CCNA 2 v7 SRWE 7.02 – Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essentials (Version 7.00) – SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers
CCNA 2 v7 SRWE 7.02 – Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essentials (Version 7.00) – SRWE v7.02 Practice Final Exam Answers Full 100% 2023 2024
This NetAcad Cisco Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essentials (Version 7.00) – SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers 2023 2024 and CCNA 2 v7 SRWE 7.02 Practice Final Exam Answers Full 100% 2023 2024.
Cisco Netacad SRWE Version 7.00 CCNA 2 v7 SRWE 7.02 Practice Final Exam Answers 2023 2024
-
A technician is configuring a new Cisco 2960 switch. What is the effect of issuing the BranchSw(config)#interface VLAN88 command?
- It enters configuration mode for a switch virtual interface.
- It applies an IPv4 address to the virtual interface.
- It applies an IPv6 address to the virtual interface.
- It permits an IPv6 address to be configured on a switch physical interface.
- It updates the MAC address table for the associated port.
-
Which problem is evident if the show ip interface command shows that the interface is down and the line protocol is down?
- An encapsulation mismatch has occurred.
- A cable has not been attached to the port.
- The no shutdown command has not been issued on the interface.
- There is an IP address conflict with the configured address on the interface.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
If an interface has not been brought up with the no shutdown command, the interface status shows administratively down. A duplicate IP address will not bring an interface down. An encapsulation error is normally found using the show interfaces command.
-
In what situation would a Layer 2 switch have an IP address configured?
- when the Layer 2 switch needs to forward user traffic to another device
- when the Layer 2 switch is the default gateway of user traffic
- when the Layer 2 switch needs to be remotely managed
- when the Layer 2 switch is using a routed port
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Layer 2 switches can be configured with an IP address so that they can be remotely managed by an administrator. Layer 3 switches can use an IP address on routed ports. Layer 2 switches do not need a configured IP address to forward user traffic or act as a default gateway.
-
What is a result of connecting two or more switches together?
- The number of broadcast domains is increased.
- The size of the broadcast domain is increased.
- The number of collision domains is reduced.
- The size of the collision domain is increased.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When two or more switches are connected together, the size of the broadcast domain is increased and so is the number of collision domains. The number of broadcast domains is increased only when routers are added.
-
Refer to the exhibit. How is a frame sent from PCA forwarded to PCC if the MAC address table on switch SW1 is empty?
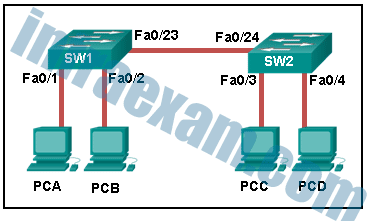
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 12 - SW1 floods the frame on all ports on the switch, excluding the interconnected port to switch SW2 and the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 floods the frame on all ports on SW1, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 forwards the frame directly to SW2. SW2 floods the frame to all ports connected to SW2, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 drops the frame because it does not know the destination MAC address.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a switch powers on, the MAC address table is empty. The switch builds the MAC address table by examining the source MAC address of incoming frames. The switch forwards based on the destination MAC address found in the frame header. If a switch has no entries in the MAC address table or if the destination MAC address is not in the switch table, the switch will forward the frame out all ports except the port that brought the frame into the switch.
-
What are two switch characteristics that could help alleviate network congestion? (Choose two.)
- fast internal switching
- frame check sequence (FCS) check
- large frame buffers
- low port density
- store-and-forward switching
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Switch characteristics that help alleviate network congestion include fast port speeds, fast internal switching, large frame buffers, and high port density.
-
A small publishing company has a network design such that when a broadcast is sent on the LAN, 200 devices receive the transmitted broadcast. How can the network administrator reduce the number of devices that receive broadcast traffic?
- Add more switches so that fewer devices are on a particular switch.
- Replace the switches with switches that have more ports per switch. This will allow more devices on a particular switch.
- Segment the LAN into smaller LANs and route between them.
- Replace at least half of the switches with hubs to reduce the size of the broadcast domain.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
By dividing the one big network into two smaller network, the network administrator has created two smaller broadcast domains. When a broadcast is sent on the network now, the broadcast will only be sent to the devices on the same Ethernet LAN. The other LAN will not receive the broadcast.
-
Refer to the exhibit. DLS1 is connected to another switch, DLS2, via a trunk link. A host that is connected to DLS1 is not able to communicate to a host that is connected to DLS2, even though they are both in VLAN 99. Which command should be added to Fa0/1 on DLS1 to correct the problem?
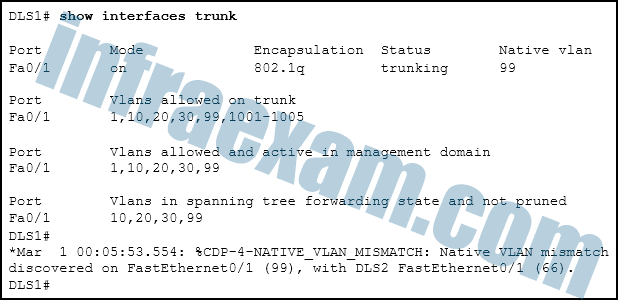
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 14 - switchport nonegotiate
- switchport mode dynamic auto
- switchport trunk native vlan 66
- switchport trunk allowed vlan add 99
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When configuring 802.1Q trunk links, the native VLAN must match on both sides of the link, or else CDP error messages will be generated, and traffic that is coming from or going to the native VLAN will not be handled correctly.
-
Refer to the exhibit. PC-A and PC-B are both in VLAN 60. PC-A is unable to communicate with PC-B. What is the problem?
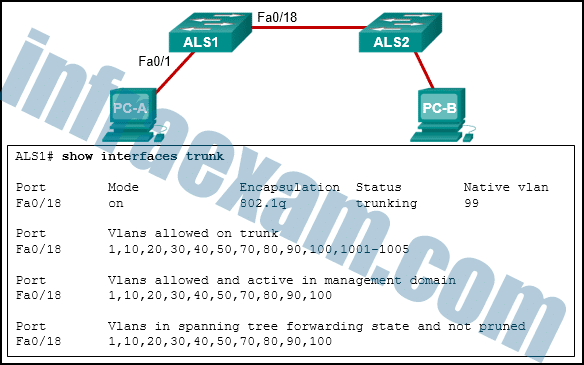
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 15 - The native VLAN should be VLAN 60.
