CCNPv8 ENCOR (Version 8.0) – Chapters 13 – 14: Multicast and QoS Exam Answers Full 100% 2024
CCNPv8 ENCOR (Version 8.0) – Chapters 13 – 14: Multicast and QoS Exam Answers Full 100% 2024
| CCNP ENCOR v8 & 8.01 | |
| Final Exam Answers | |
| This Chapters 13 - 14 | |
| Chapters 13 - 14 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Chapters 13 - 14 Quizzes Answers | Online Test |
| Next Chapters 15 - 16 | |
| Chapters 15 - 16 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Chapters 15 - 16 Quizzes Answers | Online Test |
-
Which two IGMPv3 modes are used to signal membership to a multicast host group? (Choose two.)
- include
- join
- leave
- rendezvous
- preclude
- exclude
Answers Explanation & Hints: The two IGMP modes that are used to signal membership are Include mode (the receiver announces membership to a multicast group and provides a include list) and Exclude mode (receiver announces membership to multicast group and provides exclude list).
-
A network administrator statically assigns a multicast address of 239.255.8.5 to an application running on a server. The NIC on the server is with the MAC address of AB.54.C1.01.B8.9F. Which Layer 2 multicast address will receivers use on their interfaces in order to receive the multicast feed?
- 01:00:5E:01:B8:9F
- AB:54:C1:17:A8:02
- 01:00:5E:7F:08:05
- AB:54:C1:7F:08:05
Answers Explanation & Hints: When a receiver wants to receive multicast feed from a particular multicast service, it will send a IGMP join message with the multicast IP address of the service and then reprogram the receiver interface with the matching multicast MAC address. To find the matching MAC address, do the following:
Convert the IP multicast address 239.255.8.5 to binary form, 11101111.11111111.00001000.00000101
Separate the 23 low-order binary bits from the converted address, 1111111.00001000.00000101
Convert these bits to hexadecimal: 7F:08:05
Because the first 24bits of a multicast MAC address are 01.00.5E, The resulting multicast MAC address is then 01:00:5E:7F:08:05.
-
Which statement about IGMPv3 is true?
- It sends IGMP query messages with a TTL value of 1 addressed to the all-host group (224.0.0.1).
- It does not accept a leave group message from the hosts that have already joined the multicast group.
- It rejects any group-specific query message that is sent from the hosts that want to join a multicast group.
- It enables a multicast receiver to signal to the first hop router the multicast sources from which it expects to receive traffic.
Answers Explanation & Hints: IGMPv3 is an extension of IGMPv2 with added support for multicast source filtering done through the use of a new message type called Version 3 membership report. It supports applications that explicitly signal sources that want to receive multicast traffic by using the membership report in the Include or Exclude mode.
-
Which statement describes a characteristic of IP multicast routing?
- PIM dense mode flood and prune behavior repeats every three minutes.
- PIM hello messages are sent every 60 seconds by default out each PIM enabled interface.
- PIM sparse mode and PIM dense mode require an RP on the network.
- PIM sparse mode builds the multicast tree through flooding of traffic out every interface.
Answers Explanation & Hints: PIM dense mode is used in a multicast group that is densely populated across the network. PIM dense mode (PIM-DM) prunes expire after three minutes. This means that the flood and prune behavior of PIM dense mode repeats every three minutes and should be taken into account when designing a network for PIM-DM. A rendezvous point (RP) is required only in networks running Protocol Independent Multicast sparse mode (PIM-SM).
-
An administrator has configured and enabled multicast together with PIM sparse mode on all VLANs on the network. Which feature helps to reduce multicast traffic being broadcast on the access layer switches?
- IGMP snooping
- PIM Pruning
- source registration
- SPT switchover
Answers Explanation & Hints: IGMP snooping stops multicast traffic from being broadcast on the access layer switches by examining IGMP joins that are sent by receivers and maintaining a table of interfaces to IGMP joins.
-
Which two statements describe IGMP? (Choose two.)
- IGMPv2 supports multicast source filtering.
- IGMPv3 provides support for SSM.
- Multicast flooding on a LAN segment can be mitigated by using IGMP snooping.
- An IGMPv2 router will only allow IGMPv2 hosts to execute a join request.
- IGMPv1 only supports queries sent to a predefined group.
Answers Explanation & Hints: IGMPv3 is used to provide source filtering for Source Specific Multicast (SSM). IGMP snooping can be used to mitigate multicast flooding and optimize the forwarding of multicast traffic to interested receivers.
-
Which two statements about Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) are true? (Choose two.)
- PIM does not require an IGP protocol to be configured in the network.
- PIM should be configured only on the first and the last hop routers in the multicast tree.
- PIM should be configured on the device that hosts the source of the muticast traffic.
- PIM sparse mode is most useful when there are few senders, many receivers, and the volume of multicast traffic is high.
- PIM is a multicast routing protocol that makes packet-forwarding decisions independent of the unicast IP routing protocol that is running in the network.
