CCNA 3 v7 – ENSA v7.02 – Modules 9 – 12: Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers 100% 2023 2024
CCNA 3 v7 – ENSA v7.02 – Modules 9 – 12: Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers Full 100% 2023 2024
This is NetAcad Cisco CCNA 3 v7 ENSA v7.02 Modules 9 – 12 Exam Answers 2023 2024 and Enterprise Networking, Security, and Automation (Version 7.00) – Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers Full 100%. All answers have been verified by experts.
| CCNA 3 v7 & 7.02 | |
| Final Exam Answers | |
| This Modules 9 - 12 | |
| Modules 9 - 12 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Next Modules 13 - 14 | |
| Modules 13 - 14 Exam Answers | Online Test |
Cisco Netacad ENSA Version 7.00 CCNA 3 v7 Modules 9 – 12: Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers 2023 2024 – Enterprise Networking, Security, and Automation
-
What is the benefit of deploying Layer 3 QoS marking across an enterprise network?
- Layer 3 marking can carry QoS information on switches that are not IP aware.
- Layer 3 marking can be used to carry non-IP traffic.
- Layer 3 marking can be carried in the 802.1Q fields.
- Layer 3 marking can carry the QoS information end-to-end.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Marking traffic at Layer 2 or Layer 3 is very important and will affect how traffic is treated in a network using QoS.
Layer 2 marking of frames can be performed for non-IP traffic.
Layer 2 marking of frames is the only QoS option available for switches that are not “IP aware.”
Layer 3 marking will carry the QoS information end-to-end.
-
What is the function of a QoS trust boundary?
- A trust boundary identifies the location where traffic cannot be remarked.
- A trust boundary identifies which devices trust the marking on packets that enter a network.
- A trust boundary only allows traffic to enter if it has previously been marked.
- A trust boundary only allows traffic from trusted endpoints to enter the network.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Network traffic is classified and marked as close to the source device as possible. The trust boundary is the location where the QoS markings on a packet are trusted as they enter an enterprise network.
-
What are two approaches to prevent packet loss due to congestion on an interface? (Choose two.)
- Prevent bursts of traffic.
- Drop lower-priority packets.
- Decrease buffer space.
- Disable queuing mechanisms.
- Increase link capacity.
Answers Explanation & Hints: There are three approaches to prevent sensitive traffic from being dropped:Increase link capacity to ease or prevent congestion.
Guarantee enough bandwidth and increase buffer space to accommodate bursts of traffic from fragile flows.
Prevent congestion by dropping lower-priority packets before congestion occurs.
-
What configuration scenario would offer the most protection to SNMP get and set messages?
- SNMP community strings
- SNMPv2 for in-band management with read-write community strings
- SNMPv3 configured with the auth security level
- SNMPv1 with out-of-band management in a private subnet
Answers Explanation & Hints: SNMPv3 supports authentication and encryption with the auth and priv security levels. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not support authentication or encryption. Using a default community string is not secure because the default string of “public” is well known and would allow anyone with SNMP systems to read device MIBs.
-
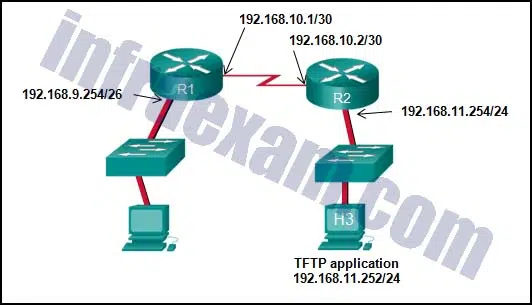
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator enters these commands into the R1 router:
R1# copy running-config tftp Address or name of remote host [ ]?
When the router prompts for an address or remote host name, what IP address should the administrator enter at the prompt?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 9 – 12 Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers 09 - 192.168.9.254
- 192.168.10.1
- 192.168.10.2
- 192.168.11.252
- 192.168.11.254
Answers Explanation & Hints: The requested address is the address of the TFTP server. A TFTP server is an application that can run on a multitude of network devices including a router, server, or even a networked PC.
-
The command ntp server 10.1.1.1 is issued on a router. What impact does this command have?
- determines which server to send system log files to
- identifies the server on which to store backup configurations
- ensures that all logging will have a time stamp associated with it
- synchronizes the system clock with the time source with IP address 10.1.1.1
Answers Explanation & Hints: The ntp server ip-address global configuration command configures the NTP server for IOS devices.
-
As the network administrator you have been asked to implement EtherChannel on the corporate network. What does this configuration consist of?
- providing redundant links that dynamically block or forward traffic
- grouping multiple physical ports to increase bandwidth between two switches
- grouping two devices to share a virtual IP address
- providing redundant devices to allow traffic to flow in the event of device failure
Answers Explanation & Hints: EtherChannel is utilized on a network to increase speed capabilities by grouping multiple physical ports into one or more logical EtherChannel links between two switches. STP is used to provide redundant links that dynamically block or forward traffic between switches. FHRPs are used to group physical devices to provide traffic flow in the event of failure.
-
What is a definition of a two-tier LAN network design?
- access and core layers collapsed into one tier, and the distribution layer on a separate tier
- access and distribution layers collapsed into one tier, and the core layer on a separate tier
- distribution and core layers collapsed into one tier, and the access layer on a separate tier
- access, distribution, and core layers collapsed into one tier, with a separate backbone layer
Answers Explanation & Hints: Maintaining three separate network tiers is not always required or cost-efficient. All network designs require an access layer, but a two-tier design can collapse the distribution and core layers into one layer to serve the needs of a small location with few users.
