98-365 : Windows Server Administration Fundamentals : Part 10
98-365 : Windows Server Administration Fundamentals : Part 10
-
You work as a System Administrator for company Inc. The company has a Windows Server 2016 domain-based network. The network has 120 Windows 10 computers and two Windows Server 2016 servers.
You want to ensure that when users log on to any client computer on the network, settings can be changed, but all settings are reset back to their default values when they log on again.
What will you do to accomplish the task?
- Create a Group Policy Object.
- Create a local user profile.
- Create a roaming user profile.
- Create a mandatory user profile.
Explanation:
In order to accomplish the task, you should create a mandatory user profile. A mandatory user profile is a preconfigured, read-only user profile that administrators can use to specify settings for users in a Windows environment. With a mandatory user profile, a user can modify the desktop, but any changes made are not saved when the user logs off. The next time the user logs on, the mandatory user profile set by the administrator is downloaded.Incorrect Answers:
A: A Group Policy Object (GPO) is a collection of group policy settings. It affects the user and computer accounts located in sites, domains, and organizational units (OUs).B: A local user profile is stored locally on the hard drive of the computer on which the user logs on. If the user logs on to a different computer, he gets the default settings for that computer.
C: A roaming user profile is stored in a centralized place and can be accessed from the network. When users log on to their computers, they receive the desktop setting as it existed when they logged off.
-
You work as a System Administrator for company Inc. The company has a Windows Server 2016 domain-based network. The network contains one Windows Server 2016 and twelve Windows 10 client computers.
You want to centralize management and configuration of operating systems, applications, and user settings.
What will you do?
- Apply NTFS permission.
- Implement an account policy.
- Apply an audit policy.
- Implement a group policy.
Explanation:
In order to centralize management and configuration of operating systems, applications, and user settings in an Active Directory environment, you should implement a group policy. A group policy that is created by an administrator affects all users on a computer or all users on a domain.
Group policies can be used for defining, customizing, and controlling the functioning of network resources, computers, and operating systems.
They can be set for a for users or computers in a domain. Administrators can configure group policy settings for users as well as for computers in many ways. Group policies can be used to allow or restrict the access of a particular program by a particular user. It can also be used to configure the desktop, the Start menu, the taskbar, the Control Panel, and security settings among other things.Incorrect Answers:
A: NTFS permission allows an administrator to control which users and groups can access files and folders on an NTFS volume.
B: An account policy controls the password expiration policy, the lockout policy, and other password features.
C: An audit policy determines whether security events are written to the security log in Event Viewer on the computer. -
You work as a Network Administrator for Perfect Solutions Inc. The company plans to establish a Windows 2016 Active Directory-based network. The network will be configured as a single forest and a multiple-domain network.
You are planning for the placement of operations master roles.
In this context, which of the following operations master roles are applied to the entire forest? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. (Choose two.)
- Domain naming master
- Schema master
- PDC emulator master
- Relative ID (RID) master
Explanation:
Schema master and domain naming master are operations master roles that are applied to the entire forest within an Active Directory network. The other operations master roles are applied per domain. -
Which of the following master roles is used for synchronizing cross-domain group membership changes?
- Domain Naming Master role
- Infrastructure Master role
- Schema Master role
- RID Master role
Explanation:
The Infrastructure Master role is used for synchronizing cross-domain group membership changes.Incorrect Answers:
A: The Domain Naming Master role is used for controlling the addition and removal of domains from the forest if they are present in the root domain.
C: The Schema Master role is used for controlling and handling updates and modifications to the Active Directory schema.
D: The RID Master role is used for allocating pools of unique identifiers to domain controllers for use when creating objects. -
What are the two different ways of creating Group Policy Object (GPO) with the help of Group Policy Management Console (GPMC)? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. (Choose two.)
- Open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) and navigate to the Group Policy Objects node. Right-click the Group Policy Objects node, and click Properties. Change the default name of the GPO to your desired name, and then click OK.
- Open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) and navigate to the container where you want to apply the GPO. Right-click the container, and click Create A GPO In This Domain And Link It Here.
