CCNA 2 v7 SRWE v7.02 – Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essentials (Version 7.00) – Modules 10 – 13 – L2 Security and WLANs Exam Answers 2023 2024 Full 100%
CCNA 2 v7 SRWE v7.02 – Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essentials (Version 7.00) – Modules 10 – 13 – L2 Security and WLANs Exam Answers 2023 2024 Full 100%
This is NetAcad Cisco CCNA 2 v7 SRWE v7.02 Modules 10 – 13 Exam Answers 2023 2024 and Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essentials ( Version 7.00) – Available and Reliable Networks Exam Answers Full 100%. All answers have been verified by experts.
| CCNA 2 v7 & 7.02 | |
| Final Exam Answers | |
| This Modules 10 - 13 | |
| Modules 10 - 13 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Next Modules 14 - 16 | |
| Modules 14 - 16 Exam Answers | Online Test |
Cisco Netacad SRWE Version 7.00 CCNA 2 v7 & v7.02 Modules 10 – 13 – L2 Security and WLANs Exam Answers 2023 2024 – Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essential
-
Which authentication method stores usernames and passwords in the router and is ideal for small networks?
- local AAA
- local AAA over RADIUS
- local AAA over TACACS+
- server-based AAA
- server-based AAA over RADIUS
- server-based AAA over TACACS+
Answers Explanation & Hints: In a small network with a few network devices, AAA authentication can be implemented with the local database and with usernames and passwords stored on the network devices. Authentication using the TACACS+ or RADIUS protocol will require dedicated ACS servers although this authentication solution scales well in a large network.
-
What are two protocols that are used by AAA to authenticate users against a central database of usernames and password? (Choose two.)
- NTP
- TACACS+
- SSH
- HTTPS
- RADIUS
- CHAP
Answers Explanation & Hints: By using TACACS+ or RADIUS, AAA can authenticate users from a database of usernames and passwords stored centrally on a server such as a Cisco ACS server.
-
What is the result of a DHCP starvation attack?
- Legitimate clients are unable to lease IP addresses.
- Clients receive IP address assignments from a rogue DHCP server.
- The attacker provides incorrect DNS and default gateway information to clients.
- The IP addresses assigned to legitimate clients are hijacked.
Answers Explanation & Hints: DCHP starvation attacks are launched by an attacker with the intent to create a DoS for DHCP clients. To accomplish this goal, the attacker uses a tool that sends many DHCPDISCOVER messages to lease the entire pool of available IP addresses, thus denying them to legitimate hosts.
-
What represents a best practice concerning discovery protocols such as CDP and LLDP on network devices?
- Use the open standard LLDP rather than CDP.
- Disable both protocols on all interfaces where they are not required.
- Use the default router settings for CDP and LLDP.
- Enable CDP on edge devices, and enable LLDP on interior devices.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Both discovery protocols can provide hackers with sensitive network information. They should not be enabled on edge devices, and should be disabled globally or on a per-interface basis if not required. CDP is enabled by default.
-
Which protocol should be used to mitigate the vulnerability of using Telnet to remotely manage network devices?
- SCP
- SSH
- TFTP
- SNMP
Answers Explanation & Hints: Telnet uses plain text to communicate in a network. The username and password can be captured if the data transmission is intercepted. SSH encrypts data communications between two network devices. TFTP and SCP are used for file transfer over the network. SNMP is used in network management solutions.
-
Which statement describes the behavior of a switch when the MAC address table is full?
- It treats frames as unknown unicast and floods all incoming frames to all ports on the switch.
- It treats frames as unknown unicast and floods all incoming frames to all ports within the local VLAN.
- It treats frames as unknown unicast and floods all incoming frames to all ports within the collision domain.
- It treats frames as unknown unicast and floods all incoming frames to all ports across multiple switches.
Answers Explanation & Hints: When the MAC address table is full, the switch treats the frame as an unknown unicast and begins to flood all incoming traffic to all ports only within the local VLAN.
-
Which feature on a switch makes it vulnerable to VLAN hopping attacks?
- the mixed duplex mode enabled for all ports by default
- the limited size of content-addressable memory space
- mixed port bandwidth support enabled for all ports by default
- the automatic trunking port feature enabled for all ports by default
Answers Explanation & Hints: A VLAN hopping attack enables traffic from one VLAN to be seen by another VLAN without routing. In a basic VLAN hopping attack, the attacker takes advantage of the automatic trunking port feature enabled by default on most switch ports.
-
Which feature or configuration on a switch makes it vulnerable to VLAN double-tagging attacks?
- mixed duplex mode enabled for all ports by default
- the limited size of content-addressable memory space
- the automatic trunking port feature enabled for all ports by default
- the native VLAN of the trunking port being the same as a user VLAN
Answers Explanation & Hints: A double-tagging (or double-encapsulated) VLAN hopping attack takes advantage of the way that hardware on most switches operates. Most switches perform only one level of 802.1Q de-encapsulation, which allows an attacker to embed a hidden 802.1Q tag inside the frame. This tag allows the frame to be forwarded to a VLAN that the original 802.1Q tag did not specify. An important characteristic of the double-encapsulated VLAN hopping attack is that it works even if trunk ports are disabled, because a host typically sends a frame on a segment that is not a trunk link. This type of attack is unidirectional and works only when the attacker is connected to a port residing in the same VLAN as the native VLAN of the trunk port.
-
Which component of AAA is used to determine which resources a user can access and which operations the user is allowed to perform?
- auditing
- accounting
- authorization
- authentication
Answers Explanation & Hints: One of the components in AAA is authorization. After a user is authenticated through AAA, authorization services determine which resources the user can access and which operations the user is allowed to perform.
-
Which component of AAA allows an administrator to track individuals who access network resources and any changes that are made to those resources?
- accessibility
- accounting
- authentication
- authorization
Answers Explanation & Hints: One of the components in AAA is accounting. After a user is authenticated through AAA, AAA servers keep a detailed log of exactly what actions the authenticated user takes on the device.
-
What device is considered a supplicant during the 802.1X authentication process?
- the client that is requesting authentication
- the switch that is controlling network access
- the authentication server that is performing client authentication
- the router that is serving as the default gateway
Answers Explanation & Hints: The devices involved in the 802.1X authentication process are as follows:The supplicant, which is the client that is requesting network access
The authenticator, which is the switch that the client is connecting to and that is actually controlling physical network access
The authentication server, which performs the actual authentication
-
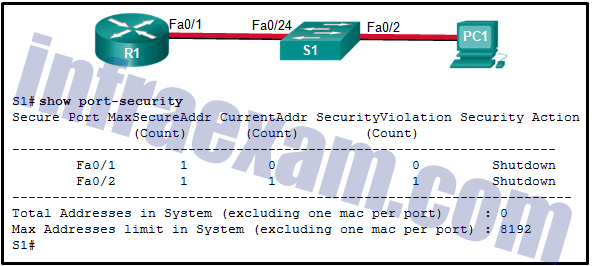
Refer to the exhibit. The Fa0/2 interface on switch S1 has been configured with the switchport port-security mac-address 0023.189d.6456 command and a workstation has been connected. What could be the reason that the Fa0/2 interface is shutdown?
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 10 – 13 – L2 Security and WLANs Exam Answers 01 - The connection between S1 and PC1 is via a crossover cable.
- The Fa0/24 interface of S1 is configured with the same MAC address as the Fa0/2 interface.
- S1 has been configured with a switchport port-security aging command.
- The MAC address of PC1 that connects to the Fa0/2 interface is not the configured MAC address.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The security violation counter for Fa0/2 has been incremented (evidenced by the 1 in the SecurityViolation column). The most secure addresses allowed on port Fa0/2 is 1 and that address was manually entered. Therefore, PC1 must have a different MAC address than the one configured for port Fa0/2. Connections between end devices and the switch, as well as connections between a router and a switch, are made with a straight-through cable.
-
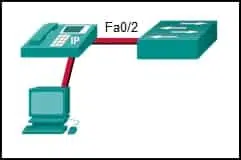
Refer to the exhibit. Port Fa0/2 has already been configured appropriately. The IP phone and PC work properly. Which switch configuration would be most appropriate for port Fa0/2 if the network administrator has the following goals?
