98-365 : Windows Server Administration Fundamentals : Part 14
98-365 : Windows Server Administration Fundamentals : Part 14
-
One advantage of a SAN is that it:
- Can be located either inside or outside the server.
- Provides USB and Firewire connectivity.
- Consolidates storage space for servers.
- Encrypts all files.
Explanation:
A storage area network (SAN) is a dedicated network that provides access to consolidated, block level data storage. -
To convert a disk from dynamic to basic, you must first:
- Mirror all disk volumes.
- Connect the disk to a different controller.
- Delete all disk volumes.
- Format all disk volumes in the NTFS file system.
Explanation:
To change a dynamic disk back to a basic disk using the Windows interface -
Which RAID level uses parity information to recover data from a failed disk?
- RAID 0
- RAID 1
- RAID 5
- RAID 10
-
Which disk types can be used for internal storage?
- SAN/iSCSI
- NFS/Distributed File System (DFS)
- PATA/SATA/SCSI
- NAS/Fiber-channel
-
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
“Hardware-based RAID” uses system processing resources.
Select the correct answer if the underlined text does not make the statement correct. Select “No change is needed” if the underlined text makes the statement correct.
- Windows-based RAID
- RAID 10
- RAID 6
- No change is needed.
-
HOTSPOT
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-365 Part 14 Q06 030 Question 
98-365 Part 14 Q06 030 Answer -
HOTSPOT
You buy a new USB hard drive for your server. After connecting the drive, you need to make this drive available to Windows.
In Computer Management Disk Management you see the drive, but it is not visible in Explorer’s Computer view, as shown in the following image:
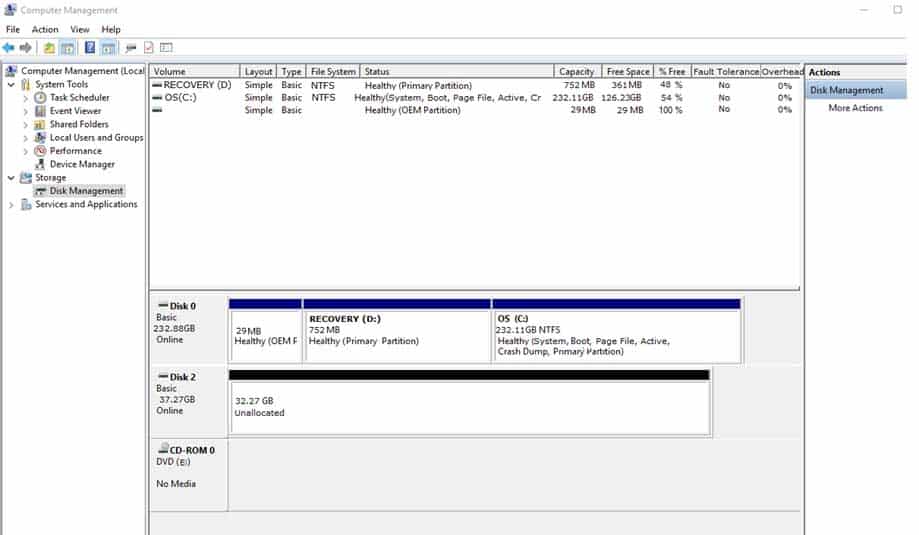
98-365 Part 14 Q07 031 Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement. Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-365 Part 14 Q07 032 Question 
98-365 Part 14 Q07 032 Answer Explanation:
Use simple to get a separate volume.
Use NTFS to be able to use the whole drive. exFAT and FAT32 have restrictions on size.Simple. This will assign a new drive letter to your new disk and each drive will work independently of the other.
Spanned. Your new HDD will show up as part of your current HDD.
Striped is RAID 0. -
HOTSPOT
The hard disk in a computer running Windows Server 2016 is configured as shown in the exhibit. (Click on the Exhibit tab.)
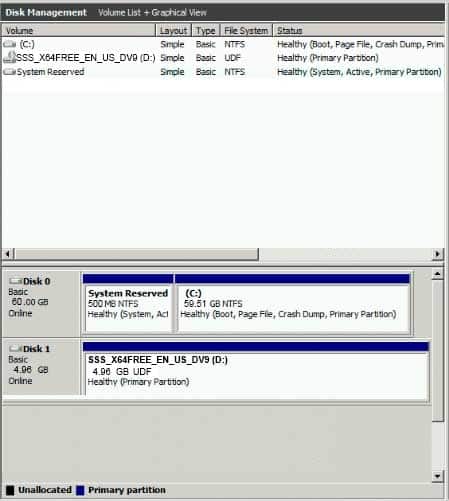
98-365 Part 14 Q08 033 You add a second hard disk to increase available storage. You need to configure hard disk storage for the computer.
For each of the following statements, select yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-365 Part 14 Q08 034 Question 
98-365 Part 14 Q08 034 Answer Explanation:
Basic disks are the storage types most often used with Windows. The term basic disk refers to a disk that contains partitions, such as primary partitions and logical drives, and these in turn are usually formatted with a file system to become a volume for file storage.