- Open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) and navigate to the Domain Controller where you want to apply the GPO. Right-click the controller, and click Create A GPO In This Domain And Link It Here.
- Open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) and navigate to the Group Policy Objects node. Right-click the Group Policy Objects node, and click New. Enter a descriptive name for the new GPO, and click OK.
Explanation:
A new Group Policy Object can be created in the following two ways:
Open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) and navigate to the container where you want to apply the GPO. Right-click the container, and click Create A GPO In This Domain And Link It Here.
Open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) and navigate to the Group Policy Objects node. Right-click the Group Policy Objects node, and click New. Enter a descriptive name for the new GPO, and click OK. -
You work as a System Administrator for company Inc. The company has a Windows Server 2016 Active Directory-based single domain single forest network. The functional level of the forest is Windows Server 2016.
You are planning to create a group that can be used only for non-security functions, such as distributing e-mail messages.
Which of the following groups will you create?
- Application group
- User group
- Distribution group
- Security group
Explanation:
You should create a distribution group. A distribution group is used for non-security related functions. Administrators use a distribution group when the only function of the group is non- security related, such as sending e-mail messages to a group of users at the same time.
Distribution groups cannot be used to assign permissions.Incorrect Answers:
A, B: There are no such group types as user and application in Windows Server 2016.
D: A security group is used to define permissions on resources and objects. It can be listed in discretionary access control lists (DACLs). Security groups can also be used for non- security purposes. A security group has all capabilities of a distribution group. -
Which of the following is an application protocol for querying and modifying data using directory services running over TCP/IP?
- Kerberos
- SNMP
- UDP
- LDAP
Explanation:
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is a standard protocol, which provides access to the directory. It also provides a common language for LDAP clients and servers to communicate with each other. The LDAP is commonly used as standard in the industry. By using a directory service such as LDAP, information existing in multiple systems and formats can be brought at one place. LDAP is an application protocol for querying and modifying data using directory services running over TCP/IP.Incorrect Answers:
A: Kerberos is a secure protocol that supports ticketing authentication. A ticket is granted in response to a client computer authentication request by the Kerberos authentication server, if the request contains valid user credentials and a valid Service Principal Name (SPN). The ticket is then used by the client computer to access network resources. To enable Kerberos authentication, the client and server computers must have a trusted connection to the domain Key Distribution Center (KDC). The task of KDC is to distribute shared secret keys to enable encryption.B: Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a part of the TCP/IP protocol suite, which allows users to manage the network. SNMP is used to keep track of what is being used on the network and how the object is behaving.
C: User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is often used for one-to-many communications, using broadcast or multicast IP datagrams. Microsoft networking uses UDP for logon, browsing, and name resolution. UDP is a connectionless and unreliable communication protocol. It does not guarantee delivery or verify sequencing for any datagram. UDP provides faster transportation of data between TCP/IP hosts than TCP.
-
You work as a Network Administrator for NetTech Inc. The company has a Windows Server 2016 Active Directory-based network. The company has three departments named Sales, Purchase, and Marketing.
You are required to create organizational units (OU) structure for each department in the network.
Which of the following are the reasons for defining an OU? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- To delegate administration.
- To administer domain controllers.
- To hide objects.
- To administer group policy.
Explanation:
Organizational units (OUs) are defined to delegate administration, to administer group policy, or to hide objects. Delegating administration is the prime reason for defining OUs. -
You work as a Server Administrator for company Inc. The company has a Windows Active Directory-based single domain single forest network. The functional level of the forest is Windows Server 2016.
You are planning to create groups for assigning permissions.
Which of the following characteristics does the universal group have? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. (Choose two.)
- It consists of global groups from multiple domains.
- Members can only come from the local domain.
- It has its memberships listed in the global catalog database.
- Its members can access resources only from the local domain.
Explanation:
The universal group consists of global groups from multiple domains. It includes global groups, other universal groups, and user accounts. The universal group has its memberships listed in the global catalog database. Global catalogs replicate universal group membership; therefore, an administrator must limit the membership to global groups.Incorrect Answers:
B: In the universal group, members can come from any domain.