-
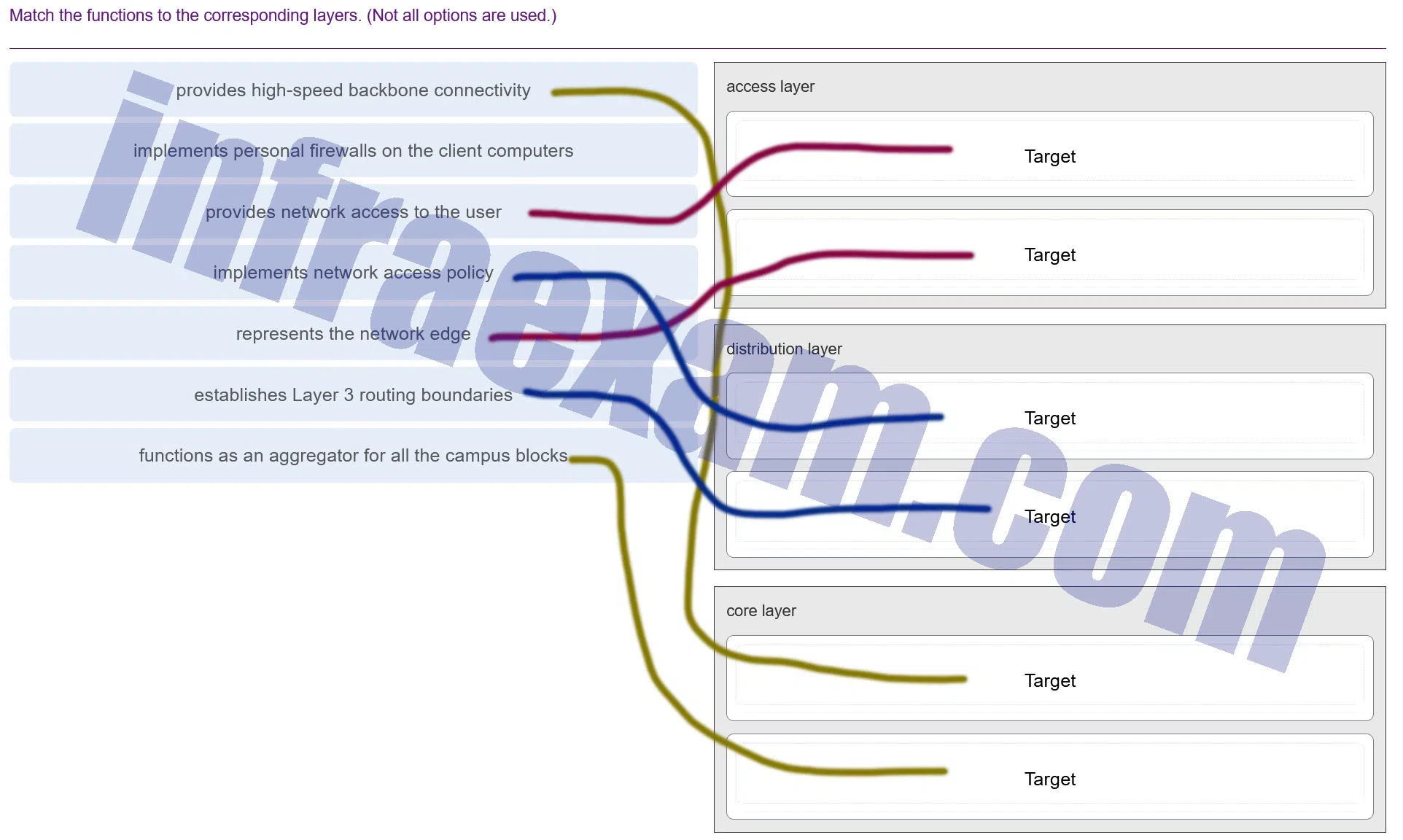
Match the functions to the corresponding layers. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 9 – 12 Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers 001 Explanation & Hint: In a typical hierarchical network design, there are three layers: the access layer, the distribution layer, and the core layer. Each of these layers has specific roles and functions in the network:
- Access Layer:
- Provides network access to the user: The access layer is where devices such as computers, phones, and printers connect to the network. This layer provides them with entry points to the network.
- Implements personal firewalls on the client computers: While this is not a function of the access layer itself, it is related to the end-user devices that connect at this layer. Personal firewalls are often installed on these devices to provide security.
- Implements network access policy: Access control lists (ACLs) and other network policies can be implemented at this layer to control which resources a user or device can access.
- Distribution Layer:
- Represents the network edge: This is where the network makes a transition from the local access-layer networks to the network core. It can serve as the boundary where routing and policy-based network segmentation occurs.
- Establishes Layer 3 routing boundaries: The distribution layer often acts as a boundary for routing domains and is where inter-VLAN routing takes place using Layer 3 switches or routers.
- Functions as an aggregator for all the campus blocks: The distribution layer aggregates the data from multiple access layer switches before it is passed to the core layer for routing to the final destination.
- Core Layer:
- Provides high-speed backbone connectivity: The core layer is the backbone of the network, providing fast and reliable transportation of large amounts of data across a network. Its primary purpose is to transmit data as quickly as possible with minimal processing.
In this hierarchy, the access layer is the closest to end devices, the distribution layer serves as an intermediary enforcing policies and routing, and the core layer connects different parts of the network, often across multiple locations, with high-speed, reliable connectivity.
- Access Layer:
-
What are two reasons to create a network baseline? (Choose two.)
- to determine what kind of equipment to implement
- to evaluate security vulnerabilities in the network
- to identify future abnormal network behavior
- to design a network according to a proper model
- to determine if the network can deliver the required policies
- to select a routing protocol
Answers Explanation & Hints: A network baseline is created to provide a comparison point, at the time that the network is performing optimally, to whatever changes are implemented in the infrastructure. A baseline helps to keep track of the performance, to track the traffic patterns, and to monitor network behavior.
-
A computer can access devices on the same network but cannot access devices on other networks. What is the probable cause of this problem?
- The cable is not connected properly to the NIC.
- The computer has an invalid IP address.
- The computer has an incorrect subnet mask.
- The computer has an invalid default gateway address.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The default gateway is the address of the device a host uses to access the Internet or another network. If the default gateway is missing or incorrect, that host will not be able to communicate outside the local network. Because the host can access other hosts on the local network, the network cable and the other parts of the IP configuration are working.
-
In which step of gathering symptoms does the network engineer determine if the problem is at the core, distribution, or access layer of the network?
- Document the symptoms.
- Determine the symptoms.
- Gather information.
- Determine ownership.
- Narrow the scope.
Answers Explanation & Hints: In the “narrow the scope” step of gathering symptoms, a network engineer will determine if the network problem is at the core, distribution, or access layer of the network. Once this step is complete and the layer is identified, the network engineer can determine which pieces of equipment are the most likely cause.
-
Voice packets are being received in a continuous stream by an IP phone, but because of network congestion the delay between each packet varies and is causing broken conversations. What term describes the cause of this condition?
- buffering
- latency
- queuing
- jitter
Answers Explanation & Hints: Jitter is the variation in the latency or delay of received packets. When data is sent, packets are sent in a continuous stream and are spaced evenly apart. Because of network congestion, the delay between each packet can vary instead of remaining constant.
-
Which queuing algorithm has only a single queue and treats all packets equally?
- FIFO
- CBWFQ
- WFQ
- LLQ
Answers Explanation & Hints: FIFO queuing sends packets out an interface in the order that they had arrived and does not make a decision about packet priority. All packets are treated equally.
-
A network administrator is deploying QoS with the ability to provide a special queue for voice traffic so that voice traffic is forwarded before network traffic in other queues. Which queuing method would be the best choice?
- FIFO
- WFQ
- CBWFQ
- LLQ
Answers Explanation & Hints: Low latency queuing (LLQ) allows delay-sensitive data, such as voice traffic, to be defined in a strict priority queue (PQ) and to always be sent first before any packets in any other queue are forwarded.
-
What are two characteristics of the best-effort QoS model? (Choose two.)
- It does not provide a delivery guarantee for packets.
- It uses a connection-oriented approach with QoS.
- It treats all network packets in the same way.
- It allows end hosts to signal their QoS needs to the network.
- It provides preferential treatment for voice packets.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The best-effort QoS model provides no guarantees and it is commonly used on the Internet. The best-effort QoS model treats all network packets in the same way.
-
What are two characteristics of voice traffic? (Choose two.)
- Dropped voice packets are not retransmitted.
- Voice traffic requires at least 384 kbs of bandwidth.
- Voice traffic consumes lots of network resources.
- Voice traffic is unpredictable and inconsistent.
