CCNA 3 v7 – ENSA v7.02 Final Exam Answers 2025 Full 100%
CCNA 3 v7 – ENSA v7.02 Final Exam Answers 2025 Full 100%
The Cisco NetAcad CCNA 3 ENSA v7.02: Enterprise Networking, Security, and Automation Final Exam Answers is a critical assessment for students pursuing the CCNA 3 v7 Final Answers Key. This exam tests knowledge in advanced networking concepts, including WAN technologies, VPNs, network security, automation, and programmability. Mastering these topics is essential for IT professionals aiming to build and secure enterprise networks. In this guide, we provide the latest and verified answers for the 2025 ENSA Final Exam, helping you prepare effectively and enhance your understanding of key networking principles.
Cisco Netacad ENSA Version 7.00 CCNA 3 v7 ENSA v7.02 Final Exam Answers 2025 Enterprise Networking, Security, and Automation
-
What functionality does mGRE provide to the DMVPN technology?
- It allows the creation of dynamically allocated tunnels through a permanent tunnel source at the hub and dynamically allocated tunnel destinations at the spokes.
- It provides secure transport of private information over public networks, such as the Internet.
- It creates a distributed mapping database of public IP addresses for all VPN tunnel spokes.
- It is a Cisco software solution for building multiple VPNs in an easy, dynamic, and scalable manner.
Explanation & Hint: DMVPN is built on three protocols, NHRP, IPsec, and mGRE. NHRP is the distributed address mapping protocol for VPN tunnels. IPsec encrypts communications on VPN tunnels. The mGRE protocol allows the dynamic creation of multiple spoke tunnels from one permanent VPN hub.
-
Which statement accurately describes a characteristic of IPsec?
- IPsec works at the transport layer and protects data at the network layer.
- IPsec works at the application layer and protects all application data.
- IPsec is a framework of open standards that relies on existing algorithms.
- IPsec is a framework of standards developed by Cisco that relies on OSI algorithms.
- IPsec is a framework of proprietary standards that depend on Cisco specific algorithms.
-
Explanation & Hint: The statement that accurately describes a characteristic of IPsec is:
IPsec is a framework of open standards that relies on existing algorithms.
IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) is indeed a framework of open, non-proprietary standards developed to ensure private, secure communications over Internet Protocol (IP) networks through the use of cryptographic security services. IPsec supports network-level peer authentication, data-origin authentication, data integrity, data confidentiality (encryption), and replay protection. It utilizes a suite of existing cryptographic algorithms for these purposes, rather than relying on proprietary or Cisco-specific algorithms.
The other statements are inaccurate for the following reasons:
- IPsec works at the transport layer and protects data at the network layer: This statement is partially correct but misleading. IPsec primarily operates at the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model, not the transport layer (Layer 4). It is designed to secure IP communications, providing protection for the entire IP packet.
- IPsec works at the application layer and protects all application data: This is incorrect. IPsec operates at the network layer, not the application layer, and it secures IP packets, not application data specifically.
- IPsec is a framework of standards developed by Cisco that relies on OSI algorithms: IPsec is not a Cisco-specific framework; it is an open standard. Additionally, it does not rely on “OSI algorithms” but rather on a range of cryptographic algorithms.
- IPsec is a framework of proprietary standards that depend on Cisco specific algorithms: This statement is incorrect. IPsec is an open standard and does not depend on proprietary or Cisco-specific algorithms.
-
Which type of API would be used to allow authorized salespeople of an organization access to internal sales data from their mobile devices?
- public
- open
- private
- partner
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of API that would be used to allow authorized salespeople of an organization access to internal sales data from their mobile devices is typically a private API.
Private APIs are designed for use within an organization and are not exposed to external users. These APIs are intended to improve internal development and operational efficiency by enabling different systems within an organization to communicate with each other. In this scenario, where the salespeople are part of the organization and need to access internal sales data securely, a private API would be appropriate as it ensures controlled access to sensitive internal data.
Other types of APIs have different intended uses:
- Public APIs are openly available to developers and other users outside the organization. They are designed for external users to interact with services provided by the organization but are not typically used for internal data access due to security concerns.
- Open APIs are similar to public APIs; they are publicly available and can be used by external developers. The term “open” often refers to the API being open-source or following open standards.
- Partner APIs are shared externally but only with specific business partners and not the general public. These APIs are used to facilitate business-to-business interactions and are more controlled than public or open APIs but are not intended for internal use only.
Given the requirement for internal access by authorized personnel, a private API would be the most secure and appropriate choice.
-
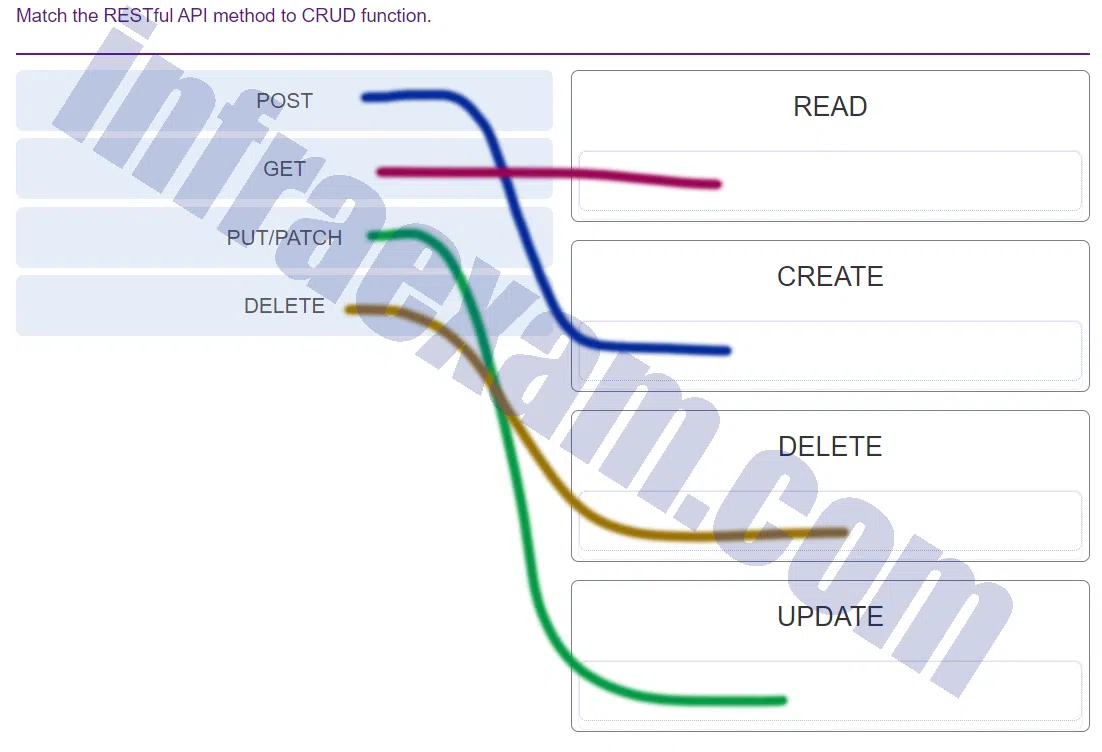
Match the RESTful API method to CRUD function.
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 001 Explanation & Hint: - POST: This method is used to CREATE a new resource.
- GET: This method is used to READ or retrieve a resource.
- PUT/PATCH: These methods are used to UPDATE an existing resource. PUT is often used when updating the entire resource, while PATCH is used for partial updates.
- DELETE: This method is used to DELETE a resource.
-
What are two syntax rules for writing a JSON array? (Choose two.)
- Each value in the array is separated by a comma.
- A semicolon separates the key and list of values.
- The array can include only one value type.
- Values are enclosed in square brackets.
- A space must separate each value in the array.
-
Explanation & Hint: When writing a JSON array, the following two syntax rules apply:
- Each value in the array is separated by a comma.
- Values are enclosed in square brackets.
To clarify further:
- Values within a JSON array are separated by commas. This is how the array denotes the end of one value and the beginning of another.
- A JSON array is always enclosed in square brackets
[]. This is the fundamental syntax that defines the start and end of an array in JSON.
The other statements are incorrect based on JSON syntax rules:
- A semicolon separates the key and list of values. This is incorrect. In JSON, a colon separates keys from their values within objects, not arrays. And in arrays, there are no keys, just a list of values.
- The array can include only one value type. This is incorrect. A JSON array can include multiple value types; for example, it can contain strings, numbers, objects, arrays, booleans, and nulls all in the same array.
- A space must separate each value in the array. This is incorrect. While spaces can improve readability, they are not required by JSON syntax. Values can be separated by commas without spaces, and JSON parsers will still be able to read the data correctly.
-
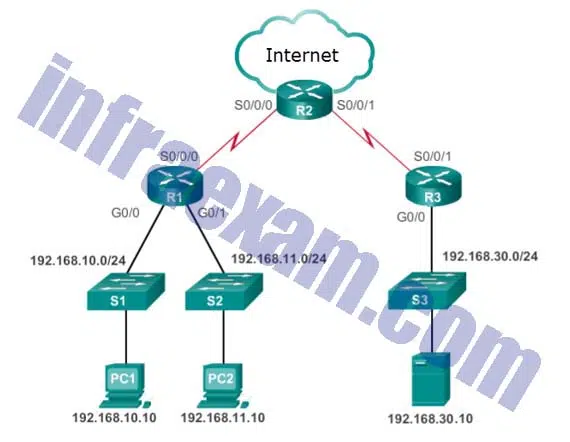
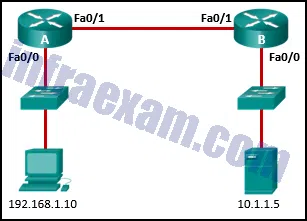
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to configure PAT on R1, but PC-A is unable to access the Internet. The administrator tries to ping a server on the Internet from PC-A and collects the debugs that are shown in the exhibit. Based on this output, what is most likely the cause of the problem?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 08 - The address on Fa0/0 should be 64.100.0.1.
- The inside and outside NAT interfaces have been configured backwards.
- The inside global address is not on the same subnet as the ISP.
- The NAT source access list matches the wrong address range.
Explanation & Hint: The output of debug ip nat shows each packet that is translated by the router. The “s” is the source IP address of the packet and the “d” is the destination. The address after the arrow (“->”) shows the translated address. In this case, the translated address is on the 209.165.201.0 subnet but the ISP facing interface is in the 209.165.200.224/27 subnet. The ISP may drop the incoming packets, or might be unable to route the return packets back to the host because the address is in an unknown subnet.
-
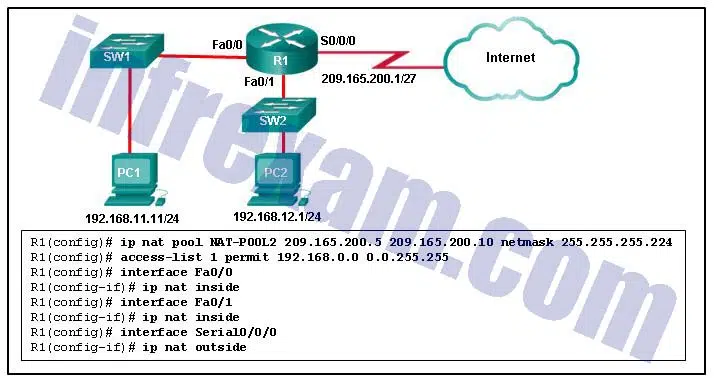
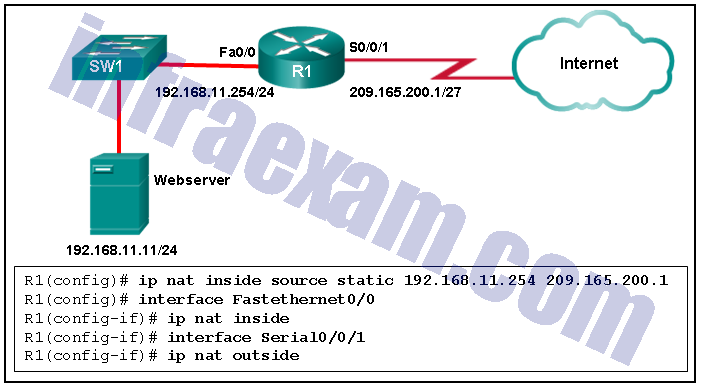
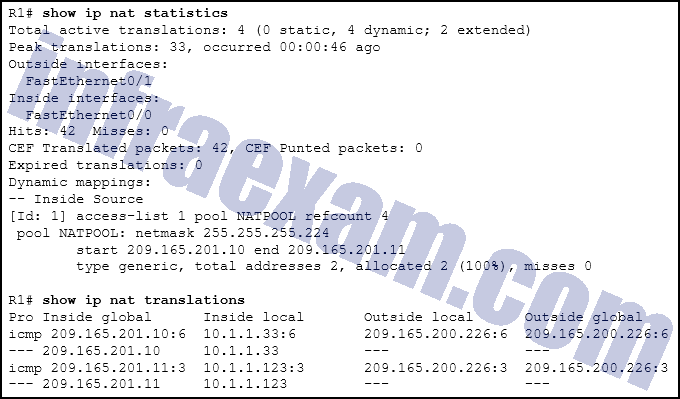
Refer to the exhibit. R1 is configured for NAT as displayed. What is wrong with the configuration?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 02 - Access-list 1 is misconfigured.
- The NAT pool is incorrect.
- NAT-POOL2 is not bound to ACL 1.
- Interface Fa0/0 should be identified as an outside NAT interface.
Explanation & Hint: R1 has to have NAT-POOL2 bound to ACL 1. This is accomplished with the command R1(config)#ip nat inside source list 1 pool NAT-POOL2. This would enable the router to check for all interesting traffic and if it matches ACL 1 it would be translated by use of the addresses in NAT-POOL2.
-
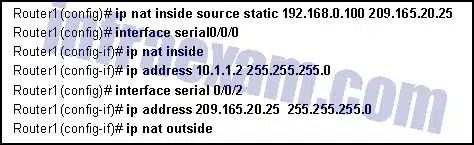
Refer to the exhibit. What is the purpose of the command marked with an arrow shown in the partial configuration output of a Cisco broadband router?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 08 - defines which addresses are assigned to a NAT pool
- defines which addresses are allowed into the router
- defines which addresses are allowed out of the router
- defines which addresses can be translated
-
Explanation & Hint: The command marked with an arrow in the exhibit is:
access-list 102 permit ip 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 anyIn the context of the configuration output for a Cisco router, this command serves as an access control list (ACL) rule. The purpose of this specific command is to define which addresses can be translated using Network Address Translation (NAT).
Here’s a breakdown of the command:
access-list 102: This specifies the ACL number 102.permit: This action allows the traffic to pass through the router.ip: This indicates that the rule applies to IP traffic.10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255: This specifies the source network as 10.10.10.0 with a subnet mask of 0.0.0.255, which corresponds to the range of IP addresses from 10.10.10.0 to 10.10.10.255.any: This means the rule applies to traffic going to any destination.
