CCNA 3 v7 – ENSA v7.02 – Modules 3 – 5: Network Security Exam Answers 100% 2023 2024
CCNA 3 v7 – ENSA v7.02 – Modules 3 – 5: Network Security Exam Answers Full 100% 2023 2024
This is NetAcad Cisco CCNA 3 v7 ENSA v7.02 Modules 3 – 5 Exam Answers 2023 2024 and Enterprise Networking, Security, and Automation (Version 7.00) – Network Security Exam Answers Full 100%. All answers have been verified by experts.
| CCNA 3 v7 & 7.02 | |
| Final Exam Answers | |
| This Modules 3 - 5 | |
| Modules 3 - 5 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Next Modules 6 - 8 | |
| Modules 6 - 8 Exam Answers | Online Test |
Cisco Netacad ENSA v7 & 7.02 Version 7.00 CCNA 3 v7 Modules 3 – 5: Network Security Exam Answers 2023 2024 – Enterprise Networking, Security, and Automation Full 100%
-
Which statement accurately characterizes the evolution of threats to network security?
- Internal threats can cause even greater damage than external threats.
- Internet architects planned for network security from the beginning.
- Early Internet users often engaged in activities that would harm other users.
- Threats have become less sophisticated while the technical knowledge needed by an attacker has grown.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Internal threats can be intentional or accidental and cause greater damage than external threats because the internal user has direct access to the internal corporate network and corporate data.
-
What commonly motivates cybercriminals to attack networks as compared to hacktivists or state-sponsored hackers?
- fame seeking
- financial gain
- political reasons
- status among peers
Answers Explanation & Hints: Cybercriminals are commonly motivated by money. Hackers are known to hack for status. Cyberterrorists are motivated to commit cybercrimes for religious or political reasons.
-
Which type of hacker is motivated to protest against political and social issues?
- script kiddie
- hacktivist
- vulnerability broker
- cybercriminal
Answers Explanation & Hints: Hackers are categorized by motivating factors. Hacktivists are motivated by protesting political and social issues.
-
What is the best description of Trojan horse malware?
- It is the most easily detected form of malware.
- It is malware that can only be distributed over the Internet.
- It is software that causes annoying but not fatal computer problems.
- It appears as useful software but hides malicious code.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The best description of Trojan horse malware, and what distinguishes it from viruses and worms, is that it appears as useful software but hides malicious code. Trojan horse malware may cause annoying computer problems, but can also cause fatal problems. Some Trojan horses may be distributed over the Internet, but they can also be distributed by USB memory sticks and other means. Specifically targeted Trojan horse malware can be some of the most difficult malware to detect.
-
A user receives a phone call from a person who claims to represent IT services and then asks that user for confirmation of username and password for auditing purposes. Which security threat does this phone call represent?
- DDoS
- spam
- social engineering
- anonymous keylogging
Answers Explanation & Hints: Social engineering attempts to gain the confidence of an employee and convince that person to divulge confidential and sensitive information, such as usernames and passwords. DDoS attacks, spam, and keylogging are all examples of software based security threats, not social engineering.
-
What is a ping sweep?
- a network scanning technique that indicates the live hosts in a range of IP addresses.
- a software application that enables the capture of all network packets that are sent across a LAN.
- a scanning technique that examines a range of TCP or UDP port numbers on a host to detect listening services.
- a query and response protocol that identifies information about a domain, including the addresses that are assigned to that domain.
Answers Explanation & Hints: A ping sweep is a tool that is used during a reconnaissance attack. Other tools that might be used during this type of attack include a ping sweep, port scan, or Internet information query. A reconnaissance attack is used to gather information about a particular network, usually in preparation for another type of network attack.
-
In what way are zombies used in security attacks?
- They are maliciously formed code segments used to replace legitimate applications.
- They target specific individuals to gain corporate or personal information.
- They are infected machines that carry out a DDoS attack.
- They probe a group of machines for open ports to learn which services are running.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Zombies are infected computers that make up a botnet. The zombies are used to deploy a distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack.
-
In what type of attack is a cybercriminal attempting to prevent legitimate users from accessing network services?
- DoS
- MITM
- session hijacking
- address spoofing
Answers Explanation & Hints: In a DoS or denial-of-service attack, the goal of the attacker is to prevent legitimate users from accessing network services.
-
Which attack involves threat actors positioning themselves between a source and destination with the intent of transparently monitoring, capturing, and controlling the communication?
- DoS attack
- ICMP attack
- SYN flood attack
- man-in-the-middle attack
Answers Explanation & Hints: The man-in-the-middle attack is a common IP-related attack where threat actors position themselves between a source and destination to transparently monitor, capture, and control the communication.
-
In which type of attack is falsified information used to redirect users to malicious Internet sites?
- DNS cache poisoning
- ARP cache poisoning
- DNS amplification and reflection
- domain generation
Answers Explanation & Hints: In a DNS cache poisoning attack, falsified information is used to redirect users from legitimate to malicious internet sites.
-
What is a feature of an IPS?
- It can stop malicious packets.
- It has no impact on latency.
- It is deployed in offline mode.
- It is primarily focused on identifying possible incidents.
Answers Explanation & Hints: An advantage of an intrusion prevention systems (IPS) is that it can identify and stop malicious packets. However, because an IPS is deployed inline, it can add latency to the network.
-
Which requirement of secure communications is ensured by the implementation of MD5 or SHA hash generating algorithms?
- confidentiality
- authentication
- integrity
- nonrepudiation
Answers Explanation & Hints: Integrity is ensured by implementing either MD5 or SHA hash generating algorithms. Many modern networks ensure authentication with protocols, such as HMAC. Data confidentiality is ensured through symmetric encryption algorithms, including DES, 3DES, and AES. Data confidentiality can also be ensured using asymmetric algorithms, including RSA and PKI.
-
If an asymmetric algorithm uses a public key to encrypt data, what is used to decrypt it?
- DH
- a private key
- a digital certificate
- a different public key
Answers Explanation & Hints: When an asymmetric algorithm is used, public and private keys are used for the encryption. Either key can be used for encryption, but the complementary matched key must be used for the decryption. For example if the public key is used for encryption, then the private key must be used for the decryption.
-
What wild card mask will match networks 172.16.0.0 through 172.19.0.0?
- 0.0.3.255
- 0.0.255.255
- 0.252.255.255
- 0.3.255.255
Answers Explanation & Hints: The subnets 172.16.0.0 through 172.19.0.0 all share the same 14 high level bits. A wildcard mask in binary that matches 14 high order bits is 00000000.00000011.11111111.11111111. In dotted decimal this wild card mask is 0.3.255.255.
-
Which two keywords can be used in an access control list to replace a wildcard mask or address and wildcard mask pair? (Choose two.)
- most
- host
- all
- any
- some
- gt
Answers Explanation & Hints: The host keyword is used when using a specific device IP address in an ACL. For example, the deny host 192.168.5.5 command is the same is the deny 192.168.5.5 0.0.0.0 command. The any keyword is used to allow any mask through that meets the criteria. For example, the permit any command is the same as permit 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 command.