- Voice traffic latency should not exceed 150 ms.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Voice traffic does not consume a lot of network resources, such as bandwidth. However, it is very sensitive to delay and dropped packets cannot be retransmitted. For good voice quality, the amount of latency should always be less than 150 milliseconds.
-
Which type of network traffic cannot be managed using congestion avoidance tools?
- TCP
- UDP
- IP
- ICMP
Answers Explanation & Hints: Queuing and compression techniques can help to reduce and prevent UDP packet loss, but there is no congestion avoidance for User Datagram Protocol (UDP) based traffic.
-
When QoS is implemented in a converged network, which two factors can be controlled to improve network performance for real-time traffic? (Choose two.)
- link speed
- delay
- packet routing
- jitter
- packet addressing
Answers Explanation & Hints: Delay is the latency between a sending and receiving device. Jitter is the variation in the delay of the received packets. Both delay and jitter need to be controlled in order to support real-time voice and video traffic.
-
Why is QoS an important issue in a converged network that combines voice, video, and data communications?
- Data communications must be given the first priority.
- Data communications are sensitive to jitter.
- Voice and video communications are more sensitive to latency.
- Legacy equipment is unable to transmit voice and video without QoS.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Without any QoS mechanisms in place, time-sensitive packets, such as voice and video, will be dropped with the same frequency as email and web browsing traffic.
-
A network administrator configures a router with the command sequence:
R1(config)# boot system tftp://c1900-universalk9-mz.SPA.152-4.M3.bin R1(config)# boot system rom
What is the effect of the command sequence?
- On next reboot, the router will load the IOS image from ROM.
- The router will copy the IOS image from the TFTP server and then reboot the system.
- The router will load IOS from the TFTP server. If the image fails to load, it will load the IOS image from ROM.
- The router will search and load a valid IOS image in the sequence of flash, TFTP, and ROM.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The boot system command is a global configuration command that allows the user to specify the source for the Cisco IOS Software image to load. In this case, the router is configured to boot from the IOS image that is stored on the TFTP server and will use the ROMmon imagethat is located in the ROM if it fails to locate the TFTP server or fails to load a valid image from the TFTP server.
-
An administrator wants to replace the configuration file on a Cisco router by loading a new configuration file from a TFTP server. What two things does the administrator need to know before performing this task? (Choose two.)
- router IP address
- TFTP server IP address
- name of the configuration file that is currently stored on the router
- name of the configuration file that is stored on the TFTP server
- configuration register value
Answers Explanation & Hints: In order to identify the exact location of the desired configuration file, the IP address of the TFTP server and the name of the configuration file are essential information. Because the file is a new configuration, the name of the current configuration file is not necessary.
-
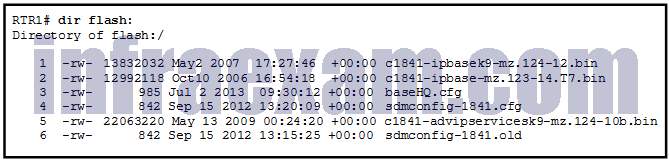
Refer to the exhibit. Which of the three Cisco IOS images shown will load into RAM?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 9 – 12 Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers 04 - The router selects an image depending on the value of the configuration register.
- The router selects the third Cisco IOS image because it is the most recent IOS image.
- The router selects the second Cisco IOS image because it is the smallest IOS image.
- The router selects an image depending on the boot system command in the configuration.
- The router selects the third Cisco IOS image because it contains the advipservicesk9 image.
Answers Explanation & Hints: When performing an upgrade or testing different IOS versions, the boot system command is used to select which image is used to boot the Cisco device.
-
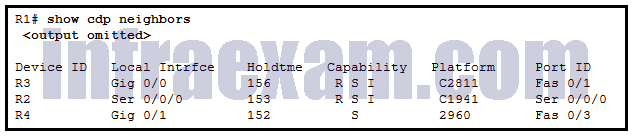
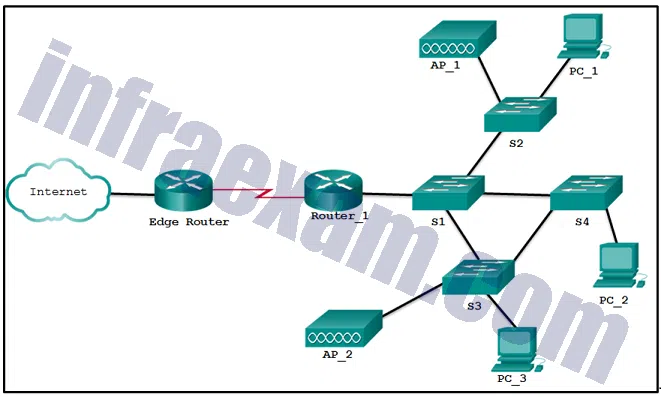
Refer to the exhibit. What two types of devices are connected to R1? (Choose two.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 9 – 12 Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers 02 - router
- switch
- repeater
- hub
- Source Route Bridge
Answers Explanation & Hints: The capabilities of the devices displayed by the output show them to be a Cisco 2811 series router, Cisco 1941 series router, and a Cisco 2960 switch.
-
What are three functions provided by the syslog service? (Choose three.)
- to gather logging information for monitoring and troubleshooting
- to select the type of logging information that is captured
- to specify the destinations of captured messages
- to periodically poll agents for data
- to provide statistics on packets that are flowing through a Cisco device
- to provide traffic analysis
Answers Explanation & Hints: There are three primary functions provided by the syslog service:
- gathering logging information
- selection of the type of information to be logged
- selection of the destination of the logged information
-
What is the function of the MIB element as part of a network management system?
- to store data about a device
- to collect data from SNMP agents
- to change configurations on SNMP agents
- to send and retrieve network management information
Answers Explanation & Hints: The Management Information Base (MIB) resides on a networking device and stores operational data about the device. The SNMP manager can collect information from SNMP agents. The SNMP agent provides access to the information.
-
Which statement describes SNMP operation?
- An NMS periodically polls the SNMP agents that are residing on managed devices by using traps to query the devices for data.
- A get request is used by the SNMP agent to query the device for data.
- An SNMP agent that resides on a managed device collects information about the device and stores that information remotely in the MIB that is located on the NMS.
- A set request is used by the NMS to change configuration variables in the agent device.
Answers Explanation & Hints: An SNMP agent that resides on a managed device collects and stores information about the device and its operation. This information is stored by the agent locally in the MIB. An NMS periodically polls the SNMP agents that are residing on managed devices by using the get request to query the devices for data.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issues the show lldp neighbors command on a switch. What are two conclusions that can be drawn? (Choose two.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 9 – 12 Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers 08 - Dev2 is a switch.
- S1 has only two interfaces.
- Dev1 is a switch with mixed types of interfaces.
- Dev1 is connected to interface Fa0/5 of S1.
- Dev1 is connected to interface Fa0/4 of Dev2.
Answers Explanation & Hints: In the output from the show lldp command, under Capability, R indicates a router and B indicates a bridge (switch). Nothing indicates that Dev1 and Dev2 are connected to one another.
-
What are the three layers of the switch hierarchical design model? (Choose three.)
