CCNA3 v7 – Practice Final – ENSA Answers
CCNA3 v7 – Practice Final – ENSA Answers Full 100% 2020 2021
Cisco Netacad ENSA Version 7.00 CCNA 3 v7 Practice Final – ENSA Answers 2020 2021 – Enterprise Networking, Security, and Automation
-
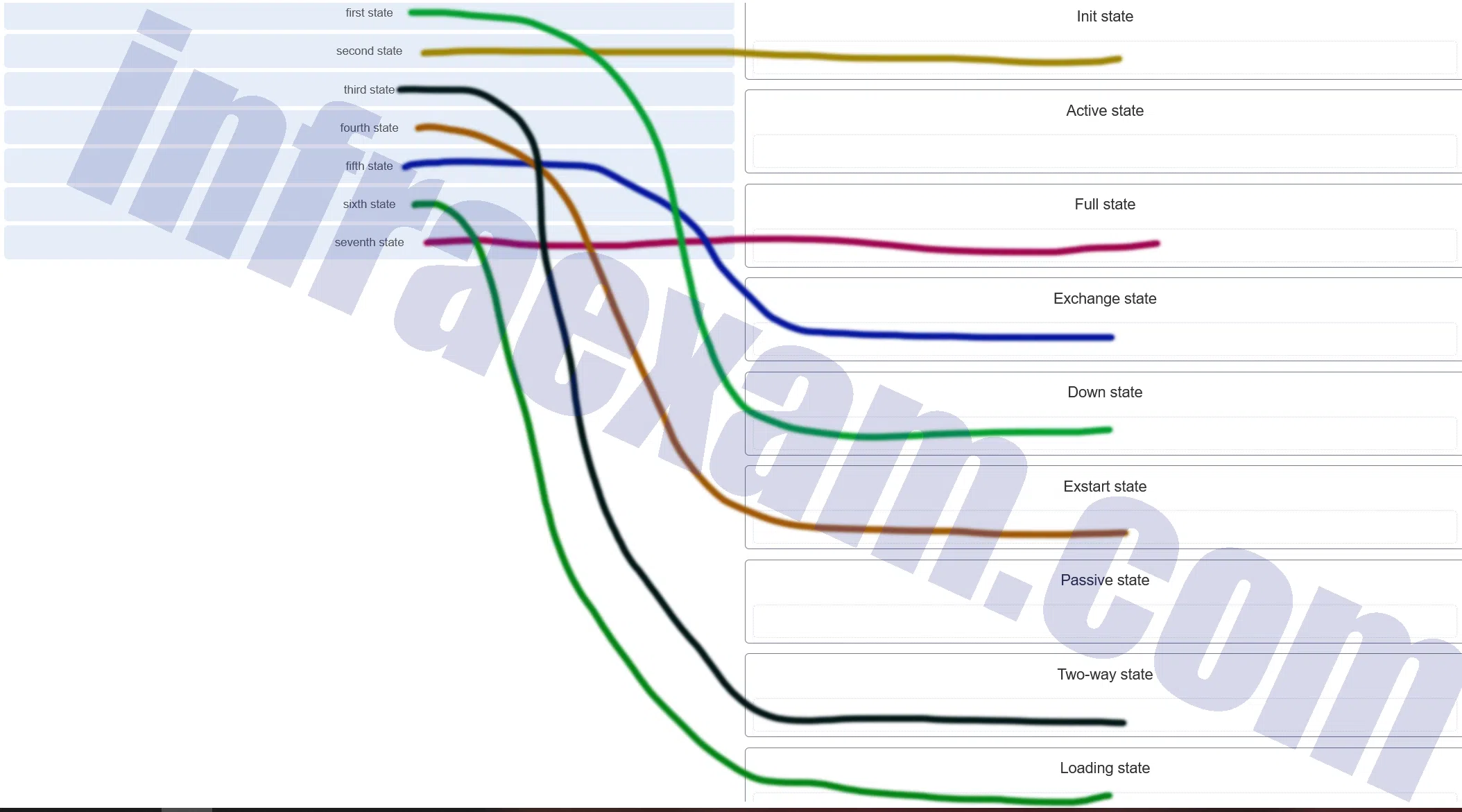
Match the OSPF state with the order in which it occurs. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA3 v7 – Practice Final – ENSA Answers 001 Answers Explanation & Hints: The active and passive states are used by EIGRP.
-
When an OSPF network is converged and no network topology change has been detected by a router, how often will LSU packets be sent to neighboring routers?
- every 5 minutes
- every 10 minutes
- every 30 minutes
- every 60 minutes
Answers Explanation & Hints: After all LSRs have been satisfied for a given router, the adjacent routers are considered synchronized and in a full state. Updates (LSUs) are sent to neighbors only under the following conditions:
when a network topology change is detected (incremental updates)
every 30 minutes
-
Which type of OSPFv2 packet contains an abbreviated list of the LSDB of a sending router and is used by receiving routers to check against the local LSDB?