D: Members of the universal group can access resources from any domain. -
You work as a Server Administrator for company Inc. The company has a Windows Active Directory-based multiple domain single forest network. The functional level of the forest is Windows Server 2016.
You want to allow some groups to take more control of their local network resources by delegating administrative control to a level of a domain tree.
What will you do? Each correct answer represents a part of the solution. (Choose two.)
- Configure the Demilitarized zone (DMZ).
- Create organizational units within a domain.
- Provide administrative privileges to particular groups.
- Delegate administrative control for specific organizational units to particular groups.
Explanation:
In order to allow some groups to take more control of their local network resources by delegating administrative control to a level of a domain tree, you should take the following steps:
Create organizational units within a domain.
Delegate administrative control for specific organizational units to particular users or groups.Incorrect Answers:
A: DMZ provides a network the ability to use the Internet while maintaining its security.
C: Providing administrative privileges to particular groups is not required to accomplish the task. -
You work as a Server Administrator for company Inc. You need to make a computer running Windows Server 2016 a domain controller.
Which of the following steps will you take to accomplish the task? Each correct answer represents a part of the solution. (Choose two.)
- Install Active Directory Domain Services.
- Create an MX resource record.
- Run the nslookup command.
- Execute the dcpromo command.
Explanation:
To make a computer running Windows Server 2016 a domain controller, you should take the following steps:Install Active Directory Domain Services.
Execute the dcpromo command. In Windows Server 2016, dcpromo is executed by clicking the link to complete the Active Directory configuration.Incorrect Answers:
B: An MX resource record is used to specify which mail exchanger to contact for a specified domain and in what order to use each mail host.
C: The nslookup command is used to check records, domain host aliases, domain host services, and operating system information by querying Internet domain name servers. -
Which of the following statements are true about group nesting? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Windows allows group nesting where an administrator can place a group as a member of another group.
- While nesting, an administrator should always keep in mind that the level of nesting should be maximized, as this will minimize the permission structure.
- It is the process of nesting a group within other groups.
- The main advantage of group nesting is that it requires less work when assigning privileges and permissions.
Explanation:
Group nesting is the process of nesting a group within other groups. The main advantage of group nesting is that is requires less work when assigning privileges and permissions. Windows allows group nesting where an administrator can place a group as a member of another group. While nesting, an administrator should always keep in mind that the level of nesting should be minimized, as this will complicate the permission structure. Naming of the group is another aspect of planning group. An administrator should establish a convention for naming groups. A consistent naming convention will help administrators identify and keep track of group membership. -
In an Active Directory, which of the following represents a geographic location hosting networks?
- Site
- OU
- Domain
- Forest
Explanation:
A site in Active Directory represents a geographic location hosting networks. Active Directory (AD) sites consist of well-connected networks defined by IP subnets that help define the physical structure of a user’s Active Directory, and give the user control over replication traffic and authentication traffic. Because AD relies on IP, all LAN segments should have a defined IP subnet. This makes creating an AD straightforward; a user can simply group well-connected subnets to form a site.Incorrect Answers:
B: An organizational unit (OU) is a type of Active Directory object (or container) in which user accounts, groups, computers, printers, applications, file shares, and other organizational units within a single domain can be placed.C: In the Windows environment, a domain is a set of network resources that are part of a network and share a common directory database. A domain is administered as a unit with common rules and procedures. Each domain has a unique name. Users just have to log on to a domain to access the network resources within it.
D: A forest is a collection of Windows domains that do not necessarily share a common namespace. Forests simplify the management of multiple domains. All domains within a forest share a common schema and Global Catalog. Resources can be shared among the domains in a forest.
-
DRAG DROP
You work as a Network Administrator for Perfect Solutions Inc. The company has a Windows Active Directory-based single domain single forest network. The functional level of the forest is Windows Server 2016. You are planning to create groups for assigning permissions.
Drag and place the appropriate group in front of the group scopes that are given.