- access
- data link
- core
- network access
- enterprise
- distribution
Answers Explanation & Hints: The access layer is the lowest layer and it provides network access to users. The distribution layer has many functions, but it aggregates data from the access layer, provides filtering, policy control, and sets Layer 3 routing boundaries. The core layer provides high speed connectivity.
-
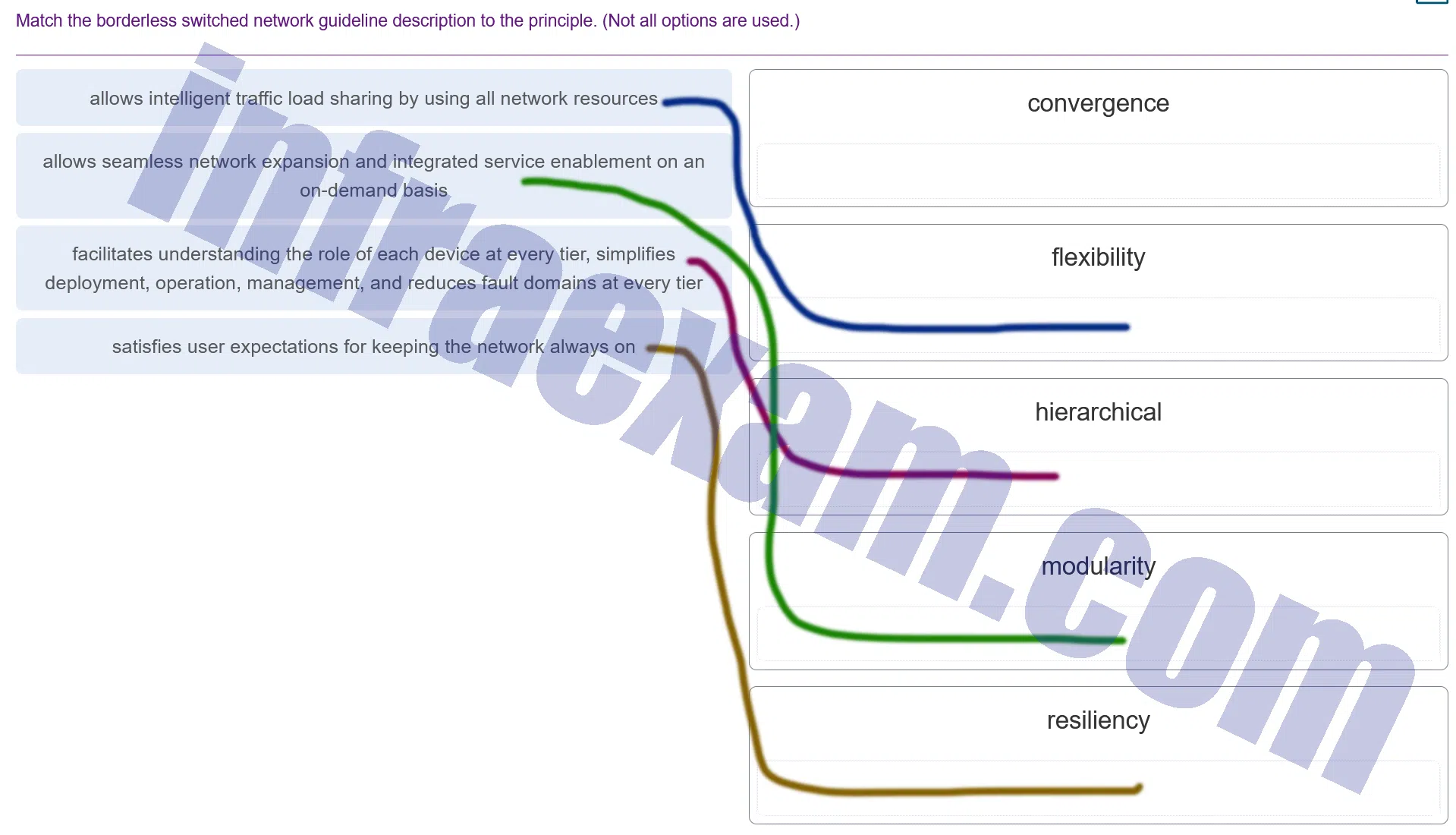
Match the borderless switched network guideline description to the principle. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 9 – 12 Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers 002 Explanation & Hint: This image seems to be from another networking exam or study material, where you are asked to match network design principles with their descriptions. I can explain these principles:
- Convergence:
- Typically refers to the ability of the network to provide a seamless user experience as the network infrastructure provides services and capabilities. When we talk about “allows intelligent traffic load sharing by using all network resources,” it could relate to the concept of convergence in that the network is designed to carry various types of traffic (like voice, data, and video) and use all available paths efficiently.
- Flexibility:
- This is the network’s ability to grow and adapt to changes without significant redesign or downtime. The phrase “allows seamless network expansion and integrated service enablement on an on-demand basis” fits this principle, as it highlights the network’s ability to expand and adapt services easily.
- Hierarchical:
- A hierarchical network design involves dividing the network into discrete layers, each with its own functions and roles. The statement “facilitates understanding the role of each device at every tier, simplifies deployment, operation, management, and reduces fault domains at every tier” describes the benefits of a hierarchical design, which organizes network components in a scalable and understandable way.
- Modularity:
- This principle refers to designing the network in modules or blocks that can be independently deployed, managed, and troubleshooted. Modularity in network design can “satisfy user expectations for keeping the network always on,” because it allows for parts of the network to be upgraded or repaired without affecting the entire network.
- Resiliency:
- Resiliency in network design means having redundancy and failover processes that allow the network to maintain continuous operation, even when individual components fail. The descriptions provided do not directly relate to this principle, but in general, resiliency is about ensuring network uptime and reliability.
These principles are fundamental for creating a robust, scalable, and efficient network infrastructure.
- Convergence:
-
What network design would contain the scope of disruptions on a network should a failure occur?
- the installation of only enterprise class equipment throughout the network
- the configuration of all access layer devices to share a single gateway
- the reduction in the number of redundant devices and connections in the network core
- the deployment of distribution layer switches in pairs and the division of access layer switch connections between them
Answers Explanation & Hints: One way to contain the impact of a failure on the network is to implement redundancy. One way this is accomplished is by deploying redundant distribution layer switches and dividing the access layer switch connections between the redundant distribution layer switches. This creates what is called a switch block. Failures in a switch block are contained to that block and do not bring down the whole network.
-
Which action should be taken when planning for redundancy on a hierarchical network design?
- immediately replace a non-functioning module, service or device on a network
- continually purchase backup equipment for the network
- implement STP portfast between the switches on the network
- add alternate physical paths for data to traverse the network
Answers Explanation & Hints: One method of implementing redundancy is path redundancy, installing alternate physical paths for data to traverse the network. Redundant links in a switched network supports high availability and can be used for load balancing, reducing congestion on the network.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which devices exist in the failure domain when switch S3 loses power?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 9 – 12 Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers 07 - S4 and PC_2
- PC_3 and AP_2
- AP_2 and AP_1
- PC_3 and PC_2
- S1 and S4
Answers Explanation & Hints: A failure domain is the area of a network that is impacted when a critical device such as switch S3 has a failure or experiences problems.
