CCNA 3 v7 – ENSA v7.02 – Modules 6 – 8: WAN Concepts Exam Answers 2023 2024 100%
CCNA 3 v7 – ENSA v7.02 – Modules 6 – 8: WAN Concepts Exam Answers Full 100% 2023 2024
This is NetAcad Cisco CCNA 3 v7 ENSA v7.02 Modules 6 – 8 Exam Answers 2023 2024 and Enterprise Networking, Security, and Automation (Version 7.00) – WAN Concepts Exam Answers Full 100%. All answers have been verified by experts.
| CCNA 3 v7 & 7.02 | |
| Final Exam Answers | |
| This Modules 6 - 8 | |
| Modules 6 - 8 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Next Modules 9 - 12 | |
| Modules 9 - 12 Exam Answers | Online Test |
Cisco Netacad ENSA Version 7.00 CCNA 3 v7 Modules 6 – 8: WAN Concepts Exam Answers 2023 2024 – Enterprise Networking, Security, and Automation
-
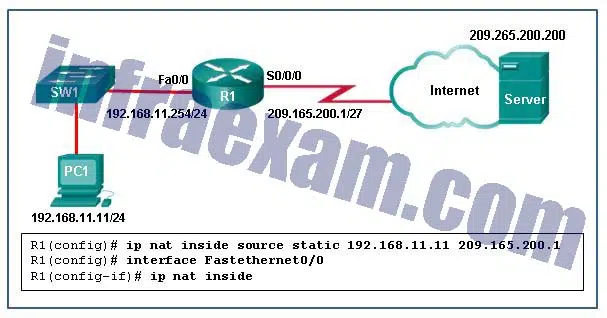
Refer to the exhibit. What has to be done in order to complete the static NAT configuration on R1?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 01 - R1 should be configured with the command ip nat inside source static 209.165.200.1 192.168.11.11 .
- R1 should be configured with the command ip nat inside source static 209.165.200.200 192.168.11.11 .
- Interface S0/0/0 should be configured with the command ip nat outside .
- Interface Fa0/0 should be configured with the command no ip nat inside .
Answers Explanation & Hints: In order for NAT translations to work properly, both an inside and outside interface must be configured for NAT translation on the router.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured R2 for PAT. Why is the configuration incorrect?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 03 - The static NAT entry is missing.
- NAT-POOL2 is bound to the wrong ACL.
- The ACL does not define the list of addresses to be translated.
- The overload keyword should not have been applied.
Answers Explanation & Hints: In the exhibit, NAT-POOL 2 is bound to ACL 100, but it should be bound to the configured ACL 1. This will cause PAT to fail. 100, but it should be bound to the configured ACL 1. This will cause PAT to fail.
-
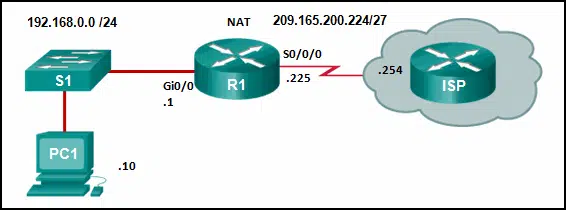
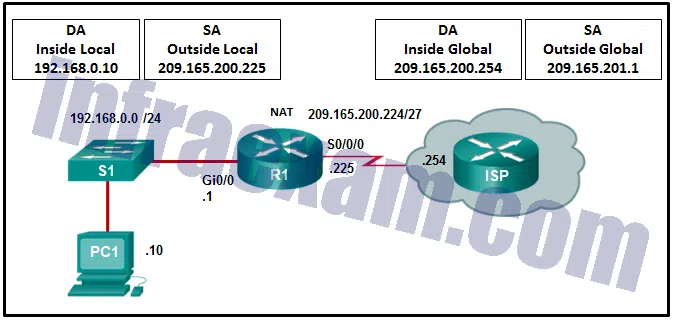
Refer to the exhibit. From the perspective of R1, the NAT router, which address is the inside global address?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 04 - 192.168.0.1
- 192.168.0.10
- 209.165.200.225
- 209.165.200.254
Answers Explanation & Hints: There are four types of addresses in NAT terminology.
Inside local address
Inside global address
Outside local address
Outside global address
The inside global address of PC1 is the address that the ISP sees as the source address of packets, which in this example is the IP address on the serial interface of R1, 209.165.200.224.
-
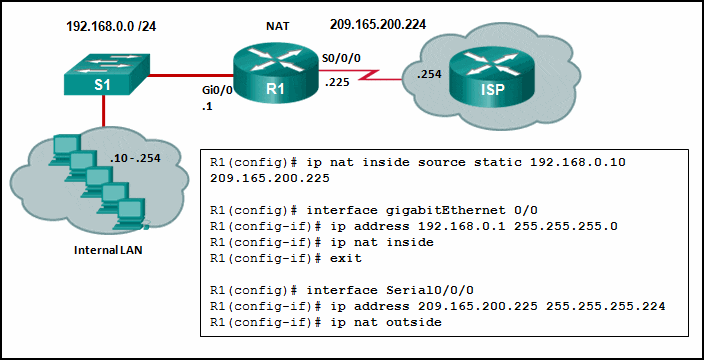
Refer to the exhibit. Given the commands as shown, how many hosts on the internal LAN off R1 can have simultaneous NAT translations on R1?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 05 - 1
- 10
- 244
- 255
Answers Explanation & Hints: The NAT configuration on R1 is static NAT which translates a single inside IP address, 192.168.0.10 into a single public IP address, 209.165.200.255. If more hosts need translation, then a NAT pool of inside global address or overloading should be configured.
-
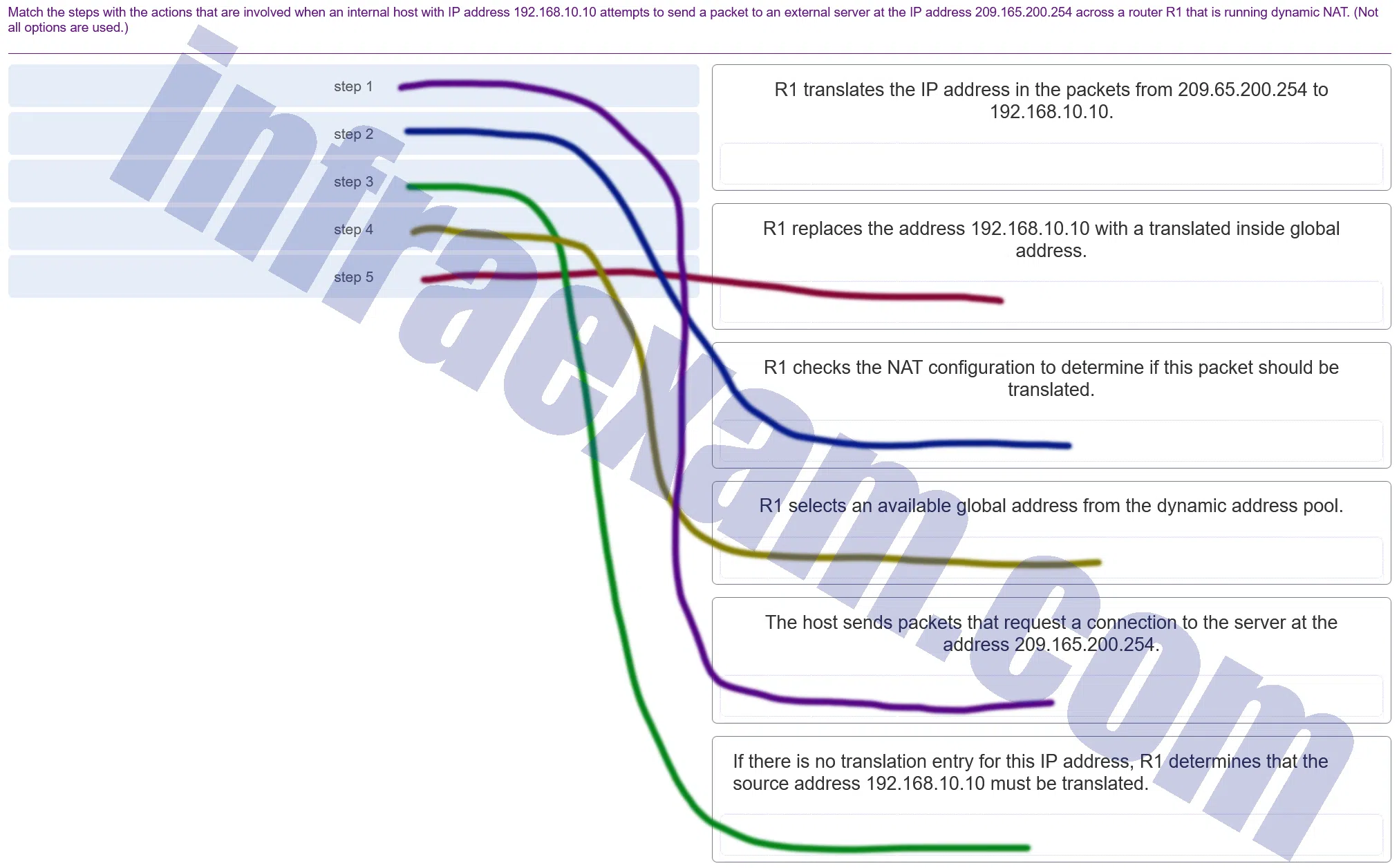
Match the steps with the actions that are involved when an internal host with IP address 192.168.10.10 attempts to send a packet to an external server at the IP address 209.165.200.254 across a router R1 that is running dynamic NAT. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 001 Answers Explanation & Hints: The translation of the IP addresses from 209.65.200.254 to 192.168.10.10 will take place when the reply comes back from the server.