No one is allowed to disconnect the IP phone or the PC and connect some other wired device.If a different device is connected, port Fa0/2 is shut down.
The switch should automatically detect the MAC address of the IP phone and the PC and add those addresses to the running configuration.
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 10 – 13 – L2 Security and WLANs Exam Answers 02 - SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky - SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 2 - SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 2
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky - SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 2
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security violation restrictAnswers Explanation & Hints: The default mode for a port security violation is to shut down the port so the switchport port-security violation command is not necessary. The switchport port-security command must be entered with no additional options to enable port security for the port. Then, additional port security options can be added.
- SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security
-
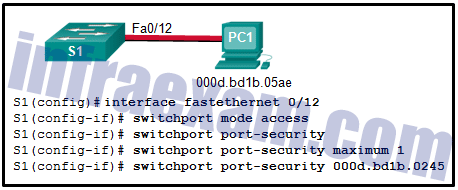
Refer to the exhibit. Port security has been configured on the Fa 0/12 interface of switch S1. What action will occur when PC1 is attached to switch S1 with the applied configuration?
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 10 – 13 – L2 Security and WLANs Exam Answers 04 - Frames from PC1 will be dropped, and a log message will be created.
- Frames from PC1 will be dropped, and there will be no log of the violation.
- Frames from PC1 will cause the interface to shut down immediately, and a log entry will be made.
- Frames from PC1 will be forwarded to its destination, and a log entry will be created.
- Frames from PC1 will be forwarded to its destination, but a log entry will not be created.
- Frames from PC1 will be forwarded since the switchport port-security violation command is missing.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Manual configuration of the single allowed MAC address has been entered for port fa0/12. PC1 has a different MAC address and when attached will cause the port to shut down (the default action), a log message to be automatically created, and the violation counter to increment. The default action of shutdown is recommended because the restrict option might fail if an attack is underway.
-
A network administrator is configuring port security on a Cisco switch. The company security policy specifies that when a violation occurs, packets with unknown source addresses should be dropped and no notification should be sent. Which violation mode should be configured on the interfaces?
- off
- restrict
- protect
- shutdown
Answers Explanation & Hints: On a Cisco switch, an interface can be configured for one of three violation modes, specifying the action to be taken if a violation occurs:
Protect – Packets with unknown source addresses are dropped until a sufficient number of secure MAC addresses are removed, or the number of maximum allowable addresses is increased. There is no notification that a security violation has occurred.
Restrict – Packets with unknown source addresses are dropped until a sufficient number of secure MAC addresses are removed, or the number of maximum allowable addresses is increased. In this mode, there is a notification that a security violation has occurred.
Shutdown – The interface immediately becomes error-disabled and the port LED is turned off.
-
What security benefit is gained from enabling BPDU guard on PortFast enabled interfaces?
- preventing rogue switches from being added to the network
- protecting against Layer 2 loops
- enforcing the placement of root bridges
- preventing buffer overflow attacks
Answers Explanation & Hints: BPDU guard immediately error-disables a port that receives a BPDU. This prevents rogue switches from being added to the network. BPDU guard should only be applied to all end-user ports.
-
Which type of VLAN-hopping attack may be prevented by designating an unused VLAN as the native VLAN?
- DTP spoofing
- DHCP spoofing
- VLAN double-tagging
- DHCP starvation
Answers Explanation & Hints: Spoofing DTP messages forces a switch into trunking mode as part of a VLAN-hopping attack, but VLAN double tagging works even if trunk ports are disabled. Changing the native VLAN from the default to an unused VLAN reduces the possibility of this type of attack. DHCP spoofing and DHCP starvation exploit vulnerabilities in the DHCP message exchange.
-
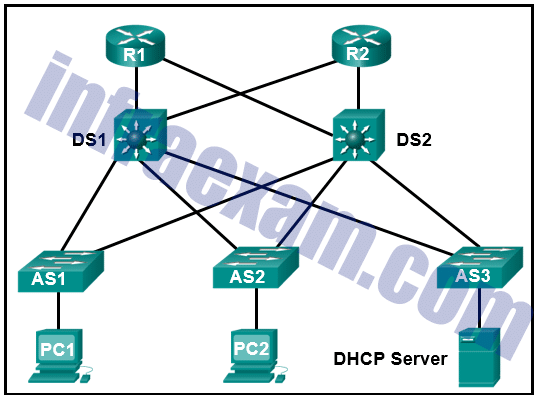
Refer to the exhibit. PC1 and PC2 should be able to obtain IP address assignments from the DHCP server. How many ports among switches should be assigned as trusted ports as part of the DHCP snooping configuration?
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 10 – 13 – L2 Security and WLANs Exam Answers 05 - 1
- 3
- 5
- 7
Answers Explanation & Hints: The DHCP snooping configuration includes building the DHCP Snooping Binding Database and assigning necessary trusted ports on switches. A trusted port points to the legitimate DHCP servers. In this network design, because the DHCP server is attached to AS3, seven switch ports should be assigned as trusted ports, one on AS3 toward the DHCP server, one on DS1 toward AS3, one on DS2 toward AS3, and two connections on both AS1 and AS2 (toward DS1 and DS2), for a total of seven.
-
An IT security specialist enables port security on a switch port of a Cisco switch. What is the default violation mode in use until the switch port is configured to use a different violation mode?
- restrict
- disabled
- protect
- shutdown
Answers Explanation & Hints: If no violation mode is specified when port security is enabled on a switch port, then the security violation mode defaults to shutdown.
-
A network administrator enters the following commands on the switch SW1.
SW1(config)# interface range fa0/5 – 10
SW1(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping limit rate 6What is the effect after these commands are entered?
- FastEthernet ports 5 through 10 can receive up to 6 DHCP discovery messages per second.
- FastEthernet ports 5 through 10 can receive up to 6 DHCP messages per second of any type.
- If any of the FastEthernet ports 5 through 10 receive more than 6 DHCP messages per second, the port will be shut down.
- If any of the FastEthernet ports 5 through 10 receive more than 6 DHCP messages per second, the port will continue to operate and an error message will be sent to the network administrator.
Answers Explanation & Hints: When DHCP snooping is being configured, the number of DHCP discovery messages that untrusted ports can receive per second should be rate-limited by using the ip dhcp snooping limit rate interface configuration command. When a port receives more messages than the rate allows, the extra messages will be dropped.
-
A network administrator is configuring DAI on a switch with the command ip arp inspection validate src-mac . What is the purpose of this configuration command?
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the MAC address table.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the user-configured ARP ACLs.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the target MAC address in the ARP body.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the sender MAC address in the ARP body.
Answers Explanation & Hints: DAI can be configured to check for both destination or source MAC and IP addresses:
Destination MAC – Checks the destination MAC address in the Ethernet header against the target MAC address in the ARP body.
Source MAC – Checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the sender MAC address in the ARP body.
IP address – Checks the ARP body for invalid and unexpected IP addresses including addresses 0.0.0.0, 255.255.255.255, and all IP multicast addresses.
-
Which two commands can be used to enable BPDU guard on a switch? (Choose two.)
- S1(config)# spanning-tree bpduguard default
- S1(config-if)# spanning-tree bpduguard enable
- S1(config-if)# enable spanning-tree bpduguard
- S1(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast bpduguard
- S1(config)# spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default
Answers Explanation & Hints: BPDU guard can be enabled on all PortFast-enabled ports by using the spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default global configuration command. Alternatively, BPDU guard can be enabled on a PortFast-enabled port through the use of the spanning-tree bpduguard enable interface configuration command.
-
As part of the new security policy, all switches on the network are configured to automatically learn MAC addresses for each port. All running configurations are saved at the start and close of every business day. A severe thunderstorm causes an extended power outage several hours after the close of business. When the switches are brought back online, the dynamically learned MAC addresses are retained. Which port security configuration enabled this?