- link-state update
- link-state request
- database description
- link-state acknowledgment
Answers Explanation & Hints: The database description (DBD) packet contains an abbreviated list of the LSDB sent by a neighboring router and is used by receiving routers to check against the local LSDB.
-
Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router building a link-state database based on received LSAs?
- building the topology table
- executing the SPF algorithm
- selecting the router ID
- declaring a neighbor to be inaccessible
-
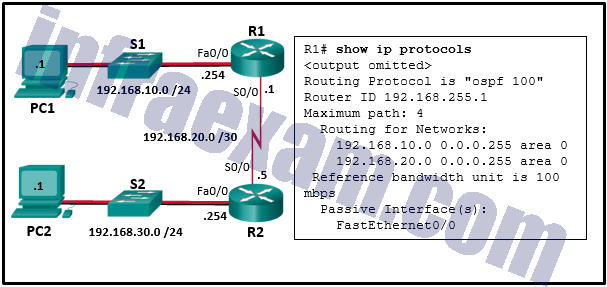
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured OSPFv2 on the two Cisco routers as shown. The routers are unable to form a neighbor adjacency. What should be done to fix the problem?
CCNA3 v7 – Practice Final – ENSA Answers 11 - Remove the FastEthernet0/0 passive interface configuration on router R1.
- Add the command network 192.168.20.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 on router R1.
- Add the command network 192.168.30.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 on router R1.
- Change the IP address on S0/0 of router R2 to 192.168.20.2.
Answers Explanation & Hints: In order to form OSPFv2 neighbor adjacencies, two connected router interfaces must share the same subnet. Router R2 is shown in the topology with an IP address of 192.168.20.5 and does not exist on the same subnet as the 192.168.20.1 /30 IP address of S0/0 on router R1.
-
Which command will a network engineer issue to verify the configured hello and dead timer intervals on a point-to-point WAN link between two routers that are running OSPFv2?
- show ip ospf neighbor
- show ip ospf interface serial 0/0/0
- show ipv6 ospf interface serial 0/0/0
- show ip ospf interface fastethernet 0/1
Answers Explanation & Hints: The show ip ospf interface serial 0/0/0 command will display the configured hello and dead timer intervals on a point-to-point serial WAN link between two OSPFv2 routers. The show ipv6 ospf interface serial 0/0/0 command will display the configured hello and dead timer intervals on a point-to-point serial link between two OSPFv3 routers. The show ip ospf interface fastethernet 0/1 command will display the configured hello and dead timer intervals on a multiaccess link between two (or more) OSPFv2 routers. The show ip ospf neighbor command will display the dead interval elapsed time since the last hello message was received, but does not show the configured value of the timer.
-
What are the two purposes of an OSPF router ID? (Choose two.)
- to facilitate the establishment of network convergence
- to uniquely identify the router within the OSPF domain
- to facilitate the transition of the OSPF neighbor state to Full
- to facilitate router participation in the election of the designated router
- to enable the SPF algorithm to determine the lowest cost path to remote networks
Answers Explanation & Hints: OSPF router ID does not contribute to SPF algorithm calculations, nor does it facilitate the transition of the OSPF neighbor state to Full. Although the router ID is contained within OSPF messages when router adjacencies are being established, it has no bearing on the actual convergence process.
-
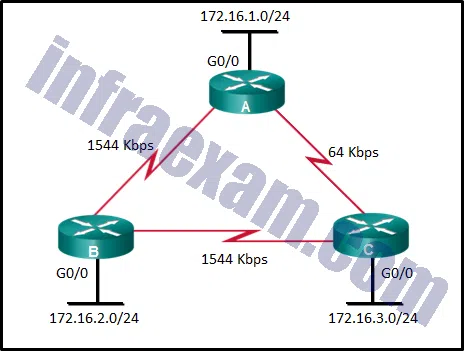
Refer to the exhibit. What is the OSPF cost to reach the router A LAN 172.16.1.0/24 from B?
CCNA3 v7 – Practice Final – ENSA Answers 10 - 782
- 74
- 128
- 65
Answers Explanation & Hints: The formula used to calculate the OSPF cost is as follows:
Cost = reference bandwidth / interface bandwidth
The default reference bandwidth is 10^8 (100,000,000); therefore, the formula is
Cost = 100,000,000 bps / interface bandwidth in bps
Thus the cost to reach the A LAN 172.16.1.0/24 from B is as follows:
Serial link (1544 Kbps) from B to A cost => 100,000,000 / 1,544,000 = 64
Gigabit Ethernet link on A cost => 100,000,000 / 1,000,000,000 = 1
Total cost to reach 172.16.1.0/24 = 64 + 1 = 65
-
Refer to the exhibit. If the switch reboots and all routers have to re-establish OSPF adjacencies, which routers will become the new DR and BDR?
CCNA3 v7 – Practice Final – ENSA Answers 09 - Router R4 will become the DR and router R1 will become the BDR.