This ACL is then referenced by the NAT configuration line:
ip nat inside source list 102 interface fastethernet 0/1 overloadThis line tells the router to perform NAT for any IP addresses on the inside network that match the ACL 102, translating them to the IP address assigned to the FastEthernet 0/1 interface, and to use PAT (Port Address Translation) to allow multiple inside addresses to share the single outside IP address, indicated by the
overloadkeyword.
-
A network administrator is writing a standard ACL that will deny any traffic from the 172.16.0.0/16 network, but permit all other traffic. Which two commands should be used? (Choose two.)
- Router(config)# access-list 95 permit any
- Router(config)# access-list 95 host 172.16.0.0
- Router(config)# access-list 95 172.16.0.0 255.255.255.255
- Router(config)# access-list 95 deny 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255
- Router(config)# access-list 95 deny 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0
- Router(config)# access-list 95 deny any
Explanation & Hint: To deny traffic from the 172.16.0.0/16 network, the access-list 95 deny 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 command is used. To permit all other traffic, the access-list 95 permit any statement is added.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator needs to add an ACE to the TRAFFIC-CONTROL ACL that will deny IP traffic from the subnet 172.23.16.0/20. Which ACE will meet this requirement?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 07 - 15 deny 172.23.16.0 0.0.15.255
- 30 deny 172.23.16.0 0.0.15.255
- 5 deny 172.23.16.0 0.0.255.255
- 5 deny 172.23.16.0 0.0.15.255
Explanation & Hint: The only filtering criteria specified for a standard access list is the source IPv4 address. The wild card mask is written to identify what parts of the address to match, with a 0 bit, and what parts of the address should be ignored, which a 1 bit. The router will parse the ACE entries from lowest sequence number to highest. If an ACE must be added to an existing access list, the sequence number should be specified so that the ACE is in the correct place during the ACL evaluation process.
-
If a router has two interfaces and is routing both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic, how many ACLs could be created and applied to it?
- 6
- 16
- 8
- 4
- 12
Explanation & Hint: In calculating how many ACLs can be configured, use the rule of “three Ps”: one ACL per protocol, per direction, per interface. In this case, 2 interfaces x 2 protocols x 2 directions yields 8 possible ACLs.
-
Which three statements are generally considered to be best practices in the placement of ACLs? (Choose three.)
- For every inbound ACL placed on an interface, there should be a matching outbound ACL.
- Place extended ACLs close to the source IP address of the traffic.
- Place standard ACLs close to the destination IP address of the traffic.
- Place standard ACLs close to the source IP address of the traffic.
- Filter unwanted traffic before it travels onto a low-bandwidth link.
- Place extended ACLs close to the destination IP address of the traffic.
Explanation & Hint: Extended ACLs should be placed as close as possible to the source IP address, so that traffic that needs to be filtered does not cross the network and use network resources. Because standard ACLs do not specify a destination address, they should be placed as close to the destination as possible. Placing a standard ACL close to the source may have the effect of filtering all traffic, and limiting services to other hosts. Filtering unwanted traffic before it enters low-bandwidth links preserves bandwidth and supports network functionality. Decisions on placing ACLs inbound or outbound are dependent on the requirements to be met.
-
What is the main function of a hypervisor?
- It is used by ISPs to monitor cloud computing resources.
- It is a device that synchronizes a group of sensors.
- It is software used to coordinate and prepare data for analysis.
- It is a device that filters and checks security credentials.
- It is used to create and manage multiple VM instances on a host machine.
-
Explanation & Hint: - It is used by ISPs to monitor cloud computing resources.
- This option is incorrect. Hypervisors are not specifically used by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to monitor cloud computing resources. ISPs may use various tools for monitoring and managing their network infrastructure, but hypervisors are primarily used in server environments for virtualization purposes, not for monitoring by ISPs.
- It is a device that synchronizes a group of sensors.
- This is also incorrect. A hypervisor is not a device for synchronizing sensors. Devices used for synchronizing sensors are typically part of an embedded system or Internet of Things (IoT) architecture, and they focus on coordinating inputs and outputs from various sensor arrays, which is different from the function of a hypervisor.
- It is software used to coordinate and prepare data for analysis.
- This option is not accurate. While hypervisors do manage resources and can be involved in systems that prepare data for analysis, their primary role is not data coordination or preparation. They are more about resource allocation and management for virtual machines rather than data processing or analytical tasks.
- It is a device that filters and checks security credentials.
- This is incorrect. Hypervisors are not devices used for filtering and checking security credentials. Security appliances or software like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and identity management solutions are typically responsible for security-related tasks like filtering and credential checking.
- It is used to create and manage multiple VM instances on a host machine.
- This is the correct answer. A hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine monitor (VMM), is software, firmware, or hardware that creates and manages virtual machines. It allows multiple operating systems to run on a single physical machine by abstracting the hardware and dividing it into distinct environments known as virtual machines. Each VM operates independently and is isolated from the others, providing an efficient way to utilize hardware resources and ensure security between different computing environments.
- It is used by ISPs to monitor cloud computing resources.
-
A data center has recently updated a physical server to host multiple operating systems on a single CPU. The data center can now provide each customer with a separate web server without having to allocate an actual discrete server for each customer. What is the networking trend that is being implemented by the data center in this situation?
- virtualization
- maintaining communication integrity
- BYOD
- online collaboration
-
Explanation & Hint: The main function of a hypervisor is:
It is used to create and manage multiple VM instances on a host machine.
A hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine monitor (VMM), is software that creates and runs virtual machines (VMs). It allows one host computer to support multiple guest VMs by virtually sharing its resources, such as memory and processing. There are two types of hypervisors: Type 1 (or bare-metal) hypervisors run directly on the host’s hardware to control the hardware and to manage guest operating systems, while Type 2 (or hosted) hypervisors run on a conventional operating system just like other computer programs.
-
What is used to pre-populate the adjacency table on Cisco devices that use CEF to process packets?
- the ARP table
- the DSP
- the FIB
- the routing table
-
Explanation & Hint: The adjacency table in Cisco devices that use Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) is pre-populated using the ARP table.
CEF uses two main components to forward packets:
- The Forwarding Information Base (FIB), which is conceptually similar to a routing table but contains the information that a router would use to forward an IP packet.
- The adjacency table, which maintains Layer 2 (L2) next-hop addresses for all FIB entries. This table is populated using the ARP table, which maps IP addresses to the MAC addresses of devices that are directly connected on the network. When CEF is enabled, the router uses ARP to find the L2 address that corresponds to the L3 address in the FIB. When a match is found, CEF adds this L2 address to the adjacency table.
The routing table is used to populate the FIB and not directly for the adjacency table. The DSP (Digital Signal Processor) is used in voice and video processing and is not related to packet forwarding or CEF.
-
Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router building a link-state database based on received LSAs?
- building the topology table
- selecting the router ID
- injecting the default route
- exchanging link-state advertisements
-
Explanation & Hint: Apologies for the confusion. In the context of link-state routing protocols such as OSPF, the process of building a link-state database (LSDB) from received LSAs is indeed akin to “building the topology table” in the sense that it is constructing a comprehensive view of the network topology.
So, for clarification:
In link-state routing, each router builds a database that represents the entire network’s topology. This is achieved by exchanging LSAs with all other routers in the same routing area. After all the routers have exchanged LSAs, each one has a complete and identical link-state database. From this database, a router constructs a shortest path tree with itself as the root. The LSDB effectively serves the role of a “topology table” by providing all the information necessary to understand the network layout and link states.
The term “topology table” is not commonly used in the strict context of link-state routing protocols like OSPF, where the term “link-state database” is more accurate. However, I understand the intention behind the term as used in your statement, and you are correct in saying that building the LSDB is a critical step in the OSPF operation, which could be seen as building a topology table of the network.
-
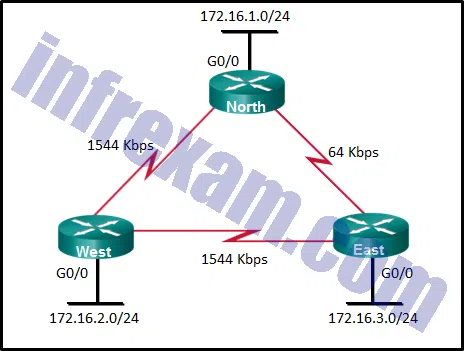
Refer to the exhibit. What is the OSPF cost to reach the West LAN 172.16.2.0/24 from East?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 06 - 782
- 74
- 128
- 65
-
Explanation & Hint:
-
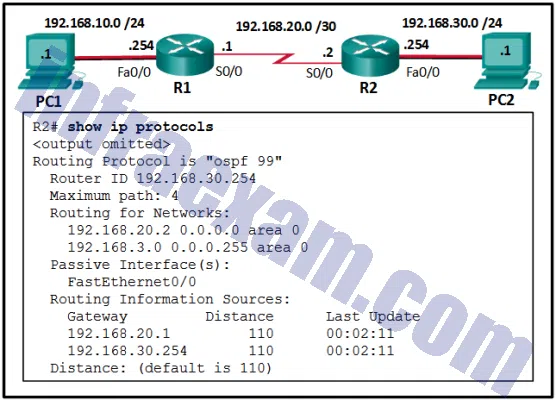
A network engineer has noted that some expected network route entries are not displayed in the routing table. Which two commands will provide additional information about the state of router adjacencies, timer intervals, and the area ID? (Choose two.)
- show running-configuration
- show ip route ospf
- show ip ospf interface
- show ip protocols
- show ip ospf neighbor
-
Explanation & Hint: To provide additional information about the state of router adjacencies, timer intervals, and the area ID in the context of OSPF, the following two commands would be most useful:
- show ip ospf interface: This command displays detailed information about OSPF-enabled interfaces on the router, including the state of the interface, its area ID, and timer intervals such as hello and dead intervals, which are critical for forming and maintaining OSPF adjacencies.
- show ip ospf neighbor: This command provides information on OSPF neighbor relationships. It shows the state of the adjacency with each neighbor, which is crucial for understanding why certain routes may not appear in the routing table.
The other commands have different primary purposes:
- show running-configuration: This command displays the current configuration on the router, which would not directly provide information about OSPF adjacencies or timer intervals unless specifically configured.
- show ip route ospf: This command displays the routes learned via OSPF, but it does not provide detailed information about OSPF adjacencies or OSPF-specific timers and area IDs.
- show ip protocols: This command provides a summary of the routing protocol configurations on the router, including timers and networks that OSPF is enabled on, but it does not show the state of OSPF adjacencies or detailed interface information.
Thus, for detailed OSPF adjacency state, area IDs, and timer intervals, “show ip ospf interface” and “show ip ospf neighbor” are the appropriate commands.
-
What is the final operational state that will form between an OSPF DR and a DROTHER once the routers reach convergence?
- full
- loading
- established
- two-way
-
Explanation & Hint: The final operational state that will form between an OSPF Designated Router (DR) and a DROTHER (a router that is neither a DR nor a BDR) once the routers reach convergence is Full.
In OSPF, “Full” is the state indicating that routers have completed the adjacency process and have full knowledge of each other’s databases. This means that they have exchanged and acknowledged all OSPF routing information, and the routers’ link-state databases are synchronized.
Here’s a brief overview of the states:
- Down: The initial state of OSPF neighbor formation. No information has been exchanged.
- Attempt: This is a state where the router has sent out OSPF Hello packets but has not received any Hello packets back from the neighbor. This state is only used in NBMA (Non-Broadcast Multi-Access) networks.
- Init: The router has received a Hello packet from its neighbor, but the receiving router’s ID was not included in the Hello packet.
- 2-Way: Bidirectional communication has been established between two routers. DR and BDR elections occur in this state.
- Exstart: DR and BDR establish a master-slave relationship and determine the sequence number for database exchange.
- Exchange: Routers send Database Description (DBD) packets to each other to exchange link-state database information.
- Loading: Routers are sending Link-State Request (LSR) and Link-State Update (LSU) packets to request and receive the actual OSPF routing information.
- Full: The routers have full knowledge of each other’s OSPF databases and are fully adjacent.
The “Established” state is not an OSPF state; it is more commonly associated with protocols like BGP (Border Gateway Protocol).
-
What protocol allows the manager to poll agents to access information from the agent MIB?
- SYSLOG
- CBWFQ
- SNMP
- TFTP
-
Explanation & Hint: The protocol that allows a manager to poll agents to access information from the agent’s Management Information Base (MIB) is SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol).
SNMP is used for network management and monitoring. A management system with SNMP capabilities can poll agents in network devices to collect information about their status and metrics, which is organized in a structured format called a MIB.
-
Which set of access control entries would allow all users on the 192.168.10.0/24 network to access a web server that is located at 172.17.80.1, but would not allow them to use Telnet?
- access-list 103 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 host 172.17.80.1
access-list 103 deny tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq telnet - access-list 103 deny tcp host 192.168.10.0 any eq 23
access-list 103 permit tcp host 192.168.10.1 eq 80 - access-list 103 permit tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 host 172.17.80.1 eq 80
access-list 103 deny tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq 23 - access-list 103 permit tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq 80
access-list 103 deny tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq 23Explanation & Hint: For an extended ACL to meet these requirements the following need to be included in the access control entries:identification number in the range 100-199 or 2000-2699
permit or deny parameter
- access-list 103 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 host 172.17.80.1
-
Which two things should a network administrator modify on a router to perform password recovery? (Choose two.)
- the startup configuration file
- system ROM
- the NVRAM file system
- the system image file
- the configuration register value
-
Explanation & Hint: To perform password recovery on a Cisco router, a network administrator typically needs to modify the following:
- The configuration register value: The configuration register setting on a Cisco router determines how the router boots up. By modifying the configuration register value, the router can be made to ignore the contents of the startup configuration file on the next reload, allowing the administrator to access the router without the need to input the password from the startup configuration.
- The startup configuration file: After changing the configuration register and restarting the router, the administrator will need to either modify the startup configuration file where the password is set or load the startup configuration into running configuration and change the password, depending on the specific password recovery process for the router model.
The system ROM, the NVRAM file system, and the system image file are not typically modified during the password recovery process. The system ROM contains the router’s boot-up instructions and basic diagnostic software; it’s not directly modified in password recovery. The NVRAM holds the router’s startup configuration file, which will be indirectly affected when the configuration register is changed to bypass this configuration on boot. The system image file contains the router’s operating system and is not altered for password recovery purposes.
-
Which statement describes a VPN?
- VPNs use logical connections to create public networks through the Internet.
- VPNs use dedicated physical connections to transfer data between remote users.
- VPNs use open source virtualization software to create the tunnel through the Internet.
- VPNs use virtual connections to create a private network through a public network.
Explanation & Hint: A VPN is a private network that is created over a public network. Instead of using dedicated physical connections, a VPN uses virtual connections routed through a public network between two network devices.
-
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator first configured an extended ACL as shown by the output of the show access-lists command. The administrator then edited this access-list by issuing the commands below.
