200-301 : Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) : Part 02
-
RouterA and RouterB, which connect two locations, are unable to communicate. You run the show running-configuration command on both router interfaces, RouterA and RouterB. The following is a partial output:
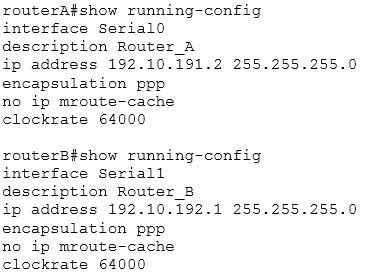
200-301 Part 02 Q01 012 Based on the information given in the output, what are two likely causes of the problem? (Choose two.)
- The IP address defined is incorrect.
- Both routers cannot have a clock rate defined.
- Both routers cannot have an identical clock rate.
- The Layer 2 framing is misconfigured.
- At least one of the routers must have the ip mroute-cache command enabled.
Explanation:
Two possible causes of the problem are that the IP addresses are incorrect as defined, or that both routers have a defined clock rate. The IP addresses on the routers are in different subnets. The IP addresses need to be changed to fall in the same subnet.Both routers cannot have a clock rate configured. Only routers with a DCE cable connected should have a clock rate, which provides synchronization to the router connected to the DTE cable. In a point-to-point serial connection, the DCE cable connects to the DTE cable, providing a communication path between the two routers. If both computers have a clock rate configured, the routers will not communicate.A matching clock rate is not the problem. The clock rates between two routers should match. The router connected to the DCE cable will provide the clock rate to the router connected to the DTE cable, resulting in matching clock rates.
The Layer 2 encapsulation refers to the Data Link protocol used on the link. In this case, the protocol is Point to Point Protocol (PPP), which is configured correctly on both ends as indicated by the matching encapsulation ppp statements in the output. The connection would be prevented from working if one of the routers were missing this setting (which would be indicated by the absence of the encapsulation ppp statement in its output), or if a different Layer 2 encapsulation type were configured, such as High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC).
The ip mroute-cache command is used to fast-switch multicast packets and would not cause the problem in this scenario.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot IPv4 addressing and subnetting -
Which of the following should be a characteristic of the core layer in the Cisco three-layer hierarchical model?
- redundant components
- emphasis on high speed
- PoE
- QoS
Explanation:
The core layer of the Cisco three-layer hierarchical network design model places an emphasis on high speed. Items such as access control lists (ACLs) and Quality of Service (QoS) should NOT be implemented on this level, as those types of service will slow the high-speed switching process desired at this level.The three layers of the hierarchical design model are the access layer, the distribution layer, and the core (backbone) layer. The core layer connects to every building block in the modular network, so it must emphasize speed and resilience.Quality of service and ACLs are implemented on the distribution layer. Layer 3 support is required at this level.
Redundant hardware components and Power over Ethernet (PoE) are characteristics of the access layer. This is the layer where user devices are connected to the network. Layer 2 Port security is also implemented at this layer.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast collapsed core and three-tier architectures -
Which of the following commands will set the line speed of a serial connection that connects to a Channel Service Unit /Digital Service Unit (CSU/DSU) at 56 Kbps?
- service-module 56000 clock rate speed
- service-module 56k clock rate speed
- bandwidth 56k
- bandwidth 56000
Explanation:
The command service-module 56k clock rate speed will configure the network line speed for a 4-wire, 56/64-kbps CSU/DSU module.The command service-module 56000 clock rate speed is incorrect because the speed must be stated in the form 56k (for Kbps), rather than 56000.The bandwidth command is used to limit the amount of bandwidth used by an application when utilizing Quality of Service (QOS). It does not set the line speed of a serial connection that connects to a Channel Service Unit /Digital Service Unit CSU/DSU. Therefore, both the bandwidth 56k and the bandwidth 56000 commands are incorrect.
Objective:
WAN Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Describe WAN access connectivity options -
You are discovering that there are differences between the configuration of EIGRP for IPv6 and EIGRP for IPv4. Which statement is true with regard to the difference?