You can add more space to existing primary partitions and logical drives by extending them into adjacent, contiguous unallocated space on the same disk. To extend a basic volume, it must be formatted with the NTFS file system. You can extend a logical drive within contiguous free space in the extended partition that contains it. If you extend a logical drive beyond the free space available in the extended partition, the extended partition grows to contain the logical drive as long as the extended partition is followed by contiguous unallocated space.
Dynamic disks provide features that basic disks do not, such as the ability to create volumes that span multiple disks (spanned and striped volumes) and the ability to create fault-tolerant volumes (mirrored and RAID-5 volumes). Like basic disks, dynamic disks can use the MBR or GPT partition styles on systems that support both. All volumes on dynamic disks are known as dynamic volumes. Dynamic disks offer greater flexibility for volume management because they use a database to track information about dynamic volumes on the disk and about other dynamic disks in the computer.
-
HOTSPOT
You are researching storage options for network servers.
For each of the following statements, select yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-365 Part 14 Q09 035 Question 
98-365 Part 14 Q09 035 Answer Explanation:
SANs are at the high end of server storage options. They come in two types, iSCSI and Fibre Channel. A SAN’s main advantage is shared storage: Unlike with locally attached storage, more than one server can access data on a SAN. On lower end SAN configurations, you have a single point of failure in the SAN chassis.
SCSI SANs use Gigabit Ethernet to transfer the data between the server nodes and the SAN, which means the server nodes don’t have to be in the same physical location; iSCSI is therefore a little more flexible to set up than Fibre Channel SANs. An iSCSI SAN is a good solution when you need high availability but don’t have extremely high disk throughput requirements.
NAS devices are appliances that are capable of holding multiple hard disk drives (usually eight or more). They have one or more built-in Ethernet network cards. NAS devices serve files but don’t have any other server capabilities, such as email, database, DNS or DHCP. Although they can be placed on a dedicated network, NAS devices are usually placed on the public Ethernet network so workstations and servers can access the NAS device. A drawback of NAS devices is their tendency to become obsolete.
-
You plan to repurpose an existing computer to run a clean installation of Windows Server 2016 Standard edition.
Which type of hard drive interface should you use for the boot drive?
- PATA
- ATA
- SATA
- IDE
-
You are deploying a virtual machine (VM) on a computer running Windows Server 2016 that is configured as a Hyper-V host. The VM will be used to test a new application. You will be testing various configurations.
You need to provide storage that can expand in size automatically to provide more storage as necessary, but without making changes to the initial VHD.
Which type of VHD should you use?
- differencing
- linked
- fixed
- dynamic
-
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
You install three 600GB hard disks in a computer running Windows Server 2016 Standard edition. You need to configure at least 1TB of fault-tolerant storage from the hard disks.
You configure that hard disks as a RAID 5 configuration.
Review the underlined text. If it makes the statement correct, select “No change is needed”. If the statement is incorrect, select the answer choice that makes the statement correct.
- RAID 0
- RAID 1
- RAID 10
- No change is needed
-
After installing a new device driver for a SCSI device adapter, you can no longer access an external SCSI hard disk. The computer is running Windows Server 2016.
You need to access the data as quickly as possible.
What should you do first?
- roll back the device driver
- replace the SCSI adapter
- restart the computer
- uninstall the device driver
-
What should be the maximum consistent processor utilization?
- 40%
- 50%
- 60%
- 80%
Explanation:
Processor Time measures how busy the processor is. Although the processor may jump to 100% processor usage, the processor should not be above 80% most of the time. If it isn’t, you should upgrade the processor (using a faster processor or additional processors) or move some of the services to other systems. -
You notice frequent writes to the page file.
Which should you monitor to determine the cause?
- CPU
- RAM
- Network
- Hard disk
Explanation:
When the RAM is full the page file is used as virtual RAM. -
You want to receive a notification when your server’s processor exceeds 80 percent utilization. You should create a:
- Performance Alert.
- Scheduled task.
- Performance Log.
- Performance counter.
- System Event.
-
You need to monitor the performance of a server.
What should you create first?
- Baseline
- Counters
- Page File
- Alerts
Explanation:
Later compare the performance to the baseline. -
Which is an advantage of 64-bit operating systems over 32-bit operating systems?
- Larger amounts of accessible RAM
- More device drivers
- More compatible applications
- Cheaper hardware
Explanation:
Can access a larger address space. -
A record of specific aspects of system performance over time is referred to as a/an:
- Threshold
- Log
- Event
- Alert
Explanation:
Working with Performance Logs
Applies To: Windows 10, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012, Windows Vista
You can view log files or log data provided by a database in Performance Monitor to see a visual representation of performance data collected by Data Collector Sets. -
Which tool should you use to track real-time system resource utilization?
- System Information
- Component Services
- Device Manager
- Perfmon
Explanation:
Example:
How to use Perfmon to collect Microsoft Windows performance countersOpen the WinX menu in Windows 8 and select Run. Type perfmon.exe and hit Enter to open the Performance Monitor. In the left pane, select the User Defined node, right-click on it and select New > Data Collector Set.