200-201 : Understanding Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals (CBROPS) : Part 02
-
Which of the following provides non-repudiation?
- hashing
- redundancy
- digital signature
- encryption
Explanation:
A digital signature provides non-repudiation, which means the signing cannot be denied at a later time. This is done by hashing the document and then encrypting the hash value with the private key of the sender. The public key of the signer is used to verify a digital signature.A digital signature provides integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation in electronic mail. Integrity involves providing assurance that a message was not modified during transmission. Authentication is the process of verifying that the sender is who says he is.
Confidentiality means preventing unauthorized access to data. One method of doing that is with encryption. Digital signatures do not provide encryption and cannot ensure availability.
Redundancy, or the use of multiple components, increases availability, the A in CIA. Redundancy ensures that there are multiple ways to control the static environment Redundancy occurs when you have systems in place ready to come when a system fails.
Hashing algorithms generate hash values which can be compared to identify if data has changed. hashing ensures integrity, not non-repudiation. Protecting data from unauthorized change provides integrity. Hashing algorithms include MD2, MD4, MD5, HAVAL, and all of the Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) variants.
Objective: Cryptography
Sub-Objective: Describe the processes of digital signature creation and verification -
Which of the following is NOT a feature of a next generation firewall?
- application visibility and control
- stateless firewall
- URL filtering
- advanced malware protection
Explanation:
Next generation firewalls (NGFW) are stateful firewalls, not stateless firewalls.Some of the features of the Cisco NGFW are:
– Stateful firewall
– Application visibility and control
– NGIPS
– Advanced malware protection
– URL filtering
– VPNWith a stateful firewall, a packet is allowed if it is a response to a previous connection. If the table holds no information about the packet, the packet is compared ti the access control list (ACL). Depending on the ACL, the packet will be forwarded to the appropriate host or dropped completely.
Objective: Security Monitoring
Sub-Objective: Describe these types of data used in security monitoring: Full packet capture, Session data, Transaction data, Statistical data, Extracted content, Alert data -
A host is sending a ping packet to another host in the same subnet.
For which IP address does the sending host perform an ARP broadcast to resolve?
- its own IP address
- the IP address of the router
- the IP address of the DNS server
- the IP address of the destination host
Explanation:
All communication within a subnet is based on MAC addresses. When the destination is in the same subnet, the source device performs an ARP broadcast to learn the MAC address of the destination host.The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is used in TCP/IP to resolve media access control (MAC) addresses to IP addresses. Mac addresses are configured on each NIC on an Ethernet network so that the nodes can be identified on the network. ARP enables the MAC addressing that Ethernet requires to interoperate with the IP addressing that TCP/IP requires. You can use the arp utility to view and manage the ARP cache on a computer. To use the arp utility, you can issue the arp command with various switches at a command prompt. The source device will perform an ARP broadcast to learn the mac address of the router in cases were the destination is in another subnet. Then the router will take over from there.
The source device will never perform an ARP broadcast to learn its own MAC address.
The only time a source device will perform an ARP broadcast to learn the MAC address of the DNS server is when communication is being done by name and not IP address.
Objective: Network Concepts
Sub-Objective: Describe IP subnets and communication within an IP subnet and between IP subnets -
At which layer does switching occur in the Cisco modified TCP/IP model?
- Internet
- Transport
- Data Link
- Physical
Explanation:
Switches make switching decisions based on MAC addresses. Because MAC address reside in the Data Link layer of the TCP/IP or DoD model, this is the layer where switching occurs. A switch is a high-speed networking device that receives incoming data packets from one of its ports and directs them to a destination port for local area network access. A switch will redirect traffic bound outside the local area to a router for forward through an appropriate WAN interface.The modified TCP/IP model is a model by Cisco that departs from the DoD model by breaking the bottom layer, the Link layer, into two layers called the Data Link and the Physical layer.
Other versions of the model refer to the Link as the Network Interface layer.