-
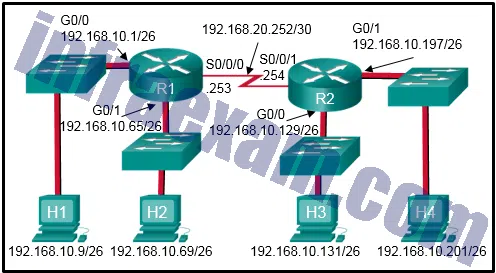
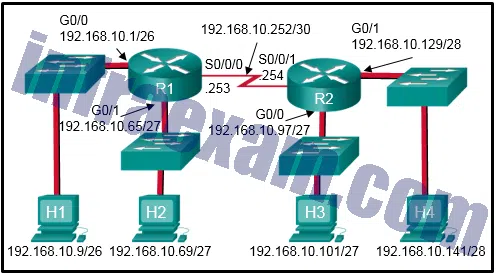
Refer to the exhibit. Which two ACLs would permit only the two LAN networks attached to R1 to access the network that connects to R2 G0/1 interface? (Choose two.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 12 - access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.127
- access-list 2 permit host 192.168.10.9
access-list 2 permit host 192.168.10.69 - access-list 3 permit 192.168.10.128 0.0.0.63
- access-list 4 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
- access-list 5 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.63
access-list 5 permit 192.168.10.64 0.0.0.63Answers Explanation & Hints: The permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.127 command ignores bit positions 1 through 7, which means that addresses 192.168.10.0 through 192.168.10.127 are allowed through. The two ACEs of permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.63 and permit 192.168.10.64 0.0.0.63 allow the same address range through the router.
-
Which two packet filters could a network administrator use on an IPv4 extended ACL? (Choose two.)
- destination MAC address
- ICMP message type
- computer type
- source TCP hello address
- destination UDP port number
Answers Explanation & Hints: Extended access lists commonly filter on source and destination IPv4 addresses and TCP or UDP port numbers. Additional filtering can be provided for protocol types.
-
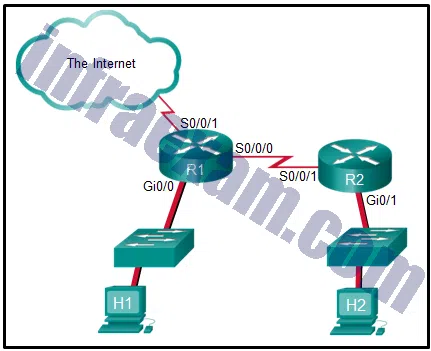
Refer to the exhibit. The student on the H1 computer continues to launch an extended ping with expanded packets at the student on the H2 computer. The school network administrator wants to stop this behavior, but still allow both students access to web-based computer assignments. What would be the best plan for the network administrator?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 07 - Apply an outbound extended ACL on R1 S0/0/1.
- Apply an outbound standard ACL on R2 S0/0/1.
- Apply an inbound standard ACL on R1 Gi0/0.
- Apply an inbound extended ACL on R2 Gi0/1.
- Apply an inbound extended ACL on R1 Gi0/0.
Answers Explanation & Hints: This access list must be an extended ACL in order to filter on specific source and destination host addresses. Commonly, the best place for an extended ACL is closest to the source, which is H1. Traffic from H1 travels into the switch, then out of the switch into the R1 Gi0/0 interface. This Gi0/0 interface would be the best location for this type of extended ACL. The ACL would be applied on the inbound interface since the packets from H1 would be coming into the R1 router.
-
Which statement describes a difference between the operation of inbound and outbound ACLs?
- In contrast to outbound ALCs, inbound ACLs can be used to filter packets with multiple criteria.
- Inbound ACLs can be used in both routers and switches but outbound ACLs can be used only on routers.
- Inbound ACLs are processed before the packets are routed while outbound ACLs are processed after the routing is completed.
- On a network interface, more than one inbound ACL can be configured but only one outbound ACL can be configured.
Answers Explanation & Hints: With an inbound ACL, incoming packets are processed before they are routed. With an outbound ACL, packets are first routed to the outbound interface, then they are processed. Thus processing inbound is more efficient from the router perspective. The structure, filtering methods, and limitations (on an interface, only one inbound and one outbound ACL can be configured) are the same for both types of ACLs.
-
What type of ACL offers greater flexibility and control over network access?
- flexible
- named standard
- extended
- numbered standard
Answers Explanation & Hints: The two types of ACLs are standard and extended. Both types can be named or numbered, but extended ACLs offer greater flexibility.
-
What is the quickest way to remove a single ACE from a named ACL?
- Use the no keyword and the sequence number of the ACE to be removed.
- Use the no access-list command to remove the entire ACL, then recreate it without the ACE.
- Copy the ACL into a text editor, remove the ACE, then copy the ACL back into the router.
- Create a new ACL with a different number and apply the new ACL to the router interface.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Named ACL ACEs can be removed using the no command followed by the sequence number.
-
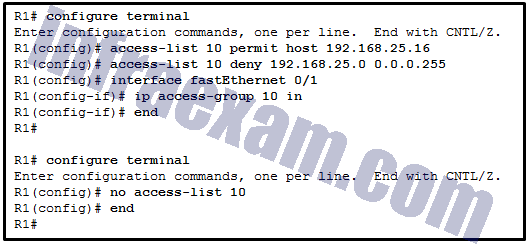
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring a standard IPv4 ACL. What is the effect after the command no access-list 10 is entered?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 02 - ACL 10 is disabled on Fa0/1.
- ACL 10 is removed from the running configuration.
- ACL 10 will be disabled and removed after R1 restarts.
- ACL 10 is removed from both the running configuration and the interface Fa0/1.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The R1(config)# no access-list < access-list number > command removes the ACL from the running-config immediately. However, to disable an ACL on an interface, the command R1(config-if)# no ip access-group should be entered.
-
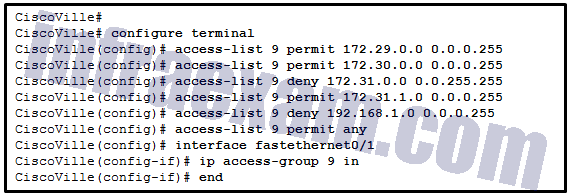
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured ACL 9 as shown. Users on the 172.31.1.0 /24 network cannot forward traffic through router CiscoVille. What is the most likely cause of the traffic failure?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 05 - The permit statement specifies an incorrect wildcard mask.
- The sequence of the ACEs is incorrect.
- The established keyword is not specified.
- The port number for the traffic has not been identified with the eq keyword.
Answers Explanation & Hints: When verifying an ACL, the statements are always listed in a sequential order. Even though there is an explicit permit for the traffic that is sourced from network 172.31.1.0 /24, it is being denied due to the previously implemented ACE of CiscoVille(config)# access-list 9 deny 172.31.0.0 0.0.255.255 . The sequence of the ACEs must be modified to permit the specific traffic that is sourced from network 172.31.1.0 /24 and then to deny 172.31.0.0 /16.
-
A network administrator needs to configure a standard ACL so that only the workstation of the administrator with the IP address 192.168.15.23 can access the virtual terminal of the main router. Which two configuration commands can achieve the task? (Choose two.)
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit host 192.168.15.23
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 0.0.0.0
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 0.0.0.255
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 255.255.255.0
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 255.255.255.255
Answers Explanation & Hints: To permit or deny one specific IP address, either the wildcard mask 0.0.0.0 (used after the IP address) or the wildcard mask keyword host (used before the IP address) can be used.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which command would be used in a standard ACL to allow only devices on the network attached to R2 G0/0 interface to access the networks attached to R1?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 13 - access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.63
- access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.96 0.0.0.31
- access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
- access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.128 0.0.0.63
Answers Explanation & Hints: Standard access lists only filter on the source IP address. In the design, the packets would be coming from the 192.168.10.96/27 network (the R2 G0/0 network). The correct ACL is access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.96 0.0.0.31 .
-
A network administrator is writing a standard ACL that will deny any traffic from the 172.16.0.0/16 network, but permit all other traffic. Which two commands should be used? (Choose two.)
- Router(config)# access-list 95 deny any
- Router(config)# access-list 95 deny 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255
- Router(config)# access-list 95 deny 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0
- Router(config)# access-list 95 permit any
- Router(config)# access-list 95 host 172.16.0.0
- Router(config)# access-list 95 172.16.0.0 255.255.255.255
Answers Explanation & Hints: To deny traffic from the 172.16.0.0/16 network, the access-list 95 deny 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 command is used. To permit all other traffic, the access-list 95 permit any statement is added.