- Router R2 will become the DR and router R3 will become the BDR.
- Router R1 will become the DR and router R2 will become the BDR.
- Router R4 will become the DR and router R3 will become the BDR.
Answers Explanation & Hints: OSPF elections of a DR are based on the following in order of precedence:highest pritority from 1 -255 (0 = never a DR)
highest router ID
highest IP address of a loopback or active interface in the absence of a manually configured router ID. Loopback IP addresses take higher precedence than other interfaces.
In this case routers R4 and R1 have the highest router priority. Between the two, R3 has the higher router ID. Therefore, R4 will become the DR and R1 will become the BDR.
-
What is the significant characteristic of worm malware?
- Worm malware disguises itself as legitimate software.
- A worm can execute independently of the host system.
- A worm must be triggered by an event on the host system.
- Once installed on a host system, a worm does not replicate itself.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Worm malware can execute and copy itself without being triggered by a host program. It is a significant network and Internet security threat.
-
What is the best description of Trojan horse malware?
- It is the most easily detected form of malware.
- It is malware that can only be distributed over the Internet.
- It is software that causes annoying but not fatal computer problems.
- It appears as useful software but hides malicious code.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The best description of Trojan horse malware, and what distinguishes it from viruses and worms, is that it appears as useful software but hides malicious code. Trojan horse malware may cause annoying computer problems, but can also cause fatal problems. Some Trojan horses may be distributed over the Internet, but they can also be distributed by USB memory sticks and other means. Specifically targeted Trojan horse malware can be some of the most difficult malware to detect.
-
Which type of security threat can be described as software that attaches itself to another program to execute a specific unwanted function?
- virus
- worm
- proxy Trojan horse
- denial of service Trojan horse
Answers Explanation & Hints: Viruses can be malicious and destructive or simply change something about the computer such as words or images, and that do not necessarily cause the computer to malfunction. Viruses can be spread through shared media such as CDs or memory sticks, but can also be delivered via the Internet and email.
-
What is a feature of an IPS?
- It can stop malicious packets.
- It has no impact on latency.
- It is deployed in offline mode.
- It is primarily focused on identifying possible incidents.
Answers Explanation & Hints: An advantage of an intrusion prevention systems (IPS) is that it can identify and stop malicious packets. However, because an IPS is deployed inline, it can add latency to the network.
-
If a router has two interfaces and is routing both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic, how many ACLs could be created and applied to it?
- 4
- 6
- 8
- 12
- 16
Answers Explanation & Hints: In calculating how many ACLs can be configured, use the rule of “three Ps”: one ACL per protocol, per direction, per interface. In this case, 2 interfaces x 2 protocols x 2 directions yields 8 possible ACLs.
-
Which three statements are generally considered to be best practices in the placement of ACLs? (Choose three.)
- Place standard ACLs close to the source IP address of the traffic.
- Place extended ACLs close to the destination IP address of the traffic.
- Filter unwanted traffic before it travels onto a low-bandwidth link.
- Place extended ACLs close to the source IP address of the traffic.
- Place standard ACLs close to the destination IP address of the traffic.
- For every inbound ACL placed on an interface, there should be a matching outbound ACL.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Extended ACLs should be placed as close as possible to the source IP address, so that traffic that needs to be filtered does not cross the network and use network resources. Because standard ACLs do not specify a destination address, they should be placed as close to the destination as possible. Placing a standard ACL close to the source may have the effect of filtering all traffic, and limiting services to other hosts. Filtering unwanted traffic before it enters low-bandwidth links preserves bandwidth and supports network functionality. Decisions on placing ACLs inbound or outbound are dependent on the requirements to be met.
-
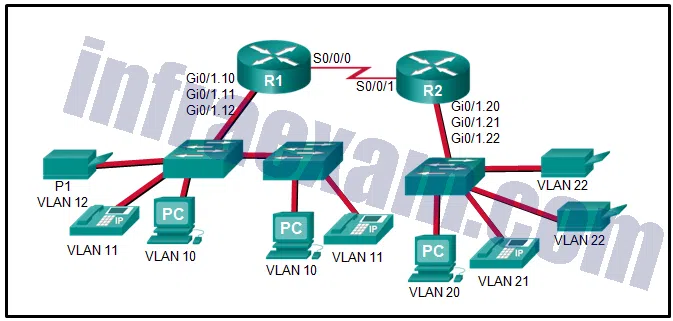
Refer to the exhibit. The Gigabit interfaces on both routers have been configured with subinterface numbers that match the VLAN numbers connected to them. PCs on VLAN 10 should be able to print to the P1 printer on VLAN 12. PCs on VLAN 20 should print to the printers on VLAN 22. What interface and in what direction should you place a standard ACL that allows printing to P1 from data VLAN 10, but stops the PCs on VLAN 20 from using the P1 printer? (Choose two.)