- The native VLAN is being pruned from the link.
- The trunk has been configured with the switchport nonegotiate command.
- The VLAN that is used by PC-A is not in the list of allowed VLANs on the trunk.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Because PC-A and PC-B are connected to different switches, traffic between them must flow over the trunk link. Trunks can be configured so that they only allow traffic for particular VLANs to cross the link. In this scenario, VLAN 60, the VLAN that is associated with PC-A and PC-B, has not been allowed across the link, as shown by the output of show interfaces trunk .
-
What type of VLAN is configured specifically for network traffic such as SSH, Telnet, HTTPS, HTTP, and SNMP?
- management VLAN
- trunk VLAN
- security VLAN
- voice VLAN
-
Which type of traffic is designed for a native VLAN?
- user-generated
- tagged
- untagged
- management
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A native VLAN carries untagged traffic, which is traffic that does not come from a VLAN. A data VLAN carries user-generated traffic. A management VLAN carries management traffic.
-
Match the DTP mode with its function. (Not all options are used.)
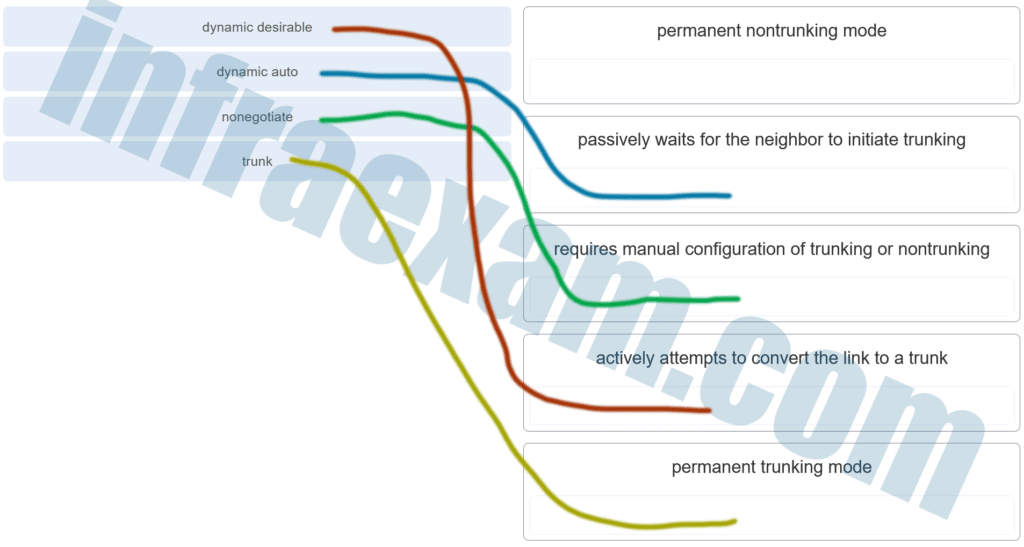
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 001 Answers Explanation & Hints:
The dynamic auto mode makes the interface become a trunk interface if the neighboring interface is set to trunk or desirable mode. The dynamic desirable mode makes the interface actively attempt to convert the link to a trunk link. The trunk mode puts the interface into permanent trunking mode and negotiates to convert the neighboring link into a trunk link. The nonegotiate mode prevents the interface from generating DTP frames.
-
A network administrator is using the router-on-a-stick method to configure inter-VLAN routing. Switch port Gi1/1 is used to connect to the router. Which command should be entered to prepare this port for the task?
- Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/1
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree vlan 1 - Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/1
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast - Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport mode trunk - Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport access vlan 1Answers Explanation & Hints:
With the router-on-a-stick method, the switch port that connects to the router must be configured as trunk mode. This can be done with the command Switch(config-if)# switchport mode trunk . The other options do not put the switch port into trunk mode.
- Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/1
-
Refer to the exhibit. The configuration shows commands entered by a network administrator for inter-VLAN routing. However, host H1 cannot communicate with H2. Which part of the inter-VLAN configuration causes the problem?
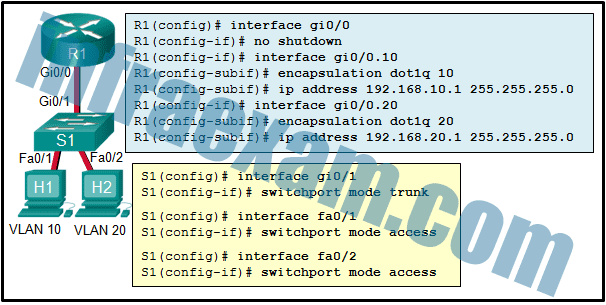
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 09 - trunking
- port mode on the two switch FastEthernet ports
- VLAN configuration
- router port configuration
Answers Explanation & Hints:
All Cisco switch ports are assigned to VLAN 1 by default. For VLAN implementation, ports Fa0/1 and Fa0/2 should be assigned to VLAN 10 and VLAN 20, respectively. The missing commands on S1 are as follows: switchport access vlan 10 and switchport access vlan 20 .
-
Refer to the exhibit. Inter-VLAN communication between VLAN 10, VLAN 20, and VLAN 30 is not successful. What is the problem?
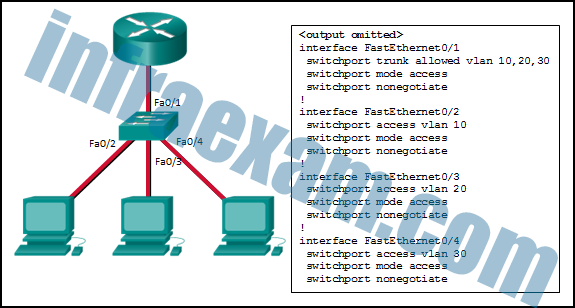
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 13 - The access interfaces do not have IP addresses and each should be configured with an IP address.
- The switch interface FastEthernet0/1 is configured as an access interface and should be configured as a trunk interface.
- The switch interface FastEthernet0/1 is configured to not negotiate and should be configured to negotiate.