-
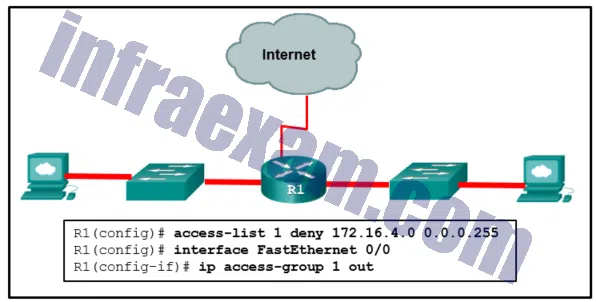
Refer to the exhibit. An ACL was configured on R1 with the intention of denying traffic from subnet 172.16.4.0/24 into subnet 172.16.3.0/24. All other traffic into subnet 172.16.3.0/24 should be permitted. This standard ACL was then applied outbound on interface Fa0/0. Which conclusion can be drawn from this configuration?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 15 - Only traffic from the 172.16.4.0/24 subnet is blocked, and all other traffic is allowed.
- An extended ACL must be used in this situation.
- The ACL should be applied to the FastEthernet 0/0 interface of R1 inbound to accomplish the requirements.
- All traffic will be blocked, not just traffic from the 172.16.4.0/24 subnet.
- The ACL should be applied outbound on all interfaces of R1.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Because of the implicit deny at the end of all ACLs, the access-list 1 permit any command must be included to ensure that only traffic from the 172.16.4.0/24 subnet is blocked and that all other traffic is allowed.
-
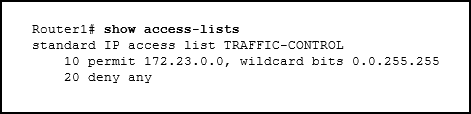
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator needs to add an ACE to the TRAFFIC-CONTROL ACL that will deny IP traffic from the subnet 172.23.16.0/20. Which ACE will meet this requirement?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 14 - 15 deny 172.23.16.0 0.0.15.255
- 5 deny 172.23.16.0 0.0.15.255
- 30 deny 172.23.16.0 0.0.15.255
- 5 deny 172.23.16.0 0.0.255.255
Answers Explanation & Hints: The only filtering criteria specified for a standard access list is the source IPv4 address. The wild card mask is written to identify what parts of the address to match, with a 0 bit, and what parts of the address should be ignored, which a 1 bit. The router will parse the ACE entries from lowest sequence number to highest. If an ACE must be added to an existing access list, the sequence number should be specified so that the ACE is in the correct place during the ACL evaluation process.
-
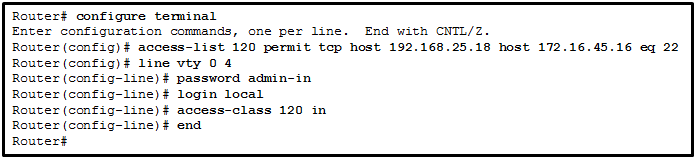
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator configures an ACL on the router. Which statement describes the result of the configuration?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 04 - An SSH connection is allowed from a workstation with IP 172.16.45.16 to a device with IP 192.168.25.18.
- An SSH connection is allowed from a workstation with IP 192.168.25.18 to a device with IP 172.16.45.16.
- A Telnet connection is allowed from a workstation with IP 172.16.45.16 to a device with IP 192.168.25.18.
- A Telnet connection is allowed from a workstation with IP 192.168.25.18 to a device with IP 172.16.45.16.
Answers Explanation & Hints: In an extended ACL, the first address is the source IP address and the second one is the destination IP address. TCP port number 22 is a well-known port number reserved for SSH connections. Telnet connections use TCP port number 23.
-
What effect would the Router1(config-ext-nacl)# permit tcp 172.16.4.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www command have when implemented inbound on the f0/0 interface?
- All TCP traffic is permitted, and all other traffic is denied.
- The command is rejected by the router because it is incomplete.
- All traffic from 172.16.4.0/24 is permitted anywhere on any port.
- Traffic originating from 172.16.4.0/24 is permitted to all TCP port 80 destinations.
-
Explanation & Hint: The command
Router1(config-ext-nacl)# permit tcp 172.16.4.0 0.0.0.255 any eq wwwwhen implemented inbound on the f0/0 interface would have the effect of:“Traffic originating from 172.16.4.0/24 is permitted to all TCP port 80 destinations.”
This command configures an extended access control list (ACL) on a router. Here’s the breakdown of the command:
permit tcp: This specifies that the rule allows TCP traffic.172.16.4.0 0.0.0.255: This is the source IP address range. 172.16.4.0 with the subnet mask 0.0.0.255 represents all IP addresses from 172.16.4.0 to 172.16.4.255, which is the 172.16.4.0/24 subnet.any: This means the rule applies to traffic going to any destination IP address.eq www: This specifies that the rule applies to traffic destined for the standard HTTP port, which is port 80 (denoted bywww).
So, the command effectively allows all TCP traffic originating from the 172.16.4.0/24 subnet and destined for port 80 (HTTP) on any host. Other types of traffic from this subnet, or TCP traffic to ports other than 80, would not be permitted by this rule. It’s important to remember that this rule is part of an access control list, and the effect of the ACL depends on the other rules in the list and the order in which they are placed.
-
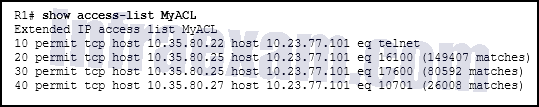
Refer to the exhibit. What can be determined from this output?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 03 - The ACL is missing the deny ip any any ACE.
- Because there are no matches for line 10, the ACL is not working.
- The ACL is only monitoring traffic destined for 10.23.77.101 from three specific hosts.
- The router has not had any Telnet packets from 10.35.80.22 that are destined for 10.23.77.101.
Answers Explanation & Hints: ACL entry 10 in MyACL matches any Telnet packets between host 10.35.80.22 and 10.23.77.101. No matches have occurred on this ACE as evidenced by the lack of a “(xxx matches)” ACE. The deny ip any any ACE is not required because there is an implicit deny ACE added to every access control list. When no matches exist for an ACL, it only means that no traffic has matched the conditions that exist for that particular line. The ACL is monitoring traffic that matches three specific hosts going to very specific destination devices. All other traffic is not permitted by the implicit deny ip any any ACE.
-
What does the CLI prompt change to after entering the command ip access-list standard aaa from global configuration mode?
- Router(config)#
- Router(config-if)#
- Router(config-router)#
- Router(config-std-nacl)#
- Router(config-line)#
-
Explanation & Hint: When you enter the command
ip access-list standard aaafrom the global configuration mode in a Cisco router, the Command-Line Interface (CLI) prompt changes to:Router(config-std-nacl)#This change in the prompt reflects that you have entered the standard named access control list (ACL) configuration mode. In this mode, you can define rules for the access control list named “aaa”. The standard ACL controls traffic based solely on the source IP address. The prompt change helps indicate the context or mode you are currently in, allowing for more specific configurations related to the standard ACL named “aaa”.