CCNA3 v7 – Practice Final – ENSA Answers 05 - R1 Gi0/1.12
- R1 S0/0/0
- R2 S0/0/1
- R2 Gi0/1.20
- inbound
- outbound
Answers Explanation & Hints: A standard access list is commonly placed as close to the destination network as possible because access control expressions in a standard ACL do not include information about the destination network.
The destination in this example is printer VLAN 12 which has router R1 Gigabit subinterface 0/1/.12 as its gateway. A sample standard ACL that only allows printing from data VLAN 10 (192.168.10.0/24), for example, and no other VLAN would be as follows:
R1(config)# access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
R1(config)# access-list 1 deny any
R1(config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/1.12
R1(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out
-
A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the access-class 20 in configuration option or command?
- to secure administrative access to the router
- to display all restricted traffic
- to secure management traffic into the router
- to remove all ACLs from the router
-
An administrator has configured an access list on R1 to allow SSH administrative access from host 172.16.1.100. Which command correctly applies the ACL?
- R1(config-if)# ip access-group 1 in
- R1(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out
- R1(config-line)# access-class 1 in
- R1(config-line)# access-class 1 out
Answers Explanation & Hints: Administrative access over SSH to the router is through the vty lines. Therefore, the ACL must be applied to those lines in the inbound direction. This is accomplished by entering line configuration mode and issuing the access-class command.
-
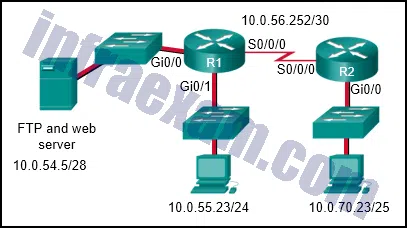
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator that has the IP address of 10.0.70.23/25 needs to have access to the corporate FTP server (10.0.54.5/28). The FTP server is also a web server that is accessible to all internal employees on networks within the 10.x.x.x address. No other traffic should be allowed to this server. Which extended ACL would be used to filter this traffic, and how would this ACL be applied? (Choose two.)
CCNA3 v7 – Practice Final – ENSA Answers 01 - access-list 105 permit ip host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5
access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq www
access-list 105 permit ip any any - access-list 105 permit tcp host 10.0.54.5 any eq www
access-list 105 permit tcp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 eq 20
access-list 105 permit tcp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 eq 21 - access-list 105 permit tcp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 eq 20
access-list 105 permit tcp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 eq 21
access-list 105 permit tcp 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 host 10.0.54.5 eq www
access-list 105 deny ip any host 10.0.54.5
access-list 105 permit ip any any - R2(config)# interface gi0/0
R2(config-if)# ip access-group 105 in - R1(config)# interface gi0/0
R1(config-if)# ip access-group 105 out - R1(config)# interface s0/0/0
R1(config-if)# ip access-group 105 outAnswers Explanation & Hints: The first two lines of the ACL allow host 10.0.70.23 FTP access to the server that has the IP address of 10.0.54.5. The next line of the ACL allows HTTP access to the server from any host that has an IP address that starts with the number 10. The fourth line of the ACL denies any other type of traffic to the server from any source IP address. The last line of the ACL permits anything else in case there are other servers or devices added to the 10.0.54.0/28 network. Because traffic is being filtered from all other locations and for the 10.0.70.23 host device, the best place to put this ACL is closest to the server.
- access-list 105 permit ip host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5
-
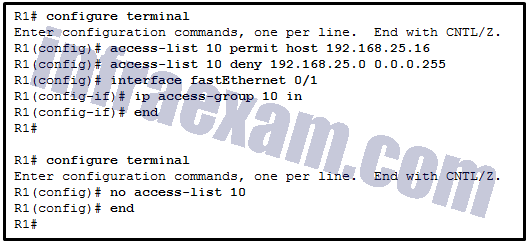
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring a standard IPv4 ACL. What is the effect after the command no access-list 10 is entered?
CCNA3 v7 – Practice Final – ENSA Answers 02 - ACL 10 is disabled on Fa0/1.
- ACL 10 is removed from the running configuration.
- ACL 10 will be disabled and removed after R1 restarts.
- ACL 10 is removed from both the running configuration and the interface Fa0/1.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The R1(config)# no access-list < access-list number > command removes the ACL from the running-config immediately. However, to disable an ACL on an interface, the command R1(config-if)# no ip access-group should be entered.
-
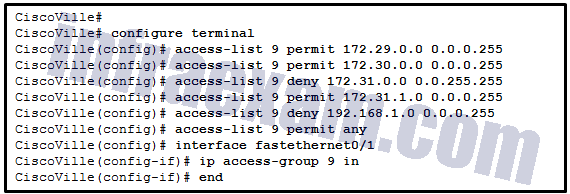
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured ACL 9 as shown. Users on the 172.31.1.0 /24 network cannot forward traffic through router CiscoVille. What is the most likely cause of the traffic failure?
CCNA3 v7 – Practice Final – ENSA Answers 04 - The permit statement specifies an incorrect wildcard mask.