- auto secure MAC addresses
- dynamic secure MAC addresses
- static secure MAC addresses
- sticky secure MAC addresses
Answers Explanation & Hints: With sticky secure MAC addressing, the MAC addresses can be either dynamically learned or manually configured and then stored in the address table and added to the running configuration file. In contrast, dynamic secure MAC addressing provides for dynamically learned MAC addressing that is stored only in the address table.
-
Which type of management frame may regularly be broadcast by an AP?
- beacon
- probe request
- authentication
- probe response
Answers Explanation & Hints: Beacons are the only management frame that may regularly be broadcast by an AP. Probing, authentication, and association frames are used only during the association (or reassociation) process.
-
What type of wireless antenna is best suited for providing coverage in large open spaces, such as hallways or large conference rooms?
- omnidirectional
- directional
- Yagi
- dish
Answers Explanation & Hints: Omnidirectional antennas send the radio signals in a 360 degree pattern around the antenna. This provides coverage to devices situated anywhere around the access point. Dishes, directional, and Yagi antennas focus the radio signals in a single direction, making them less suitable for covering large, open areas.
-
What is an advantage of SSID cloaking?
- It provides free Internet access in public locations where knowing the SSID is of no concern.
- Clients will have to manually identify the SSID to connect to the network.
- SSIDs are very difficult to discover because APs do not broadcast them.
- It is the best way to secure a wireless network.
Answers Explanation & Hints: SSID cloaking is a weak security feature that is performed by APs and some wireless routers by allowing the SSID beacon frame to be disabled. Although clients have to manually identify the SSID to be connected to the network, the SSID can be easily discovered. The best way to secure a wireless network is to use authentication and encryption systems. SSID cloaking does not provide free Internet access in public locations, but an open system authentication could be used in that situation.
-
What are the two methods that are used by a wireless NIC to discover an AP? (Choose two.)
- sending an ARP request
- delivering a broadcast frame
- transmitting a probe request
- initiating a three-way handshake
- receiving a broadcast beacon frame
Answers Explanation & Hints: Two methods can be used by a wireless device to discover and register with an access point: passive mode and active mode. In passive mode, the AP sends a broadcast beacon frame that contains the SSID and other wireless settings. In active mode, the wireless device must be manually configured for the SSID, and then the device broadcasts a probe request.
-
Which wireless network topology would be used by network engineers to provide a wireless network for an entire college building?
- ad hoc
- hotspot
- infrastructure
- mixed mode
Answers Explanation & Hints: Ad hoc mode (also known as independent basic service set or IBSS) is used in a peer-to-peer wireless network such as when Bluetooth is used. A variation of the ad hoc topology exists when a smart phone or tablet with cellular data access is enabled to create a personal wireless hotspot. Mixed mode allows older wireless NICs to attach to an access point that can use a newer wireless standard.
-
What is a wireless security mode that requires a RADIUS server to authenticate wireless users?
- enterprise
- personal
- shared key
- WEP
Answers Explanation & Hints: WPA and WPA2 come in two types: personal and enterprise. Personal is used in home and small office networks. Shared key allows three different authentication techniques: (1) WEP, (2) WPA, and (3) 802.11i/WPA2. WEP is an encryption method.
-
What two IEEE 802.11 wireless standards operate only in the 5 GHz range? (Choose two.)
- 802.11a
- 802.11b
- 802.11g
- 802.11n
- 802.11ac
- 802.11ad
Answers Explanation & Hints: The 802.11a and 802.11ac standards operate only in the 5 GHZ range. The 802.11b and 802.11g standards operate only in the 2.4 GHz range. The 802.11n standard operates in both the 2.4 and 5 GHz ranges. The 802.11ad standard operates in the 2.4, 5, and 60 GHz ranges.
-
A technician is configuring the channel on a wireless router to either 1, 6, or 11. What is the purpose of adjusting the channel?
- to disable broadcasting of the SSID
- to enable different 802.11 standards
- to provide stronger security modes
- to avoid interference from nearby wireless devices
Answers Explanation & Hints: Channels 1, 6, and 11 are selected because they are 5 channels apart. thus minimizing the interference with adjacent channels. A channel frequency can interfere with channels on either side of the main frequency. All wireless devices need to be used on nonadjacent channels.
-
While attending a conference, participants are using laptops for network connectivity. When a guest speaker attempts to connect to the network, the laptop fails to display any available wireless networks. The access point must be operating in which mode?
- active
- mixed
- open
- passive
Answers Explanation & Hints: Active is a mode used to configure an access point so that clients must know the SSID to connect to the access point. APs and wireless routers can operate in a mixed mode meaning that that multiple wireless standards are supported. Open is an authentication mode for an access point that has no impact on the listing of available wireless networks for a client. When an access point is configured in passive mode, the SSID is broadcast so that the name of wireless network will appear in the listing of available networks for clients.
-
A network administrator is required to upgrade wireless access to end users in a building. To provide data rates up to 1.3 Gb/s and still be backward compatible with older devices, which wireless standard should be implemented?
- 802.11n
- 802.11ac
- 802.11g
- 802.11b
Answers Explanation & Hints: 802.11ac provides data rates up to 1.3 Gb/s and is still backward compatible with 802.11a/b/g/n devices. 802.11g and 802.11n are older standards that cannot reach speeds over 1Gb/s. 802.11ad is a newer standard that can offer theoretical speeds of up to 7 Gb/s.
-
A company has recently implemented an 802.11n wireless network. Some users are complaining that the wireless network is too slow. Which solution is the best method to enhance the performance of the wireless network?
- Replace the wireless NICs on the computers that are experiencing slow connections.
- Split the traffic between the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands.
- Disable DHCP on the access point and assign static addresses to the wireless clients.
- Upgrade the firmware on the wireless access point.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Because some users are complaining about the network being too slow, the correct option would be to split the traffic so that there are two networks using different frequencies at the same time. Replacing the wireless NICs will not necessarily correct the network being slow and it could be expensive for the company. DHCP versus static addressing should have no impact of the network being slow and it would be a huge task to have all users assigned static addressing for their wireless connection. Upgrading the firmware on the wireless access point is always a good idea. However, if some of the users are experiencing a slow network connection, it is likely that this would not substantially improve network performance.
-
A technician is about to install and configure a wireless network at a small branch office. What is the first security measure the technician should apply immediately upon powering up the wireless router?
- Configure encryption on the wireless router and the connected wireless devices.
- Disable the wireless network SSID broadcast.
- Change the default user-name and password of the wireless router.
- Enable MAC address filtering on the wireless router.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The first action a technician should do to secure a new wireless network is to change the default user-name and password of the wireless router. The next action would usually be to configure encryption. Then once the initial group of wireless hosts have connected to the network, MAC address filtering would be enabled and SSID broadcast disabled. This will prevent new unauthorized hosts from finding and connecting to the wireless network.
-
On a Cisco 3504 WLC dashboard, which option provides access to the full menu of features?
- Rogues
- Advanced
- Access Points
- Network Summary
Answers Explanation & Hints: The Cisco 3504 WLC dashboard displays when a user logs into the WLC. It provides some basic settings and menus that users can quickly access to implement a variety of common configurations. By clicking the Advanced button, the user will access the advanced Summary page and access all the features of the WLC.
-
On a Cisco 3504 WLC Summary page ( Advanced > Summary ), which tab allows a network administrator to access and configure a WLAN for a specific security option such as WPA2?
- WLANs
- SECURITY
- WIRELESS
- MANAGEMENT
Answers Explanation & Hints: The WLANs tab in the Cisco 3504 WLC advanced Summary page allows a user to access the configuration of WLANs including security, QoS, and policy-mapping.
-
Which protocol can be used to monitor the network?
- AAA
- SNMP
- DHCP
- RADIUS
Answers Explanation & Hints: Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is used to monitor the network.
-
A network administrator deploys a wireless router in a small law firm. Employee laptops join the WLAN and receive IP addresses in the 10.0.10.0/24 network. Which service is used on the wireless router to allow the employee laptops to access the internet?
- DNS
- NAT
- DHCP
- RADIUS
Answers Explanation & Hints: Any address with the 10 in the first octet is a private IPv4 address and cannot be routed on the internet. The wireless router will use a service called Network Address Translation (NAT) to convert private IPv4 addresses to internet-routable IPv4 addresses for wireless devices to gain access to the internet.