-
What is a disadvantage when both sides of a communication use PAT?
- Host IPv4 addressing is complicated.
- End-to-end IPv4 traceability is lost.
- The flexibility of connections to the Internet is reduced.
- The security of the communication is negatively impacted.
Answers Explanation & Hints: With the use of NAT, especially PAT, end-to-end traceability is lost. This is because the host IP address in the packets during a communication is translated when it leaves and enters the network. With the use of NAT/PAT, both the flexibility of connections to the Internet and security are actually enhanced. Host IPv4 addressing is provided by DHCP and not related to NAT/PAT.
-
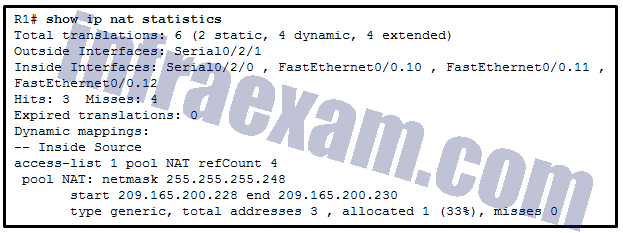
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has just configured address translation and is verifying the configuration. What three things can the administrator verify? (Choose three.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 08 - Address translation is working.
- Three addresses from the NAT pool are being used by hosts.
- The name of the NAT pool is refCount.
- A standard access list numbered 1 was used as part of the configuration process.
- Two types of NAT are enabled.
- One port on the router is not participating in the address translation.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The show ip nat statistics , show ip nat translations , and debug ip nat commands are useful in determining if NAT is working and and also useful in troubleshooting problems that are associated with NAT. NAT is working, as shown by the hits and misses count. Because there are four misses, a problem might be evident. The standard access list numbered 1 is being used and the translation pool is named NAT as evidenced by the last line of the output. Both static NAT and NAT overload are used as seen in the Total translations line.
-
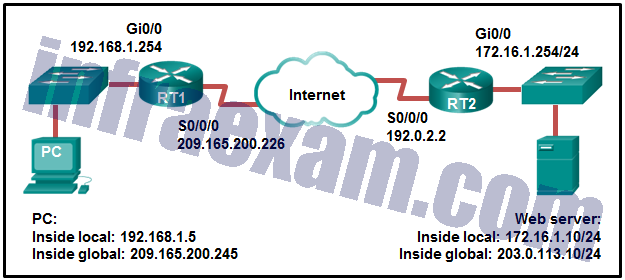
Refer to the exhibit. NAT is configured on RT1 and RT2. The PC is sending a request to the web server. What IPv4 address is the source IP address in the packet between RT2 and the web server?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 10 - 192.0.2.2
- 172.16.1.10
- 203.0.113.10
- 172.16.1.254
- 192.168.1.5
- 209.165.200.245
Answers Explanation & Hints: Because the packet is between RT2 and the web server, the source IP address is the inside global address of PC, 209.165.200.245.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output that is shown, what type of NAT has been implemented?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 15 - dynamic NAT with a pool of two public IP addresses
- PAT using an external interface
- static NAT with one entry
- static NAT with a NAT pool
Answers Explanation & Hints: The output shows that there are two inside global addresses that are the same but that have different port numbers. The only time port numbers are displayed is when PAT is being used. The same output would be indicative of PAT that uses an address pool. PAT with an address pool is appropriate when more than 4,000 simultaneous translations are needed by the company.
-
In NAT terms, what address type refers to the globally routable IPv4 address of a destination host on the Internet?
- inside global
- outside local
- outside global
- inside local
Answers Explanation & Hints: From the perspective of a NAT device, inside global addresses are used by external users to reach internal hosts. Inside local addresses are the addresses assigned to internal hosts. Outside global addresses are the addresses of destinations on the external network. Outside local addresses are the actual private addresses of destination hosts behind other NAT devices.
-
Refer to the exhibit. From the perspective of users behind the NAT router, what type of NAT address is 209.165.201.1?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 13 - outside global
- outside local
- inside local
- inside global
Answers Explanation & Hints: From the perspective of users behind NAT, inside global addresses are used by external users to reach internal hosts. Inside local addresses are the addresses assigned to internal hosts. Outside global addresses are the addresses of destinations on the external network. Outside local addresses are the actual private addresses of destination hosts behind other NAT devices.
-
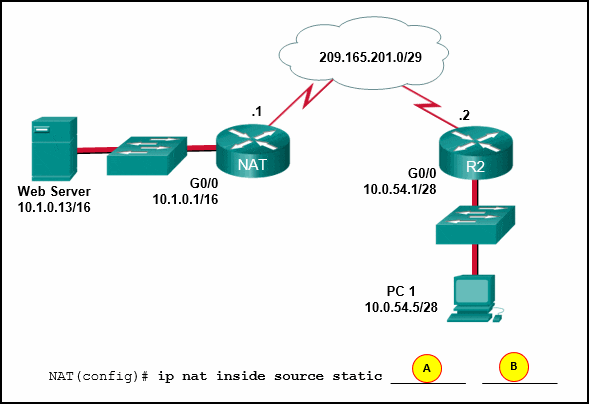
Refer to the exhibit. Static NAT is being configured to allow PC 1 access to the web server on the internal network. What two addresses are needed in place of A and B to complete the static NAT configuration? (Choose two.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 14 - A = 209.165.201.2
- A = 10.1.0.13
- B = 209.165.201.1
- B = 209.165.201.7
- B = 10.0.254.5
Answers Explanation & Hints: Static NAT is a one-to-one mapping between an inside local address and an inside global address. By using static NAT, external devices can initiate connections to internal devices by using the inside global addresses. The NAT devices will translate the inside global address to the inside local address of the target host.
-
What is the purpose of the overload keyword in the ip nat inside source list 1 pool NAT_POOL overload command?
- It allows many inside hosts to share one or a few inside global addresses.
- It allows a pool of inside global addresses to be used by internal hosts.
- It allows external hosts to initiate sessions with internal hosts.
- It allows a list of internal hosts to communicate with a specific group of external hosts.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Dynamic NAT uses a pool of inside global addresses that are assigned to outgoing sessions. If there are more internal hosts than public addresses in the pool, then an administrator can enable port address translation with the addition of the overload keyword. With port address translation, many internal hosts can share a single inside global address because the NAT device will track the individual sessions by Layer 4 port number.
-
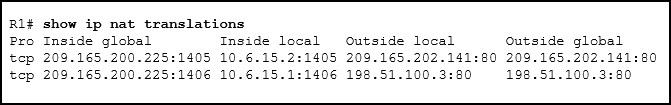
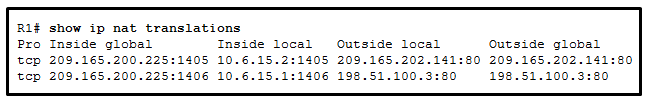
Refer to the exhibit. Which source address is being used by router R1 for packets being forwarded to the Internet?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 12 - 198.51.100.3
- 209.165.202.141
- 10.6.15.2
- 209.165.200.225
Answers Explanation & Hints: The source address for packets forwarded by the router to the Internet will be the inside global address of 209.165.200.225. This is the address that the internal addresses from the 10.6.15.0 network will be translated to by NAT.
-
What two addresses are specified in a static NAT configuration?
- the inside local and the inside global
- the inside global and the outside local
- the inside local and the outside global
- the outside global and the outside local
Answers Explanation & Hints: Static NAT configuration specifies a single inside local address and a single inside global address.
