98-365 : Windows Server Administration Fundamentals : Part 13
98-365 : Windows Server Administration Fundamentals : Part 13
-
The network-attached storage (NAS) device is a file server running on a dedicated device connected to the network.
Which of the following are the advantages of the NAS device? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- It enables the Windows, UNIX/Linux, and MacOS to use the same storage and to access the shared data.
- It is easy to install, configure, and manage by using a web browser.
- It is used when computer systems are retired and disk drives are required to be zeroed out.
- It permits the addition of more hard disk storage space to a network without shutting them down for maintenance and upgrades.
Explanation:
The network-attached storage (NAS) device is a server used for file sharing. It is a file server running on a dedicated device connected to the network. These types of devices are based on Linux or UNIX derivatives.
Various advantages of the NAS device are as follows:
– It is easy to install, configure, and manage by using a web browser.
– It enables the Windows, UNIX/Linux, and MacOS to use the same storage and to access the shared data.
– It does not require to be located within the server but can be placed anywhere in LAN.
– It permits the addition of more hard disk storage space to a network without shutting them down for maintenance and upgrades.Incorrect Answers:
C: Hard drive wiping is a degaussing process that applies a strong magnetic field for the purpose of initializing the media. It is used to remove data from the hard drive permanently. It is used when computer systems are retired and disk drives are required to be zeroed out. -
You work as a System Administrator for company Inc. The Microsoft iSCSI initiator service is deployed in the organization in order to allow Windows Server 2016 to connect to SCSI devices that are attached to a network.
You want to remove all persistently bound volumes and devices for the iSCSI service.
Which of the following iSCSICLI commands will you use to accomplish the task?
- iSCSICLI AddPersistentDevices
- iSCSICLI AddTarget
- iSCSICLI ClearPersistentDevices
- iSCSICLI RemovePersistentDevices
Explanation:
In order to accomplish the task, you should use the iSCSICLI ClearPersistentDevices command. When you use this command on the command-line interface, it removes all persistently bound volumes and devices for the iSCSI service. -
Which of the following file systems centralizes data and can be used to replicate shared folders to other servers?
- ADFS
- FAT32
- DFS
- NTFS
Explanation:
DFS (Distributed File System) centralizes data and can be used to replicate shared folders to other servers. Distributed File System (DFS) allows users to access files located on another remote host as though working on the actual host computer. This makes it possible for multiple users on multiple machines to share files and storage resources. The client nodes do not have direct access to the underlying block storage but interact over the network using a protocol.
Distributed file systems may include facilities for transparent replication and fault tolerance. That is, when a limited number of nodes in a file system go offline, the system continues to work without any data loss.Incorrect Answers:
A: Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) is used to extend the ability to use single sign-on functionality to Internet-facing applications. With the help of single sign-on and ADFS, a user can give their customers, partners, and suppliers easy access to Web based applications in the organization, such as Outlook Web App.B: The FAT32 file system is an enhancement of the FAT file system. It is more advanced and reliable than all the earlier versions of the FAT file system. It manages storage space on large hard disks more efficiently than the FAT16 file system. It uses a smaller cluster size than the FAT16 file system on the hard disk, thereby reducing the amount of space on the hard disk when users save small files. The FAT32 file system supports hard disk drives larger than 2GB and up to 2TB.
D: NTFS is a high-performance file system proprietary to Microsoft. NTFS supports file-level security, compression, and auditing. It also supports large volumes and powerful storage solution such as RAID. The latest feature of NTFS is its ability to encrypt files and folders to protect sensitive data.
-
You are configuring a RAID 5 solution on a server running Windows Server 2016. You are using five 750GB hard drives in the RAID array.
How much free space will you get after configuring the RAID 5 solution?
- 2,250
- 1,500
- 3,000
- 3,750
Explanation:
After configuring the RAID 5 solution, you get 3,000GB free space.
You can calculate free space for a RAID 5 solution using the following formula:
Available free space for RAID 5 = Total drive space – 1/n (Total drive space) where, n is the number of hard drives
According to the question: = 5 x 750 = 3,750GB
Free space for the RAID 5 solution = 3,750 – 1/5 (3,750) = 3,750 – 750 = 3,000GB -
Which of the following protocols do iSCSI fabrics use to provide discoverability and partitioning of resources?
