200-301 : Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) : Part 10
-
Which Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) command is used to make the running configuration in Random Access Memory (RAM) to the configuration the router will use at startup?
- copy running-config startup-config
- copy flash running-config
- copy tftp flash
- copy running-config flash memory
- copy startup-config tftp
- copy tftp running-config
- copy running-config tftp
Explanation:
The copy running-config startup-config command is used to make the running configuration in Random Access Memory (RAM) the configuration the router will use at startup. It saves the running configuration in RAM to the router’s NVRAM. This command should always follow changes to the configuration; otherwise, the changes will be lost at the next router restart. The startup configuration loads into memory from NVRAM at boot and resides in memory. When the router restarts, memory information is lost. The copy flash running-config command is incorrect because this would copy a configuration from the router’s flash memory to the running configuration, causing it to be the active configuration. While this can be done, it is not a common practice. Configuration files are normally stored in NVRAM. The copy tftp flash command is incorrect because this command is used to replace the IOS image with a backup IOS image stored on a TFTP server to the target router. A router can also act as a TFTP server for another router. When you execute this command, you will be prompted for the IP address or hostname of the TFTP server. This prompt will display as in this example:router#enable router#copy tftp flash Address or name of remote host []? 192.168.1.5.2
Before performing an upgrade of the IOS version from a TFTP server, you should verify that the upgrade is necessary by verifying the current IOS version number. The IOS version number can be found in the output of the following commands:
– show running-config
– show version
– show flashThe copy running-config flash memory command is incorrect because this command would copy the running configuration to the router’s flash memory. It is the opposite of the copy flash-running config command. While this can be done, it is not a common practice. Flash is typically used to store the Cisco IOS or operating system. Configuration files are normally stored in NVRAM.
The copy startup-config tftp command is incorrect because this command would be used to copy the current configuration stored in NVRAM to a TFTP server. When you execute this command, you will be prompted for the IP address or hostname of the TFTP server. This prompt will display as below:
router#copy start tftp
Address or name of remote host []? 192.168.1.5
Destination filename [router-confg]?The address 192.168.1.5 is the address of the TFTP server. If no file name is given, it will save the file as router-config.
The copy tftp running-config is incorrect. This command is used to merge a backup configuration located on a TFTP server with the configuration in RAM.
The copy running-config tftp command in incorrect. It is used to make a backup copy of the configuration residing in RAM to a TFTP server.
Objective:
Infrastructure Management
Sub-Objective:
Perform device maintenance -
Which of the following is NOT a benefit of cloud computing to cloud users?
- On-demand self-service resources provisioning
- Centralized appearance of resources
- Highly available, horizontally scaled applications
- Cost reduction from standardization and automation
Explanation:
Cost reduction from standardization and automation is a benefit that accrues to the cloud provider, not the cloud users. Additional benefits to cloud providers are:
– High utilization through virtualization and shared resources
– Easier administration
– Fail-in-place operations modelBenefits that accrue to cloud users include:
– On-demand self-service resources provisioning
– Centralized appearance of resources
– Highly available, horizontally scaled applications
– No local backups requiredCloud users can also benefit from new services such as intelligent DNS, which can direct user requests to locations that are using fewer resources.Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Describe the effects of cloud resources on enterprise network architecture -
When the auth keyword is used in the snmp-server host command, which of the following must be configured with an authentication mechanism?
- the interface
- the host
- the user
- the user
Explanation:
The auth keyword specifies that the user should be authenticated using either the HMAC-MD5 or HMAC-SHA algorithms. These algorithms are specified during the creation of the SNMP user. For example, the following command creates a user named V3User who will be a member of the SNMP group V3Group and will use HMAC-MD5 with a password of Password:snmp-server user V3User V3Group v3 auth md5 Password
The authentication mechanism is not configured on the interface. All SNMP commands are executed at the global configuration prompt.
The authentication mechanism is not configured at the host level. The version and security model (authentication, authentication and encryption, or neither) are set at the host level.