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 04 Router(config)# ip access-list extended 101 Router(config-ext-nacl)# no 20 Router(config-ext-nacl)# 5 permit tcp any any eq 22 Router(config-ext-nacl)# 20 deny udp any any
Which two conclusions can be drawn from this new configuration? (Choose two.)
- Ping packets will be permitted.
- TFTP packets will be permitted.
- Telnet packets will be permitted.
- SSH packets will be permitted.
- All TCP and UDP packets will be denied.
Explanation & Hint: After the editing, the final configuration is as follows:
Router# show access-lists
Extended IP access list 101
5 permit tcp any any eq ssh
10 deny tcp any any
20 deny udp any any
30 permit icmp any any
So, only SSH packets and ICMP packets will be permitted.
-
In which step of gathering symptoms does the network engineer determine if the problem is at the core, distribution, or access layer of the network?
- Narrow the scope.
- Document the symptoms.
- Gather information.
- Determine the symptoms.
- Determine ownership.
Explanation & Hint: In the “narrow the scope” step of gathering symptoms, a network engineer will determine if the network problem is at the core, distribution, or access layer of the network. Once this step is complete and the layer is identified, the network engineer can determine which pieces of equipment are the most likely cause.
-
What type of network uses one common infrastructure to carry voice, data, and video signals?
- switched
- converged
- borderless
- managed
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of network that uses one common infrastructure to carry voice, data, and video signals is known as a converged network.
Converged networks are designed to deliver multiple types of communications such as telephone calls, video conferencing, emails, file sharing, and more over the same network infrastructure. This convergence allows for more efficient management of resources and can reduce operational costs.
-
What are three advantages of using private IP addresses and NAT? (Choose three.)
- improves the performance of the router that is connected to the Internet
- reduces CPU usage on customer routers
- permits LAN expansion without additional public IP addresses
- creates multiple public IP addresses
- conserves registered public IP addresses
- hides private LAN addressing from outside devices that are connected to the Internet
-
Explanation & Hint: Three advantages of using private IP addresses and Network Address Translation (NAT) are:
- Permits LAN expansion without additional public IP addresses: By using private IP address ranges within a LAN, organizations can create large networks without the need for a unique public IP address for each device.
- Conserves registered public IP addresses: NAT allows multiple devices on a private network to share a single public IP address when accessing the Internet, which helps in conserving the limited number of available public IP addresses.
- Hides private LAN addressing from outside devices that are connected to the Internet: NAT provides a level of security by masking the internal IP addresses of a network from the external Internet, effectively hiding the structure of the internal network.
The other options provided are not direct advantages of using private IP addresses and NAT:
- Improves the performance of the router that is connected to the Internet: NAT does not inherently improve the performance of a router. In fact, the translation process can add a small amount of processing overhead.
- Reduces CPU usage on customer routers: NAT can actually increase the CPU usage on a router because it has to translate between private and public IP addresses for packets passing through the device.
- Creates multiple public IP addresses: NAT does not create multiple public IP addresses; it allows multiple private IP addresses to be mapped to one or a few public IP addresses.
-
What is a characteristic of a single-area OSPF network?
- All routers have the same routing table.
- All routers have the same neighbor table.
- All routers share a common forwarding database.
- All routers are in the backbone area.
-
Explanation & Hint: In a single-area OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) network, a characteristic feature is that all routers are in the backbone area.
The backbone area in OSPF is also known as Area 0. In a single-area OSPF network, all routers belong to this Area 0. This is a defining characteristic of such a network because OSPF mandates that all areas must connect to the backbone area, and in a single-area network, there are no other areas.
The other statements are not accurate characteristics:
- All routers have the same routing table: While the routers in a single OSPF area do learn about the same networks, their routing tables may not be identical. The routing table of a router includes routes to each network along with the next hop to reach that network, which can differ from router to router depending on their location in the network.
- All routers have the same neighbor table: Routers in a single area do learn about each other, but their neighbor tables will differ. The neighbor table on an OSPF router lists only those routers to which it has formed an OSPF adjacency, which varies based on the router’s direct connections.
- All routers share a common forwarding database: While it’s true that all routers in an OSPF area share a common link-state database (not forwarding database), this statement is a bit misleading. The link-state database is used to compute the routing table, but the term “forwarding database” is not typically used in the context of OSPF.
-
Which statement describes a characteristic of standard IPv4 ACLs?
- They can be created with a number but not with a name.
- They can be configured to filter traffic based on both source IP addresses and source ports.
- They are configured in the interface configuration mode.
- They filter traffic based on source IP addresses only.
Explanation & Hint: A standard IPv4 ACL can filter traffic based on source IP addresses only. Unlike an extended ACL, it cannot filter traffic based on Layer 4 ports. However, both standard and extended ACLs can be identified with either a number or a name, and both are configured in global configuration mode.
-
Which two statements are characteristics of a virus? (Choose two.)
- A virus has an enabling vulnerability, a propagation mechanism, and a payload.
- A virus typically requires end-user activation.
- A virus replicates itself by independently exploiting vulnerabilities in networks.
- A virus can be dormant and then activate at a specific time or date.
- A virus provides the attacker with sensitive data, such as passwords.
Explanation & Hint: The type of end user interaction required to launch a virus is typically opening an application, opening a web page, or powering on the computer. Once activated, a virus may infect other files located on the computer or other computers on the same network.
-
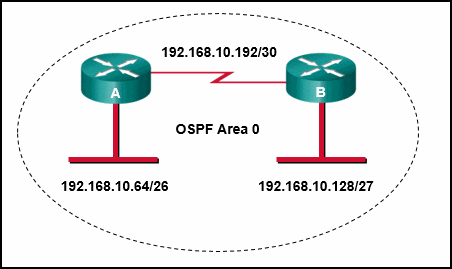
Refer to the exhibit. Which sequence of commands should be used to configure router A for OSPF?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 10 - router ospf 1
network 192.168.10.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
network 192.168.10.192 0.0.0.3 area 0 - router ospf 1
network 192.168.10.0 - router ospf 1
network 192.168.10.64 255.255.255.192
network 192.168.10.192 255.255.255.252 - router ospf 1
network 192.168.10.0 area 0 -
Explanation & Hint: To configure router A for OSPF with the network addresses shown in the exhibit, you’d need to use the following sequence of commands:
router ospf 1network 192.168.10.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
network 192.168.10.192 0.0.0.3 area 0
Here’s the breakdown:
- The
router ospf 1command starts OSPF configuration and assigns a process ID of 1. The process ID is locally significant to the router. - The
networkcommands are used to specify which interfaces will participate in OSPF. The addresses are the network addresses, and the numbers following them are wildcard masks. The wildcard mask is the inverse of the subnet mask. For a /26 subnet, the subnet mask is 255.255.255.192, which translates to a wildcard mask of 0.0.0.63. For a /30 subnet, the subnet mask is 255.255.255.252, which translates to a wildcard mask of 0.0.0.3. - Each
networkcommand is followed byarea 0, which assigns the interfaces to OSPF Area 0, as indicated in the diagram.
The other sequences of commands have either incomplete network statements, missing area designations, or incorrect wildcard masks.
- The
- router ospf 1
-
What are three benefits of cloud computing? (Choose three.)
- It streamlines the IT operations of an organization by subscribing only to needed services.
- It uses open-source software for distributed processing of large datasets.
- It utilizes end-user clients to do a substantial amount of data preprocessing and storage.
- It turns raw data into meaningful information by discovering patterns and relationships.
- It eliminates or reduces the need for onsite IT equipment, maintenance, and management.
- It enables access to organizational data anywhere and at any time.
-
Explanation & Hint: Three benefits of cloud computing are:
- It streamlines the IT operations of an organization by subscribing only to needed services: Cloud computing allows organizations to subscribe to and pay for only the services they need, often on a pay-as-you-go basis. This can lead to more efficient use of resources and cost savings.
- It eliminates or reduces the need for onsite IT equipment, maintenance, and management: With cloud computing, the cloud service provider is responsible for maintaining the data centers and infrastructure, which reduces the need for organizations to invest in and manage their own IT equipment.
- It enables access to organizational data anywhere and at any time: Cloud services are typically available over the Internet, which means that users can access applications and data from any location at any time, provided they have an Internet connection. This facilitates remote work and global collaboration.
The other options provided do not directly describe the benefits of cloud computing:
- It uses open-source software for distributed processing of large datasets: While cloud services can run open-source software and can be used for distributed processing, this is not a defining benefit of cloud computing itself.
- It utilizes end-user clients to do a substantial amount of data preprocessing and storage: Cloud computing typically involves processing and storing data in the cloud rather than on end-user clients.
- It turns raw data into meaningful information by discovering patterns and relationships: This is more descriptive of data analytics and big data processing capabilities, which can be performed in the cloud but are not benefits exclusive to cloud computing.
-
What is a WAN?
- a network infrastructure that provides access in a small geographic area
- a network infrastructure designed to provide data storage, retrieval, and replication
- a network infrastructure that spans a limited physical area such as a city
- a network infrastructure that provides access to other networks over a large geographic area
-
Explanation & Hint: A WAN, or Wide Area Network, is:
a network infrastructure that provides access to other networks over a large geographic area.
WANs are used to connect smaller networks, like local area networks (LANs) or metro area networks (MANs), across long distances, which can range from different cities to across the globe. WANs enable businesses and other organizations to communicate and share data regardless of the distance between their respective locations. The Internet is the largest WAN, as it is a vast network of networks connecting billions of computers worldwide.
-
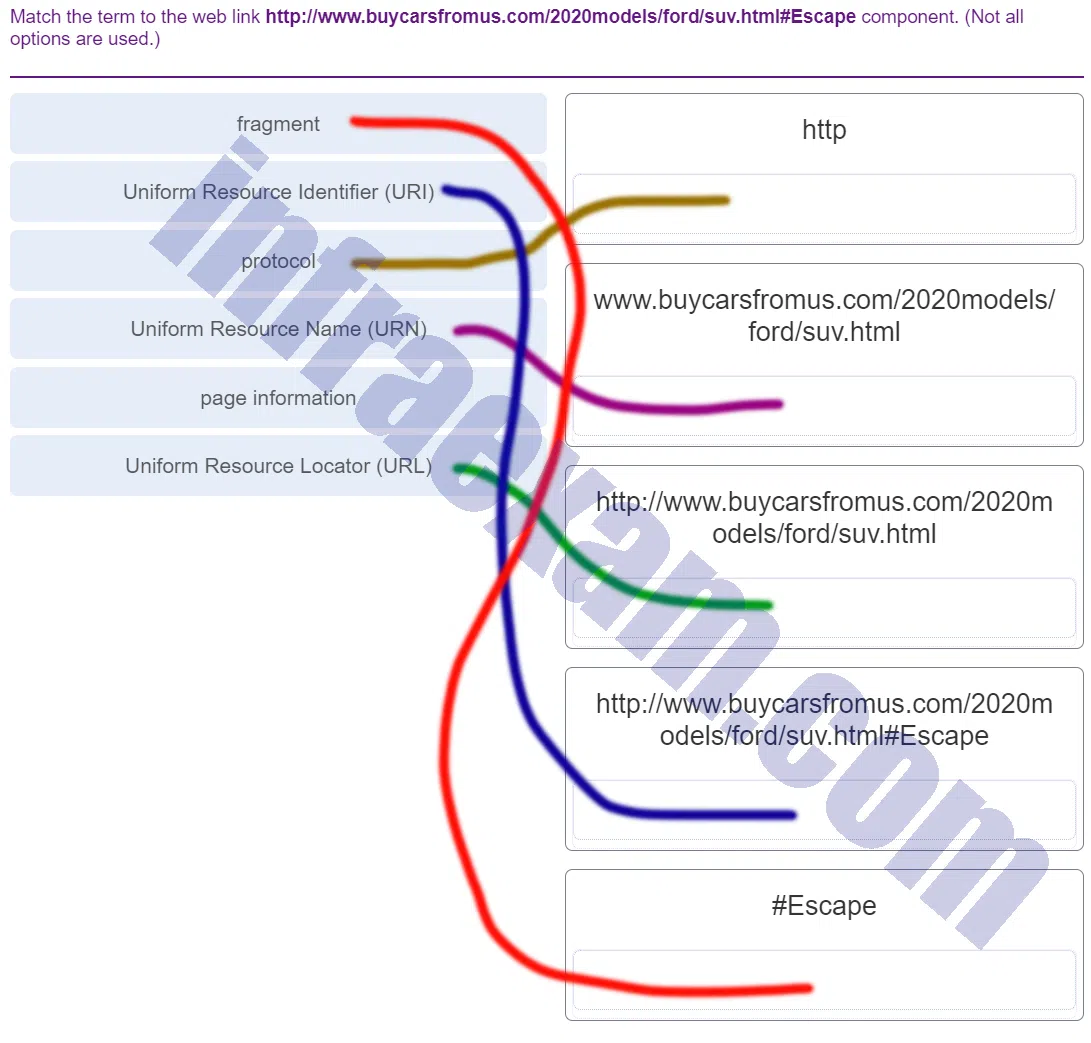
Match the term to the web link http://www.buycarsfromus.com/2020models/ford/suv.html#Escape component. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 002 Explanation & Hint: - Fragment: The fragment in this URL is
#Escape. It refers to a specific section within the webpagesuv.html. When this URL is accessed, the browser will attempt to locate and display the portion of the page marked with an ID of “Escape.” - Uniform Resource Identifier (URI): The entire string
http://www.buycarsfromus.com/2020models/ford/suv.html#Escapeis the URI. It uniquely identifies a resource on the internet – in this case, a particular section on a webpage dedicated to the “Escape” model of a Ford SUV. - Protocol: The protocol specified in this URL is
http. It defines the method used for data transfer between the web server and the client. “http” indicates that the Hypertext Transfer Protocol is used here. - Uniform Resource Name (URN): It would be
www.buycarsfromus.com/2020models/ford/suv.html. A URN is intended to serve as a persistent, location-independent resource identifier, and while a URL does provide a location, in the absence of a protocol and other access-specifying components, the remaining part serves as a unique name for the resource on the web. So, in this case, the combination of the domain and the path to the resource could be seen as a name that uniquely identifies the resource, even though it is not a URN in the strictest sense as defined by the URI standard.In the strictest sense, URNs are not typically used on the web like URLs are. They are part of the larger URI family and are used for resources that need persistent, location-independent identifiers, such as ISBNs for books or DOIs for academic papers. A URL, on the other hand, not only identifies a resource but also provides the means to locate it on the web. - Page Information: While not a standardized term, if we were to infer its meaning, the page information in this URL would be
/2020models/ford/suv.html, which provides the path to the specific page about the Ford SUV models, including the filesuv.htmlwhich is likely an HTML document. - Uniform Resource Locator (URL): The URL here is
http://www.buycarsfromus.com/2020models/ford/suv.html. This URL includes the protocol (http), the domain name (www.buycarsfromus.com), and the path to a specific page (/2020models/ford/suv.html) on that domain. It locates the web page where information about the Ford SUV models can be found. The fragment#Escapeis not typically considered part of the URL; instead, it is a secondary component that provides additional navigation within the page.