-
Which service can be used on a wireless router to prioritize network traffic among different types of applications so that voice and video data are prioritized over email and web data?
- NAT
- QoS
- DNS
- DHCP
Answers Explanation & Hints: Many wireless routers have an option for configuring quality of service (QoS). By configuring QoS, certain time-sensitive traffic types, such as voice and video, are prioritized over traffic that is not as time-sensitive, such as email and web browsing.
-
Which step is required before creating a new WLAN on a Cisco 3500 series WLC?
- Create a new SSID.
- Create a new VLAN interface.
- Build or have an SNMP server available.
- Build or have a RADIUS server available.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Each new WLAN configured on a Cisco 3500 series WLC needs its own VLAN interface. Thus it is required that a new VLAN interface to be created first before a new WLAN can be created.
-
A network engineer is troubleshooting a newly deployed wireless network that is using the latest 802.11 standards. When users access high bandwidth services such as streaming video, the wireless network performance is poor. To improve performance the network engineer decides to configure a 5 Ghz frequency band SSID and train users to use that SSID for streaming media services. Why might this solution improve the wireless network performance for that type of service?
- The 5 GHz band has a greater range and is therefore likely to be interference-free.
- Requiring the users to switch to the 5 GHz band for streaming media is inconvenient and will result in fewer users accessing these services.
- The 5 GHz band has more channels and is less crowded than the 2.4 GHz band, which makes it more suited to streaming multimedia.
- The only users that can switch to the 5 GHz band will be those with the latest wireless NICs, which will reduce usage.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Wireless range is determined by the access point antenna and output power, not the frequency band that is used. In this scenario it is stated that all users have wireless NICs that comply with the latest standard, and so all can access the 5 GHz band. Although some users may find it inconvenient to switch to the 5 Ghz band to access streaming services, it is the greater number of channels, not just fewer users, that will improve network performance.
-
A network administrator is working to improve WLAN performance on a dual-band wireless router. What is a simple way to achieve a split-the-traffic result?
- Require all wireless devices to use the 802.11n standard.
- Check and keep the firmware of the wireless router updated.
- Make sure that different SSIDs are used for the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
- Add a Wi-Fi range extender to the WLAN and set the AP and the range extender to serve different bands.
Answers Explanation & Hints: By default, dual-band routers and APs use the same network name on both the 2.4 GHz band and the 5 GHz band. The simplest way to segment traffic is to rename one of the wireless networks.
-
A network administrator is configuring a RADIUS server connection on a Cisco 3500 series WLC. The configuration requires a shared secret password. What is the purpose for the shared secret password?
- It allows users to authenticate and access the WLAN.
- It is used by the RADIUS server to authenticate WLAN users.
- It is used to authenticate and encrypt user data on the WLAN.
- It is used to encrypt the messages between the WLC and the RADIUS server.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The RADIUS protocol uses security features to protect communications between the RADIUS server and clients. A shared secret is the password used between the WLC and the RADIUS server. It is not for end users.
-
A laptop cannot connect to a wireless access point. Which two troubleshooting steps should be taken first? (Choose two.)
- Ensure that the wireless NIC is enabled.
- Ensure that the laptop antenna is attached.
- Ensure that the wireless SSID is chosen.
- Ensure that the correct network media is selected.
- Ensure that the NIC is configured for the proper frequency.
Answers Explanation & Hints: A wireless laptop normally does not have an antenna attached unless a repair has recently been implemented. If the wireless NIC is enabled, the correct media, radio, will be used. When the NIC detects an access point, the correct frequency is automatically used.
-
Which three parameters would need to be changed if best practices are being implemented for a home wireless AP? (Choose three.)
- SSID
- AP password
- antenna frequency
- wireless beacon time
- wireless network password
- wireless client operating system password
Answers Explanation & Hints: As soon as an AP is taken out of a box, the default device password, SSID, and security parameters (wireless network password) should be set. The frequency of a wireless antenna can be adjusted, but doing so is not required. The beacon time is not normally configured. The wireless client operating system password is not affected by the configuration of a home wireless network.
-
Which access control component, implementation, or protocol controls what users can do on the network?
- authorization
- authentication
- accounting
- 802.1X
-
Explanation & Hint: The access control component that controls what users can do on a network is Authorization. Here’s a brief overview of each term you mentioned and their roles in network security:
- Authorization: This determines what a user can and cannot do within a network, such as what resources they can access, the kind of operations they can perform (like read, write, delete), and what areas of the network they can enter. It’s essentially about permissions and rights assigned to a user or a program.
- Authentication: This process verifies the identity of a user or device trying to access the network. It’s about ensuring that the user is who they claim to be. This could involve passwords, biometrics, or other methods.
- Accounting: This is often associated with keeping track of what users do on the network – monitoring their activities, recording the information for various purposes like billing, auditing, and reporting. It’s important for understanding user behavior and resource usage.
- 802.1X: This is a network protocol that provides an authentication mechanism for devices wishing to attach to a LAN or WLAN. It’s a layer 2 protocol that enhances security by requiring devices to be authenticated before they can access the network.
In summary, for controlling what users can do on the network, the key concept is Authorization. Authentication and 802.1X are more about verifying identity before granting network access, while accounting deals with monitoring and recording user activities.
-
Which access control component, implementation, or protocol is implemented either locally or as a server-based solution?
- authentication
- authorization
- accounting
- 802.1X
-
Explanation & Hint: The access control component that can be implemented either locally or as a server-based solution is Authentication. Here’s why:
- Authentication: This process verifies a user’s identity and can be implemented both locally and through server-based solutions. Locally, it might involve something as simple as a login password on a device. Server-based authentication systems are more complex, involving centralized servers that manage authentication for multiple users and devices across a network. Examples include LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol), Kerberos, and RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service).
- Authorization: While authorization rules can be stored and applied locally or on a server, the actual implementation of authorization is typically more integrated with the resource being accessed rather than a standalone local or server-based solution. It’s more about defining and enforcing policies rather than the method of implementation.
- Accounting: This involves tracking and recording user activities for purposes like billing, auditing, and reporting. While accounting data can be collected locally, it is often managed and analyzed through a server-based solution, especially in larger networks, for centralized management and better scalability.
- 802.1X: This is a network access control protocol and is not typically described in terms of local or server-based implementation. It’s a standard for port-based Network Access Control, used in various networking environments, often with a RADIUS server for authentication.
In essence, Authentication is the component that fits the description of being implemented either locally or as a server-based solution, as it directly involves verifying user identities in both standalone devices and networked environments.
-
Which access control component, implementation, or protocol audits what users actions are performed on the network?
- accounting
- authorization
- 802.1X
- authentication
-
Explanation & Hint: The access control component that audits what user actions are performed on the network is Accounting. Here’s a brief overview of each component and their primary functions:
- Accounting: This aspect of network security is concerned with tracking user activities on the network. It records and measures resource usage for billing, auditing, and reporting. Accounting ensures that there is a record of what an individual user has done on the network, such as the amount of time spent in the network, the services accessed, the amount of data transferred, etc.
- Authorization: This process determines the resources and services a user is permitted to access on the network. While it controls access rights, it does not typically audit user actions.
- 802.1X: This is an IEEE Standard for port-based Network Access Control (PNAC). It is part of the network’s access control and authentication policy but does not directly involve auditing user actions.
- Authentication: This is the process of verifying the identity of a user or device. Authentication confirms who the user is but does not track or record their actions on the network.
In summary, Accounting is the component specifically designed to audit and keep a record of user actions on a network.
-
Which access control component, implementation, or protocol restricts LAN access through publicly accessible switch ports?
- 802.1X
- accounting
- authorization
- authentication
-
Explanation & Hint: The access control component that restricts LAN access through publicly accessible switch ports is 802.1X. Here’s how it fits into this context:
- 802.1X: This is an IEEE standard for port-based Network Access Control (PNAC). It is used to provide authentication to devices trying to connect to a LAN or WLAN. 802.1X restricts access to the network through publicly accessible switch ports until the device is authenticated. It’s a key protocol used in securing wired and wireless networks by preventing unauthorized network access at the port level.