-
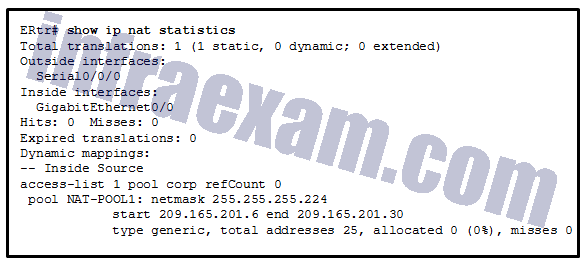
Refer to the exhibit. The NAT configuration applied to the router is as follows:
ERtr(config)# access-list 1 permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 ERtr(config)# ip nat pool corp 209.165.201.6 209.165.201.30 netmask 255.255.255.224 ERtr(config)# ip nat inside source list 1 pool corp overload ERtr(config)# ip nat inside source static 10.10.10.55 209.165.201.4 ERtr(config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/0 ERtr(config-if)# ip nat inside ERtr(config-if)# interface serial 0/0/0 ERtr(config-if)# ip nat outside
Based on the configuration and the output shown, what can be determined about the NAT status within the organization?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 02 - NAT is working.
- Static NAT is working, but dynamic NAT is not.
- Dynamic NAT is working, but static NAT is not.
- Not enough information is given to determine if both static and dynamic NAT are working.
Answers Explanation & Hints: There is not enough information given because the router might not be attached to the network yet, the interfaces might not have IP addresses assigned yet, or the command could have been issued in the middle of the night. The output does match the given configuration, so no typographical errors were made when the NAT commands were entered.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are correct based on the output as shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 06 - The output is the result of the show ip nat translations command.
- The host with the address 209.165.200.235 will respond to requests by using a source address of 192.168.10.10.
- The host with the address 209.165.200.235 will respond to requests by using a source address of 209.165.200.235.
- Traffic with the destination address of a public web server will be sourced from the IP of 192.168.1.10.
- The output is the result of the show ip nat statistics command.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The output displayed in the exhibit is the result of the show ip nat translations command. Static NAT entries are always present in the NAT table, while dynamic entries will eventually time out.
-
Which situation describes data transmissions over a WAN connection?
- An employee prints a file through a networked printer that is located in another building.
- A manager sends an email to all employees in the department with offices that are located in several buildings.
- An employee shares a database file with a co-worker who is located in a branch office on the other side of the city.
- A network administrator in the office remotely accesses a web server that is located in the data center at the edge of the campus.
Answers Explanation & Hints: When two offices across a city are communicating , it is most likely that the data transmissions are over some type of WAN connection. Data communications within a campus are typically over LAN connections.
-
A company is considering updating the campus WAN connection. Which two WAN options are examples of the private WAN architecture? (Choose two.)
- cable
- leased line
- Ethernet WAN
- municipal Wi-Fi
- digital subscriber line
Answers Explanation & Hints: An organization can connect to a WAN through basic two options:
Private WAN infrastructure – such as dedicated point-to-point leased lines, PSTN, ISDN, Ethernet WAN, ATM, or Frame Relay
Public WAN infrastructure – such as digital subscriber line (DSL), cable, satellite access, municipal Wi-Fi, WiMAX, or wireless cellular including 3G/4G
-
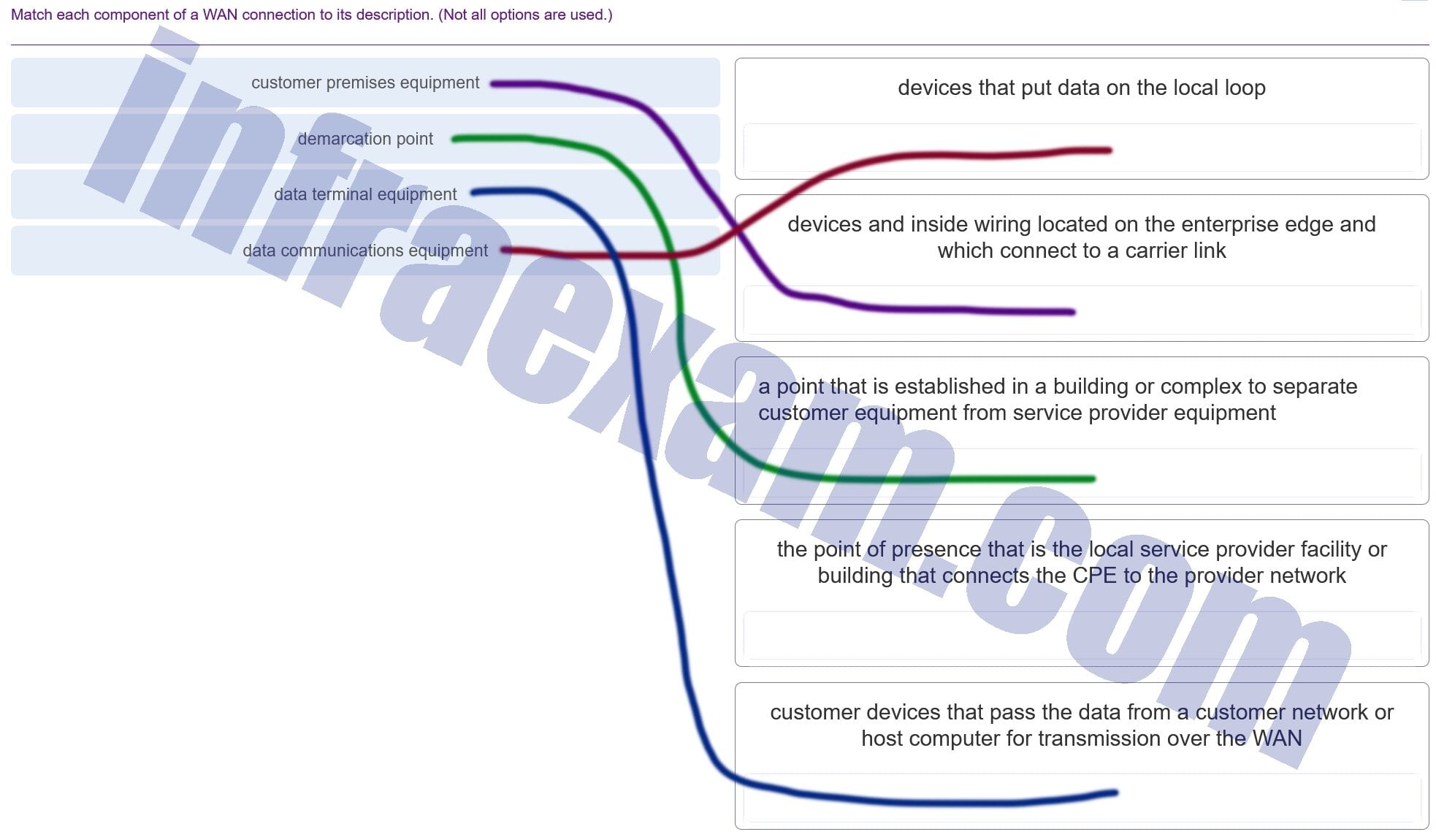
Match each component of a WAN connection to its description. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 002 Explanation & Hint: - Customer Premises Equipment (CPE): This refers to any equipment that is located on the customer’s premises (physical location) rather than on the provider’s network. This can include routers, switches, and modems that the customer uses to connect to the WAN service provided by a carrier.
- Demarcation Point: This is the point where the responsibility for the connection switches from the provider to the customer. It’s essentially the boundary between the customer’s equipment and the service provider’s infrastructure. This is usually where troubleshooting responsibility transitions from the provider to the customer.
- Data Terminal Equipment (DTE): These devices are typically located at the customer’s premises and are used to pass data to or from a computer or network. Examples of DTE are computers, routers, and bridges.
- Data Communications Equipment (DCE): These devices are responsible for establishing, maintaining, and terminating the communication link across the WAN. They convert the data format of the DTE into a form that can be transmitted over a carrier’s facility. Examples include modems and WAN switches.
-
Which two technologies are categorized as private WAN infrastructures? (Choose two.)
- cable
- DSL
- Frame Relay
- MetroE
- VPN
Answers Explanation & Hints: Private WAN technologies include leased lines, dialup, ISDN, Frame Relay, ATM, Ethernet WAN (an example is MetroE), MPLS, and VSAT.
-
Which network scenario will require the use of a WAN?
- Employee workstations need to obtain dynamically assigned IP addresses.
- Employees need to connect to the corporate email server through a VPN while traveling.
- Employees in the branch office need to share files with the headquarters office that is located in a separate building on the same campus network.
- Employees need to access web pages that are hosted on the corporate web servers in the DMZ within their building.