- The sequence of the ACEs is incorrect.
- The established keyword is not specified.
- The port number for the traffic has not been identified with the eq keyword.
Answers Explanation & Hints: When verifying an ACL, the statements are always listed in a sequential order. Even though there is an explicit permit for the traffic that is sourced from network 172.31.1.0 /24, it is being denied due to the previously implemented ACE of CiscoVille(config)# access-list 9 deny 172.31.0.0 0.0.255.255 . The sequence of the ACEs must be modified to permit the specific traffic that is sourced from network 172.31.1.0 /24 and then to deny 172.31.0.0 /16.
-
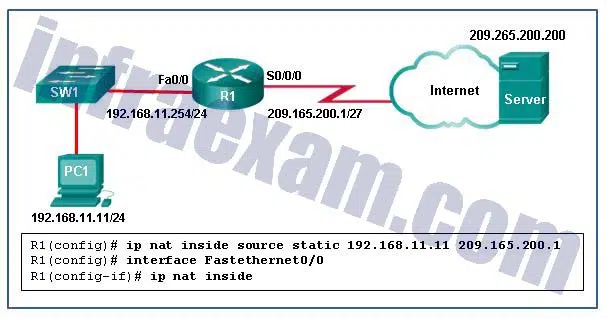
Refer to the exhibit. What has to be done in order to complete the static NAT configuration on R1?
CCNA3 v7 – Practice Final – ENSA Answers 03 - R1 should be configured with the command ip nat inside source static 209.165.200.1 192.168.11.11 .
- R1 should be configured with the command ip nat inside source static 209.165.200.200 192.168.11.11 .
- Interface S0/0/0 should be configured with the command ip nat outside .
- Interface Fa0/0 should be configured with the command no ip nat inside .
Answers Explanation & Hints: In order for NAT translations to work properly, both an inside and outside interface must be configured for NAT translation on the router.
-
A network administrator is troubleshooting the dynamic NAT that is configured on router R2. Which command can the administrator use to see the total number of active NAT translations and the number of addresses that are allocated from the NAT pool?
- R2# show ip nat statistics
- R2# show ip nat translations
- R2# show running-config
- R2# clear ip nat translation
Answers Explanation & Hints: R2# show ip nat translations will display the current NAT translations. It will not provide the information on how many addresses are still left in the pool. R2# clear ip nat translation is used to clear the translation table of old entries so that when the R2# show ip nat translations command is issued, the current NAT translation entries are displayed. R2# show running-config will display the configuration parameters only. R2# show ip nat statistics will display information about the total number of active translations, NAT configuration parameters, the number of addresses in the pool, and the number that have been allocated.
-
Which type of NAT maps a single inside local address to a single inside global address?
- dynamic
- static
- port address translation
- overloading
Answers Explanation & Hints: A one-to-one mapping of an inside local address to an inside global address is accomplished through static NAT.
-
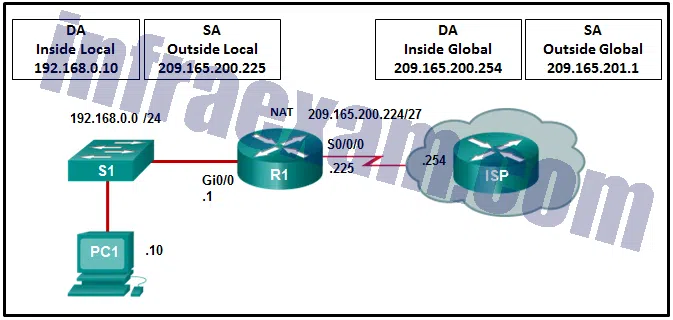
Refer to the exhibit. R1 is configured for static NAT. What IP address will Internet hosts use to reach PC1?
CCNA3 v7 – Practice Final – ENSA Answers 06 - 192.168.0.10
- 192.168.0.1
- 209.165.200.225
- 209.165.201.1
Answers Explanation & Hints: In static NAT a single inside local address, in this case 192.168.0.10, will be mapped to a single inside global address, in this case 209.165.200.225. Internet hosts will send packets to PC1 and use as a destination address the inside global address 209.165.200.225.
-
What is correct in relation to NAT for IPv6?
- It is used to convert private IPv6 addresses to public IPv6 addresses.
- It is a temporary mechanism to assist in the migration from IPv4 to IPv6.
- NAT64 has been deprecated by IETF in favor of NAT-PT.
- Dual stack is an example of implementation of NAT for IPv6.
Answers Explanation & Hints: NAT for IPv6 is a temporary measure to aid in the move from IPv4 to IPv6. NAT64 is replacing NAT-PT. Dual stack is a method for running IPv4 and IPv6 on the same network.
-
Which three traffic-related factors would influence selecting a particular WAN link type? (Choose three.)
