CyberOps Associate 1.0 & CA 1.02 Final Exam Answers 2025 Full 100%
CyberOps Associate 1.0 & CA 1.02 Final Exam Answers Full 100% 2025
These are both versions of NetAcad Cisco CA 1.02 and CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Full 100% in 2025 verified by experts with explanations and hints.
| CyberOps - Associate 1.0 & 1.01 | |
| Final Exam | |
| Practice Final Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Final Exam Answers | Online Test |
| 200-201 Certification Practice | Online Test |
CA 1.02 CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 2025
-
Which two techniques are used in a smurf attack? (Choose two.)
- session hijacking
- reflection
- amplification
- botnets
- resource exhaustion
-
Explanation & Hint: In a Smurf attack, two primary techniques are used:
- Amplification: This technique involves increasing the volume of the attack traffic. In the context of a Smurf attack, a small query is sent to a network broadcast address, causing every device on that network to respond to the request. This multiplies the amount of traffic sent to the victim, effectively amplifying the attack.
- Reflection: This is where the attacker spoofs the source IP address of their packets to be the IP address of the victim. When the network responds to the broadcast request, it sends its response to the victim’s IP address instead of back to the attacker. This not only hides the identity of the attacker but also directs the response traffic to the victim, causing a denial of service.
The other options listed, such as session hijacking, botnets, and resource exhaustion, are not specific techniques used in a Smurf attack, although botnets might be used to carry out such an attack and resource exhaustion is a consequence of it.
-
What are three goals of a port scan attack? (Choose three.)
- to discover system passwords
- to identify operating systems
- to identify active services
- to identify peripheral configurations
- to determine potential vulnerabilities
- to disable used ports and services
-
Explanation & Hint: Three goals of a port scan attack are:
- To Identify Active Services: By scanning the ports of a target system, an attacker can discover which services are running on those ports. Each open port can be associated with specific services, and knowing which services are active can provide insights into the potential functions and roles of the system.
- To Determine Potential Vulnerabilities: By identifying which ports are open and what services are running on a system, an attacker can determine potential vulnerabilities. For instance, certain services might be known to have specific vulnerabilities that can be exploited. Understanding what’s running on a system helps in crafting targeted attacks.
- To Identify Operating Systems: Port scanning can also be used to infer the type of operating system running on a target system. Certain operating systems use specific ports and respond to scans in unique ways. By analyzing these responses, an attacker can often determine the operating system, which aids in tailoring further attacks to exploit OS-specific vulnerabilities.
Other options, such as discovering system passwords, identifying peripheral configurations, and disabling used ports and services, are not direct goals of a port scan attack. Port scanning is primarily about information gathering rather than direct action like disabling services.
-
After host A receives a web page from server B, host A terminates the connection with server B. Match each step to its correct option in the normal termination process for a TCP connection. (Not all options are used.)
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 001 Explanation & Hint: In the TCP connection termination process after Host A has received a web page from Server B and Host A initiates the termination, the steps would be matched as follows:
- Host A sends a FIN to server B. This is the first step when Host A wants to start the termination of the TCP connection after the data transfer is complete.
- Server B sends an ACK to host A. Server B acknowledges the FIN packet from Host A, which is part of the graceful closing of a TCP session.
- Server B sends a FIN to host A. After sending the ACK, Server B will also want to terminate its side of the connection and will send a FIN packet to Host A.
- Host A sends an ACK to server B. Finally, Host A acknowledges the FIN packet from Server B, completing the four-way termination handshake.
The option “Server B sends a SYN-ACK to Host A” is not used in the termination process; it is part of the initial three-way handshake when establishing a TCP connection.
-
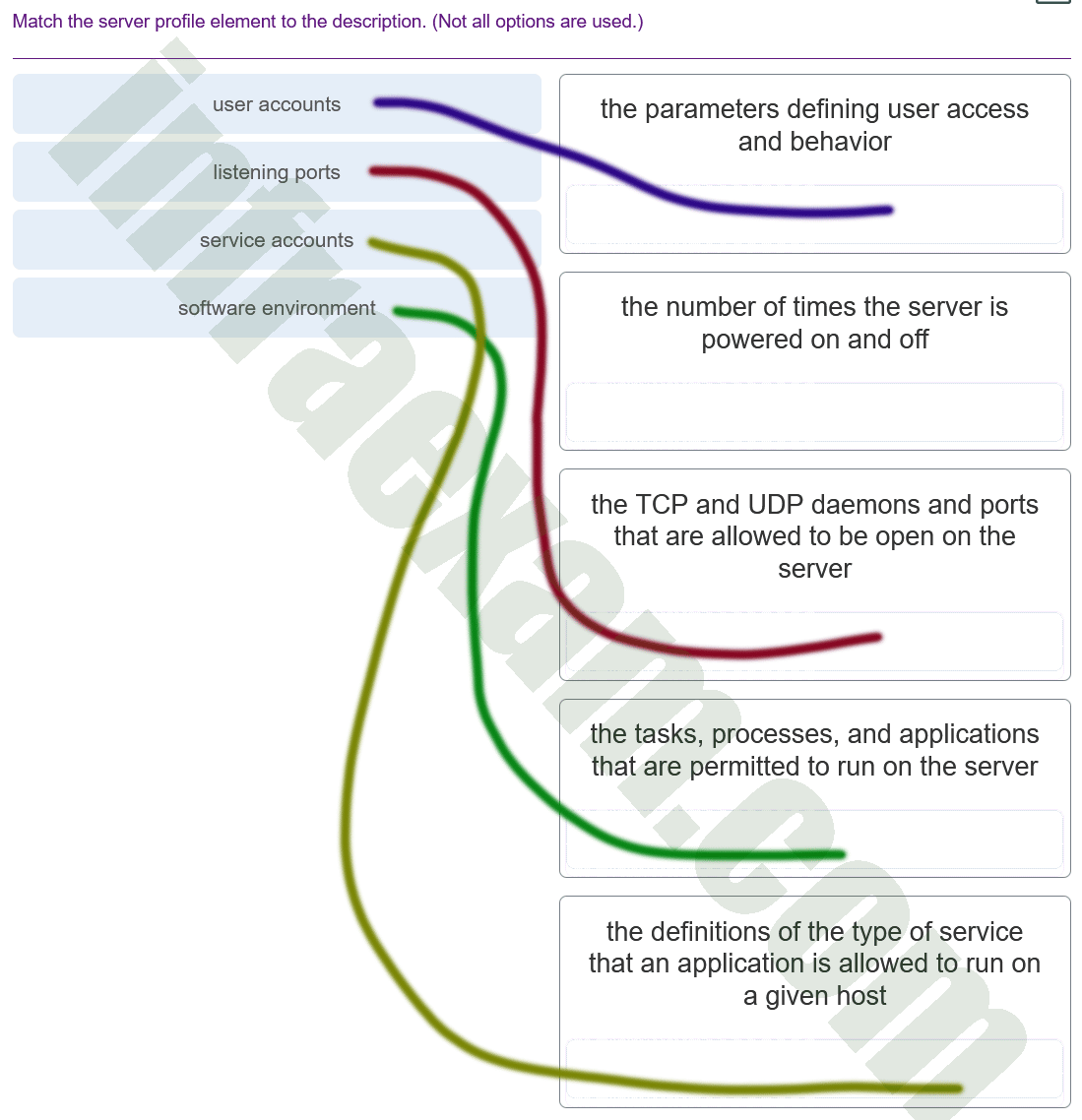
When establishing a network profile for an organization, which element describes the time between the establishment of a data flow and its termination?
- routing protocol convergence
- total throughput
- session duration
- bandwidth of the Internet connection
Answers Explanation & Hints: A network profile should include some important elements, such as the following:
- Total throughput – the amount of data passing from a given source to a given destination in a given period of time
- Session duration – the time between the establishment of a data flow and its termination
- Ports used – a list of TCP or UDP processes that are available to accept data
- Critical asset address space – the IP addresses or the logical location of essential systems or data
-
In addressing an identified risk, which strategy aims to shift some of the risk to other parties?
- risk avoidance
- risk retention
- risk reduction
- risk sharing
-
Explanation & Hint: Risk Sharing: As explained earlier, risk sharing involves distributing the risk among different parties. It is often used when a risk is too large for a single entity to bear alone. For instance, a company might enter into a partnership where both companies share the potential risks and rewards of a project. Insurance is another form of risk sharing, where the risk is transferred to an insurance company in exchange for regular payments (premiums).
Risk Avoidance: This strategy involves changing plans to avoid the risk entirely. For instance, if a business identifies a potential legal risk in entering a new market, it might choose not to expand its operations there. Risk avoidance is the most conservative approach to handling risk, and while it can be effective, it can also result in missed opportunities.
Risk Retention: Sometimes referred to as risk acceptance, this strategy means that the organization accepts the risk and decides to deal with any potential fallout internally. This is usually chosen when the cost of mitigating the risk may be more than the cost of the risk itself. Companies often retain risks that are not severe and are within their capacity to absorb.
Risk Reduction: This strategy aims to reduce the likelihood or impact of a risk. This can be done through implementing controls, safety measures, and policies. For example, a company might install fire suppression systems to reduce the risk of damage from a fire. Risk reduction doesn’t eliminate the risk entirely, but it helps to manage and minimize its potential impacts.
-
Match the security management function with the description.
Explanation & Hint: -
A computer is presenting a user with a screen requesting payment before the user data is allowed to be accessed by the same user. What type of malware is this?
- a type of virus
- a type of worm
- a type of ransomware
- a type of logic bomb
Answers Explanation & Hints: Ransomware commonly encrypts data on a computer and makes the data unavailable until the computer user pays a specific sum of money
-
What characterizes a threat actor?
- They are all highly-skilled individuals.
- They always try to cause some harm to an individual or organization.
- They always use advanced tools to launch attacks.
- They all belong to organized crime.
-
Explanation & Hint: Indeed, the most consistent characteristic of a threat actor in the context of cybersecurity is their intention to cause harm or disruption to an individual or organization. This harm can manifest in various forms, such as stealing sensitive data, disrupting services, damaging systems, or other malicious activities. The motivation behind these actions can vary widely, ranging from financial gain, espionage, political objectives, personal vendettas, to ideological beliefs. Regardless of their skill level, tools used, or affiliation with organized crime, the defining aspect of a threat actor is their malicious intent towards their targets.
-
What subnet mask is represented by the slash notation /20?
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.224.0
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.240.0
- 255.255.255.0
Answers Explanation & Hints: The slash notation /20 represents a subnet mask with 20 1s. This would translate to: 11111111.11111111.11110000.0000, which in turn would convert into 255.255.240.0.
-
A device has been assigned the IPv6 address of 2001:0db8:cafe:4500:1000:00d8:0058:00ab/64. Which is the network identifier of the device?
- 1000:00d8:0058:00ab
- 2001
- 2001:0db8:cafe:4500:1000:00d8:0058:00ab
- 2001:0db8:cafe:4500:1000
- 2001:0db8:cafe:4500
Answers Explanation & Hints: The address has a prefix length of /64. Thus the first 64 bits represent the network portion, whereas the last 64 bits represent the host portion of the IPv6 address.
-
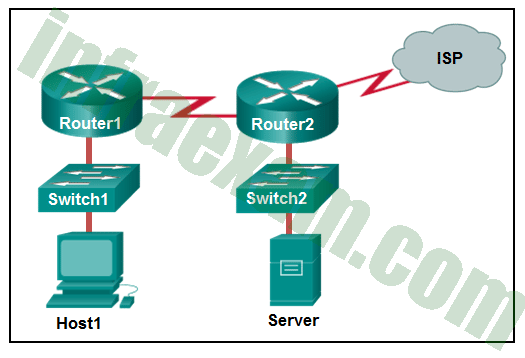
Refer to the exhibit. If Host1 were to transfer a file to the server, what layers of the TCP/IP model would be used?
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 02 - only application and Internet layers
- only application, transport, network, data link, and physical layers
- application, session, transport, network, data link, and physical layers
- application, transport, Internet, and network access layers
- only Internet and network access layers
- only application, Internet, and network access layers
Answers Explanation & Hints: The TCP/IP model contains the application, transport, internet, and network access layers. A file transfer uses the FTP application layer protocol. The data would move from the application layer through all of the layers of the model and across the network to the file server.
-
What best describes the destination IPv4 address that is used by multicasting?
- a single IP multicast address that is used by all destinations in a group
- an IP address that is unique for each destination in the group
- a 48 bit address that is determined by the number of members in the multicast group
- a group address that shares the last 23 bits with the source IPv4 address
Answers Explanation & Hints: The destination multicast IPv4 address is a group address, which is a single IP multicast address within the Class D range.
-
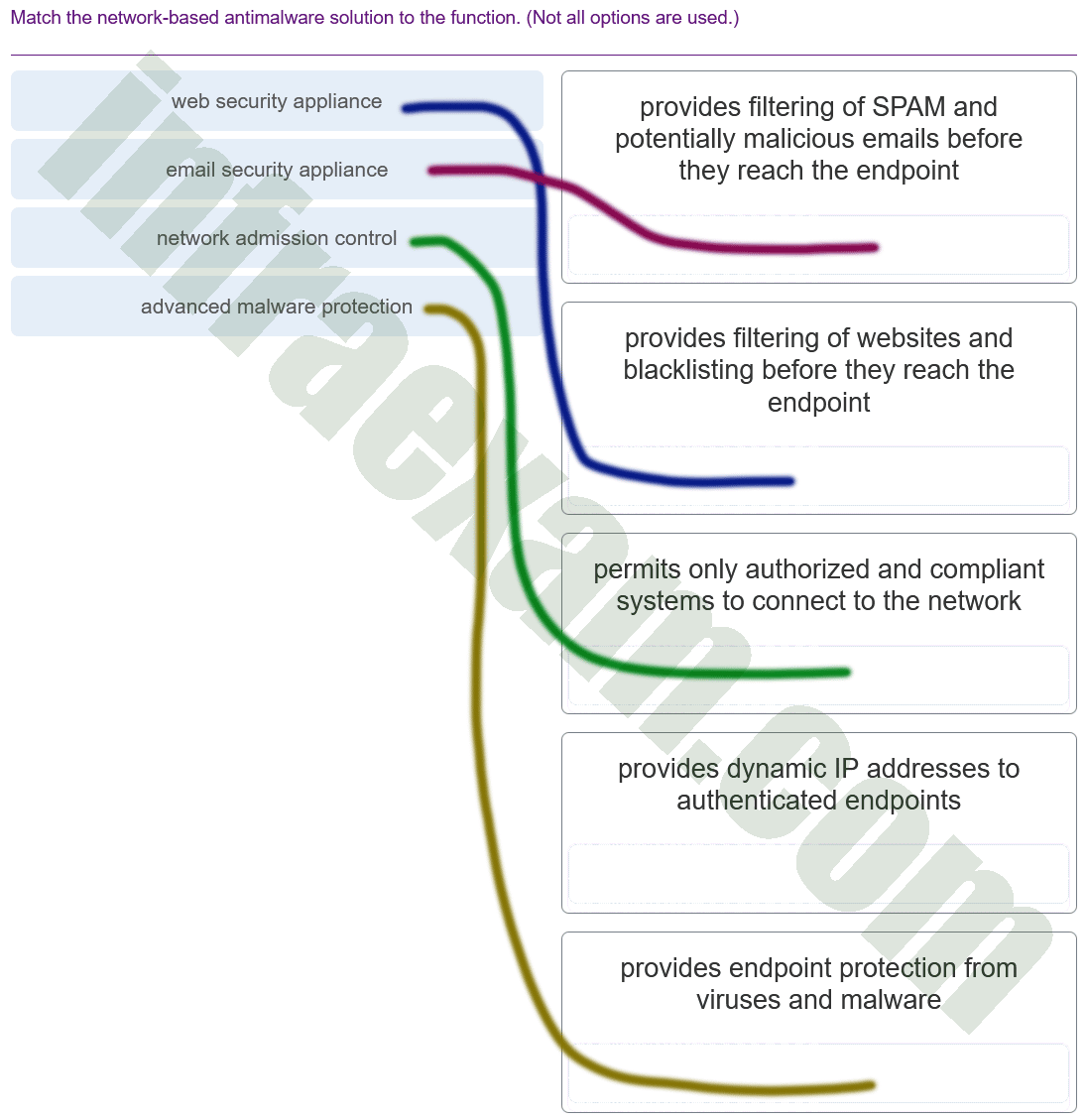
Match the network-based antimalware solution to the function. (Not all options are used.)
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 003 Explanation & Hint: - Web Security Appliance – This is generally responsible for providing filtering of websites and blacklisting before they reach the endpoint. It helps in preventing access to malicious websites.
- Email Security Appliance – This typically provides filtering of SPAM and potentially malicious emails before they reach the endpoint. It scans emails for spam, phishing attempts, and malware.
- Network Admission Control – This system permits only authorized and compliant systems to connect to the network. It ensures that only devices that meet the organization’s security policies are allowed network access.
- Advanced Malware Protection – This solution provides endpoint protection from viruses and malware. It uses advanced methods to detect and block sophisticated malware.
The function that mentions providing dynamic IP addresses to authenticated endpoints is not directly related to antimalware but more to network access control or DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) services, which are not listed among the options provided in your image.
-
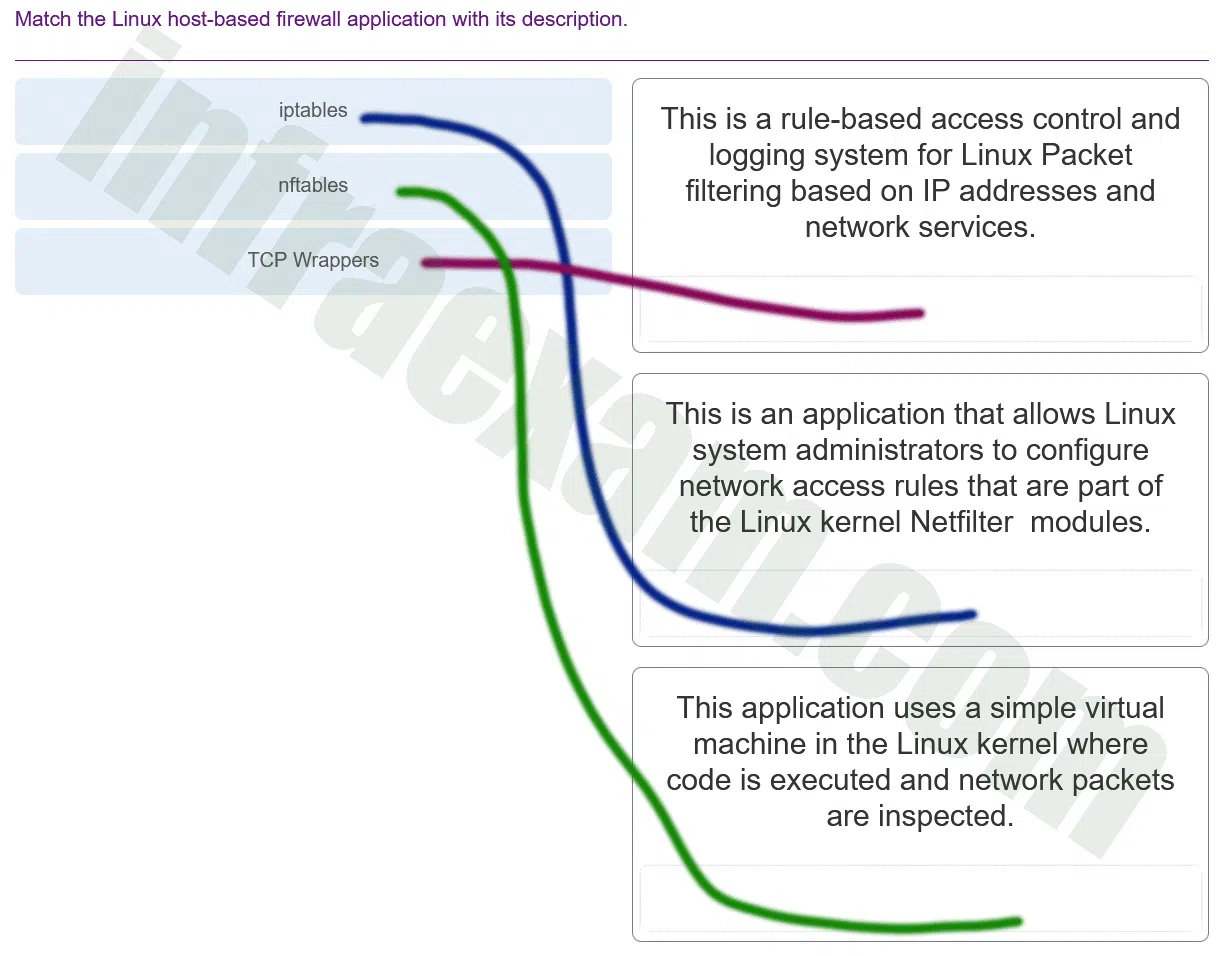
Match the Linux host-based firewall application with its description.