- Three of the forwarding modes for PIM are PIM dense mode (PIM-DM), PIM sparse mode (PIM-SM), and PIM sparse-dense mode.
Answers Explanation & Hints: PIM is a multicast routing protocol that routes multicast traffic between network segments by creating distribution trees. It makes packet-forwarding decisions independent of the unicast IP routing protocol that is running in the network. There are five operating PIM modes:
PIM dense mode (PIM-DM)
PIM sparse mode (PIM-SM)
PIM sparse dense Mode
PIM source specific multicast (PIM-SSM)
PIM bidirectional mode (Bidir-PIM)
-
A network administrator is troubleshooting an IP multicast problem. Where can the administrator view source S, group G, incoming interfaces (IIF), outgoing interfaces (OIFs), and RPF neighbor information for each multicast route?
- in unicast routing table
- in the multicast forwarding information base
- in the multicast routing information base
- in the routing information base
Answers Explanation & Hints: The multicast routing information base (MRIB) is a topology table that is also known as the multicast route table (mroute). The MRIB is built using PIM and the routing table. It contains the source S, group G, incoming interfaces (IIF), outgoing interfaces (OIFs), and RPF neighbor information for each multicast route as well as other multicast-related information. The command show ip mroute is used to display the full contents of the IP multicast routing table.
-
To which multicast group does a candidate RP send announcement messages to advertise its willingness to be an RP?
- 224.0.0.13
- 224.0.1.40
- 224.0.1.39
- 224.0.0.2
Answers Explanation & Hints: A C-RP advertises its willingness to be an RP every 60 seconds via RP announcement messages to the reserved well-known multicast group 224.0.1.39 (Cisco-RP-Announce). RP mapping agents join group 224.0.1.39 to receive the RP announcements.
-
Which well-know multicast group is joined by all PIM-enabled routers to receive RP mappings?
- 224.0.0.13
- 224.0.1.39
- 224.0.1.40
- 224.0.0.2
Answers Explanation & Hints: RP mapping agents advertise the RP mappings to the well-known multicast group address, 224.0.1.40 (Cisco-RP-Discovery). Advertisements are sent every 60 seconds by default, or when changes are detected. All PIM-enabled routers join 224.0.1.40 and store the RP mappings in cache.
-
Which is a characteristic of PIM sparse mode?
- It builds the multicast tree by flooding traffic out all interfaces.
- It requires an RP on the network to act as the root of the shared distribution tree.
- It is designed for networks where receivers are located on every subnet in the network.
- It uses a pruning mechanism to stop the flow of unwanted multicast traffic on interfaces with no downstream neighbors.
Answers Explanation & Hints: PIM sparse mode chooses one or more routers to operate as rendezvous points (RPs). An RP is a single common root placed at a chosen point of a shared distribution tree.
-
Which notation is used to refer to the forwarding state in PIM shared trees?
- (*,G)
- (S,G)
- (G,S)
- (*,S)
Answers Explanation & Hints: In a shared tree uses a rendezvous point (RP) as the tree root instead of the multicast source. Multicast traffic is forwarded down the shared tree to the group address (G). For this reason the forwarding state is referred to as (*,G).
-
The bootstrap router (BSR) mechanism of automating the distribution of rendezvous point (RP) information uses which IP address to disseminate information to all protocol independent multicast (PIM) routers?
- 224.0.0.13
- 224.0.1.13
- 224.1.0.13
- 224.1.1.13
Answers Explanation & Hints: BSR (bootstrap router) messages are forwarded out of every PIM-enabled interface and use the all PIM router address 224.0.0.13 with a TTL of 1.
-
What is the IP address for the Cisco-RP-announce multicast group?
- 224.0.0.1
- 224.0.1.39
- 224.0.1.49
- 224.0.0.40
Answers Explanation & Hints: The internet Assigned Numbers authority has assigned two group addresses, 224.0.0.39 and 224.0.1.40, for Auto-RP configuration in order to announce the RP in the multicast group.
-
Which nonproprietary mechanism does PIM use to discover and announce RP set information for each group prefix for all the routers in a PIM domain?
- BSR
- Auto-RP
- RPF
- Static RP
Answers Explanation & Hints: The bootstrap router (BSR) mechanism is used by PIM to discover and announce RP set information for each group prefix for all the routers in a PIM domain. This mechanism provides a fault-tolerant, automated RP discovery and distribution mechanism.
-
What happens when an edge router using IntServ QoS determines that the data pathway cannot support the level of QoS requested?
- Data is forwarded along the pathway using a best-effort approach.
- Data is forwarded along the pathway using DiffServ.
- Data is not forwarded along the pathway.
- Data is forwarded along the pathway using IntServ but not provided preferential treatment.
Answers Explanation & Hints: When the IntServ QoS model is being used, if network devices along a data path can reserve the required bandwidth, the originating application can begin transmitting. If the requested resource reservation cannot be allocated along the path, the originating application does not send any data.
