outputs
1. Project charter4.1.1.2 Business Case
The business case or similar document describes the necessary information from a business standpoint to determine whether or not the project is worth the required investment. It is commonly used for decision making by managers or executives above the project level. Typically, the business need and the cost-benefit analysis are contained in the business case to justify and establish boundaries for the project, and such analysis is usually completed by a business analyst using various stakeholder inputs. The sponsor should agree to the scope and limitations of the business case. The business case is created as a result of one or more of the following:
– Market demand (e.g., a car company authorizing a project to build more fuel-efficient cars in response to gasoline shortages),
Organizational need (e.g., due to high overhead costs a company may combine staff functions and streamline processes to reduce costs.),
– Customer request (e.g., an electric utility authorizing a project to build a new substation to serve a new industrial park),
– Technological advance (e.g., an airline authorizing a new project to develop electronic tickets instead of paper tickets based on technological advances),
– Legal requirement (e.g., a paint manufacturer authorizing a project to establish guidelines for handling toxic materials),
– Ecological impacts (e.g., a company authorizing a project to lessen its environmental impact), or
– Social need (e.g., a nongovernmental organization in a developing country authorizing a project to provide potable water systems, latrines, and sanitation education to communities suffering from high rates of cholera).Each of the examples in this list may contain elements of risk that should be addressed. In the case of multiphase projects, the business case may be periodically reviewed to ensure that the project is on track to deliver the business benefits. In the early stages of the project life cycle, periodic review of the business case by the sponsoring organization also helps to confirm that the project is still aligned with the business case. The project manager is responsible for ensuring that the project effectively and efficiently meets the goals of the organization and those requirements of a broad set of stakeholders, as defined in the business case.
-
The diagram below is an example of a:
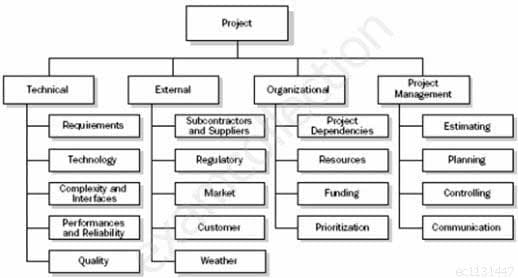
CAPM Certified Associate in Project Management (PMI-100) Part 32 Q04 023 - Risk breakdown structure (RBS).
- Project team.
- SWOT Analysis.
- Work breakdown structure (WBS).
-
Who is responsible for initiating a project?
- Project sponsor
- Project manager
- Program manager
- Project management office (PMO)
-
Which type of diagram includes groups of information and shows relationships between factors, causes, and objectives?
- Affinity
- Scatter
- Fishbone
- Matrix
Explanation:
Matrix diagrams. A quality management and control tool used to perform data analysis within the organizational structure created in the matrix. The matrix diagram seeks to show the strength of relationships between factors, causes, and objectives that exist between the rows and columns that form the matrix. -
Activity cost estimates are quantitative assessments of the probable costs required to:
- Create WBS.
- complete project work.
- calculate costs.
- Develop Project Management Plan.
Explanation:
7.2.3.1 Activity Cost Estimates
Activity cost estimates are quantitative assessments of the probable costs required to complete project work. Cost estimates can be presented in summary form or in detail. Costs are estimated for all resources that are applied to the activity cost estimate. This includes, but is not limited to, direct labor, materials, equipment, services, facilities, information technology, and special categories such as cost of financing (including interest charges), an inflation allowance, exchange rates, or a cost contingency reserve. Indirect costs, if they are included in the project estimate, can be included at the activity level or at higher levels. -
The item that provides more detailed descriptions of the components in the work breakdown structure (WB5) is called a WBS:
- dictionary.
- chart.
- report.
- register.
Explanation:
• WBS dictionary. The WBS dictionary is a document that provides detailed deliverable, activity, and scheduling information about each component in the WBS. The WBS dictionary is a document that supports the WBS. Information in the WBS dictionary may include, but is not limited to:
– Code of account identifier,
– Description of work,
– Assumptions and constraints,
– Responsible organization,
– Schedule milestones,
– Associated schedule activities,
– Resources required,
– Cost estimates,
– Quality requirements,
– Acceptance criteria,
– Technical references, and
– Agreement information. -
How should a stakeholder who is classified as high power and low interest be grouped in a power/interest grid during stakeholder analysis?