The layers in ascending order are:
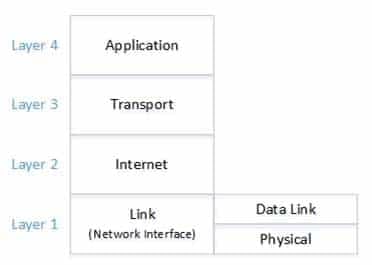
200-201 Part 02 Q04 002 Switches do not operate on the Internet layer. Routers are an example of devices that operate on this layer, which is where IP addresses are located. A router is a device that examines the contents of data packets transmitted within or across networks. Routers determine if a source and destination are on the same network, or whether data mist be transferred from one network to another, either between locally available network segments, or across a wide-area link to access other, more distant networks.
Switches do not operate on the Transport layer. This is the layer where port numbers are added to the packet.
Switches do not operate on the Physical layer. This is the layer where the information is transmitted as ones and zeros using the underlying technology of the medium.
The Application layer of the TCP/IP model corresponds to the Application, Presentation, and Session layers of the OSI model.
The Transport layer of the TCP/IP model correspond to the Transport layer of the OSI model.
The Internet layer of the TCP/IP model correspond to the Network layer of the OSI model. Internet protocol (IP), address resolution protocol (ARP), and Internet control message protocol (ICMP) operate at the Internet layer.
The Link layer of the TCP/IP model corresponds to the Data Link and Physical layers of the OSI model.
Objective: Network Concepts
Sub-Objective: Describe the function of the network models -
Which of the following is used to prevent malicious software systems?
- HIDS
- HIPS
- network AV
- host AV
Explanation:
To protect multiple devices from malware, network antivirus (AV) should be used. These tools can protect an entire network of devices.A host antivirus (AV) can only protect the device on which it is installed.
A host intrusion prevention system (HIPS) can prevent multiple attack types, but it can only protect the device on which it is installed.
A host intrusion detection system (HIPS) can detect multiple attack types, but it can only detect attacks against the device on which it is installed.
Intrusion prevention systems (IPS) and intrusion detection systems (IDS) work together to complement each other. IPS systems can block activities on certain Web sites. Users may be allowed to access the sites but may be prevented from accessing certain features within the site. In other cases, the entire site may be blocked, depending on the security requirements for the organization.
Objective: Security Concepts
Sub-Objective: Compare and contrast these terms: Network and host antivirus, Agentless and agent-based protections, SIEM and log collection -
What terms represents the leveraging of a security weakness present in a system?
- breach
- threat
- vulnerability
- exploit
Explanation:
When a security weakness or vulnerability exists in a system and threat actor takes advantage of it, the attack is considered an exploit.A vulnerability is a susceptibility to a threat that exists in a system. An example of a vulnerability is keeping ports open for nonessential services.
A threat is an external danger to which a system may or may not be vulnerable. It is a potential danger that could take advantage of a system if it is vulnerable. A hacker is a threat actor. An attacker picking the lock of the back entrance to a facility is an example of a threat, not a vulnerability.
A breach is when an exploit is successful in providing unauthorized access to data.
Objective: Security Concepts
Sub-Objective: Compare and contrast these concepts: Risk, Threat, Vulnerability, Exploit -
Which of the following uses port 443?
- DNS
- SSH
- SSL
- Telnet
- HTTP
Explanation: Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a security protocol that uses both encryption and authentication to protect data sent in network communications. SSL and HTTPS use port 443.
Port number 22 is reserved for Secure Shell (SSH) remote login.
Telnet uses port 23. Telnet is a terminal emulation protocol. You can use Telnet to establish a remote session with a server and to issue commands on a server. Telnet client software provides you with a text-based interface and a command line from which you can issue commands on a server that supports the Telnet protocol. Telnet works at the Application layer of the OSI model.
HTTP uses port 80. HTTP is used to traverse web pages.
DNS uses port 53. Domain Name System (DNS) is the protocol that will manage the FQDN to IP address mappings.