- A router ID is required for both versions
- A router ID must be configured under the routing process for EIGRP for IPv4
- AS numbers are not required in EIGRP for IPv6
- AS numbers are not required in EIGRP for IPv4
Explanation:
Both versions of EIGRP require a router ID. The difference is that with EIGRP for IPv6, you must configure a router ID under the routing process if there are no IPv4 addresses on the router. In EIGRP for IPv4, the router can select one of the configured IPv4 addresses as the router ID.A router ID can be configured under the routing process for EIGRP for IPv4, but it is not required. In EIGRP for IPv4, the router can select one of the configured Pv4 addresses as the router ID.AS numbers are required in both versions of EIGRP.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot EIGRP for IPv6 (excluding authentication, filtering, manual summarization, redistribution, stub) -
Which of the following techniques is NOT used by distance vector protocols to stop routing loops in a network?
- Split horizon
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- Holddowns
- Route poisoning
Explanation:
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is not used by distance vector protocols to stop routing loops in a network. STP is used to prevent switching loops in a switched network.Routing loops can occur due to slow convergence and inconsistent routing tables, and can cause excessive use of bandwidth or complete network failure. An example of a routing table problem would be incorrectly configured static default routes. Suppose that Router A is connected to Router B, and the addresses of the interfaces on each end of the link connecting the two routers are as follows:Router A 192.168.5.1/24
Router B 192.168.5.2/24A partial output of the routing tables of the two routers is shown below. Router B hosts the connection to the Internet.
routerA# show ip route Gateway of last resort is 192.168.5.2 to network 0.0.0.0 <Output omitted> routerB# show ip route Gateway of last resort is 192.168.5.1 to network 0.0.0.0 <<output omitted>>
From the limited information shown above, you can see that Router A is pointing to Router B for the default route, and Router B is pointing to Router A for the default route. This will cause a routing loop for any traffic that is not in their routing tables. For example, if a ping were initiated to the address 103.5.6.8 and that address was not in the routing tables of Routers A and B, the most likely message received back would NOT be “destination unreachable” but “TTL expired in transit.” This would be caused by the packet looping between the two routers until the TTL expired.
The following techniques are used by distance vector protocols to stop routing loops in a network:
– Split horizon stops routing loops by preventing route update information from being sent back over the same interface on which it arrived.
– Holddown timers prevent regular update messages from reinstating a route that is unstable. The holddown timer places the route in a suspended, or “possibly down” state in the routing table and regular update messages regarding this route will be ignored until the timer expires.
– Route poisoning “poisons” a failed route by increasing its cost to infinity (16 hops, if using RIP). Route poisoning is combined with triggered updates to ensure fast convergence in the event of a network change.Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast distance vector and link-state routing protocols -
You are creating a configuration to use on a switch. The configuration must enable you to remotely manage the switch.
Which of the following command sets is correct? (Assume the commands are executed at the correct prompt.)
-
interface vlan 1 ip address 192.168.20.244 255.255.255.240 no shutdown exit ip default-gateway 192.168.20.241 line vty 0 15 password cisco login exit -
interface fastethernet 0/1 ip address 192.168.20.244 255.255.255.240 no shutdown exit ip default-gateway 192.168.20.241 line vty 0 15 password cisco login exit
-
interface vlan 1 ip address 192.168.20.244 255.255.255.240 no shutdown exit ip route 192.168.20.241 line vty 0 15 login exit
-
interface vlan 1 ip address 192.168.20.244 255.255.255.240 no shutdown exit ip default-gateway 192.168.20.241 line con 0 15 password cisco login exit
-
interface vlan 1 ip address 192.168.20.244 255.255.255.240 no shutdown exit ip default-gateway 192.168.20.27 line vty 0 15 password cisco login exit
-
interface vlan 1 ip address 192.168.20.244 255.255.255.240 shutdown exit ip default-gateway 192.168.20.241 line vty 0 15 password cisco login exit
Explanation:
The following command set is correct:interface vlan 1 ip address 192.168.20.244 255.255.255.240 no shutdown exit ip default-gateway 192.168.20.241 line vty 0 15 password cisco login exit
It sets an IP address for VLAN 1, which is the management VLAN. Next, it sets a default gateway that is in the same network with the IP address. It correctly enables the interface, sets a required password on the VTY lines, and sets the switch to prompt for the password.
Switches do not need IP addresses unless you want to remotely manage the devices. When an IP address is assigned to a switch for this purpose, it is not applied to a physical interface. It is applied to the VLAN 1 interface, which is the management VLAN by default.