- The switch interfaces FastEthernet0/2, FastEthernet0/3, and FastEthernet0/4 are configured to not negotiate and should be configured to negotiate.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
To forward all VLANs to the router, the switch interface Fa0/1 must be configured as a trunk interface with the switchport mode trunk command.
-
What is an advantage of PVST+?
- PVST+ requires fewer CPU cycles for all the switches in the network.
- PVST+ reduces bandwidth consumption compared to traditional implementations of STP that use CST.
- PVST+ optimizes performance on the network through autoselection of the root bridge.
- PVST+ optimizes performance on the network through load sharing.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
PVST+ results in optimum load balancing. However, this is accomplished by manually configuring switches to be elected as root bridges for different VLANs on the network. The root bridges are not automatically selected. Furthermore, having spanning-tree instances for each VLAN actually consumes more bandwidth and it increases the CPU cycles for all the switches in the network.
-
Which three components are combined to form a bridge ID?
- port ID
- IP address
- extended system ID
- MAC address
- bridge priority
- cost
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The three components that are combined to form a bridge ID are bridge priority, extended system ID, and MAC address.
-
Match the spanning-tree feature with the protocol type. (Not all options are used.)
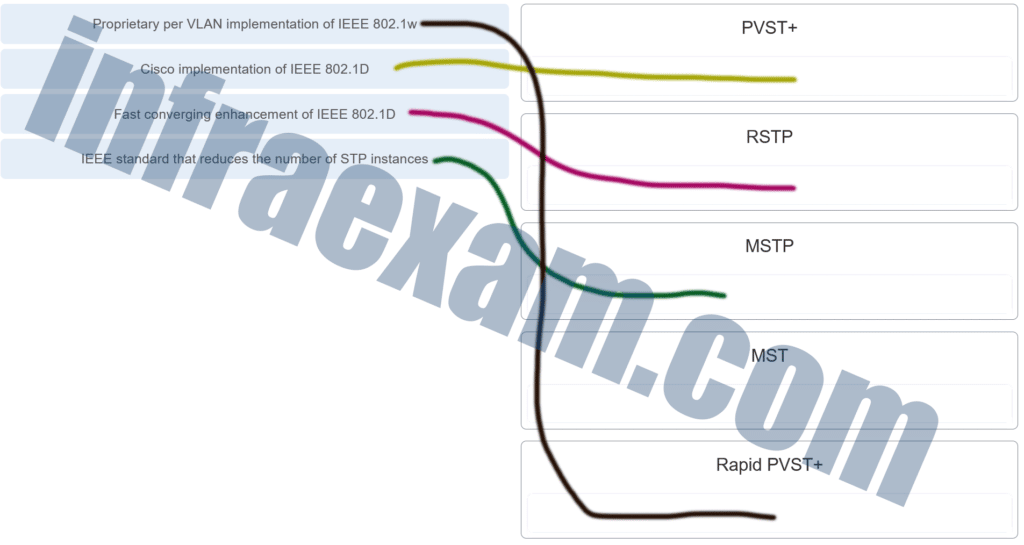
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 002 Answers Explanation & Hints:
MST is the Cisco implementation of MSTP (IEEE 802.1s).
-
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the command output shown, what is the status of the EtherChannel?
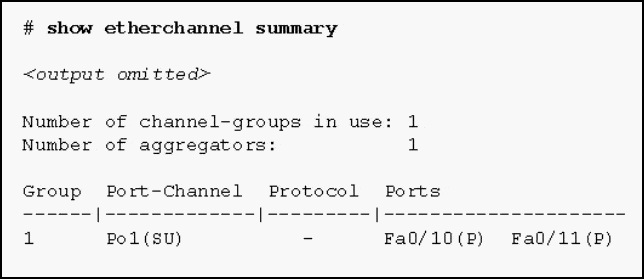
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 04 - The EtherChannel is dynamic and is using ports Fa0/10 and Fa0/11 as passive ports.
- The EtherChannel is down as evidenced by the protocol field being empty.
- The EtherChannel is partially functional as indicated by the P flags for the FastEthernet ports.
- The EtherChannel is in use and functional as indicated by the SU and P flags in the command output.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The command output shows the port channel as SU , which means Layer 2 and in use ; and the FastEthernet 0/10 and 0/11 interfaces are bundled in port-channel as indicated by the P flag. Configuring the EtherChannel using the channel-group 1 mode on command will cause the Protocol field in the command output to be empty.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is troubleshooting a problem with EtherChannel. What command was used to produce the exhibited output?
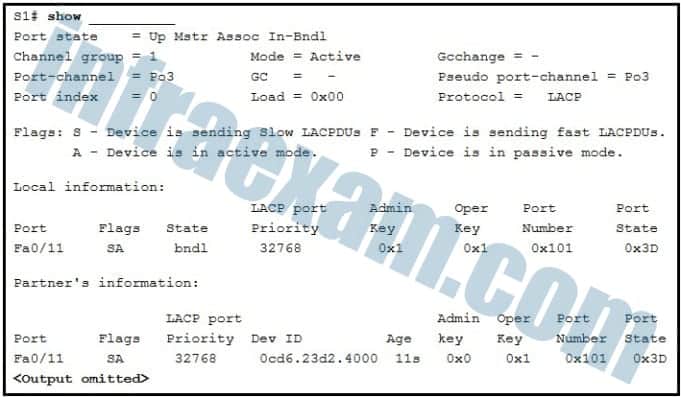
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 10 - show interfaces fastethernet 0/11 etherchannel
- show etherchannel Port-channel
- show etherchannel summary
- show interfaces Port-channel11
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The show interfaces fastethernet 0/11 etherchannel command will show the EtherChannel information for the FastEthernet 0/11 interface. The displayed information includes the port channel it belongs to, the current mode, and the channel group, among other information.
-
Which command will start the process to bundle two physical interfaces to create an EtherChannel group via LACP?
- channel-group 2 mode auto
- interface port-channel 2
- channel-group 1 mode desirable
- interface range GigabitEthernet 0/4 – 5
Answers Explanation & Hints:
To specify the interfaces in an EtherChannel group, use the interface range interface global configuration command for the range of interfaces used. The interface range GigabitEthernet 0/4 – 5 command is the correct option because it specifies two interfaces for the EtherChannel group.