-
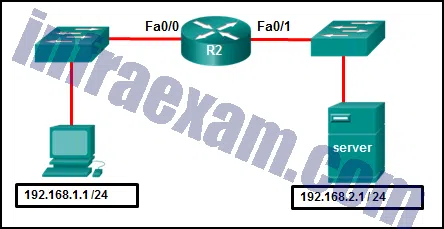
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator wants to permit only host 192.168.1.1 /24 to be able to access the server 192.168.2.1 /24. Which three commands will achieve this using best ACL placement practices? (Choose three.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 08 - R2(config)# access-list 101 permit ip host 192.168.1.1 host 192.168.2.1
- R2(config)# access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0
- R2(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0
- R2(config-if)# ip access-group 101 out
- R2(config)# access-list 101 permit ip any any
- R2(config)# interface fastethernet 0/1
- R2(config-if)# ip access-group 101 in
Answers Explanation & Hints: An extended ACL is placed as close to the source of the traffic as possible. In this case.it is placed in an inbound direction on interface fa0/0 on R2 for traffic entering the router from host with the IP address192.168.1.1 bound for the server with the IP address192.168.2.1.
-
Which ACE will permit a packet that originates from any network and is destined for a web server at 192.168.1.1?
- access-list 101 permit tcp host 192.168.1.1 any eq 80
- access-list 101 permit tcp host 192.168.1.1 eq 80 any
- access-list 101 permit tcp any eq 80 host 192.168.1.1
- access-list 101 permit tcp any host 192.168.1.1 eq 80
-
Explanation & Hint: To permit a packet that originates from any network and is destined for a web server at 192.168.1.1, the appropriate Access Control Entry (ACE) would be:
access-list 101 permit tcp any host 192.168.1.1 eq 80This ACE is a part of an extended access control list (ACL) configuration in Cisco devices. Let’s break down what this specific ACE does:
access-list 101: This indicates the ACL number, in this case, 101, which is an extended ACL.permit: This keyword allows the traffic that matches the criteria set in the ACE.tcp: This specifies the protocol type. TCP is used because web traffic (HTTP) operates over TCP.any: This indicates that the source can be any IP address.host 192.168.1.1: This specifies the destination IP address as a single host, which in this case is the web server with the IP address 192.168.1.1.eq 80: This denotes that the destination port number must be 80, which is the standard port for HTTP traffic.
So, this ACE allows TCP traffic from any source IP address to the specific host 192.168.1.1 on port 80, which is typically used for web server communication.
-
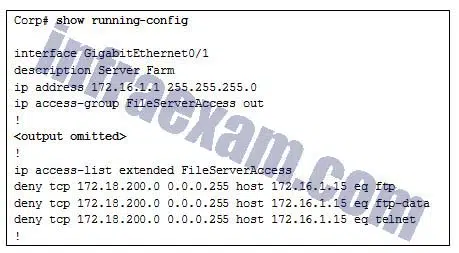
Refer to the exhibit. A new network policy requires an ACL denying FTP and Telnet access to a Corp file server from all interns. The address of the file server is 172.16.1.15 and all interns are assigned addresses in the 172.18.200.0/24 network. After implementing the ACL, no one in the Corp network can access any of the servers. What is the problem?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 11 - Inbound ACLs must be routed before they are processed.
- The ACL is implicitly denying access to all the servers.
- Named ACLs require the use of port numbers.
- The ACL is applied to the interface using the wrong direction.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Both named and numbered ACLs have an implicit deny ACE at the end of the list. This implicit deny blocks all traffic.
-
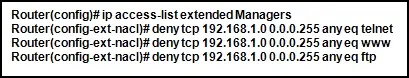
Refer to the exhibit. The named ACL “Managers” already exists on the router. What will happen when the network administrator issues the commands that are shown in the exhibit?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 01 - The commands overwrite the existing Managers ACL.
- The commands are added at the end of the existing Managers ACL.
- The commands are added at the beginning of the existing Managers ACL.
- The network administrator receives an error that states that the ACL already exists.
-
Explanation & Hint: When the network administrator issues the commands shown in the exhibit for a named ACL “Managers” that already exists, the following will happen:
The commands are added at the end of the existing Managers ACL.
In Cisco IOS, when you enter the named access control list configuration mode for an ACL that already exists, the default behavior is to append new entries to the end of the ACL. Existing entries are not overwritten, and there is no error unless there is a syntax issue with the new commands themselves. It is also possible to insert commands in specific positions if required by using sequence numbers, but that is not being done in the provided exhibit.
-
Consider the following access list.access-list 100 permit ip host 192.168.10.1 any
access-list 100 deny icmp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any echo access-list 100 permit ip any any
Which two actions are taken if the access list is placed inbound on a router Gigabit Ethernet port that has the IP address 192.168.10.254 assigned? (Choose two.)
- A Telnet or SSH session is allowed from any device on the 192.168.10.0 into the router with this access list assigned.
- Devices on the 192.168.10.0/24 network are allowed to reply to any ping requests.
- Only Layer 3 connections are allowed to be made from the router to any other network device.
- Only the network device assigned the IP address 192.168.10.1 is allowed to access the router.
- Devices on the 192.168.10.0/24 network can sucessfully ping devices on the 192.168.11.0 network.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The first ACE allows the 192.168.10.1 device to do any TCP/IP-based transactions with any other destination. The second ACE stops devices on the 192.168.10.0/24 network from issuing any pings to any other location. Everything else is permitted by the third ACE. Therefore, a Telnet/SSH session or ping reply is allowed from a device on the 192.168.10.0/24 network.
-
In which TCP attack is the cybercriminal attempting to overwhelm a target host with half-open TCP connections?
- reset attack
- port scan attack
- SYN flood attack
- session hijacking attack
Answers Explanation & Hints: In a TCP SYN flood attack, the attacker sends to the target host a continuous flood of TCP SYN session requests with a spoofed source IP address. The target host responds with a TCP-SYN-ACK to each of the SYN session requests and waits for a TCP ACK that will never arrive. Eventually the target is overwhelmed with half-open TCP connections.
-
Which protocol is attacked when a cybercriminal provides an invalid gateway in order to create a man-in-the-middle attack?
- DNS
- ICMP
- HTTP or HTTPS
- DHCP
Answers Explanation & Hints: A cybercriminal could set up a rogue DHCP server that provides one or more of the following:Wrong default gateway that is used to create a man-in-the-middle attack and allow the attacker to intercept data
Wrong DNS server that results in the user being sent to a malicious website
Invalid default gateway IP address that results in a denial of service attack on the DHCP client
-
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator has configured a standard ACL on R1 and applied it to interface serial 0/0/0 in the outbound direction. What happens to traffic leaving interface serial 0/0/0 that does not match the configured ACL statements?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 09 - The resulting action is determined by the destination IP address.
- The resulting action is determined by the destination IP address and port number.
- The source IP address is checked and, if a match is not found, traffic is routed out interface serial 0/0/1.
- The traffic is dropped.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Any traffic that does not match one of the statements in an ACL has the implicit deny applied to it, which means the traffic is dropped.
-
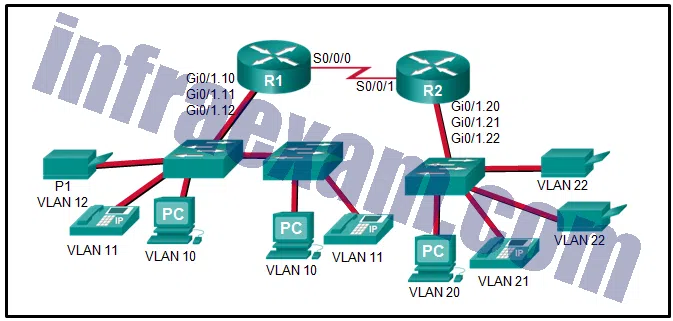
Refer to the exhibit. The Gigabit interfaces on both routers have been configured with subinterface numbers that match the VLAN numbers connected to them. PCs on VLAN 10 should be able to print to the P1 printer on VLAN 12. PCs on VLAN 20 should print to the printers on VLAN 22. What interface and in what direction should you place a standard ACL that allows printing to P1 from data VLAN 10, but stops the PCs on VLAN 20 from using the P1 printer? (Choose two.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 06 - R1 Gi0/1.12
- R1 S0/0/0
- R2 S0/0/1
- R2 Gi0/1.20
- inbound
- outbound
Answers Explanation & Hints: A standard access list is commonly placed as close to the destination network as possible because access control expressions in a standard ACL do not include information about the destination network.