- Accounting: This component involves tracking and recording user activities on the network, mainly for auditing and billing purposes. It does not restrict access to network resources.
- Authorization: While authorization determines what an authenticated user is allowed to do on the network (like accessing certain resources or services), it doesn’t directly restrict access through physical switch ports.
- Authentication: This process verifies the identity of a user or device. While it’s a crucial step before granting access to the network, it doesn’t specifically address the control of access through switch ports.
In summary, 802.1X is specifically designed to control access to a LAN through publicly accessible switch ports, making it the correct answer.
-
Which access control component, implementation, or protocol logs EXEC and configuration commands configured by a user?
- accounting
- 802.1X
- authorization
- authentication
-
Explanation & Hint: The access control component that logs EXEC and configuration commands configured by a user is Accounting. This component of network security and management is specifically focused on tracking and recording user activities, including the logging of EXEC commands (commands a user executes in a network session) and configuration changes made by a user. Here’s a brief overview of each term for clarity:
- Accounting: In the context of network management, accounting refers to the process of keeping track of a user’s activity while accessing network resources. This includes logging every command a user issues (like EXEC commands in a network session) and tracking configuration changes made by the user. It’s an essential part of auditing and monitoring network security.
- 802.1X: This is an IEEE standard for port-based Network Access Control, primarily used for authenticating devices that are attempting to connect to a LAN or WLAN. It does not involve logging user commands or configurations.
- Authorization: Authorization is about granting or denying rights to access resources. It does not involve logging user activities but rather sets what a user is permitted to do.
- Authentication: This process involves verifying the identity of a user or device. Authentication is about establishing who a user is, not what actions they perform or logging their commands.
In summary, Accounting is the component involved in logging EXEC and configuration commands configured by a user on a network.
-
Which access control component, implementation, or protocol controls who is permitted to access a network?
- authentication
- authorization
- accounting
- 802.1X
-
Explanation & Hint: The access control component that controls who is permitted to access a network is Authentication. Here’s a brief explanation of each component:
- Authentication: This is the process of verifying the identity of a user or device. Authentication is the first step in access control, determining whether a user or device is who they claim to be, often through credentials like usernames and passwords, biometric data, or security tokens. It’s directly responsible for deciding who is allowed to access a network.
- Authorization: Once a user is authenticated, authorization determines what they are allowed to do on the network, such as which resources they can access and what actions they can perform. It does not control network access per se but rather governs the level of access after authentication.
- Accounting: This component involves tracking and recording network resource usage for auditing and billing purposes. It does not control access to the network but monitors and logs activities after access is granted.
- 802.1X: This is a network protocol used for network access control, particularly in securing WLANs and LANs. It is a means of enforcing authentication, often working in conjunction with a RADIUS server. While 802.1X plays a crucial role in network security, the fundamental control of who is permitted to access the network is grounded in the authentication process.
In summary, Authentication is the key component that controls who is permitted to access a network.
-
Which access control component, implementation, or protocol collects and reports usage data?
- accounting
- authorization
- 802.1X
- authentication
-
Explanation & Hint: The access control component that collects and reports usage data is Accounting. Here’s a brief overview of its role compared to the other components:
- Accounting: In the context of network access control, accounting is responsible for collecting and reporting usage data. This involves tracking and logging user activities, such as the amount of time users spend on the network, the services they access, and the amount of data they transmit or receive. The data collected is crucial for purposes like billing, auditing, resource allocation, and monitoring network usage.
- Authorization: This component determines what resources and services a user is allowed to access on the network. It sets permissions and restrictions for users but does not collect or report usage data.
- 802.1X: This is a protocol used for network access control, particularly in securing WLANs and LANs through authentication. While it plays a role in securing network access, it does not collect and report usage data.
- Authentication: Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user or device trying to access the network. It establishes the user’s identity but does not involve the collection or reporting of usage data.
In summary, Accounting is the specific component that deals with the collection and reporting of usage data on a network.
-
Which access control component, implementation, or protocol indicates success or failure of a client-requested service with a PASS or FAIL message?
- authorization
- accounting
- authentication
- 802.1X
-
Explanation & Hint: The access control component that indicates the success or failure of a client-requested service with a PASS or FAIL message is Authentication. Here’s the rationale for each component:
- Authentication: This process involves verifying the identity of a user or device attempting to access a network or service. If the credentials provided by the user (like a username and password) are valid, the authentication process typically indicates success with a message akin to “PASS.” Conversely, if the credentials are invalid or the authentication process otherwise fails, it indicates failure, often with a “FAIL” message. This PASS or FAIL feedback is a direct part of the authentication process.
- Authorization: Once a user is authenticated, authorization determines what they are allowed to do on the network, such as accessing specific resources or executing certain operations. While it grants or denies access to resources based on policies, it doesn’t typically use PASS or FAIL messages in the same way as authentication.
- Accounting: This component involves tracking and recording network resource usage, focusing on monitoring user activities rather than granting or denying access. It doesn’t provide PASS or FAIL messages related to user requests.
- 802.1X: This is a network access control protocol used for securing networks, particularly through authentication mechanisms. While 802.1X is integral to managing network access, the specific indication of success or failure with PASS or FAIL messages is a function of the underlying authentication process.
In summary, Authentication is the component that directly involves indicating the success (PASS) or failure (FAIL) of a client-requested service.
-
Which access control component, implementation, or protocol is based on device roles of supplicant, authenticator, and authentication server?
- 802.1X
- accounting
- authorization
- authentication
-
Explanation & Hint: The access control component that is based on the device roles of supplicant, authenticator, and authentication server is 802.1X. Here’s an explanation of its roles:
- 802.1X: This is a network access and control protocol that operates with three key roles:
- Supplicant: The client device that wants to gain access to the network.
- Authenticator: Typically a network device, such as a switch or wireless access point, that acts as an intermediary between the supplicant and the authentication server. It enforces authentication before allowing access to network resources.
- Authentication Server: Often a RADIUS server, this verifies the credentials provided by the supplicant and informs the authenticator whether access should be granted or denied.
The other components mentioned (Accounting, Authorization, Authentication) do not specifically utilize this triad of roles in their processes. Accounting involves tracking and logging network usage, Authorization deals with granting permissions to a user or device, and Authentication is the process of verifying identity, but none of these use the specific supplicant-authenticator-authentication server model inherent to 802.1X.
- 802.1X: This is a network access and control protocol that operates with three key roles:
-
Which access control component, implementation, or protocol is based upon usernames and passwords?
- authentication
- authorization
- accounting
- 802.1X
-
Explanation & Hint: The access control component that is based upon usernames and passwords is Authentication. Here’s a brief explanation:
- Authentication: This is the process of verifying the identity of a user or device. Usernames and passwords are the most common forms of credentials used in the authentication process. During authentication, the user provides a username and password, which are then checked against a database to confirm their identity.
- Authorization: Once a user is authenticated, authorization determines what the user is allowed to do on the network, such as accessing specific resources or services. It is more about permissions and rights than about verifying identity and does not directly involve usernames and passwords.
- Accounting: This component involves tracking and recording the usage of network resources. It focuses on monitoring activities rather than verifying identities and doesn’t directly use usernames and passwords.
- 802.1X: While this network access control protocol does involve authentication, it’s a broader standard that encompasses more than just the use of usernames and passwords. It often works in conjunction with an authentication server (like RADIUS) and can use various forms of authentication methods.
In summary, Authentication specifically involves the use of usernames and passwords to verify the identity of users or devices trying to access a network or service.
-
Which type of wireless network uses transmitters to provide coverage over an extensive geographic area?
- wireless wide-area network
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless local-area network
- wireless personal-area network
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of wireless network that uses transmitters to provide coverage over an extensive geographic area is a Wireless Wide-Area Network (WWAN). Here’s a brief overview of each type mentioned for clarity:
- Wireless Wide-Area Network (WWAN): This type of network covers large geographic areas, often spanning cities or even countries. WWANs use cellular network technologies to provide wireless connectivity over long distances, and are commonly used for mobile internet access on smartphones, laptops, and other mobile devices.
- Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN): This network type is designed to cover a larger area than a LAN but typically is confined to a city or a metropolitan area. It’s larger than a Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN) but smaller than a WWAN.
- Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN): WLANs provide wireless network communication over short distances, often within a building or a small group of buildings. A common example of WLAN technology is Wi-Fi.
- Wireless Personal-Area Network (WPAN): This is a network for interconnecting devices within a relatively small area, typically within a person’s reach. Bluetooth is a well-known example of WPAN technology.
In summary, to cover an extensive geographic area, the appropriate type of network is a Wireless Wide-Area Network (WWAN).
-
Which type of wireless network commonly uses Bluetooth or ZigBee devices?
- wireless personal-area network
- wireless local-area network
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless wide-area network
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of wireless network that commonly uses Bluetooth or ZigBee devices is a Wireless Personal-Area Network (WPAN). Here’s a brief overview of each type for clarity:
- Wireless Personal-Area Network (WPAN): This network is designed for interconnecting devices within a short range, typically within a person’s immediate vicinity (up to a few meters). Bluetooth and ZigBee are common technologies used in WPANs for connecting devices like smartphones, wireless headphones, keyboards, and smart home devices.
- Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN): WLANs provide wireless network communication over short distances, typically within a building or a small group of buildings. The most common technology used in WLANs is Wi-Fi.
- Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN): This type of network is designed to cover a city or a metropolitan area. It’s larger than a WLAN but smaller than a Wireless Wide-Area Network (WWAN).
- Wireless Wide-Area Network (WWAN): WWANs cover large geographic areas, often spanning cities or countries, using cellular network technologies. They are not typically associated with short-range technologies like Bluetooth or ZigBee.
In summary, for the use of Bluetooth or ZigBee devices, the appropriate type of network is a Wireless Personal-Area Network (WPAN).
-
Which type of wireless network uses transmitters to provide wireless service over a large urban region?
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless local-area network
- wireless wide-area network
- wireless personal-area network
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of wireless network that uses transmitters to provide wireless service over a large urban region is a Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN). Here’s a brief explanation of each network type:
- Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN): WMANs are designed to cover larger areas than a Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN), typically encompassing an urban region or a city. They are used to provide connectivity over a metropolitan area, linking multiple networks together within that region.
- Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN): WLANs are used to provide wireless network coverage within a smaller, localized area, such as within a home, school, or office building. The most common technology used in WLANs is Wi-Fi.
- Wireless Wide-Area Network (WWAN): WWANs cover very large geographic areas, such as cities, regions, or even entire countries, and are typically based on cellular network technologies. They offer broader coverage than WMANs but are not specifically designed just for urban areas.
- Wireless Personal-Area Network (WPAN): WPANs are for interconnecting devices within a very short range, usually within a few meters, and are not intended for urban-wide coverage. Common technologies used in WPANs include Bluetooth and ZigBee.
In summary, for covering a large urban region, the appropriate type of network is a Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN).
-
Which type of wireless network is suitable for use in a home or office?
- wireless local-area network
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless personal-area network
- wireless wide-area network
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of wireless network that is suitable for use in a home or office is a Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN). Here’s why:
- Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN): WLANs are designed to provide wireless network coverage within a smaller, localized area, such as within a home, office, or school. The most common technology used in WLANs is Wi-Fi. This allows devices like laptops, smartphones, tablets, and printers to connect wirelessly within a limited range, typically extending to the boundaries of a home or office space.
- Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN): This type of network covers larger areas than WLANs, typically encompassing an entire city or metropolitan area. It is more extensive than what is needed for home or office use.
- Wireless Personal-Area Network (WPAN): Although WPANs, using technologies like Bluetooth, are also used in homes and offices, they are meant for interconnecting devices over a much shorter range (a few meters), typically focusing on individual or small-scale personal use rather than providing a network for multiple devices over a larger area like a home or office.
- Wireless Wide-Area Network (WWAN): WWANs cover very large geographic areas, such as entire cities or regions, using technologies like cellular networks. They are much broader in scale compared to what is typically needed for a home or office environment.
In summary, a Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN) is the most suitable type of wireless network for home or office use, primarily due to its range and capacity to connect multiple devices in a localized area.
-
Which type of wireless network often makes use of devices mounted on buildings?
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless wide-area network
- wireless local-area network
- wireless personal-area network
-
Explanation & Hint: - Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN)
- Correct: WMANs often make use of devices mounted on buildings. These networks are designed to cover metropolitan areas and typically require the use of base stations or access points placed on tall structures, such as buildings or towers, to provide adequate coverage across the city.
- Incorrect: None. This is the correct answer.
- Wireless Wide-Area Network (WWAN)
- Correct: WWANs are designed to cover large geographic areas, such as entire cities or regions. However, they typically rely on cellular towers and infrastructure rather than building-mounted devices. So, the use of devices mounted on buildings is less common in WWANs.
- Incorrect: While WWANs can still provide wireless connectivity over a wide area, they are not primarily associated with devices mounted on buildings.
- Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN)
- Correct: WLANs are typically used within a limited geographic area, such as a home, office, or campus. They often make use of access points installed within buildings to provide wireless connectivity, but the emphasis is on local coverage.
- Incorrect: While WLANs can indeed involve devices inside buildings, they are not designed to cover metropolitan areas, so the use of devices mounted on buildings for city-wide coverage is not common.
- Wireless Personal-Area Network (WPAN)
- Correct: WPANs are the smallest type of wireless network, designed for short-range connections between personal devices. They do not require devices mounted on buildings.
- Incorrect: None. This is the correct answer.
In summary, the correct answer is “Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN)” because these networks often utilize devices mounted on buildings to provide wireless coverage over a city or metropolitan area. The other options are incorrect because they do not typically rely on building-mounted devices for their primary network infrastructure.
- Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN)
-
Which type of wireless network is suitable for national and global communications?
- wireless wide-area network
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless local-area network
- wireless personal-area network
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of wireless network that often makes use of devices mounted on buildings is a Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN). Here’s the rationale:
- Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN): WMANs are designed to cover larger areas, typically a city or metropolitan area. To achieve this coverage, they often use devices such as antennas or wireless transmitters/receivers mounted on buildings. This setup helps in providing network access across the urban landscape, connecting various local networks and offering wireless services over a metropolitan area.
- Wireless Wide-Area Network (WWAN): While WWANs also cover large areas (like cities or entire countries), they typically rely on cellular towers rather than devices mounted on individual buildings. WWANs provide broader coverage and are more focused on mobile and wide-ranging connectivity.
- Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN): WLANs, commonly implemented using Wi-Fi technology, are designed for smaller, localized areas such as homes, offices, or specific buildings. The equipment for WLANs is usually contained within the premises of the home or office, rather than mounted externally on buildings.
- Wireless Personal-Area Network (WPAN): WPANs are intended for very short-range personal or individual use, connecting devices like smartphones, headphones, and wearable tech. They don’t typically involve equipment mounted on buildings.
In summary, devices mounted on buildings are typically associated with Wireless Metropolitan-Area Networks (WMANs), as this setup helps them provide network coverage across urban or metropolitan areas.
-
Which type of wireless network uses transmitters to cover a medium-sized network, usually up to 300 feet (91.4 meters)?
- wireless local-area network
- wireless personal-area network
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless wide-area network
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of wireless network that uses transmitters to cover a medium-sized network, usually up to 300 feet (91.4 meters), is a Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN). Here’s a brief overview:
- Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN): WLANs are designed to cover a relatively small area like a home, office, or a building. The most common technology used in WLANs is Wi-Fi. This type of network typically provides coverage up to 300 feet, which is ideal for these kinds of environments.
- Wireless Personal-Area Network (WPAN): WPANs are meant for very short-range personal or individual use, connecting devices over a range of only a few meters. Technologies like Bluetooth and ZigBee are common in WPANs.
- Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN): WMANs are designed to cover larger areas than WLANs, typically a city or metropolitan area. They extend well beyond the 300 feet range of a typical WLAN.
- Wireless Wide-Area Network (WWAN): WWANs cover very large geographic areas, like cities, regions, or even entire countries, and use cellular network technologies. They provide much broader coverage than a WLAN.