-
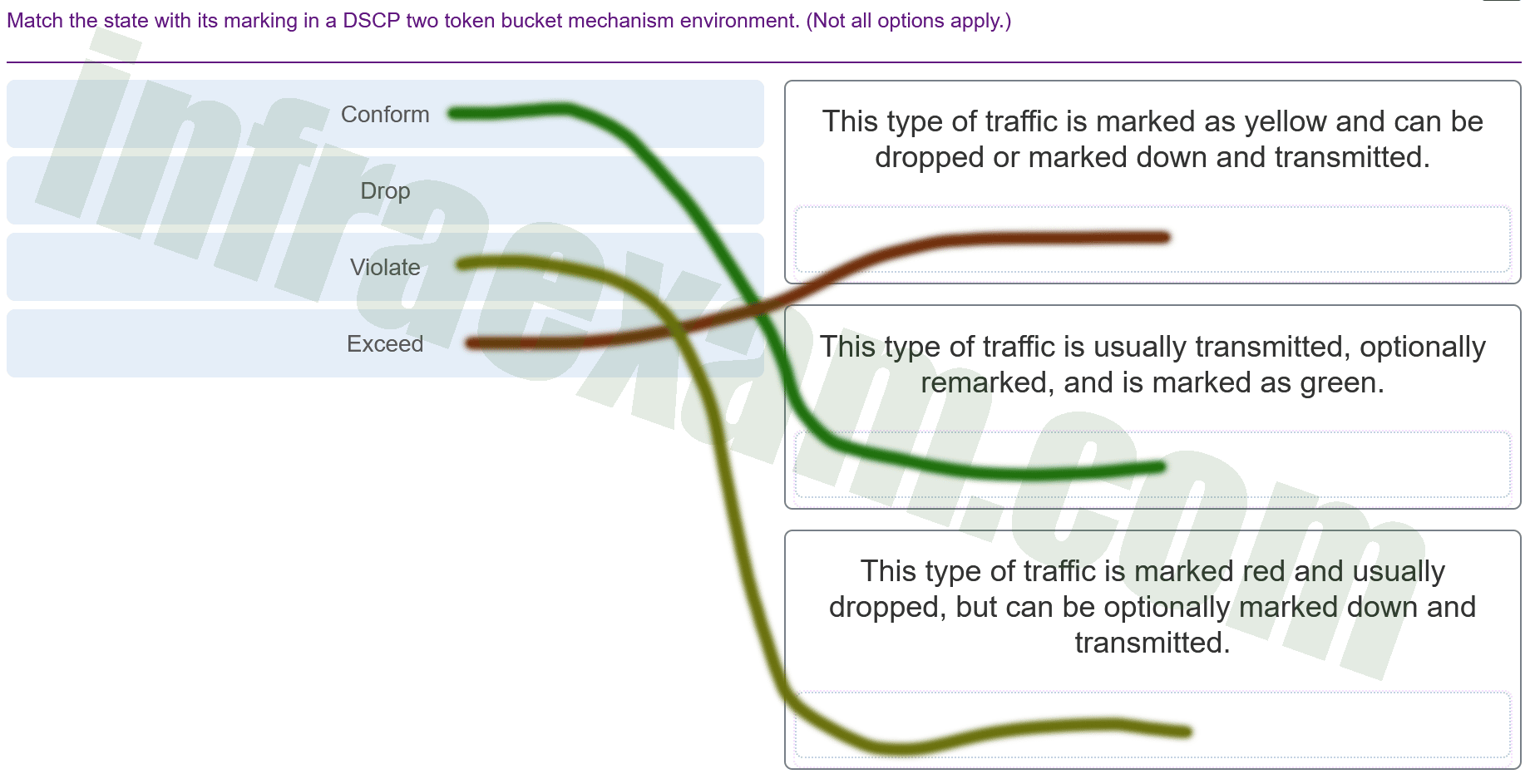
Match the state with its marking in a DSCP two token bucket mechanism environment. (Not all options apply.)
CCNPv8 ENCOR (Version 8.0) – Chapters 13 – 14 Multicast and QoS Exam Answers 001 Explanation & Hint: -
What two fields are available in IPv4 and IPv6 headers to mark packets for QoS? (Choose two.)
- Class of Service
- Traffic Class
- Type of Service
- Priority
- VLAN ID
Answers Explanation & Hints: IPv4 uses an 8-bit Type of Service field to mark packets at Layer 3 and IPv6 uses an 8-bit Traffic Class field to mark packets at Layer 3. The fields are used by receiving devices to forward the packets based on the appropriate assigned QoS policy.
-
A network administrator has defined the trust boundary of a network. What is the function of trusted endpoints deployed across the network?
- Trusted endpoints are devices designed to provide network security features.
- Trusted endpoints provide monitoring and logging solutions.
- Trusted endpoints have the ability to mark application traffic.
- Trusted endpoints provide the ability to drop previously marked traffic during congestions.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Trusted endpoints are devices that have the capability to mark application traffic at Layer 2 or Layer 3. Trusted endpoints include the following:IP phones
Wireless access points
Videoconferencing gateways and systems
IP conferencing stations and more
-
Which is a QoS model that a network engineer would implement to ensure a source to destination quality of service standard for a specified data flow?