98-365 Part 10 Q14 024 Question 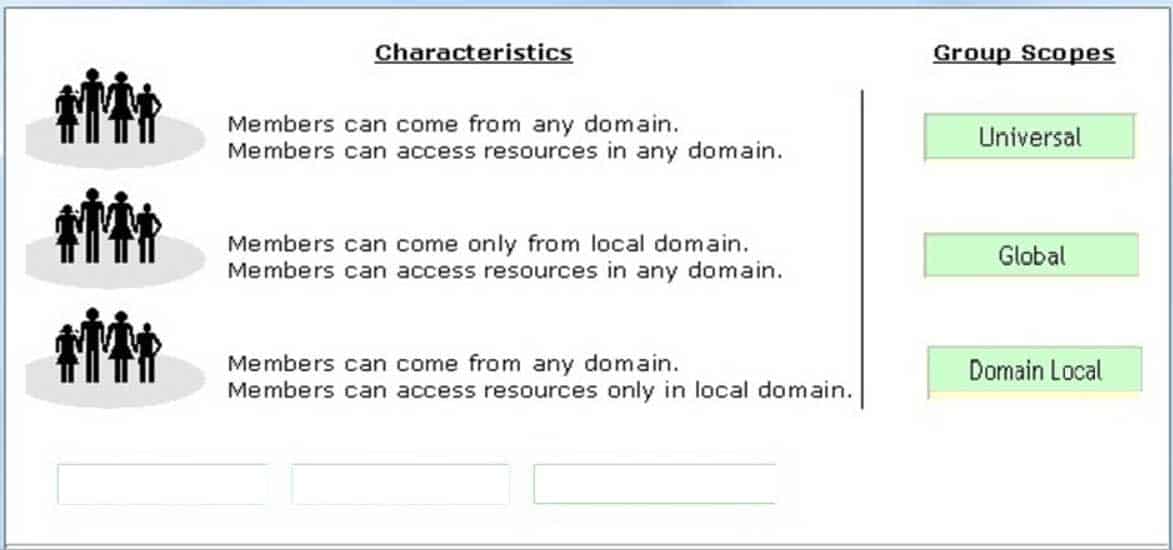
98-365 Part 10 Q14 024 Answer Explanation:
The scope of a group defines two characteristics:
It determines the level of security applying to a group. It determines which users can be added to a group. Windows Server 2016 supports the following scopes:
Domain Local: Domain local groups are used to assign permissions to local resources such as files and printers. Members can come from any domain.
Global: Members of this group can access resources in any domain. Members can only come from the local domain.
Universal: Members can be added from any domain in the forest. Members can access resources from any domain. Universal groups are used for managing the security across domains. Universal groups can also contain global groups. -
DRAG DROP
Choose from the list below the tasks that you can do with the help of the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC).

98-365 Part 10 Q15 025 Question 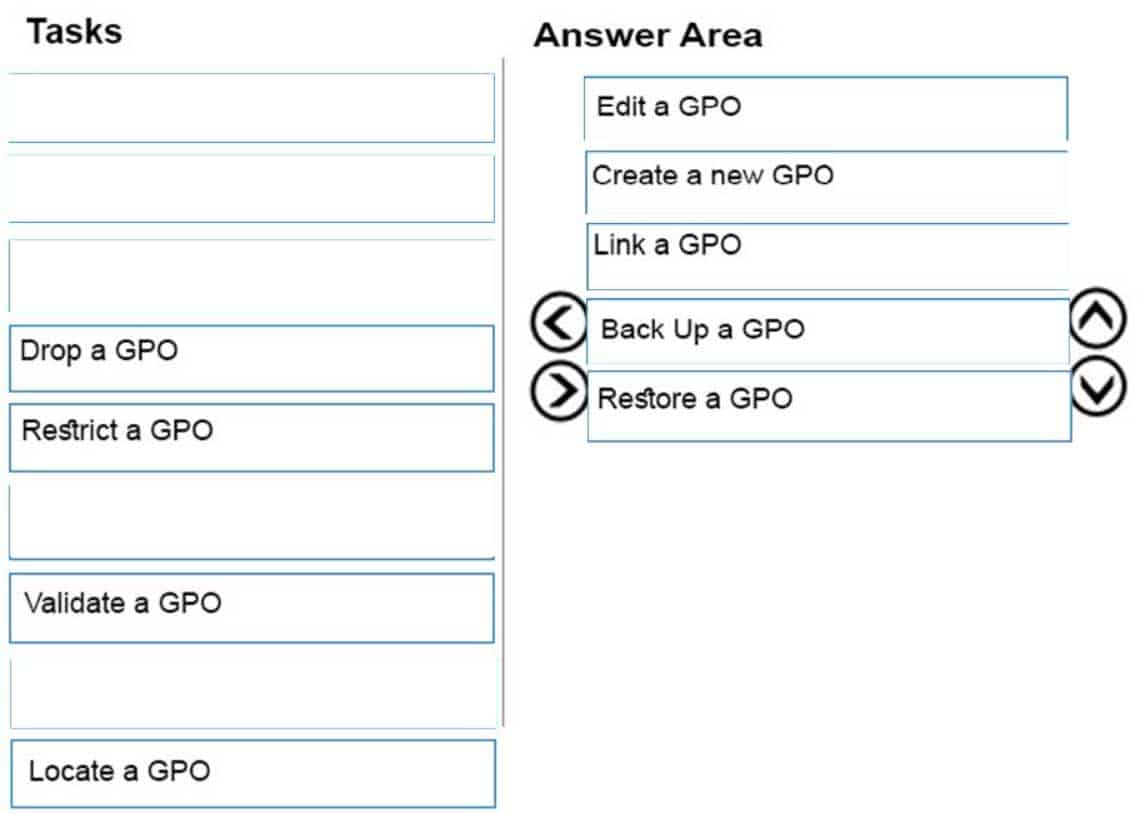
98-365 Part 10 Q15 025 Answer Explanation:
GPMC enables a user to complete the following tasks:
Create a new GPO: It is good measure to create new descriptive GPOs instead of modifying existing GPOs.
Link a GPO: In the GPMC, right-click a container, click Link an Existing GPO, and select a GPO from the Group Policy Objects list.
Edit a GPO: In GPMC, right-click the GPO that a user wants to edit, and click Edit. The Group Policy Management Editor (GPME) opens so that a user can edit the computer and user configuration instantly. Any modifications made in the GPO are saved instantly.
Back Up a GPO: In the GPMC, open the Group Policy Objects node, and right-click a GPO. Click Back Up and select a location in which to back up the GPO. Give the GPO an appropriate description. By default, the backup will use the GPO ID as the name for the backup folder. By using a description, the user makes it easier to identify the GPO in case he needs to restore it.
Restore a GPO: In the GPMC Group Policy Object node, right-click the GPO that a user wants to restore, and click Restore From Backup. In the Restore Group Policy Object Wizard, select the backup location and the source GPO, and then finish the wizard. -
DRAG DROP
In an Active Directory infrastructure, the group policies are applied in a particular order. Rearrange the levels in the correct order in which the group policies are applied.