- type of traffic
- amount of traffic
- cost of the link
- security needs
- distance between sites
- reliability
Answers Explanation & Hints: The traffic-related factors that influence selecting a particular WAN link type include the type of traffic, amount of traffic, quality requirements, and security requirements. Quality requirements include ensuring that traffic that cannot tolerate delay gets priority treatment as well as important business transactional traffic.
-
Which two types of devices are specific to WAN environments and are not found on a LAN? (Choose two.)
- access layer switch
- broadband modem
- core switch
- CSU/DSU
- distribution layer router
Answers Explanation & Hints: Broadband modems and CSU/DSUs are examples of WAN devices. Core switches can be found on both WANs and LANs. Access layer switches and distribution layer routers are found only on LANs.
-
Which technology provides laptops the ability to function on a cellular network?
- mobile hotspot
- Bluetooth
- infrared
- 802.11 Wi-Fi
Answers Explanation & Hints: Mobile hotspots allow a laptop to connect to a cellular network and gain WAN access. Bluetooth and infrared wireless work for short distances. 802.11 Wi-Fi technology provides laptops with access to a local network.
-
Which two statements describe remote access VPNs? (Choose two.)
- Remote access VPNs are used to connect entire networks, such as a branch office to headquarters.
- End users are not aware that VPNs exists.
- A leased line is required to implement remote access VPNs.
- Client software is usually required to be able to access the network.
- Remote access VPNs support the needs of telecommuters and mobile users.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Remote access VPNs are designed to provide for the needs of telecommuters and mobile users through the use of software that is installed on the client to encrypt and encapsulate the data. Remote access VPNs can be used across a variety of WAN connections. Users must access the client software to initiate the VPN connection.
-
Which VPN solution allows the use of a web browser to establish a secure, remote-access VPN tunnel to the ASA?
- clientless SSL
- client-based SSL
- site-to-site using a preshared key
- site-to-site using an ACL
Answers Explanation & Hints: When a web browser is used to securely access the corporate network, the browser must use a secure version of HTTP to provide SSL encryption. A VPN client is not required to be installed on the remote host, so a clientless SSL connection is used.
-
Which statement describes a feature of site-to-site VPNs?
- The VPN connection is not statically defined.
- VPN client software is installed on each host.
- Internal hosts send normal, unencapsulated packets.
- Individual hosts can enable and disable the VPN connection.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Site-to-site VPNs are statically defined VPN connections between two sites that use VPN gateways. The internal hosts do not require VPN client software and send normal, unencapsulated packets onto the network where they are encapsulated by the VPN gateway.
-
Which two types of VPNs are examples of enterprise-managed remote access VPNs? (Choose two.)
- IPsec VPN
- clientless SSL VPN
- GRE over IPsec VPN
- client-based IPsec VPN
- IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface VPN
Answers Explanation & Hints: Enterprise managed VPNs can be deployed in two configurations:
Remote Access VPN – This VPN is created dynamically when required to establish a secure connection between a client and a VPN server. Remote access VPNs include client-based IPsec VPNs and clientless SSL VPNs.
Site-to-site VPN – This VPN is created when interconnecting devices are preconfigured with information to establish a secure tunnel. VPN traffic is encrypted only between the interconnecting devices, and internal hosts have no knowledge that a VPN is used. Site-to-site VPNs include IPsec, GRE over IPsec, Cisco Dynamic Multipoint (DMVPN), and IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface (VTI) VPNs.
-
What term describes adding a value to the packet header, as close to the source as possible, so that the packet matches a defined policy?
- traffic marking
- policing
- traffic shaping
- weighted random early detection (WRED)
- tail drop
-
Which QoS mechanism allows delay-sensitive data, such as voice, to be sent first before packets in other queues are sent?
- CBWFQ
- FIFO
- LLQ
- FCFS
Answers Explanation & Hints: Low latency queuing (LLQ) adds a priority queue to CBWFQ from which delay-sensitive traffic, such as voice traffic, can be transmitted ahead of packets in other queues.
-
Which QoS technique retains excess packets in a separate queue for later transmission?
- classifying
- marking
- queuing
- shaping
Answers Explanation & Hints: As network traffic exits an interface it is queued and then shaped to smooth out the packet output rate. Classification and marking should occur early on to identify traffic and classify how the traffic should be treated.
-
Why would a network administrator use the config-register 0x2102 command on a Cisco network device?
- to ensure that the device loads the startup configuration file during startup
- to learn device names, IOS versions, and the number and type of interfaces of connected devices
- to back up the running configuration onto a USB drive
- to monitor and manage network performance, find and solve network problems, and plan for network growth
-
Which command will backup the configuration that is stored in NVRAM to a TFTP server?
- copy running-config tftp
- copy tftp running-config
- copy startup-config tftp
- copy tftp startup-config
Answers Explanation & Hints: The startup configuration file is stored in NVRAM, and the running configuration is stored in RAM. The copy command is followed by the source, then the destination.
-
Which number represents the most severe level of syslog logging?