- SCSI
- SSL
- TLS
- iSNS
Explanation:
Internet Storage Name Service (iSNS) is a protocol that allows automated discovery, management, and configuration of iSCSI and Fibre Channel devices (using iFCP gateways) on a TCP/IP network.
iSNS provides management services similar to those found in Fibre Channel networks, allowing a standard IP network to operate in much the same way that a Fibre Channel storage area network does. Because iSNS is able to emulate Fibre Channel fabric services and manage both iSCSI and Fibre Channel devices, an iSNS server can be used as a consolidated configuration point for an entire storage network.Incorrect Answers:
A: Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) is the second most popular drive interface in use today after the Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) interface. SCSI is faster than IDE and supports more devices. SCSI devices, such as hard disk drive and CD-ROM drive, are better suited in a network environment in which many users access shared drives simultaneously. SCSI has three standards: SCSI-1, SCSI-2, and SCSI-3.B: The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a commonly-used protocol for managing the security of a message transmission on the Internet. SSL has recently been succeeded by Transport Layer Security (TLS), which is based on SSL. SSL uses a program layer located between the Internet’s Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and Transport Control Protocol (TCP) layers. URLs that require an SSL connection start with https: instead of http:.
C: Transport Layer Security is a standard protocol used to secure Web communications on the Internet or intranets by means of encryption. With the help of TLS, clients can authenticate servers or servers can authenticate clients. TLS is the latest version of the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol.
-
Which of the following technologies is considered a network attached storage protocol?
- NFS
- FCoE
- Fiber Channel
- iSCSI
Explanation:
NFS (Network File System) is considered a network attached storage protocol. It is used to enable communication between an NFS client and an NFS server. The NFS client that is built into ESX supports in accessing the NFS server and in using NFS volumes for storage.Incorrect Answers:
B, C, D: These are all considered block storage protocols. -
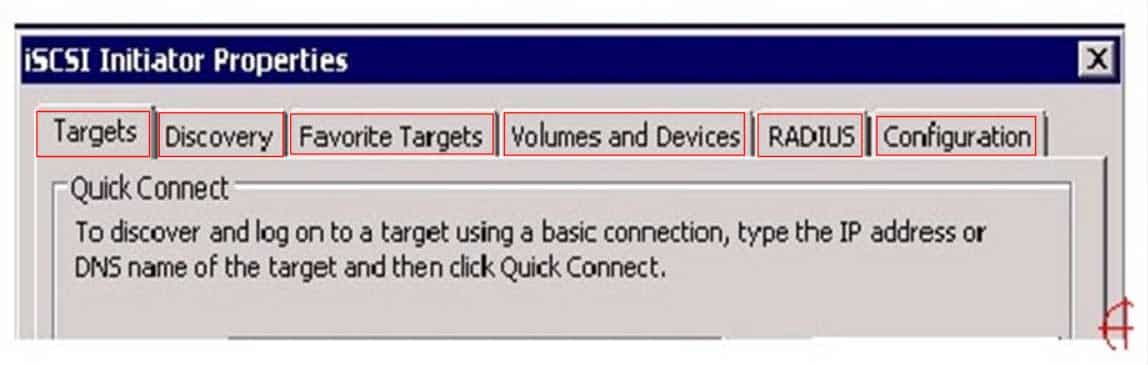
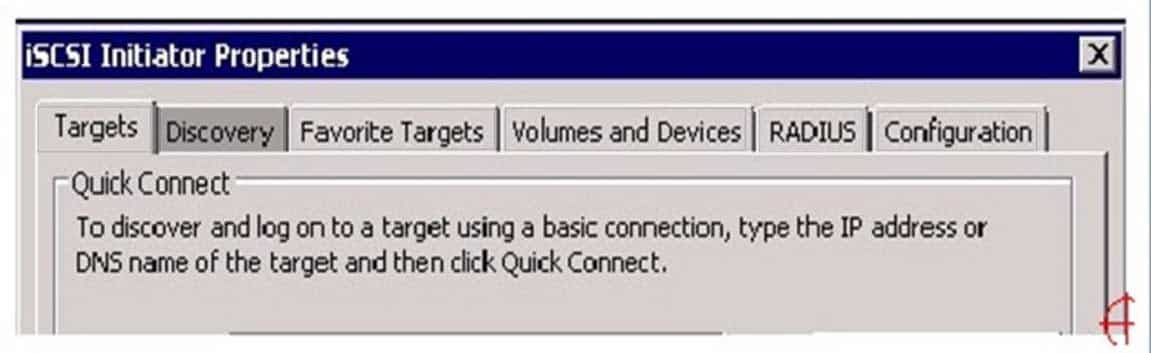
HOTSPOT
You work as a System Administrator for company Inc. You are configuring the iSCSI Initiator program in order to connect a host computer running Windows Server 2016 to an external iSCSI-based storage array.