-
An administrator has configured a DHCPv4 relay router and issued these commands:
Router(config)# interface g0/0
Router(config-if)# ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
Router(config-if)# exit
Router(config)# ip dhcp pool RELAY
Router(dhcp-config)# endThe clients are not receiving IP parameters from the DHCPv4 server. What is a possible cause?
- The pool cannot be named ‘RELAY’.
- The router is configured as a DHCPv4 client.
- The IP address is incorrect for the subnet mask that is used.
- The ip helper-address command is missing.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
This router should be configured with the ip helper-address command, followed with the IP address of the DHCPv4 server, because the router is meant to be used as a relay agent. The ip dhcp pool RELAY command just names the DHCPv4 pool, and it does not enable the relay function.
-
A small coffee shop is offering free Wi-Fi to customers. The network includes a wireless router and a DSL modem that is connected to the local phone company. What method is typically used to configure the connection to the phone company?
- Set the WAN connection in the wireless router as a DHCP client.
- Set the DSL modem as a DHCP client to get a public IP address from the wireless router.
- Set the connection between the wireless router and the DSL modem as a private IP network.
- Set the DSL modem as a DHCP client to the phone company and a DHCP server for the internal connection.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
In a SOHO environment, a wireless router connects to an ISP via a DSL or cable modem. The IP address between the wireless router and ISP site is typically assigned by the ISP through DHCP. The DSL modem does not manage IP address allocation.
-
Match the purpose with its DHCP message type. (Not all options are used.)
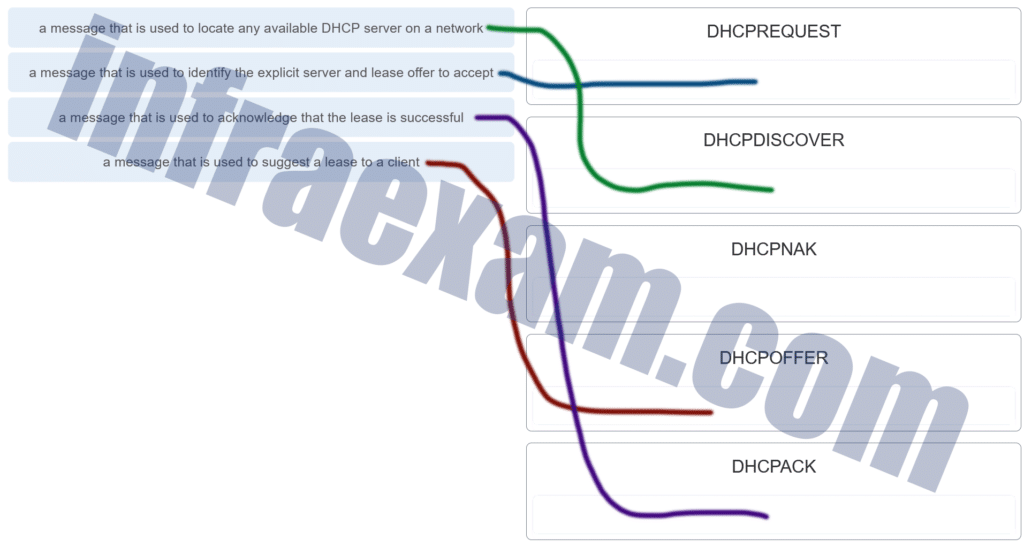
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 003 Answers Explanation & Hints:
The DHCPDISCOVER message is used to identify any DHCP servers on a network. The DHCPOFFER message is used by a server to offer a lease to a client. The DHCPREQUEST message is used to identify both the specific DHCP server and the lease that the client is accepting.<br />The DHCPACK message is used by a server to finalize a successful lease with a client.<br />The DHCPNAK message is used when an offered lease is no longer valid.
-
A network administrator is implementing DHCPv6 for the company. The administrator configures a router to send RA messages with M flag as 1 by using the interface command ipv6 nd managed-config-flag . What effect will this configuration have on the operation of the clients?
- Clients must use the information that is contained in RA messages.
- Clients must use all configuration information that is provided by a DHCPv6 server.
- Clients must use the prefix and prefix length that are provided by a DHCPv6 server and generate a random interface ID.
- Clients must use the prefix and prefix length that are provided by RA messages and obtain additional information from a DHCPv6 server.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Under stateful DHCPv6 configuration, which is indicated by setting M flag as 1 (through the interface command ipv6 nd managed-config-flag ), the dynamic IPv6 address assignments are managed by the DHCPv6 server. Clients must obtain all configuration information from a DHCPv6 server.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The users on the LAN network of R1 cannot receive an IPv6 address from the configured stateful DHCPv6 server. What is missing from the stateful DHCPv6 configuration on router R1?
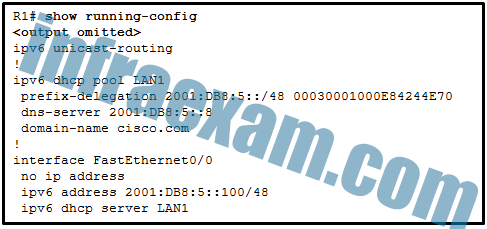
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 11 - IPv6 has not been enabled globally on router R1.
- The DHCPv6 pool has not been bound to the LAN interface.
- The FA0/0 interface is missing the command that informs the clients to use stateful DHCPv6.
- The DHCPv6 pool does not match the IPv6 address configured on interface FA0/0.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When configuring a router interface for stateful DHCPv6, the router must be able to inform the host PC’s to receive IPv6 addressing from a stateful DHCPv6 server. The interface command is ipv6 nd managed-config-flag
-
Match the FHRP protocols to the appropriate description. (Not all options are used.)