- Fragment: The fragment in this URL is
-
Which two scenarios are examples of remote access VPNs? (Choose two.)
- All users at a large branch office can access company resources through a single VPN connection.
- An employee who is working from home uses VPN client software on a laptop in order to connect to the company network.
- A toy manufacturer has a permanent VPN connection to one of its parts suppliers.
- A small branch office with three employees has a Cisco ASA that is used to create a VPN connection to the HQ.
- A mobile sales agent is connecting to the company network via the Internet connection at a hotel.
-
Explanation & Hint: Two scenarios that are examples of remote access VPNs are:
An employee who is working from home uses VPN client software on a laptop in order to connect to the company network.
- This is a classic example of a remote access VPN. Individual users, such as employees working from home, use client software on their devices to establish a secure connection to the company network over the internet. This type of VPN provides access to the company’s resources and services as if the user were physically present in the office.
A mobile sales agent is connecting to the company network via the Internet connection at a hotel.
- Similar to the first example, this scenario involves an individual user (a mobile sales agent) who connects to the company network using a VPN. The sales agent’s connection, which is made through a potentially insecure hotel internet service, is secured and encrypted by the VPN, allowing safe access to company resources.
The other scenarios described are not examples of remote access VPNs:
- The large branch office using a single VPN connection to access company resources is an example of a site-to-site VPN, not a remote access VPN.
- The permanent VPN connection between the toy manufacturer and its parts supplier is also an instance of a site-to-site VPN.
- The small branch office with a Cisco ASA creating a VPN connection to HQ is another example of a site-to-site VPN, used to connect entire networks to each other over the internet.
-
What is a purpose of establishing a network baseline?
- It creates a point of reference for future network evaluations.
- It provides a statistical average for network performance.
- It checks the security configuration of network devices.
- It manages the performance of network devices.
Explanation & Hint: A baseline is used to establish normal network or system performance. It can be used to compare with future network or system performances in order to detect abnormal situations.
-
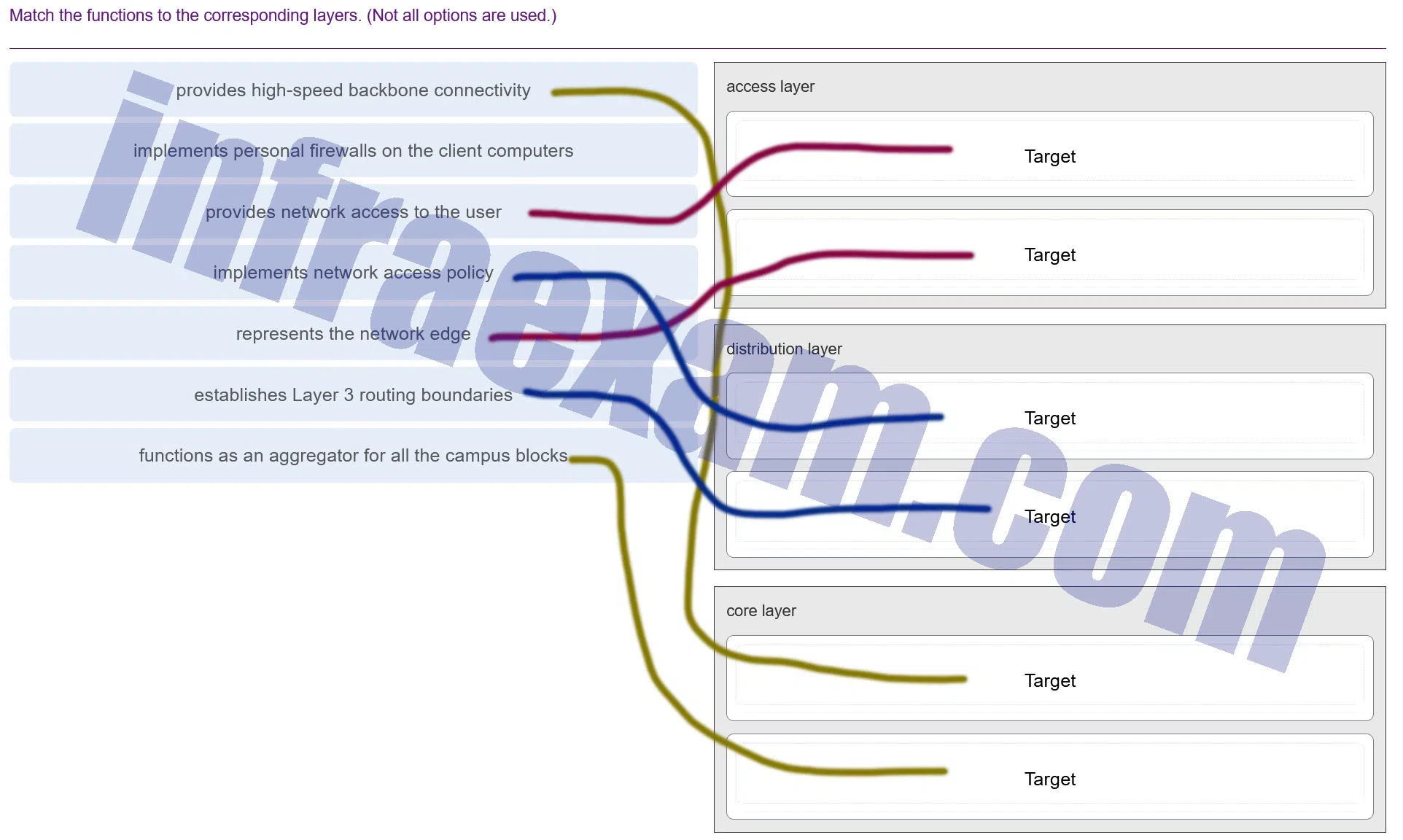
Match the functions to the corresponding layers. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 9 – 12 Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers 001 Explanation & Hint: In a typical three-tier network design, the functionalities would be distributed across the access, distribution, and core layers as follows:
- Access Layer:
- Provides network access to the user.
- Implements personal firewalls on the client computers (though this is more of a client-side security feature, it can be enforced at the access layer).
- Implements network access policy.
- Distribution Layer:
- Establishes Layer 3 routing boundaries.
- Functions as an aggregator for all the campus blocks.
- Represents the network edge.
- Core Layer:
- Provides high-speed backbone connectivity.
- Access Layer:
-
Why is QoS an important issue in a converged network that combines voice, video, and data communications?
- Data communications are sensitive to jitter.
- Data communications must be given the first priority.
- Legacy equipment is unable to transmit voice and video without QoS.
- Voice and video communications are more sensitive to latency.
Explanation & Hint: Without any QoS mechanisms in place, time-sensitive packets, such as voice and video, will be dropped with the same frequency as email and web browsing traffic.
-
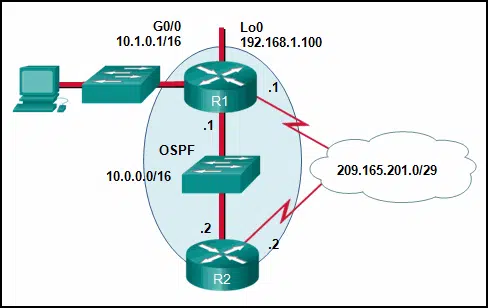
Refer to the exhibit. If no router ID was manually configured, what would router R1 use as its OSPF router ID?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 05 - 10.0.0.1
- 10.1.0.1
- 192.168.1.100
- 209.165.201.1
Explanation & Hint: In OSPF (Open Shortest Path First), the router ID is chosen based on one of the following methods, in order of preference:
- The router ID manually configured by an administrator.
- The highest IP address of any of the router’s active interfaces.
- The highest IP address of any of the router’s loopback interfaces.
If no router ID is manually configured, OSPF will choose the highest IP address of any of the router’s active interfaces. Since loopback interfaces are considered more stable (they are always up if configured), the IP address of a loopback interface is preferred over physical interfaces.
In the provided exhibit, we see the following IP addresses:
- G0/0: 10.1.0.1/16
- Lo0: 192.168.1.100
- The OSPF network: 10.0.0.0/16
- The external network: 209.165.201.1/29
Given these choices, the highest IP address on an active interface is 192.168.1.100, which is the IP address of the loopback interface Lo0. Therefore, router R1 would use 192.168.1.100 as its OSPF router ID.
-
Which type of OSPF packet is used by a router to discover neighbor routers and establish neighbor adjacency?
- link-state request
- hello
- database description
- link-state update
Explanation & Hint: In OSPF (Open Shortest Path First), the Hello packet is used by routers to discover neighbor routers on OSPF-enabled interfaces and to establish and maintain neighbor adjacencies. Hello packets are sent periodically on all OSPF interfaces, including virtual links, to establish and test the link to neighbors. If a router stops receiving Hello packets from a neighbor, after a specified interval, the neighbor relationship is considered down.
-
Which statement describes a characteristic of Cisco Catalyst 2960 switches?
- They are modular switches.
- New Cisco Catalyst 2960-C switches support PoE pass-through.
- They do not support an active switched virtual interface (SVI) with IOS versions prior to 15.x.
- They are best used as distribution layer switches.
Explanation & Hint: Cisco Catalyst 2960 switches are fixed-configuration switches, meaning they are not modular and do not allow for the addition or swapping of modules like some other types of switches do. Here are the characteristics of the Cisco Catalyst 2960 switches based on your options:
They are modular switches.
- This statement is incorrect. Cisco Catalyst 2960 switches are not modular but fixed-configuration switches.
New Cisco Catalyst 2960-C switches support PoE pass-through.
- This statement is correct. Some models of the Cisco Catalyst 2960-C series switches support Power over Ethernet (PoE) pass-through, which allows them to pass power to downstream devices such as IP phones or wireless access points without needing a separate power supply for those devices.
They do not support an active switched virtual interface (SVI) with IOS versions prior to 15.x.
- This statement is generally incorrect. Cisco Catalyst 2960 switches do support an active SVI in earlier IOS versions, but with some limitations on certain models or configurations. The SVI is used for managing the switch over the network.
They are best used as distribution layer switches.
- This statement is incorrect. Cisco Catalyst 2960 switches are typically used at the access layer within a hierarchical network design. They are designed to provide network connectivity and access to end devices rather than serve as distribution layer switches, which typically require more advanced features and higher performance.
The most accurate description of Cisco Catalyst 2960 switches from the given options is that the new 2960-C models support PoE pass-through.
-
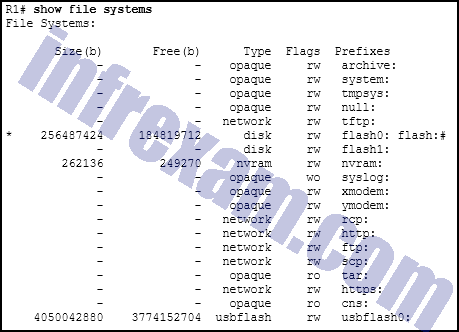
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to back up the current running configuration of the router to a USB drive, and enters the command copy usbflash0:/R1-config running-config on the router command line. After removing the USB drive and connecting it to a PC, the administrator discovers that the running configuration was not properly backed up to the R1-config file. What is the problem?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 01 - There is no space left on the USB drive.
- The file already exists on the USB drive and cannot be overwritten.
- The drive was not properly formatted with the FAT16 file system.
- The USB drive is not recognized by the router.
- The command that the administrator used was incorrect.
Explanation & Hint: Based on the information provided, the administrator’s command was intended to back up the router’s running configuration to a file on a USB drive. The command used was
copy usbflash0:/R1-config running-config. However, the correct syntax to copy the running configuration to a file on a USB drive should be the opposite; it should start from the source file and then specify the destination file. Thus, the command should becopy running-config usbflash0:/R1-config.In the
copycommand, the first part is the source, and the second part is the destination. So if the administrator wanted to back up the running configuration of the router to a file named “R1-config” on the USB drive, the correct command should be:copy running-config usbflash0:/R1-config
The exhibit shows that there is available space on the USB flash drive, so space is not the issue, and there is no indication that the file system is incorrectly formatted or that the USB drive is not recognized by the router.
Therefore, the problem is that the command that the administrator used was incorrect.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1 and R2 are connected via a serial link. One router is configured as the NTP master, and the other is an NTP client. Which two pieces of information can be obtained from the partial output of the show ntp associations detail command on R2? (Choose two.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 09 - The IP address of R1 is 192.168.1.2.
- Both routers are configured to use NTPv2.
- Router R2 is the master, and R1 is the client.
- Router R1 is the master, and R2 is the client.
- The IP address of R2 is 192.168.1.2.
Explanation & Hint: With the show NTP associations command, the IP address of the NTP master is given.
-
What is a characteristic of a Trojan horse as it relates to network security?
- An electronic dictionary is used to obtain a password to be used to infiltrate a key network device.
- Extreme quantities of data are sent to a particular network device interface.
- Too much information is destined for a particular memory block, causing additional memory areas to be affected.
- Malware is contained in a seemingly legitimate executable program.
Explanation & Hint: A Trojan horse carries out malicious operations under the guise of a legitimate program. Denial of service attacks send extreme quantities of data to a particular host or network device interface. Password attacks use electronic dictionaries in an attempt to learn passwords. Buffer overflow attacks exploit memory buffers by sending too much information to a host to render the system inoperable.
-
An attacker is redirecting traffic to a false default gateway in an attempt to intercept the data traffic of a switched network. What type of attack could achieve this?
- DNS tunneling
- DHCP spoofing
- TCP SYN flood
- ARP cache poisoning
Explanation & Hint: In DHCP spoofing attacks, a threat actor configures a fake DHCP server on the network to issue DHCP addresses to clients with the aim of forcing the clients to use a false or invalid default gateway. A man-in-the-middle attack can be created by setting the default gateway address to the IP address of the threat actor.
-
A company is developing a security policy for secure communication. In the exchange of critical messages between a headquarters office and a branch office, a hash value should only be recalculated with a predetermined code, thus ensuring the validity of data source. Which aspect of secure communications is addressed?
- origin authentication
- data integrity
- data confidentiality
- non-repudiation
Explanation & Hint: Secure communications consists of four elements:
Data confidentiality – guarantees that only authorized users can read the message
Data integrity – guarantees that the message was not altered
Origin authentication – guarantees that the message is not a forgery and does actually come from whom it states
Data nonrepudiation – guarantees that the sender cannot repudiate, or refute, the validity of a message sent
-
Which troubleshooting approach is more appropriate for a seasoned network administrator rather than a less-experienced network administrator?
- an approach comparing working and nonworking components to spot significant differences
- a structured approach starting with the physical layer and moving up through the layers of the OSI model until the cause of the problem is identified
- a less-structured approach based on an educated guess
- an approach that starts with the end-user applications and moves down through the layers of the OSI model until the cause of the problem has been identified
Explanation & Hint: A less-structured approach based on an educated guess is more appropriate for a seasoned network administrator rather than a less-experienced network administrator. This approach leverages the extensive experience and deep understanding of the network that a seasoned administrator has, allowing them to intuitively narrow down potential causes and directly test the most probable theories, often referred to as the “top-down” or “intuitive” approach.