- integrated services
- differentiated services
- best effort
- class-based weighted fair queuing
- low latency queuing
Answers Explanation & Hints: Best effort is the default packet forwarding design and provides no QoS. The differentiated services model enforces and applies QoS mechanisms on a hop-by-hop basis, not source to destination. Class-based weighted fair queuing and low latency queuing are queuing algorithms.
-
What would be the Tc value in ms for a 1 Gbps interface configured with a policer defined with a CIR of 150 Mbps and a Bc of 12 Mb?
- 100 ms
- 1000 ms
- 10 ms
- 10,000 ms
Answers Explanation & Hints: The Tc value is calculated by using the formula Bc (bits)/ CIR (bps) X 1000
TC = (15 Mb/150 Mbps) X 1000
Tc = (15,000,000 bits/150,000,000 pbs) X 1000
Tc = 100 ms
-
What statement describes the Class of Service field?
- It is a Layer 1 field.
- It is a Layer 2 field.
- It is a field that is 8 bits long.
- It is a field that is 6 bits long.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The Class of Service is a 3-bit, Layer 2 field that is used as part of quality of service (QOS) between switches. The CoS is also one of the values used for classification and marking of traffic.
-
Which protocol operates at Layer 3 and is used for marking packets?
- CoS
- DSCP
- QoE
- IntServ
Answers Explanation & Hints: The differentiated services code point (DSCP) protocol is used to mark a 6-bit field within the DiffServ field that allows for classification of up to 64 values used for QoS.
-
What is the recommended maximum one-way latency when implementing video over IP for real-time video applications?
- Latency is not a factor for smooth video over IP implementation.
- Latency should be defined for voice traffic only (not for video).
- The recommended maximum one-way latency should not be more than 150 ms.
- When mixed video and voice packets are included in the video stream, the latency should be 300 ms.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Because voice traffic is very sensitive to delay and jitter, to avoid packet drops care must taken to be ensure a maximum one-way latency of not more then 150ms.
-
Which two procedures should be implemented when deploying VoIP in a campus network? (Choose two.)
- voice and data traffic in the same VLAN and mark the traffic for high priority treatment
- a voice class low-latency queuing (LLQ) QoS policy
- a traffic shaping QoS policy to guarantee minimum delay for the voice traffic
- packet marking for voice traffic with a 802.1p CoS value of 5
- priority queuing with voice traffic given the high-priority queue
Answers Explanation & Hints: Because voice traffic is very sensitive to latency and jitter, it would be better to keep it on a separate vlan and prioritize the traffic using QoS mechanisms. Such actions will ensure that the voice traffic has a dedicated bandwidth that is sufficient to meet its needs and the traffic is marked as priority over any other traffic.