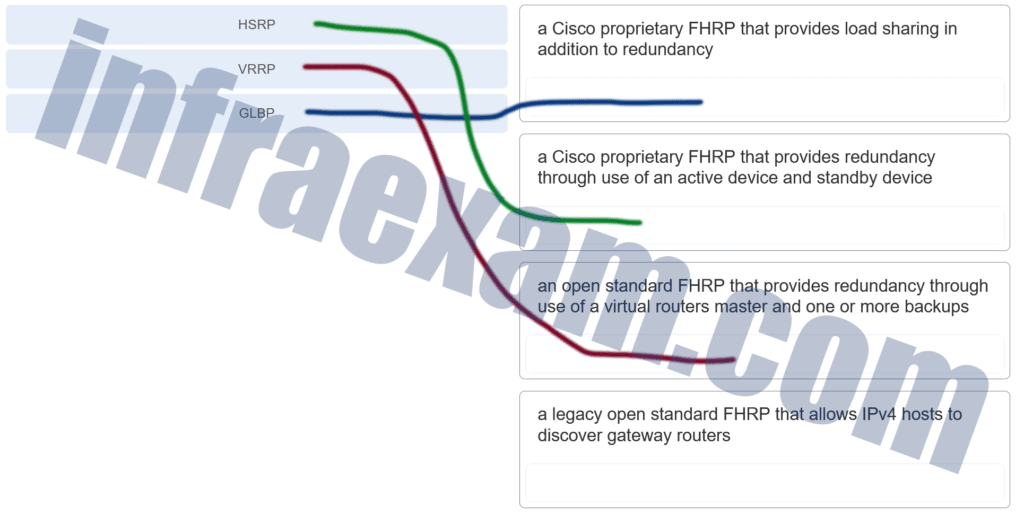
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 004 Answers Explanation & Hints:
GLBP, A Cisco proprietary FHRP that provides load sharing in addition to redundancy. HSRP A Cisco proprietary FHRP that provides redundancy through use of an active device and standby device. VRRP, An open standard FHRP that provides redundancy through use of a virtual routers master and one or more backups. Distractor, A legacy open standard FHRP that allows IPv4 hosts to discover gateway routers.
-
A network engineer is configuring a LAN with a redundant first hop to make better use of the available network resources. Which protocol should the engineer implement?
- FHRP
- GLBP
- HSRP
- VRRP
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) provides load sharing between a group of redundant routers while also protecting data traffic from a failed router or circuit.
-
Which term describes the role of a Cisco switch in the 802.1X port-based access control?
- agent
- supplicant
- authenticator
- authentication server
Answers Explanation & Hints:
802.1X port-based authentication defines specific roles for the devices in the network: Client (Supplicant) – The device that requests access to LAN and switch services
Switch (Authenticator) – Controls physical access to the network based on the authentication status of the client
Authentication server – Performs the actual authentication of the client
-
Which Cisco solution helps prevent ARP spoofing and ARP poisoning attacks?
- Port Security
- DHCP Snooping
- IP Source Guard
- Dynamic ARP Inspection
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Cisco provides solutions to help mitigate Layer 2 attacks. The solutions include the following:
IP Source Guard (IPSG) – prevents MAC and IP address spoofing attacks
Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) – prevents ARP spoofing and ARP poisoning attacks
DHCP Snooping – prevents DHCP starvation and SHCP spoofing attacks
Port Security – prevents many types of attacks including MAC table overflow attacks and DHCP starvation attacks
-
Which statement describes the behavior of a switch when the MAC address table is full?
- It treats frames as unknown unicast and floods all incoming frames to all ports on the switch.
- It treats frames as unknown unicast and floods all incoming frames to all ports within the local VLAN.
- It treats frames as unknown unicast and floods all incoming frames to all ports within the collision domain.
- It treats frames as unknown unicast and floods all incoming frames to all ports across multiple switches.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When the MAC address table is full, the switch treats the frame as an unknown unicast and begins to flood all incoming traffic to all ports only within the local VLAN.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The administrator wants to enable port security on an interface on switch S1, but the command was rejected. Which conclusion can be drawn?
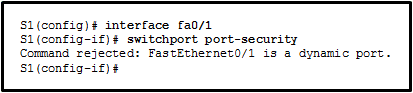
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 08 - The interface must be initially configured with the switchport mode trunk command.
- The interface needs to be configured initially with an IP address.
- The interface must be initially configured with the switchport mode access command.
- The interface needs to be previously configured with the no shutdown command.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
To enable port security, use the switchport port-security interface configuration command on an access port. By default, Layer 2 switch ports are set to dynamic auto (trunking on); therefore, the port must be initially configured as an access port before port security can be enabled.
-
After sticky learning of MAC addresses is enabled, what action is needed to prevent dynamically learned MAC addresses from being lost in the event that an associated interface goes down?
- Shut down the interface then enable it again with the no shutdown command.
- Configure port security for violation protect mode.
- Reboot the switch.
- Copy the running configuration to the startup configuration.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When sticky learning is enabled, dynamically learned MAC addresses are stored in the running configuration in RAM and will be lost if the switch is rebooted or an interface goes down. To prevent the loss of learned MAC addresses, an administrator can save the running configuration into the startup configuration in NVRAM.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring DAI on switch SW1. What is the result of entering the exhibited commands?

CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 02 - DAI will validate only the IP addresses.
- DAI will validate only the destination MAC addresses.
- DAI will validate both source and destination MAC addresses as well as the IP addresses in the order specified. When one set of parameters are valid, the ARP packet is allowed to pass.
- DAI will validate both source and destination MAC addresses as well as the IP addresses in the order specified. If all parameters are valid then the ARP packet is allowed to pass.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
DAI can be configured to check for destination MAC, source MAC, and IP addresses. However, only one ip arp inspection validate command can be configured. Entering multiple ip arp inspection validate commands overwrites the previous command.
-
On which port should Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) be configured on a switch?
- an uplink port to another switch
- any untrusted port
- access ports only
- on any port where DHCP snooping is disabled
Answers Explanation & Hints:
DHCP snooping must be enabled on a port where DAI is configured, because DAI requires the DHCP snooping table to operate. Only a trusted interface, such as an uplink port between switches, is configured to implement DAI. All access ports are untrusted.
-
What is the best way to prevent a VLAN hopping attack?
- Disable STP on all nontrunk ports.
- Use ISL encapsulation on all trunk links.
- Use VLAN 1 as the native VLAN on trunk ports.
- Disable trunk negotiation for trunk ports and statically set nontrunk ports as access ports.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
VLAN hopping attacks rely on the attacker being able to create a trunk link with a switch. Disabling DTP and configuring user-facing ports as static access ports can help prevent these types of attacks. Disabling the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) will not eliminate VLAN hopping attacks.
-
What are the two methods that a wireless NIC can use to discover an AP? (Choose two.)