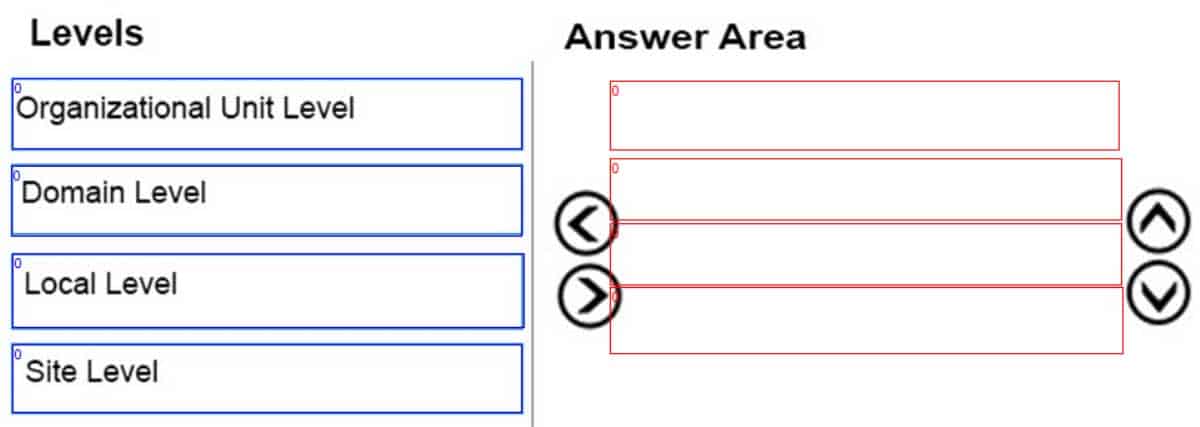
98-365 Part 10 Q16 026 Question 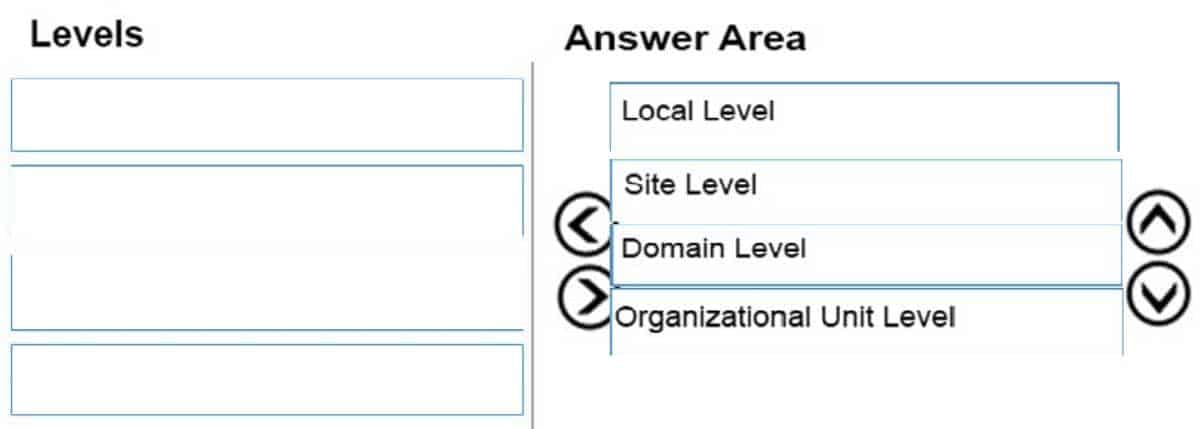
98-365 Part 10 Q16 026 Answer Explanation:
In an Active Directory infrastructure, the group policies are applied in the following order:1. Local Level
2. Site Level
3. Domain Level
4. Organizational Unit (OU) LevelIf a Group Policy setting is configured at the site, domain, or OU level and that setting contradicts a setting configured at the local policy level, the local policy setting will be overridden.
-
What type of environment has each computer keep its own security database?
- workgroup
- domain
- conglomerate
- association
Explanation:
By default, a computer is part of a workgroup. A workgroup is usually associated with a peer-to- peer network in which user accounts are decentralized and stored on each individual computer. -
What logical unit of computers shares the same security database?
- workgroup
- domain
- conglomerate
- association
Explanation:
A domain is a logical unit of computers that define a security boundary, and it is usually associated with Microsoft’s Active Directory. The security of the domain is generally centralized and controlled by Windows servers acting as domain controllers.
As a result, you can manage the security much easier for multiple computers while providing better security. -
What protocol is used to query and modify data contained within a structure that reflect geographical or organizational structure?
- LDAP
- DNS
- GlobalZones
- Kerberos
Explanation:
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol, or LDAP, is an application protocol for querying and modifying data using directory services running over TCP/IP. Within the directory, the sets of objects are organized in a logical hierarchical manner so that you can easily find and manage them. -
What Windows server attached to a domain is not a domain controller?
- member server
- bridgehead server
- LDAP server
- Kerberos server
Explanation:
A server that is not running as a domain controller is known as a member server.
To demote a domain controller to a member server, you rerun the dcpromo program.