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 004 Explanation & Hint: - iptables: This is a rule-based access control and logging system for Linux packet filtering based on IP addresses and network services. It is a legacy tool that has been widely used for configuring the Linux kernel’s netfilter framework.
- nftables: This is an application that allows Linux system administrators to configure network access rules that are part of the Linux kernel Netfilter modules. It is the successor to iptables and provides a new syntax for rule configuration.
- TCP Wrappers: This application uses a simple virtual machine in the Linux kernel where code is executed and network packets are inspected. However, the description might be a bit misleading as TCP Wrappers typically refers to a host-based networking ACL system, used to filter network access to Internet protocol servers on Unix-like operating systems. It does not use a virtual machine but instead is based on the libc wrappers.
-
A threat actor has identified the potential vulnerability of the web server of an organization and is building an attack. What will the threat actor possibly do to build an attack weapon?
- Collect credentials of the web server developers and administrators.
- Install a webshell on the web server for persistent access.
- Obtain an automated tool in order to deliver the malware payload through the vulnerability.
- Create a point of persistence by adding services.
-
Explanation & Hint: - Collect credentials of the web server developers and administrators: This can be a preparatory step to facilitate unauthorized access. With credentials, a threat actor could gain legitimate access to the system and potentially escalate privileges or make changes without immediately triggering security measures.
- Install a webshell on the web server for persistent access: This is a common attack method where the attacker places a webshell—a malicious script that can be accessed via a web browser—on the compromised server. This allows the attacker to maintain access to the server and remotely execute commands.
- Obtain an automated tool in order to deliver the malware payload through the vulnerability: Automated tools or exploit kits can be used to deliver a malware payload to a vulnerable server. These tools often include multiple exploits for different vulnerabilities and are designed to automate the process of finding and exploiting weaknesses.
- Create a point of persistence by adding services: By adding new services or modifying existing ones, an attacker can ensure that they maintain access to the system even after the initial entry point is closed or the vulnerability is patched.
Obtain an automated tool in order to deliver the malware payload through the vulnerability.
This step is typically one of the first in the exploitation phase of an attack. Automated tools can exploit known vulnerabilities quickly and efficiently. Once the vulnerability is exploited and the attacker has gained entry into the system, they may then proceed to install web shells for persistent access or create points of persistence by adding services, and potentially collect credentials to further their access and control within the network.
-
Which type of data would be considered an example of volatile data?
- web browser cache
- log files
- memory registers
- temp files
Answers Explanation & Hints: Volatile data is data stored in memory such as registers, cache, and RAM, or it is data that exists in transit. Volatile memory is lost when the computer loses power.
-
What type of attack targets an SQL database using the input field of a user?
- XML injection
- SQL injection
- buffer overflow
- Cross-site scripting
Answers Explanation & Hints: A criminal can insert a malicious SQL statement in an entry field on a website where the system does not filter the user input correctly.
-
What network attack seeks to create a DoS for clients by preventing them from being able to obtain a DHCP lease?
- CAM table attack
- DHCP spoofing
- IP address spoofing
- DHCP starvation
Answers Explanation & Hints: DCHP starvation attacks are launched by an attacker with the intent to create a DoS for DHCP clients. To accomplish this goal, the attacker uses a tool that sends many DHCPDISCOVER messages in order to lease the entire pool of available IP addresses, thus denying them to legitimate hosts.
-
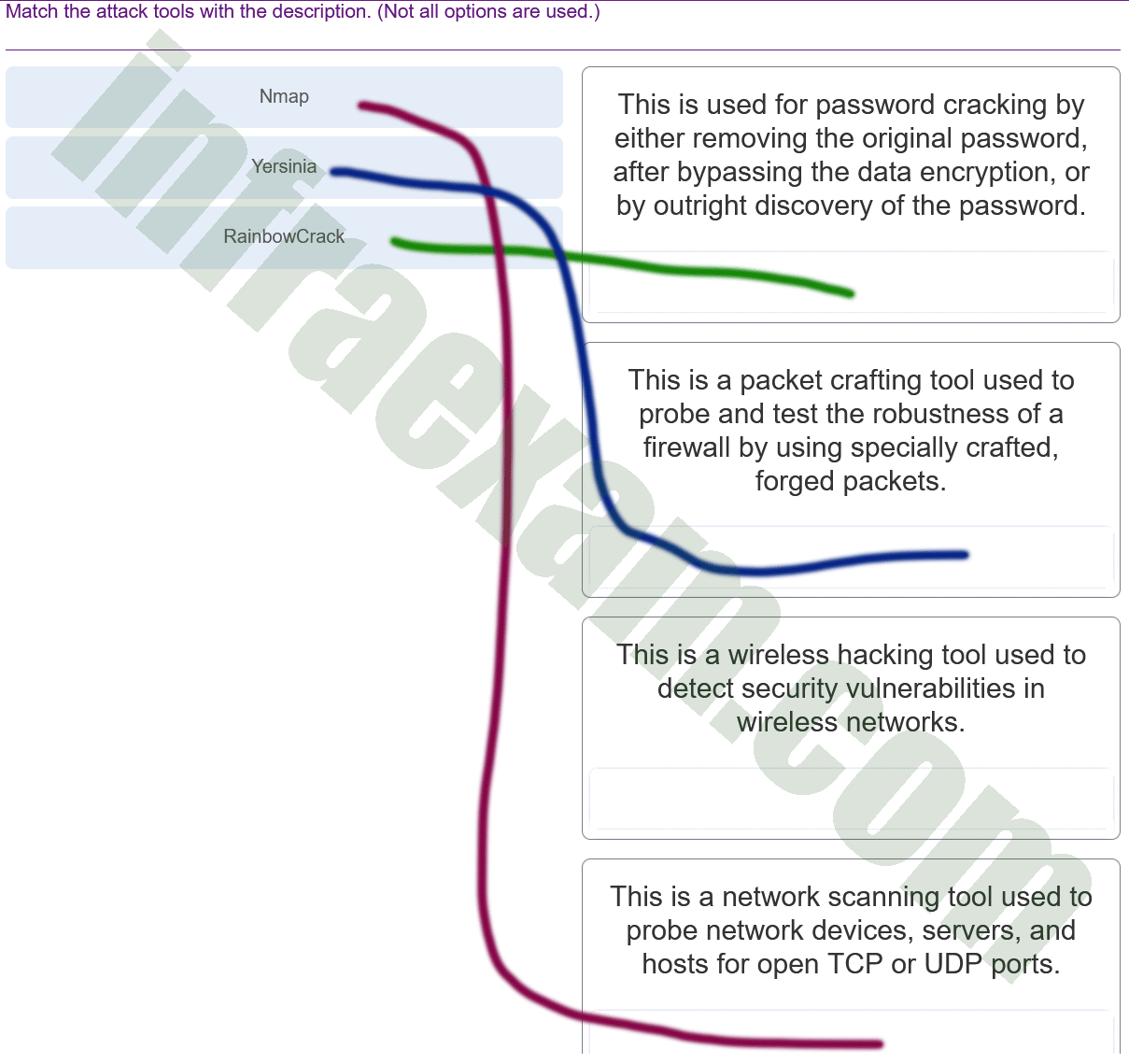
Match the attack tools with the description. (Not all options are used.)
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 005 Explanation & Hint: - RainbowCrack – This tool is used for password cracking by either removing the original password, after bypassing the data encryption, or by outright discovery of the password. It uses rainbow tables to perform attacks on password hashes.
- Yersinia – This is a network tool that is capable of exploiting vulnerabilities in network protocols, but it is not specifically described in the options provided. It’s not a wireless hacking tool, nor is it used for network scanning.
- Nmap – This is a network scanning tool used to probe network devices, servers, and hosts for open TCP or UDP ports. It’s used for network discovery and security auditing.
-
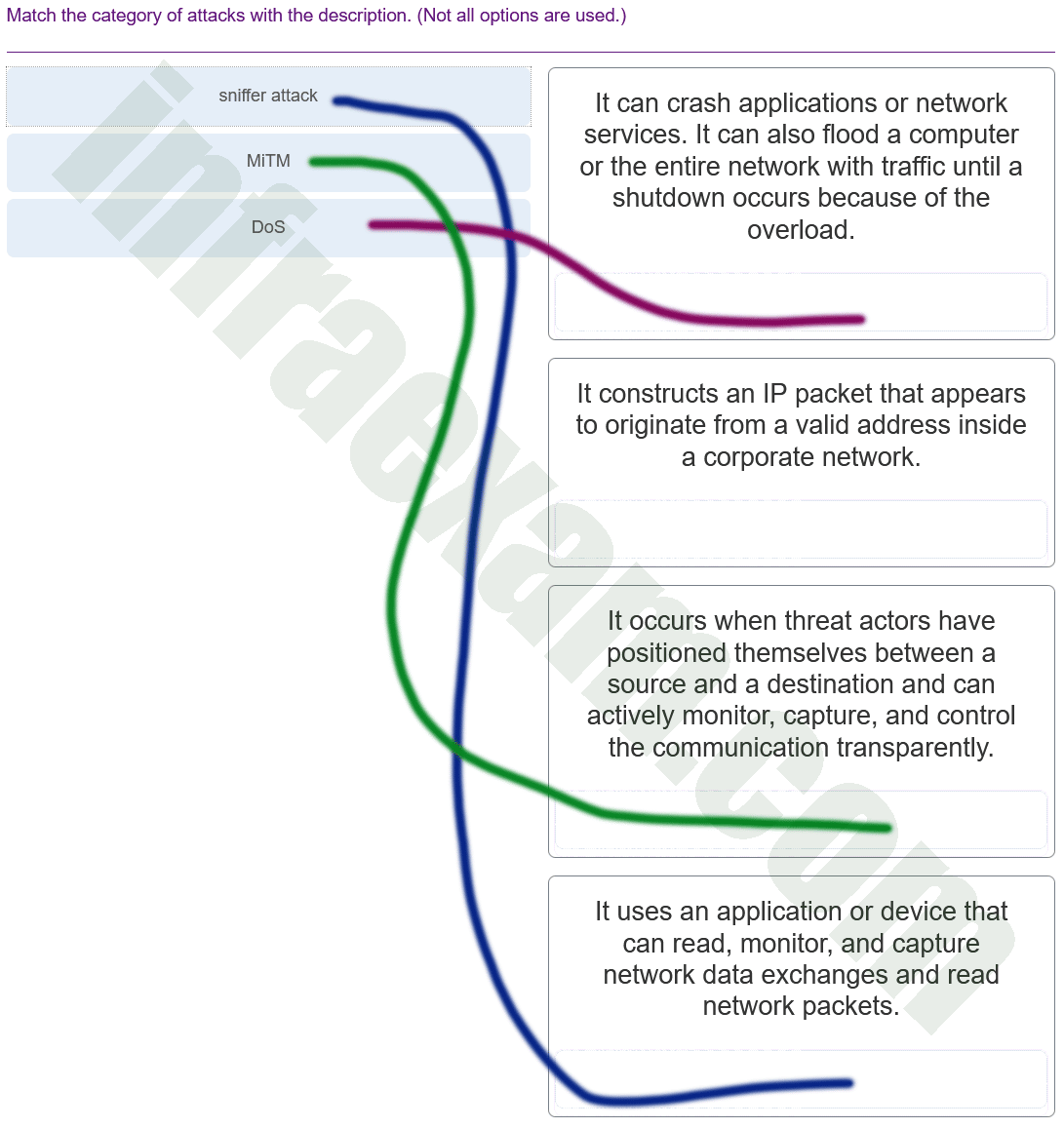
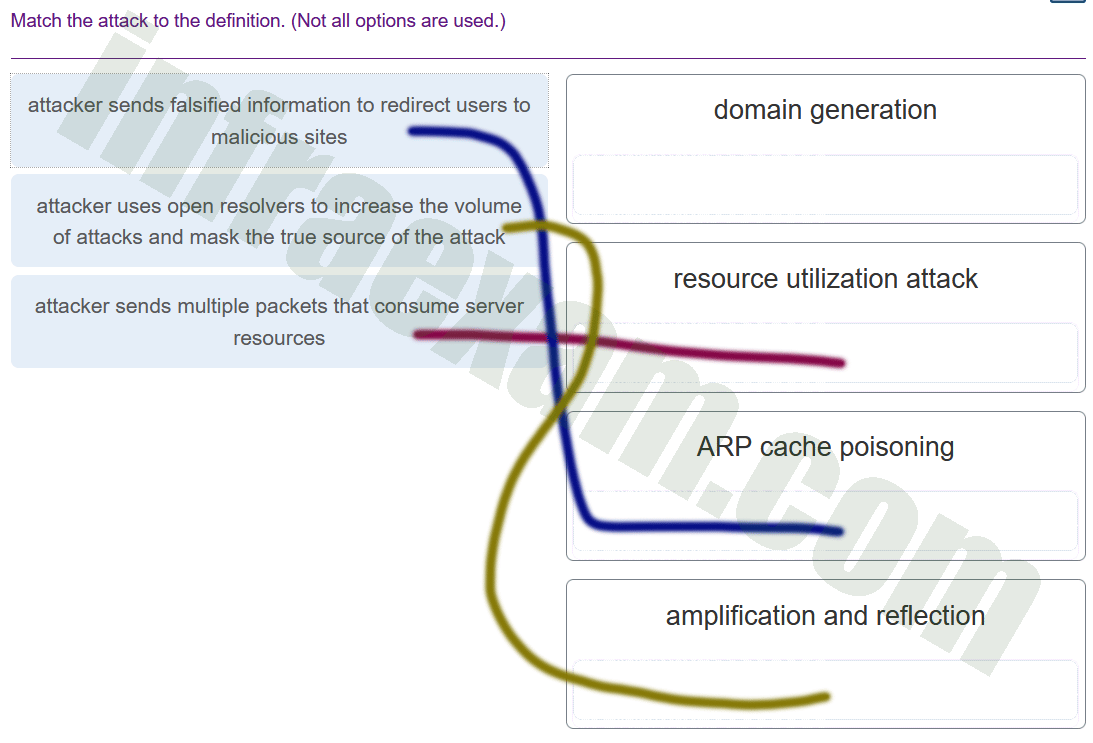
Match the category of attacks with the description. (Not all options are used.)
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 006 Explanation & Hint: The image you’ve uploaded is a matching exercise for categories of attacks and their descriptions. Based on the descriptions provided in the image, here is the correct matching:
- DoS (Denial of Service) – It can crash applications or network services. It can also flood a computer or the entire network with traffic until a shutdown occurs because of the overload.
- MITM (Man-In-The-Middle) – It occurs when threat actors have positioned themselves between a source and a destination and can actively monitor, capture, and control the communication transparently.
- Sniffer attack – It uses an application or device that can read, monitor, and capture network data exchanges and read network packets.
The description “It constructs an IP packet that appears to originate from a valid address inside a corporate network” could be referring to spoofing attacks, where an attacker deceives a system by masquerading as a legitimate entity. However, since there is no corresponding category for this description in the provided list, it does not match any of the listed attack categories.
-
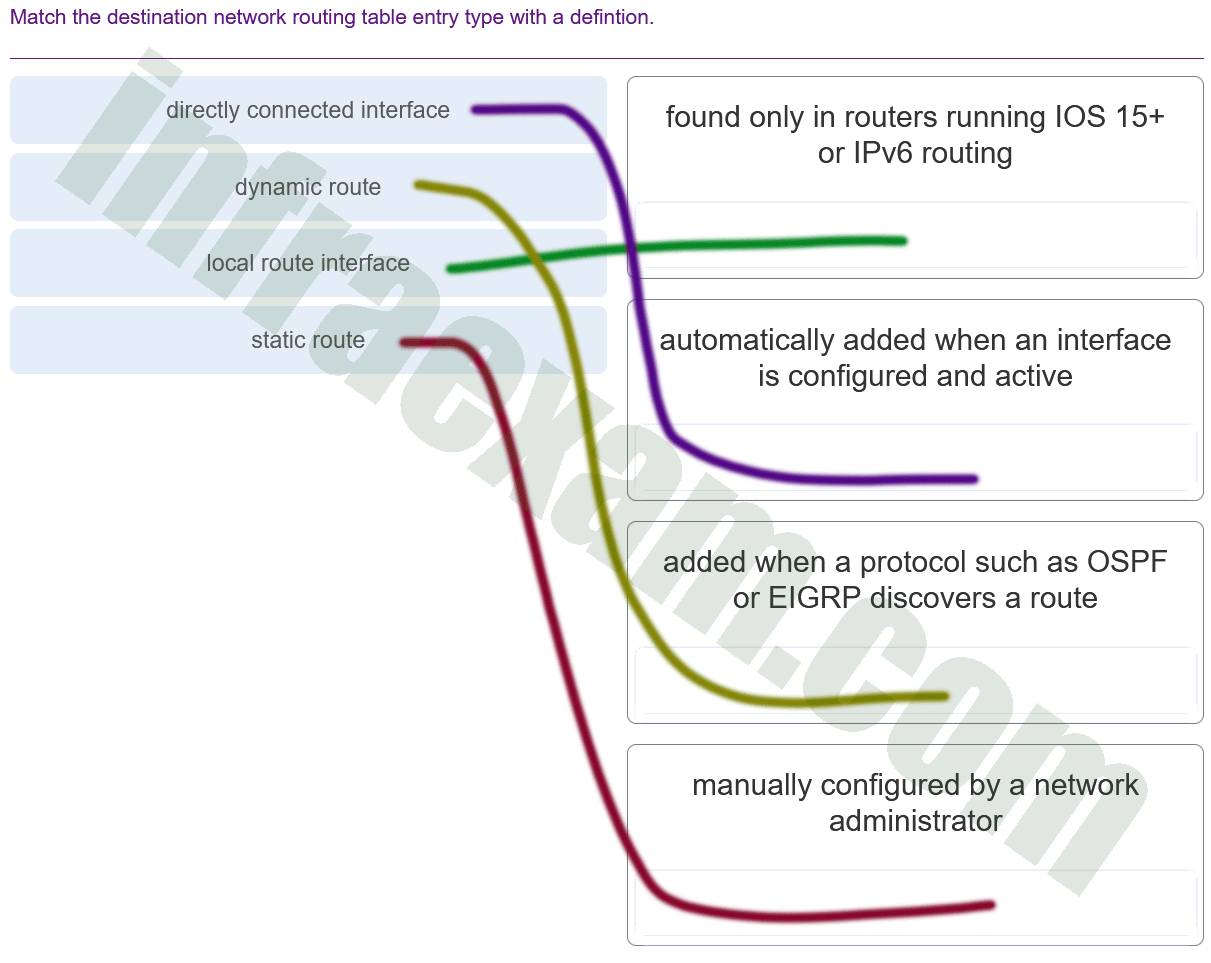
Match the destination network routing table entry type with a defintion.
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 007 Explanation & Hint: - DoS (Denial of Service) – It can crash applications or network services. It can also flood a computer or the entire network with traffic until a shutdown occurs because of the overload.
- MITM (Man-In-The-Middle) – It occurs when threat actors have positioned themselves between a source and a destination and can actively monitor, capture, and control the communication transparently.
- Sniffer attack – It uses an application or device that can read, monitor, and capture network data exchanges and read network packets.
The description “It constructs an IP packet that appears to originate from a valid address inside a corporate network” could be referring to spoofing attacks, where an attacker deceives a system by masquerading as a legitimate entity. However, since there is no corresponding category for this description in the provided list, it does not match any of the listed attack categories.
-
Which wireless parameter is used by an access point to broadcast frames that include the SSID?
- passive mode
- active mode
- channel setting
- security mode
Answers Explanation & Hints: The two scanning or probing modes an access point can be placed into are passive or active. In passive mode, the AP advertises the SSID, supported standards, and security settings in broadcast beacon frames. In active mode, the wireless client must be manually configured for the same wireless parameters as the AP has configured.