- sending an ARP request broadcast
- sending a multicast frame
- transmitting a probe request
- initiating a three-way handshake
- receiving a broadcast beacon frame
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Two methods can be used by a wireless device to discover and register with an access point: passive mode and active mode. In passive mode, the AP sends a broadcast beacon frame that contains the SSID and other wireless settings. In active mode, the wireless device must be manually configured for the SSID, and then the device broadcasts a probe request.
-
An employee connects wirelessly to the company network using a cell phone. The employee then configures the cell phone to act as a wireless access point that will allow new employees to connect to the company network. Which type of security threat best describes this situation?
- cracking
- denial of service
- rogue access point
- spoofing
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Configuring the cell phone to act as a wireless access point means that the cell phone is now a rogue access point. The employee unknowingly breached the security of the company network by allowing a user to access the network without connecting through the company access point. Cracking is the process of obtaining passwords from data stored or transmitted on a network. Denial of service attacks refer to sending large amounts of data to a networked device, such as a server, to prevent legitimate access to the server. Spoofing refers to access gained to a network or data by an attacker appearing to be a legitimate network device or user.
-
Which combination of WLAN authentication and encryption is recommended as a best practice for home users?
- WEP and TKIP
- WPA2 and AES
- EAP and AES
- WPA and PSK
- WEP and RC4
Answers Explanation & Hints:
WPA2 is the Wi-Fi alliance version of 802.11i, the industry standard for authentication. Neither WEP nor WPA possess the level of authentication provided by WPA2. AES aligns with WPA2 as an encryption standard, and is stronger than TKIP or RC4. PSK refers to pre-shared passwords, an authentication method that can be used by either WPA or WPA2. EAP is intended for use with enterprise networks which use a RADIUS server.
-
What is the reason for disabling SSID broadcasting and changing the default SSID on a wireless access point?
- Anyone with the default SSID can gain access to the access point and change the configuration.
- Disabling SSID broadcasting frees up radio frequency bandwidth and increases the data throughput of the access point.
- The access point stops broadcasting its own MAC address, thus preventing unauthorized wireless clients from connecting to the network.
- Wireless clients must then have the SSID manually configured to connect to the wireless network.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The SSID is the name of the wireless network. Changing the default SSID forces device users to manually enter the SSID in order to gain access to the network. Broadcasting the SSID does not allow other devices to access the configuration, or to discover the MAC address of the device. SSID broadcasts do not affect radio frequency bandwidth.
-
A network administrator of a college is configuring WLAN security with WPA2 Enterprise authentication. Which server is required when deploying this type of authentication?
- AAA
- DHCP
- SNMP
- RADIUS
Answers Explanation & Hints:
WAP2 Enterprise provides stronger secure user authentication than WPA2 PSK does. Instead of using a pre-shared key for all users to access a WLAN, WPA2 Enterprise requires that users enter their own username and password credentials to be authenticated before they can access the WLAN. The RADIUS server is required for deploying WPA2 Enterprise authentication.
-
A network administrator is configuring a WLC to provide WLAN access to users in an office building. When testing the newly created WLAN, the administrator does not see the SSID from a wireless device. What is a possible cause?
- The new WLAN needs to be enabled.
- The RADUIS server is not operational.
- The WLAN security setting is incorrect.
- The APs have not been configured for the new WLAN.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
After a new WLAN is created and configured on a WLC, it should be enabled before it can be accessed by users.
-
What is a potential issue when using the WLC to upgrade and deploy the latest firmware image to all APs?
- Users will not be able to use the WLAN.
- Only one of the two bands would work at a time.
- Old 802.11 standards may not be supported anymore.
- Usernames and passwords must be manually entered into the AP so that WLAN authentication continues during the upgrade.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When APs are performing a firmware upgrade, users will be disconnected from the WLAN and the internet until the upgrade finishes. The wireless router may need to reboot several times before normal network operations are restored.
-
Match the dynamic routing protocol component to the characteristic. (Not all options are used.)
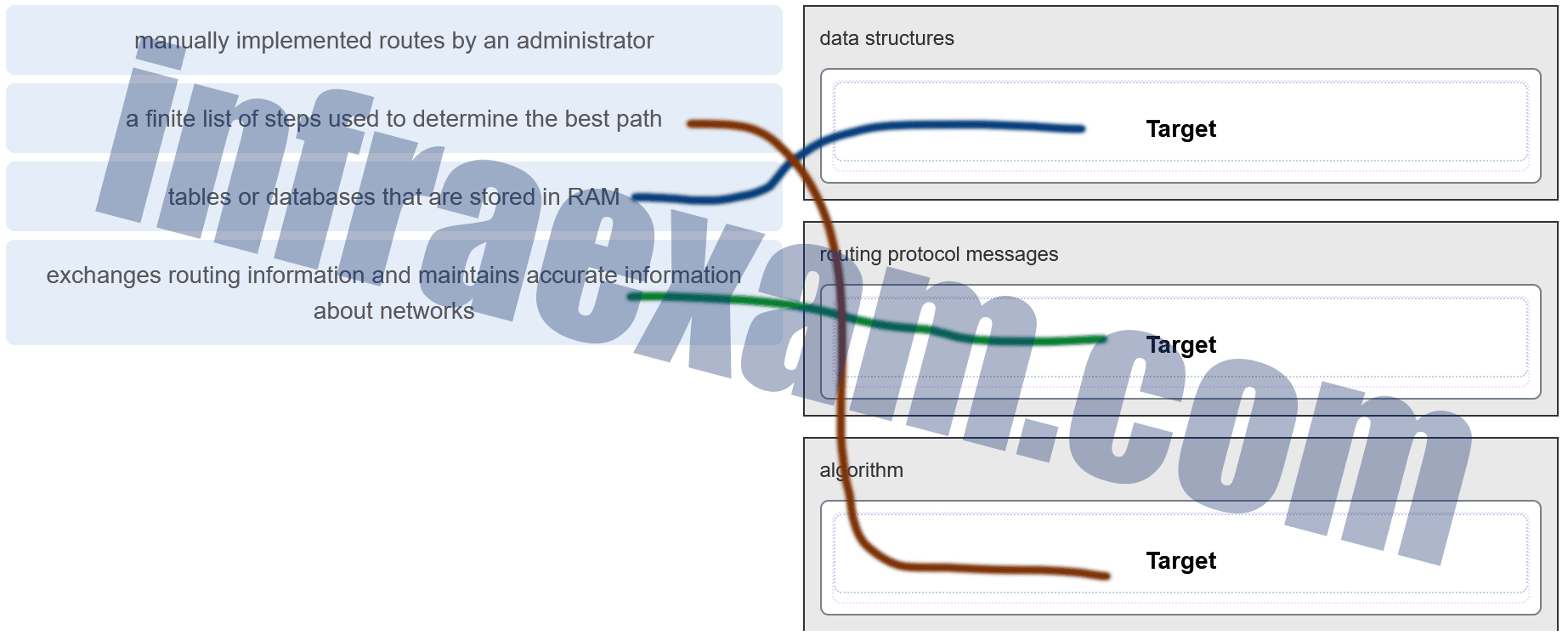
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 005 Answers Explanation & Hints:
The three components of dynamic routing protocols include:
- Data structures
- Routing protocol messages
- Algorithm
-
What address and prefix length is used when configuring an IPv6 default static route?