The destination in this example is printer VLAN 12 which has router R1 Gigabit subinterface 0/1/.12 as its gateway. A sample standard ACL that only allows printing from data VLAN 10 (192.168.10.0/24), for example, and no other VLAN would be as follows:
R1(config)# access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
R1(config)# access-list 1 deny any
R1(config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/1.12
R1(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out
-
Which statement describes a characteristic of standard IPv4 ACLs?
- They are configured in the interface configuration mode.
- They filter traffic based on source IP addresses only.
- They can be created with a number but not with a name.
- They can be configured to filter traffic based on both source IP addresses and source ports.
Answers Explanation & Hints: A standard IPv4 ACL can filter traffic based on source IP addresses only. Unlike an extended ACL, it cannot filter traffic based on Layer 4 ports. However, both standard and extended ACLs can be identified with either a number or a name, and both are configured in global configuration mode.
-
What is considered a best practice when configuring ACLs on vty lines?
- Use only extended access lists.
- Place identical restrictions on all vty lines.
- Apply the ip access-group command inbound.
- Remove the vty password since the ACL restricts access to trusted users.
-
Explanation & Hint: A best practice when configuring ACLs on vty (virtual terminal) lines is to:
Place identical restrictions on all vty lines.
This ensures consistent security across all potential remote access points to the router. If different vty lines had different restrictions, it could lead to confusion and potentially leave the router more vulnerable on less restricted lines. By applying the same restrictions, you maintain a uniform security posture. You should not remove the vty password, as multiple layers of security are advised; an ACL is an additional layer, not a replacement for password authentication. The
ip access-groupcommand can be applied to vty lines, but it is not specifically inbound or outbound as it is when applied to interfaces; it simply controls access to the vty lines themselves. Whether to use standard or extended ACLs depends on the specific requirements of the network security policy, but extended ACLs provide more granularity and control.
-
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator first configured an extended ACL as shown by the output of the show access-lists command. The administrator then edited this access-list by issuing the commands below.
Router(config)# ip access-list extended 101 Router(config-ext-nacl)# no 20 Router(config-ext-nacl)# 5 permit tcp any any eq 22 Router(config-ext-nacl)# 20 deny udp any any
Which two conclusions can be drawn from this new configuration? (Choose two.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 10 - Ping packets will be permitted.
- Telnet packets will be permitted.
- All TCP and UDP packets will be denied.
- SSH packets will be permitted.
- TFTP packets will be permitted.
Answers Explanation & Hints: After the editing, the final configuration is as follows:
Router# show access-lists
Extended IP access list 101
5 permit tcp any any eq ssh
10 deny tcp any any
20 deny udp any any
30 permit icmp any any
So, only SSH packets and ICMP packets will be permitted.
-
Which set of access control entries would allow all users on the 192.168.10.0/24 network to access a web server that is located at 172.17.80.1, but would not allow them to use Telnet?
- access-list 103 deny tcp host 192.168.10.0 any eq 23
access-list 103 permit tcp host 192.168.10.1 eq 80 - access-list 103 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 host 172.17.80.1
access-list 103 deny tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq telnet - access-list 103 permit tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 host 172.17.80.1 eq 80
access-list 103 deny tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq 23 - access-list 103 permit tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq 80
access-list 103 deny tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq 23Answers Explanation & Hints: For an extended ACL to meet these requirements the following need to be included in the access control entries:identification number in the range 100-199 or 2000-2699
permit or deny parameter
protocol
source address and wildcard
destination address and wildcard
port number or name
- access-list 103 deny tcp host 192.168.10.0 any eq 23
-
What is the term used to describe unethical criminals who compromise computer and network security for personal gain, or for malicious reasons?
- black hat hackers
- vulnerability broker
- hacktivists
- script kiddies
-
Explanation & Hint: The term used to describe unethical criminals who compromise computer and network security for personal gain or for malicious reasons is:
Black hat hackers.
Black hat hackers are individuals with extensive knowledge of internet security and networking who use their skills for illegal or malicious purposes. They are the antithesis of white hat hackers, who also have deep knowledge of networks and security but use their skills to improve security and protect against black hat hackers. Hacktivists typically hack for politically or socially motivated purposes, while script kiddies are unskilled individuals who use existing computer scripts or codes to hack into computers, lacking the expertise to write their own.
-
What is the term used to describe a mechanism that takes advantage of a vulnerability?
- exploit
- threat
- vulnerability
- mitigation
-
Explanation & Hint: The term used to describe a mechanism that takes advantage of a vulnerability is:
Exploit.
An exploit is a piece of software, a chunk of data, or a sequence of commands that takes advantage of a bug or vulnerability in order to cause unintended or unanticipated behavior to occur on computer software, hardware, or something electronic (usually computerized). This frequently includes such things as gaining control of a computer system, allowing privilege escalation, or a denial-of-service attack.
-
What is the term used to describe the same pre-shared key or secret key, known by both the sender and receiver to encrypt and decrypt data?
- symmetric encryption algorithm
- data integrity
- risk
- mitigation
-
Explanation & Hint: The term used to describe the same pre-shared key or secret key, known by both the sender and receiver to encrypt and decrypt data, is:
Symmetric encryption algorithm.
Symmetric encryption algorithms use the same key for both encryption of plaintext and decryption of ciphertext. The key must be kept secret from all but the authorized parties.
-
What is the term used to describe the same pre-shared key or secret key, known by both the sender and receiver to encrypt and decrypt data?
- symmetric encryption algorithm
- data integrity
- risk
- exploit
-
Explanation & Hint: The term used to describe the same pre-shared key or secret key, known by both the sender and receiver to encrypt and decrypt data, is:
Symmetric encryption algorithm.
In symmetric encryption, the same key is used for both encryption and decryption, and it must be shared and kept secret between the two parties.
-
What is the term used to describe a guarantee that the message is not a forgery and does actually come from whom it states?
- origin authentication
- mitigation
- exploit
- risk
-
Explanation & Hint: The term used to describe a guarantee that the message is not a forgery and does actually come from whom it states is:
Origin authentication.
Origin authentication ensures that a message, transaction, or other form of data is from the entity it claims to be from, providing assurance of the data’s origin’s legitimacy.
-
What is the term used to describe a guarantee that the message is not a forgery and does actually come from whom it states?
- origin authentication
- mitigation
- exploit
- data non-repudiation
-
Explanation & Hint: Origin Authentication.
Origin authentication is the assurance that a message, communication, or transaction is from the source it claims to be from. This prevents an attacker from forging the source of the data.
-
What is the term used to describe gray hat hackers who publicly protest organizations or governments by posting articles, videos, leaking sensitive information, and performing network attacks?
- hacktivists
- grey hat hackers
- white hat hackers
- state-sponsored hacker
-
Explanation & Hint: The term used to describe gray hat hackers who publicly protest organizations or governments by posting articles, videos, leaking sensitive information, and performing network attacks is:
Hacktivists.
Hacktivists are individuals who use hacking techniques and digital tools to promote a political agenda, social change, or ideological beliefs. Their actions often include unauthorized access to systems, data leaks, website defacements, and denial-of-service attacks, all motivated by activism rather than personal gain or malicious intent.
-
What is the term used to describe gray hat hackers who publicly protest organizations or governments by posting articles, videos, leaking sensitive information, and performing network attacks?