-
Which statement is true about the Single-Rate Two-Color Markers algorithm?
- It uses a single token bucket algorithm and traffic can be marked or dropped in both states (conforming to or exceeding the CIR).
- It uses a two bucket algorithm and traffic can be classified as conforming to, exceeding, or violating the CIR.
- It uses a single bucket algorithm and uses three colors or states to classify the traffic.
- It uses a two bucket algorithm that causes fewer TCP transmissions and is more efficient for bandwidth utilization.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The Single-Rate Two-Color Markers use a single token algorithm while the Single-Rate Three-Color markers use the two token bucket algorithm.
-
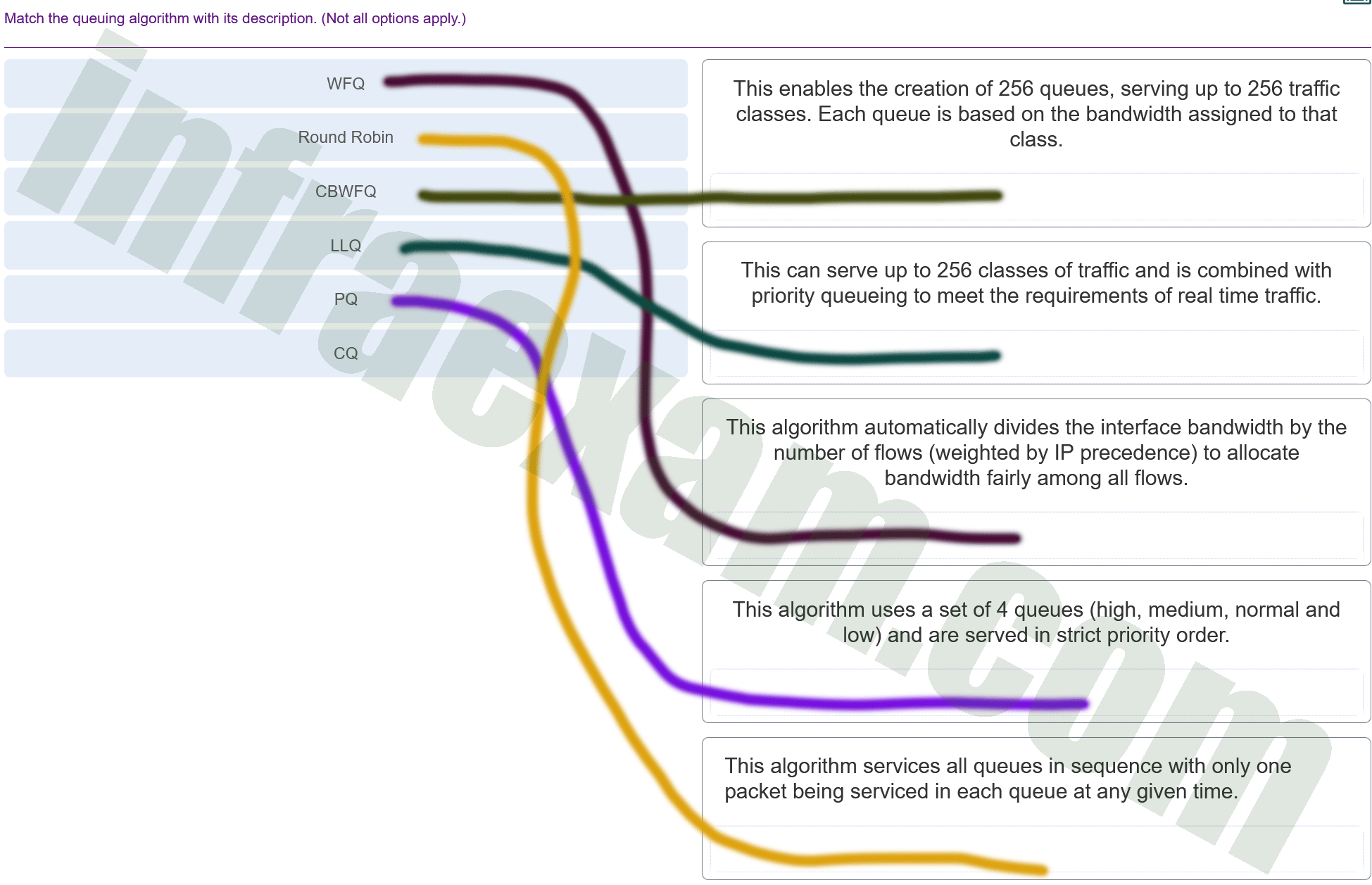
Match the queuing algorithm with its description. (Not all options apply.)
CCNPv8 ENCOR (Version 8.0) – Chapters 13 – 14 Multicast and QoS Exam Answers 002 Explanation & Hint: The image appears to be a matching exercise for different queuing algorithms and their descriptions. I will provide you with the correct matches based on the descriptions provided in the image:
- WFQ (Weighted Fair Queuing): This algorithm automatically divides the interface bandwidth by the number of flows (weighted by IP precedence) to allocate bandwidth fairly among all flows.
- CBWFQ (Class-Based Weighted Fair Queuing): This enables the creation of 256 queues, serving up to 256 traffic classes. Each queue is based on the bandwidth assigned to that class.
- LLQ (Low Latency Queuing): This can serve up to 256 classes of traffic and is combined with priority queuing to meet the requirements of real-time traffic.
- PQ (Priority Queuing): This algorithm uses a set of 4 queues (high, medium, normal, and low) and are served in strict priority order.
- CQ (Custom Queuing): This algorithm services all queues in sequence with only one packet being serviced in each queue at any given time.
- Round Robin: Not described in the provided options, but Round Robin is a method where each queue is served equally in a rotating order.
Please use the provided descriptions to match with the queuing algorithms in the exercise you are working on.
-
What is the value of the DSCP marker for video traffic on a WLAN?
- EF
- AF41
- AF11
- O
Answers Explanation & Hints: The traffic types and their associated DSCP values in a WLAN are as follows:
Voice-EF
Video-AF41
Best Effort-O
Background-AF11
-
Which statement describes NBAR2?
- NBAR2 can identify a variety of protocols and applications by using up to Layer 6 data.
- NBAR2 does not require monthly protocol packs to identify new and emerging applications.
- NBAR2 uses MQC to match traffic to specific protocols.
- NBAR2 supports only scavenger traffic.
Answers Explanation & Hints: NBAR2 is a deep packet inspection engine that uses Layer 3 through 7 data to identify a variety of protocols. it can operate in either Protocol discovery mode or Modular QoS CLI (MQC) mode.