Answers Explanation & Hints: When traveling employees need to connect to a corporate email server through a WAN connection, the VPN will create a secure tunnel between an employee laptop and the corporate network over the WAN connection. Obtaining dynamic IP addresses through DHCP is a function of LAN communication. Sharing files among separate buildings on a corporate campus is accomplished through the LAN infrastructure. A DMZ is a protected network inside the corporate LAN infrastructure.
-
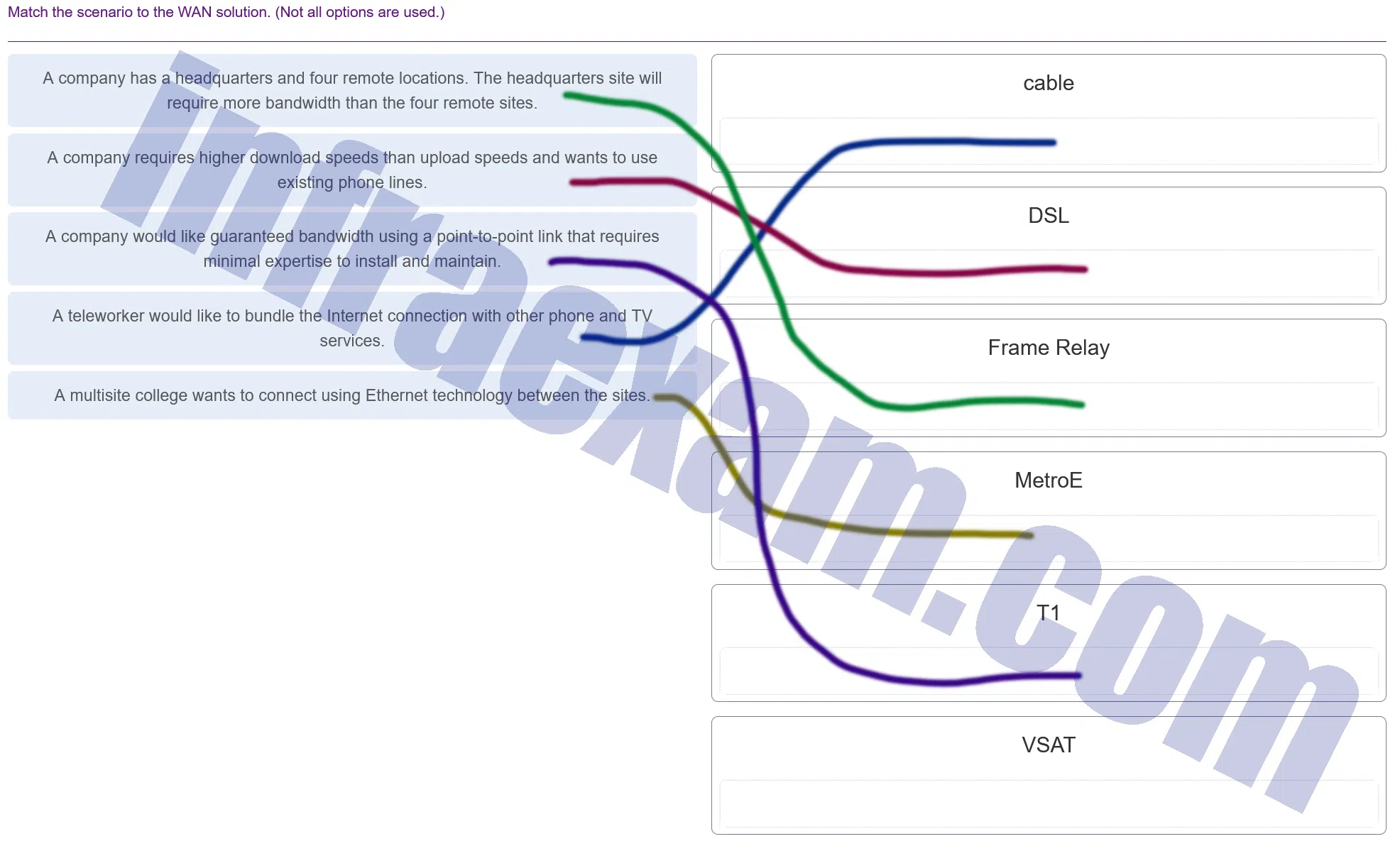
Match the scenario to the WAN solution. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 003 Explanation & Hint: - Cable: This is a broadband Internet service using the same infrastructure as cable television. It’s ideal for general broadband access with high download speeds, and it is often used in residential and business Internet services.
- DSL (Digital Subscriber Line): This technology provides Internet access by transmitting digital data over the wires of a local telephone network. DSL is asymmetrical, meaning it typically offers higher download speeds than upload speeds, which is suitable for most Internet users.
- Frame Relay: Frame Relay is a packet-switched WAN technology that provides cost-effective communication between local area networks (LANs). It can be used for point-to-point and point-to-multipoint connections and was widely used in the past for telecommunication services.
- Metro Ethernet (MetroE): This is a network based on Ethernet standards and is used to connect subscribers to a larger service network or the Internet. Businesses often use Metro Ethernet when they need to connect multiple locations within the same metropolitan area.
- T1: A T1 line is a specific type of fiber optic or copper line that can carry more data than traditional telephone lines. The bandwidth of a T1 line is dedicated and consistent, unlike broadband services. It’s often used for connecting remote offices with guaranteed bandwidth.
- VSAT (Very Small Aperture Terminal): This is a satellite communication technology that is used to create private WANs or to provide Internet access in remote areas. It involves a small satellite dish that is used for both sending and receiving data.
-
Which circumstance would result in an enterprise deciding to implement a corporate WAN?
- when its employees become distributed across many branch locations
- when the network will span multiple buildings
- when the number of employees exceeds the capacity of the LAN
- when the enterprise decides to secure its corporate LAN
Answers Explanation & Hints: WANs cover a greater geographic area than LANs do, so having employees distributed across many locations would require the implementation of WAN technologies to connect those locations. Customers will access corporate web services via a public WAN that is implemented by a service provider, not by the enterprise itself. When employee numbers grow, the LAN has to expand as well. A WAN is not required unless the employees are in remote locations. LAN security is not related to the decision to implement a WAN.
-
What is the function of the Hashed Message Authentication Code (HMAC) algorithm in setting up an IPsec VPN?
- guarantees message integrity
- authenticates the IPsec peers
- protects IPsec keys during session negotiation
- creates a secure channel for key negotiation
Answers Explanation & Hints: The IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key exchange. The Hashed Message Authentication Code (HMAC) is a data integrity algorithm that uses a hash value to guarantee the integrity of a message.
-
What algorithm is used with IPsec to provide data confidentiality?
- MD5
- Diffie-Hellman
- RSA
- AES
- SHA
Answers Explanation & Hints: The IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key exchange. Two popular algorithms that are used to ensure that data is not intercepted and modified (data integrity) are MD5 and SHA. AES is an encryption protocol and provides data confidentiality. DH (Diffie-Hellman) is an algorithm that is used for key exchange. RSA is an algorithm that is used for authentication.
-
What are two hashing algorithms used with IPsec AH to guarantee authenticity? (Choose two.)
- MD5
- SHA
- AES
- DH
- RSA
Answers Explanation & Hints: The IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key exchange. Two popular algorithms used to ensure that data is not intercepted and modified (data integrity and authenticity) are MD5 and SHA.
-
What two algorithms can be part of an IPsec policy to provide encryption and hashing to protect interesting traffic? (Choose two.)
- AES
- SHA
- DH
- RSA
- PSK
Answers Explanation & Hints: The IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key exchange. Two algorithms that can be used within an IPsec policy to protect interesting traffic are AES, which is an encryption protocol, and SHA, which is a hashing algorithm.
-
Which protocol creates a virtual point-to-point connection to tunnel unencrypted traffic between Cisco routers from a variety of protocols?
- OSPF
- IPsec
- IKE
- GRE
Answers Explanation & Hints: Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) is a tunneling protocol developed by Cisco that encapsulates multiprotocol traffic between remote Cisco routers. GRE does not encrypt data. OSPF is a open source routing protocol. IPsec is a suite of protocols that allow for the exchange of information that can be encrypted and verified. Internet Key Exchange (IKE) is a key management standard used with IPsec.
-
Which two end points can be on the other side of an ASA site-to-site VPN? (Choose two.)
- DSL switch
- router
- another ASA
- multilayer switch
- Frame Relay switch
Answers Explanation & Hints: In a site-to-site VPN, end hosts send and receive normal unencrypted TCP/IP traffic through a VPN terminating device, typically called a VPN gateway. A VPN gateway device could be a router or a firewall. A Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) is a standalone firewall device that combines firewall, VPN concentrator, and intrusion prevention functionality into one software image.