- hacktivists
- grey hat hackers
- white hat hackers
- script kiddies
-
Explanation & Hint: The term used to describe gray hat hackers who publicly protest organizations or governments by posting articles, videos, leaking sensitive information, and performing network attacks is:
Hacktivists.
Hacktivists are individuals who use hacking as a tool for activism to promote political ends, often by breaking into systems and networks, leaking confidential information, and conducting various forms of cyber protests. Their actions are typically motivated by social or political causes.
-
What is the term used to describe a potential danger to a company’s assets, data, or network functionality?
- threat
- vulnerability
- exploit
- asset
-
Explanation & Hint: The term used to describe a potential danger to a company’s assets, data, or network functionality is:
Threat.
A threat in the context of cybersecurity refers to any potential danger that could exploit a vulnerability to breach security and cause harm to an organization’s assets or operations. This includes a wide range of malicious activities like cyber attacks, data breaches, and other forms of unauthorized access or damage to the system.
-
What is the term used to describe a potential danger to a company’s assets, data, or network functionality?
- threat
- vulnerability
- exploit
- asymmetric encryption algorithm
-
Explanation & Hint: The term used to describe a potential danger to a company’s assets, data, or network functionality is:
Threat.
A threat in cybersecurity and risk management is anything that has the potential to cause serious harm to a digital system. It can be an intentional attack like malware, phishing, and ransomware, or it can be accidental, like a system failure or human error. The concept of a threat is focused on the potential for harm, rather than a weakness or the method of attack.
-
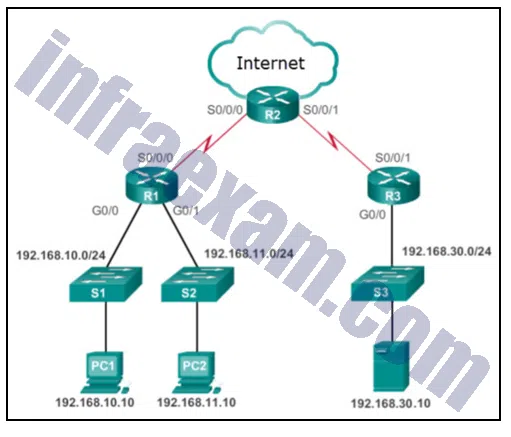
Refer to the exhibit. Employees on 192.168.11.0/24 work on critically sensitive information and are not allowed access off their network. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 16 - standard ACL inbound on R1 G0/1
- extended ACL inbound on R2 S0/0/0
- standard ACL inbound on R1 vty lines
- standard ACL inbound on R2 WAN interface connecting to the internet
-
Explanation & Hint: In the context of the given network where the employees on the network 192.168.11.0/24 should not have access off their network, using a standard ACL inbound on R1 G0/1 would be the best approach to restrict the traffic. Standard ACLs are typically applied closest to the destination, but in this case, it’s used to prevent a specific subnet from accessing any outside resources, so it makes sense to place it close to the source of the traffic you want to control.
Standard ACL inbound on R1 G0/1 would be the correct choice to restrict all traffic from the 192.168.11.0/24 network from going to any destinations beyond the router R1.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Only authorized remote users are allowed remote access to the company server 192.168.30.10. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 16 - extended ACL inbound on R2 WAN interface connected to the internet
- extended ACLs inbound on R1 G0/0 and G0/1
- extended ACL outbound on R2 WAN interface towards the internet
- extended ACL inbound on R2 S0/0/0
-
Explanation & Hint: In the scenario where only authorized remote users are allowed to access the company server at 192.168.30.10, the best ACL type and placement would be:
Extended ACL inbound on R2 WAN interface connected to the internet.
Here’s why this is the best choice:
- Extended ACLs are capable of filtering traffic based on both source and destination IP addresses, as well as protocols and ports, which allows for precise control over which remote users are allowed to access the server.
- Placing this ACL on the R2 WAN interface that connects to the internet is strategic because it can filter the traffic from remote users as it enters the network. This placement ensures that only authorized users are allowed access before the traffic traverses the internal network, thus providing efficient and effective access control.
- The ACL should be applied inbound to filter the traffic as it comes into the network from the internet destined for the server, rather than outbound where it would be filtering traffic leaving the network.
By placing the extended ACL inbound on the R2 WAN interface, you are ensuring that only specified traffic from authorized remote users can reach the server, and all other unauthorized attempts are blocked at the network’s edge.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Many employees are wasting company time accessing social media on their work computers. The company wants to stop this access. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 16 - extended ACLs inbound on R1 G0/0 and G0/1
- standard ACL inbound on R1 G0/1
- standard ACL inbound on R1 G0/0
- standard ACL inbound on R2 WAN interface connecting to the internet
-
Explanation & Hint: To stop employees from accessing social media on their work computers, the best ACL type and placement would be:
Extended ACLs inbound on R1 G0/0 and G0/1.
The reasoning for this choice is:
- Extended ACLs allow for filtering based on the protocol type, source and destination IP addresses, and destination ports. This means you can specifically block access to the IP addresses and ports associated with social media sites.
- Placing these ACLs inbound on R1’s G0/0 and G0/1 interfaces will filter traffic from the PCs within the company network before it exits out to the internet, thus stopping the traffic as close to the source as possible, which is a recommended best practice.
- Using extended ACLs instead of standard ACLs allows the company to block only specific types of traffic (like HTTP and HTTPS typically used for social media) without blocking other internet traffic that might be necessary for work purposes.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The company has provided IP phones to employees on the 192.168.10.0/24 network and the voice traffic will need priority over data traffic. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 16 - extended ACL inbound on R1 G0/0
- extended ACL inbound on R3 S0/0/1
- extended ACLs inbound on R1 G0/0 and G0/1
- standard ACL outbound on R2 S0/0/0
-
Explanation & Hint: For giving priority to voice traffic over data traffic for IP phones on the 192.168.10.0/24 network, the best approach would not typically involve an ACL for traffic prioritization. Instead, you would use Quality of Service (QoS) configurations. However, if an ACL is needed to identify the traffic for QoS policies, then you would likely use:
Extended ACL inbound on R1 G0/0.
Here’s the reasoning:
- Extended ACLs can match on the specific types of traffic (e.g., voice) by using access control entries that classify the traffic based on source and destination IP addresses, protocols, and port numbers.
- Applying the ACL inbound on R1 G0/0 would be effective since this is the interface that connects to the 192.168.10.0/24 network where the IP phones are located. The ACL can be used to identify the voice traffic so that QoS policies can then prioritize it accordingly.
- Since the question is about prioritizing traffic from a specific network, you do not need to apply the ACL on both G0/0 and G0/1, just on the interface where the IP phones’ traffic originates.
Remember, ACLs by themselves do not prioritize traffic; they are typically used in conjunction with QoS configurations that reference the ACL to apply the appropriate traffic prioritization.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Network 192.168.30.0/24 contains all of the company servers. Policy dictates that traffic from the servers to both networks 192.168.10.0 and 192.168.11.0 be limited to replies for original requests. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 16 - extended ACL inbound on R3 G0/0
- extended ACLs inbound on R1 G0/0 and G0/1
- standard ACL inbound on R1 vty lines
- standard ACL inbound on R1 G0/0
-
Explanation & Hint: To limit traffic from the servers in the network 192.168.30.0/24 to networks 192.168.10.0 and 192.168.11.0 so that only replies to original requests are allowed, an extended ACL should be used because standard ACLs cannot match on the TCP “established” option needed for this purpose.
The best ACL type and placement would be:
Extended ACL inbound on R3 G0/0.
Here’s why:
- Extended ACLs are required because they can inspect the traffic deeply enough to determine if it is a reply to an established connection. The “established” keyword in extended ACLs allows the ACL to permit inbound responses to requests originated from the internal networks.