-
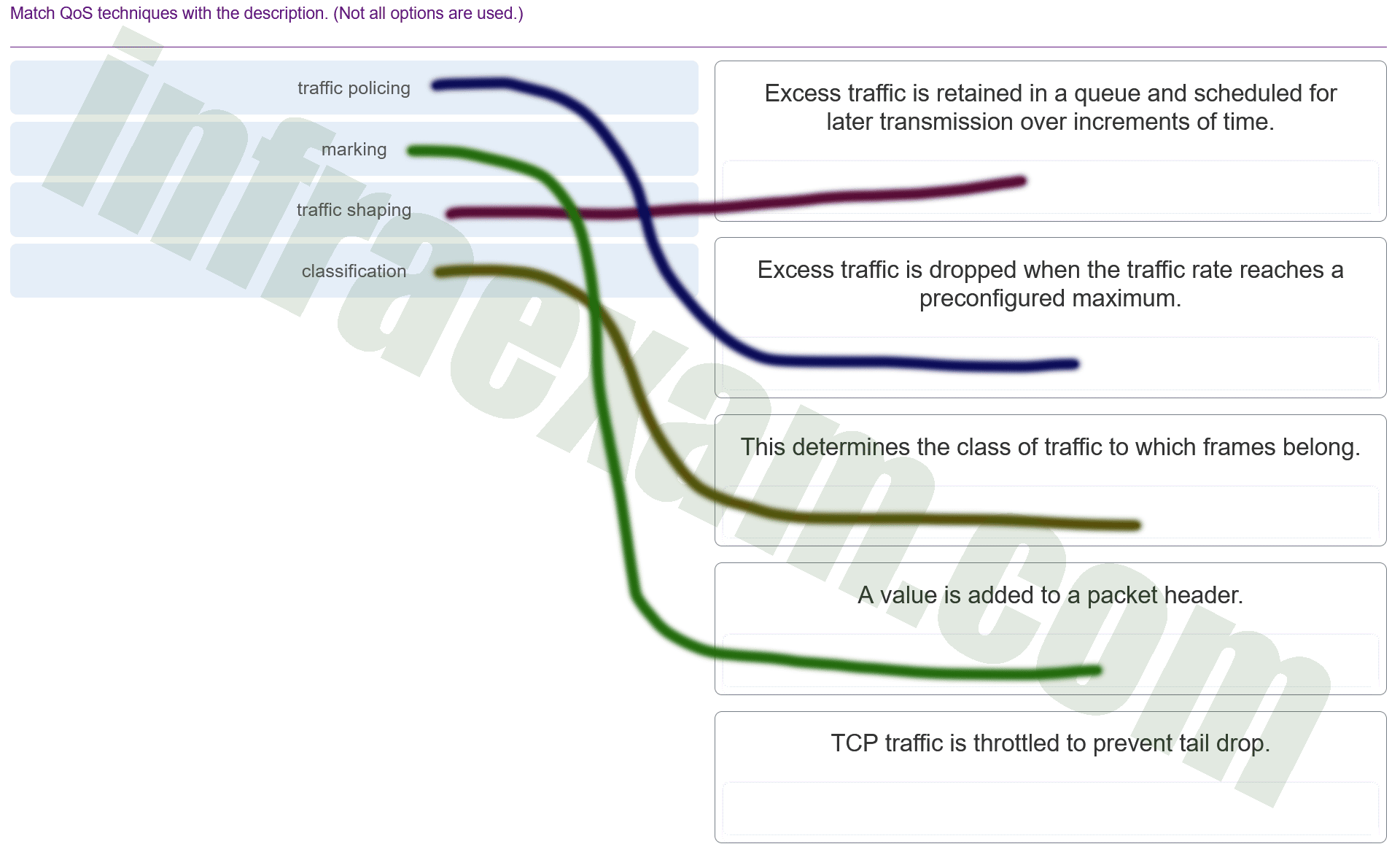
Match QoS techniques with the description. (Not all options are used.)
CCNPv8 ENCOR (Version 8.0) – Chapters 13 – 14 Multicast and QoS Exam Answers 003 Explanation & Hint: Based on the image you’ve provided, which contains descriptions of various Quality of Service (QoS) techniques, the correct matches for each technique are as follows:
- Traffic Shaping: Excess traffic is retained in a queue and scheduled for later transmission over increments of time.
- Traffic Policing: Excess traffic is dropped when the traffic rate reaches a preconfigured maximum.
- Classification: This determines the class of traffic to which frames belong.
- Marking: A value is added to a packet header.
The final description provided, “TCP traffic is throttled to prevent tail drop,” is typically associated with TCP traffic management mechanisms, such as TCP rate control or congestion avoidance techniques, rather than a specific QoS technique. However, if it were related to a QoS technique, it might be describing a behavior similar to traffic shaping or a congestion management technique that ensures fair queuing among TCP flows.