Less-experienced network administrators are usually recommended to follow a more structured approach, such as starting with the physical layer and moving up through the layers of the OSI model (a bottom-up approach) or comparing working and nonworking components to spot significant differences. This ensures a thorough investigation and helps in learning and understanding the network systematically.
-
Which two pieces of information should be included in a logical topology diagram of a network? (Choose two.)
- OS/IOS version
- interface identifier
- cable type and identifier
- cable specification
- device type
- connection type
Explanation & Hint: In a logical topology diagram, the inclusion of an interface identifier can indeed be important in addition to connection type. The interface identifier can help in understanding how different networks or devices are interconnected logically. It allows one to identify specific points of interconnection that can be crucial when considering routing, switching, VLAN configuration, and other logical functions of the network.
The connection type is essential as it indicates the logical path or the method of data transfer within the network, such as leased lines, MPLS, VPN tunnels, or simple Ethernet connectivity within a LAN.
While device types can be represented in both logical and physical diagrams, the specific interface identifiers are key to logical diagrams as they relate to the configuration and operation of the network at the logical level.
-
What command would be used as part of configuring NAT or PAT to link the inside local addresses to the pool of addresses available for PAT translation?
- ip nat inside source static 172.19.89.13 198.133.219.65
- ip nat inside source list ACCTNG pool POOL-STAT
- ip nat inside source list 14 pool POOL-STAT overload
- ip nat translation timeout 36000
Explanation & Hint: The command used as part of configuring Network Address Translation (NAT) or Port Address Translation (PAT) to link the inside local addresses to a pool of addresses available for PAT translation is:
ip nat inside source list <access-list-number> pool <pool-name> overload
In this case, the correct command from the given options would be:
ip nat inside source list 14 pool POOL-STAT overload
This command specifies that the router should use the access list numbered 14 to match which inside local addresses should be translated, use the address pool named POOL-STAT for the translation, and apply PAT (the overload keyword allows multiple inside local addresses to be mapped to a single inside global address by using different port numbers).
-
Which public WAN access technology utilizes copper telephone lines to provide access to subscribers that are multiplexed into a single T3 link connection?
- cable
- ISDN
- dialup
- DSL
Explanation & Hint: The public WAN access technology that utilizes copper telephone lines to provide access to subscribers and can be multiplexed into a single T3 link connection is DSL (Digital Subscriber Line). DSL technology uses existing copper telephone lines to provide high-bandwidth data communication for subscribers. It allows for data and voice to be transmitted simultaneously, which is why it can be used alongside regular telephone service.
-
A company is considering updating the campus WAN connection. Which two WAN options are examples of the private WAN architecture? (Choose two.)
- municipal Wi-Fi
- digital subscriber line
- Ethernet WAN
- leased line
- cable
Explanation & Hint: Private WAN architecture refers to dedicated connections that are not shared with other customers, providing more control and security for the company using them. Among the options provided, the two that are examples of private WAN architecture are:
- Ethernet WAN – This can refer to dedicated metropolitan Ethernet, which is a private data connection securely linking two or more locations for private data services.
- Leased line – A leased line is a private high-capacity telecom line that provides dedicated, point-to-point, and continuous connection between two sites.
Other options like municipal Wi-Fi, digital subscriber line (DSL), and cable are typically considered shared public WAN connections because the infrastructure is shared among multiple customers.
-
Which type of VPN routes packets through virtual tunnel interfaces for encryption and forwarding?
- IPsec virtual tunnel interface
- GRE over IPsec
- dynamic multipoint VPN
- MPLS VPN
Explanation & Hint: The type of VPN that routes packets through virtual tunnel interfaces for encryption and forwarding is an IPsec virtual tunnel interface (VTI). IPsec VTI creates a secure tunnel for transporting IP traffic using IPsec encryption. Unlike traditional IPsec VPN configurations which rely on crypto maps, VTI provides a routable interface that can be used similarly to any other physical interface, allowing for the use of routing protocols and simplifying the configuration process for IPsec VPN.
-
What type of traffic is described as requiring at least 384 Kbps of bandwidth?
- data
- voice
- video
Explanation & Hint: The type of traffic that is typically described as requiring at least 384 Kbps of bandwidth is video traffic. Video conferencing applications, for example, often require minimum bandwidths ranging from 384 Kbps for standard-definition video on older systems, and much more for high-definition video. Voice traffic and most data applications usually require significantly less bandwidth compared to video.
-
An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 172.16.91.0 255.255.255.192. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?
- 0.0.0.15
- 0.0.0.7
- 0.0.0.3
- 0.0.0.63
Explanation & Hint: A wildcard mask is used in OSPF configurations to indicate which IP addresses should be included in OSPF advertisements. It is the inverse of the subnet mask.
For the subnet mask 255.255.255.192, the binary representation is 11111111.11111111.11111111.11000000. When we invert this, we get the wildcard mask:
00000000.00000000.00000000.00111111This translates to the wildcard mask 0.0.0.63 in decimal. Therefore, the administrator would use a wildcard mask of 0.0.0.63 in the OSPF network statement to advertise the network 172.16.91.0 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Internet privileges for an employee have been revoked because of abuse but the employee still needs access to company resources. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 11 - standard ACL inbound on R1 G0/0
- standard ACL outbound on R2 WAN interface towards the internet
- standard ACL inbound on R2 WAN interface connecting to the internet
- standard ACL outbound on R1 G0/0
Explanation & Hint: – Standard ACLs permit or deny packets based only on the source IPv4 address. Because all traffic types are permitted or denied, standard ACLs should be located as close to the destination as possible.
– Extended ACLs permit or deny packets based on the source IPv4 address and destination IPv4 address, protocol type, source and destination TCP or UDP ports and more. Because the filtering of extended ACLs is so specific, extended ACLs should be located as close as possible to the source of the traffic to be filtered. Undesirable traffic is denied close to the source network without crossing the network infrastructure.
-
An ACL is applied inbound on a router interface. The ACL consists of a single entry:
access-list 100 permit tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www .
If a packet with a source address of 192.168.10.45, a destination address of 10.10.3.27, and a protocol of 80 is received on the interface, is the packet permitted or denied?
- permitted
- denied
Explanation & Hint: The ACL (Access Control List) entry is:
access-list 100 permit tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www
This entry permits TCP traffic from the source IP address range 192.168.10.0 to 192.168.10.255 (as indicated by the subnet mask 0.0.0.255) to any destination, as long as the destination port is 80 (which is indicated by
eq www, wherewwwrepresents the well-known port for HTTP).The packet in question has:
- Source address: 192.168.10.45
- Destination address: 10.10.3.27
- Protocol: 80 (TCP)
Since the packet’s source address falls within the specified range (192.168.10.0 to 192.168.10.255), is using TCP, and is destined for port 80, it matches the criteria set by the ACL entry. Therefore, the packet is permitted.
-
A network administrator modified an OSPF-enabled router to have a hello timer setting of 20 seconds. What is the new dead interval time setting by default?
- 40 seconds
- 60 seconds
- 80 seconds
- 100 seconds
Explanation & Hint: In OSPF (Open Shortest Path First), the dead interval is typically set to four times the hello interval by default. If a network administrator modified an OSPF-enabled router to have a hello timer setting of 20 seconds, then the new dead interval time, by default, would be:
20 seconds (hello interval) * 4 = 80 seconds
So, the new dead interval time setting by default would be 80 seconds.
-
When will an OSPF-enabled router transition from the Down state to the Init state?
- when the router receives a hello packet from a neighbor router
- when an OSPF-enabled interface starts sending hello packets
- as soon as the router starts
- as soon as the DR/BDR election process is complete
Explanation & Hint: An OSPF-enabled router transitions from the Down state to the Init state when the router receives a hello packet from a neighbor router. In the Down state, the OSPF process is inactive on the interface, and it transitions to the Init state when the router detects a neighbor (by receiving a Hello packet on that interface). This indicates that there is at least one OSPF router in the network reachable via that interface. The Init state is the beginning of the OSPF neighbor formation process.
-
Which queuing mechanism has no provision for prioritizing or buffering but simply forwards packets in the order they arrive?
- LLQ
- CBWFQ
- WFQ
- FIFO
Explanation & Hint: The queuing mechanism that has no provision for prioritizing or buffering and simply forwards packets in the order they arrive is FIFO (First In, First Out). In FIFO queuing, packets are processed in the order they arrive, with no differentiation based on priority or class of service. There is no mechanism to prioritize certain types of traffic; each packet is handled identically, in the order of its arrival. This is the simplest form of queuing but can be inefficient for mixed traffic types, especially in high-bandwidth or congested networks.
-
ABCTech is investigating the use of automation for some of its products. In order to control and test these products, the programmers require Windows, Linux, and MAC OS on their computers. What service or technology would support this requirement?
- software defined networking
- dedicated servers
- Cisco ACI
- virtualization
Explanation & Hint: The service or technology that would best support the requirement of having Windows, Linux, and MAC OS on the programmers’ computers for ABCTech is virtualization. Virtualization allows you to run multiple operating systems on a single physical machine as virtual machines (VMs). Each VM operates independently and can run its own operating system, making it possible to have Windows, Linux, and MAC OS environments on the same hardware. This approach is highly efficient for development and testing purposes, as it allows programmers to easily switch between different operating systems and test their applications in various environments without needing multiple physical machines.
-
What command would be used as part of configuring NAT or PAT to display all static translations that have been configured?
- show ip nat translations
- show ip nat statistics
- show ip interfaces
- show ip route
Explanation & Hint: To display all static translations that have been configured in Network Address Translation (NAT) or Port Address Translation (PAT), the appropriate command is:
show ip nat translations
This command displays the NAT translation table, including both dynamic and static entries. It’s a useful tool for troubleshooting and verifying the operation of NAT/PAT on a router. Static translations, which are manually configured by the network administrator, will also be shown in this table.
-
When QoS is implemented in a converged network, which two factors can be controlled to improve network performance for real-time traffic? (Choose two.)
- jitter
- packet routing
- link speed
- packet addressing
- delay
Explanation & Hint: Delay is the latency between a sending and receiving device. Jitter is the variation in the delay of the received packets. Both delay and jitter need to be controlled in order to support real-time voice and video traffic.
-
What type of traffic is described as predictable and smooth?
- video
- data
- voice
Explanation & Hint: The type of traffic described as predictable and smooth is typically voice traffic. Voice traffic, especially in a well-configured network, tends to have a steady, consistent flow and requires consistent bandwidth and low latency. This predictability and smoothness are crucial for maintaining the quality of voice communications. In contrast, video and data traffic can be more variable in terms of bandwidth requirements and can experience bursts of high and low activity.
-
In an OSPF network which two statements describe the link-state database (LSDB)? (Choose two.)
- It can be viewed by using the show ip ospf database command.
- It contains a list of all neighbor routers to which a router has established bidirectional communication.
- All routers within an area have an identical link-state database.
- It contains a list of only the best routes to a particular network.
- A neighbor table is created based on the LSDB.
-
Explanation & Hint: In an OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) network, the link-state database (LSDB) is a crucial component. Here are the descriptions that apply:
It can be viewed by using the show ip ospf database command.
- This statement is true. The
show ip ospf databasecommand is used to display the contents of the OSPF link-state database. This database contains all the OSPF link-state advertisements (LSAs) that the router has received and processed, which are used to build the network topology.
All routers within an area have an identical link-state database.
- This statement is also true. In OSPF, all routers within the same area should have an identical LSDB. This synchronization of the LSDB across all routers in an area is crucial for the correct operation of OSPF, as it ensures that all routers have a consistent view of the network topology. OSPF achieves this through the flooding of LSAs throughout the area.
The other statements are not accurate descriptions of the LSDB:
- The LSDB does not simply contain a list of neighbor routers; it contains LSAs which describe the state of each router’s interfaces and links, the network’s topology, and more.
- The LSDB does not only list the best routes. It contains comprehensive topology information that OSPF uses to compute the best routes.
- While the neighbor table is an important part of OSPF’s operation, it is not directly created from the LSDB. The neighbor table is developed from direct communication between OSPF routers, independent of the LSDB.
- This statement is true. The
-
A network administrator is troubleshooting an OSPF problem that involves neighbor adjacency. What should the administrator do?
- Make sure that the router ID is included in the hello packet.
- Make sure that the hello and dead interval timers are the same on all routers.
- Make sure that the router priority is unique on each router.
- Make sure that the DR/BDR election is complete.
Explanation & Hint: When troubleshooting an OSPF problem that involves neighbor adjacency, the network administrator should focus on the aspects that directly impact the formation and maintenance of OSPF neighbor relationships. Here are the steps they should consider:
- Make sure that the hello and dead interval timers are the same on all routers.
- This is a critical step. OSPF routers must have matching Hello and Dead interval timers to form a neighbor relationship. These timers are advertised in OSPF Hello packets, and if they don’t match between neighboring routers, the routers will not become neighbors.
- Make sure that the DR/BDR election is complete.
- While ensuring the DR (Designated Router) and BDR (Backup Designated Router) election is complete can be important in some OSPF scenarios, it’s not typically a direct cause of OSPF neighbor adjacency issues. However, understanding the status of the DR/BDR election can be useful in complex network topologies, especially in broadcast and non-broadcast multi-access networks.
The other options are less directly related to solving OSPF neighbor adjacency issues:
- Router ID in the hello packet: The router ID is indeed included in OSPF Hello packets, but it’s not something that typically needs to be “checked” for troubleshooting, as it’s automatically included. However, ensuring that each router in the OSPF network has a unique router ID is important.
- Router priority uniqueness: The OSPF router priority is used in the DR/BDR election process on broadcast and non-broadcast networks. It does not need to be unique on each router. In fact, routers can have the same priority, and it’s a common configuration. The priority affects which router becomes the DR or BDR, but having the same priority is not inherently a problem for neighbor adjacency.
- Make sure that the hello and dead interval timers are the same on all routers.
-
Which group of APIs are used by an SDN controller to communicate with various applications?
- westbound APIs
- northbound APIs
- southbound APIs
- eastbound APIs
Explanation & Hint: In the context of Software-Defined Networking (SDN), the group of APIs used by an SDN controller to communicate with various applications is referred to as northbound APIs.
- Northbound APIs are used for communication between the SDN controller and the higher-level applications and business logic. These APIs allow the network to be programmed and managed by these applications, facilitating automation, orchestration, and network programmability.
- Southbound APIs, on the other hand, are used for communication between the SDN controller and the network devices (like switches and routers). A common example of a southbound API is OpenFlow.
- Westbound APIs and eastbound APIs are not standard terms in the context of SDN architecture.
-
Which is a characteristic of a Type 2 hypervisor?
- best suited for enterprise environments
- does not require management console software
- has direct access to server hardware resources
- installs directly on hardware
Explanation: Type 2 hypervisors are hosted on an underlaying operating system and are best suited for consumer applications and those experimenting with virtualization. Unlike Type 1 hypervisors, Type 2 hypervisors do not require a management console and do not have direct access to hardware.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured OSPFv2 on the two Cisco routers. The routers are unable to form a neighbor adjacency. What should be done to fix the problem on router R2?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 16 - Change the router-id of router R2 to 2.2.2.2.