-
Which VPN solution allows the use of a web browser to establish a secure, remote-access VPN tunnel to the ASA?
- clientless SSL
- client-based SSL
- site-to-site using a preshared key
- site-to-site using an ACL
Answers Explanation & Hints: When a web browser is used to securely access the corporate network, the browser must use a secure version of HTTP to provide SSL encryption. A VPN client is not required to be installed on the remote host, so a clientless SSL connection is used.
-
Which IPsec security function provides assurance that the data received via a VPN has not been modified in transit?
- confidentiality
- integrity
- authentication
- secure key exchange
Answers Explanation & Hints: Integrity is a function of IPsec and ensures data arrives unchanged at the destination through the use of a hash algorithm. Confidentiality is a function of IPsec and utilizes encryption to protect data transfers with a key. Authentication is a function of IPsec and provides specific access to users and devices with valid authentication factors. Secure key exchange is a function of IPsec and allows two peers to maintain their private key confidentiality while sharing their public key.
-
Which two technologies provide enterprise-managed VPN solutions? (Choose two.)
- Frame Relay
- site-to-site VPN
- Layer 2 MPLS VPN
- Layer 3 MPLS VPN
- remote access VPN
Answers Explanation & Hints: VPNs can be managed and deployed as either of two types:
Enterprise VPNs – Enterprise-managed VPNs are a common solution for securing enterprise traffic across the internet. Site-to-site and remote access VPNs are examples of enterprise managed VPNs.
Service Provider VPNs – Service provider managed VPNs are created and managed over the provider network. Layer 2 and Layer 3 MPLS are examples of service provider managed VPNs. Other legacy WAN solutions include Frame Relay and ATM VPNs.
-
Which two types of VPNs are examples of enterprise-managed remote access VPNs? (Choose two.)
- IPsec VPN
- clientless SSL VPN
- GRE over IPsec VPN
- client-based IPsec VPN
- IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface VPN
Answers Explanation & Hints: Enterprise managed VPNs can be deployed in two configurations:
Remote Access VPN – This VPN is created dynamically when required to establish a secure connection between a client and a VPN server. Remote access VPNs include client-based IPsec VPNs and clientless SSL VPNs.
Site-to-site VPN – This VPN is created when interconnecting devices are preconfigured with information to establish a secure tunnel. VPN traffic is encrypted only between the interconnecting devices, and internal hosts have no knowledge that a VPN is used. Site-to-site VPNs include IPsec, GRE over IPsec, Cisco Dynamic Multipoint (DMVPN), and IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface (VTI) VPNs.
-
Which is a requirement of a site-to-site VPN?
- It requires a client/server architecture.
- It requires the placement of a VPN server at the edge of the company network.
- It requires hosts to use VPN client software to encapsulate traffic.
- It requires a VPN gateway at each end of the tunnel to encrypt and decrypt traffic.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Site-to-site VPNs are static and are used to connect entire networks. Hosts have no knowledge of the VPN and send TCP/IP traffic to VPN gateways. The VPN gateway is responsible for encapsulating the traffic and forwarding it through the VPN tunnel to a peer gateway at the other end which decapsulates the traffic.
-
What is the function of the Diffie-Hellman algorithm within the IPsec framework?
- allows peers to exchange shared keys
- provides strong data encryption
- guarantees message integrity
- provides authentication
Answers Explanation & Hints: The IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key exchange. DH (Diffie-Hellman) is an algorithm used for key exchange. DH is a public key exchange method that allows two IPsec peers to establish a shared secret key over an insecure channel.
-
What does NAT overloading use to track multiple internal hosts that use one inside global address?
- MAC addresses
- port numbers
- IP addresses
- autonomous system numbers
Answers Explanation & Hints: NAT overloading, also known as Port Address Translation (PAT), uses port numbers to differentiate between multiple internal hosts.
-
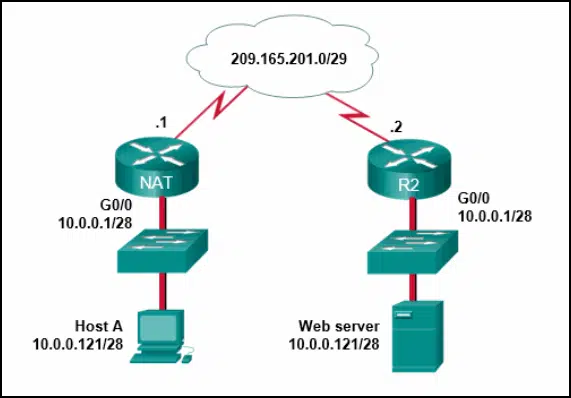
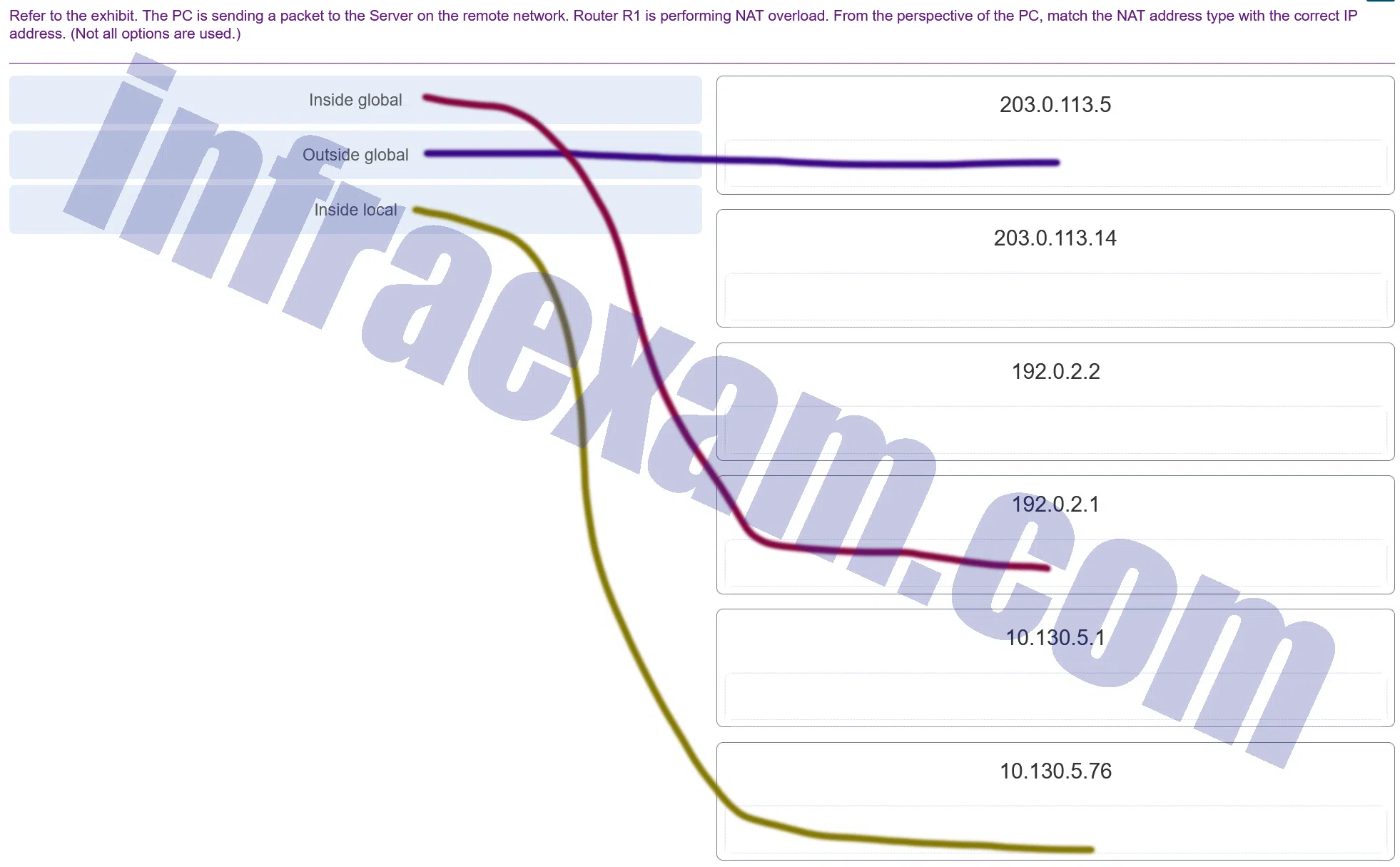
Refer to the exhibit. The PC is sending a packet to the Server on the remote network. Router R1 is performing NAT overload. From the perspective of the PC, match the NAT address type with the correct IP address. (Not all options are used.)