-
What are two benefits of extending access layer connectivity to users through a wireless medium? (Choose two.)
- increased flexibility
- decreased number of critical points of failure
- reduced costs
- increased bandwidth availability
- increased network management options
Answers Explanation & Hints: Wireless connectivity at the access layer provides increased flexibility, reduced costs, and the ability to grow and adapt to changing business requirements. Utilizing wireless routers and access points can provide an increase in the number of central points of failure. Wireless routers and access points will not provide an increase in bandwidth availability.
-
A network designer is considering whether to implement a switch block on the company network. What is the primary advantage of deploying a switch block?
- A single core router provides all the routing between VLANs.
- The failure of a switch block will not impact all end users.
- This is a security feature that is available on all new Catalyst switches.
- This is network application software that prevents the failure of a single network device.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The configuration of a switch block provides redundancy so that the failure of a single network device generally has little or no effect on end users.
-
What is a basic function of the Cisco Borderless Architecture access layer?
- aggregates Layer 2 broadcast domains
- aggregates Layer 3 routing boundaries
- provides access to the user
- provides fault isolation
Answers Explanation & Hints: A function of the Cisco Borderless Architecture access layer is providing network access to the users. Layer 2 broadcast domain aggregation, Layer 3 routing boundaries aggregation, and high availability are distribution layer functions. The core layer provides fault isolation and high-speed backbone connectivity.
-
Which characteristic would most influence a network design engineer to select a multilayer switch over a Layer 2 switch?
- ability to build a routing table
- ability to aggregate multiple ports for maximum data throughput
- ability to provide power to directly-attached devices and the switch itself
- ability to have multiple forwarding paths through the switched network based on VLAN number(s)
Answers Explanation & Hints: Multilayer switches, also known as Layer 3 switches, can route and build a routing table. This capability is required in a multi-VLAN network and would influence the network designer to select a multilayer switch. The other options are features also available on Layer 2 switches, so they would not influence the decision to select a multilayer switch.
-
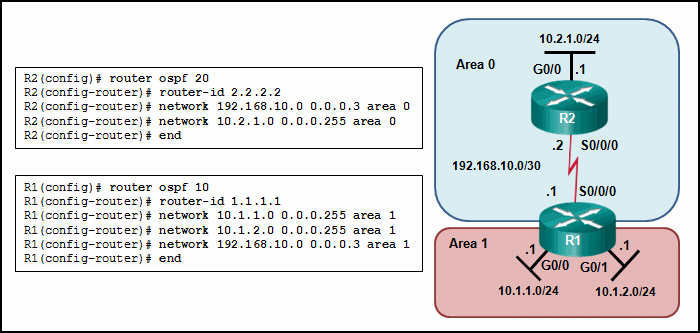
Refer to the exhibit. Why are routers R1 and R2 not able to establish an OSPF adjacency?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 9 – 12 Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers 05 - The router ID values are not the same in both routers.
- The serial interfaces are not in the same area.
- The process numbers are not the same in both routers.
- A backbone router cannot establish an adjacency with an ABR router.
Answers Explanation & Hints: On router R1, the network 192.168.10.0/30 is defined in the wrong area (area 1). It has to be defined in area 0 in order to establish adjacency with router R2, which has the network 192.168.10.0/30 defined in area 0.
-
When is the most appropriate time to measure network operations to establish a network performance baseline?
- at random times during a 10 week period, so that abnormal traffic levels can be detected
- during quiet vacation periods, so that the level of non-data traffic can be determined
- whenever high network use is detected, so that how the network performs under stress can be monitored
- at the same time each day across a set period of average working days, so that typical traffic patterns can be established
Answers Explanation & Hints: The purpose of establishing a network performance baseline is to provide a reference of normal or average network use to enable data traffic anomalies to be detected and then investigated. Network operations that are not average, or are not normal, cannot be used to establish a network performance baseline.
-
What is the principle that is applied when a network technician is troubleshooting a network fault by using the divide-and-conquer method?
- Testing is performed at all layers of the OSI model until a non-functioning component is found.
- Once it is verified that a component in a particular layer is functioning properly, testing can then be performed on any other layer.
- Testing is performed at Layer 7 and at Layer 1, then at Layers 6 and 2, and so on, working towards the middle of the stack until all layers are verified as operational.
- Once it is verified that components in a particular layer are functioning properly, it can then be assumed that components in the layers below it are also functional.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The nature of the OSI and TCP/IP layered models is that upper layers are dependent on lower layers. So when troubleshooting, if a particular layer is found to be working correctly then it can be assumed that all layers below it are also functioning correctly.
-
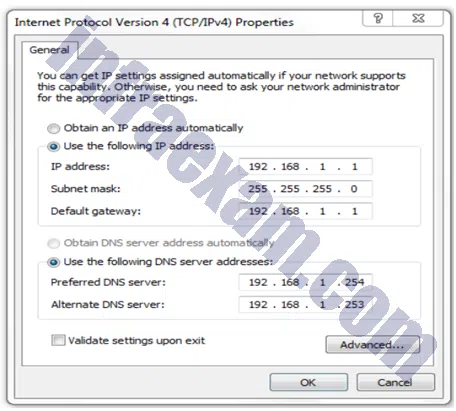
Refer to the exhibit. A user has configured a NIC on the PC as shown but finds that the PC is unable to access the Internet. What is the problem?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 9 – 12 Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers 01 - The preferred DNS address is incorrect.
- There should not be an alternate DNS server.
- The settings were not validated upon exit.
- The default gateway address is incorrect.
Answers Explanation & Hints: In order for a computer to communicate outside its network, it must have a valid default gateway configured.This address cannot be the same as the IP address of the computer.
-
Which troubleshooting tool would a network administrator use to check the Layer 2 header of frames that are leaving a particular host?
- protocol analyzer
- baselining tool
- knowledge base
- CiscoView
Answers Explanation & Hints: A protocol analyzer such as Wireshark is capable of displaying the headers of data at any OSI Layer.
-
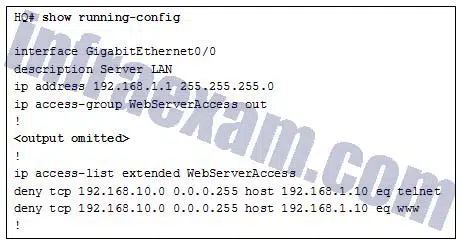
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer configured an ACL preventing Telnet and HTTP access to the HQ web server from guest users in the Branch LAN. The address of the web server is 192.168.1.10 and all guest users are assigned addresses in the 192.168.10.0/24 network. After implementing the ACL, no one can access any of the HQ servers. What is the problem?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 9 – 12 Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers 06 - Inbound ACLs must be routed before they are processed.
- The ACL is implicitly denying access to all the servers.
- Named ACLs require the use of port numbers.
- The ACL is applied to the interface using the wrong direction.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Both named and numbered ACLs have an implicit deny ACE at the end of the list. This implicit deny blocks all traffic.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured OSPFv2 on the two Cisco routers as shown. PC1 is unable to connect to PC2. What should the administrator do first when troubleshooting the OSPFv2 implementation?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 9 – 12 Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers 10 - Test Layer 3 connectivity between the directly connected routers.