-
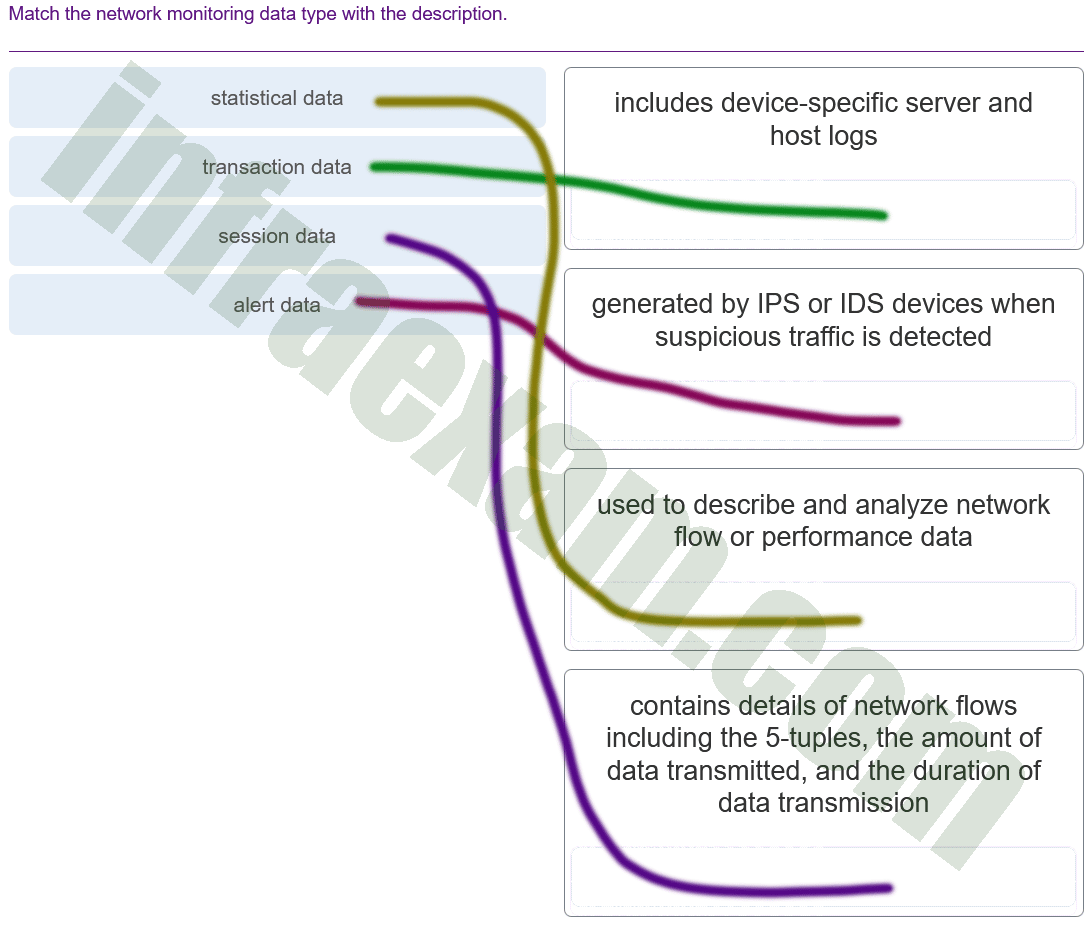
How can statistical data be used to describe or predict network behavior?
- by displaying alert messages that are generated by Snort
- by comparing normal network behavior to current network behavior
- by recording conversations between network endpoints
- by listing results of user web surfing activities
Answers Explanation & Hints: Statistical data is created through the analysis of other forms of network data. Statistical characteristics of normal network behavior can be compared to current network traffic in an effort to detect anomalies. Conclusions resulting from analysis can be used to describe or predict network behavior.
-
Which Windows Event Viewer log includes events regarding the operation of drivers, processes, and hardware?
- application logs
- security logs
- setup logs
- system logs
Answers Explanation & Hints: By default Windows keeps four types of host logs:
- Application logs – events logged by various applications
- System logs – events about the operation of drivers, processes, and hardware
- Setup logs – information about the installation of software, including Windows updates
- Security logs – events related to security, such as logon attempts and operations related to file or object management and access
-
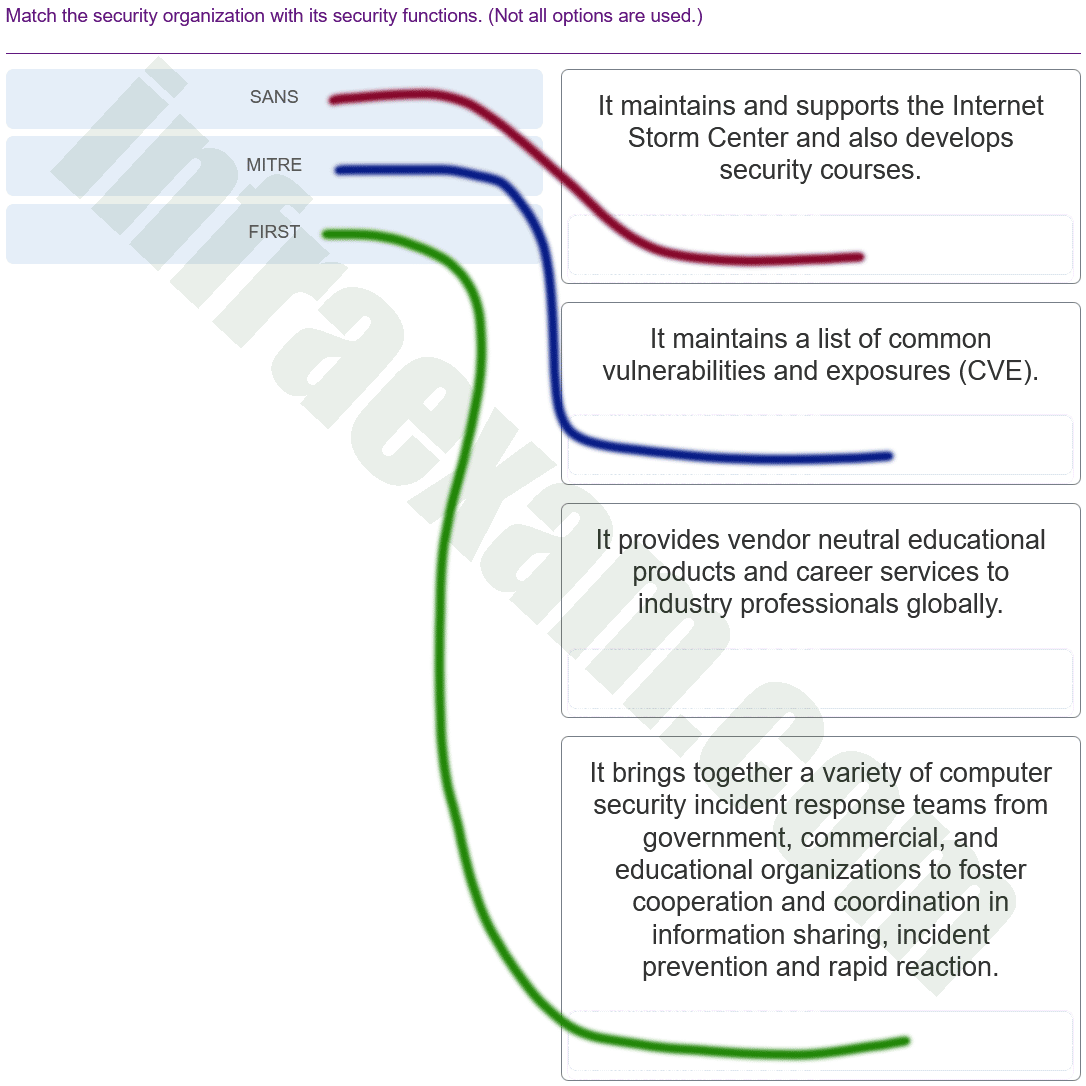
Match the security organization with its security functions. (Not all options are used.)
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 008 Explanation & Hint: - SANS – It provides vendor-neutral educational products and career services to industry professionals globally. SANS Institute is known for its courses on cybersecurity and information security.
- MITRE – It maintains a list of common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVE). MITRE is a not-for-profit organization that manages federally funded research and development centers supporting several U.S. government agencies.
- FIRST (Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams) – It brings together a variety of computer security incident response teams from government, commercial, and educational organizations to foster cooperation and coordination in information sharing, incident prevention, and rapid reaction.
The description about maintaining and supporting the Internet Storm Center and also developing security courses is typically associated with the SANS Institute. The Internet Storm Center is part of the services provided by SANS to monitor the level of malicious activity on the Internet.
-
What is the primary objective of a threat intelligence platform (TIP)?
- to provide a specification for an application layer protocol that allows the communication of CTI over HTTPS
- to provide a security operations platform that integrates and enhances diverse security tools and threat intelligence
- to aggregate the data in one place and present it in a comprehensible and usable format
- to provide a standardized schema for specifying, capturing, characterizing, and communicating events and properties of network operations
-
Explanation & Hint: The primary objective of a Threat Intelligence Platform (TIP) is:
to aggregate the data in one place and present it in a comprehensible and usable format.
A TIP is designed to collect intelligence from various sources, normalize the data, and present it in a way that is actionable for security teams. This allows organizations to better understand the threats they face and to make informed decisions about how to protect themselves. It provides a centralized repository where threat intelligence from different sources can be correlated and analyzed.
The other options you mentioned relate to other aspects or tools within the cybersecurity domain:
- A specification for an application layer protocol that allows the communication of Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) over HTTPS refers to protocols such as STIX (Structured Threat Information eXpression) and TAXII (Trusted Automated Exchange of Indicator Information).
- A security operations platform that integrates and enhances diverse security tools and threat intelligence could describe a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system, which aggregates data from many different security sources and provides real-time analysis of security alerts.
- A standardized schema for specifying, capturing, characterizing, and communicating events and properties of network operations might refer to a framework like STIX, which provides a structured language for describing cyber threat information in a standardized and machine-readable format.
-
An IT enterprise is recommending the use of PKI applications to securely exchange information between the employees. In which two cases might an organization use PKI applications to securely exchange information between users? (Choose two.)
- HTTPS web service
- file and directory access permission
- 802.1x authentication
- FTP transfers
- local NTP server
-
Explanation & Hint: Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) applications are used to secure communications through the use of certificates for encryption and identity verification. An organization might use PKI applications to securely exchange information between users in the following two cases:
- HTTPS web service: PKI is used to issue SSL/TLS certificates which are fundamental to the HTTPS protocol. These certificates encrypt the data transmitted between the web server and the client, ensuring the secure exchange of information.
- 802.1x authentication: PKI can be used in the context of 802.1x authentication to establish a network access control protocol. Here, certificates are used to authenticate devices before they are allowed to connect to a network, ensuring that only authorized users can access network resources.
The other options, such as file and directory access permission, FTP transfers, and a local NTP server, can utilize PKI for securing communications, but they are not as directly associated with PKI as HTTPS services and 802.1x authentication. File permissions are typically managed by operating system controls rather than PKI, FTP does not inherently use PKI for encryption (though FTP over SSL, known as FTPS, can), and NTP servers typically use other means for securing time synchronization, although PKI could be used for server authentication.
-
Which two statements describe the use of asymmetric algorithms? (Choose two.)
- If a private key is used to encrypt the data, a private key must be used to decrypt the data.
- If a public key is used to encrypt the data, a public key must be used to decrypt the data.
- Public and private keys may be used interchangeably.
- If a private key is used to encrypt the data, a public key must be used to decrypt the data.
- If a public key is used to encrypt the data, a private key must be used to decrypt the data.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Asymmetric algorithms use two keys: a public key and a private key. Both keys are capable of the encryption process, but the complementary matched key is required for decryption. If a public key encrypts the data, the matching private key decrypts the data. The opposite is also true. If a private key encrypts the data, the corresponding public key decrypts the data.
-
Which measure can a security analyst take to perform effective security monitoring against network traffic encrypted by SSL technology?
- Require remote access connections through IPsec VPN.
- Deploy a Cisco SSL Appliance.
- Deploy a Cisco ASA.
- Use a Syslog server to capture network traffic.
-
Explanation & Hint: To effectively monitor network traffic that is encrypted by SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or its successor TLS (Transport Layer Security), a security analyst would need to be able to decrypt the traffic for inspection before it is re-encrypted and sent to its destination. This is typically achieved using an SSL decryption appliance or service, which acts as an intermediary for SSL/TLS communications. Here’s how the measure aligns with the options provided:
Deploy a Cisco SSL Appliance: This would be the correct approach. A Cisco SSL appliance, often referred to as a decryption appliance, can be used to intercept, decrypt, and inspect encrypted SSL/TLS network traffic. After inspection, the traffic is re-encrypted and sent to its final destination. This allows a security analyst to monitor for potential threats and data leakage within encrypted traffic.
The other options have different primary security functions that do not directly address the monitoring of SSL/TLS encrypted traffic:
- Require remote access connections through IPsec VPN: While this would secure remote connections, it does not facilitate the monitoring of SSL/TLS encrypted traffic within the network itself.
- Deploy a Cisco ASA: Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) is a security device that combines firewall, antivirus, intrusion prevention, and virtual private network (VPN) capabilities. While it can inspect some encrypted traffic with the proper configuration, its main function is not SSL/TLS decryption.
- Use a Syslog server to capture network traffic: Syslog servers are used to collect logs from various network devices for monitoring and analysis. However, they do not decrypt SSL/TLS traffic; they are used for logging and do not handle the actual network traffic itself.
Therefore, deploying an SSL decryption appliance is the best option among those listed for monitoring encrypted network traffic.
-
What are two characteristics of the SLAAC method for IPv6 address configuration? (Choose two.)
- Clients send router advertisement messages to routers to request IPv6 addressing.
- IPv6 addressing is dynamically assigned to clients through the use of ICMPv6.
- This stateful method of acquiring an IPv6 address requires at least one DHCPv6 server.
- The default gateway of an IPv6 client on a LAN will be the link-local address of the router interface attached to the LAN.
- Router solicitation messages are sent by the router to offer IPv6 addressing to clients.
-
Explanation & Hint: SLAAC, or Stateless Address Autoconfiguration, is a method that allows devices on an IPv6 network to automatically configure their own IP addresses without the need for a centralized server like DHCPv6. Here are two characteristics of the SLAAC method:
- IPv6 addressing is dynamically assigned to clients through the use of ICMPv6: With SLAAC, IPv6 addresses are generated by clients using a combination of locally available information and router advertisements. The Internet Control Message Protocol version 6 (ICMPv6) is used by routers to announce their presence and by hosts to configure their own IPv6 address based on the prefix advertised by the router.
- The default gateway of an IPv6 client on a LAN will be the link-local address of the router interface attached to the LAN: In a SLAAC configuration, the router’s link-local address is used as the default gateway for devices on the network. The link-local address is derived from the router’s interface MAC address and the FE80::/10 prefix.
The other options listed are not characteristics of SLAAC:
- Clients send router advertisement messages to routers to request IPv6 addressing: This is incorrect. In SLAAC, routers send Router Advertisement (RA) messages that clients listen for. Clients do not request addressing; they listen for these unsolicited RA messages.
- This stateful method of acquiring an IPv6 address requires at least one DHCPv6 server: SLAAC is stateless and does not require a DHCPv6 server. A stateful method that requires a DHCPv6 server would be DHCPv6 itself, not SLAAC.
- Router solicitation messages are sent by the router to offer IPv6 addressing to clients: This is incorrect. Router solicitation messages are sent by clients when they first start up to prompt routers to send a Router Advertisement immediately rather than at their next scheduled time.
-
Which two ICMPv6 messages are used during the Ethernet MAC address resolution process? (Choose two.)
- router solicitation
- neighbor advertisement
- router advertisement
- neighbor solicitation
- echo request
Answers Explanation & Hints: IPv6 uses neighbor solicitation (NS) and neighbor advertisement (NA) ICMPv6 messages for MAC address resolution.
-
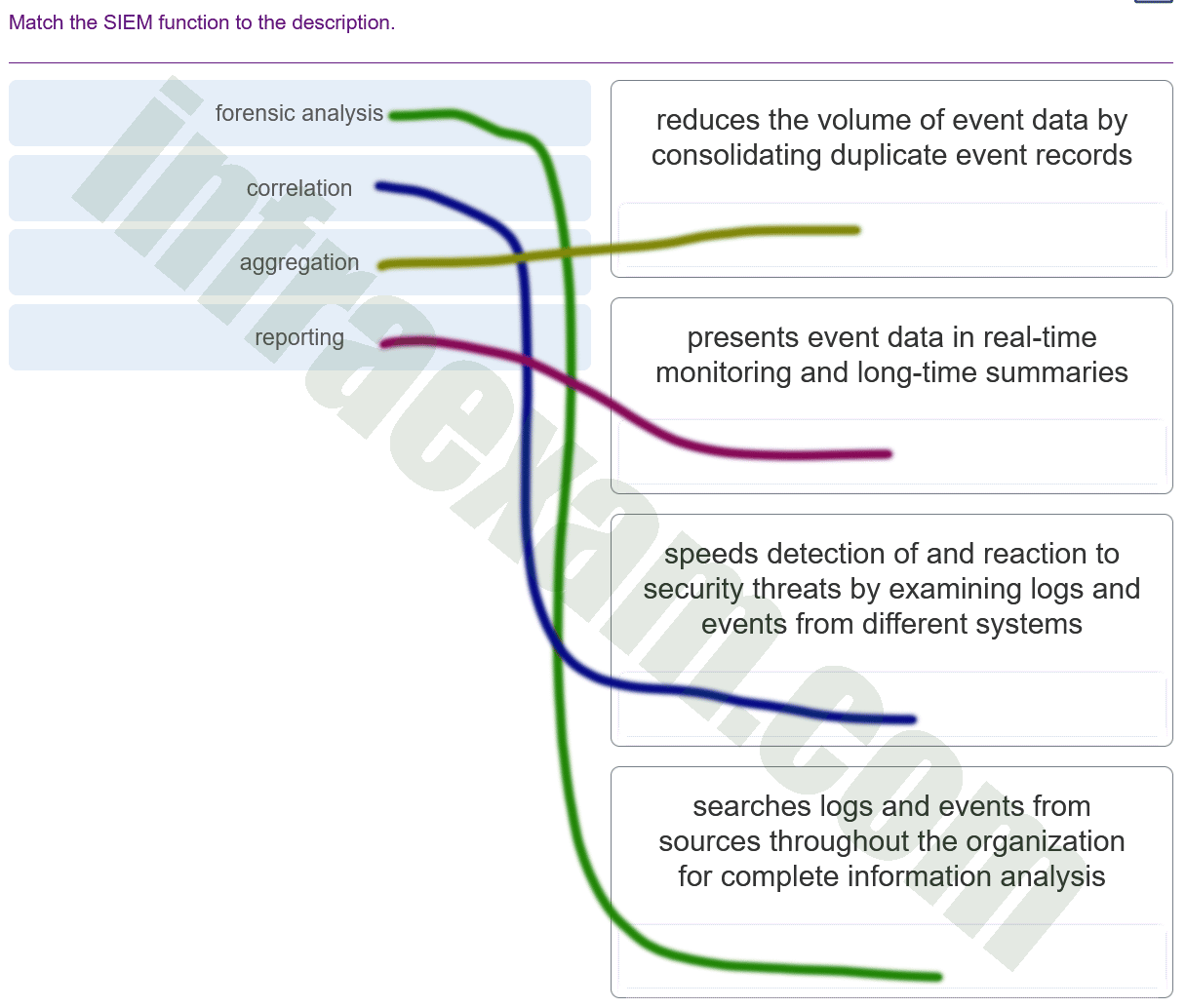
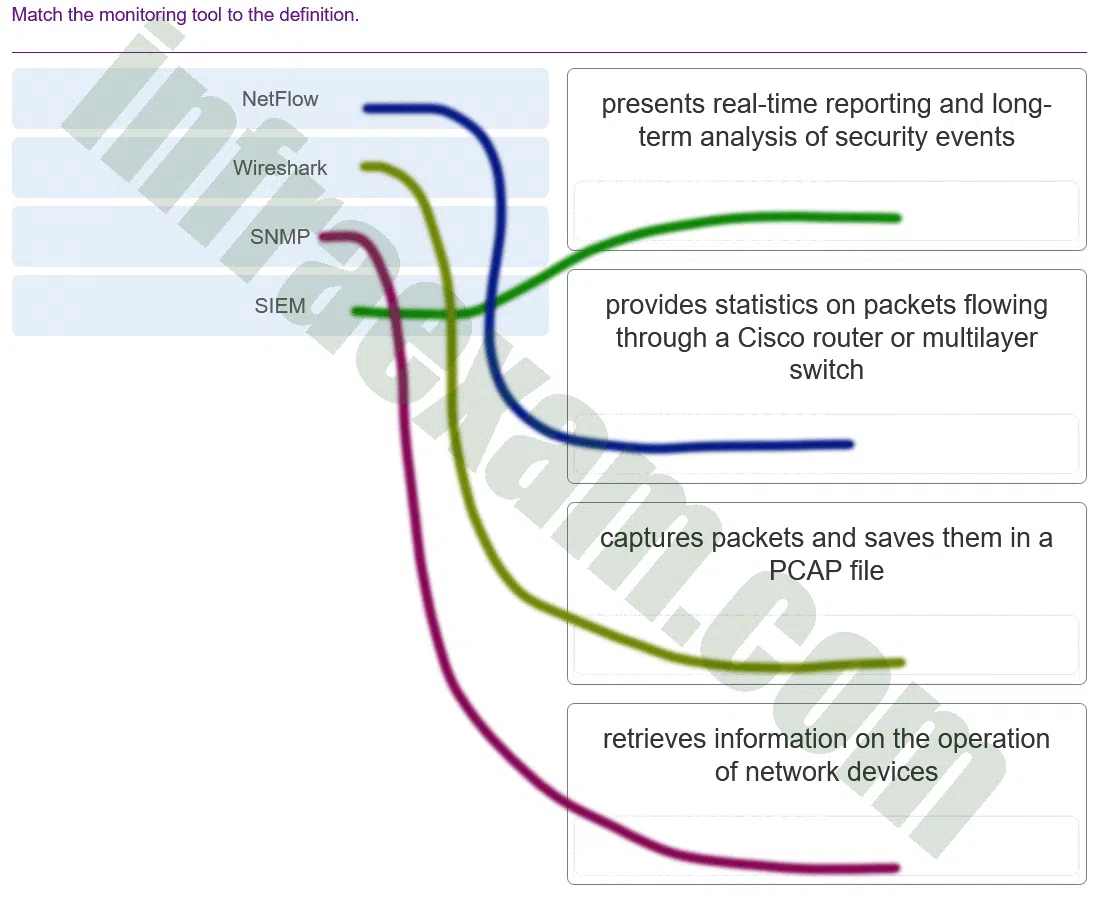
Match the SIEM function to the description.