There are a total of 65,535 ports in the TCP/IP protocol that are vulnerable to attacks. The following are the most commonly used ports and protocols:
– FTP – ports 20 and 21
– SSH, SCP, and SFTP – port 22
– Telnet – port 23
– SMTP – port 25
– TACACS – port 49
– DNS server – port 53
– DHCP – port 67 and 68
– TFTP – port 69
– HTTP – port 80
– Kerberos – port 88
– POP3 – port 110
– NetBIOS – ports 137-139
– IMAP4 – port 143
– SNMP – port 161
– LDAP – port 389
– SSL and HTTPS – port 443
– SMB – port 445
– LDAP with SSL – port 636
– FTPs – ports 989, 990
– Microsoft SQL Server – port 1433
– Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) – port 1723
– RDP protocol and terminal Services – port 3389Objective: Cryptography
Sub-Objective: Describe the security impact of these commonly used encryption algorithms and secure communications protocols: DES, 3DES, AES, AES256-CTR, RSA, DSA, SSH, SSL/TLS -
What is the process of scoring risks by their likelihood and their impact?
- quantitative risk analysis
- qualitative risk analysis
- business impact analysis
- disaster recovery
Explanation:
When scoring is used to rate risks by likelihood and impact, it is called qualitative risk analysis. Qualitative risk analysis does not assign monetary values. It is simply a subjective report that is compiled by the risk analysis team that describes the threats, countermeasures, and likelihood an event will occur.
Quantitative risk analysis attempts to attach dollar figures to potential risk outcomes. Quantitative risk analysis attempts to predict the likelihood a threat will occur and assigns a monetary value in the event a loss occurs. The likelihood of risk occurrence is usually based ob subject matter expert opinion and rankings from statistical data.
A business impact analysis (BIA) focuses on critical business systems and the impact if they are lost to an outage. A BIA is created to identify the company’s vital functions and prioritize them based on need. It identifies vulnerabilities and threats and calculates the associated risks.
A disaster recovery plan is a short term plan that is implemented when a large disaster event occurs. The plan is created to ensure that your company can resume operations in a timely manner. It mainly focuses on alternative procedures for processing transactions in the short term. It is carried out when the emergency occurs and immediately following the emergency.
Objective: Security Concepts
Sub-Objective: Describe these security terms: Principle of least privilege, Risk scoring/risk weighting, Risk reduction, Risk assessment -
Which of the following is not a hashing algorithm?
- DES
- MD5
- SHA-1
- SHA-3
Explanation:
Digital encryption standard (DES) is an encryption algorithm, not a hashing algorithm. DES is a private key encryption standard that is used in IPSec to ensure that data packets are confidentially transmitted.MD5 is a one-way hashing algorithm. One-way hashing inserts a string of variable length into a hashing algorithm and produces a hash value of fixed length. This hash is appended to the end of the message being sent. The receiver recomputes the hash by using the same computational logic. If the recomputed hash value is the same as the generated hash value, the message was not altered during the course of transmission.
Secure Hashing Algorithm 1 (SHA 1) is the first and least secure version of SHA.
Secure Hashing Algorithm 3 (SHA 3) is the first and least secure version of SHA.Objective: Cryptography
Sub-Objective: Describe the security impact of these commonly used hash algorithms: MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, SHA-512 -
Which of the following is the most widely used public key cipher?
- 3DES
- EI Gamal
- RSA
- AES
Explanation:
Rivest, Shamir, Adleman (RSA) is the most widely used public key or asymmetric cipher. RSA supports encryption and decryption and secures data with an algorithm that is based on the difficulty of factoring large numbers.A public key encryption algorithm is sometimes referred to as an asymmetric encryption algorithm. With asymmetric encryption, the public key is shared and used to encrypt information, and the private key is secret and used to decrypt data that was encrypted with the matching public key. Using RSA, messages travelling between two points are encrypted and authenticated. RSA tokens are used to provide a rolling password for one-time use.
Triple DES or 3DES is a symmetric algorithm, which means the key used to encrypt is identical to the key used to decrypt. Triple DES is a later version of Data Encryption Standard (DES) that performs three rounds of encryption. The encryption and decryption process performed by 3ES takes longer due to the higher processing power required.
While EI Gamal is a public key or asymmetric cipher, it is not the most widely used.