- ::/0
- ::1/128
- 0.0.0.0/0
- FF02::1/8
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The IPv6 address and prefix for a default static route is ::/0. This represents all zeros in the address and a prefix length of zero.
-
Gateway of last resort is not set.
172.18.109.0/26 is variously subnetted, 7 subnets, 3 masks
O 172.18.109.0/26 [110/10] via 172.18.32.1, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0
O 172.18.109.64/26 [110/20] via 172.18.32.6, 00:00:56, Serial 0/0/1
O 172.18.109.128/26 [110/10] via 172.18.32.1, 00:00:24, Serial 0/0/0
C 172.18.109.192/27 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 172.18.109.193/27 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
C 172.18.109.224/27 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 172.18.109.225/27 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
172.18.32.0/24 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks
C 172.18.32.0/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
L 172.18.32.2/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
C 172.18.32.4/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
L 172.18.32.5/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
S 172.18.33.0/26 [1/0] via 172.18.32.1, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0
R1#Refer to the exhibit. Which interface will be the exit interface to forward a data packet that has the destination IP address 172.18.109.152?
- Serial0/0/0
- GigabitEthernet0/0
- GigabitEthernet0/1
- None, the packet will be dropped.
-
What are two characteristics of Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF)? (Choose two.)
- Packets are forwarded based on information in the FIB and an adjacency table.
- When a packet arrives on a router interface, it is forwarded to the control plane where the CPU matches the destination address with a matching routing table entry.
- When a packet arrives on a router interface, it is forwarded to the control plane where the CPU searches for a match in the fast-switching cache.
- With this switching method, flow information for a packet is stored in the fast-switching cache to forward future packets to the same destination without CPU intervention.
- This is the fastest forwarding mechanism on Cisco routers and multilayer switches.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) builds a forwarding information base (FIB) and an adjacency table to be able to route packets quicker than traditional packet forwarding methods can.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Match the description with the routing table entries. (Not all options are used.)
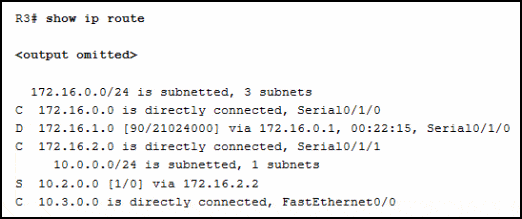
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 05 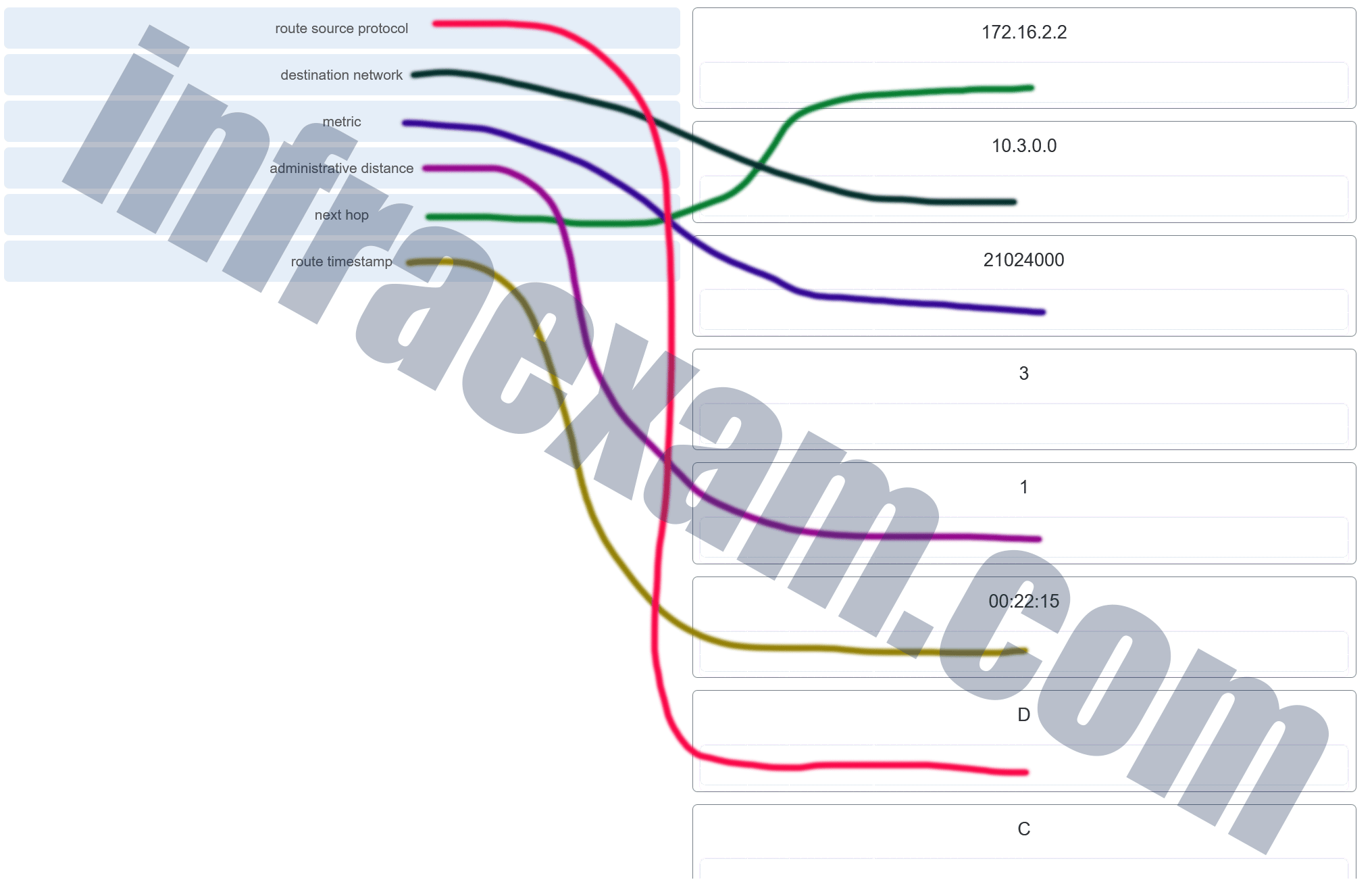
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 006 Answers Explanation & Hints:
route source protocol = D (which is EIGRP)
destination network = 10.3.0.0
metric = 21024000
administrative distance = 1
next hop = 172.16.2.2
route timestamp = 00:22:15 -
Refer to the exhibit. Router R1 has an OSPF neighbor relationship with the ISP router over the 192.168.0.32 network. The 192.168.0.36 network link should serve as a backup when the OSPF link goes down. The floating static route command ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 S0/0/1 100 was issued on R1 and now traffic is using the backup link even when the OSPF link is up and functioning. Which change should be made to the static route command so that traffic will only use the OSPF link when it is up?