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 009 Explanation & Hint: - Aggregation: This function reduces the volume of event data by consolidating duplicate event records. It collects log data from various sources and consolidates it to minimize redundancy and volume.
- Correlation: This function speeds detection of and reaction to security threats by examining logs and events from different systems. Correlation involves analyzing and cross-referencing logs and events to identify patterns that may indicate a security incident.
- Reporting: This function presents event data in real-time monitoring and long-time summaries. Reporting tools within a SIEM system help in visualizing data, providing summaries, and detailing security events over time for analysis.
- Forensic Analysis: This function involves searching logs and events from sources throughout the organization for complete information analysis. It is a deeper examination of logs to investigate and uncover the root cause or the full scope of a security incident after it has been identified.
-
Which device supports the use of SPAN to enable monitoring of malicious activity?
- Cisco IronPort
- Cisco Security Agent
- Cisco Catalyst switch
- Cisco NAC
-
Explanation & Hint: The device that supports the use of SPAN (Switched Port Analyzer) to enable monitoring of malicious activity is the:
Cisco Catalyst switch
SPAN, also known as port mirroring or port monitoring, is a feature on Cisco Catalyst switches that allows the copying of network packets seen on one switch port (or an entire VLAN) to another switch port, where the packet can be analyzed. This is commonly used for network troubleshooting and for security monitoring purposes.
- Cisco IronPort: Cisco IronPort is a line of appliances designed for email and web security. They include advanced threat prevention capabilities and are often used to control outbound messaging, prevent spam, and manage encryption. While these appliances provide security monitoring, they do not utilize the SPAN feature, which is specific to network switches for mirroring traffic.
- Cisco Security Agent: Cisco Security Agent was an endpoint security solution that provided threat protection for server and desktop computing systems. It focused on policy enforcement, malware protection, and threat mitigation at the host level, not on the network traffic monitoring that SPAN facilitates. The Cisco Security Agent does not support network traffic mirroring.
- Cisco Catalyst switch: This is the correct answer. Cisco Catalyst is a series of network switches that provide connectivity and network management to enterprise networks. The SPAN feature on Cisco Catalyst switches allows you to select network ports or VLANs to be monitored and to send a copy of the traffic seen on these ports or VLANs to another port on the switch where it can be captured and analyzed. This is useful for monitoring for malicious activity without interfering with the normal flow of network traffic.
- Cisco NAC (Network Admission Control): Cisco NAC was a set of security solutions that enforced security policy compliance on devices seeking to access network resources, ensuring that they met certain security criteria before they were allowed access. While it played a role in security monitoring by controlling access based on compliance, it did not support the SPAN feature, which is for monitoring and analyzing traffic on a network switch.
In summary, among the listed devices, only the Cisco Catalyst switch has the capability to support the SPAN feature, which enables the monitoring of network traffic, including potentially malicious activity.
-
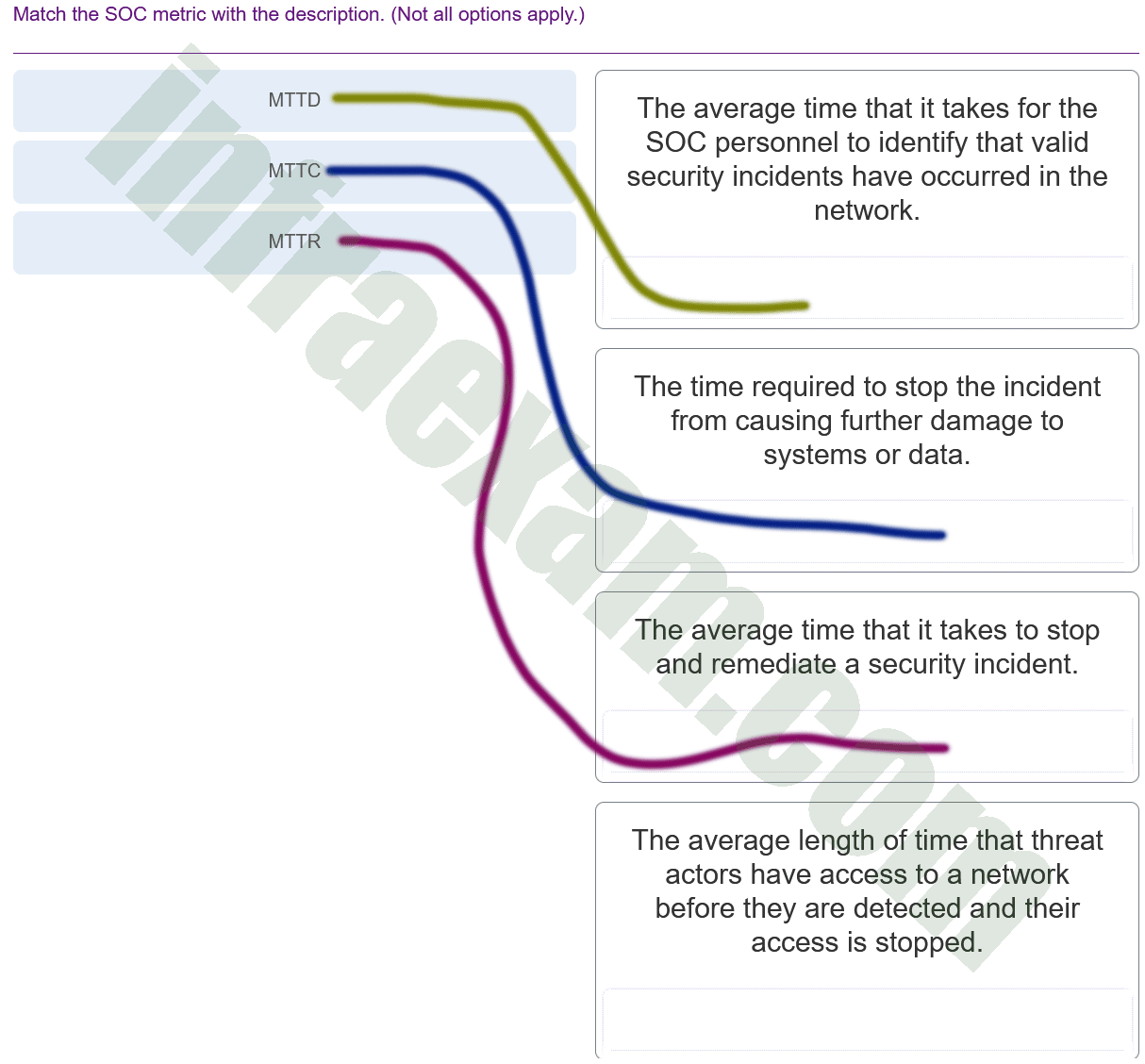
Match the SOC metric with the description. (Not all options apply.)
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 010 Explanation & Hint: - MTTD (Mean Time to Detect) – This metric corresponds to “The average time that it takes for the SOC personnel to identify that valid security incidents have occurred in the network.” It measures the efficiency of the SOC in detecting security incidents.
- MTTC (Mean Time to Contain) – This metric should match with “The time required to stop the incident from causing further damage to systems or data.” It assesses the speed at which a security team can limit the impact of the incident.
- MTTR (Mean Time to Respond) – This metric is typically associated with “The average time that it takes to stop and remediate a security incident.” It evaluates how quickly the SOC can address and resolve the incident after it has been detected.
The last description given, “The average length of time that threat actors have access to a network before they are detected and their access is stopped,” is a definition that could be associated with Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) as it involves the detection time, but it could also refer to another metric known as “Mean Time to Identify” (MTTI), which is not listed here. It’s important to note that in some contexts, MTTR can also refer to Mean Time to Recover/Repair, which is the average time taken to recover from an incident and restore services to normal. However, in the context of the options provided, the match to MTTR as explained is the most appropriate.
-
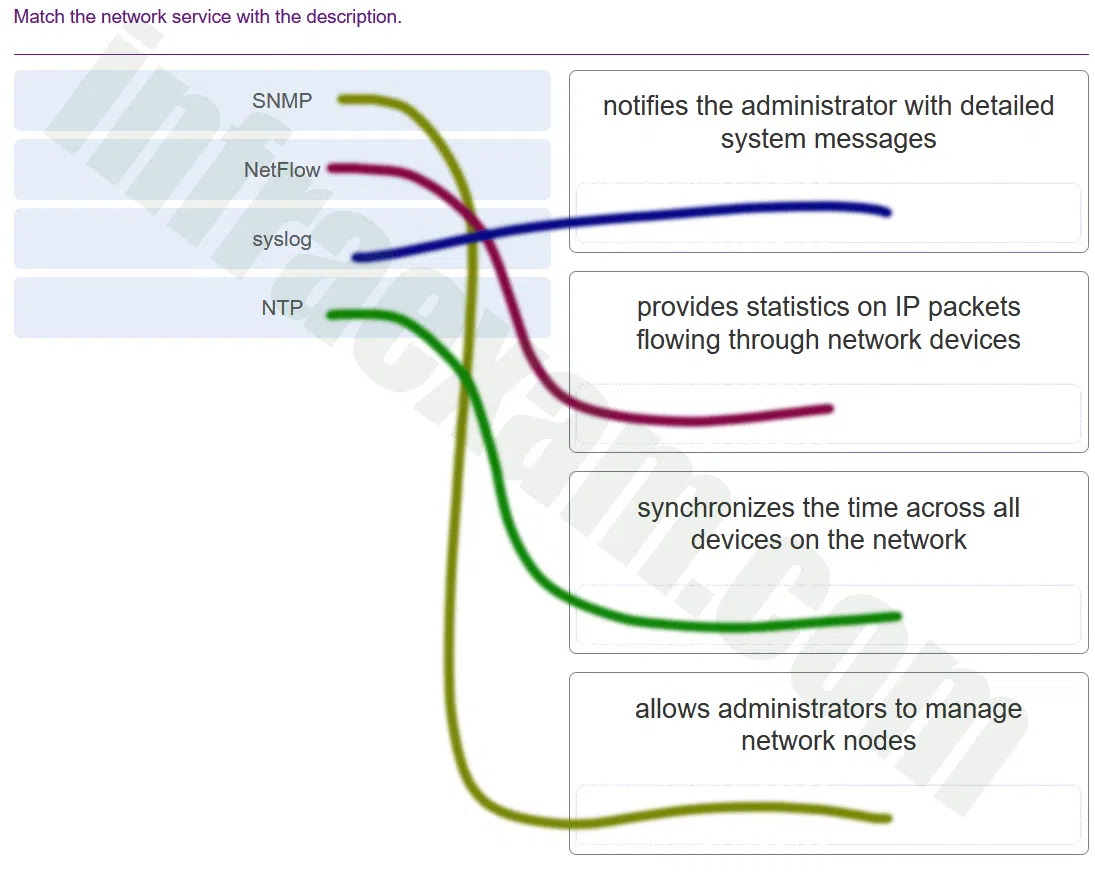
What are the two ways threat actors use NTP? (Choose two.)
- Threat actors use NTP systems to direct DDoS attacks.
- They place iFrames on a frequently used corporate web page.
- They encode stolen data as the subdomain portion where the nameserver is under control of an attacker.
- They place an attachment inside an email message.
- They attack the NTP infrastructure in order to corrupt the information used to log the attack.
-
Explanation & Hint: Network Time Protocol (NTP) can be exploited by threat actors in a few ways, primarily due to its ability to respond to requests with significantly more data than is contained within the request. Two ways that threat actors use NTP are:
- Threat actors use NTP systems to direct DDoS attacks: NTP can be used in amplification attacks, which are a type of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack. The attacker sends a request to the NTP server with a spoofed source IP address (the target’s address). The server, which sends significantly more data in response to the request, floods the target with traffic, overwhelming the target’s resources.
- They attack the NTP infrastructure in order to corrupt the information used to log the attack: By disrupting the NTP infrastructure, threat actors could potentially alter timestamps in logs, making it difficult for security analysts to correlate events and understand the sequence of an attack. This could be used to obfuscate the details of an attack or to confuse the incident response process.
The other options listed, such as placing iFrames on a web page, encoding stolen data in DNS queries, and sending malicious email attachments, do not directly involve the abuse of the NTP protocol. Those are separate attack methods not specifically related to NTP exploitation.
-
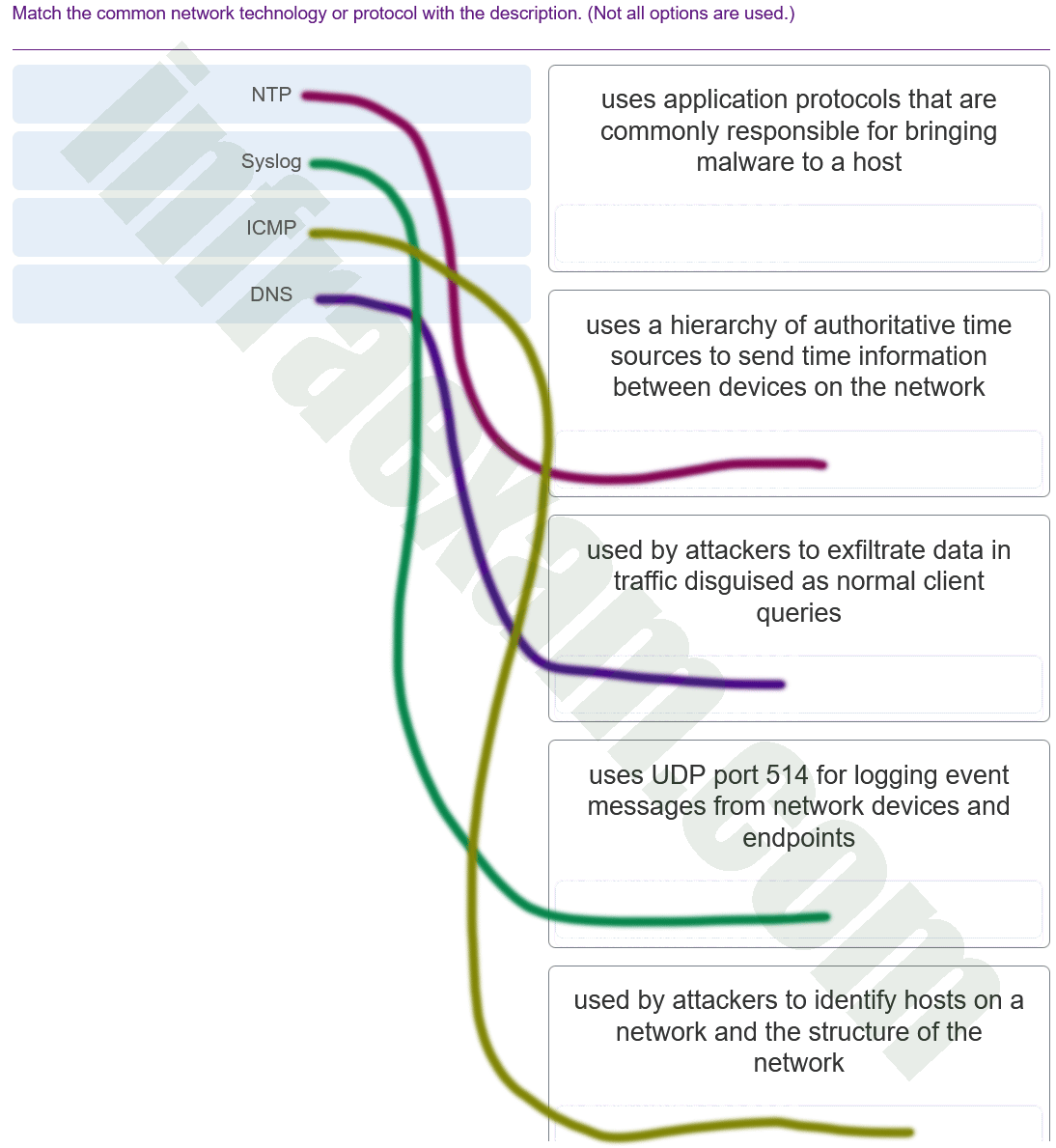
Which two network protocols can be used by a threat actor to exfiltrate data in traffic that is disguised as normal network traffic? (Choose two.)
- syslog
- DNS
- SMTP
- NTP
- HTTP
-
Explanation & Hint: Threat actors often use common network protocols to exfiltrate data because they can blend in with normal traffic and may not be blocked by firewalls. Two protocols that can be used for this purpose are:
- DNS (Domain Name System): Because DNS requests are usually allowed out of networks and can be difficult to monitor due to their high volume, DNS queries can be used to covertly send data to an external server controlled by the attacker. This technique involves encoding data within DNS query requests or responses, which can then be reconstructed outside the network.
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): HTTP is commonly used for web traffic, which makes it a prime candidate for data exfiltration. Malicious data can be embedded in HTTP requests and responses, and since web traffic is very common, it might not be flagged as suspicious. Additionally, if the communication is encrypted using HTTPS, it becomes even harder to detect the malicious content without SSL/TLS inspection.
The other protocols listed can potentially be used for exfiltration as well, but they are not as commonly used for disguising traffic as normal activity:
- Syslog: While syslog is used for logging events and messages, it is not commonly used for exfiltration due to its easier detection and less frequent use across external network boundaries.
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): SMTP is used for sending emails and could be used for data exfiltration; however, it would typically be more conspicuous than DNS or HTTP traffic because large amounts of outgoing email could raise suspicions.
- NTP (Network Time Protocol): NTP is used for time synchronization and is not typically used for data exfiltration due to the limited amount of payload data that can be sent. However, it can be used for smaller data leaks or for other malicious activities such as DDoS attacks.
-
Which application layer protocol is used to provide file-sharing and print services to Microsoft applications?
- SMB
- DHCP
- HTTP
- SMTP
Answers Explanation & Hints: SMB is used in Microsoft networking for file-sharing and print services. The Linux operating system provides a method of sharing resources with Microsoft networks by using a version of SMB called SAMBA.
-
What information is required for a WHOIS query?
- outside global address of the client
- FQDN of the domain
- ICANN lookup server address
- link-local address of the domain owner
-
Explanation & Hint: To perform a WHOIS query, which is a protocol used to query databases that store the registered users or assignees of an internet resource such as a domain name, IP address block, or an autonomous system, you generally need the following information:
- FQDN of the domain: The Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) is commonly used to perform a WHOIS query to find out information about the domain registration, such as the domain owner, registration dates, and the nameservers associated with the domain.
The other options are not typically used for a WHOIS query:
- Outside global address of the client: This refers to a public IP address that is assigned to a device on a network, translating the private IP address to a global address. This information is not necessary for a WHOIS query.