- Turn off OSPFv2.
- Disconnect the serial link between router R1 and R2.
- Implement the network 192.168.255.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 command on router R1.
Answers Explanation & Hints: A prerequisite for OSPFv2 neighbor relationships to form between two routers is Layer 3 connectivity. A successful ping confirms that a router interface is active and may be able to form an OSPF neighbor adjacency.
-
A user is unable to reach the website when typing http://www.cisco.com in a web browser, but can reach the same site by typing http://72.163.4.161 . What is the issue?
- default gateway
- DHCP
- DNS
- TCP/IP protocol stack
Answers Explanation & Hints: Domain Name Service (DNS) is used to translate a web address to an IP address. The address of the DNS server is provided via DHCP to host computers.
-
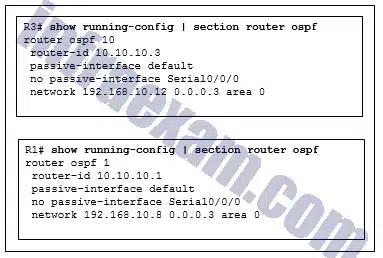
Refer to the exhibit. R1 and R3 are connected to each other via the local serial 0/0/0 interface. Why are they not forming an adjacency?
CCNA3 v7 – ENSA – Modules 9 – 12 Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers 03 - They are in different subnets.
- They have different routing processes.
- They have different router IDs.
- The connecting interfaces are configured as passive.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The routers need to be in the same subnet in order to form an adjacency. The routing processes can be different on each router. The router IDs must be different for routers that participate in the same routing domain. The interfaces are not passive.
-
What type of traffic is described as consisting of traffic that gets a lower priority if it is not mission-critical?
- data
- video
- voice
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of traffic that is generally given a lower priority when it is not mission-critical is typically referred to as data traffic.
- Data: This category includes traffic such as emails, file transfers, and general web browsing. It is considered less sensitive to delays, which means that if packets arrive out of order or take a bit longer to be delivered, it does not impact the functionality as severely as it would with voice or video. Hence, in a QoS context, data traffic can be deprioritized in favor of more sensitive traffic.
- Video: Video streaming, especially high-definition content, requires significant bandwidth and is moderately sensitive to delay and loss. For certain applications like video conferencing, it is mission-critical and thus given higher priority. However, in a non-critical context, it might be given less priority than voice due to its higher bandwidth consumption.
- Voice: Voice traffic is highly sensitive to delay (latency) and jitter (variance in packet arrival times). Since even small delays can cause noticeable disruptions in communication, voice traffic is often given the highest priority in network traffic management to ensure clear, uninterrupted conversation.
-
What type of traffic is described as predictable and smooth?
- voice
- video
- data
-
Explanation & Hint: Voice traffic is typically described as predictable and smooth.
- Voice: Voice traffic tends to have a steady and predictable flow because voice communications generate packets at a consistent rate. Quality of Service (QoS) settings for voice traffic are designed to maintain a smooth and consistent delivery to prevent issues like jitter and latency, which can severely impact the quality of a voice call.
- Video: Video can be somewhat predictable if the streaming is constant, but it is not necessarily smooth due to variations in compression and the amount of data being transmitted. Video packets can be larger and require more bandwidth compared to voice. Video streaming quality can adjust dynamically based on network conditions, which can lead to variability in traffic flow.
- Data: Data traffic is the most variable of the three. It can be bursty and unpredictable, with significant fluctuations in the amount of bandwidth used. Data applications do not generally require the same level of smoothness or predictability as voice communications, as they can tolerate some level of latency and jitter without significant impact on user experience.
-
What type of traffic is described as not resilient to loss?
- video
- voice
- data
-
Explanation & Hint: Video: Although modern video streaming technologies use various error correction and buffering techniques, loss of packets can still cause degradation in quality. This might manifest as pixelation, glitches, or temporary freezes in the video stream. For live video or video conferencing, the impact of packet loss can be more pronounced, as there is limited opportunity for error correction without introducing latency. Thus, while video can handle some loss better than voice due to buffering, it is still not considered resilient to loss, especially when the loss is substantial.
-
What type of traffic is described as being able to tolerate a certain amount of latency, jitter, and loss without any noticeable effects?
- voice
- video
- data
-
Explanation & Hint: Actually, voice traffic is typically the least tolerant to latency, jitter, and loss, because it is a real-time form of communication. Here’s an explanation for each type of traffic:
- Voice: Voice traffic is real-time and requires a consistent and timely delivery of packets to maintain a conversation’s flow. Latency must be kept low to avoid noticeable delays that can disrupt the natural flow of conversation. Jitter can cause voice packets to arrive out of sequence, leading to garbled audio. Loss is also problematic for voice because even small amounts of lost data can result in noticeable gaps or drops in audio.
- Video: Video streaming can tolerate a certain degree of latency and jitter, thanks to buffering. However, too much latency or jitter can lead to a degraded viewing experience, with issues such as buffering delays or reduced video quality. Loss of packets in video can result in pixelation or freezing of the image, but many streaming services use error correction to mitigate some of the problems caused by packet loss.
- Data: Non-real-time data traffic is the most tolerant of latency, jitter, and loss. Protocols like TCP can recover lost packets through retransmission and can handle packets arriving out of sequence by reordering them. This means that applications like web browsing, email, and file transfers can operate without noticeable effects from these network issues, as long as the delays are not excessively long.
-
What type of traffic is described as having a high volume of data per packet?
- video
- data
- voice
-
Explanation & Hint: Video traffic is described as having a high volume of data per packet.
- Video: Streaming video generally involves large amounts of data due to the complexity and quality of the content. High-definition and 4K videos, in particular, require a significant amount of data to maintain quality, resulting in larger packet sizes compared to other types of traffic.
- Data: The size of data packets can vary greatly depending on the type of application. For instance, file transfers might involve large packets, but typical web browsing or email may not. However, on average, data packets are usually not as consistently large as video packets.
- Voice: Voice traffic typically consists of relatively small packets. Voice encoding is designed to be bandwidth-efficient, transmitting enough data to convey speech clearly but without the large file sizes associated with video.
-
What type of traffic is described as consisting of traffic that requires a higher priority if interactive?
- data
- video
- voice
-
Explanation & Hint: The answer is Data, it might be in the context of certain types of interactive or time-sensitive data applications that require higher priority to function effectively. This can include:
- Data: In specific scenarios, such as interactive online gaming, real-time financial transactions, or certain types of remote desktop operations, data traffic can be highly sensitive to delays. These applications require a swift and responsive network experience to function properly, hence the need for higher priority in the network. While not all data traffic falls into this category, these specific types of interactive data applications are exceptions.
- Video: Generally, video traffic is prioritized for streaming quality, but it’s usually less critical for interactivity compared to certain types of data traffic, except in real-time video conferencing scenarios.
- Voice: Voice traffic, while typically prioritized in networks for its real-time nature, may not be as interactive in the sense of dynamic, bidirectional data exchanges like those in interactive gaming or real-time control systems.