DtdCEA3 CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 004 Answers Explanation & Hints: The inside local address is the private IP address of the source or the PC in this instance. The inside global address is the translated address of the source or the address as seen by the outside device. Since the PC is using the outside address of the R1 router, the inside global address is 192.0.2.1. The outside addressing is simply the address of the server or 203.0.113.5.
-
Refer to the exhibit. R1 is configured for static NAT. What IP address will Internet hosts use to reach PC1?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 09 - 192.168.0.10
- 192.168.0.1
- 209.165.200.225
- 209.165.201.1
Answers Explanation & Hints: In static NAT a single inside local address, in this case 192.168.0.10, will be mapped to a single inside global address, in this case 209.165.200.225. Internet hosts will send packets to PC1 and use as a destination address the inside global address 209.165.200.225.
-
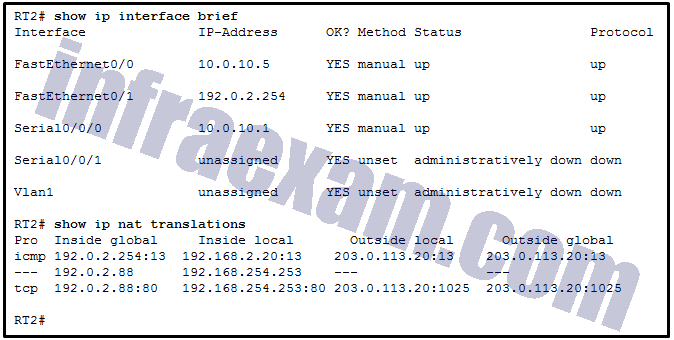
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is viewing the output from the command show ip nat translations . Which statement correctly describes the NAT translation that is occurring on router RT2?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 6 – 8 WAN Concepts Exam Answers 07 - The traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.0.2.88 is being translated by router RT2 to reach a destination IPv4 address of 192.168.254.253.
- The traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.168.254.253 is being translated to 192.0.2.88 by means of static NAT.
- The traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.168.2.20 is being translated by router RT2 to reach a destination IPv4 address of 192.0.2.254.
- The traffic from a source IPv4 public address that originates traffic on the internet would be able to reach private internal IPv4 addresses.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Because no outside local or outside global address is referenced, the traffic from a source IPv4 address of 192.168.254.253 is being translated to 192.0.2.88 by using static NAT. In the output from the command show ip nat translations , the inside local IP address of 192.168.2.20 is being translated into an outside IP address of 192.0.2.254 so that the traffic can cross the public network. A public IPv4 device can connect to the private IPv4 device 192.168.254.253 by targeting the destination IPv4 address of 192.0.2.88.
-
Which two WAN infrastructure services are examples of private connections? (Choose two.)
- T1/E1
- wireless
- DSL
- cable
- Frame Relay
Answers Explanation & Hints: Private WANs can use T1/E1, T3/E3, PSTN, ISDN, Metro Ethernet, MPLS, Frame Relay, ATM, or VSAT technology.
-
Which two statements about the relationship between LANs and WANs are true? (Choose two.)
- Both LANs and WANs connect end devices.
- WANs connect LANs at slower speed bandwidth than LANs connect their internal end devices.
- LANs connect multiple WANs together.
- WANs must be publicly-owned, but LANs can be owned by either public or private entities.
- WANs are typically operated through multiple ISPs, but LANs are typically operated by single organizations or individuals.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Although LANs and WANs can employ the same network media and intermediary devices, they serve very different areas and purposes. The administrative and geographical scope of a WAN is larger than that of a LAN. Bandwidth speeds are slower on WANs because of their increased complexity. The Internet is a network of networks, which can function under either public or private management.
-
Which statement describes an important characteristic of a site-to-site VPN?
- It must be statically set up.
- It is ideally suited for use by mobile workers.
- It requires using a VPN client on the host PC.
- It is commonly implemented over dialup and cable modem networks.
- After the initial connection is established, it can dynamically change connection information.
Answers Explanation & Hints: A site-to-site VPN is created between the network devices of two separate networks. The VPN is static and stays established. The internal hosts of the two networks have no knowledge of the VPN.
-
How is “tunneling” accomplished in a VPN?
- New headers from one or more VPN protocols encapsulate the original packets.
- All packets between two hosts are assigned to a single physical medium to ensure that the packets are kept private.
- Packets are disguised to look like other types of traffic so that they will be ignored by potential attackers.
- A dedicated circuit is established between the source and destination devices for the duration of the connection.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Packets in a VPN are encapsulated with the headers from one or more VPN protocols before being sent across the third party network. This is referred to as “tunneling”. These outer headers can be used to route the packets, authenticate the source, and prevent unauthorized users from reading the contents of the packets.
-
Which statement describes a VPN?
- VPNs use dedicated physical connections to transfer data between remote users.
- VPNs use logical connections to create public networks through the Internet.
- VPNs use open source virtualization software to create the tunnel through the Internet.
- VPNs use virtual connections to create a private network through a public network.
Answers Explanation & Hints: A VPN is a private network that is created over a public network. Instead of using dedicated physical connections, a VPN uses virtual connections routed through a public network between two network devices.
-
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
What problem is causing PC-A to be unable to communicate with the Internet?
- The static route should not reference the interface, but the outside address instead.
- This router should be configured to use static NAT instead of PAT.
- The ip nat inside source command refers to the wrong interface.
- The access list used in the NAT process is referencing the wrong subnet.
- The NAT interfaces are not correctly assigned.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The output of show ip nat statistics shows that the inside interface is FastEthernet0/0 but that no interface has been designated as the outside interface. This can be fixed by adding the command ip nat outside to interface Serial0/0/0.
-
What type of address is 10.131.48.7?
- private
- public
-
Explanation & Hint: The IP address 10.131.48.7 is a private IP address. It falls within the IP address range 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255, which is one of the IP ranges reserved for private networks by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). Private IP addresses are not routable on the public internet and are used within private networks to identify and locate devices within that network only.
-
What type of address is 10.19.6.7?
- private
- public
-
Explanation & Hint: The IP address 10.19.6.7 is a private IP address. It is within the range 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255, which is reserved for private networks according to the standards set by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). This range is not routable on the public internet and is typically used for local area networks (LANs).
-
What type of address is 192.168.7.98?
- private
- public
-
Explanation & Hint: The IP address 192.168.7.98 is a private IP address. It falls within the IP address range 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255, which is one of the IP ranges reserved for private networks by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). This range is used for local area networks (LANs) and is not routable on the public internet.
-
What type of address is 64.100.190.189?
- public
- private
-
Explanation & Hint: IP addresses, like 64.100.190.189, are numerical labels used to identify devices on a network. They are part of the Internet Protocol (IP), which is a set of rules governing the format of data sent over the Internet or other networks.
There are two main types of IP addresses: Public and Private.
- Public IP Addresses:
- Uniqueness: Public IP addresses are unique across the entire internet. This means that no two devices on the internet can have the same public IP address at the same time.
- Assignment: They are assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) and its regional registries. Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) obtains a range of public IP addresses from these registries and assigns one to your network.
- Accessibility: A public IP address can be accessed from any device on the internet, making it essential for online communication, such as browsing websites, sending emails, and more.
- Example Use: If you have a website hosted on a server, that server will have a public IP address so that people around the world can access your site.
- Private IP Addresses:
- Uniqueness: Private IP addresses do not need to be unique except within their own network. This means different networks can use the same private IPs without causing conflicts.
- Assignment: These addresses are typically assigned by the router within a home or business network. They are not routable on the wider internet.
- Accessibility: Devices with private IP addresses can communicate with each other within the same network, but they cannot directly communicate with devices on the internet.
- Example Use: In a home network, your laptop, phone, and other devices will each have a private IP address assigned by your router.
The address 64.100.190.189 falls within the range of public IP addresses. It’s designated for use on the internet, and it’s not part of the ranges reserved for private networks (like 192.168.x.x, 10.x.x.x, or 172.16.x.x to 172.31.x.x). Therefore, this IP address can be used for communication over the internet and is accessible from any place in the world, assuming no firewall or other network security tools are blocking access.
- Public IP Addresses:
-
What type of address is 198.133.219.148?
- public
- private
-
Explanation & Hint: The IP address 198.133.219.148 is a public IP address.
Public IP addresses are assigned for use on the internet and are unique across the entire internet, ensuring that each device connected to the internet has a distinct address. This is in contrast to private IP addresses, which are used within private networks and are not unique across the entire internet. Private IP addresses follow certain designated ranges (such as 10.x.x.x, 172.16.x.x to 172.31.x.x, and 192.168.x.x), and 198.133.219.148 does not fall within any of these ranges, confirming it is a public IP address.