-
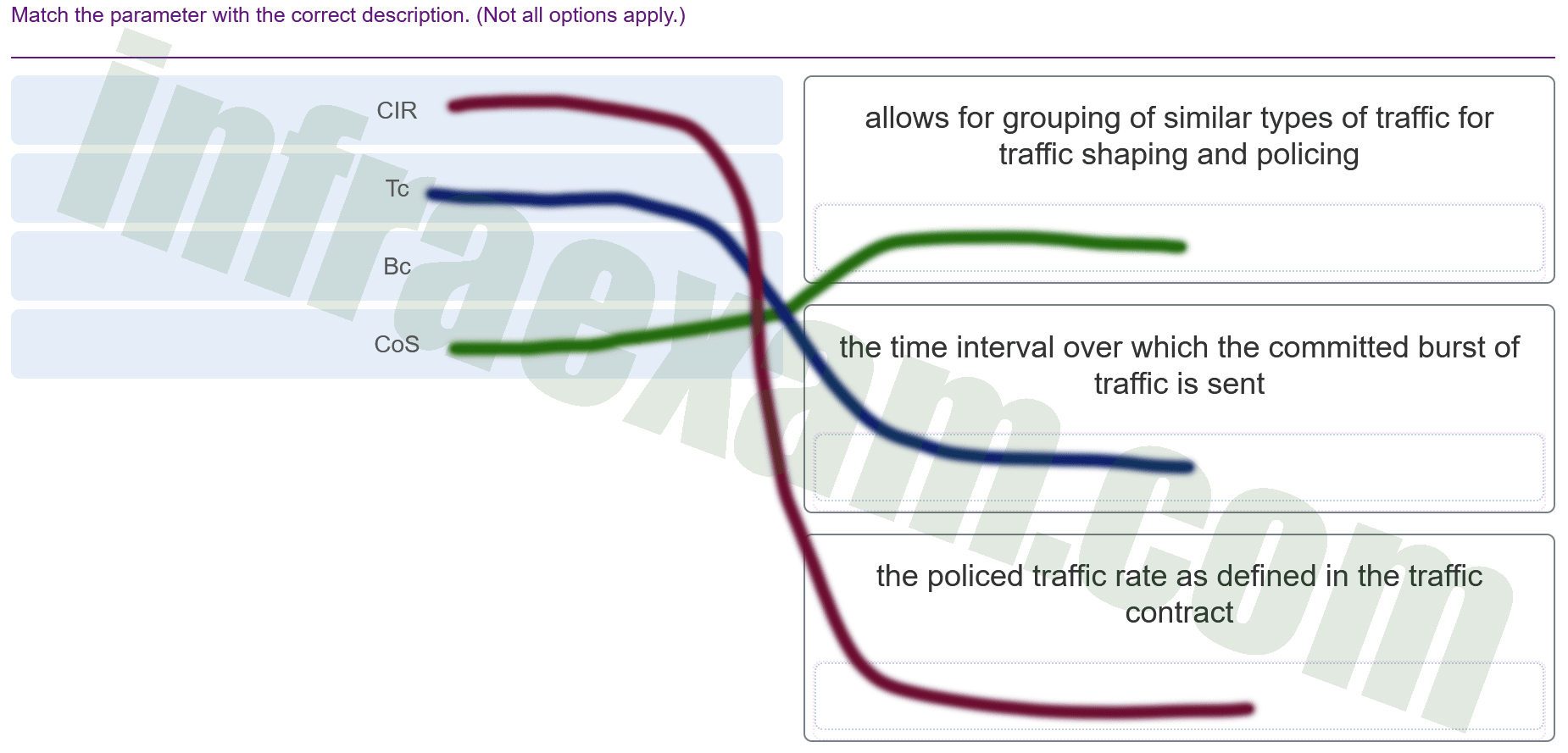
Match the parameter with the correct description. (Not all options apply.)
CCNPv8 ENCOR (Version 8.0) – Chapters 13 – 14 Multicast and QoS Exam Answers 004 Explanation & Hint: Based on the image you’ve provided, which contains descriptions of various Quality of Service (QoS) parameters, the correct matches for each parameter are as follows:
- CIR (Committed Information Rate): the policed traffic rate as defined in the traffic contract.
- Tc (Time Interval): the time interval over which the committed burst of traffic is sent.
- Bc (Burst Size): Not explicitly described here, but it generally refers to the amount of data that is allowed to be sent during the Tc time interval in a traffic policing or shaping scenario.
- CoS (Class of Service): allows for grouping of similar types of traffic for traffic shaping and policing.
These QoS parameters are typically used in the configuration of traffic policing and shaping policies to manage network bandwidth and performance.