- Placing this ACL inbound on R3 G0/0 is strategic because this is the interface directly connected to the network 192.168.30.0/24 where the company servers are located. The ACL will filter the traffic as it leaves the server network and heads towards R1 and the other internal networks.
This setup ensures that unsolicited traffic from the server network to the internal user networks is not allowed, while responses to traffic originated from the internal user networks are permitted.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Network 192.168.30.0/24 contains all of the company servers. Policy dictates that traffic from the servers to both networks 192.168.10.0 and 192.168.11.0 be limited to replies for original requests. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 16 - extended ACL inbound on R3 G0/0
- extended ACL outbound on R2 S0/0/1
- standard ACL inbound on R2 WAN interface connecting to the internet
- extended ACL outbound on R2 WAN interface towards the internet
-
Explanation & Hint: For the given policy and network configuration, the correct ACL type and placement to ensure that traffic from the servers is limited to replies to original requests is:
Extended ACL inbound on R3 G0/0.
Applying an extended ACL inbound on the R3 G0/0 interface would allow the router to filter incoming traffic to the server network, ensuring that only established connections, or responses to requests from the 192.168.10.0 and 192.168.11.0 networks, are allowed through. This setup effectively restricts the server network from initiating traffic to these networks, in compliance with the company policy.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Many employees are wasting company time accessing social media on their work computers. The company wants to stop this access. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 16 - extended ACLs inbound on R1 G0/0 and G0/1
- standard ACL outbound on R2 S0/0/0
- extended ACL outbound on R2 S0/0/1
- extended ACL inbound on R2 S0/0/0
-
Explanation & Hint: To prevent employees from accessing social media on their work computers, the company should implement an ACL that can filter traffic based on the destination IP addresses and ports typically used by social media platforms. This requires the use of an extended ACL because standard ACLs cannot match on destination addresses or ports.
The best ACL type and placement in this scenario would be:
Extended ACLs inbound on R1 G0/0 and G0/1.
Here’s why:
- Extended ACLs are suitable as they can filter based on both IP addresses and the port numbers associated with social media websites (often TCP ports 80 for HTTP and 443 for HTTPS).
- Placing these ACLs inbound on R1’s G0/0 and G0/1 interfaces allows the router to inspect and filter the traffic as it originates from the local networks (192.168.10.0/24 and 192.168.11.0/24) before it leaves the company network towards the internet.
This approach ensures that access to social media can be controlled as close to the source as possible, which is a best practice in network security to conserve network resources and to provide effective control.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The company has provided IP phones to employees on the 192.168.10.0/24 network and the voice traffic will need priority over data traffic. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 16 - extended ACL inbound on R1 G0/0
- extended ACLs inbound on R1 G0/0 and G0/1
- standard ACL inbound on R1 G0/1
- standard ACL outbound on R1 G0/0
-
Explanation & Hint: To prioritize voice traffic over data traffic for IP phones on the 192.168.10.0/24 network, you would typically use Quality of Service (QoS) configurations. An ACL can be used to identify the voice traffic so that QoS policies can prioritize it. Given that the voice traffic is originating from the 192.168.10.0/24 network, you would want to match this traffic as it enters the router from this network.
The best ACL type and placement in this situation would be:
Extended ACL inbound on R1 G0/0.
Here’s why:
- Extended ACLs are necessary because you need to match not just the source IP address but also typically the protocol and port numbers that signify voice traffic (like the ports used for SIP or RTP).
- Placing this ACL inbound on R1’s G0/0 interface allows the router to inspect and classify the traffic as it comes from the IP phones in the 192.168.10.0/24 network. Once classified by the ACL, QoS policies can then be applied to give priority to this traffic over other data traffic.
This setup allows the voice traffic to be identified and treated with higher priority as it competes for bandwidth with other types of traffic on the network.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator has an IP address of 192.168.11.10 and needs access to manage R1. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 16 - standard ACL inbound on R1 vty lines
- standard ACL outbound on R1 G0/0
- standard ACL inbound on R2 WAN interface connecting to the internet
- extended ACL inbound on R3 G0/0
-
Explanation & Hint: For a network administrator with an IP address of 192.168.11.10 who needs access to manage R1, the best ACL type and placement would be to control access to the vty (virtual terminal) lines of R1. This is because vty lines are used for remote management of the router via protocols such as SSH or Telnet.
The best ACL type and placement in this situation would be:
Standard ACL inbound on R1 vty lines.
Here’s why:
- Standard ACLs can be used for controlling access to vty lines because they are typically sufficient for filtering by source IP address, which is what you need when you want to restrict access to a specific management station.
- Applying the ACL inbound on R1’s vty lines means that the ACL will filter incoming management connections to the router. You would configure the ACL to permit only the specific IP address of the network administrator’s computer and deny all others.
This setup ensures that only the network administrator with the specified IP address can remotely manage R1, enhancing the security of the router by preventing unauthorized remote access.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Network 192.168.30.0/24 contains all of the company servers. Policy dictates that traffic from the servers to both networks 192.168.10.0 and 192.168.11.0 be limited to replies for original requests. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 16 - extended ACL inbound on R3 G0/0
- standard ACL inbound on R1 G0/1
- standard ACL inbound on R2 WAN interface connecting to the internet
- extended ACL outbound on R2 S0/0/1
-
Explanation & Hint: For a policy that dictates traffic from the company servers in network 192.168.30.0/24 should be limited to replies to original requests to networks 192.168.10.0 and 192.168.11.0, an extended ACL is required. This is because extended ACLs can match on the TCP “established” condition, which allows the ACL to permit traffic that is part of an existing session.
The best ACL type and placement for this scenario would be:
Extended ACL inbound on R3 G0/0.
This choice is based on the following:
- Extended ACLs: These are capable of filtering traffic not just based on IP addresses but also based on the type of traffic, such as established TCP connections. This is crucial for allowing only reply traffic and not new sessions.
- Inbound on R3 G0/0: Applying the ACL inbound on R3’s interface G0/0, which connects to the server network, ensures that the servers can only send traffic as replies to requests coming from the other networks (192.168.10.0 and 192.168.11.0). This way, the ACL is checked as soon as the traffic from the servers reaches the router, which is efficient and ensures compliance with the policy.
This configuration would effectively enforce the policy, only allowing traffic from the servers in response to internal requests, preventing the servers from initiating any new connections to those internal networks.
-
A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the established configuration option or command?
- to allow returning reply traffic to enter the internal network
- to allow specified traffic through an interface
- to display all restricted traffic
- to add a text entry for documentation purposes
-
Explanation & Hint: The technician would use the
establishedconfiguration option or command:To allow returning reply traffic to enter the internal network.
This option is used in extended ACLs to allow inbound traffic that is part of an already established session, typically TCP sessions where the initial handshake (SYN, SYN-ACK, ACK) has been completed. This ensures that only responses to requests that originated from inside the network are allowed back through the firewall or router. It’s useful for permitting return traffic for sessions that were initiated from inside the network, without allowing unsolicited incoming connections.
-
A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the any configuration option or command?
- to identify any IP address
- to insert a comment into the packet header
- to identify one specific IP address
- to restrict specific traffic access through an interface
-
Explanation & Hint: The technician would use the
anyconfiguration option or command:To identify any IP address.
In the context of Access Control Lists (ACLs), the keyword
anyis used to represent any IP address, effectively serving as a wildcard that matches all IP addresses when specifying either a source or destination in an ACL entry.
-
A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the established configuration option or command?
- to allow returning reply traffic to enter the internal network
- to add a text entry for documentation purposes
- to generate and send an informational message whenever the ACE is matched
- to insert a comment into the packet header
-
Explanation & Hint: The technician would use the
establishedconfiguration option or command:To allow returning reply traffic to enter the internal network.