AES is a symmetric algorithm that is currently the best encryption algorithm available commercially.
Advanced Encryption Algorithm that is currently the best encryption algorithm available commercially. The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) uses 128-bit, 192-bit, and 256-bit encryption keys.Objective: Cryptography
Sub-objective: Describe the security impact of these commonly used encryption algorithms and secure communications protocols: DES, 33DES, AES, AES256-CTR, RSA, DSA, SSH, SSL/TLS. -
Which of the following provides the ability to allow scripting languages to manage Windows computers both locally and remotely?
- STP
- RMI
- EMI
- WMI
Explanation:
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) consists of a set of extension that allow access to settings and information through the command line, making the scripting of operations possible. The command-line interface to WMI called Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line (WMI).Electromagnetic interference (EMI) is the inference with data traversing cables by strong electromagnetic energy generated by sources such as machinery. The transformers in fluorescent lighting systems are a common cause of network communications problems. If a network cable that is highly susceptible to EMI, such as unshielded-twisted pair (UTP) cable, is placed near lighting transformers, then the magnetic field produced by the transformers can cause network communications problems. You can replace UTP cable that runs near sources of EMI with shielded cable, such as shielded twisted-pair 9STP) cable or coaxial cable. Fiber-optic cable is immune to EMI.
Radio frequency interference (RFI) occurs near sources of high power radio transmissions. TV stations, radio stations, cellular telephones, and CB radios can be sources of RFI. RFI can cause network communications problems, and intermittent computer problems such as spontaneously rebooting computers and data errors.
Spanning tree protocol (STP) is a loop avoidance protocol used with switches. Switching loops occur when multiple Layer 2 paths to a network cause to flood broadcasts endlessly. This endless broadcast flood is called a “broadcast storm”, and it causes severe network congestion. STP can be used to prevent these problems on a switched or bridged network.
Objective: Host-Based Analysis
Sub-Objective: Define terms as they pertain to Microsoft Windows: Processes, Threads, Memory allocation, Windows Registry, WMI, Handles, Services -
What is the function of ARP?
- resolves IP addresses to MAC addresses
- resolves host names to IP addresses
- resolves MAC addresses to IP addresses
- resolves port numbers to IP addresses
Explanation:
Address resolution Protocol (ARP) resolves IP addresses to MAC addresses. It uses a broadcast mechanism to learn the MAC address of a host known only by its address. The media access control (MAC) address uniquely identifies a node on a network segment. ARP tables show the relationship of IP addresses to MAC addresses and are located on most devices.There is no mechanism for translating port numbers to IP addresses. The IP address and port number combination of a source or destination is called a socket.
Domain Name System (DNS) is the service that translates host names to IP addresses. DNS uses UDP when resolution queries are sent to a server by a client, but its uses TCP for zone transfers between DNS servers. According to RFC 1035, UDP is the recommended method for queries. A DNS server provides a centralized database of domain name-to –IP address resolutions on a server that other computers on a network can use for name resolution.
There is currently no service that resolves MAC addresses to IP addresses.
Objective: Network Concepts
Sub-Objective: Describe the operation of these network services: ARP, DNS, DHCP -
Which hashing algorithm is the strongest?
- SHA-1
- MD5
- SHA-256
- SHA-512
Explanation: SHA-512 is a more secure version of SHA-256 and differs only in the number of rounds of computation.
MD5 is the least secure of the listed hashing algorithms. MD5 is a one-way hashing algorithm. One-way hashing inserts a string of variable length into a hashing algorithm and produces a hash value of fixed length. This hash is appended to the end of the message being sent. The receiver recomputes the hash by using the same computational logic. If the recomputed hash value is the same as the generated hash value, the message was not altered during the course of transmission.SHA-1 is the first version of SHA and is the least secure version of SHA hashing algorithm. The MD5 algorithm produces 128-bit checksums, and SHA produces 160-bit checksums.
The SHA-256 hashing algorithm is part of the SHA-2 family. SHA-256, also referred to as SHA-2, is a newer version of SHA and uses 256-bit checksum.