- 0
- 1
- 7
- 10
- 100
Answers Explanation & Hints: Syslog levels are numbered 0 through 7, with 0 being the most severe and 7 being the least severe.
-
Which SNMP message type informs the network management system (NMS) immediately of certain specified events?
- GET request
- SET request
- GET response
- Trap
Answers Explanation & Hints: A GET request retrieves the value of a specific MIB variable. A SET request modifies the value of an MIB variable. A GET response contains the value of the requested variable. A Trap transmits an unsolicited alarm condition immediately after the event occurs.
-
What is a characteristic of the distribution layer in the three layer hierarchical model?
- acts as the backbone for the network, aggregating and distributing network traffic throughout the campus
- provides access to the rest of the network through switching, routing, and network access policies
- distributes access to end users
- represents the network edge
Answers Explanation & Hints: One of the functions of the distribution layer is aggregating large-scale wiring closet networks. Providing access to end users is a function of the access layer, which is the network edge. Acting as a backbone is a function of the core layer.
-
Which two methods help to prevent the disruption of network services? (Choose two.)
- using VLANs to segment network traffic
- changing the routing protocols at regular intervals
- installing duplicate equipment to provide failover services
- using redundant connections to provide alternate physical paths
- removing switches which cause loops
Answers Explanation & Hints: Using duplicate equipment and using redundant paths are two methods to help prevent network disruptions. The use of VLANs would not affect network availability. Changing the routing protocol could actually reduce availability during convergence. Loops, which are created by the provision of redundant paths, are managed by protocols without removing devices.
-
What is the function of ASICs in a multilayer switch?
- They provide power to devices such as IP phones and wireless access points through Ethernet ports.
- They streamline forwarding of IP packets in a multilayer switch by bypassing the CPU.
- They prevent Layer 2 loops by disabling redundant links between switches.
- They aggregate multiple physical switch ports into a single logical port.
Answers Explanation & Hints: ASICs are application-specific integrated circuits and they allow a multilayer switch to forward IP packets without calling on the CPU to make routing decisions. By using ASICs a switch can forward IP packets almost as fast as it can forward Layer 2 frames.
-
What is the port density of a switch?
- the bandwidth of a port
- the throughput of a port
- the number of available ports on a switch
- the combined bandwidth of all ports on a switch
Answers Explanation & Hints: Port density refers to the number of available ports on a switch. Bandwidth is the wire speed of a single port on a switch. The combined bandwidth of all ports on a switch is the forwarding rate.
-
A network technician has used the access-llst 1 permit 172.16.0.0 0.0.0.255 command to configure NAT on an edge router to translate only four networks, 172.16.0.0 /24, 172.16.1.0 /24, 172.16.2.0 /24, and 172.16.3.0 /24. After receiving complaints about limited access to the Internet, issuing the show ip nat translations command reveals that some networks are missing from the output. Which change will resolve the problem?
- The access list should be replaced with access-list 1 permit 172.16.0.0 255.255.255.0.
- The access list should be replaced with access-list 1 permit 172.16.0.0 0.0.1.255 .
- The access list should be replaced with access-list 1 permit 172.16.0.0 0.0.0.255
- The access list should be replaced with access-list 1 permit 172.16.0.0 0.0.3.255
Answers Explanation & Hints: The ACL in the original configuration will only permit the first subnet, 172.16.0.0, to be translated. The first option uses a subnet mask when it should use a wildcard mask. The second option will only permit the first two networks, 172.16.0.0 and 172.16.1.0. The third option uses an invalid wildcard mask that will allow translation of the entire 172.16.0.0 network. The fourth option is the correct option as it allows translation of just the four subnets.
-
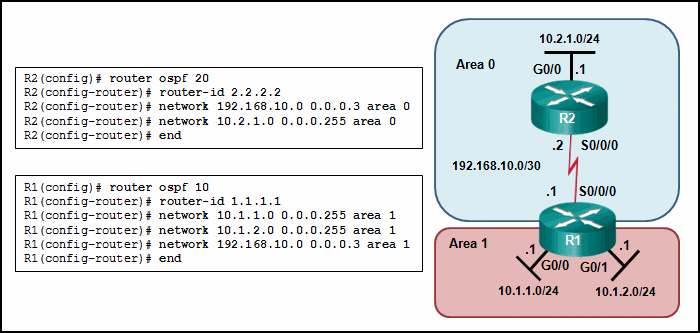
Refer to the exhibit. Why are routers R1 and R2 not able to establish an OSPF adjacency?
CCNA3 v7 – Practice Final – ENSA Answers 08 - The router ID values are not the same in both routers.
- The serial interfaces are not in the same area.
- The process numbers are not the same in both routers.
- A backbone router cannot establish an adjacency with an ABR router.
Answers Explanation & Hints: On router R1, the network 192.168.10.0/30 is defined in the wrong area (area 1). It has to be defined in area 0 in order to establish adjacency with router R2, which has the network 192.168.10.0/30 defined in area 0.