The following command set is incorrect because it applies the IP address to the fastethernet 0/1 interface, rather than the management VLAN. When you set an IP address for the switch, you do so on the management VLAN, not one of the physical interfaces.
interface fastethernet 0/1 ip address 192.168.20.244 255.255.255.240 no shutdown exit ip default-gateway 192.168.20.241 line vty 0 15 password cisco login exit
The following command set is incorrect because it does not set a password on the VTY lines, which is required to connect with Telnet unless you include the no login command.
interface vlan 1 ip address 192.168.20.244 255.255.255.240 no shutdown exit ip default-gateway 192.168.20.241 line con 0 15 login exit
The following command set is incorrect because it sets the password in the console line rather than the VTY lines.
interface vlan 1 ip address 192.168.20.244 255.255.255.240 no shutdown exit ip default-gateway 192.168.20.241 line con 0 15 password cisco login exit
The following command set is incorrect because the address for VLAN1 and the gateway are not in the same subnet. With a 28-bit mask the interval is 16, which means the network that the gateway is in is the 192.168.20.16/28 network and VLAN 1 is in the 192.1683.20.240/28 network.
interface vlan 1 ip address 192.168.20.244 255.255.255.240 no shutdown exit ip default-gateway 192.168.20.27 line vty 0 15 password cisco login exit
The following command set is incorrect because the VLAN 1 interface has been disabled with the shutdown command.
interface vlan 1 ip address 192.168.20.244 255.255.255.240 shutdown exit ip default-gateway 192.168.20.241 line vty 0 15 password cisco login exit
Objective:
Infrastructure Management
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify device management -
-
What command should you use to quickly view the HSRP state of the switch for all HSRP groups of which the switch is a member?
-
switch# show standby brief -
switch# show ip interface brief
-
switch# show hsrp
-
switch# show standby
Explanation:
The command show standby brief should be used to quickly view the HSRP state of a switch for all HSRP groups of which it is a member. The summary information it provides includes the group number, priority, state, active device address, standby address, and group address. The command show standby can be used to display detailed information about HSRP groups of which a switch is a member. This command would not provide a quick view. This command displays information about HSRP on all configured interfaces and for all HSRP groups. It also displays hello timer information and the expiration timer for the standby switch.The command show ip interface brief is useful in that lists the interfaces and displays the basic IP configuration of each. This output would include the IP address of the interface and the state of the interface, but not HSRP information.
The command show hsrp is not a valid command due to incorrect syntax.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic HSRP -
-
When packets are transmitted from one host to another across a routed segment, which two addresses are changed? (Choose two.)
- source IP address
- source MAC address
- destination IP address
- destination MAC address
Explanation:
When packets move from one LAN segment to another LAN segment across a router, the source and destination Media Access Control (MAC) addresses in the packet change. Packets destined for a remote network must be forwarded by a router that is typically the sending host’s default gateway. The IP address of the remote host is inserted into the packet, while the MAC address of the default gateway is inserted as the Layer 2 address. This ensures that the packet is received by the default gateway. The router then examines the destination IP address, performs a route lookup, and forwards the packet toward the destination, inserting its MAC address as the source MAC address. If the next hop is another router, then the destination MAC address is replaced with the next router’s MAC address. This process is repeated by each router along the path (inserting its own MAC address as the source MAC address and inserting the MAC address of the next router interface as the destination MAC address) until the packet is received by the remote host’s default gateway. The destination gateway then replaces the destination MAC address with the host’s MAC address and forwards the packet.In the diagram below, when the host located at the IP address 10.0.1.3 sends data to the host located at IP address 10.1.1.3, the Layer 2 and Layer 3 destination addresses will be bb.bb.bb.bb.bb.bb and 10.1.1.3, respectively. Note that the Layer 2 destination address matches the host’s default gateway and not the address of the switch or the destination host.
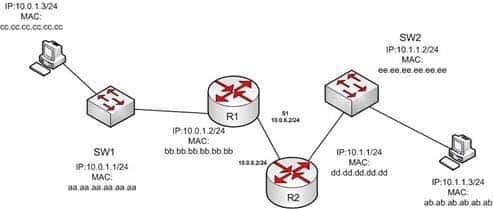
200-301 Part 02 Q08 013 It is incorrect to state that the source IP address or the destination IP address change when packets transfer from one host to another across a routed segment. The Internet Protocol (IP) addresses within the packets do not change because this information is needed to route the packet, including any data returned to the sender.