Objective: Cryptography
Sub-Objective: Describe the security impact of these commonly used hash algorithms: MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, SHA-512 -
Which of the following is NOT an email protocol?
- SMTP
- IMAP
- NTP
- POP
Explanation:
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is used to synchronize the clock of computers on the network. Synchronization of time is important in areas such as event logs, billing services, e-commerce, banking and HIPAA Security Rules.Simple Mail Transport Protocol (SMTP) is an application protocol, so it operates at the top layer of the OSI model. SMTP is the default protocol for sending e-mail in Microsoft operating systems. SMTP provides client and server functions and works with the Internet and UNIX. it is used to send and receive messages.
Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP3) and Internet Mail Access Protocol 4 (IMAP4) are client email programs. They are used to retrieve email from the server. POP3 and IMAP are the most popular protocols for receiving e-mail protocols.
The following is a list of the common ports in use:
– TCP Port 20 – FTP (File transfer Protocol) data
– TCP Port 21 – FTP
– TCP Port 22 – Secure Shell (ssh), Secure Copy (scp), or Secure FTP (SFTP)
– TCP Port 23 – Telnet
– TCP Port 25 – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
– TCP/UDP Port 53 – Domain Name System (DNS)
– UDP Port 67 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server
– UDP Port 68 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Client
– TCP Port 80 HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
– TCP Port 110 – Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP3)
– TCP Port 123 – Network Time Protocol (NTP)
– TCP Port 143 – Internet Mail Access ProtocolObjective: Security Monitoring
Sub-Objective: Describe the function of these protocols in the context of security monitoring: DNS, NTP, SMTP/POP/IMAP, HTTP/HTTPS -
Which of the following is Layer 3 attack?
- ARP attacks
- IP spoofing
- VLAN hopping
- MAC spoofing
Explanation:
As IP addresses reside on Layer 3 of the OSI model, IP spoofing is considered a Layer 3 attack.Other types of spoofing attacks apart from IP spoofing are e-mail spoofing and Web spoofing. Do not confuse e-mail spoofing with pharming attacks. While both do involve being redirected to a fake Web site to obtain confidential information, pharming often involves poisoning the DNS cache to ensure the user is redirected to the fake site even if they correctly enter the real site’s URL. E-mail spoofing just involves clicking links in a hoax e-mail. Pharming is considered a more browser-related attack because it is designed to affect browser usage over the long term.
As ARP resolves IP addresses to MAC addresses, and MAC addresses reside on layer2 of the OSI model, ARP attacks are considered a Layer 2 attack.
As MAC addresses reside on layer 2 of the OSI model, MAC spoofing attacks are also considered Layer 2 attacks. MAC addresses are 48-bit addresses in hexadecimal that are permanently attached to the network interface by the manufacturer.
VLANs are Layer 2 concepts, therefore VLAN hopping attacks are considered Layer 2 attacks. Switches are typically deployed to create virtual local area networks (VLNs). The switch isolates the VLAN from the rest of the network to provide better security for the VLAN.
Objective: Attack Methods
Sub-Objective: Describe these attacks: Social engineering, Phishing, Evasion methods -
Which of the following describes a resource exhaustion attack?
- receiving an abnormally low volume of scanning from numerous source
- performing actions slower than normal
- waiting for an opportune moment
- receiving an abnormally high volume of scanning from numerous source
Explanation:
In a resource exhaustion attack, the goal is to the IPS or IDS such that it cannot keep up. Therefore, this attack uses an abnormally high volume of scanning from numerous sources. Resource exhaustion occurs when a system runs out of limited resources, such as bandwidth, RAM, or hard drive space. Without the required storage space (as an example), the system can no longer perform as expected, and crashes.A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) is one in which the attacker recruits hundreds or thousands of devices to assist in the attack. The helpers are called zombies and as a group they are called a botnet. A DDoS attack usually involves the hijacking of several computers and routers to use as agents of the attack. Multiple servers and routers involved in the attack often overwhelm the bandwidth of the attack victim. For example, if a server has intermittent connection issues, the logs show repeated connection attempts from the same IP addresses, and the attempts are overloading the server to the point it cannot respond to traffic, then the server is experiencing a DDoS attack.