- Keep satisfied
- Keep informed
- Manage closely
- Monitor
Explanation:13.1.2.1 Stakeholder Analysis
Stakeholder analysis is a technique of systematically gathering and analyzing quantitative and qualitative information to determine whose interests should be taken into account throughout the project. It identifies the interests, expectations, and influence of the stakeholders and relates them to the purpose of the project. It also helps to identify stakeholder relationships (with the project and with other stakeholders) that can be leveraged to build coalitions and potential partnerships to enhance the project’s chance of success, along with stakeholder relationships that need to be influenced differently at different stages of the project or phase.Stakeholder analysis generally follows the steps described below:
– Identify all potential project stakeholders and relevant information, such as their roles, departments, interests, knowledge, expectations, and influence levels. Key stakeholders are usually easy to identify. They include anyone in a decision-making or management role who is impacted by the project outcome, such as the sponsor, the project manager, and the primary customer. Identifying other stakeholders is usually done by interviewing identified stakeholders and expanding the list until all potential stakeholders are included.
– Analyze the potential impact or support each stakeholder could generate, and classify them so as to define an approach strategy. In large stakeholder communities, it is important to prioritize the stakeholders to ensure the efficient use of effort to communicate and manage their expectations.
– Assess how key stakeholders are likely to react or respond in various situations, in order to plan how to influence them to enhance their support and mitigate potential negative impacts.There are multiple classification models used for stakeholders analysis, such as:
– Power/interest grid, grouping the stakeholders based on their level of authority (“power”) and their level or concern (“interest”) regarding the project outcomes;
– Power/influence grid, grouping the stakeholders based on their level of authority (“power”) and their active involvement (“influence”) in the project;
– Influence/impact grid, grouping the stakeholders based on their active involvement (“influence”) in the project and their ability to effect changes to the project’s planning or execution (“impact”); and
– Salience model, describing classes of stakeholders based on their power (ability to impose their will), urgency (need for immediate attention), and legitimacy (their involvement is appropriate). -
The project has a current cost performance index of 0.80. Assuming this performance will continue, the new estimate at completion is $1000. What was the original budget at completion for the project?
- $800
- $1000
- $1250
- $1800
-
Who determines which dependencies are mandatory during the Sequence Activities process?
- Project manager
- External stakeholders
- Internal stakeholders
- Project team
Explanation:
Who determines which dependencies are mandatory during the Sequence Activities process? -
Risk exists the moment that a project is:
- planned.
- conceived.
- chartered.
- executed.
-
Which type of contract is a hybrid of both a cost-reimbursable and a fixed-price contract?
- Cost Plus Award Fee Contract (CPAF)
- Firm-Fixed -Price Contract (FFP)
- Time and Material Contract (T&M)
- Cost Plus Incentive Fee Contract (CPIF)
Explanation:
Time and Material Contracts (T&M). Time and material contracts are a hybrid type of contractual arrangement that contain aspects of both cost-reimbursable and fixed-price contracts. They are often used for staff augmentation, acquisition of experts, and any outside support when a precise statement of work cannot be quickly prescribed. These types of contracts resemble cost-reimbursable contracts in that they can be left open ended and may be subject to a cost increase for the buyer. The full value of the agreement and the exact quantity of items to be delivered may not be defined by the buyer at the time of the contract award. Thus, T&M contracts can increase in contract value as if they were costreimbursable contracts. Many organizations require not-to-exceed values and time limits placed in all T&M contracts to prevent unlimited cost growth. Conversely, T&M contracts can also resemble fixed unit price arrangements when certain parameters are specified in the contract. Unit labor or material rates can be preset by the buyer and seller, including seller profit, when both parties agree on the values for specific resource categories, such as senior engineers at specified rates per hour, or categories of materials at specified rates per unit. -
Which characteristics do effective project managers possess?