-
What type of address is 128.107.240.239?
- public
- private
-
Explanation & Hint: The IP address 128.107.240.239 is a public IP address.
Public IP addresses are those that are unique across the entire internet and are used for communication between hosts on the global internet. They are assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) and its registries.
The given address, 128.107.240.239, does not fall within any of the ranges designated for private networks. Private IP addresses are typically in the ranges of 10.x.x.x, 172.16.x.x to 172.31.x.x, and 192.168.x.x, and are used within local networks (like a home or office network) and are not routable on the internet. Since 128.107.240.239 is outside these ranges, it is classified as a public IP address.
-
What type of address is 64.101.198.197?
- public
- private
-
Explanation & Hint: The IP address 64.101.198.197 is a public IP address.
Public IP addresses are those that are used on the internet and must be unique across the entire internet. This is in contrast to private IP addresses, which are used within private networks (like a home or office network) and do not need to be unique across the internet.
Private IP addresses fall within specific ranges defined by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). These ranges are 10.x.x.x, 172.16.x.x to 172.31.x.x, and 192.168.x.x. Since 64.101.198.197 does not fall within these ranges, it is classified as a public IP address. Public IP addresses are assigned by ISPs and are necessary for accessing the internet.
-
What type of address is 10.100.34.34?
- private
- public
-
Explanation & Hint: The IP address 10.100.34.34 is a private IP address.
Private IP addresses are used within private networks, such as home or office networks, and are not routable on the public internet. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has reserved certain IP address ranges specifically for private use. These ranges include:
- 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
- 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
- 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
Since the IP address 10.100.34.34 falls within the 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 range, it is classified as a private IP address. Devices using this IP address can communicate with each other within the same local network, but they use a different, public IP address for accessing the internet.
-
What type of address is 10.100.126.126?
- private
- public
-
Explanation & Hint: The IP address 10.100.126.126 is a private IP address.
Private IP addresses are used within local networks such as homes, offices, or internal enterprise networks and are not routable on the internet. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has reserved specific ranges of IP addresses for private use, and 10.100.126.126 falls within one of these ranges. The ranges for private IP addresses are:
- 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
- 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
- 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
Since 10.100.126.126 is within the 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 range, it is clearly a private IP address. Devices with private IP addresses can communicate with each other within the same network, but they cannot directly interact with devices on the internet without going through a router or other network device that provides Network Address Translation (NAT).
-
What type of address is 192.168.7.126?
- private
- public
-
Explanation & Hint: The IP address 192.168.7.126 is a private IP address.
Private IP addresses are used within local networks, like home, office, or internal enterprise networks, and are not directly exposed to the internet. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has reserved specific ranges of IP addresses for private use, and 192.168.7.126 falls within one of these ranges. The designated ranges for private IP addresses are:
- 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
- 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
- 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
Since 192.168.7.126 is within the 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 range, it is classified as a private IP address. Devices with private IP addresses can communicate with each other within the same network, but they use a public IP address provided by a router or network gateway to access the internet.
-
Which type of VPN involves passenger, carrier, and transport protocols?
- GRE over IPsec
- IPsec virtual tunnel interface
- MPLS VPN
- dynamic multipoint VPN
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of VPN that involves passenger, carrier, and transport protocols is GRE over IPsec.
Here’s a brief explanation of these terms and how they apply to GRE over IPsec:
- Passenger Protocol: This is the original data packet protocol that is being encapsulated and transported. In the case of GRE over IPsec, the passenger protocol can be any network layer protocol (like IPv4 or IPv6).
- Carrier Protocol: This is the protocol used to encapsulate the original data packet. In GRE over IPsec, GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) is the carrier protocol. GRE encapsulates the original data packet so that it can be transported over an IP network.
- Transport Protocol: This is the protocol used to secure the encapsulated data packets as they are transported across the network. In GRE over IPsec, IPsec is the transport protocol. It provides security for the data packets as they travel through the VPN tunnel.
The other options mentioned have different characteristics:
- IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface: This is primarily focused on IPsec for both encapsulation and security, without the additional GRE encapsulation layer.
- MPLS VPN: MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) VPNs use label-switching technology and are typically used within service provider networks. They don’t necessarily involve GRE or IPsec.
- Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN): This is a technique that creates dynamic tunnels between sites on an as-needed basis, usually using a combination of GRE and IPsec, but its focus is on the dynamic nature of the tunnel creation rather than the encapsulation and security protocols per se.
-
Which type of VPN supports multiple sites by applying configurations to virtual interfaces instead of physical interfaces?
- IPsec virtual tunnel interface
- dynamic multipoint VPN
- MPLS VPN
- GRE over IPsec
-
Explanation & Hint: Correct:
IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface
- In this setup, the VPN configurations are applied to virtual interfaces, which are logical interfaces created within the VPN device.
- This method is highly effective for managing VPNs that connect multiple sites, as it allows for easier and more flexible configuration and management compared to applying settings directly to physical interfaces.
- Each virtual tunnel interface is associated with an IPsec tunnel. In environments with multiple VPN connections, this approach simplifies management by treating each tunnel as a distinct interface.
- The IPsec virtual tunnel interface approach enhances scalability and adaptability, making it easier to adjust configurations as the network evolves or expands.
Incorrect:
MPLS VPN
- MPLS VPNs use label-switching techniques and are primarily used in service provider networks or for large-scale enterprise deployments. While they offer efficient management of multiple sites, their focus is on traffic segregation and routing efficiency rather than applying configurations to virtual interfaces in the context of IPsec tunnels.
Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN)
- DMVPN dynamically establishes GRE tunnels between sites on an as-needed basis. While it provides efficient and scalable connections between multiple sites, the key aspect of DMVPN is its ability to dynamically create and manage these connections, rather than the use of virtual tunnel interfaces.
GRE over IPsec
- This type of VPN uses GRE for encapsulation combined with IPsec for encryption. While it can support multiple sites, the focus is on the encapsulation and encryption methods rather than on applying configurations to virtual interfaces.
In summary, IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface is the correct answer because it specifically supports multiple sites by applying configurations to virtual interfaces, offering a flexible and scalable solution for managing complex VPN networks.
-
Which type of VPN connects using the Transport Layer Security (TLS) feature?
- SSL VPN
- GRE over IPsec
- dynamic multipoint VPN
- IPsec virtual tunnel interface
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of VPN that connects using the Transport Layer Security (TLS) feature is SSL VPN (Secure Sockets Layer Virtual Private Network).
SSL VPNs use the SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) protocol and its successor, TLS (Transport Layer Security), to provide a secure connection between a remote user and the internal network resources. They are typically used for providing remote access to users outside the corporate network. SSL/TLS provides encryption and the secure identification of the server to the client. This type of VPN is often preferred for its ease of use, as it can be accessed through a standard web browser without the need for installing specialized client software.
To briefly explain the other options:
- GRE over IPsec: This is a VPN configuration that combines Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) with IPsec. GRE provides a way to encapsulate a wide variety of network layer protocols inside virtual point-to-point links, while IPsec provides secure encrypted tunnels. This method does not use TLS.
- Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN): DMVPN is a technique that creates dynamic tunneling in a VPN network, allowing for the creation of direct tunnels between nodes as needed. It typically uses GRE along with IPsec for encryption but not TLS.
- IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface: This approach involves using IPsec for creating secure VPN connections and typically involves configuring virtual tunnel interfaces for each connection. Like GRE over IPsec, it does not utilize TLS.
-
Which type of VPN connects using the Transport Layer Security (TLS) feature?
- SSL VPN
- MPLS VPN
- IPsec virtual tunnel interface
- dynamic multipoint VPN
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of VPN that connects using the Transport Layer Security (TLS) feature is an SSL VPN (Secure Sockets Layer Virtual Private Network).
SSL VPNs use the SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and its successor, TLS (Transport Layer Security), protocols to establish secure connections. These VPNs are widely used for providing remote access to private networks, typically through a web browser or a specialized client. The use of SSL/TLS allows for the secure transmission of data and is particularly favored for its ability to provide secure remote access without the need for client software on every user’s device.
To briefly differentiate from the other options:
- MPLS VPN: Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPNs are used primarily in service provider networks or large enterprise networks. They do not typically use TLS for connection, but rather rely on MPLS technology to direct and manage traffic within a private network.
- IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface: This type of VPN utilizes IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) to secure communications across a network. It does not use TLS; instead, it relies on IPsec protocols for encryption and secure communications.
- Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN): DMVPN allows for the creation of dynamic, on-demand VPN connections using technologies like GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) and IPsec. It does not use TLS for its connections.