Data return to the sending host is critically dependent on the destination having a default gateway configured and its router having a route back to the sender. If either is missing or configured incorrectly, a return is not possible. For example, when managing a switch remotely with Telnet, the switch cannot be located on the other side of a router from the host being used to connect if the switch does not have a gateway configured. In this case, there will no possibility of a connection being made because the switch will not have a return path to the router.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Describe the routing concepts -
You are connecting a new computer to Switch55. The new computer should be placed in the Accounting VLAN. You execute the show vlan command and get the following output:

200-301 Part 02 Q09 014 Examine the additional network diagram.
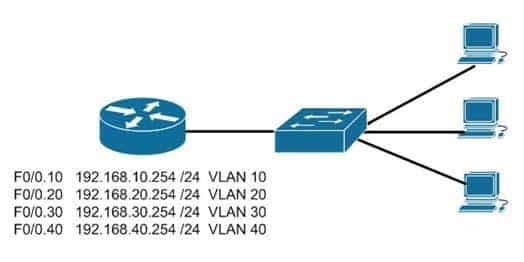
200-301 Part 02 Q09 015 What action should you take to place the new computer in the Accounting VLAN and allow for inter-VLAN routing?
- Connect the new computer to Fa0/1
- Connect the new computer to Fa0/14
- Connect the new computer to Fa0/5
- Configure a dynamic routing protocol on the router interface
Explanation:
Switchport Fa0/5 can be used to place the computer in the Accounting VLAN. The diagram indicates that a router has been configured as a “router-on-a-stick” to perform inter-VLAN routing between VLANs 10, 20, 30 and 40. The show vlan output indicates that interfaces Fa0/5, Fa0/15, and Fa0/6 have been assigned to VLAN 20, the Accounting VLAN:20 accounting active Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/15
Switchports Fa0/1 and Fa0/14 are both in the default VLAN, as indicated by the portion of the output describing the switch ports that are unassigned and therefore still residing in the default VLAN:
1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9, Fa0/14, Fa0/16, Fa0/23, Fa0/19, Fa0/20, Fa0/23
It is not necessary to configure a dynamic routing protocol on the router. Since the router is directly connected to all four subinterfaces and their associated networks, the networks will automatically be in the router’s routing table, making inter-VLAN routing possible.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot VLANs (normal/extended range) spanning multiple switches -
What two devices can be connected to a router WAN serial interface that can provide clocking? (Choose two.)
- CSU/DSU
- switch
- modem
- hub
Explanation:
A router DTE interface must receive a clock rate from the DCE end and the rate can be provided by either a CSU/DSU or a modem. Therefore, the connection between the local router and the service provider can be successfully completed by adding either of these devices between the service provider and the local router. Switches and hubs are neither capable of providing the clock rate nor able to complete the connection between the local router and the service provider.Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Describe the impact of infrastructure components in an enterprise network -
You are a network administrator for your organization. Your organization has two Virtual LANs, named Marketing and Production. All Cisco 2950 switches in the network have both VLANs configured on them. Switches A, C, F, and G have user machines connected for both VLANs, whereas switches B, D, and E have user machines connected for the Production VLAN only. (Click the Exhibit(s) button to view the network diagram.)
You receive a request to configure Fast Ethernet port 0/2 on Switch B for a user computer in the Marketing VLAN. VLAN numbers for the Marketing and Production VLANs are 15 and 20, respectively.
Which Cisco 2950 switch command should you use to configure the port?
-
SwitchB(config-if)#switchport trunk vlan 15
-
SwitchB(config)#switchport access vlan 15
-
SwitchB(config-if)#switchport access vlan 15 -
SwitchB(config-if)#switchport trunk vlan 15, 20
Explanation:
The SwitchB(config-if)#switchport access vlan 15 command should be used to enable the port for the Marketing VLAN in access link mode. You must first enter the interface configuration mode by using the following command:SwitchB(config)#interface fast 0/2
When executing the command switchport access vlan vlan #, if the VLAN number does NOT match that of the correct VLAN, the host connected to this port will not be in the correct VLAN. If the VLAN number doesn’t exist, the host will not be able to communicate with any resources on the LAN.
User machines are always connected to an access link. A trunk link is used to span multiple VLANs from one switch to another or from a switch to a router. For inter- VLAN routing to function, the port that is connected to the router must be configured as a trunk port. To configure a port into trunk mode, you should use the following command:
SwitchB(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
The SwitchB(config)#switchport access vlan 15 command is incorrect because the router is in global configuration mode. The switchport command is applied in the interface configuration mode.