The authentication mechanism is not configured at the SNMP group level. The group level is where access permissions like read and write are set. This is why a user account must be a member of a group to derive an access level, even if it is a group of one.
Objective:
Infrastructure Management
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify device-monitoring protocols -
You need to manually assign IPv6 addresses to the interfaces on an IPv6-enabled router. While assigning addresses, you need to ensure that the addresses participate in neighbor discovery and in stateless auto-configuration process on a physical link.
Which of the following addresses can be assigned to the interfaces?
- FEC0:0:0:1::1/64
- FE80::260:3EFF:FE11:6770/10
- 2001:0410:0:1:0:0:0:1/64
- 2002:500E:2301:1:20D:BDFF:FE99:F559/64
Explanation:
The FE80::260:3EFF:FE11:6770/10 address can be assigned to an interface of the IPv6-enabled router. This address is a link-local address as it has the prefix FE80::/10. Link-local addresses can be configured for an interface either automatically or manually. Link-local addresses are IPv6 unicast addresses that are configured on the interfaces of an IPv6-enabled router. With link-local addresses, the nodes can connect to a network (local link) and communicate with other nodes. In addition, these addresses participate in the neighbor discovery protocol and the stateless auto-configuration process. The FEC0:0:0:1::1/64 address should not be used for the interfaces because this address is a site-local address. Site-local addresses are IPv6 equivalent addresses to IPv4’s private address classes. These addresses are available only within a site or an intranet, which typically is made of several network links.You should not use the 2001:0410:0:1:0:0:0:1/64 and 2002:500E:2301:1:20D:BDFF:FE99:F559 addresses for the interfaces. These two addresses are global unicast addresses as they fall in the range from 2000::/3 and to E000::/3. A global address is used on links that connect organizations to the Internet service providers (ISPs).
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify IPv6 Stateless Address Auto Configuration -
Which technique is used to stop routing loops by preventing route update information from being sent back over the interface on which it arrived?
- Holddown timer
- Triggered updates
- Route poisoning
- Split horizon
- Maximum hop count
Explanation:
Split horizon stops routing loops by preventing route update information from being sent back over the interface on which it arrived. Routing loops can occur due to slow convergence and inconsistent routing tables, and can cause excessive use of bandwidth or even complete network failure. Split horizon can prevent routing loops between adjacent routers. Holddown timers prevent regular update messages from reinstating a route that is unstable. The holddown timer places the route in a suspended, or “possibly down” state in the routing table, and regular update messages regarding this route will be ignored until the timer expires. Triggered updates are sent as soon as a change in network topology is discovered, as opposed to waiting until the next regular update interval (every 30 seconds in RIP networks). This speeds convergence and helps prevent problems caused by outdated information.Route poisoning “poisons” a failed route by increasing its cost to infinity (16 hops, if using RIP). Route poisoning is combined with triggered updates to ensure fast convergence in the event of a network change.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast distance vector and link-state routing protocols -
Multiple routes to a destination already exist from various routing protocols.
Which of the following values is used FIRST to select the route that is inserted into the route table?
- composite metric
- administrative distance
- prefix length
- hop count
Explanation:
When multiple routes to a destination exist from various routing protocols, the first value to be evaluated is the administrative distance of the source of the route. The following are examples of default administrative distance values:

200-301 Part 10 Q06 093 The second value to be compared is the composite metric, or any metric value for that matter. It is only used when multiple routes exist that have the same administrative distance.
The prefix length is only used to compare two existing routes in the routing table that lead to the destination, yet have different mask or prefix lengths. In that case, the route with the longest prefix length will be chosen.
Hop count is ONLY used when comparing multiple RIP routes. It is not the first consideration when multiple routes from various routing protocols exist in a routing table.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Describe how a routing table is populated by different routing information sources -
You are the Cisco administrator for Verigon Incorporated. The given exhibit displays some of the devices in the network. (Click the Exhibit(s) button.) Workstation A can communicate with Workstation C but cannot communicate with Workstation B.