In summary, for coverage up to 300 feet, the suitable type of network is a Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN).
-
Which type of wireless network is based on the 802.11 standard and a 2.4-GHz or 5-GHz radio frequency?
- wireless local-area network
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless personal-area network
- wireless wide-area network
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of wireless network that is based on the 802.11 standard and operates on a 2.4-GHz or 5-GHz radio frequency is a Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN). Here’s why:
- Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN): WLANs, commonly known as Wi-Fi networks, are based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards. These networks operate primarily on two frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. WLANs are designed to provide wireless network coverage within a limited area such as a home, office, or campus.
- Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN): WMANs are designed to cover larger areas than WLANs, typically a city or metropolitan area. They are not specifically tied to the 802.11 standards or the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands.
- Wireless Personal-Area Network (WPAN): WPANs, such as those using Bluetooth or ZigBee technologies, are for very short-range personal use. They also operate on different standards and frequencies, typically not using 802.11 standards.
- Wireless Wide-Area Network (WWAN): WWANs cover very large geographic areas, using technologies like cellular networks. They operate on different standards and frequencies than the 802.11 standard.
In summary, a Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN), commonly known as Wi-Fi, is the type of wireless network that uses the 802.11 standard and operates on 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz radio frequencies.
-
Which type of wireless network is suitable for providing wireless access to a city or district?
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless local-area network
- wireless wide-area network
- wireless personal-area network
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of wireless network that is suitable for providing wireless access to a city or district is a Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN). Here’s a brief explanation:
- Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN): WMANs are designed to cover larger areas than Wireless Local-Area Networks (WLANs), typically spanning an entire city or metropolitan area. They are used for connecting multiple wireless LANs and providing network access across a larger urban area.
- Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN): WLANs are used to provide wireless network coverage within a smaller, localized area, such as within a home, office, or specific building. They are not designed to cover city-wide areas.
- Wireless Wide-Area Network (WWAN): WWANs cover very large geographic areas, such as entire regions or countries, and are typically based on cellular network technologies. While they also cover cities, they are broader in scope than WMANs.
- Wireless Personal-Area Network (WPAN): WPANs are for interconnecting devices within a very short range, usually within a person’s immediate vicinity, and are not intended for city-wide coverage. Technologies like Bluetooth are common in WPANs.
In summary, for providing wireless access across a city or district, the appropriate type of network is a Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN).
-
Which type of wireless network uses low powered transmitters for a short-range network, usually 20 to 30 ft. (6 to 9 meters)?
- wireless personal-area network
- wireless local-area network
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless wide-area network
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of wireless network that uses low powered transmitters for a short-range network, usually spanning 20 to 30 feet (6 to 9 meters), is a Wireless Personal-Area Network (WPAN). Here’s a brief overview:
- Wireless Personal-Area Network (WPAN): WPANs are designed for very short-range communications, typically within the range of a person’s immediate area (about 6 to 9 meters). Technologies like Bluetooth and ZigBee are common examples of WPANs, used for connecting devices such as smartphones, headsets, and wearable devices.
- Wireless Local-Area Network (WLAN): WLANs, like those using Wi-Fi technology, are designed for slightly larger areas such as homes, offices, or buildings. They typically cover a range larger than WPANs, often up to 100 meters.
- Wireless Metropolitan-Area Network (WMAN): WMANs are intended to cover large urban areas, like cities or metropolitan regions, much larger than the range of a WPAN.
- Wireless Wide-Area Network (WWAN): WWANs cover very large geographic areas, often spanning cities, regions, or even countries. They use cellular network technologies and have a much broader range than WPANs.
In summary, for a network with a short range of about 20 to 30 feet, the suitable type is a Wireless Personal-Area Network (WPAN).
-
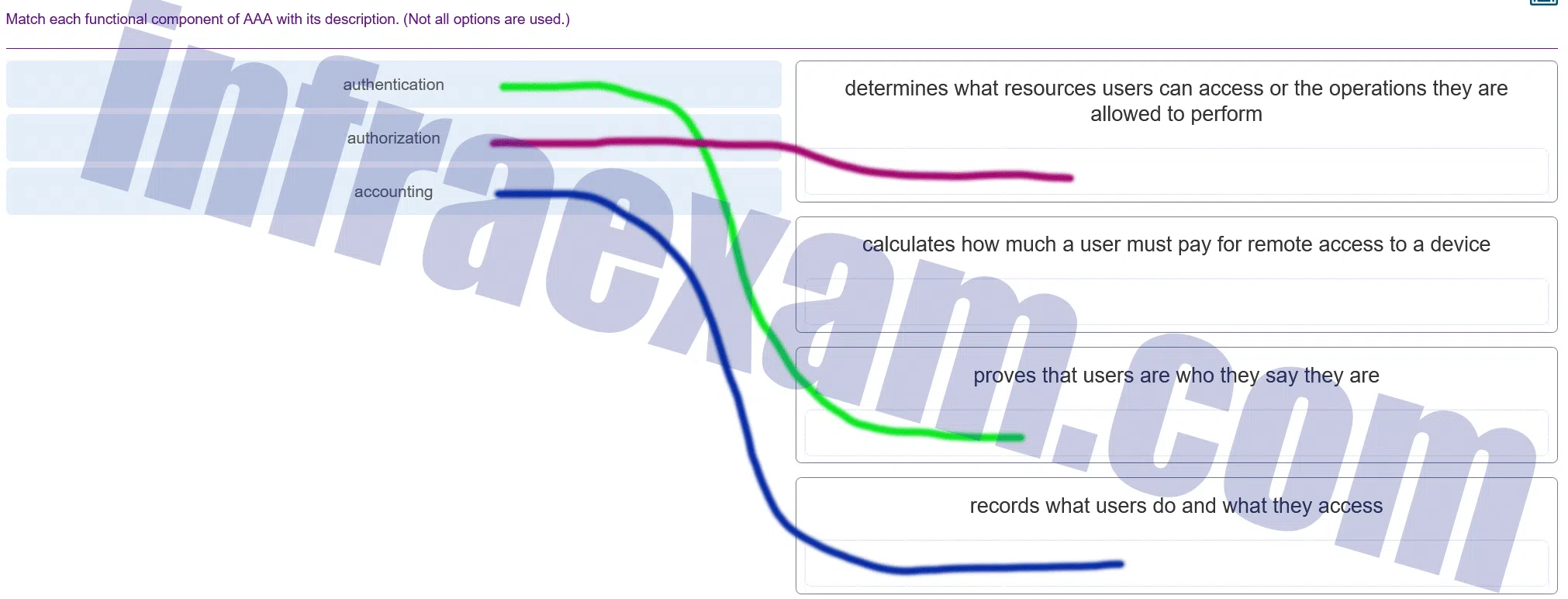
Match each functional component of AAA with its description. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 10 – 13 – L2 Security and WLANs Exam Answers 001 -
Explanation & Hint: - Authentication: This is the process that proves that users are who they say they are. It typically involves verifying a user’s identity through methods such as passwords, biometrics, tokens, etc.
- Authorization: This component determines what resources users can access or the operations they are allowed to perform. Once a user is authenticated, authorization dictates what they are allowed to do on the network.
- Accounting: This process records what users do and what they access. It often involves collecting data on user activities, such as start and stop times of sessions, executed commands, used network resources, and other activities for the purpose of billing, auditing, and reporting.
-
-
Which two Cisco solutions help prevent DHCP starvation attacks? (Choose two.)
- Port Security
- IP Source Guard
- DHCP Snooping
- Web Security Appliance
- Dynamic ARP Inspection
Answers Explanation & Hints: Cisco provides solutions to help mitigate Layer 2 attacks including these:
IP Source Guard (IPSG) – prevents MAC and IP address spoofing attacks
Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) – prevents ARP spoofing and ARP poisoning attacks
DHCP Snooping – prevents DHCP starvation and SHCP spoofing attacks
Port Security – prevents many types of attacks including MAC table overflow attacks and DHCP starvation attacks
Web Security Appliance (WSA) is a mitigation technology for web-based threats.