Timing attacks are those in which the operations carried out are done much slower than normal to keep the IPS or IDS from assembling the operation into a recognizable attack.
Objective: Attack Methods
Sub-Objective: Describe these evasion methods: Encryption and tunneling, Resource exhaustion, Traffic fragmentation, Protocol-level misinterpretation, Traffic substitution and insertion, Pivot. -
Which attack requires a botnet?
- DDoS
- password theft
- DoS
- man in the middle
Explanation:
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is one in which the attacker recruits hundreds or thousands of devices to assist in the attack. The helpers are called zombies, and as a group they are called a botnet.
A DDoS attack usually involves the hijacking of several computers and routers and routers to use as agents of the attack. Multiple servers and routers overwhelm the bandwidth of the attack victim. For example, if a server has intermittent connection issues, the logs will show repeated connection attempts from the same IP addresses, and the attempts are overloading the server to the point it cannot respond to traffic, then the server is experiencing a DDoS attack.
A man in the middle attack makes use a single attack machine. The intent is to position the attacker between two communicating devices such that they are sending to the attacker rather than sending to one another. Using a packet analyzer to gather packets from a network connection between two computers is a method that can be used to initiate a man in the middle (MITM) attack.
A DoS attack is one that is sourced from a single machine. A denial of service (DoS) attack occurs when attackers overrun a server with requests so that ligitimate users cannot access the server.
Password theft uses a single attack machine as well.
Objective: Attack methods
Sub-Objective: Describe these network attacks: Denial of service, Distributed denial of service, Man-in-the-middle. -
When the facility has a fence, guards, a locked front door and locked interior doors, it called what?
- AUP
- separation of duties
- defense in depth
- piggybacking
Explanation:
A defense in depth strategy prescribes that multiple impediments be presented to a malicious individual. In this case, multiple physical hurdles are presented, but they can also be technical hurdles such as multiple firewalls. Defense in-depth is a multi-layered approach to security that establishes a robust defensive strategy against attackers. This strategy prevents a single attack from being sufficient to breach an environment, forcing attackers to use complex, multi-pronged, daisy-chain attacks that are more likely to fail or be detected during the attempt.Separation of duties prescribes that any operation susceptible to fraud should be broken into two tasks, with each task given to a different person.
Piggybacking is a social engineering attack in which an unauthorized individual enters a locked door after an authorized individual unlocks the door.
An acceptable use policy defines the manner in which employees are allowed to use a company’s network equipment and resources, such as bandwidth, Internet access, and e-mail services.
Objective: Security Concepts
Sub-Objective: Describe the principles of the defense in depth strategy -
You are reading the output of a Syslog message.
What type of information is contained in the facility section?
- message type (UDP or TCP)
- process that submitted the message
- relationship to other messages
- security level
Explanation:
The facility section identifies the process or application that submitted the message.
The relationship to other messages is contained in the priority section.
The security level of the message is contained in the severity section.
The message type is contained in the transport section.Syslog messages and SNMP traps trigger notification messages that can be sent via email and SMS. A syslog server receives and stores log messages sent from syslog clients. A syslog client sends logging information to a syslog server. A syslog server ensures that a network administrator can review device error information from a central location.
Objective: Host-Based Analysis
Sub-Objective: Interpret these operating system log data to identify an event: Windows security event logs, Unix-based syslog, Apache access logs, IIS access logs -
Which of the following is NOT an event category in the Windows Security Log?
- Account management
- Logoff events
- Object access
- Directory service access
Explanation:
While there is a category called Logon events (which will also contain logoff vents), there is no Logoff events category. This category records all local logons and logoffs both successful and unsuccessful.Object access records all attempts to access resources such as files and folders. Account management records all attempts to make changed to user accounts. Directory service access records all attempts to make changes to Active Directory.
Objective: Host-Based Analysis
Sub-Objective: Interpret these operating system log data to identify an event: Windows security event logs, Unix-based syslog, Apache access logs, IIS access logs