-
What type of traffic is described as requiring latency to be no more than 150 milliseconds (ms)?
- voice
- data
- video
-
Explanation & Hint: Voice traffic is described as requiring latency to be no more than 150 milliseconds (ms).
- Voice: For voice communications, especially in telephony and VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol), it is crucial to keep latency under 150 ms to ensure clear and understandable conversations. Latency beyond this threshold can lead to noticeable delays and echoes, disrupting the natural flow of conversation and making communication difficult.
- Video: While video conferencing also benefits from low latency, video streaming services are generally more tolerant of higher latency compared to voice. Buffering techniques can compensate for some delay, although in interactive video scenarios (like video calls), lower latency is still desirable.
- Data: Most data applications, such as web browsing or email, can tolerate higher levels of latency than voice traffic without significant impact on user experience. For these types of data traffic, latency of more than 150 ms is usually acceptable, although it might slow down the communication process.
-
What type of traffic is described as requiring latency to be no more than 400 milliseconds (ms)?
- video
- data
- voice
-
Explanation & Hint: The answer is Video, it implies that the traffic type described as requiring latency to be no more than 400 milliseconds (ms) is video traffic. This can be contextualized as follows:
- Video: In certain types of video communication, particularly interactive or real-time video like video conferencing, keeping latency below 400 ms is important for maintaining a smooth and coherent experience. Delays beyond this threshold can disrupt the natural flow of conversation and lead to a disjointed and frustrating experience. For non-interactive video streaming, higher latencies can be tolerated due to buffering, but for real-time interactions, lower latency is crucial.
- Voice: Generally, voice traffic is more sensitive to latency than video. For voice calls and VoIP, the recommended latency is typically lower, often cited as less than 150 ms for optimal performance.
- Data: Data traffic, such as web browsing, email, or file transfers, is usually the least sensitive to latency. These applications can typically handle higher latency without significant impact on functionality, although user experience might be affected with very high latencies.
-
What type of traffic is described as tending to be unpredictable, inconsistent, and bursty?
- video
- voice
- data
-
Explanation & Hint: The answer is Video, then it indicates that video traffic is described as tending to be unpredictable, inconsistent, and bursty. This can be understood in the following context:
- Video: In certain scenarios, video traffic can indeed be unpredictable and bursty. This is especially true for high-definition and 4K video streams, where the amount of data transmitted can vary significantly, depending on the complexity of the image or scene being displayed. Additionally, activities like starting a video stream or changing the resolution can cause sudden bursts of data. In video conferencing, the variability in data rate can be even more pronounced due to the dynamic nature of the content being transmitted (like screen sharing or changes in video quality).
- Voice: Typically, voice traffic is more consistent and less bursty compared to video. Voice streams have a relatively steady data rate, as the audio is usually encoded at a constant bit rate.
- Data: Data traffic, such as web browsing or file transfers, can also be bursty, but this characteristic is generally more associated with video, particularly in high-bandwidth or high-quality scenarios.
-
What type of traffic is described as traffic that requires at least 30 Kbps of bandwidth?
- voice
- video
- data
-
Explanation & Hint: Voice traffic is typically described as requiring at least 30 Kbps of bandwidth.
- Voice: Standard voice codecs used in VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) typically require bandwidth in the range of 30 Kbps to 100 Kbps per call, depending on the codec and the desired quality. For example, the G.729 codec, commonly used in VoIP systems, requires approximately 8 Kbps for the codec itself, with additional bandwidth needed for packetization, resulting in a total of around 30 Kbps per call.
- Video: Video traffic requires significantly more bandwidth than voice, often measured in Mbps (Megabits per second), especially for high-definition or 4K streams.
- Data: The bandwidth requirements for data traffic can vary widely based on the application. Simple tasks like sending an email require very little bandwidth, while more data-intensive tasks like file downloads or cloud backups can require much more, often surpassing even video in terms of peak bandwidth usage.
-
A network manager wants to add a time to log messages so that there is record of when the message was generated. What command should the administrator use on a Cisco router?
- service timestamps log datetime
- show cdp interface
- ntp server 10.10.14.9
- clock timezone PST -7
-
Explanation & Hint: To add a timestamp to log messages on a Cisco router, the network manager should use the command:
service timestamps log datetime
This command configures the router to include the date and time in the log messages, providing a record of when each message was generated. Here’s a brief overview of the purpose of each command you mentioned:
service timestamps log datetime: Enables timestamping of log messages with the date and time. This is the correct command for adding a time record to log messages.show cdp interface: This command is used to display information about the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) on interfaces. It’s not related to logging or timekeeping.ntp server 10.10.14.9: This command is used to configure the router to synchronize its clock with a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server (in this case, the server at IP address 10.10.14.9). While it’s important for ensuring that the router’s clock is accurate, it doesn’t directly enable timestamping in log messages.clock timezone PST -7: This command sets the router’s time zone to Pacific Standard Time (PST), with an offset of -7 hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). This is useful for ensuring that the router’s clock displays the correct local time, but it doesn’t enable timestamping in log messages.
-
A network manager wants to add a time to log messages so that there is record of when the message was generated. What command should the administrator use on a Cisco router?
- service timestamps log datetime
- show cdp interface
- ntp server 10.10.14.9
- copy running-config tftp
-
Explanation & Hint: To add a timestamp to log messages on a Cisco router, the network manager should use the command:
service timestamps log datetime
This command configures the router to include the date and time in its log messages, which is essential for maintaining a clear record of when each message was generated. Here’s a quick rundown of the commands you mentioned:
service timestamps log datetime: This is the correct command to use. It enables the logging of timestamps on the router, showing the date and time when each log message was generated.show cdp interface: This command displays information about Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) on router interfaces. It’s not related to timestamping log messages.ntp server 10.10.14.9: This command sets up the router to synchronize its system clock with an NTP server (at the specified IP address). While it’s important for ensuring accurate time on the device, it doesn’t directly control the logging of timestamps in log messages.copy running-config tftp: This command is used to copy the router’s current running configuration to a TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) server. It’s not related to log message timestamps, but is used for configuration backup and management.
-
A network manager wants to backup the running configuration to a file server. What command should the administrator use on a Cisco router?
- copy running-config tftp
- dir
- show file systems
- cd usbflash0:
-
Explanation & Hint: To backup the running configuration of a Cisco router to a file server, the network manager should use the command:
copy running-config tftp
This command initiates the process to copy the current running configuration from the router to a TFTP server. The administrator will be prompted to enter the IP address of the TFTP server and the desired filename for the backup.
Here’s an explanation of the other commands:
dir: This command displays a list of files in the device’s memory. It’s used to view files but not for backing up configurations.show file systems: This command provides information about the file systems available on the device, which can be useful to understand where configurations and other files can be stored or are located.cd usbflash0:: This command is used to change the directory to a USB flash drive attached to the router (if available). It’s for navigating the device’s file system, not for backing up configurations.
-
A network manager wants lists the contents of flash. What command should the administrator use on a Cisco router?