- ICANN lookup server address: While ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers) provides a WHOIS lookup service, you do not need to know the specific server address to perform a query. You can go to the ICANN website or use various WHOIS lookup tools available online.
- Link-local address of the domain owner: Link-local addresses are used in a local network segment and are not routable or registered globally. WHOIS queries do not use or provide link-local addresses.
Typically, a WHOIS query is performed using a domain name or an IP address to find out ownership and registration information.
-
Which tool included in the Security Onion is a series of software plugins that send different types of data to the Elasticsearch data stores?
- OSSEC
- Curator
- Beats
- ElastAlert
-
Explanation & Hint: The tool included in Security Onion that acts as a series of software plugins to send different types of data to Elasticsearch data stores is Beats.
Beats are lightweight, single-purpose data shippers that you install on your servers to send different types of operational data to Elasticsearch. Beats can send a wide array of information, including logs (Filebeat), network data (Packetbeat), metrics (Metricbeat), and more, which makes it an essential part of the Elastic Stack within Security Onion for monitoring and security data analysis.
- OSSEC: This stands for Open Source HIDS Security, and it is an open-source Host-based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS). It performs log analysis, file integrity checking, policy monitoring, rootkit detection, real-time alerting, and active response. It doesn’t directly send data to Elasticsearch but is used for monitoring and alerting on the individual system’s security posture.
- Curator: Elasticsearch Curator helps manage Elasticsearch indices and snapshots by automating maintenance tasks. You can use Curator to clean up old data by deleting or archiving indices based on defined policies. While Curator interacts with Elasticsearch, it does not ship data to it; rather, it’s used for managing data within Elasticsearch.
- Beats: This is the correct answer to your original question. Beats is a collection of open-source data shippers that you install as agents on your servers to send various types of operational data to Elasticsearch. Each Beat is purpose-built for different kinds of data — for example, Filebeat for log files, Metricbeat for metrics, Packetbeat for network data, etc.
- ElastAlert: This is an alerting tool that works with Elasticsearch. It is used to trigger alerts based on anomalies, patterns, or other conditions detected in the data stored in Elasticsearch. ElastAlert does not ship data to Elasticsearch, but rather it is a consumer of data within Elasticsearch, monitoring it and sending out alerts when its configured rules are met.
Each of these tools serves a different function in the context of security monitoring and analysis, and they can be used in conjunction to provide a comprehensive security posture for an organization.
-
Which term is used to describe the process of identifying the NSM-related data to be gathered?
- data archiving
- data normalization
- data reduction
- data retention
-
Explanation & Hint: The term used to describe the process of identifying the Network Security Monitoring (NSM)-related data to be gathered is data reduction.
Data reduction in the context of NSM refers to the process of determining and collecting only the relevant data necessary for security monitoring purposes. This can involve filtering out irrelevant or low-value data to focus on the high-value information that will be most useful for detecting and analyzing security incidents. This is an important step because it can significantly reduce the volume of data that needs to be stored and analyzed, making the monitoring process more efficient and effective.
- Data Archiving: This refers to the process of moving data that is no longer actively used to a separate storage device for long-term retention. Archived data is kept for compliance or reference purposes and is generally stored in a way that preserves the original content and metadata. In the context of NSM, data archiving is important because it ensures that historical data is available for future reference or investigation, potentially years after it was initially collected.
- Data Normalization: This process involves standardizing and formatting data from various sources into a consistent format. In NSM, data normalization is crucial because it allows security tools to analyze and correlate data from different systems and formats. By normalizing data, analysts can more easily spot trends, identify anomalies, and apply consistent security measures across disparate data sets.
- Data Reduction: This is the process of identifying and collecting only the most relevant and necessary data for the task at hand. For NSM, data reduction involves filtering out noise, such as irrelevant traffic and benign events, to focus on the data that could indicate potential security threats or incidents. This is important because it allows security professionals to concentrate their efforts on high-priority issues without being overwhelmed by the sheer volume of data.
- Data Retention: This term describes the policies and processes that determine how long data is kept by an organization. Data retention is guided by regulatory requirements, operational needs, and storage capacities. In NSM, establishing a proper data retention policy is essential for ensuring that data is available for as long as it is needed for analysis and compliance purposes, but not longer than necessary, which can help in managing storage costs and data privacy concerns.
All these processes are part of managing the lifecycle of data in an NSM system, from the moment it is collected to when it is eventually archived or deleted. They help ensure that the data is usable, secure, and available for as long as needed.
-
An administrator is trying to develop a BYOD security policy for employees that are bringing a wide range of devices to connect to the company network. Which three objectives must the BYOD security policy address? (Choose three.)
- All devices must have open authentication with the corporate network.
- The level of access of employees when connecting to the corporate network must be defined.
- Rights and activities permitted on the corporate network must be defined.
- All devices should be allowed to attach to the corporate network flawlessly.
- Safeguards must be put in place for any personal device being compromised.
- All devices must be insured against liability if used to compromise the corporate network.
-
Explanation & Hint: When developing a Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) security policy, the primary objectives are to ensure the security of the corporate network while allowing employees the flexibility to use their personal devices. Here are three objectives that such a policy must address:
- The level of access of employees when connecting to the corporate network must be defined: It’s crucial to specify what resources each user can access when they connect their personal device to the corporate network. This helps to maintain security by ensuring that employees can only reach the necessary data and systems for their roles.
- Rights and activities permitted on the corporate network must be defined: The policy should clearly outline what employees can and cannot do on the corporate network. This includes acceptable use policies, prohibited activities, and potential restrictions on certain types of applications or services to mitigate security risks.
- Safeguards must be put in place for any personal device being compromised: The policy must address the steps to be taken to protect corporate data in case an employee’s personal device is lost, stolen, or compromised. This often includes requirements for encryption, remote wiping capabilities, and strong authentication measures.
The other options listed are not typical or recommended objectives of a BYOD security policy:
- All devices must have open authentication with the corporate network: This would be a significant security risk. Instead, strong authentication should be enforced.
- All devices should be allowed to attach to the corporate network flawlessly: While ease of connectivity is important, it should not override security considerations. Devices should meet certain security standards before being allowed to connect.
- All devices must be insured against liability if used to compromise the corporate network: While it is important to consider the implications of a compromised device, requiring insurance is not a practical or enforceable policy for individual employee-owned devices. Instead, the focus should be on prevention, detection, and response to security incidents.
-
Which device in a layered defense-in-depth approach denies connections initiated from untrusted networks to internal networks, but allows internal users within an organization to connect to untrusted networks?
- internal router
- IPS
- access layer switch
- firewall
Answers Explanation & Hints: A firewall is typically a second line of defense in a layered defense-in-depth approach to network security. The firewall typically connects to an edge router that connects to the service provider. The firewall tracks connections initiated within the company going out of the company and denies initiation of connections from external untrusted networks going to internal trusted networks.
-
A network administrator is configuring an AAA server to manage RADIUS authentication. Which two features are included in RADIUS authentication? (Choose two.)
- single process for authentication and authorization
- separate processes for authentication and authorization
- hidden passwords during transmission
- encryption for all communication
- encryption for only the data
-
Explanation & Hint: in the context of RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) authentication:
- Single process for authentication and authorization: This is correct. In RADIUS, authentication and authorization are typically handled together in a single process. When a RADIUS server receives an authentication request, it checks the credentials and simultaneously determines the network resources that the user is permitted to access. This combined approach is a fundamental aspect of how RADIUS operates, differentiating it from protocols that strictly separate authentication and authorization processes.
- Separate processes for authentication and authorization: This option does not typically describe RADIUS. While RADIUS can technically support separate processes, in practice, authentication and authorization are usually combined in RADIUS transactions. Other protocols, like TACACS+, are known for more distinct separation of these functions.
- Hidden passwords during transmission: This is also correct. RADIUS protocol ensures that passwords are hidden or obscured during transmission. Typically, the user’s password is encrypted to prevent it from being sent in clear text across the network, enhancing security by protecting the user credentials during transit.
- Encryption for all communication: RADIUS does not encrypt the entire packet content; it only encrypts the user’s password. Therefore, while RADIUS provides some level of security for authentication, it is not as secure as protocols that encrypt the entire communication, such as Secure RADIUS (RadSec).
- Encryption for only the data: This is partially true. RADIUS encrypts the user’s password, which is part of the data within the communication packet. However, other parts of the RADIUS packet, like the username and authorization information, are sent in clear text. This partial encryption is a consideration when assessing the overall security of RADIUS in a network environment.
In summary, RADIUS is known for hiding passwords during transmission and typically handles authentication and authorization in a single process, though it does not encrypt all communication data.
-
A company has a file server that shares a folder named Public. The network security policy specifies that the Public folder is assigned Read-Only rights to anyone who can log into the server while the Edit rights are assigned only to the network admin group. Which component is addressed in the AAA network service framework?
- authentication
- accounting
- automation
- authorization
Answers Explanation & Hints: After a user is successfully authenticated (logged into the server), the authorization is the process of determining what network resources the user can access and what operations (such as read or edit) the user can perform.
-
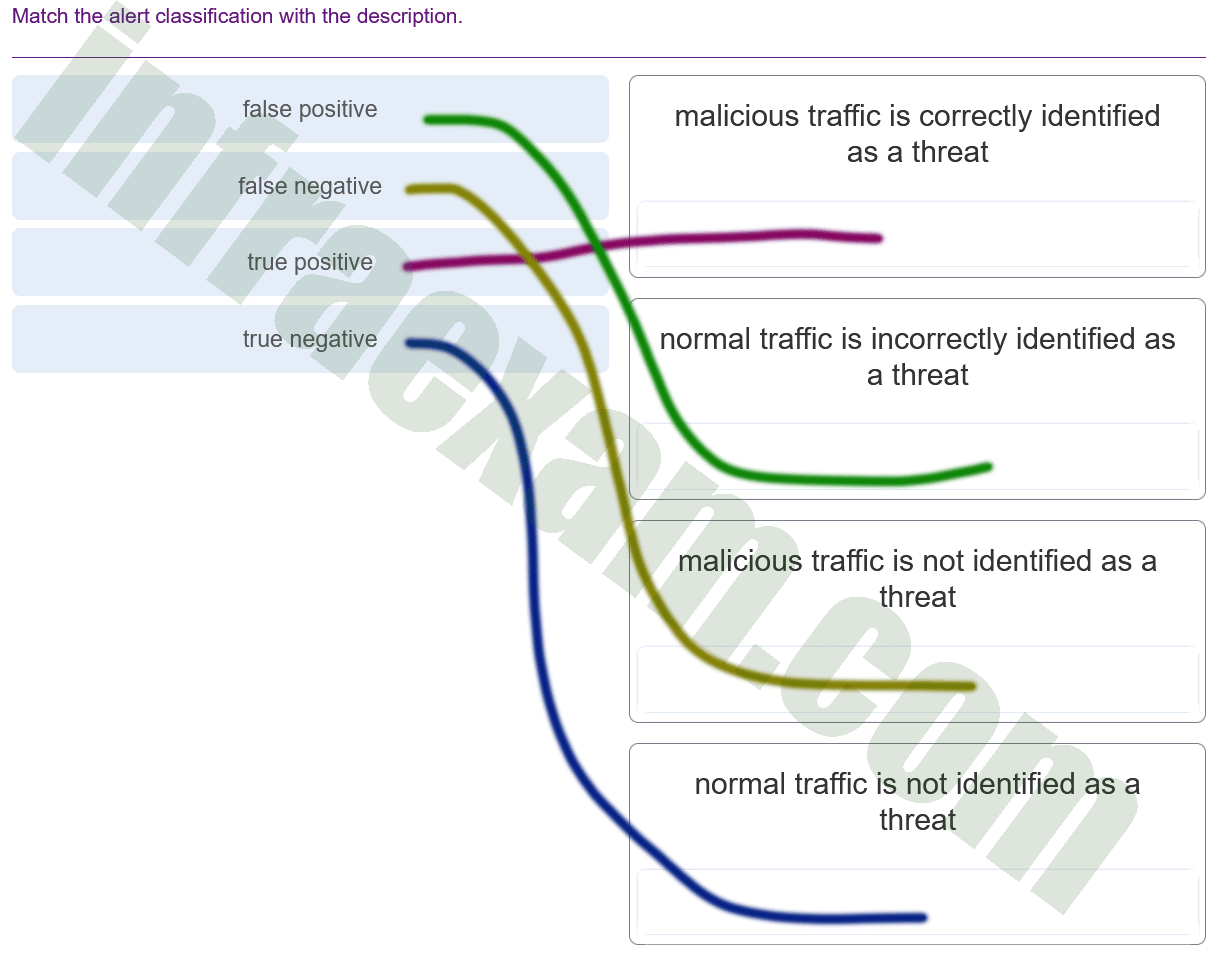
Match the alert classification with the description.
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 011 Explanation & Hint: - True Positive: Malicious traffic is correctly identified as a threat. This means the system accurately detected actual malicious activity.
- False Positive: Normal traffic is incorrectly identified as a threat. This occurs when benign activity is mistakenly flagged as malicious, leading to unnecessary investigation or action.
- False Negative: Malicious traffic is not identified as a threat. In this case, the system fails to detect actual malicious activity, which could allow a security breach to occur undetected.
- True Negative: Normal traffic is not identified as a threat. This is the desired outcome for benign activity, where the system correctly identifies that there is no threat present.
-
What are the three core functions provided by the Security Onion? (Choose three.)
- business continuity planning
- alert analysis
- security device management
- threat containment
- intrusion detection
- full packet capture
Answers Explanation & Hints: Security Onion is an open source suite of Network Security Monitoring (NSM) tools for evaluating cybersecurity alerts. For cybersecurity analysts the Security Onion provides full packet capture, network-based and host-based intrusion detection systems, and alert analysis tools.
-
What best describes the security threat of spoofing?
- sending bulk email to individuals, lists, or domains with the intention to prevent users from accessing email
- intercepting traffic between two hosts or inserting false information into traffic between two hosts
- making data appear to come from a source that is not the actual source
- sending abnormally large amounts of data to a remote server to prevent user access to the server services
-
Explanation & Hint: The security threat of spoofing is best described by:
Making data appear to come from a source that is not the actual source.
Spoofing is a fraudulent or malicious practice in which communication is sent from an unknown source disguised as a source known to the receiver. Spoofing can apply to emails, phone calls, and websites, or can be more technical, such as a computer spoofing an IP address, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), or Domain Name System (DNS) server.
-
What is a property of the ARP table on a device?
- Every operating system uses the same timer to remove old entries from the ARP cache.
- Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
- Static IP-to-MAC address entries are removed dynamically from the ARP table.
- Windows operating systems store ARP cache entries for 3 minutes.
-
Explanation & Hint: A property of the ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) table on a device is:
Entries in an ARP table are time-stamped and are purged after the timeout expires.
The ARP table, also known as the ARP cache, maintains a mapping of IP addresses to MAC addresses. When an IP address needs to be resolved to a MAC address, ARP is used. Once the MAC address is discovered, it is stored in the ARP table for a certain period. These entries are time-stamped, and after the timeout (which varies depending on the operating system and its configuration), if not used, they are purged to make space for new entries and to ensure that changes in the network topology are respected.
The other statements are incorrect or not universally applicable:
- Every operating system uses the same timer to remove old entries from the ARP cache: This is incorrect. Different operating systems have different default timers for ARP entry expiration, and these can often be adjusted by an administrator.
- Static IP-to-MAC address entries are removed dynamically from the ARP table: This is incorrect. Static entries are manually added to the ARP table to prevent them from expiring and are not purged automatically. They remain in the ARP table until manually removed or until the device is rebooted.
- Windows operating systems store ARP cache entries for 3 minutes: This statement is not entirely accurate. The timeout for ARP cache entries in Windows can vary, and the typical default ARP cache entry life is 2 minutes for stale entries and 10 minutes for unresolved entries, but this can be changed via registry settings or system policies.
-
A newly created company has fifteen Windows 10 computers that need to be installed before the company can open for business. What is a best practice that the technician should implement when configuring the Windows Firewall?
- The technician should create instructions for corporate users on how to allow an app through the WIndows Firewall using the Administrator account.
- The technician should remove all default firewall rules and selectively deny traffic from reaching the company network.
- The technician should enable the Windows Firewall for inbound traffic and install other firewall software for outbound traffic control.
- After implementing third party security software for the company, the technician should verify that the Windows Firewall is disabled.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Only disable Windows Firewall if other firewall software is installed. Use the Windows Firewall (Windows 7 or 8) or the Windows Defender Firewall (Windows 10) Control Panel to enable or disable the Windows Firewall.
-
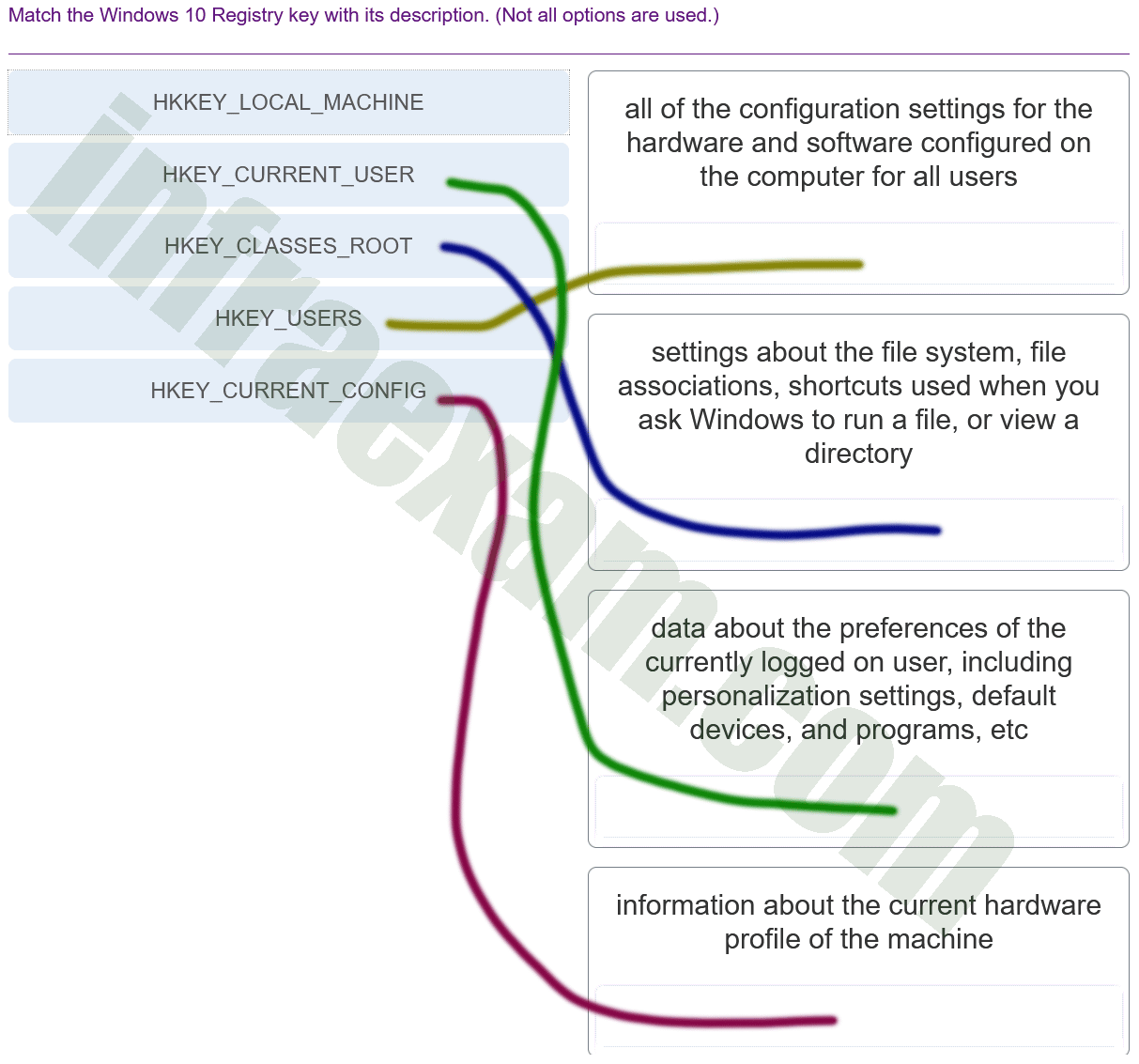
Match the Windows 10 Registry key with its description. (Not all options are used.)
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 012 Explanation & Hint: - HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT (HKCR): Contains settings about the file system, file associations, shortcuts used when you ask Windows to run a file, or view a directory. It is primarily used for OLE (Object Linking and Embedding) and file association configurations.