All other options are incorrect because the access parameter should be used with the switchport command. The trunk parameter is used to add allowed VLANs on the trunk. The correct command syntax is:
switchport trunk {{allowed vlan vlan-list} | {native vlan vlan-id} | {pruning vlan vlan-list}}Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot VLANs (normal/extended range) spanning multiple switches -
-
Which Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) command is used to view the number of Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) packets that are sent and received?
- show eigrp neighbors
- show ip eigrp interfaces
- show ip eigrp packets
- show ip eigrp traffic
- show ip route
- show ip eigrp topology
Explanation:
The show ip eigrp traffic command is used to view the number of EIGRP packets that are sent and received. The syntax of the command is:Router# show ip eigrp traffic [autonomous-system-number]
The autonomous-system-number parameter is optional. The output of the command is as follows:
Router# show ip eigrp traffic IP-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 78 Hellos sent/received: 2180/2005 Updates sent/received: 70/21 Queries sent/received: 3/1 Replies sent/received: 0/3 Acks sent/received: 22/11
The show ip eigrp neighbors command is incorrect because it does not show the number of packets sent or received. It does show IP addresses of the devices with which the router has established an adjacency, as well as the retransmit interval and the queue count for each neighbor, as shown below:
Router# show ip eigrp neighbors IP-EIGRP Neighbors for process 49 Address Interface Holdtime Uptime Q Seq SRTT RTO (secs) (h:m:s) Count Num (ms) (ms) 146.89.81.28 Ethernet1 13 0:00:41 0 11 4 20 146.89.80.28 Ethernet0 12 0:02:01 0 10 12 24 146.89.80.31 Ethernet0 11 0:02:02 0 4 5 20
The show ip eigrp interfaces command is incorrect because this command is used to view information about the interfaces configured for EIGRP.
The show ip eigrp packets command is incorrect because it is not a valid Cisco IOS commands.
The show ip route command will not display EIGRP packets that are sent and received. It is used to view the routing table. When connectivity problems occur between subnets, this is the logical first command to execute. Routers must have routes to successfully send packets to remote subnets. Using this command is especially relevant when the underlying physical connection to the remote network has been verified as functional, but routing is still not occurring.
The show ip eigrp topology command is incorrect because it does not show the number of packets sent or received. This command displays all successor and feasible successor routes (if they exist) to each network. If you are interested in that information for only a specific destination network, you can specify that as shown in the output below. When you do, the command output displays all possible routes, including those that are not feasible successors:

200-301 Part 02 Q12 016 In the above output, four routers are providing a route to the network specified in the command. However, only one of the submitted routes satisfies the feasibility test. This test dictates that to be a feasible successor, the advertised distance of the route must be less than the feasible distance of the current successor route.
The current successor route has a FD of 41152000, as shown in the first section of the output. In the values listed for each of the four submitted routes, the first number is the feasible distance and the second is the advertised distance. Only the route received from 10.0.0.2 (second section) with FD/AD values of 53973240/120256 satisfies this requirement, and thus this route is the only feasible successor route present in the topology table for the network specified in the command.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot EIGRP for IPv4 (excluding authentication, filtering, manual summarization, redistribution, stub) -
You are configuring a PPP connection between two routers, R1 and R2. The password for the connection will be poppycock. When you are finished you execute the show run command on R1 to verify the configuration.
Which of the following examples of partial output of the show run command from R1 represents a correct configuration of PPP on R1?
-
enable password griswald hostname R1 username R1 password poppycock interface serial 0/0 ip address 192.168.5.5 255.255.255.0 encapsulation ppp ppp authentication chap
-
enable password griswald hostname R1 username R1 password poppycok interface serial 0/1 ip address 192.168.5.5 255.255.255.0 encapsulation ppp ppp authentication chap
-
enable password griswald hostname R1 username R2 password poppycock interface serial 0/0 ip address 192.168.5.5 255.255.255.0 encapsulation ppp ppp authentication chap -
enable password griswald hostname R1 username R1 password griswald interface serial 0/0 ip address 192.168.5.5 255.255.255.0 encapsulation ppp ppp authentication chap
Explanation:
The correct configuration is as follows:enable password griswald hostname R1 username R2 password poppycock interface serial 0/0 ip address 192.168.5.5 255.255.255.0 encapsulation ppp ppp authentication chap
The key settings that are common problems are as follows:
– The username is set to the hostname of the other router (in this case, R2)
– The password is set poppycock which must be the same in both routersThe following set is incorrect because the username is set to the local hostname (R1) and not the hostname of the other router (R2):
enable password griswald hostname R1 username R1 password poppycock interface serial 0/0 ip address 192.168.5.5 255.255.255.0 encapsulation ppp ppp authentication chap
The following set is incorrect because the password is misspelled. It should be poppycock, not poppycok.