- Implement the command no passive-interface Serial0/1.
- Implement the command network 192.168.2.6 0.0.0.0 area 0 on router R2.
- Implement the command network 192.168.3.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 on router R2.
Explanation & Hint: The exhibit shows that OSPF has been configured on router R2, and the output indicates that interface Serial0/1 has been set as passive. In OSPF, marking an interface as passive means that the router will not form OSPF neighbor adjacencies over that interface. However, since the goal is to form an OSPF adjacency between the routers connected by Serial0/1, the passive setting is preventing the adjacency from forming.
To fix the problem and allow OSPF to form a neighbor adjacency on R2, the command that should be implemented is:
no passive-interface Serial0/1
This command will remove the passive interface status from Serial0/1, allowing OSPF neighbor relationships to be established on that interface. The other options are not relevant to the problem of forming neighbor adjacency as described in the context.
-
An OSPF router has three directly connected networks; 10.0.0.0/16, 10.1.0.0/16, and 10.2.0.0/16. Which OSPF network command would advertise only the 10.1.0.0 network to neighbors?
- router(config-router)# network 10.1.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
- router(config-router)# network 10.1.0.0 0.0.15.255 area 0
- router(config-router)# network 10.1.0.0 255.255.255.0 area 0
- router(config-router)# network 10.1.0.0 0.0.0.0 area 0
Explanation & Hint: The OSPF network command requires the use of a wildcard mask, which is the inverse of the subnet mask. For the network 10.1.0.0/16, the subnet mask is 255.255.0.0. The inverse of this mask is 0.0.255.255.
Therefore, the correct command to advertise only the 10.1.0.0/16 network to OSPF neighbors is:
router(config-router)This command uses the correct wildcard mask corresponding to the /16 subnet mask and will match only the 10.1.0.0 network.
-
What are two benefits of extending access layer connectivity to users through a wireless medium? (Choose two.)
- increased network management options
- increased flexibility
- reduced costs
- increased bandwidth availability
- decreased number of critical points of failure
Explanation & Hint: Wireless connectivity at the access layer provides increased flexibility, reduced costs, and the ability to grow and adapt to changing business requirements. Utilizing wireless routers and access points can provide an increase in the number of central points of failure. Wireless routers and access points will not provide an increase in bandwidth availability.
-
A student, doing a summer semester of study overseas, has taken hundreds of pictures on a smartphone and wants to back them up in case of loss. What service or technology would support this requirement?
- dedicated servers
- cloud services
- Cisco ACI
- software defined networking
Explanation & Hint: To back up hundreds of pictures from a smartphone, the most appropriate service would be cloud services. These services allow users to store and back up their data on remote servers accessed via the internet, providing a convenient and secure way to ensure data is not lost if something happens to the physical device. Popular cloud services for photo backup include Google Photos, iCloud for Apple devices, Amazon Photos, Dropbox, and Microsoft OneDrive. These services often offer automatic syncing, so photos taken on the smartphone would be backed up without requiring manual intervention.
-
What are the two types of VPN connections? (Choose two.)
- site-to-site
- Frame Relay
- PPPoE
- leased line
- remote access
Explanation & Hint: The two types of VPN (Virtual Private Network) connections are:
Site-to-site – This type of VPN is used to connect different networks together over the internet. For example, it can connect the network of a branch office to the network at the company’s main office, allowing seamless access between the two as if they were on the same local network.
Remote access – Also known as a client-to-site VPN, this type of VPN allows individual users to connect to a network over the internet as if they were physically connected to the network’s internal infrastructure, typically through a VPN client software.
Frame Relay and PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) are types of data link layer communication protocols used to establish direct connections between two nodes on a network, while leased lines refer to dedicated symmetric telecommunications lines connecting two locations. Neither Frame Relay, PPPoE, nor leased lines are types of VPN connections.
-
Which type of VPN connects using the Transport Layer Security (TLS) feature?
- dynamic multipoint VPN
- SSL VPN
- IPsec virtual tunnel interface
- GRE over IPsec
Explanation & Hint: The type of VPN that connects using the Transport Layer Security (TLS) feature is an SSL VPN (Secure Sockets Layer Virtual Private Network). SSL VPNs use the TLS protocol to provide a secure connection between a client and a network. TLS is the successor to SSL and is widely used to secure web transactions, such as in HTTPS. SSL VPNs can provide remote access to a network from virtually any internet-connected device without the need for specialized client software.
-
Which two scenarios would result in a duplex mismatch? (Choose two.)
- connecting a device with an interface running at 100 Mbps to another with an interface running at 1000 Mbps
- manually setting the two connected devices to different duplex modes
- connecting a device with autonegotiation to another that is manually set to full-duplex
- starting and stopping a router interface during a normal operation
- configuring dynamic routing incorrectly
Explanation & Hint: A duplex mismatch occurs when two connected network devices operate in different duplex modes (one in full-duplex and the other in half-duplex). The two scenarios that would result in a duplex mismatch are:
- Manually setting the two connected devices to different duplex modes – If one device is set to full-duplex and the other to half-duplex manually, they will not be able to communicate properly, resulting in a duplex mismatch.
- Connecting a device with autonegotiation to another that is manually set to full-duplex – If one end of a connection is configured to autonegotiate the duplex mode and the other end is manually set to full-duplex, the autonegotiation can fail, often causing the autonegotiating end to default to half-duplex, thus causing a duplex mismatch.
The other scenarios listed are not directly related to duplex mismatches:
- Connecting devices running at different speeds (100 Mbps to 1000 Mbps) can lead to performance issues but not a duplex mismatch.
- Starting and stopping a router interface during normal operation would not cause a duplex mismatch unless it led to one side changing its duplex settings.
- Configuring dynamic routing incorrectly does not affect duplex settings; it would cause routing issues instead.
-
A company needs to interconnect several branch offices across a metropolitan area. The network engineer is seeking a solution that provides high-speed converged traffic, including voice, video, and data on the same network infrastructure. The company also wants easy integration to their existing LAN infrastructure in their office locations. Which technology should be recommended?
- ISDN
- VSAT
- Frame Relay
- Ethernet WAN
Explanation & Hint: The technology that should be recommended for interconnecting several branch offices across a metropolitan area with high-speed converged traffic and easy integration into existing LAN infrastructure is Ethernet WAN.
Ethernet WAN, often referred to as Metro Ethernet in the context of a metropolitan area, is a network service that extends Ethernet beyond the local area network (LAN) across a metropolitan area network (MAN) or wide area network (WAN). It allows for the seamless connection of geographically separated offices as if they are on the same local network, providing high bandwidth and supporting a variety of data types, including voice, video, and data. Ethernet WAN is known for its simplicity, scalability, and ease of integration with existing Ethernet LANs.
ISDN, VSAT, and Frame Relay are older technologies that are typically not used for high-speed converged networks and do not offer the same level of integration with Ethernet LANs as Ethernet WAN does. ISDN and Frame Relay are also becoming obsolete and are being replaced by more modern technologies like Ethernet WAN and MPLS. VSAT, which stands for Very Small Aperture Terminal, is a satellite-based communication technology and would not be the optimal choice for high-speed data and easy LAN integration.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator that has the IP address of 10.0.70.23/25 needs to have access to the corporate FTP server (10.0.54.5/28). The FTP server is also a web server that is accessible to all internal employees on networks within the 10.x.x.x address. No other traffic should be allowed to this server. Which extended ACL would be used to filter this traffic, and how would this ACL be applied? (Choose two.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 14 - R2(config)# interface gi0/0
R2(config-if)# ip access-group 105 in - access-list 105 permit tcp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 eq 20
access-list 105 permit tcp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 eq 21
access-list 105 permit tcp 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 host 10.0.54.5 eq www
access-list 105 deny ip any host 10.0.54.5
access-list 105 permit ip any any - access-list 105 permit ip host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5
access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq www
access-list 105 permit ip any any - access-list 105 permit tcp host 10.0.54.5 any eq www
access-list 105 permit tcp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 eq 20
access-list 105 permit tcp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 eq 21 - R1(config)# interface s0/0/0
R1(config-if)# ip access-group 105 out - R1(config)# interface gi0/0
R1(config-if)# ip access-group 105 outExplanation & Hint: The first two lines of the ACL allow host 10.0.70.23 FTP access to the server that has the IP address of 10.0.54.5. The next line of the ACL allows HTTP access to the server from any host that has an IP address that starts with the number 10. The fourth line of the ACL denies any other type of traffic to the server from any source IP address. The last line of the ACL permits anything else in case there are other servers or devices added to the 10.0.54.0/28 network. Because traffic is being filtered from all other locations and for the 10.0.70.23 host device, the best place to put this ACL is closest to the server.
- R2(config)# interface gi0/0
-
In JSON, what is held within square brackets [ ]?
- an array
- an object
- key/value pairs
- nested values
Explanation & Hint: In JSON (JavaScript Object Notation), square brackets
[ ]are used to hold an array. An array is an ordered collection of values, which can be strings, numbers, objects, other arrays, booleans, or null values. Here’s an example of a JSON array:{
"colors": ["red", "green", "blue"]
}In this example, “colors” is an array consisting of three string values.
-
An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 192.168.0.0 255.255.254.0. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?
- 0.0.15.255
- 0.0.3.255
- 0.0.1.255
- 0.0.7.255
-
Explanation & Hint: A wildcard mask is the inverse of a subnet mask. For the subnet mask 255.255.254.0, the binary representation is:
11111111.11111111.11111110.00000000
Inverting this binary representation gives us the wildcard mask:
00000000.00000000.00000001.11111111
This corresponds to the decimal wildcard mask:
0.0.1.255
Therefore, the administrator would use a wildcard mask of 0.0.1.255 in the OSPF network statement to advertise the network 192.168.0.0 with a subnet mask of 255.255.254.0.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured a standard ACL to permit only the two LAN networks attached to R1 to access the network that connects to R2 G0/1 interface. When following the best practices, in what location should the standard ACL be applied?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 18 - R2 G0/1 outbound
- R2 G0/0 outbound
- R2 S0/0/1 outbound
- R2 G0/1 inbound
- R1 S0/0/0 outbound
-
Explanation & Hint: Applying the standard ACL on R2 G0/1 outbound means that the ACL is placed on the G0/1 interface of router R2, and it is configured to filter traffic as it leaves that interface and goes towards its destination. In this case, the destination is the network connected to R2’s G0/1 interface.
Here’s an explanation of how this setup works:
- Traffic Flow: When devices from the LAN networks attached to R1 (e.g., H1 and H2) attempt to communicate with devices in the network connected to R2’s G0/1 interface, the traffic flows from R1 to R2 via R2’s G0/1 interface.
- Outbound ACL: Placing the ACL outbound on R2’s G0/1 interface means that the ACL is applied to this interface’s outbound traffic path, which is the traffic leaving the G0/1 interface. The ACL is evaluated when the traffic is leaving R2 and heading towards its destination.
- Filtering Criteria: The standard ACL configured on R2’s G0/1 outbound interface should contain rules that permit specific source IP addresses (belonging to the LAN networks of R1) and deny other source IP addresses. This effectively filters out unwanted traffic at the exit point of R2.
- Permitted Traffic: Traffic from R1’s LAN networks that matches the ACL’s permit rules is allowed to pass through R2’s G0/1 interface and reach the destination network connected to G0/1.
- Denied Traffic: Traffic from R1’s LAN networks that does not match the ACL’s permit rules will be denied at R2’s G0/1 interface and will not reach its destination.
- Effectiveness: This configuration allows you to control which traffic from R1’s LAN networks is allowed to access the network connected to R2’s G0/1 interface. It effectively filters the traffic as it exits R2, ensuring that only permitted traffic can reach its destination.
While applying ACLs outbound on an interface can be a valid configuration, it’s important to ensure that the ACL rules are correctly defined to achieve the desired security and access control objectives for your network.
-
What are two features to consider when creating a named ACL? (Choose two.)
- Use a space for ease of reading to separate the name from the description.
- Be descriptive when creating the ACL name.
- Use alphanumeric characters if needed.
- Modify the ACL using a text editor.
- Use special characters, such as ! or * to show the importance of the ACL.
-
Explanation & Hint: When creating a named Access Control List (ACL), two important features to consider are:
- Be descriptive when creating the ACL name: This is crucial for ease of management and understanding. A descriptive name helps in quickly identifying the purpose and scope of the ACL. It should ideally reflect the function or the area of the network it is intended to control access for.
- Use alphanumeric characters if needed: Employing alphanumeric characters in the ACL name can be beneficial for creating more specific or structured naming conventions. This can include using numbers for versioning or sequencing, and letters for easily distinguishing between different ACLs.
The other options provided are less relevant or not best practices for naming ACLs. For instance, using special characters like ! or * is generally avoided as they might not be supported in all systems and can lead to confusion. Modifying an ACL using a text editor is more about the process of editing an existing ACL rather than a consideration for initially naming it. While using a space for ease of reading is generally good advice for writing and documentation, in the context of ACL naming, spaces might not be supported, and even if they are, it’s usually better to use other methods like underscores (_) to separate words or concepts in names.
-
What are two purposes of launching a reconnaissance attack on a network? (Choose two.)
- to escalate access privileges
- to prevent other users from accessing the system
- to scan for accessibility
- to retrieve and modify data
- to gather information about the network and devices
-
Explanation & Hint: Two primary purposes of launching a reconnaissance attack on a network are:
- To Gather Information about the Network and Devices: The main goal of a reconnaissance attack is to collect as much information as possible about the target network and its devices. This includes identifying network topology, discovering devices connected to the network, understanding the network’s security posture, finding out software versions, and detecting services running on various devices. This information can be used to plan more targeted and effective attacks.
- To Scan for Accessibility: Reconnaissance attacks often involve scanning the network to identify open ports, live hosts, and available services. This helps attackers find potential entry points into the network or vulnerable spots that can be exploited. Scanning can reveal weaknesses like unpatched software, misconfigured devices, or weak points in the network’s defense that can be leveraged in subsequent attacks.
The other options, such as escalating access privileges or preventing other users from accessing the system, are more aligned with the objectives of different types of attacks that may follow reconnaissance, like privilege escalation or denial-of-service attacks, respectively. Retrieving and modifying data is typically a goal of later stages of an attack, after initial reconnaissance has been conducted and vulnerabilities have been exploited.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The company has provided IP phones to employees on the 192.168.10.0/24 network and the voice traffic will need priority over data traffic. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 17 - extended ACL inbound on R1 G0/0
- standard ACL inbound on R1 vty lines
- standard ACL inbound on R1 G0/1
- extended ACL inbound on R3 G0/0
-
Explanation & Hint: To prioritize voice traffic over data traffic, an Access Control List (ACL) can be used to identify the traffic and then classify it so that Quality of Service (QoS) policies can be applied. In this scenario, you’d typically want to use an extended ACL because standard ACLs can only filter traffic based on source IP addresses, whereas extended ACLs can filter based on both source and destination IP addresses as well as the protocol type, which is necessary to identify voice traffic specifically.