Mark the tab or button that specifies the location of the SAN and Internet Storage Name Service (iSNS) servers when you open the iSCSI Initiator program.
-
Which form of RAID is not fault tolerant?
- RAID 0
- RAID 1
- RAID 5
- RAID 0+1
Explanation:
RAID 0 stripes data across all drives. Because RAID 0 has no parity control or fault tolerance, it is not a true form of RAID. Here, if one drive fails, you lose all data on the array. -
Which form of RAID is known as striping?
- RAID 0
- RAID 1
- RAID 5
- RAID 0+1
Explanation:
RAID 0 stripes data across all drives. With striping, all available hard drives are combined into a single large virtual file system, with the file system’s blocks arrayed so that they are spread evenly across all the drives. -
Which type of RAID is known as disk mirroring?
- RAID 0
- RAID 1
- RAID 5
- RAID 0+1
Explanation:
RAID 1 is another common form of RAID used in networked PCs and servers. RAID 1 is sometimes known as disk mirroring, which copies a disk or partition onto a second hard drive. Specifically, as information is written, it is written to both hard drives simultaneously. -
Which type of RAID is striping with parity?
- RAID 0
- RAID 1
- RAID 5
- RAID 0+1
Explanation:
RAID 5 is similar to striping, except the space equivalent to one of the hard drives is used for parity (error correction) to provide fault tolerance. To increase performance, the error- correction function is spread across all hard drives in the array to avoid having one drive doing all the work in calculating the parity bits. -
What file-level data storage device is accessed for a network and often uses SMB/CIFS?
- NAS
- SAN
- VOL
- Dynamic Drive
Explanation:
Network attached storage (NAS) is a file-level data storage device connected to a computer network to provide shared drives or folders, usually using SMB/CIFS. NAS devices usually contain multiple drives in a form of RAID for fault tolerance and are managed usually using a web interface. -
What device contains many hard drives and is used by multiple servers as a central storage area?
- NAS
- SAN
- VOL
- Dynamic Drive
Explanation:
A storage area network (SAN) is an architecture used for disk arrays, tape libraries, and optical jukeboxes to appear as locally attached drives on a server. A SAN always uses some form of RAID and other technology to make the system redundant against drive failure and to offer high performance. -
What is the default port used by iSCSI?
- 8080
- 3128
- 3260
- 9000
Explanation:
Internet Small Computing System Interface (iSCSI) is an Internet Protocol (IP) – based storage networking standard for linking data storage facilities. iSCSI allows clients to send SCSI commands over a TCP/IP network using TCP port 3260. -
Which file storage system can be used on a Windows Server?
- NFS
- NTFS
- EXT3
- FAT16
-
Which RAID level can consist of two disks and provides redundancy?
- RAID 0
- RAID 1
- RAID 5
- RAID 10
-
Which version of RAID uses between 3 – 32 discs?
- RAID 0
- RAID 1
- RAID 5
- RAID 10
-
An external storage unit that is self-contained and provides shared file-level access is referred to as:
- Small Computer System Interface (SCSI).
- Storage Area Network (SAN).
- Network Attached Storage (NAS).
- Direct Attached Storage (DAS).
Explanation:
Network-attached storage (NAS) is file-level computer data storage connected to a computer network providing data access to a heterogeneous group of clients. NAS not only operates as a file server, but is specialized for this task either by its hardware, software, or configuration of those elements. NAS is often manufactured as a computer appliance – a specialized computer built from the ground up for storing and serving files – rather than simply a general purpose computer being used for the role. -
Which RAID level mirrors a set of disks and then stripes across the disks?
- RAID 0
- RAID 1
- RAID 5
- RAID 10
Explanation:
A RAID 1+0, sometimes called RAID 1&0 or RAID 10. RAID 10 is a stripe of mirrors. -
Disk mirroring occurs when data is:
- Duplicated on the same disk.
- Backed up by using parity.
- Duplicated on separate disks.
- Split between disks.