enable password griswald hostname R1 username R1 password poppycok interface serial 0/0 ip address 192.168.5.5 255.255.255.0 encapsulation ppp ppp authentication chap
The following set is incorrect because the password is set to the enable password of the local router (R1) rather than the agreed upon PPP password, which is poppycock.
enable password griswald hostname R1 username R1 password griswald interface serial 0/0 ip address 192.168.5.5 255.255.255.0 encapsulation ppp ppp authentication chap
Objective:
WAN Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify PPP and MLPPP on WAN interfaces using local authentication -
-
Which statement is NOT true regarding Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)?
- ICMP can identify network problems.
- ICMP is documented in RFC 792.
- ICMP provides reliable transmission of data in an Internet Protocol (IP) environment.
- An ICMP echo-request message is generated by the ping command.
Explanation:
ICMP does NOT provide reliable transmission of data in an Internet Protocol (IP) environment. The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is used to provide reliable transmission of data in an IP environment. The following statements are TRUE regarding ICMP:– ICMP can identify network problems.
– ICMP is documented in RFC 792.
– An ICMP echo-request message is generated by the ping command.
– An ICMP echo-reply message is an indicator that the destination node is reachable.
– ICMP is a network-layer protocol that uses message packets for error reporting and informational messages.Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast TCP and UDP protocols -
What is the valid host address range for the subnet 172.25.4.0 /23?
- 172.25.4.1 to 172.25.5.254
- 172.25.4.10 to 172.25.5.210
- 172.25.4.35 to 172.25.5.64
- 172.25.4.21 to 172.25.5.56
Explanation:
For the subnet 172.25.4.0, the valid host range will start at 172.25.4.1 and end at 172.25.5.254.To determine the valid range of addresses in a subnet, one must determine the subnet number or network ID and the broadcast address of the subnet and all valid addresses will lie within those boundaries.In this case:
Network address: 172.25.0.0
Subnet mask in decimal: 255.255.254.0 (/23 indicates 23 bit in the mask)
Subnet mask in binary: 11111111.11111111.11111110.00000000The formulas to calculate the number of subnets and hosts are:
Number of subnets = 2number-of-subnet-bits
Number of hosts per subnet = 2number-of-host-bits – 2In this scenario:
Number of subnet bits: 7 (the binary 1s in the third octet of the subnet mask)
Number of subnets: 27 = 128
Number of host bits: 9 (the binary 0s in the subnet mask)
Number of hosts: 29 – 2 = 510These formulas are useful when determining if a subnet mask/network ID combination will support a given number of hosts.
To determine the boundaries of each of the 128 subnets that this mask will yield, you should utilize a concept called the interval or block size. This number helps to identify the distance between network IDs. Determining the network IDs allows the identification of the broadcast address for each subnet, because the broadcast address for any particular subnet will always be the last address before the next network ID. The interval is determined by the value of the far right-hand bit in the mask, which is 2 in this case. Then it is applied to the octet where the mask ends. In this case, the first 4 network IDs are:
172.25.0.0
172.25.2.0
172.25.4.0
172.25.6.0
…incrementing by two at each pointTherefore, the valid addresses in the 172.25.4.0 network are framed by the two addresses that cannot be used: 172.25.4.0 (network ID) and 172.25.5.255 (broadcast address, or the last address before the next network ID). The addresses within these boundaries are 172.25.4.1 to 172.25.5.254.
For subnet 172.25.0.0, the valid host range will run from 172.25.0.1 to 172.25.1.254. The broadcast address for subnet 172.25.0.0 will be 172.25.1.255.
For subnet 172.25.2.0, the valid host range will run from 172.25.2.1 to 172.25.3.254. The broadcast address for subnet 172.25.2.0 is 172.25.3.255.
For the subnet 172.25.4.0, the valid host range will run from 172.25.4.1 to 172.25.5.254. The broadcast address for subnet 172.25.4.0 is 172.25.5.255.
Always remember that the first address of each subnet is the network ID, and as such cannot be used as a host or router IP address. Also, the last address of each subnet is the broadcast address for the subnet, and as such cannot be used as a host or router IP address.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast IPv4 address types -
Which of the following are port roles in the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)? (Choose three.)