-
Which type of VPN has both Layer 2 and Layer 3 implementations?
- MPLS VPN
- IPsec virtual tunnel interface
- dynamic multipoint VPN
- GRE over IPsec
-
Explanation & Hint: The answer is MPLS VPN.
MPLS VPNs are unique in their ability to operate at both Layer 2 and Layer 3 of the OSI model:
- Layer 2 MPLS VPNs: Often referred to as Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) or Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS), these provide Layer 2 connectivity, allowing for the extension of LANs across different geographic locations.
- Layer 3 MPLS VPNs: These operate at the network layer, where the service provider can either manage routing for the customer or allow the customer to manage their own IP routing, facilitating the connection of multiple sites over a wide area.
The other options, like IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface, Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN), and GRE over IPsec, primarily operate at Layer 3 and do not inherently offer both Layer 2 and Layer 3 implementations like MPLS VPN does.
-
Which type of VPN has both Layer 2 and Layer 3 implementations?
- MPLS VPN
- SSL VPN
- GRE over IPsec
- dynamic multipoint VPN
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of VPN that has both Layer 2 and Layer 3 implementations is MPLS VPN (Multiprotocol Label Switching VPN).
MPLS VPNs are versatile and can be implemented at both the data link layer (Layer 2) and the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model:
- Layer 2 MPLS VPNs: These include Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) and Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS). They provide point-to-point or point-to-multipoint connectivity, extending local area networks (LANs) over a wide area.
- Layer 3 MPLS VPNs: These involve MPLS IP VPNs where the service provider participates in routing, connecting multiple sites across a large area with complex routing managed either by the service provider or the customer.
The other options listed are typically limited to either Layer 2 or Layer 3:
- SSL VPN: An SSL VPN operates at Layer 7 (the application layer) and is primarily used for providing secure remote access to web-based applications and services.
- GRE over IPsec: This combination is generally considered a Layer 3 VPN solution, as it involves IPsec for encryption and GRE for tunneling IP packets.
- Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN): DMVPN operates at Layer 3, creating dynamic GRE tunnels for IPsec VPNs and is used for scalable branch-to-branch secure connectivity.
-
Which type of VPN allows multicast and broadcast traffic over a secure site-to-site VPN?
- GRE over IPsec
- SSL VPN
- dynamic multipoint VPN
- IPsec virtual tunnel interface
-
Explanation & Hint: 1. GRE over IPsec
- GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) is a protocol that can encapsulate a wide variety of network layer protocols inside virtual point-to-point and point-to-multipoint connections. This encapsulation includes the ability to handle multicast and broadcast traffic.
- IPsec provides secure encrypted tunnels for the traffic.
- When combined, GRE over IPsec supports multicast and broadcast traffic in a secure manner. GRE encapsulates the multicast/broadcast traffic, which is then encrypted and transported via an IPsec tunnel. This makes it ideal for secure site-to-site VPNs that need to transmit such types of traffic.
2. SSL VPN
- SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) VPN, primarily used for providing secure remote access to individual clients, operates at the application layer.
- It’s designed for client-to-server connections and is commonly used for secure access to web-based applications.
- SSL VPNs typically do not support multicast or broadcast traffic, as these are not common requirements for the remote access scenarios for which SSL VPNs are designed.
3. Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN)
- DMVPN allows for the creation of dynamic, on-demand GRE tunnels over IPsec between multiple sites.
- While DMVPN can handle multicast and broadcast traffic (thanks to GRE), its primary feature is the dynamic establishment of VPN tunnels, reducing the need for static point-to-point tunnel configurations.
- DMVPN is well-suited for networks where the communication requirements between sites frequently change.
4. IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface
- In this setup, IPsec is used to create secure VPN connections, with each connection typically configured on a virtual tunnel interface.
- By default, IPsec does not support multicast or broadcast traffic as it operates at the network layer (Layer 3) and is designed for unicast traffic.
- To handle multicast or broadcast traffic, IPsec would need to be combined with another protocol like GRE, similar to the GRE over IPsec setup.
In summary, while GRE over IPsec is specifically designed to support multicast and broadcast traffic in a secure site-to-site VPN configuration, the other options have different primary functionalities and limitations regarding such traffic.
-
Which type of VPN uses the public key infrastructure and digital certificates?
- SSL VPN
- GRE over IPsec
- dynamic multipoint VPN
- IPsec virtual tunnel interface
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of VPN that typically uses the public key infrastructure (PKI) and digital certificates is SSL VPN (Secure Sockets Layer Virtual Private Network).
- SSL VPN:
- SSL/TLS, the underlying protocols used in SSL VPNs, extensively use PKI and digital certificates for authentication.
- Digital certificates are crucial in establishing a secure and trustworthy connection between the VPN client and server.
- The PKI provides a framework for managing digital certificates and public-key encryption, enabling secure communications over potentially insecure networks like the internet.
To briefly explain why the other options are less focused on PKI and digital certificates:
- GRE over IPsec:
- This VPN type primarily uses IPsec for encryption and GRE for tunneling.
- While IPsec can utilize certificates for authentication, its use of PKI is not as inherent or mandatory as in SSL VPNs. IPsec often employs pre-shared keys in addition to or instead of digital certificates.
- Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN):
- DMVPN, which uses GRE and IPsec, can leverage certificates for authentication purposes, but like GRE over IPsec, its reliance on PKI and digital certificates is not as integral as in SSL VPNs.
- IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface:
- This setup also uses IPsec for secure communications.
- As with GRE over IPsec and DMVPN, while it can use PKI and digital certificates, it often employs other methods of authentication, such as pre-shared keys.
In summary, SSL VPNs are most closely associated with the use of PKI and digital certificates due to their reliance on SSL/TLS protocols, which inherently use these technologies for secure communications.
- SSL VPN:
-
Which type of VPN involves a nonsecure tunneling protocol being encapsulated by IPsec?
- GRE over IPsec
- dynamic multipoint VPN
- IPsec virtual tunnel interface
- SSL
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of VPN that involves a nonsecure tunneling protocol being encapsulated by IPsec is GRE over IPsec.
- GRE over IPsec:
- GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) is a tunneling protocol that can encapsulate a wide variety of network layer protocols but does not provide encryption or confidentiality by itself.
- By encapsulating GRE with IPsec, the data gets the necessary encryption and security features. IPsec secures the GRE tunnel with its encryption capabilities, thus combining the flexibility of GRE with the security of IPsec.
- This setup is often used in site-to-site VPNs to securely pass traffic such as multicast or broadcast, which are not natively supported by IPsec.
The other options have different characteristics:
- Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN): While DMVPN typically uses GRE combined with IPsec, the key feature of DMVPN is the dynamic establishment of VPN tunnels, rather than the specific encapsulation of a nonsecure tunneling protocol by IPsec.
- IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface: This is primarily focused on IPsec for creating secure VPN connections and does not inherently involve the encapsulation of a separate nonsecure tunneling protocol.
- SSL VPN: This type of VPN uses SSL/TLS for security and does not involve encapsulating a nonsecure tunneling protocol with IPsec.
- GRE over IPsec:
-
Which type of VPN routes packets through virtual tunnel interfaces for encryption and forwarding?
- IPsec virtual tunnel interface
- MPLS VPN
- dynamic multipoint VPN
- GRE over IPsec
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of VPN that routes packets through virtual tunnel interfaces for encryption and forwarding is IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface.
- IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface:
- In this configuration, virtual tunnel interfaces are created for each IPsec VPN connection.
- Packets are routed through these virtual interfaces, where they are encrypted and then forwarded to their destination.
- This approach allows for the separation of routing and encryption functions, providing flexibility in how traffic is handled and encrypted in a VPN setup.
To provide context for the other options:
- MPLS VPN: Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPNs route packets based on labels rather than IP addresses but do not inherently use virtual tunnel interfaces for encryption. MPLS VPNs are more focused on efficient data routing and are typically used in service provider networks or large corporate networks.
- Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN): DMVPN allows for dynamic creation of GRE tunnels over IPsec. While it does use IPsec for encryption, its defining feature is the dynamic, on-demand nature of its tunnel establishment, rather than routing packets through virtual tunnel interfaces.
- GRE over IPsec: This combines GRE for tunneling with IPsec for encryption. It does not specifically use virtual tunnel interfaces for routing packets; instead, it focuses on encapsulating a wide variety of protocols in a GRE tunnel and securing them with IPsec.
- IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface:
| CCNA 3 v7 & 7.02 | |
| Final Exam Answers | |
| This Modules 6 - 8 | |
| Modules 6 - 8 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Next Modules 9 - 12 | |
| Modules 9 - 12 Exam Answers | Online Test |