- Project management knowledge, performance skills, and personal effectiveness
- Preparedness, project management knowledge, and personality characteristics
- General management, preparedness, and project management knowledge
- Assertiveness, collaboration, and performance skills
Explanation:1.7.1 Responsibilities and Competencies of the Project Manager
In general, project managers have the responsibility to satisfy the needs: task needs, team needs, and individual needs. As project management is a critical strategic discipline, the project manager becomes the link between the strategy and the team. Projects are essential to the growth and survival of organizations. Projects create value in the form of improved business processes, are indispensable in the development of new products and services, and make it easier for companies to respond to changes in the environment, competition, and the marketplace. The project manager’s role therefore becomes increasingly strategic. However, understanding and applying the knowledge, tools, and techniques that are recognized as good practice are not sufficient for effective project management. In addition to any area-specific skills and general management proficiencies required for the project, effective project management requires that the project manager possess the following competencies:– Knowledge—Refers to what the project manager knows about project management.
– Performance—Refers to what the project manager is able to do or accomplish while applying his or her project management knowledge.
– Personal—Refers to how the project manager behaves when performing the project or related activity. Personal effectiveness encompasses attitudes, core personality characteristics, and leadership, which provides the ability to guide the project team while achieving project objectives and balancing the project constraints. -
In the basic communication model, which term refers to the method that is used to convey the message?
- Decode
- Encode
- Medium
- Noise
-
During project selection, which factor is most important?
- Types of constraints
- Internal business needs
- Budget
- Schedule
Explanation:
Projects are initiated by an entity external to the project such as a sponsor, program or project management offce (PMO) staff person, or a portfolio governing body chairperson or authorized representative. The project initiator or sponsor should be at the level that is appropriate to procure funding and commit resources to the project. Projects are initiated due to internal business needs or external influences. These needs or influences often trigger the creation of a needs analysis, feasibility study, business case, or description of the situation that the project will address. Chartering a project validates alignment of the project to the strategy and ongoing work of the organization. A project charter is not considered to be a contract, because there is no consideration or money promised or exchanged in its creation. -
The staffing management plan is part of the:
- organizational process assets.
- resource calendar.
- human resource plan.
- Develop Project Team process.
-
Which is an output of the Collect Requirements process?
- Requirements traceability matrix
- Project scope statement
- WBS dictionary
- Work performance measurements
Explanation:5.2.3.2 Requirements Traceability Matrix
The requirements traceability matrix is a grid that links product requirements from their origin to the deliverables that satisfy them. The implementation of a requirements traceability matrix helps ensure that each requirement adds business value by linking it to the business and project objectives. It provides a means to track requirements throughout the project life cycle, helping to ensure that requirements approved in the requirements documentation are delivered at the end of the project. Finally, it provides a structure for managing changes to the product scope.
Tracing includes, but is not limited to, tracing requirements for the following:– Business needs, opportunities, goals, and objectives;
– Project objectives;
– Project scope/WBS deliverables;
– Product design;
– Product development;
– Test strategy and test scenarios; and
– High-level requirements to more detailed requirements.
Attributes associated with each requirement can be recorded in the requirements traceability matrix. These attributes help to define key information about the requirement. Typical attributes used in the requirements traceability matrix may include: a unique identifier, a textual description of the requirement, the rationale for inclusion, owner, source, priority, version, current status (such as active, cancelled, deferred, added, approved, assigned, completed), and status date. Additional attributes to ensure that the requirement has met stakeholders’ satisfaction may include stability, complexity, and acceptance criteria.Process: 5.2 Collect Requirements
Definition: The process of determining, documenting, and managing stakeholder needs and requirements to meet project objectives.
Key Benefit: The key benefit of this process is that it provides the basis for defining and managing the project scope including product scope.
Inputs
1. Scope management plan
2. Requirements management plan
3. Stakeholder management plan
4. Project charter
5. Stakeholder register
Tools & Techniques
1. Interviews
2. Focus groups
3. Facilitated workshops
4. Group creativity techniques
5. Group decision-making techniques
6. Questionnaires and surveys
7. Observations
8. Prototypes
9. Benchmarking
10. Context diagrams
11. Document analysis
Outputs
1. Requirements documentation
2. Requirements traceability matrix -
Which activity may occur at project or phase closure?
- Acceptance of deliverables
- Change requests
- Project management plan updates
- Benchmarking
-
Which of the following is an input to Direct and Manage Project Execution?
- Performance reports
- Project charter
- Outputs from planning processes
- Enterprise environmental factors