The placement of the ACL is also important. To ensure that voice traffic is given priority, the ACL should be applied as close to the source of the traffic as possible. This means applying the ACL on the interface where the traffic originates or enters the router, which in this case would be Router R1’s G0/0 interface because it is directly connected to the 192.168.10.0/24 network where the IP phones are located.
So, the best ACL type and placement in this situation would be: Extended ACL inbound on R1 G0/0.
This configuration allows you to match the IP phones’ traffic specifically and set the necessary QoS policies right as the traffic enters R1, before it gets mixed with other traffic on the network.
-
An ACL is applied inbound on a router interface. The ACL consists of a single entry:
access-list 210 permit tcp 172.18.20.0 0.0.0.31 172.18.20.32 0.0.0.31 eq ftp .
If a packet with a source address of 172.18.20.14, a destination address of 172.18.20.40, and a protocol of 21 is received on the interface, is the packet permitted or denied?
- permitted
- denied
-
Explanation & Hint: Access Control Lists (ACLs) operate by matching packet information against entries in the ACL. If a packet matches an entry, the corresponding action (permit or deny) is taken. If no match is found, the implicit default is to deny the packet.
The ACL entry provided is as follows:
access-list 210 permit tcp 172.18.20.0 0.0.0.31 172.18.20.32 0.0.0.31 eq ftp
This entry specifies the following conditions for permitting traffic:
- Protocol: TCP
- Source IP address: 172.18.20.0/27, which translates to the range 172.18.20.0 to 172.18.20.31
- Destination IP address: 172.18.20.32/27, which translates to the range 172.18.20.32 to 172.18.20.63
- Destination port: FTP (port 21)
The packet in question has:
- Protocol: TCP (since FTP uses TCP and the protocol number for FTP control is 21)
- Source IP address: 172.18.20.14 (which falls within the source range 172.18.20.0 to 172.18.20.31)
- Destination IP address: 172.18.20.40 (which falls within the destination range 172.18.20.32 to 172.18.20.63)
- Destination port: 21 (which matches the ‘eq ftp’ condition)
Since the packet matches all the specified conditions in the ACL entry, it is permitted.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Router R1 is configured with static NAT. Addressing on the router and the web server are correctly configured, but there is no connectivity between the web server and users on the Internet. What is a possible reason for this lack of connectivity?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 13 - The NAT configuration on interface S0/0/1 is incorrect.
- Interface Fa0/0 should be configured with the command ip nat outside .
- The inside global address is incorrect.
- The router NAT configuration has an incorrect inside local address.
-
Explanation & Hint: Based on the information in the exhibit, the configuration for static NAT is provided along with interface roles in NAT (inside, outside). Here are the relevant parts of the configuration:
- Static NAT configuration:
ip nat inside source static 192.168.11.254 209.165.200.1
- Interface configuration:
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip nat inside
interface Serial0/0/1
ip nat outside
Given the configuration and the issue of no connectivity between the web server and users on the Internet, we can analyze the potential reasons:
- The NAT configuration on interface S0/0/1 is incorrect. The interface S0/0/1 is correctly configured as
ip nat outside, which is necessary for NAT to function correctly. This is not likely the cause of the lack of connectivity. - Interface Fa0/0 should be configured with the command
ip nat outside. This is incorrect. The FastEthernet0/0 interface connects to the internal network (where the web server resides), so it should be configured asip nat inside, which is correctly done in the configuration shown. - The inside global address is incorrect. The inside global address should be an address that is routable on the Internet. In the static NAT command, the global address used is
209.165.200.1. We don’t have information about the correctness of this address in relation to the Internet connectivity, but if this address is not correctly routed on the Internet or is not the correct public IP for NAT, it could indeed be a reason for the lack of connectivity. - The router NAT configuration has an incorrect inside local address. The inside local address is the address of the web server as recognized within the local (inside) network. According to the exhibit, the web server has the IP address
192.168.11.11, but the static NAT command is using192.168.11.254as the inside local address. This mismatch is the cause of the lack of connectivity since NAT is configured with the wrong local IP address.
Based on this analysis, the most likely reason for the lack of connectivity is that the router NAT configuration has an incorrect inside local address. The static NAT command needs to be corrected to match the actual IP address of the web server (
192.168.11.11), not192.168.11.254. - Static NAT configuration:
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which address or addresses represent the inside global address?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 15 - 10.1.1.2
- 192.168.0.100
- 209.165.20.25
- any address in the 10.1.1.0 network
-
Explanation & Hint: In NAT (Network Address Translation) terminology:
- Inside local address is the IP address assigned to a host on the internal network. This address is not routable on the internet.
- Inside global address is the public IP address that represents one or more inside local IP addresses to the outside world.
Based on the configuration commands provided in the exhibit:
ip nat inside source static 192.168.0.100 209.165.20.25
This line indicates a static NAT translation is being set up, where the inside local address
192.168.0.100is being translated to a global address209.165.20.25.Therefore, the address that represents the inside global address is
209.165.20.25. This is the address that external hosts on the internet will see as the source or destination when communicating with the host at192.168.0.100.
-
What are two benefits of using SNMP traps? (Choose two.)
- They reduce the load on network and agent resources.
- They limit access for management systems only.
- They eliminate the need for some periodic polling requests.
- They can passively listen for exported NetFlow datagrams.
- They can provide statistics on TCP/IP packets that flow through Cisco devices.
-
Explanation & Hint: SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) traps are alert messages sent from an SNMP-enabled device to a management station. The two benefits of using SNMP traps among the options provided are:
- They reduce the load on network and agent resources: SNMP traps are asynchronous notifications sent to the SNMP manager without the need for the manager to send a request for information. This means that the network devices do not have to respond to as many polling requests, thereby reducing the load on both the network and the agent resources.
- They eliminate the need for some periodic polling requests: Because SNMP traps are sent automatically in response to certain events, there is no need for the SNMP manager to constantly poll the devices for that specific information. This can significantly reduce the amount of polling traffic on the network, which is especially beneficial for large-scale networks.
The other options listed are not directly benefits of using SNMP traps:
- They limit access for management systems only: SNMP itself can be configured to limit access to management systems, but this is not a benefit unique to traps; it applies to SNMP as a whole through the use of community strings and SNMPv3’s authentication and encryption.
- They can passively listen for exported NetFlow datagrams: NetFlow is a separate protocol used for monitoring network traffic flows. SNMP traps do not listen for NetFlow datagrams; they are a different mechanism for reporting events and do not directly interact with NetFlow data.
- They can provide statistics on TCP/IP packets that flow through Cisco devices: While SNMP can be used to collect a wide range of data, including statistics on TCP/IP packets, this is not a unique benefit of SNMP traps. Traps are specifically for alerting and event notification, not for providing detailed statistics. Detailed statistics are typically gathered through SNMP gets and bulk operations.
-
Refer to the exhibit. From which location did this router load the IOS?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 12 - a TFTP server
- flash memory
- NVRAM
- RAM
- ROM
-
Explanation & Hint: The output of the
show versioncommand in the exhibit provides information about the Cisco router’s software and hardware. In the output, the line “System image file is ‘flash:c1841-advipservicesk9-mz.124-15.T1.bin'” indicates where the IOS (Internetwork Operating System) was loaded from. This line tells us that the IOS image was loaded from the router’s flash memory. Therefore, the IOS was loaded from flash memory
-
What protocol uses smaller stratum numbers to indicate that the server is closer to the authorized time source than larger stratum numbers?
- NTP
- SYSLOG
- TFTP
- MPLS
-
Explanation & Hint: NTP (Network Time Protocol) uses stratum levels to indicate the distance from the reference time source. A lower stratum number means the server is closer to the reference source, with stratum 0 being the reference clock itself and stratum 1 being a server directly connected to the reference clock. As the stratum number increases, it indicates that the server is further away from the reference clock.
SYSLOG is a protocol used for system management and security auditing, not for time synchronization. It does not use stratum numbers but rather severity levels to indicate the importance of log messages.
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) is a simple, lightweight file transfer protocol with no provisions for security. It is used for transferring files, typically within a local area network, and does not utilize stratum numbers as it is not related to time synchronization.
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) is a data-carrying technique for high-performance telecommunications networks. MPLS directs data from one network node to the next based on short path labels rather than long network addresses. It does not deal with time synchronization and does not use stratum numbers.
-
Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router flooding link-state and cost information about each directly connected link?
- electing the designated router
- exchanging link-state advertisements
- injecting the default route
- building the topology table
-
Explanation & Hint: Exchanging link-state advertisements is the step in the link-state routing process that is described by a router flooding link-state and cost information about each directly connected link. Routers use Link-State Advertisements (LSAs) to share information about their own links and the state of those links with all other routers in the same area. This allows all routers to have an identical database of the network topology, which can then be used to build a complete and synchronized view of the network.
- Electing the designated router is a process in OSPF used on multi-access networks like Ethernet. A designated router (DR) is elected among all routers on a particular segment to reduce the amount of LSA flooding. This is not the step where link-state and cost information is flooded; it’s a prelude to more efficient flooding.
- Injecting the default route refers to the process of a router introducing a default route (0.0.0.0/0) into the routing process. This is typically done to provide a gateway of last resort in a routing domain, not for flooding link-state information.
- Building the topology table is a term more associated with Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), which is a distance-vector routing protocol, not a link-state protocol. In link-state protocols like OSPF or IS-IS, the equivalent process would be building the link-state database from received LSAs.
-
How does virtualization help with disaster recovery within a data center?
- Server provisioning is faster.
- Power is always provided.
- Less energy is consumed.
- Hardware at the recovery site does not have to be identical to production equipment.*
-
Explanation & Hint: Hardware at the recovery site does not have to be identical to production equipment.
Virtualization abstracts the underlying hardware from the operating systems and applications running on it. In a disaster recovery scenario, this abstraction is extremely beneficial because it allows virtual machines (VMs) to be moved easily between different servers, which may not be identical. This means that the recovery site’s hardware can be different in terms of configuration, make, or model, and still host the VMs from the production environment. This flexibility significantly reduces the complexity and cost associated with maintaining an identical hardware environment at a secondary disaster recovery site.
- Server provisioning is faster. This is true of virtualization in general, as virtual machines can be provisioned much more quickly than physical servers. However, while this does contribute to the overall agility and responsiveness of a disaster recovery strategy, the core benefit in a disaster recovery context is the hardware abstraction mentioned earlier.
- Power is always provided. Virtualization itself does not guarantee power provision; this is typically managed through power supply infrastructure such as uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and backup generators.
- Less energy is consumed. While virtualization can lead to more efficient use of server resources and potentially reduce energy consumption, this is not directly related to disaster recovery capabilities. It’s more of a side benefit in terms of operational cost savings and sustainability.
-
What is a characteristic of the REST API?
- considered slow, complex, and rigid
- used for exchanging XML structured information over HTTP or SMTP
- evolved into what became SOAP
- most widely used API for web services
-
Explanation & Hint: Most widely used API for web services
REST (Representational State Transfer) API is a set of architectural principles that uses the HTTP protocol’s existing features to interact with resources. It is known for being fast, lightweight, and flexible. RESTful APIs use standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc., and can handle multiple types of calls, return different data formats, and even change structurally with the correct implementation of hypermedia. This has led to its widespread adoption for web services.
- Considered slow, complex, and rigid is not a characteristic of REST API. In fact, REST APIs are considered the opposite: they are generally viewed as faster and more flexible compared to other web service APIs like SOAP.
- Used for exchanging XML structured information over HTTP or SMTP more accurately describes SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol), which is a protocol for exchanging structured information in the implementation of web services. SOAP can use HTTP or SMTP for transport, and while REST APIs can also exchange XML data, they are not limited to XML as they can also use JSON, YAML, or other formats.
- Evolved into what became SOAP is not correct for REST API. REST and SOAP are distinct approaches to web services; REST is an architectural style, while SOAP is a protocol. SOAP predates REST and is more rigid in its operation and more tightly coupled to the XML format for message exchange. REST was proposed as a lighter-weight alternative.
-
In a large enterprise network, which two functions are performed by routers at the distribution layer? (Choose two.)
- connect remote networks
- provide Power over Ethernet to devices
- provide data traffic security
- connect users to the network
- provide a high-speed network backbone
-
Explanation & Hint: In a large enterprise network, routers at the distribution layer typically perform the following two functions:
- Provide data traffic security: The distribution layer often implements security policies through access control lists (ACLs), firewall features, and packet filtering to manage the flow of network traffic between different subnets and prevent unauthorized access.
- Connect users to the network: The distribution layer serves as the intermediary between the access layer and the core layer, aggregating the data from multiple access layer switches before it is transmitted to the core network. It manages the routing and switching operations that direct packets from the user-access layer to the network services layer, often handling policy-based connectivity and directing traffic flows around the network.
The other options provided are less typical for routers at the distribution layer:
- Connect remote networks: This is usually the role of the core layer, which provides high-speed, high-capacity transport to various parts of the network including remote connections. The distribution layer can route traffic towards remote networks, but the long-distance connectivity is generally managed at the core.
- Provide Power over Ethernet (PoE) to devices: This is not a function of routers at any layer; instead, it is typically a feature provided by switches at the access layer where endpoint devices are connected.
- Provide a high-speed network backbone: This function is associated with the core layer of the network, which is designed to be highly redundant and optimized for fast and reliable data transport across the entire network. The distribution layer manages traffic between the access and core layers but is not typically considered the high-speed backbone itself.
-
A group of users on the same network are all complaining about their computers running slowly. After investigating, the technician determines that these computers are part of a zombie network. Which type of malware is used to control these computers?
- botnet
- rootkit
- spyware
- virus
-
Explanation & Hint: The correct answer is:
botnet
Now, let’s explain each of the options:
Botnet: This is a network of computers that have been infected with malicious software and are controlled as a group without the owners’ knowledge. They are commonly used for various nefarious activities, including sending spam, stealing data, or launching Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. In this scenario, the computers being part of a ‘zombie network’ indicates that they are being remotely controlled as part of a botnet.
Rootkit: A rootkit is a type of malware that provides unauthorized, root-level access to a computer or network. While it can be used to control computers covertly, its primary purpose is to hide the existence of certain processes or programs from normal methods of detection and enable continued privileged access to a computer.
Spyware: Spyware is a type of malware that is designed to collect and transmit personal information, such as internet usage habits, keystrokes, or sensitive data like credit card information. While it can slow down a computer, it does not typically control it in a networked manner like a botnet.
Virus: A virus is a type of malware that replicates by inserting copies of itself into other computer programs, data files, or the boot sector of the hard drive. While viruses can cause harm to computer systems and may slow them down, they do not usually control multiple computers as part of a network like a botnet.
-
What type of traffic is described as using either TCP or UDP depending on the need for error recovery?