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER (HKCU): Stores data about the preferences of the currently logged-on user, including personalization settings, default devices, and programs, etc. This hive is specific to the user profile currently in use on the machine.
- HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG (HKCC): Contains information about the current hardware profile of the machine. It provides access to configuration information for the current hardware profile of the local computer.
- HKEY_USERS (HKU): Stores all of the configuration settings for the hardware and software configured on the computer for all users. This hive contains information about the system’s hardware and software configuration.
-
What is a characteristic of a Trojan horse as it relates to network security?
- Malware is contained in a seemingly legitimate executable program.
- Extreme quantities of data are sent to a particular network device interface.
- Too much information is destined for a particular memory block, causing additional memory areas to be affected.
- An electronic dictionary is used to obtain a password to be used to infiltrate a key network device.
Answers Explanation & Hints: A Trojan horse carries out malicious operations under the guise of a legitimate program. Denial of service attacks send extreme quantities of data to a particular host or network device interface. Password attacks use electronic dictionaries in an attempt to learn passwords. Buffer overflow attacks exploit memory buffers by sending too much information to a host to render the system inoperable.
-
What technique is used in social engineering attacks?
- man-in-the-middle
- phishing
- buffer overflow
- sending junk email
Answers Explanation & Hints: A threat actor sends fraudulent email which is disguised as being from a legitimate, trusted source to trick the recipient into installing malware on their device, or to share personal or financial information.
-
What are two evasion techniques that are used by hackers? (Choose two.)
- phishing
- Trojan horse
- reconnaissance
- rootkit
- pivot
Answers Explanation & Hints: The following methods are used by hackers to avoid detection:Encryption and tunneling – hide or scramble the malware content
Resource exhaustion – keeps the host device too busy to detect the invasion
Traffic fragmentation – splits the malware into multiple packets
Protocol-level misinterpretation – sneaks by the firewall
Pivot – uses a compromised network device to attempt access to another device
Rootkit – allows the hacker to be undetected and hides software installed by the hacker
-
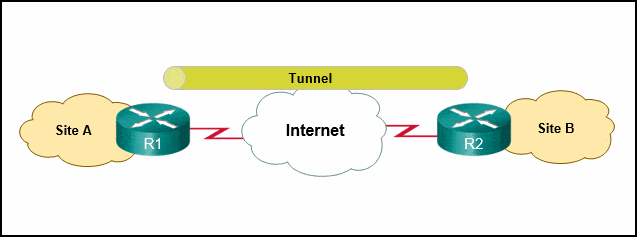
Refer to the exhibit. What solution can provide a VPN between site A and site B to support encapsulation of any Layer 3 protocol between the internal networks at each site?
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 01 - a GRE tunnel
- an IPsec tunnel
- Cisco SSL VPN
- a remote access tunnel
Answers Explanation & Hints: A Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) tunnel is a non-secure, site-to-site VPN tunneling solution that is capable of encapsulating any Layer 3 protocol between multiple sites across over an IP internetwork.
-
What are two drawbacks to using HIPS? (Choose two.)
- With HIPS, the success or failure of an attack cannot be readily determined.
- If the network traffic stream is encrypted, HIPS is unable to access unencrypted forms of the traffic.
- HIPS installations are vulnerable to fragmentation attacks or variable TTL attacks.
- HIPS has difficulty constructing an accurate network picture or coordinating events that occur across the entire network.
- With HIPS, the network administrator must verify support for all the different operating systems used in the network.
Explanation & Hint: Two disadvantages of deploying HIPS are (1) that it cannot create a complete view of the network or have knowledge of events that might be occurring beyond an individual host and (2) every host operating system within the organization must be supported. However, an advantage of using HIPS is that it can monitor and protect the operating system as well as critical system processes on each network host.
-
What are three functions provided by the syslog service? (Choose three.)
- to gather logging information for monitoring and troubleshooting
- to provide statistics on packets that are flowing through a Cisco device
- to periodically poll agents for data
- to specify the destinations of captured messages
- to provide traffic analysis
- to select the type of logging information that is captured
Answers Explanation & Hints: There are three primary functions provided by the syslog service:
- gathering logging information
- selection of the type of information to be logged
- selection of the destination of the logged information
-
A technician needs to verify file permissions on a specific Linux file. Which command would the technician use?
- sudo
- cd
- vi
- ls -l
-
Explanation & Hint: To verify file permissions on a specific file in Linux, the technician would use the command:
ls -l
The
ls -lcommand lists files in ‘long format’, which includes the file permissions, number of links, owner name, owner group, file size, timestamp, and filename. If the technician needs to check the permissions of a specific file, they can append the filename to the command. For example:ls -l /path/to/file
This will display the permissions for the specified file at the given path.
- sudo: This command stands for “superuser do” and is used to execute a command with superuser (root) privileges. It’s a powerful command that allows a permitted user to perform tasks that require administrative or root permissions, such as installing software, changing important system configurations, or accessing secured files.Example:
sudo apt-get updatewould run the update process for package lists with root privileges. - cd: Short for “change directory,” this command is used to change the current working directory in the shell environment. It’s one of the most basic and frequently used commands in Linux.Example:
cd /var/wwwwould change the current working directory to/var/www. - vi: This is a text editor in the Unix and Linux systems.
vistands for “visual editor,” and it allows a user to create or modify text files. It has different modes like insert mode, command mode, and ex mode, which the user needs to switch between to perform various tasks.Example:vi myfile.txtwould openmyfile.txtin thevieditor, or create it if it doesn’t exist. - ls -l: The
lscommand is used to list the contents of a directory. When used with the-loption (long listing format), it displays detailed information about each file and directory, such as permissions, number of links, owner, group, size, and date of last modification.Example:ls -lwould list the detailed contents of the current directory, whilels -l /path/to/directorywould list the contents of/path/to/directory.
For the specific task of verifying file permissions,
ls -lis the appropriate command because it provides the detailed permissions view needed for this purpose. - sudo: This command stands for “superuser do” and is used to execute a command with superuser (root) privileges. It’s a powerful command that allows a permitted user to perform tasks that require administrative or root permissions, such as installing software, changing important system configurations, or accessing secured files.Example:
-
Why would a network administrator choose Linux as an operating system in the Security Operations Center (SOC)?
- It is easier to use than other server operating systems.
- The administrator has control over specific security functions, but not standard applications.
- More network applications are created for this environment.
- It can be acquired at no charge.
-
Explanation & Hint: A network administrator might choose Linux as an operating system in the Security Operations Center (SOC) for several reasons. While ease of use is subjective and may depend on the administrator’s familiarity with different operating systems, here are the reasons related to the options provided:
- The administrator has control over specific security functions, but not standard applications: Linux offers granular control over both security functions and standard applications. An administrator can fine-tune the security settings, user permissions, and the firewall, and can choose from a wide range of security tools that are either pre-built or can be easily installed and configured. This level of control is due to the open-source nature of Linux, which allows for customization and modification as needed for the security environment.
The other options are less likely to be the primary reasons for choosing Linux in a SOC:
- It can be acquired at no charge: Many Linux distributions are available free of charge, which can be a significant advantage, especially for organizations with budget constraints. While there are also paid versions that come with enterprise support, the free versions are fully functional and can be a cost-effective solution for a SOC.
- It is easier to use than other server operating systems: This is subjective and depends on the administrator’s expertise. Linux has a reputation for being more command-line and configuration file-centric, which some may find less intuitive than GUI-based operating systems.
- More network applications are created for this environment: While there are many network applications available for Linux, the claim that “more” are created for Linux than other operating systems is too broad and not necessarily accurate. The choice of operating system often depends on the specific applications and tools that the SOC team is looking to employ. Linux is known for a strong set of open-source security and network monitoring tools, but the best platform depends on the specific use case.
In summary, the primary reason a network administrator might choose Linux for a SOC is the level of control over security functions and the cost-effectiveness of the platform.
-
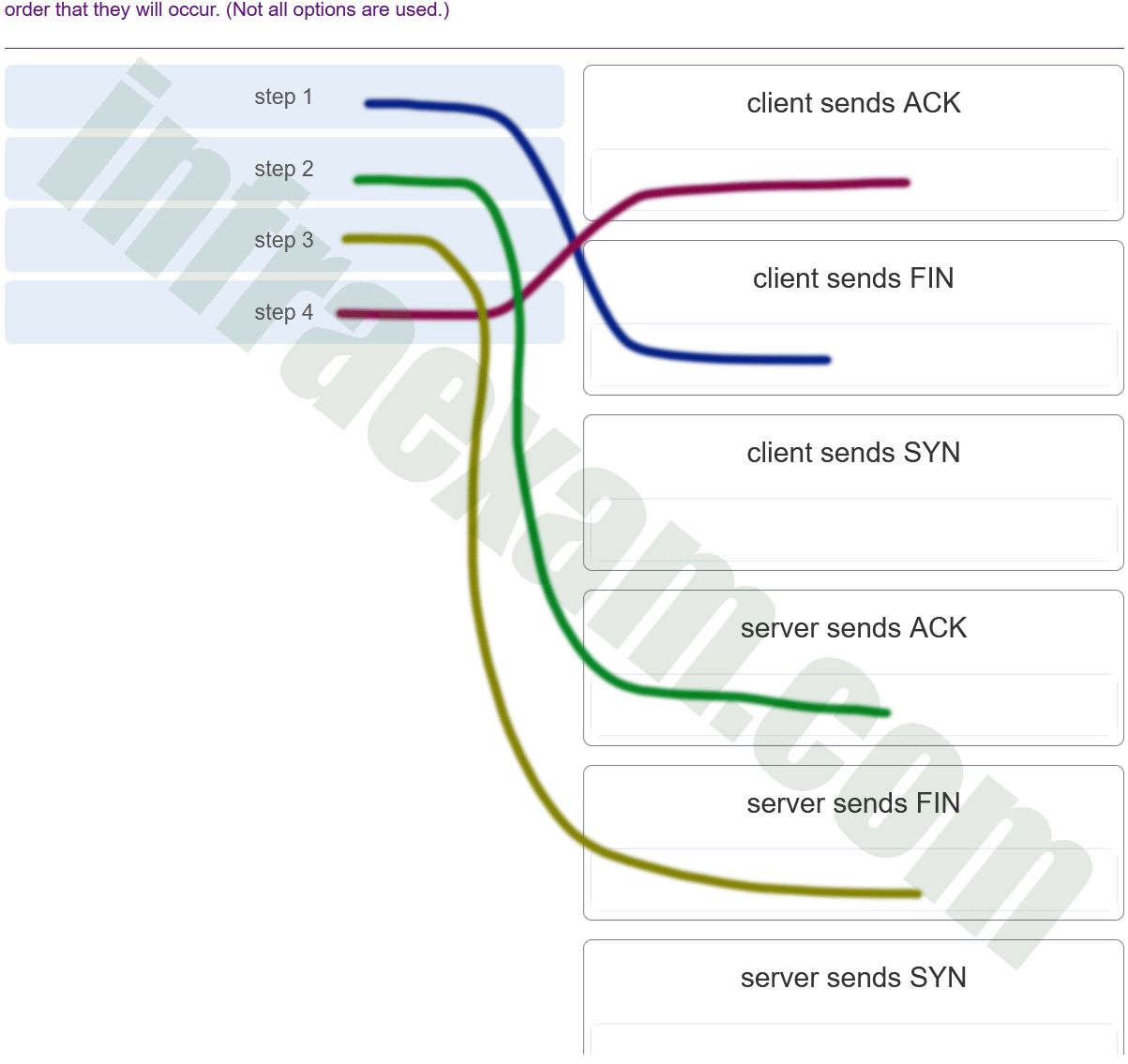
A client application needs to terminate a TCP communication session with a server. Place the termination process steps in the order that they will occur. (Not all options are used.)
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 013 Explanation & Hint: Here’s the correct sequence for establishing a TCP connection (the three-way handshake):
- Client sends SYN: This is the first step where the client wants to establish a connection with a server, so it sends a synchronize (SYN) message to the server.
- Server sends SYN-ACK: Upon receiving the SYN message, the server responds with a synchronize-acknowledgment (SYN-ACK) message.
- Client sends ACK: The client acknowledges the server’s SYN-ACK message with an acknowledgment (ACK) message, and the connection is established.
For terminating a TCP connection, the sequence (not fully depicted in the provided options) typically involves a FIN (finish) message:
- Client sends FIN: This step would be initiated when the client wants to close the connection. It sends a FIN message to the server.
- Server sends ACK: The server acknowledges the FIN message from the client, indicating it received the request to close the connection.
- Server sends FIN: The server then sends its own FIN message to the client to close its side of the connection.
- Client sends ACK: Finally, the client acknowledges the server’s FIN message.
The server does not send a SYN as part of the termination process; that’s only used during the connection establishment phase. If the lines in the image do not match the steps as described here, they should be corrected accordingly.
-
Which protocol or service uses UDP for a client-to-server communication and TCP for server-to-server communication?
- DNS
- HTTP
- FTP
- SMTP
Answers Explanation & Hints: Some applications may use both TCP and UDP. DNS uses UDP when clients send requests to a DNS server, and TCP when two DNS serves directly communicate.
-
Which two statements describe the characteristics of symmetric algorithms? (Choose two.)
- They provide confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- They are commonly used with VPN traffic.
- They use a pair of a public key and a private key.
- They are referred to as a pre-shared key or secret key.
- They are commonly implemented in the SSL and SSH protocols.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Symmetric encryption algorithms use the same key (also called shared secret) to encrypt and decrypt the data. In contrast, asymmetric encryption algorithms use a pair of keys, one for encryption and another for decryption.
-
What are two properties of a cryptographic hash function? (Choose two.)
- The hash function is one way and irreversible.
- The input for a particular hash algorithm has to have a fixed size.
- Hash functions can be duplicated for authentication purposes.
- Complex inputs will produce complex hashes.
- The output is a fixed length.
-
Explanation & Hint: Two properties of a cryptographic hash function are:
- The hash function is one way and irreversible: This means that once data has gone through the hash function, the process cannot be reversed. The resulting hash cannot be ‘decoded’ back into the original data, which is a fundamental aspect of hash functions used in cryptography.
- The output is a fixed length: Regardless of the size of the input data, a hash function for a given algorithm will always produce an output of a fixed length. For example, an MD5 hash is always 128 bits long, and a SHA-256 hash is always 256 bits long.
The other options do not correctly describe the properties of cryptographic hash functions:
- The input for a particular hash algorithm has to have a fixed size: This is incorrect. Cryptographic hash functions can process input data of any size.
- Hash functions can be duplicated for authentication purposes: This is misleading. While hash functions themselves are deterministic and will always produce the same output for the same input, the phrase “can be duplicated” is vague. In the context of authentication, hash functions are used in conjunction with other techniques (like digital signatures or HMAC) to ensure integrity and authenticity, not duplicated per se.
- Complex inputs will produce complex hashes: This is not accurate. The complexity of the input has no bearing on the complexity of the hash. A simple input can produce a hash that looks just as ‘complex’ as one from a complex input. Hash functions are designed to produce a seemingly random output that does not correlate in any simple way to the input.
-
Which two statements are characteristics of a virus? (Choose two.)
- A virus provides the attacker with sensitive data, such as passwords.
- A virus has an enabling vulnerability, a propagation mechanism, and a payload.
- A virus typically requires end-user activation.
- A virus replicates itself by independently exploiting vulnerabilities in networks.
- A virus can be dormant and then activate at a specific time or date.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The type of end user interaction required to launch a virus is typically opening an application, opening a web page, or powering on the computer. Once activated, a virus may infect other files located on the computer or other computers on the same network.
-
What is a network tap?
- a Cisco technology that provides statistics on packets flowing through a router or multilayer switch
- a passive device that forwards all traffic and physical layer errors to an analysis device
- a technology used to provide real-time reporting and long-term analysis of security events
- a feature supported on Cisco switches that enables the switch to copy frames and forward them to an analysis device
Answers Explanation & Hints: A network tap is used to capture traffic for monitoring the network. The tap is typically a passive splitting device implemented inline on the network and forwards all traffic, including physical layer errors, to an analysis device.
-
Which type of evidence cannot prove an IT security fact on its own?
- best
- corroborative
- indirect
- hearsay
Answers Explanation & Hints: Indirect evidence cannot prove a fact on its own, but direct evidence can. Corroborative evidence is supporting information. Best evidence is most reliable because it is something concrete such as a signed contract.
-
According to NIST, which step in the digital forensics process involves preparing and presenting information that resulted from scrutinizing data?
- examination
- collection
- reporting
- analysis
Answers Explanation & Hints: NIST describes the digital forensics process as involving the following four steps:
- Collection – the identification of potential sources of forensic data and acquisition, handling, and storage of that data
- Examination – assessing and extracting relevant information from the collected data. This may involve decompression or decryption of the data
- Analysis – drawing conclusions from the data. Salient features, such as people, places, times, events, and so on should be documented
- Reporting – preparing and presenting information that resulted from the analysis. Reporting should be impartial and alternative explanations should be offered if appropriate
-
What is privilege escalation?
- Everyone is given full rights by default to everything and rights are taken away only when someone abuses privileges.
- A security problem occurs when high ranking corporate officials demand rights to systems or files that they should not have.
- Vulnerabilities in systems are exploited to grant higher levels of privilege than someone or some process should have.
- Someone is given rights because she or he has received a promotion.
Answers Explanation & Hints: With privilege escalation, vulnerabilities are exploited to grant higher levels of privilege. After the privilege is granted, the threat actor can access sensitive information or take control of the system.
-
Which PDU format is used when bits are received from the network medium by the NIC of a host?
- frame
- segment
- packet
- file
Answers Explanation & Hints: When received at the physical layer of a host, the bits are formatted into a frame at the data link layer. A packet is the PDU at the network layer. A segment is the PDU at the transport layer. A file is a data structure that may be used at the application layer.
-
Which statement is correct about network protocols?
- They are only required for exchange of messages between devices on remote networks.
- Network protocols define the type of hardware that is used and how it is mounted in racks.
- They all function in the network access layer of TCP/IP.
- They define how messages are exchanged between the source and the destination.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Network protocols are implemented in hardware, or software, or both. They interact with each other within different layers of a protocol stack. Protocols have nothing to do with the installation of the network equipment. Network protocols are required to exchange information between source and destination devices in both local and remote networks.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A cybersecurity analyst is using Sguil to verify security alerts. How is the current view sorted?
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 03 - by sensor number
- by source IP
- by date/time
- by frequency
Answers Explanation & Hints: The CNT column, between the ST and Sensor columns, displays the frequency of alerts. By sorting with frequency, the analyst will get a better sense of what has happened on the network.
-
What are three characteristics of an information security management system? (Choose three.)
- It involves the implementation of systems that track the location and configuration of networked devices and software across an enterprise.
- It consists of a management framework through which an organization identifies, analyzes, and addresses information security risks.
- It consists of a set of practices that are systematically applied to ensure continuous improvement in information security.
- It is a systematic and multilayered approach to cybersecurity.
- It addresses the inventory and control of hardware and software configurations of systems.
- It is based on the application of servers and security devices.
Answers Explanation & Hints: An Information Security Management System (ISMS) consists of a management framework through which an organization identifies, analyzes, and addresses information security risks. ISMSs are not based in servers or security devices. Instead, an ISMS consists of a set of practices that are systematically applied by an organization to ensure continuous improvement in information security. ISMSs provide conceptual models that guide organizations in planning, implementing, governing, and evaluating information security programs.
ISMSs are a natural extension of the use of popular business models, such as Total Quality Management (TQM) and Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies (COBIT), into the realm of cybersecurity.
An ISMS is a systematic, multi-layered approach to cybersecurity. The approach includes people, processes, technologies, and the cultures in which they interact in a process of risk management.
-
In network security assessments, which type of test is used to evaluate the risk posed by vulnerabilities to a specific organization including assessment of the likelihood of attacks and the impact of successful exploits on the organization?
- vulnerability assessment
- risk analysis
- port scanning
- penetration testing
-
Explanation & Hint: In network security assessments, the type of test used to evaluate the risk posed by vulnerabilities to a specific organization, including assessment of the likelihood of attacks and the impact of successful exploits on the organization, is:
Risk Analysis
Risk analysis in the context of network security involves evaluating vulnerabilities, considering potential threats, and examining how these vulnerabilities could be exploited. It assesses the likelihood of these events occurring and the potential impact on the organization, which helps in prioritizing remediation efforts based on the level of risk. It combines both the qualitative and quantitative assessment of risk, encompassing the broader context of the organization’s security posture.
Here’s a brief explanation of the other terms:
- Vulnerability Assessment: This is a process that identifies and quantifies security vulnerabilities in a system. It is a comprehensive evaluation of security weaknesses but typically does not include an in-depth risk analysis of the impact and likelihood of exploitation.