-
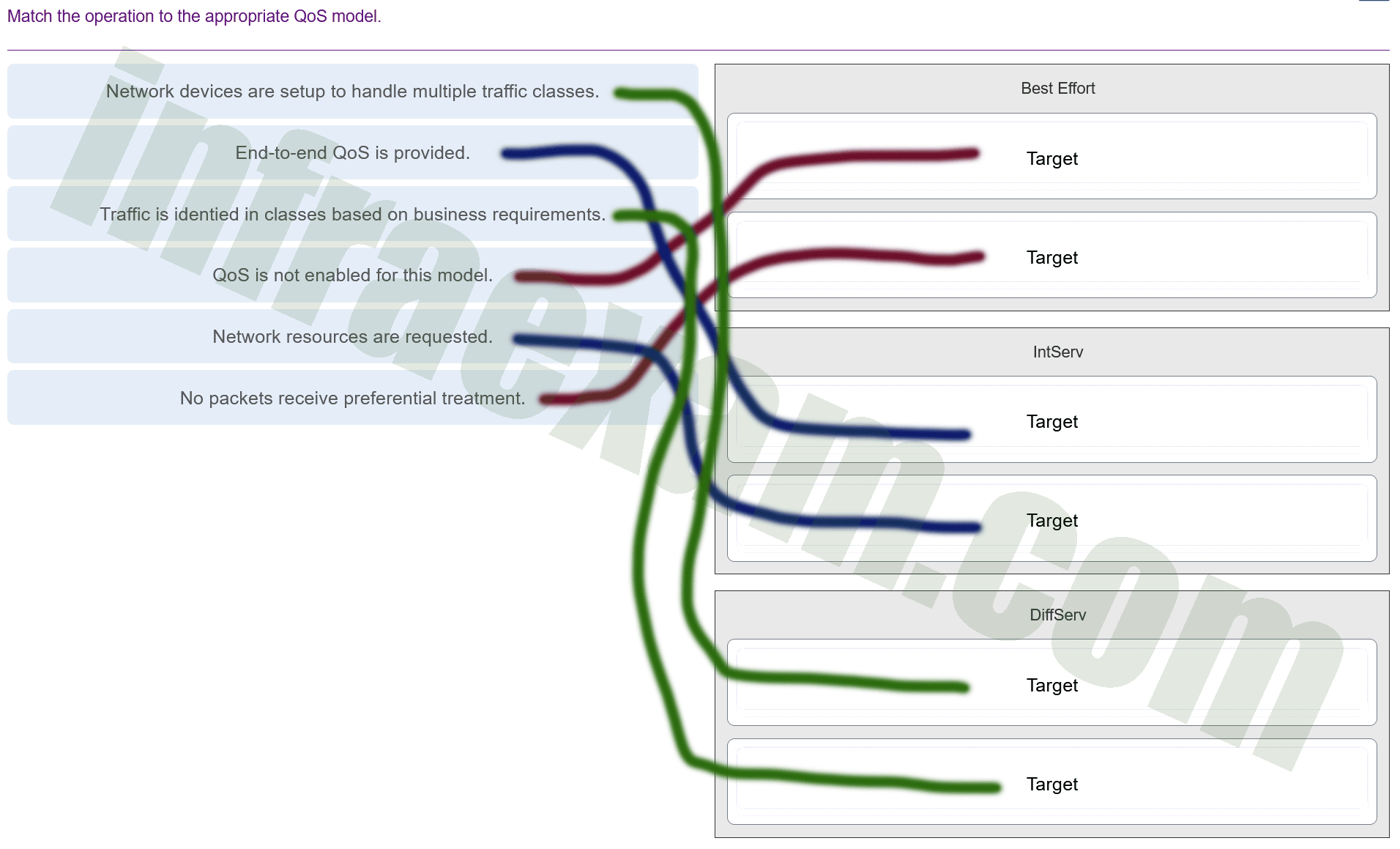
Match the operation to the appropriate QoS model.
CCNPv8 ENCOR (Version 8.0) – Chapters 13 – 14 Multicast and QoS Exam Answers 005 Explanation & Hint: Based on the image you’ve provided, which contains descriptions of Quality of Service (QoS) models, the correct matches for each operation to the appropriate QoS model are as follows:
- Network devices are set up to handle multiple traffic classes: This is characteristic of the DiffServ (Differentiated Services) model, where traffic is classified and managed in multiple classes of service.
- End-to-end QoS is provided: This aligns with the IntServ (Integrated Services) model, which is designed to provide end-to-end QoS on networks.
- Traffic is identified in classes based on business requirements: This also pertains to the DiffServ model, where traffic is classified into different classes based on business policies and requirements.
- QoS is not enabled for this model: This would be indicative of the Best Effort model, where no QoS is implemented, and packets are processed as they come, without any guarantee of delivery or prioritization.
- Network resources are requested: This is a function of the IntServ model, which uses RSVP (Resource Reservation Protocol) to reserve resources across a network.
- No packets receive preferential treatment: This is another hallmark of the Best Effort service model, where all packets are treated equally, and no priority is given to any traffic type.
Please use the provided descriptions to match with the QoS models in the exercise you are working on.
-
What would be the Tc value in ms for a 1 Gbps interface configured with a policer defined with a CIR of 150 Mbps and a Bc of 15 Mb?
- 100 ms
- 1000 ms
- 10 ms
- 10,000 ms
Answers Explanation & Hints: The Tc value is calculated by using the formula Bc (bits)/ CIR (bps) X 1000
Tc = (15 Mb/150 Mbps) X 1000
Tc = (15,000,000 bits/150,000,000 pbs) X 1000
Tc = 100 ms
| CCNP ENCOR v8 & 8.01 | |
| Final Exam Answers | |
| This Chapters 13 - 14 | |
| Chapters 13 - 14 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Chapters 13 - 14 Quizzes Answers | Online Test |
| Next Chapters 15 - 16 | |
| Chapters 15 - 16 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Chapters 15 - 16 Quizzes Answers | Online Test |