- dir
- lldp enable
- service timestamps log datetime
- show file systems
-
Explanation & Hint: To list the contents of the flash memory on a Cisco router, the network manager should use the command:
dir flash:
This command displays the list of files stored in the flash memory of the router. Here’s a brief overview of the commands mentioned:
dir: This is the correct command to use when prefixed with the specific memory location, in this case,flash:. It lists the contents of the specified file system.lldp enable: This command is used to enable the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) on the router, which is a network protocol used to discover information about neighboring devices. It’s not related to listing file contents.service timestamps log datetime: This command configures the router to include timestamps in the log messages. It’s unrelated to viewing the contents of flash memory.show file systems: This command shows information about all the file systems available on the device. While it doesn’t list the contents of flash, it provides information about the file systems, including flash, and their available space.
-
A network manager wants to ensure that the device will ignore the startup config file during startup and bypass the required passwords. What command should the administrator use on a Cisco router?
- confreg 0x2142
- copy usbflash0:/R1-Config
- copy running-config tftp
- config-register 0x2102
-
Explanation & Hint: To ensure that a Cisco device ignores the startup configuration file during startup and bypasses the required passwords, the network administrator should use the command:
confreg 0x2142This command sets the configuration register to
0x2142, which tells the router to bypass the startup configuration (stored in NVRAM) on its next reload. This is a common step in password recovery procedures, as it allows access to the router without the need for existing passwords.Here’s a brief explanation of the other commands:
copy usbflash0:/R1-Config: This command is used to copy a file from a USB flash drive to the router. The exact usage would depend on the specific filename and destination.copy running-config tftp: This command is used to back up the current running configuration of the router to a TFTP server.config-register 0x2102: This command sets the configuration register back to its default value (0x2102), which tells the router to load the startup configuration from NVRAM during the boot process. This is typically used after accessing the device usingconfreg 0x2142and making necessary changes to the configuration.
-
A network manager wants to configure the router to load a new image from flash during bootup. What command should the administrator use on a Cisco router?
- boot system
- clock set 14:25:00 nov 13 2018
- copy tftp startup-config
- copy flash: tftp:
-
Explanation & Hint: To configure a Cisco router to load a new image from flash during bootup, the network manager should use the
boot systemcommand. Specifically, the command to specify an image in the flash memory to be loaded at bootup is:boot system flash [filename]Where
[filename]is the name of the IOS image file stored in the router’s flash memory.Here’s a brief overview of the other commands mentioned:
clock set 14:25:00 nov 13 2018: This command sets the system clock of the router to the specified date and time. It is not related to configuring the boot image.copy tftp startup-config: This command is used to copy a startup configuration file from a TFTP server to the router’s NVRAM. It’s for configuration management, not for setting the boot image.copy flash: tftp:: This command copies files from the router’s flash memory to a TFTP server. It is typically used for backing up IOS images or configuration files but does not set the boot image.
-
A network manager wants to determine the size of the Cisco IOS image file on the networking device. What command should the administrator use on a Cisco router?
- show flash:0
- copy flash: tftp:
- config-register 0x2102
- confreg 0x2142
-
Explanation & Hint: To determine the size of the Cisco IOS image file on a networking device, the network manager should use the command:
show flash:0
This command displays detailed information about the contents of the router’s flash memory, including the size of each file stored in flash, which includes the Cisco IOS image file. It is the appropriate command for checking file sizes and other attributes of files in the flash memory.
Here’s a brief explanation of the other commands:
copy flash: tftp:: This command is used to copy files from the router’s flash memory to a TFTP server. While it’s related to managing files in flash, it doesn’t display file sizes.config-register 0x2102: This command sets the configuration register value to0x2102, which is the default setting that tells the router to load the startup configuration from NVRAM during bootup. It’s unrelated to checking file sizes.confreg 0x2142: This command is used to set the configuration register value to0x2142, typically for password recovery purposes, as it instructs the router to bypass the startup configuration on next boot. It’s not used for viewing file information.
-
A network manager wants to determine the size of the Cisco IOS image file on the networking device. What command should the administrator use on a Cisco router?
- show flash:0
- clock timezone PST -7
- lldp enable
- ntp server 10.10.14.9
-
Explanation & Hint: To determine the size of the Cisco IOS image file on the networking device, the network manager should use the command:
show flash:or, depending on the device,
dir flash:
Both commands will display the contents of the flash memory, including file names, sizes, and other details about each file stored there, such as the Cisco IOS image file. The command
show flash:0ordir flash:0specifically refers to the first partition of flash memory, which is generally correct, but the exact command might vary slightly based on the device’s file system structure.Here’s a brief explanation of the other commands:
clock timezone PST -7: This command sets the device’s time zone to Pacific Standard Time with a -7-hour offset from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). It’s unrelated to viewing the contents of flash memory.lldp enable: This command enables the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) on the device, which is used for discovering neighboring devices on a network. It doesn’t provide information about the device’s flash memory.ntp server 10.10.14.9: This command configures the device to synchronize its system clock with the specified NTP server. Like the others, it’s not used for checking the size of files in flash memory.
-
A network manager wants to view the amount of available and free memory, the type of file system, and its permissions. What command should the administrator use on a Cisco router?
- show file systems
- clock timezone PST -7
- lldp enable
- ntp server 10.10.14.9
-
Explanation & Hint: To view the amount of available and free memory, the type of file system, and its permissions on a Cisco router, the network manager should use the command:
show file systems
This command provides detailed information about all the file systems available on the device, including the total and available space, the type of file system, and the permissions associated with each file system.
Here’s a brief overview of the other commands:
clock timezone PST -7: This command is used to set the router’s time zone to Pacific Standard Time with a -7-hour offset from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). It’s not related to file systems or memory.lldp enable: This command enables the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) on the router, which is used for discovering and identifying neighboring devices on a network. It’s unrelated to memory or file system information.ntp server 10.10.14.9: This command sets up the router to synchronize its clock with a specified NTP (Network Time Protocol) server. While important for accurate timekeeping, it doesn’t provide information about memory or file systems.
-
A network manager wants to view the amount of available and free memory, the type of file system, and its permissions. What command should the administrator use on a Cisco router?
- show file systems
- clock timezone PST -7
- copy usbflash0:/R1-Config
- copy running-config tftp
-
Explanation & Hint: To view the amount of available and free memory, the type of file system, and its permissions on a Cisco router, the network manager should use the command:
show file systems
This command provides comprehensive details about all the file systems available on the router, including the total space, free space, file system type, and permissions for each file system.
The other commands listed have different functions:
clock timezone PST -7: This command sets the router’s time zone to Pacific Standard Time with a UTC offset of -7 hours. It’s used for time configuration and is unrelated to memory or file system information.copy usbflash0:/R1-Config: This command is used to copy a file named ‘R1-Config’ from a USB flash drive attached to the router. It’s a file operation command and does not provide information about memory or file systems.copy running-config tftp: This command is used to copy the router’s current running configuration to a TFTP server. Again, it’s a file operation command and does not display details about the router’s memory or file systems.
| CCNA 3 v7 & 7.02 | |
| Final Exam Answers | |
| This Modules 9 - 12 | |
| Modules 9 - 12 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Next Modules 13 - 14 | |
| Modules 13 - 14 Exam Answers | Online Test |