- Alternate
- Listening
- Routing
- Designated
- Backup
- Blocking
- Discarding
Explanation:
There are five port roles in RSTP:
– Root port: the closest port to the root bridge in terms of path cost. There can be only one root port on each switch, and the root switch is the only switch in the network that does not have a root port.
– Designated port: a forwarding port to the root bridge. All versions of STP require each network segment to have only one path toward the root bridge, to avoid bridging loops in redundantly connected environments. All bridges connected to a given segment listen to one another’s BPDUs and agree that the bridge that is sending the best BPDU is the designated bridge for the segment.
– Alternate port: a blocking port that becomes the root port if the active root port fails.
– Backup port: a blocking port that becomes the designated port if an existing designated port fails.
– Disabled port: a disabled port has no role within the operation of spanning tree.
– RSTP was designed to provide rapid convergence of the spanning tree in case of changes to the active topology, such as switch failure. RSTP has the following similarities to STP:
– RSTP elects the root switch using the same parameters as STP.
– RSTP elects the root port using the same rules as STP.
– Designated ports on each LAN segment are elected in RSTP in the same way as STP.Listening is a port state, not a port role. Listening is the STP transitional state while a port is preparing to enter a root or designated role.
Blocking is a port state, not a port role. A blocking port is inactive in STP spanning tree, and blocking is not a port state in RSTP. In RSTP that port state is called discarding.
The routing port does not exist in the RSTP topology.
Discarding is an RSTP port state, not a port role.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot STP protocols -
Which of the following cables would be used to connect a router to a switch?
- v.35
- crossover
- rollover
- straight-through
Explanation:
A straight-through cable would be used. When connecting “unlike” devices, such as a switch to a router, a straight-through cable is used. This is a cable where the wires are in the same sequence at both ends of the cable. NOTE: The one exception to this general rule of connecting unlike devices with a straight-through cable is when a computer NIC is connected to an Ethernet port on a router. In that case, a crossover cable is used.A v.35 cable is used to connect serial connections between routers. This cable has a male DB-60 connector on the Cisco end and a male Winchester connector on the network end. It comes in two types: DCE and DTE. It is often used to simulate a WAN connection in lab environments. In that case, the DCE end acts as the CSU/DSU and is the end where the clock rate is set. A CSU/DSU (Channel Service Unit/Data Service Unit) is a device that connects the router to the T1 or T3 line.
A crossover cable has two wires reversed and is used to connect “like” devices, such as a switch to a switch. It is also used when a computer NIC is connected to an Ethernet port on a router.
A rollover cable is used to connect to the console port of a router to configure the router. It is also called a console cable.
The diagram below illustrates the correct usage of each of the cable types shown using the following legend:
– SO Ethernet Straight through Cable
– CO Ethernet Crossover Cable
– Serial Serial cable
– RO Rollover cable
200-301 Part 02 Q17 017 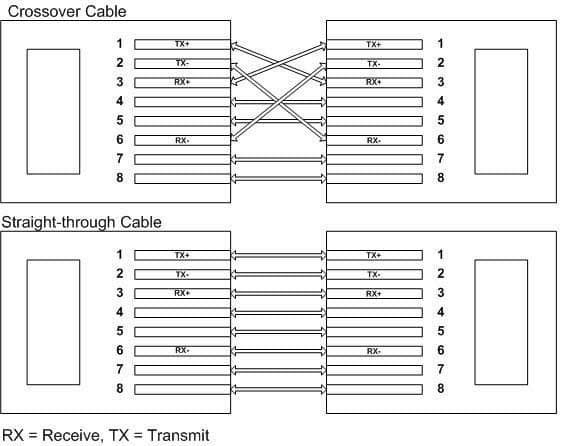
200-301 Part 02 Q17 018 Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Select the appropriate cabling type based on implementation requirements -
In the diagram below, if the workstation at 10.0.1.3 sends a packet to the workstation at 10.1.1.3, what will be the source physical address when the packet arrives at 10.1.1.3?