- video
- voice
- data
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of traffic described as using either TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) or UDP (User Datagram Protocol) depending on the need for error recovery is:
data
To elaborate:
- Video: Video streaming typically uses UDP for most real-time streaming applications because it allows for faster transmission of data. The loss of some packets (which might happen with UDP) is generally tolerable in video streaming, as it might only result in minor quality degradation, which is often preferable to the delay that would be caused by using TCP for error recovery.
- Voice: Similar to video, voice communication often uses UDP. In voice-over-IP (VoIP) and other real-time voice services, maintaining the timely delivery of packets is usually more critical than ensuring every single packet is received. The minor packet loss characteristic of UDP does not significantly impact the overall quality of voice communication and is preferable to the latency that TCP’s error recovery mechanisms would introduce.
- Data: General data transmission can use either TCP or UDP, depending on the need for reliability and error recovery. TCP is used when it’s essential to ensure that every packet of data is received accurately (e.g., file downloads, web page loads, and sending emails). In contrast, UDP might be used for scenarios where speed is more critical than reliability, such as live data feeds or certain types of gaming traffic. The choice between TCP and UDP in data transmission hinges on the specific requirements for error recovery and speed.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which conclusion can be drawn from this OSPF multiaccess network?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 21 - All DROTHER routers will send LSAs to the DR and BDR to multicast 224.0.0.5.
- When a DR is elected all other non-DR routers become DROTHER.
- If the DR stops producing Hello packets, a BDR will be elected, and then it promotes itself to assume the role of DR.
- With an election of the DR, the number of adjacencies is reduced from 6 to 3.
Explanation & Hint:
-
In which OSPF state is the DR/BDR election conducted?
- ExStart
- Init
- Exchange
- Two-Way
-
Explanation & Hint:
-
An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 10.27.27.0 255.255.255.0. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?
- 0.0.0.15
- 0.0.0.31
- 0.0.0.63
- 0.0.0.255
-
Explanation & Hint: In OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) configuration, a wildcard mask is used in network statements to specify which IP addresses should be included. The wildcard mask is the inverse of a subnet mask.
Given the subnet mask 255.255.255.0, we can determine the corresponding wildcard mask by subtracting each octet from 255.
- For the first octet of the subnet mask (255), subtract it from 255: 255−255=0
- For the second octet (255), do the same: 255−255=0
- For the third octet (255), again: 255−255=0
- For the fourth octet (0), subtract it from 255: 255−0=255
So, the wildcard mask corresponding to the subnet mask 255.255.255.0 is 0.0.0.255.
-
Which protocol provides authentication, integrity, and confidentiality services and is a type of VPN?
- IPsec
- ESP
- MD5
- AES
-
Explanation & Hint: The protocol that provides authentication, integrity, and confidentiality services, and is commonly used as a type of VPN (Virtual Private Network), is IPsec (Internet Protocol Security).
Here’s an explanation of all the options:
- IPsec: This is a suite of protocols for securing internet protocol (IP) communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet of a communication session. IPsec includes protocols for establishing mutual authentication between agents at the beginning of the session and negotiating cryptographic keys to be used during the session. It’s widely used for VPNs.
- ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload): This is a component of IPsec used for providing confidentiality, data-origin authentication, connectionless integrity, an anti-replay service (a form of partial sequence integrity), and limited traffic flow confidentiality. While ESP is a part of IPsec, it’s not a standalone protocol for VPNs.
- MD5 (Message-Digest Algorithm 5): This is a widely used cryptographic hash function that produces a 128-bit (16-byte) hash value. It’s commonly used to check the integrity of files. However, MD5 is not used for creating VPNs and is considered insecure for many cryptographic purposes.
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): This is a symmetric encryption algorithm widely used across the globe. AES is used in various applications, including securing VPNs. It’s a key component of many security protocols but on its own, it’s not a VPN protocol.
So, among these options, IPsec is the correct answer as it’s the protocol suite providing a full range of security services for VPNs.
-
What QoS step must occur before packets can be marked?
- queuing
- shaping
- policing
- classifying
-
Explanation & Hint: Before packets can be marked in a Quality of Service (QoS) process, they must be classified.
Classification is the step in QoS where packets are identified and categorized into specific traffic flows based on various criteria such as source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, or protocol type. This step is crucial as it determines how the network will handle these packets in subsequent QoS processes like marking, queuing, policing, or shaping.
Here’s a brief explanation of the other options:
- Queuing: This involves managing packets in queues based on their classification and marking. It comes after packets are marked.
- Shaping: This refers to adjusting the traffic rate of certain packets. Shaping usually occurs after classification and marking.
- Policing: This is the process of monitoring the rate of a flow and can result in re-marking or dropping packets that exceed a specified rate. Like shaping, policing typically happens after classification.
-
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator configures the following ACL in order to prevent devices on the 192.168.1.0 subnet from accessing the server at 10.1.1.5:
access-list 100 deny ip 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 host 10.1.1.5 access-list 100 permit ip any any
Where should the administrator place this ACL for the most efficient use of network resources?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 20 - outbound on router A Fa0/1
- outbound on router B Fa0/0
- inbound on router A Fa0/0
- inbound on router B Fa0/1
-
Explanation & Hint: In a network, Access Control Lists (ACLs) are best placed to filter traffic as close to the source as possible when denying traffic, to conserve bandwidth and processing on the network devices along the path. For permitting traffic, it is generally placed as close to the destination as possible. Since the goal here is to prevent devices on the 192.168.1.0 subnet from accessing the server at 10.1.1.5, you want to stop the unwanted traffic as soon as it originates.
Given the options provided and the scenario described, the ACL should be placed:
- Inbound on router A Fa0/0
This will ensure that traffic from the 192.168.1.0 subnet is filtered as it leaves the local network and before it traverses any part of the network infrastructure, thus conserving network resources.
-
Consider the following output for an ACL that has been applied to a router via the access-class in command. What can a network administrator determine from the output that is shown?
R1# <output omitted> Standard IP access list 2 10 permit 192.168.10.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255 (2 matches) 20 deny any (1 match)
- Traffic from one device was not allowed to come into one router port and be routed outbound a different router port.
- Traffic from two devices was allowed to enter one router port and be routed outbound to a different router port.
- Two devices connected to the router have IP addresses of 192.168.10. x .
- Two devices were able to use SSH or Telnet to gain access to the router.
Explanation & Hint: The access-class command is used only on VTY ports. VTY ports support Telnet and/or SSH traffic. The match permit ACE is how many attempts were allowed using the VTY ports. The match deny ACE shows that a device from a network other than 192.168.10.0 was not allowed to access the router through the VTY ports.
-
What protocol synchronizes with a private master clock or with a publicly available server on the internet?
- TFTP
- NTP
- MPLS
- CBWFQ
-
Explanation & Hint: The protocol that synchronizes with a private master clock or with a publicly available server on the internet is NTP (Network Time Protocol).
Here is an explanation of all the options provided:
- TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol): This is a simple, lockstep, file transfer protocol that is used to transfer files typically within a local network. It’s not used for synchronization purposes.
- NTP (Network Time Protocol): This protocol is used to synchronize the clocks of computers to a reference time source, such as a master clock or an internet time server.
- MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching): MPLS is a data-carrying technique for high-performance telecommunications networks. It does not deal with time synchronization but rather with directing data from one network node to the next based on short path labels rather than long network addresses.
- CBWFQ (Class-Based Weighted Fair Queueing): This is a queueing mechanism used in network quality of service (QoS) that provides bandwidth allocation to specific classes of traffic. It does not provide time synchronization services.
So, for time synchronization with a master clock or public time servers, NTP is the correct protocol.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A PC at address 10.1.1.45 is unable to access the Internet. What is the most likely cause of the problem?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 19 - The wrong netmask was used on the NAT pool.
- The inside and outside interfaces have been configured backwards.
- The NAT pool has been exhausted.
- Access-list 1 has not been configured properly.
Explanation & Hint: The output of show ip nat statistics shows that there are 2 total addresses and that 2 addresses have been allocated (100%). This indicates that the NAT pool is out of global addresses to give new clients. Based on the show ip nat translations, PCs at 10.1.1.33 and 10.1.1.123 have used the two available addresses to send ICMP messages to a host on the outside network.
-
In setting up a small office network, the network administrator decides to assign private IP addresses dynamically to workstations and mobile devices. Which feature must be enabled on the company router in order for office devices to access the internet?
- MAC filtering
- QoS
- UPnP
- NAT
Explanation & Hint: Network Address Translation (NAT) is the process used to convert private addresses to internet-routable addresses that allow office devices to access the internet.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured OSPFv2 on the two Cisco routers but PC1 is unable to connect to PC2. What is the most likely problem?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 23 - Interface Fa0/0 is configured as a passive-interface on router R2.
- Interface s0/0 has not been activated for OSPFv2 on router R2.
- Interface S0/0 is configured as a passive-interface on router R2.
- Interface Fa0/0 has not been activated for OSPFv2 on router R2.
Explanation & Hint: If a LAN network is not advertised using OSPFv2, a remote network will not be reachable. The output displays a successful neighbor adjacency between router R1 and R2 on the interface S0/0 of both routers.
-
What command would be used as part of configuring NAT or PAT to identify an interface as part of the external global network?
- access-list 10 permit 172.19.89.0 0.0.0.255
- ip pat inside
- ip nat inside
- ip nat outside
-
Explanation & Hint: The command used as part of configuring Network Address Translation (NAT) or Port Address Translation (PAT) to identify an interface as part of the external global network is:
- ip nat outside
This command is applied to the interface that connects to the external network, typically the internet, marking it as the outside interface in the context of NAT or PAT. Traffic leaving this interface will be translated to an address or port that is routable on the external network.
Here’s a brief explanation of the other options:
- access-list 10 permit 172.19.89.0 0.0.0.255: This is an access control list (ACL) command used to permit traffic from the 172.19.89.0 network. ACLs can be used in NAT configurations to define which local addresses are allowed to be translated.
- ip pat inside: This is not a valid command. The correct command for identifying an interface as part of the internal network in the context of PAT would be
ip nat inside, which would be used on the internal interface facing the local network. - ip nat inside: This command is used to designate an interface as part of the internal network that connects to private local network resources in a NAT or PAT configuration.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator has an IP address of 192.168.11.10 and needs access to manage R1. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 24 - standard ACL inbound on R1 vty lines
- standard ACL inbound on R2 WAN interface connecting to the internet
- extended ACL outbound on R2 S0/0/1
- extended ACLs inbound on R1 G0/0 and G0/1
-
Explanation & Hint: Access Control Lists (ACLs) can be used to restrict access to a router’s VTY (Virtual Teletype) lines for management purposes. In the scenario where a network administrator with an IP address of 192.168.11.10 needs to manage R1, the ACL should be applied to R1 to control access to its VTY lines. This is typically done with a standard ACL because only the source IP address needs to be evaluated.
The best type of ACL for this situation would be:
- Standard ACL inbound on R1 vty lines
This ACL will filter traffic coming into the VTY lines of R1, allowing only the administrator’s IP address to access the router for management while denying all others. The use of a standard ACL is sufficient since the requirement is to filter based on source IP addresses only.
Here’s why the other options are less suitable:
- Standard ACL inbound on R2 WAN interface connecting to the internet: This would be inefficient and potentially insecure, as it would apply the filter too broadly, affecting all traffic passing through the WAN interface, not just management traffic to R1.
- Extended ACL outbound on R2 S0/0/1: While extended ACLs are more precise because they can filter based on both source and destination IP addresses as well as ports, applying this ACL on R2’s interface would be incorrect because it would not effectively restrict access to R1’s management interface.
- Extended ACLs inbound on R1 G0/0 and G0/1: Using extended ACLs on R1’s interfaces would be overly complex for the requirement and might inadvertently block legitimate traffic. The goal is to restrict access to the VTY lines, not to filter general traffic coming into the router’s interfaces.
So, a standard ACL applied to the VTY lines of R1 is the best choice to ensure that only the administrator can access R1 for management purposes.
-
A network administrator has been tasked with creating a disaster recovery plan. As part of this plan, the administrator is looking for a backup site for all of the data on the company servers. What service or technology would support this requirement?
- virtualization
- data center
- software defined networking
- dedicated servers
-
Explanation & Hint: For creating a disaster recovery plan that includes a backup site for all of the data on the company servers, the service or technology that would support this requirement is a data center.
A data center is a facility used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. It generally includes redundant or backup power supplies, redundant data communications connections, environmental controls (e.g., air conditioning, fire suppression), and various security devices. A data center can be used to create a secure and resilient environment where a backup of the company’s servers and data can be stored.
Here’s a brief explanation of the other options:
- Virtualization: This technology allows you to create and manage multiple virtual instances of devices (like servers) on a single set of hardware. While virtualization is a key component of modern disaster recovery solutions because it allows for rapid provisioning and flexibility, it is not a service or technology for offsite data storage by itself.
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): SDN is an approach to networking that uses software-based controllers or application programming interfaces (APIs) to direct traffic on the network and communicate with the underlying hardware infrastructure. It’s more about managing network resources efficiently and doesn’t directly relate to data storage for disaster recovery.
- Dedicated Servers: These are physical servers dedicated to a single customer or task. While they can be part of a disaster recovery plan, the term ‘dedicated servers’ by itself doesn’t imply a backup site or disaster recovery functionality.
For the specified need of a backup site for disaster recovery, a data center is the most relevant because it can provide a secure and resilient offsite location to store critical backups and ensure business continuity in the event of a disaster.
-
Refer to the exhibit. What method can be used to enable an OSPF router to advertise a default route to neighboring OSPF routers?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA Final Exam Answers 22 - Use a static route pointing to the ISP and redistribute it.
- Use the default-information originate command on ISP.
- Use the redistribute static command on R0-A.
- Use the default-information originate command on R0-A.
- Use the redistribute static command on ISP.
-
Explanation & Hint: To enable an OSPF router to advertise a default route to neighboring OSPF routers, the method used is:
- Use the default-information originate command on R0-A.
This command is used on the OSPF router that has a connection to an external network (such as an ISP) to generate a default route into the OSPF domain. If R0-A has the connection to the ISP, then it would be the router to originate the default route to the other OSPF routers.
Here’s why the other options are less suitable:
- Use a static route pointing to the ISP and redistribute it: While redistributing a static default route into OSPF is a valid method, the option is incomplete because it doesn’t specify where to apply the redistribution. Redistribution would typically be done on the router connected to the ISP, in this case, R0-A.
- Use the default-information originate command on ISP: This command should be used on the OSPF router within your network that you want to advertise the default route, not on the ISP’s router.
- Use the redistribute static command on R0-A: Redistributing static routes is also a method to propagate default routes in OSPF, but this option is not specifying which static route to redistribute. To properly redistribute a default route, there should be a static default route configured on R0-A that is then redistributed into OSPF.
- Use the redistribute static command on ISP: The ISP router is typically not under your administrative control, and even if it were, you would not generally redistribute routes from the ISP into your OSPF process; rather, you would generate a default route from your edge router using the default-information originate command.
Therefore, the correct method to advertise a default route to neighboring OSPF routers is to use the default-information originate command on R0-A, assuming it has the direct connection to the ISP.