- Port Scanning: This is a technique used to discover open ports on a networked system. It’s a way to identify potentially vulnerable points on a target machine but does not, on its own, assess the risk to the organization.
- Penetration Testing: Often referred to as a pen test, this is a simulated cyber attack against a computer system to check for exploitable vulnerabilities. Pen testing involves an active analysis of the system for any potential vulnerabilities that could result from poor or improper system configuration, known and unknown hardware or software flaws, or operational weaknesses in process or technical countermeasures. While it can inform risk analysis, it is not a risk analysis itself.
-
Which NIST Cybersecurity Framework core function is concerned with the development and implementation of safeguards that ensure the delivery of critical infrastructure services?
- protect
- recover
- detect
- identify
- respond
-
Explanation & Hint: Sure, each of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework’s core functions has a specific role in the overall framework designed to help organizations manage and mitigate cybersecurity risk. Here are explanations for each of the options:
- Identify: This function is about developing an organizational understanding to manage cybersecurity risk to systems, people, assets, data, and capabilities. It involves understanding the business context, the resources that support critical functions, and the related cybersecurity risks, enabling an organization to focus and prioritize its efforts, consistent with its risk management strategy and business needs.
- Protect: This function outlines appropriate safeguards to ensure the delivery of critical infrastructure services. The Protect function supports the ability to limit or contain the impact of a potential cybersecurity event. It includes user access control, data security measures, protective technology, maintenance of security policies, and training to inform users of their role in maintaining security.
- Detect: The Detect function defines the appropriate activities to identify the occurrence of a cybersecurity event. This function enables timely discovery of cybersecurity events. Detection processes help to identify the occurrence of an event promptly, thereby facilitating a swift response to mitigate the impact of an incident. This includes continuous monitoring and detection processes.
- Respond: This function includes appropriate activities to take action regarding a detected cybersecurity incident. The Respond function supports the ability to contain the impact of a potential cybersecurity incident. This includes response planning, communications, and analysis, as well as mitigation and improvements to prevent future incidents.
- Recover: This function identifies appropriate activities to maintain plans for resilience and to restore any capabilities or services that were impaired due to a cybersecurity incident. The Recover function supports timely recovery to normal operations to reduce the impact from a cybersecurity incident. This includes recovery planning, improvements, and communications.
Each function plays a critical role in a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, from understanding and managing potential risks, to actively safeguarding against threats, detecting and responding to incidents, and recovering normal operations.
-
What is a characteristic of CybOX?
- It is the specification for an application layer protocol that allows the communication of CTI over HTTPS.
- It enables the real-time exchange of cyberthreat indicators between the U.S. Federal Government and the private sector.
- It is a set of standardized schemata for specifying, capturing, characterizing, and communicating events and properties of network operations.
- It is a set of specifications for exchanging cyberthreat information between organizations.
-
Explanation & Hint: CybOX, which stands for Cyber Observable eXpression, is characterized by being “a set of standardized schemata for specifying, capturing, characterizing, and communicating events and properties of network operations.” This definition highlights its role in providing a framework for the exchange and representation of information about cybersecurity incidents, threats, and behaviors. CybOX is not specifically an application layer protocol for communication over HTTPS, nor is it limited to the exchange of cyberthreat indicators between the U.S. Federal Government and the private sector. Instead, it is more broadly aimed at facilitating the sharing of cyberthreat information between various organizations and entities in a standardized format.
-
What part of the URL, http://www.cisco.com/index.html, represents the top-level DNS domain?
- index
- www
- http
- .com
Answers Explanation & Hints: The components of the URL http://www.cisco.com/index.htm are as follows:
http = protocol
www = part of the server name
cisco = part of the domain name
index = file name
com = the top-level domain
-
In NAT terms, what address type refers to the globally routable IPv4 address of a destination host on the Internet?
- inside local
- outside local
- inside global
- outside global
Answers Explanation & Hints: From the perspective of a NAT device, inside global addresses are used by external users to reach internal hosts. Inside local addresses are the addresses assigned to internal hosts. Outside global addresses are the addresses of destinations on the external network. Outside local addresses are the actual private addresses of destination hosts behind other NAT devices.
-
A piece of malware has gained access to a workstation and issued a DNS lookup query to a CnC server. What is the purpose of this attack?
- to send stolen sensitive data with encoding
- to request a change of the IP address
- to masquerade the IP address of the workstation
- to check the domain name of the workstation
Answers Explanation & Hints: A piece of malware, after accessing a host, may exploit the DNS service by communicating with command-and-control (CnC) servers and then exfiltrate data in traffic disguised as normal DNS lookup queries. Various types of encoding, such as base64, 8-bit binary, and hex can be used to camouflage the data and evade basic data loss prevention (DLP) measures.
-
What are two ways that ICMP can be a security threat to a company? (Choose two.)
- by corrupting network IP data packets
- by providing a conduit for DoS attacks
- by the infiltration of web pages
- by collecting information about a network
- by corrupting data between email servers and email recipients
Answers Explanation & Hints: ICMP can be used as a conduit for DoS attacks. It can be used to collect information about a network such as the identification of hosts and network structure, and by determining the operating systems being used on the network.
-
Which three IPv4 header fields have no equivalent in an IPv6 header? (Choose three.)
- fragment offset
- flag
- protocol
- version
- identification
- TTL
Answers Explanation & Hints: Unlike IPv4, IPv6 routers do not perform fragmentation. Therefore, all three fields supporting fragmentation in the IPv4 header are removed and have no equivalent in the IPv6 header. These three fields are fragment offset, flag, and identification. IPv6 does support host packet fragmentation through the use of extension headers, which are not part of the IPv6 header.
-
A technician is troubleshooting a network connectivity problem. Pings to the local wireless router are successful but pings to a server on the Internet are unsuccessful. Which CLI command could assist the technician to find the location of the networking problem?
- ipconfig
- ipconfig/renew
- tracert
- msconfig
Answers Explanation & Hints: The tracert utlility (also known as the tracert command or tracert tool) will enable the technician to locate the link to the server that is down. The ipconfig command displays the computer network configuration details. The ipconfig/renew command requests an IP address from a DHCP server. Msconfig is not a network troubleshooting command.
-
Which ICMPv6 message type provides network addressing information to hosts that use SLAAC?
- neighbor solicitation
- neighbor advertisement
- router solicitation
- router advertisement
-
Explanation & Hint: The ICMPv6 message types and explain why they are not the correct answer for providing network addressing information to hosts using SLAAC, in contrast to router advertisement:
- Neighbor Solicitation: This ICMPv6 message is used in the process of neighbor discovery. It is sent by a node to determine the link-layer address (such as a MAC address) of another node on the same local network. The neighbor solicitation message is also used to verify the reachability of a neighbor after the initial discovery. It does not provide network addressing information for SLAAC.
- Neighbor Advertisement: This is a response to the neighbor solicitation message. When a node receives a neighbor solicitation message, it replies with a neighbor advertisement message, confirming its presence and link-layer address. Like neighbor solicitation, this message is involved in the neighbor discovery process, not in providing network addressing information.
- Router Solicitation: When a device initially connects to a network, it sends out a router solicitation message to prompt routers on the local network to immediately send a router advertisement, rather than waiting for their next scheduled advertisement. While this message triggers the sending of router advertisements, by itself, it does not provide network addressing information. It’s more of a request for such information.
- Router Advertisement: This is the correct answer. Router advertisement messages are sent periodically by routers or in response to router solicitations. They provide necessary network information for SLAAC, including network prefixes, flags indicating whether additional information (like DNS) is available via DHCPv6, and other parameters needed for address configuration and general network settings.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The switches have a default configuration. Host A needs to communicate with host D, but host A does not have the MAC address for the default gateway. Which network devices will receive the ARP request sent by host A?
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 04 - only hosts B and C
- only router R1
- only hosts A, B, and C
- only hosts B, C, and router R1
- only host D
- only hosts A, B, C, and D
Explanation and Hint: Because host A does not have the MAC address of the default gateway in the ARP table, host A sends an ARP broadcast. The ARP broadcast would be sent to every device on the local network. Hosts B, C, and router R1 would receive the broadcast. Router R1 would not forward the message.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A cybersecurity analyst is viewing packets forwarded by switch S2. What addresses will identify frames containing data sent from PCA to PCB?
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 05 - Src IP: 192.168.1.212
Src MAC: 00-60-0F-B1-33-33
Dst IP: 192.168.2.101
Dst MAC: 08-CB-8A-5C-BB-BB - Src IP: 192.168.1.212
Src MAC: 01-90-C0-E4-AA-AA
Dst IP: 192.168.2.101
Dst MAC: 08-CB-8A-5C-BB-BB - Src IP: 192.168.2.1
Src MAC: 00-60-0F-B1-33-33
Dst IP: 192.168.2.101
Dst MAC: 08-CB-8A-5C-BB-BB - Src IP: 192.168.1.212
Src MAC: 00-60-0F-B1-33-33
Dst IP: 192.168.2.101
Dst MAC: 00-D0-D3-BE-00-00Answers Explanation & Hints: When a message sent from PCA to PCB reaches router R2, some frame header fields will be rewritten by R2 before forwarding to switch S2. The frames will contain the source MAC address of router R2 and the destination MAC address of PCB. The frames will retain the original IPv4 addressing applied by PCA which is the IPv4 address of PCA as the source address and the IPv4 address of PCB as the destination.
- Src IP: 192.168.1.212
-
Which three IP addresses are considered private addresses? (Choose three.)
- 172.17.254.4
- 128.37.255.6
- 10.234.2.1
- 198.168.6.18
- 172.68.83.35
- 192.168.5.29
-
Explanation & Hint: The concept of private IP addresses is defined in RFC 1918, which specifies certain IP address ranges that are reserved for use within private networks. These addresses are not routable on the public internet. Based on this definition, the three IP addresses from your list that are considered private are:
- 172.17.254.4 – This address falls within the 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255 range, which is reserved for private networks in the 172.16.0.0/12 block.
- 10.234.2.1 – This address is part of the 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 range, reserved for private networks in the 10.0.0.0/8 block.
- 192.168.5.29 – This address is within the 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 range, which is reserved for private networks in the 192.168.0.0/16 block.
The other addresses listed (128.37.255.6, 198.168.6.18, and 172.68.83.35) do not fall within the private IP address ranges as defined by RFC 1918.
-
An administrator wants to create four subnetworks from the network address 192.168.1.0/24. What is the network address and subnet mask of the second useable subnet?
- subnetwork 192.168.1.32
subnet mask 255.255.255.240 - subnetwork 192.168.1.64
subnet mask 255.255.255.192 - subnetwork 192.168.1.128
subnet mask 255.255.255.192 - subnetwork 192.168.1.8
subnet mask 255.255.255.224 - subnetwork 192.168.1.64
subnet mask 255.255.255.240 -
Explanation & Hint: To create four subnetworks from a 192.168.1.0/24 network, we need to divide this network into smaller parts. The original network has a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 (or /24 in CIDR notation), which allows for 256 addresses (from 192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.255).
Dividing this into four equal parts, each part will have 256 / 4 = 64 addresses. Therefore, the subnet mask needs to be extended to accommodate this division. Each subnet will take up an additional 2 bits (as 2^2 = 4), changing the subnet mask from /24 to /26. This results in a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192.
Now, let’s determine the network addresses for the four subnetworks:
- First Subnet: 192.168.1.0/26 – Covers 192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.63
- Second Subnet: 192.168.1.64/26 – Covers 192.168.1.64 to 192.168.1.127
- Third Subnet: 192.168.1.128/26 – Covers 192.168.1.128 to 192.168.1.191
- Fourth Subnet: 192.168.1.192/26 – Covers 192.168.1.192 to 192.168.1.255
Therefore, the network address and subnet mask of the second usable subnet are:
- Subnetwork: 192.168.1.64
- Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.192
- subnetwork 192.168.1.32
-
A user opens three browsers on the same PC to access www.cisco.com to search for certification course information. The Cisco web server sends a datagram as a reply to the request from one of the web browsers. Which information is used by the TCP/IP protocol stack in the PC to identify which of the three web browsers should receive the reply?
- the source IP address
- the destination port number
- the source port number
- the destination IP address
Answers Explanation & Hints: Each web browser client application opens a randomly generated port number in the range of the registered ports and uses this number as the source port number in the datagram that it sends to a server. The server then uses this port number as the destination port number in the reply datagram that it sends to the web browser. The PC that is running the web browser application receives the datagram and uses the destination port number that is contained in this datagram to identify the client application.
-
A cybersecurity analyst needs to collect alert data. What are three detection tools to perform this task in the Security Onion architecture? (Choose three.)
- Wazuh
- CapME
- Zeek
- Kibana
- Sguil
- Wireshark
-
Explanation & Hint: Security Onion is a popular Linux distribution for intrusion detection, network security monitoring, and log management. Within its architecture, several tools can be used for detecting and collecting alert data. Out of the options listed, the three detection tools that are integral to Security Onion for this purpose are:
- Wazuh: Wazuh is a security monitoring tool that can perform log analysis, file integrity monitoring, rootkit detection, real-time alerting, and active response. It’s particularly useful for gathering alert data related to system changes, file integrity, and potential security incidents.
- Zeek (formerly known as Bro): Zeek is a powerful network analysis framework that is much different from the typical IDS (Intrusion Detection System). Rather than solely focusing on signature-based detection, Zeek provides a comprehensive platform for more general network traffic analysis, making it an excellent tool for gathering detailed network information and security alerts.
- Sguil: Sguil (pronounced like “squill”) is built on top of Network Security Monitoring (NSM) principles and provides an analyst-friendly interface to network-based alerts and traffic. It combines the functionality of an IDS, log analysis, and real-time network session data, making it a valuable tool for a cybersecurity analyst to collect and analyze alert data.
While CapME, Kibana, and Wireshark are also part of the Security Onion suite, they serve different primary purposes. CapME is a tool for session data and packet capture analysis, Kibana is used for log and data visualization, and Wireshark is a network protocol analyzer useful for packet inspection and network troubleshooting, rather than specifically for alert detection in the context of Security Onion.
-
Match the attack to the definition. (Not all options are used.)
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 014 Explanation & Hint: - Attacker sends falsified information to redirect users to malicious sites: The given answer is “ARP cache poisoning.” However, ARP cache poisoning is more accurately associated with attackers sending falsified ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) messages onto a local network. This manipulates the ARP cache of the hosts and can redirect local traffic through the attacker’s machine. If the definition is specifically about redirecting users to malicious sites, the more appropriate term would be “DNS spoofing” or “phishing.” Nonetheless, in some contexts, ARP cache poisoning could indirectly lead to users being redirected to malicious sites if the attacker uses their position in the network to manipulate traffic.
- Attacker uses open resolvers to increase the volume of attacks and mask the true source of the attack: The given answer is “amplification and reflection.” This is correct; amplification and reflection attacks use open resolvers, among other techniques, to magnify the volume of the attack data sent to the victim while obscuring the source of the attack.
- Attacker sends multiple packets that consume server resources: The given answer is “resource utilization attack.” This term is broad, but it can describe a situation where multiple packets are sent to consume resources, which aligns with the definition of a DDoS attack, where many compromised systems (often part of a botnet) target a single system with a flood of traffic.
-
What debugging security tool can be used by black hats to reverse engineer binary files when writing exploits?
- WinDbg
- Firesheep
- AIDE
- Skipfish
-
Explanation & Hint: The tool among the options provided that can be used by black hat hackers to reverse engineer binary files when writing exploits is WinDbg.
WinDbg is a multipurpose debugger for the Windows operating system, used by developers and IT professionals for debugging and analyzing the crash dumps to determine the cause of system crashes or application failures. However, like many powerful tools, it can also be misused by black hat hackers for reverse engineering purposes to understand how software works, which can aid in the creation of exploits by analyzing the binary for vulnerabilities.
- Firesheep: This is an extension for the Firefox web browser that uses a packet sniffer to intercept unencrypted cookies from certain websites (such as Facebook and Twitter) as they are transmitted over networks, allowing an attacker to carry out session hijacking attacks. It is not a tool for reverse engineering binary files or writing exploits in the context of analyzing binary code.
- AIDE (Advanced Intrusion Detection Environment): AIDE is a host-based intrusion detection system (HIDS) that is used to monitor and analyze the internals of a computing system. It typically works by detecting changes to files on the system, which can be indicative of a security breach. It’s not designed for reverse engineering or exploit development; instead, it’s intended for system integrity checking.
- Skipfish: This is an active web application security reconnaissance tool. It prepares an interactive sitemap for the targeted site by carrying out a recursive crawl and dictionary-based probes. The resulting map is then annotated with the output from a number of active (not purely passive) security checks. It’s not used for reverse engineering binaries but for finding vulnerabilities in web applications.
Out of the tools listed, only WinDbg is suited for the task of reverse engineering binary files, which can be a part of exploit development by analyzing how software operates at a binary level to find security flaws.
-
Which two net commands are associated with network resource sharing? (Choose two.)
- net start
- net accounts
- net share
- net stop
- net use
Answers Explanation & Hints: The
netcommand is a very important command. Some commonnetcommands include these:net accounts– sets password and logon requirements for usersnet session– lists or disconnects sessions between a computer and other computers on the networknet share– creates, removes, or manages shared resourcesnet start– starts a network service or lists running network servicesnet stop– stops a network servicenet use– connects, disconnects, and displays information about shared network resourcesnet view– shows a list of computers and network devices on the network
-
Match the attack surface with attack exploits.
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 015 Explanation & Hint: - Network Attack Surface: These attacks include conventional wired and wireless network protocols, as well as other wireless protocols used by smartphones or IoT devices. The attacks target vulnerabilities at the transport layer.
- Software Attack Surface: These attacks are delivered through exploitation of vulnerabilities in web, cloud, or host-based software applications.
- Human Attack Surface: These attacks include social engineering, malicious behavior by trusted insiders, and user error.
-
What is a key difference between the data captured by NetFlow and data captured by Wireshark?
- NetFlow collects metadata from a network flow whereas Wireshark captures full data packets.
- NetFlow provides transaction data whereas Wireshark provides session data.
- NetFlow data shows network flow contents whereas Wireshark data shows network flow statistics.
- NetFlow data is analyzed by tcpdump whereas Wireshark data is analyzed by nfdump .
Answers Explanation & Hints: Wireshark captures the entire contents of a packet. NetFlow does not. Instead, NetFlow collects metadata, or data about the flow.
-
Match the network monitoring data type with the description.
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 016 Explanation & Hint: - Statistical Data: Used to describe and analyze network flow or performance data. Statistical data typically includes summaries of performance metrics like utilization percentages, error rates, and other figures that quantify the operation of the network.
- Transaction Data: Includes device-specific server and host logs. Transaction logs record the details of transactions processed by the server, including individual requests from users and the system’s response.
- Session Data: Contains details of network flows including the 5-tuples (source IP, destination IP, source port, destination port, and protocol), the amount of data transmitted, and the duration of data transmission. Session data provides a record of each discrete interaction or ‘session’ that occurs between two endpoints on the network.
- Alert Data: Generated by IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) or IDS (Intrusion Detection System) devices when suspicious traffic is detected. Alert data comprises notifications that are triggered when network traffic patterns match known signatures of malicious activity or when anomalies are detected.
-
Which two options are window managers for Linux? (Choose two.)
- File Explorer
- Kali
- Gnome
- PenTesting
- KDE
Explanation & Hint: The X Window System provides the basic framework for a GUI, but the GUI itself varies greatly between different distributions. Two window managers are Gnome and KDE.
-
Which method can be used to harden a device?
- allow USB auto-detection
- maintain use of the same passwords
- use SSH and disable the root account access over SSH
- allow default services to remain enabled
Answers Explanation & Hints: The basic best practices for device hardening are as follows:
Ensure physical security.
Minimize installed packages.
Disable unused services.
Use SSH and disable the root account login over SSH.
Keep the system updated.
Disable USB auto-detection.
Enforce strong passwords.
Force periodic password changes.
Keep users from re-using old passwords.
Review logs regularly.
-
What are two uses of an access control list? (Choose two.)
- ACLs can control which areas a host can access on a network.
- Standard ACLs can restrict access to specific applications and ports.
- ACLs provide a basic level of security for network access.
- ACLs can permit or deny traffic based upon the MAC address originating on the router.
- ACLs assist the router in determining the best path to a destination.
Answers Explanation & Hints: ACLs can be used for the following:Limit network traffic in order to provide adequate network performance
Restrict the delivery of routing updates
Provide a basic level of security
Filter traffic based on the type of traffic being sent
Filter traffic based on IP addressing
-
Which two features are included by both TACACS+ and RADIUS protocols? (Choose two.)