-
A user reports that the workstation cannot connect to a networked printer in the office in order to print a report created with word processing software. Which troubleshooting action by the helpdesk technician would follow the divide-and-conquer approach?
- Ask the user to launch the web browser.
- Ask the user to save the working document.
- Ask the user to issue the ipconfig command.
- Ask the user to unplug and reattach the network cable.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The ipconfig command can be used to check the IP settings of the workstation, an internet layer issue, so this is the divide-and-conquer approach. Based on the result, the technician can further investigate either from the lower layer (for example, looking for a network connectivity issue) or the upper layer (for example, checking whether the application is working properly). To ask the user to unplug and reattach the network cable is the bottom-up approach. Asking the user to launch a web browser (to check if an application can start normally) and to save the document (to check that the application is performing normally and to preserve the working document) is the top-down approach.
-
Which type of tool would an administrator use to capture packets that are going to and from a particular device?
- NMS tool
- knowledge base
- baselining tool
- protocol analyzer
Answers Explanation & Hints: Protocol analyzers capture packets as they enter or leave a device and can display those packets in real time. An NMS tool is used to monitor and configure network devices. A knowledge base is a repository of information that pertains to the operation and troubleshooting of a specific device or service. A baselining tool is used to measure network or device performance during normal operations, so that abnormal conditions can be easily spotted.
-
What is a difference between the functions of Cloud computing and virtualization?
- Cloud computing utilizes data center technology whereas virtualization is not used in data centers.
- Cloud computing requires hypervisor technology whereas virtualization is a fault tolerance technology.
- Cloud computing separates the application from the hardware whereas virtualization separates the OS from the underlying hardware.
- Cloud computing provides services on web-based access whereas virtualization provides services on data access through virtualized Internet connections.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Cloud computing separates the application from the hardware. Virtualization separates the OS from the underlying hardware. Virtualization is a typical component within cloud computing. Virtualization is also widely used in data centers. Although the implementation of virtualization facilitates an easy server fault tolerance setup, it is not a fault tolerance technology by design. The Internet connection from a data center or service provider needs redundant physical WAN connections to ISPs.
-
What defines a two-tier spine-leaf topology?
- The spine tier can be implemented with Cisco Nexus 9500 switches connected to each other and to the leaf switches.
- Everything is two hops from everything else.
- The APIC controller manipulates the data path directly.
- The Cisco APICs and all other devices in the network physically attach to leaf switches.
Answers Explanation & Hints: In this two-tier topology, everything is one hop from everything else. The leaf switches (Cisco Nexus 9300) always attach to the spines (Cisco Nexus 9500), but never to each other. Similarly, the spine switches only attach to the leaf and core switches. The Cisco APICs and all other devices in the network physically attach to leaf switches. When compared to SDN, the APIC controller does not manipulate the data path directly.
-
Which type of Hypervisor is implemented when a user with a laptop running the Mac OS installs a Windows virtual OS instance?
- virtual machine
- bare metal
- type 1
- type 2
Answers Explanation & Hints: Type 2 hypervisors, also know as hosted hypervisors, are installed on top of an existing operating system, such as Mac OS, Windows, or Linux.
-
Which two layers of the OSI model are associated with SDN network control plane functions that make forwarding decisions? (Choose two.)
- Layer 1
- Layer 2
- Layer 3
- Layer 4
- Layer 5
Answers Explanation & Hints: The SDN control plane uses the Layer 2 ARP table and the Layer 3 routing table to make decisions about forwarding traffic.
-
When JSON data format is being used, what characters are used to hold objects?
- double braces { }
- double brackets [ ]
- double quotations ” “
- double colons : :
Answers Explanation & Hints: A JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) object is a key-value data format that is typically rendered in curly braces { }.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which data format is used to represent the data for network automation applications?
CCNA3 v7 – Practice Final – ENSA Answers 12 - XML
- HTML
- YAML
- JSON
Answers Explanation & Hints: Common data formats that are used in many applications including network automation and programmability include these:
JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) – In JSON, the data known as an object is one or more key/value pairs enclosed in braces { }. Keys must be strings within double quotation marks ” “. Keys and values are separated by a colon.
eXtensible Markup Language (XML) – In XML, the data is enclosed within a related set of tags <tag>data</tag>.
YAML Ain’t Markup Language (YAML) – In YAML, the data known as an object is one or more key value pairs. Key value pairs are separated by a colon without the use of quotation marks. YAML uses indentation to define its structure, without the use of brackets or commas.
-
A user is reading a book from the website https://www.books-info.com/author1a/book2.html#page100 . Which part of the web link is called a fragment?
- https://
- /author1a
- #page100
- /book2.html
Answers Explanation & Hints: In the website URI https://www.books-info.com/author1a/book2.html#page100 , the components include the following:
Protocol/scheme – HTTPS, FTP, SFTP, mailto, NNTP, etc.
Hostname – www.books-info.com
Path and file name – /author1a/book2.html
Fragment – #page100