-
What are three techniques for mitigating VLAN attacks? (Choose three.)
- Disable DTP.
- Enable trunking manually.
- Set the native VLAN to an unused VLAN.
- Enable BPDU guard.
- Enable Source Guard.
- Use private VLANs.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Mitigating a VLAN attack can be done by disabling Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP), manually setting ports to trunking mode, and by setting the native VLAN of trunk links to VLANs not in use.
-
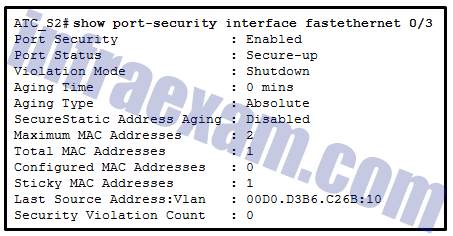
Refer to the exhibit. What can be determined about port security from the information that is shown?
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 10 – 13 – L2 Security and WLANs Exam Answers 03 - The port has been shut down.
- The port has two attached devices.
- The port violation mode is the default for any port that has port security enabled.
- The port has the maximum number of MAC addresses that is supported by a Layer 2 switch port which is configured for port security.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The Port Security line simply shows a state of Enabled if the switchport port-security command (with no options) has been entered for a particular switch port. If a port security violation had occurred, a different error message appears such as Secure-shutdown . The maximum number of MAC addresses supported is 50. The Maximum MAC Addresses line is used to show how many MAC addresses can be learned (2 in this case). The Sticky MAC Addresses line shows that only one device has been attached and learned automatically by the switch. This configuration could be used when a port is shared by two cubicle-sharing personnel who bring in separate laptops.
-
A network administrator of a college is configuring the WLAN user authentication process. Wireless users are required to enter username and password credentials that will be verified by a server. Which server would provide such service?
- AAA
- NAT
- SNMP
- RADIUS
Answers Explanation & Hints: Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) is a protocol and server software that provides user-based authentication for an organization. When a WLAN is configured to use a RADIUS server, users will enter username and password credentials that are verified by the RADIUS server before allowing to the WLAN.
-
A technician is troubleshooting a slow WLAN that consists of 802.11b and 802.11g devices . A new 802.11n/ac dual-band router has been deployed on the network to replace the old 802.11g router. What can the technician do to address the slow wireless speed?
- Change the SSID.
- Configure devices to use a different channel.
- Split the wireless traffic between the 802.11n 2.4 GHz band and the 5 GHz band.
- Update the firmware on the new router.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Splitting the wireless traffic between the 802.11n 2.4 GHz band and the 5 GHz band will allow for the 802.11n to use the two bands as two separate wireless networks to help manage the traffic, thus improving wireless performance.
-
The company handbook states that employees cannot have microwave ovens in their offices. Instead, all employees must use the microwave ovens located in the employee cafeteria. What wireless security risk is the company trying to avoid?
- accidental interference
- improperly configured devices
- interception of data
- rogue access points
Answers Explanation & Hints: Denial of service attacks can be the result of improperly configured devices which can disable the WLAN. Accidental interference from devices such as microwave ovens and cordless phones can impact both the security and performance of a WLAN. Man-in-the-middle attacks can allow an attacker to intercept data. Rogue access points can allow unauthorized users to access the wireless network.
-
What is the function provided by CAPWAP protocol in a corporate wireless network?
- CAPWAP provides the encapsulation and forwarding of wireless user traffic between an access point and a wireless LAN controller.
- CAPWAP provides the encryption of wireless user traffic between an access point and a wireless client.
- CAPWAP provides connectivity between an access point using IPv6 addressing and a wireless client using IPv4 addressing.
- CAPWAP creates a tunnel on Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) ports in order to allow a WLC to configure an autonomous access point.
Answers Explanation & Hints: CAPWAP is an IEEE standard protocol that enables a WLC to manage multiple APs and WLANs. CAPWAP is also responsible for the encapsulation and forwarding of WLAN client traffic between an AP and a WLC.
-
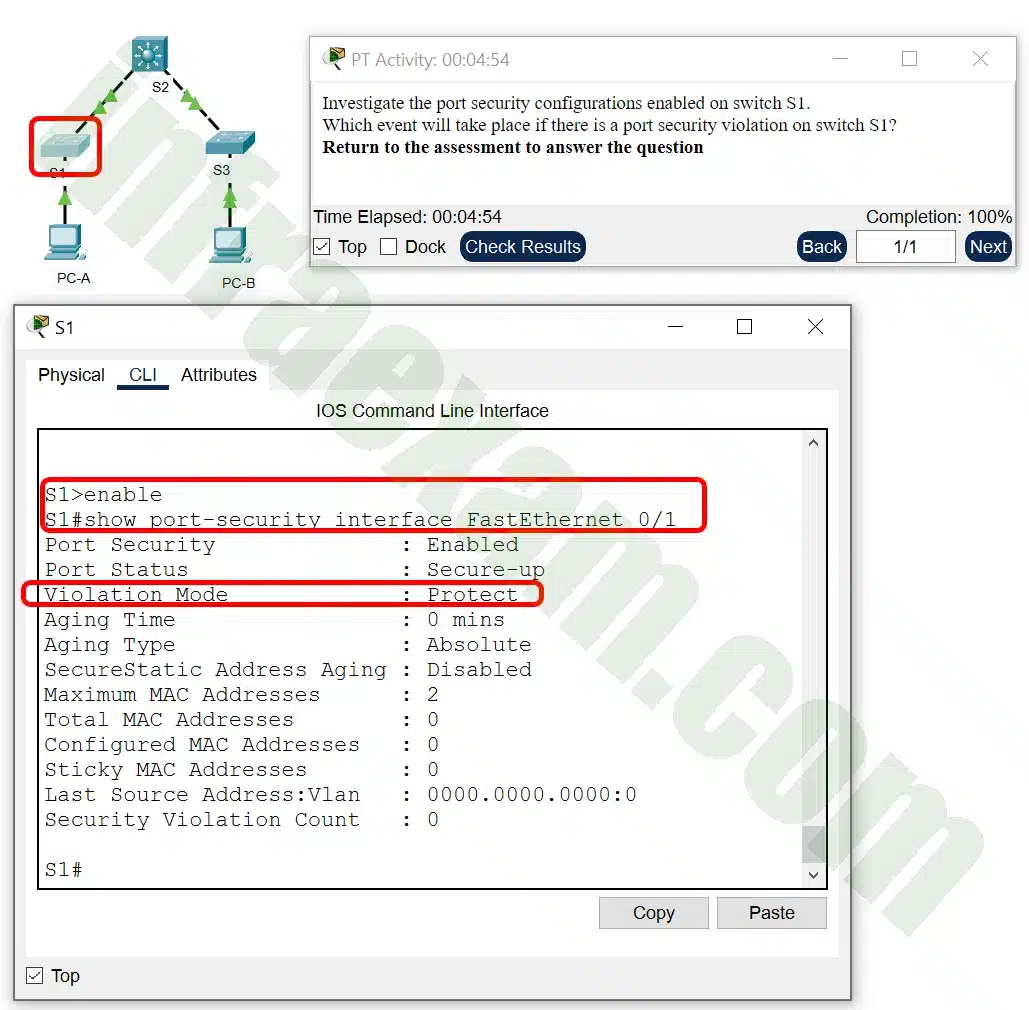
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
CCNA 2 SRWE v7 Modules 10 – 13 – L2 Security and WLANs Exam Answers PT 001 Which event will take place if there is a port security violation on switch S1 interface Fa0/1?
- A notification is sent.
- A syslog message is logged.
- Packets with unknown source addresses will be dropped.
- The interface will go into error-disabled state.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The violation mode can be viewed by issuing the show port-security interface <int> command. Interface FastEthernet 0/1 is configured with the violation mode of protect. If there is a violation, interface FastEthernet 0/1 will drop packets with unknown MAC addresses.
| CCNA 2 v7 & 7.02 | |
| Final Exam Answers | |
| This Modules 10 - 13 | |
| Modules 10 - 13 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Next Modules 14 - 16 | |
| Modules 14 - 16 Exam Answers | Online Test |