- SIP support
- 802.1X support
- password encryption
- utilization of transport layer protocols
- separate authentication and authorization processes
Answers Explanation & Hints: Both TACACS+ and RADIUS support password encryption (TACACS+ encrypts all communication) and use Layer 4 protocol (TACACS+ uses TCP and RADIUS uses UDP). TACACS+ supports separation of authentication and authorization processes, while RADIUS combines authentication and authorization as one process. RADIUS supports remote access technology, such as 802.1x and SIP; TACACS+ does not.
-
Which approach can help block potential malware delivery methods, as described in the Cyber Kill Chain model, on an Internet-faced web server?
- Audit the web server to forensically determine the origin of exploit.
- Collect malware files and metadata for future analysis.
- Build detections for the behavior of known malware.
- Analyze the infrastructure storage path used for files.
Answers Explanation & Hints: A threat actor may send the weapon through web interfaces to the target server, either in file uploads or coded web requests. By analyzing the infrastructure storage path used for files, security measures can be implemented to monitor and detect malware deliveries through these methods.
-
In the NIST incident response process life cycle, which type of attack vector involves the use of brute force against devices, networks, or services?
- loss or theft
- media
- impersonation
- attrition
Answers Explanation & Hints: Common attack vectors include media, attrition, impersonation, and loss or theft. Attrition attacks are any attacks that use brute force. Media attacks are those initiated from storage devices. Impersonation attacks occur when something or someone is replaced for the purpose of the attack, and loss or theft attacks are initiated by equipment inside the organization.
-
What two assurances does digital signing provide about code that is downloaded from the Internet? (Choose two.)
- The code has not been modified since it left the software publisher.
- The code is authentic and is actually sourced by the publisher.
- The code was encrypted with both a private and public key.
- The code contains no viruses.
- The code contains no errors.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Digitally signing code provides several assurances about the code:
The code is authentic and is actually sourced by the publisher.
The code has not been modified since it left the software publisher.
The publisher undeniably published the code. This provides nonrepudiation of the act of publishing.
-
When a user visits an online store website that uses HTTPS, the user browser queries the CA for a CRL. What is the purpose of this query?
- to check the length of key used for the digital certificate
- to negotiate the best encryption to use
- to request the CA self-signed digital certificate
- to verify the validity of the digital certificate
Answers Explanation & Hints: A digital certificate must be revoked if it is invalid. CAs maintain a certificate revocation list (CRL), a list of revoked certificate serial numbers that have been invalidated. The user browser will query the CRL to verify the validity of a certificate.
-
Match the tabs of the Windows 10 Task Manager to their functions. (Not all options are used.)
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 017 Explanation & Hint: - Performance: Displays resource utilization information for CPU, memory, network, disk, and others. This tab provides a dynamic overview of the system’s performance, including real-time graphs and data.
- Startup: Allows programs that are running on system startup to be disabled. This tab lists all the applications that are set to start automatically when Windows boots up, and you can enable or disable them from here.
- Services: Allows for a start, stop, or restart of a particular service. The Services tab shows the services that are running or stopped and lets you manage their state.
- Details: Allows for a process to have its affinity set. This tab provides detailed information about each process running on your system, and you can set the affinity, which dictates which CPU cores the process can run on.
-
What are two potential network problems that can result from ARP operation? (Choose two.)
- Network attackers could manipulate MAC address and IP address mappings in ARP messages with the intent of intercepting network traffic.
- Manually configuring static ARP associations could facilitate ARP poisoning or MAC address spoofing.
- Multiple ARP replies result in the switch MAC address table containing entries that match the MAC addresses of hosts that are connected to the relevant switch port.
- Large numbers of ARP request broadcasts could cause the host MAC address table to overflow and prevent the host from communicating on the network.
- On large networks with low bandwidth, multiple ARP broadcasts could cause data communication delays.
-
Explanation & Hint: - Network attackers could manipulate MAC address and IP address mappings in ARP messages with the intent of intercepting network traffic. This type of attack is known as ARP spoofing or ARP poisoning. Attackers send falsified ARP messages over a local area network to link their MAC address with the IP address of a legitimate computer or server on the network. This causes the traffic that was supposed to be directed to that IP address to be misdirected to the attacker instead, which can lead to man-in-the-middle attacks or session hijacking.
- On large networks with low bandwidth, multiple ARP broadcasts could cause data communication delays. ARP operates by broadcasting requests to all hosts on the network. On a large network, particularly with limited bandwidth, this can lead to significant network congestion as a result of ARP traffic, causing delays in data communication. This can be exacerbated in situations where hosts or network devices are incorrectly configured to send out excessive ARP requests.
-
What is a disadvantage of DDNS?
- DDNS is considered malignant and must be monitored by security software.
- DDNS is unable to co-exist on a network subdomain that also uses DNS.
- Using DDNS, a change in an existing IP address mapping can take over 24 hours and could result in a disruption of connectivity.
- Using free DDNS services, threat actors can quickly and easily generate subdomains and change DNS records.
-
Explanation & Hint: A disadvantage of Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is:
Using free DDNS services, threat actors can quickly and easily generate subdomains and change DNS records.
This can be exploited for malicious purposes, such as creating command and control channels for malware or setting up phishing sites. Since the DNS records can be updated dynamically, it becomes difficult for law enforcement and security professionals to track and mitigate the threat. Additionally, because many DDNS services are legitimate and widely used, blocking them outright can have negative impacts on legitimate users.
-
Which host-based firewall uses a three-profile approach to configure the firewall functionality?
- TCP Wrapper
- nftables
- iptables
- Windows Firewall
Answers Explanation & Hints: Windows Firewall uses a profile-based approach to configuring firewall functionality. It uses three profiles, Public, Private, and Domain, to define firewall functions.
-
What is the benefit of converting log file data into a common schema?
- allows easy processing and analysis of datasets
- creates a data model based on fields of data from a source
- allows the implementation of partial normalization and inspection
- creates a set of regex-based field extractions
Answers Explanation & Hints: When data is converted into a universal format, it can be effectively structured for performing fast queries and event analysis.
-
Which core open source component of the Elastic-stack is responsible for accepting the data in its native format and making elements of the data consistent across all sources?
- Beats
- Elasticsearch
- Kibana
- Logstash
-
Explanation & Hint: - Beats: Beats are lightweight, single-purpose data shippers. They are used to send data from hundreds or thousands of machines and systems to Logstash or Elasticsearch. Each Beat is tailored to ship specific types of data, like logs, metrics, or network packet data.
- Elasticsearch: This is a distributed search and analytics engine. It is the core component that stores all the data you send to the Elastic Stack. Elasticsearch allows you to search, analyze, and visualize the data in real time.
- Kibana: Kibana is a web interface for searching and visualizing logs and time-stamped data. It provides graphical representation of the Elasticsearch data and is used to create dashboards that enable users to interact with their data.
- Logstash: This is the correct answer for the question. Logstash is a server-side data processing pipeline that ingests data from multiple sources simultaneously, transforms it, and then sends it to Elasticsearch. Logstash is equipped with an extensive plugin ecosystem that transforms and prepares your data regardless of the source or format – this includes making disparate data from various sources consistent and queryable.
In summary, Logstash is responsible for centralizing, transforming, and preparing data before it is indexed into Elasticsearch. It can dynamically unify data from disparate sources and normalize the data, making it ready for further analysis and visualization in Kibana.
-
A client is using SLAAC to obtain an IPv6 address for the interface. After an address has been generated and applied to the interface, what must the client do before it can begin to use this IPv6 address?
- It must wait for an ICMPv6 Router Advertisement message giving permission to use this address.
- It must send an ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation message to ensure that the address is not already in use on the network.
- It must send an ICMPv6 Router Solicitation message to request the address of the DNS server.
- It must send an ICMPv6 Router Solicitation message to determine what default gateway it should use.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Stateless DHCPv6 or stateful DHCPv6 uses a DHCP server, but Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) does not. A SLAAC client can automatically generate an address that is based on information from local routers via Router Advertisement (RA) messages. Once an address has been assigned to an interface via SLAAC, the client must ensure via Duplicate Address Detection (DAD) that the address is not already in use. It does this by sending out an ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation message and listening for a response. If a response is received, then it means that another device is already using this address.
-
Which step in the Vulnerability Management Life Cycle determines a baseline risk profile to eliminate risks based on asset criticality, vulnerability threat, and asset classification?
- assess
- discover
- verify
- prioritize assets
Answers Explanation & Hints: The steps in the Vulnerability Management Life Cycle include these:
- Discover – inventory all assets across the network and identify host details, including operating systems and open services, to identify vulnerabilities
- Prioritize assets – categorize assets into groups or business units, and assign a business value to asset groups based on their criticality to business operations
- Assess – determine a baseline risk profile to eliminate risks based on asset criticality, vulnerability threats, and asset classification
- Report – measure the level of business risk associated with assets according to security policies. Document a security plan, monitor suspicious activity, and describe known vulnerabilities.
- Remediate – prioritize according to business risk and fix vulnerabilities in order of risk
- Verify – verify that threats have been eliminated through follow-up audits
-
The IT security personnel of an organization notice that the web server deployed in the DMZ is frequently targeted by threat actors. The decision is made to implement a patch management system to manage the server. Which risk management strategy method is being used to respond to the identified risk?
- risk sharing
- risk retention
- risk reduction
- risk avoidance
Answers Explanation & Hints: There are four potential strategies for responding to risks that have been identified:
Risk avoidance – Stop performing the activities that create risk.
Risk reduction – Decrease the risk by taking measures to reduce vulnerability.
Risk sharing – Shift some of the risk to other parties.
Risk retention – Accept the risk and its consequences.
-
Match the server profile element to the description. (Not all options are used.)
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 018 Explanation & Hint: - User Accounts: These are typically associated with “the parameters defining user access and behavior.” User accounts determine what resources a user can access on a server and how they can interact with the system.
- Listening Ports: This corresponds to “the TCP and UDP daemons and ports that are allowed to be open on the server.” Listening ports are network ports on which the server listens for incoming connections from clients or other services.
- Service Accounts: These would match with “the definitions of the type of service that an application is allowed to run on a given host.” Service accounts are special user accounts that are used by applications or services to interact with the operating system and other services.
- Software Environment: This element is aligned with “the tasks, processes, and applications that are permitted to run on the server.” The software environment includes the setup of installed applications and the runtime environment configuration on the server.
-
Match the network service with the description.
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 019 Explanation & Hint: - SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol): This service “allows administrators to manage network nodes.” SNMP is used for network management and monitoring and can be used to configure network devices such as servers, workstations, routers, switches, and hubs.
- NetFlow: This service “provides statistics on IP packets flowing through network devices.” NetFlow is a network protocol developed by Cisco for collecting IP traffic information and monitoring network flow.
- syslog: The service that “notifies the administrator with detailed system messages.” Syslog is a standard for message logging and allows separation of the software that generates messages from the system that stores them and the software that reports and analyzes them.
- NTP (Network Time Protocol): This service “synchronizes the time across all devices on the network.” NTP is used to synchronize the clocks of computers over a network.
-
A help desk technician notices an increased number of calls relating to the performance of computers located at the manufacturing plant. The technician believes that botnets are causing the issue. What are two purposes of botnets? (Choose two.)
- to transmit viruses or spam to computers on the same network
- to record any and all keystrokes
- to withhold access to a computer or files until money has been paid
- to attack other computers
- to gain access to the restricted part of the operating system
Answers Explanation & Hints: Botnets can be used to perform DDoS attacks, obtain data, or transmit malware to other devices on the network.
-
Which two data types would be classified as personally identifiable information (PII)? (Choose two.)
- house thermostat reading
- hospital emergency use per region
- average number of cattle per region
- vehicle identification number
- Facebook photographs
-
Explanation & Hint: Personally Identifiable Information (PII) refers to data that could potentially identify a specific individual. Among the options provided, the two that would be classified as PII are:
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN): A VIN is unique to an individual vehicle and can be traced back to the owner, thus potentially identifying them.
- Facebook Photographs: Photographs posted on Facebook or any social media can reveal the identity of individuals, making them a form of PII. They can often be used to directly recognize a person’s face or link to their personal profile.
-
Which statement defines the difference between session data and transaction data in logs?
- Session data is used to make predictions on network behaviors, whereas transaction data is used to detect network anomalies.
- Session data shows the result of a network session, whereas transaction data is in response to network threat traffic.
- Session data records a conversation between hosts, whereas transaction data focuses on the result of network sessions.
- Session data analyzes network traffic and predicts network behavior, whereas transaction data records network sessions.
-
Explanation & Hint: Session data and transaction data are both types of information that can be found in logs, and they serve different purposes:
- Session Data: This typically records the “conversation” between hosts. It includes details such as session initiation, duration, termination, and the amount of data transferred. It’s a broader overview of interactions between two endpoints over a network for a given period.
- Transaction Data: This is more specific and focuses on individual “transactions” or exchanges that occur within the network sessions. It might detail specific requests and responses, such as file access or database queries, and their outcomes.
Session data records a conversation between hosts, whereas transaction data focuses on the result of network sessions.
-
An administrator discovers that a user is accessing a newly established website that may be detrimental to company security. What action should the administrator take first in terms of the security policy?
- Ask the user to stop immediately and inform the user that this constitutes grounds for dismissal.
- Revise the AUP immediately and get all users to sign the updated AUP.
- Create a firewall rule blocking the respective website.
- Immediately suspend the network privileges of the user.
-
Explanation & Hint: The administrator should first review the existing Acceptable Use Policy (AUP) and the security policies of the company to determine the appropriate response. Typically, an administrator would take the following steps:
- Verify the Policy: Ensure that accessing this website is indeed not in compliance with the company’s Acceptable Use Policy (AUP) or other relevant policies.
- Gather Evidence: Collect data on the access of the website that may be detrimental to company security.
- Follow Established Procedures: The company should have a protocol for dealing with security policy violations. This usually starts with a formal warning to the user, possibly involving their direct supervisor or HR, and documentation of the incident.
If the AUP and security policies do not currently cover this type of activity, then the administrator should work on revising the AUP to include it. However, this would typically be a follow-up action rather than the first step, as policies need to be clear and known to users before enforcement.
Blocking the website through a firewall rule may be appropriate but should be done in accordance with the company’s change management procedures, ensuring that any changes to the network are properly documented and authorized.
Immediate suspension of network privileges is generally considered a severe action and would typically be reserved for egregious or repeated violations, or where there is an imminent threat to the company’s network security.
Therefore, the first action should be to ensure that the user’s activity is against the AUP, inform them of the violation, and proceed according to the company’s established disciplinary procedures. This approach upholds the principles of fair warning and due process.
-
Which Cisco sponsored certification is designed to provide the first step in acquiring the knowledge and skills to work with a SOC team?
- CCNA Data Center
- CCNA CyberOps Associate
- CCNA Cloud
- CCNA Security
-
Explanation & Hint: - CCNA Data Center: This certification is focused on data center solutions and technologies. Candidates who earn this certification are recognized to have the skills necessary to work in data centers, managing data center infrastructure such as switches, routers, and storage networks. It is not specifically oriented towards cybersecurity or SOC operations.
- CCNA CyberOps Associate (formerly CCNA Cybersecurity Operations): This is the certification that is tailored for individuals who are aiming to work in cybersecurity, particularly in roles associated with a Security Operations Center (SOC). It covers knowledge and skills needed to monitor, detect, and respond to cybersecurity threats, as well as understanding cybersecurity operations, policies, and procedures.
- CCNA Cloud: This certification is designed for cloud engineers and administrators, focusing on skills required for cloud computing. It includes knowledge about Cisco Cloud solutions and enables individuals to develop, advance, and validate their cloud skill set. While cloud security is a component of this certification, it does not specifically prepare individuals for working within a SOC.
- CCNA Security: The CCNA Security certification is aimed at establishing an associate level of cybersecurity knowledge and focuses on securing Cisco networks. It teaches skills necessary to develop a security infrastructure, recognize threats and vulnerabilities to networks, and mitigate security threats. It’s more broad in terms of general security practices and less focused on the day-to-day operations of a SOC team compared to the CCNA CyberOps Associate.
The CCNA CyberOps Associate certification is the most relevant for those looking to engage specifically with a SOC team, providing an understanding of cybersecurity operations, which is essential for the monitoring and analysis tasks performed in security operations centers.
-
What are the two methods that a wireless NIC can use to discover an AP? (Choose two.)
- transmitting a probe request
- sending an ARP request broadcast
- initiating a three-way handshake
- receiving a broadcast beacon frame
- sending a multicast frame
Answers Explanation & Hints: Two methods can be used by a wireless device to discover and register with an access point: passive mode and active mode. In passive mode, the AP sends a broadcast beacon frame that contains the SSID and other wireless settings. In active mode, the wireless device must be manually configured for the SSID, and then the device broadcasts a probe request.
-
What term describes a set of software tools designed to increase the privileges of a user or to grant access to the user to portions of the operating system that should not normally be allowed?
- compiler
- penetration testing
- package manager
- rootkit
Answers Explanation & Hints: A rootkit is used by an attacker to secure a backdoor to a compromised computer, grant access to portions of the operating system normally not permitted, or increase the privileges of a user.
-
A client device has initiated a secure HTTP request to a web browser. Which well-known port address number is associated with the destination address?
- 110
- 80
- 443
- 404
Answers Explanation & Hints: Port numbers are used in TCP and UDP communications to differentiate between the various services running on a device. The well-known port number used by HTTPs is port 443.
-
Match the monitoring tool to the definition.
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 020 Explanation & Hint: - NetFlow: “provides statistics on packets flowing through a Cisco router or multilayer switch.” NetFlow is a network protocol developed by Cisco for collecting IP traffic information and monitoring network flow.
- Wireshark: “captures packets and saves them in a PCAP file.” Wireshark is a network protocol analyzer that captures packets in real-time and displays them in detailed format. It can save this data in PCAP (Packet Capture) files for later analysis.
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol): “retrieves information on the operation of network devices.” SNMP is used to monitor, configure, and manage network devices. It can also collect various types of data from these devices, such as performance metrics.
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management): “presents real-time reporting and long-term analysis of security events.” A SIEM system combines security information management (SIM) and security event management (SEM) to provide real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware.
-
A network administrator is reviewing server alerts because of reports of network slowness. The administrator confirms that an alert was an actual security incident. What is the security alert classification of this type of scenario?
- true negative
- false negative
- false positive
- true positive
-
Explanation & Hint: The security alert classification for this scenario, where an alert was confirmed to be an actual security incident, is a true positive.
A true positive occurs when the security system correctly identifies a genuine threat or incident. Here are all the classifications for clarity:
- True Positive: The alert indicates a security threat and, upon investigation, is confirmed to be an actual threat.
- True Negative: The alert indicates no security threat, and there is indeed no threat present.
- False Positive: The alert indicates a security threat, but there is no actual threat upon investigation.
- False Negative: The alert indicates no security threat, but in reality, a security threat is present.
-
Match the common network technology or protocol with the description. (Not all options are used.)
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Final exam Answers 021 Explanation & Hint: - NTP (Network Time Protocol): “uses a hierarchy of authoritative time sources to send time information between devices on the network.” NTP is designed to synchronize the clocks of computers over a network.
- Syslog: “uses UDP port 514 for logging event messages from network devices and endpoints.” Syslog is a standard for message logging and often uses UDP port 514.
- ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol): “used by attackers to identify hosts on a network and the structure of the network.” ICMP is used for diagnostic and control purposes, such as the ping command, but can also be utilized by attackers for network scanning.
- DNS (Domain Name System): “used by attackers to exfiltrate data in traffic disguised as normal client queries.” While DNS is actually a system that translates domain names to IP addresses, attackers can misuse DNS queries to covertly move data out of a compromised system because DNS traffic is often allowed through firewalls.
-
A user is executing a tracert to a remote device. At what point would a router, which is in the path to the destination device, stop forwarding the packet?
- when the RTT value reaches zero
- when the value in the TTL field reaches zero
- when the router receives an ICMP Time Exceeded message
- when the host responds with an ICMP Echo Reply message
- when the values of both the Echo Request and Echo Reply messages reach zero
Answers Explanation & Hints: When a router receives a traceroute packet, the value in the TTL field is decremented by 1. When the value in the field reaches zero, the receiving router will not forward the packet, and will send an ICMP Time Exceeded message back to the source.
| CyberOps - Associate 1.0 & 1.01 | |
| Final Exam | |
| Practice Final Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Final Exam Answers | Online Test |
| 200-201 Certification Practice | Online Test |