This is used in extended ACLs to match established TCP sessions, allowing traffic that is part of an existing, established connection (such as return traffic from a web server) to pass through the router, while blocking unsolicited incoming connections.
-
A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the host configuration option or command?
- to identify a single IP address
- to allow specified traffic through an interface
- to insert a comment into the packet header
- to add a text entry for documentation purposes
-
Explanation & Hint: The technician would use the
hostconfiguration option or command:To identify a single IP address.
In ACLs, the
hostkeyword is used to specify a single IP address in an access control entry (ACE). It’s effectively a shortcut for using the standard subnet mask of 255.255.255.255, which denotes a single host.
-
A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the ip access-group 101 in configuration option or command?
- to apply an extended ACL to an interface
- to secure administrative access to the router
- to display all restricted traffic
- to verify the ACL applied on the interface
-
Explanation & Hint: The technician would use the
ip access-group 101 inconfiguration option or command:To apply an extended ACL to an interface.
This command is used to apply an already defined Access Control List (ACL) to an interface on the router. In this case,
101is the identifier of the ACL, andinspecifies that the ACL is to be applied to inbound traffic passing through the interface. This is a common way to enforce security policies by filtering traffic entering the interface based on the rules defined in the ACL.
-
A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the access-class 20 in configuration option or command?
- to secure remote administrative access to the router
- to secure management traffic into the router
- to remove a configured ACL
- to apply a standard ACL to an interface
-
Explanation & Hint: The technician would use the
access-class 20 inconfiguration option or command:To secure remote administrative access to the router.
This command is applied to vty lines (virtual terminal lines) for securing remote administrative access to the router, such as through Telnet or SSH. In this context,
20refers to the number of the Access Control List (ACL) that contains the rules for allowing or denying remote access, andinspecifies that the ACL is applied to inbound connections to the vty lines. This is an essential security measure to control which IP addresses are allowed to initiate a remote management session with the router.
-
A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the established configuration option or command?
- to allow returning reply traffic to enter the internal network
- to insert a comment into the packet header
- to identify one specific IP address
- to generate and send an informational message whenever the ACE is matched
-
Explanation & Hint: The technician would use the
establishedconfiguration option or command:To allow returning reply traffic to enter the internal network.
In the context of Access Control Lists (ACLs), particularly extended ACLs, the
establishedoption is used to permit inbound packets that are part of an existing, established TCP connection. This option is valuable for allowing response traffic from external servers in response to requests initiated from inside the network, while blocking unsolicited inbound connections.
-
A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the deny configuration option or command?
- to restrict specific traffic access through an interface
- to generate and send an informational message whenever the ACE is matched
- to display all restricted traffic
- to identify one specific IP address
-
Explanation & Hint: The technician would use the
denyconfiguration option or command:To restrict specific traffic access through an interface.
In ACLs (Access Control Lists), the
denystatement is used to specify which types of traffic should be blocked or not allowed through a router interface. When an ACL is applied to an interface, any packet that matches the criteria set in adenystatement is not permitted to pass through that interface. This is a fundamental component of network security, allowing network administrators to control the flow of traffic and protect network resources from unauthorized access or unwanted traffic.
-
A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the 40 deny host 192.168.23.8 configuration option or command?
- to create an entry in a numbered ACL
- to secure management traffic into the router
- to remove an ACL from an interface
- to apply an extended ACL to an interface
-
Explanation & Hint: The technician would use the
40 deny host 192.168.23.8configuration option or command:To create an entry in a numbered ACL.
In this command,
40represents the sequence number or entry number within the ACL,denyspecifies that this entry is denying traffic, andhost 192.168.23.8is specifying the source IP address to be denied. This command is used to define a specific rule within an ACL, and it’s commonly used in numbered extended ACLs to control traffic based on various criteria, including source and destination IP addresses, protocols, and ports.
-
A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the any configuration option or command?
- to identify any IP address
- to insert a comment into the packet header
- to generate and send an informational message whenever the ACE is matched
- to identify one specific IP address
-
Explanation & Hint: The technician would use the
anyconfiguration option or command:To identify any IP address.
In ACLs (Access Control Lists), the
anykeyword is used as a wildcard to represent any IP address. It allows the ACL rule to match traffic from or to any IP address. This can be useful when creating general rules that apply to all IP addresses without specifying a particular source or destination address.
-
A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the remark configuration option or command?
- to restrict specific traffic access through an interface
- to add a text entry for documentation purposes
- to identify one specific IP address
- to generate and send an informational message whenever the ACE is matched
-
Answers Explanation & Hints: The remark configuration option or command is typically used by a technician to add a text entry for documentation purposes.
When configuring Access Control Lists (ACLs) to secure a router, the remark command can be used to add comments or descriptions to individual lines of the ACL for the purpose of documenting what each line is meant to do. This can help other network administrators understand the purpose of the ACL and make changes or troubleshoot issues with it more easily.
The other options you listed do not relate to the use of the remark command. To restrict specific traffic access through an interface, the technician would typically use ACL rules to permit or deny traffic based on criteria such as source IP address, destination IP address, protocol type, and port number. To identify one specific IP address, the technician may use an ACL rule that matches that IP address in either the source or destination field. To generate and send an informational message whenever the ACE is matched, the technician would use the logging command in conjunction with the ACL rule.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The company CEO demands that one ACL be created to permit email traffic to the internet and deny FTP access. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 16 - extended ACL outbound on R2 WAN interface towards the internet
- standard ACL inbound on R2 WAN interface connecting to the internet
- extended ACL inbound on R2 S0/0/0
- standard ACL outbound on R2 S0/0/0
Answers Explanation & Hints: Standard ACLs permit or deny packets based only on the source IPv4 address. Because all traffic types are permitted or denied, standard ACLs should be located as close to the destination as possible.
Extended ACLs permit or deny packets based on the source IPv4 address and destination IPv4 address, protocol type, source and destination TCP or UDP ports and more. Because the filtering of extended ACLs is so specific, extended ACLs should be located as close as possible to the source of the traffic to be filtered. Undesirable traffic is denied close to the source network without crossing the network infrastructure.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Internet privileges for an employee have been revoked because of abuse but the employee still needs access to company resources. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 3 – 5 Network Security Exam Answers 16 - standard ACL outbound on R2 WAN interface towards the internet
- standard ACL outbound on R1 G0/0
- standard ACL inbound on R1 G0/0
- standard ACL inbound on R2 WAN interface connecting to the internet
Answers Explanation & Hints: Standard ACLs permit or deny packets based only on the source IPv4 address. Because all traffic types are permitted or denied, standard ACLs should be located as close to the destination as possible.
Extended ACLs permit or deny packets based on the source IPv4 address and destination IPv4 address, protocol type, source and destination TCP or UDP ports and more. Because the filtering of extended ACLs is so specific, extended ACLs should be located as close as possible to the source of the traffic to be filtered. Undesirable traffic is denied close to the source network without crossing the network infrastructure.
-
A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the no ip access-list 101 configuration option or command?
- to remove a configured ACL
- to remove all ACLs from the router
- to apply an ACL to all router interfaces
- to secure administrative access to the router
-
Explanation & Hint: The technician would use the
no ip access-list 101configuration option or command:To remove a configured ACL.
This command is used to remove an existing Access Control List (ACL) from the router’s configuration. When you specify the ACL number (in this case, 101) with the
no ip access-listcommand, it effectively deletes or removes that ACL from the router’s configuration. This can be useful if you need to change or remove an existing ACL that is no longer needed or if you want to replace it with a different ACL.
| CCNA 3 v7 & 7.02 | |
| Final Exam Answers | |
| This Modules 3 - 5 | |
| Modules 3 - 5 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Next Modules 6 - 8 | |
| Modules 6 - 8 Exam Answers | Online Test |