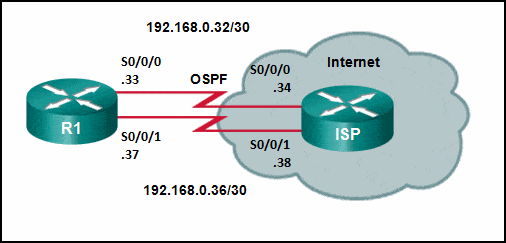
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 01 - Add the next hop neighbor address of 192.168.0.36.
- Change the administrative distance to 1.
- Change the destination network to 192.168.0.34.
- Change the administrative distance to 120.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The problem with the current floating static route is that the administrative distance is set too low. The administrative distance will need to be higher than that of OSPF, which is 110, so that the router will only use the OSPF link when it is up.
-
Which command would create a valid IPv6 default route?
- ipv6 route ::/0 fe80::1
- ipv6 route 2001:db8:acad:1::/64 ::1
- ipv6 route ::/0 2001:db8:acad:2::a
- ipv6 route ::/128 2001:db8:acad:1::1
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The correct prefix and prefix length for a default route is ::/0, which matches any address. ::/128 matches only the specific address of all zeros. When creating a static route that uses a link-local address as the next hop, an exit interface must also be specified for the route to be valid.
-
Consider the following command:
ip route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.2 5
What does the 5 at the end of the command signify?
- metric
- exit interface
- administrative distance
- maximum number of hops to the 192.168.10.0/24 network
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The 5 at the end of the command signifies administrative distance. This value is added to floating static routes or routes that only appear in the routing table when the preferred route has gone down. The 5 at the end of the command signifies administrative distance configured for the static route. This value indicates that the floating static route will appear in the routing table when the preferred route (with an administrative distance less than 5) is down.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The routing table for R2 is as follows:

CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 06 Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.0.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
C 10.0.0.4 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
192.168.10.0/26 is subnetted, 3 subnets
S 192.168.10.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
C 192.168.10.64 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
S 192.168.10.128 [1/0] via 10.0.0.6What will router R2 do with a packet destined for 192.168.10.129?
- drop the packet
- send the packet out interface Serial0/0/0
- send the packet out interface Serial0/0/1
- send the packet out interface FastEthernet0/0
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When a static route is configured with the next hop address (as in the case of the 192.168.10.128 network), the output of the show ip route command lists the route as “via” a particular IP address. The router has to look up that IP address to determine which interface to send the packet out. Because the IP address of 10.0.0.6 is part of network 10.0.0.4, the router sends the packet out interface Serial0/0/1.
-
A junior technician was adding a route to a LAN router. A traceroute to a device on the new network revealed a wrong path and unreachable status. What should be done or checked?
- Check the configuration of the exit interface on the new static route.
- Verify that the static route to the server is present in the routing table.
- Check the configuration on the floating static route and adjust the AD.
- Create a floating static route to that network.
-
Refer to the exhibit. How was the host route 2001:DB8:CAFE:4::1/128 installed in the routing table?
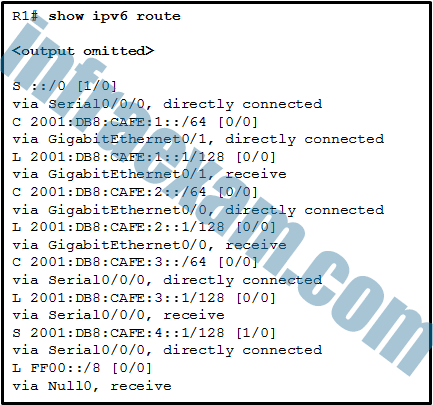
CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 07 - The route was automatically installed when an IP address was configured on an active interface.
- The route was dynamically learned from another router.
- The route was manually entered by an administrator.
- The route was dynamically created by router R1.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A host route is an IPv6 route with a 128-bit mask. A host route can be installed in a routing table automatically when an IP address is configured on a router interface or manually if a static route is created.
-
Refer to the exhibit. When a packet arrives on interface Serial0/0/0 on R1, with a destination IP address of PC1, which two events occur? (Choose two)

CCNA2 SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers v7 03 - Router R1 will forward the packet out Gig0/0.
- Router R1 will forward the packet out Gig0/1.
- Router R1 will forward the packet out S0/0/0.
- Router R1 will de-encapsulate the packet and encapsulate it in a PPP frame.
- Router R1 will de-encapsulate the packet and encapsulate it in an Ethernet frame.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A router will look in the routing table for a destination network and locate an exit interface to forward a packet to a destination. After the exit interface is determined, the router will encapsulate a packet into the correct frame type.