200-301 Part 02 Q18 019 - ab.ab.ab.ab.ab.ab
- ee.ee.ee.ee.ee.ee
- dd.dd.dd.dd.dd.dd
- cc.cc.cc.cc.cc.cc
- aa.aa.aa.aa.aa.aa
- bb.bb.bb.bb.bb.bb
Explanation:
The source physical address of the packet when it arrives at 10.1.1.3 will be that of the interface on the R2 router, dd.dd.dd.dd.dd.dd . Each router will change the MAC address field to the MAC address of its sending interface as it sends the packet and will leave the IP address field unchanged. The switches will change neither field, but will simply use the MAC address field to determine the forwarding path and switch the frame to the port where the MAC address is located. The R2 router is the last device that will make a change to the MAC address field. The source (10.0.1.3) and destination (10.1.1.3) IP address fields will stay the same at each device. The MAC address field changes when R1 sends the frame to R2 and when R2 send the frame to the workstation at 10.1.1.3.Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Describe and verify switching concepts -
What command was used to generate the output shown below?
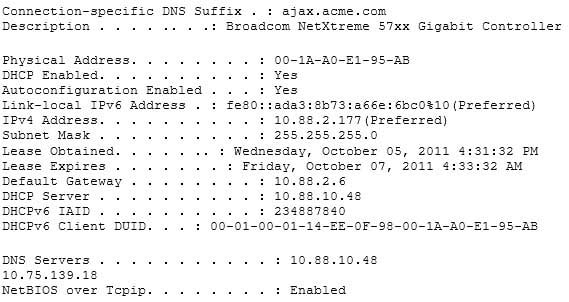
200-301 Part 02 Q19 020 - winipcfg
- ipconfig
- ifconfig
- ipconfig/all
Explanation:
The output displayed is that generated by the ipconfig/all command as executed on a Windows computer. This command displays a wealth of information about the current configuration. Examples of information that can be gleaned from the sample output include:
– The router for computer is at 10.88.2.6.
– The primary DNS server is 10.88.10.49.
– The address of the computer is 10.88.2.177. Any packets that need to be sent to any computers in the 10.88.2.0/24 network will not use the default gateway but will be switched to the destination by MAC address. Packets that need to be sent to any other network, however, will require the use of the default gateway and so the frame will be switched to MAC address of the gateway. This information can be used with other utilities for troubleshooting. For example, if you can ping the primary DNS server at 10.88.10.49, which in a remote network, then the IP address is correct and your router (10.88.2.6) knows a route to the network where the DNS server is located. However, this result would NOT prove that DNS is working correctly. Verification would require successfully pinging local or remote hosts by name rather than IP address.It is not the output of winipcfg. This command was used in Windows 95 to generate a subset of this information in a GUI dialog box.
It is not the output of ifconfig. This command is used to generate a subset of this information in a Linux/Unix environment.
It is not the output of ipconfig. This command generates IP address subnet mask and gateway only.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot IPv4 addressing and subnetting -
Which two security features can be configured to prevent unauthorized access into the network through a networking device? (Choose two.)
- Anti-Replay
- Traffic filtering
- Authentication
- IPSec network security
Explanation:
Traffic filtering and authentication security can be configured to prevent unauthorized access into the network through a networking device. Unauthorized access to the company’s network should be blocked because unauthorized access can damage a company’s network. Attackers may access confidential data, plant a virus in the network, or flood the network with illegitimate packets. Therefore, preventive measures should be taken to block any unauthorized access. The traffic filtering security feature uses two measures to prevent unauthorized access into the network: access lists and Cisco IOS firewalls.Access lists are configured to determine which traffic to block and which traffic should be forwarded at the router interfaces. The following types of access lists are available when using Cisco devices:
– Basic access lists: Allow only specific traffic through the device; other traffic is dropped.
– Extended access lists: Used to filter the traffic based on source IP address, destination IP address, port numbers, or protocols.Cisco IOS firewalls provide various security features according to your needs. Following are the key components of Cisco IOS firewall:
– Context-based Access Control (CBAC): Filters TCP and UDP packets on the basis of application layer protocol session information.
– Cisco IOS firewall Intrusion Detection System (IDS): Used to detect suspicious activity. IDS are used to watch packets and sessions as they flow through the router and scan then to match IDS signatures. If the packet is detected as suspicious, the packet is dropped.
– Authentication Proxy: Used to apply specific security policies on a per-user basis.Authentication security can be used to prevent unauthorized access to the network. When a user attempts to access a service or host within the network, they must enter credentials such as their user name and password. If the credentials are correct, then access is provided; otherwise, the user is not allowed to access the service.
Anti-replay and IPSec network security cannot prevent unauthorized access through a networking device into the network. Anti-replay prevents the capture and replay of packets on a network. Although a good security feature to deploy it does not specifically address access to the network through a device. IPSec is used to encrypt and protect the integrity of data that travels through the network, not control access through a device.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic device hardening