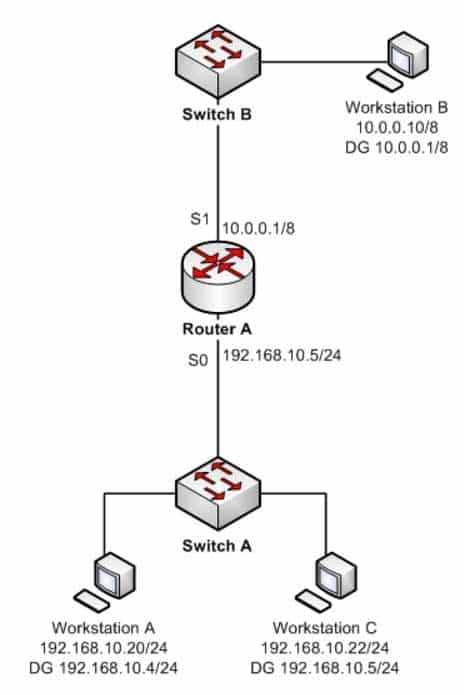
200-301 Part 10 Q07 094 What is the problem?
- Workstation B has an incorrect default gateway
- Workstation A has an incorrect subnet mask
- Workstation A has an incorrect default gateway
- Workstation B has an incorrect subnet mask
Explanation:
Workstation A has an incorrect default gateway. To communicate with remote computers or those computers outside of its own subnet, a computer must have the address of the nearest router interface as its default gateway. In this case, the default gateway of Workstation A should be 192.168.10.5/24, which is the Serial0 address of Router A. The diagram shows that it is instead configured as 192.168.10.4/24. This will not cause a problem for Workstation A to communicate with Workstation C, but it will make communication with remote subnets impossible. Workstation B does not have an incorrect default gateway. Its nearest router interface is 10.0.0.1/8, which is the configuration of its default gateway. Workstation A does not have an incorrect subnet mask. The mask used by Workstation C and the router interface of Router A, which are in the same subnet, is /24, or 255.255.255.0, which is also the subnet mask used by Workstation A.Workstation B does not have an incorrect subnet mask. Since the subnet mask of the router interface that is nearest to Workstation B is /8, or 255.0.0.0, then Workstation B also should have an 8-bit mask.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Troubleshoot basic Layer 3 end-to-end connectivity issues -
Examine the following partial output of the show interfaces command.
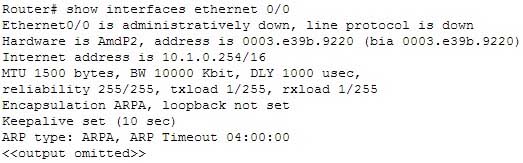
200-301 Part 10 Q08 095 Which of the following statements are true? (Choose all that apply.)
- the interface is functional
- the largest frame allowed through this connection is 1500 bytes
- the interface needs the no shutdown command executed to be functional
- the largest frame allowed through this connection is 10000 Kbs
Explanation:
From this output, we can determine that the largest frame allowed through this connection is 1500 bytes and that the interface needs the no shutdown command executed to be functional. The portions of the output that tell us this are:MTU 1500 bytes indicates that the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) is 1500 bytes. The MTU is the largest frame size allowed.Ethernet0/0 is administratively down indicates that the interface has either been disabled or has never been enabled. The command no shutdown is used to enable an interface, and until enabled, it will not function.The interface is not functional, as indicated by the Ethernet0/0 is administratively down portion of the output.
The largest frame allowed through this connection is not 10000 Kbs. It is 1500 bytes. It is interesting to note that the bandwidth of the connection is 10000 Kbs, as indicated by the section:
BW 10000 Kbit
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Troubleshoot interface and cable issues (collisions, errors, duplex, speed) -
You are in the process of verifying the operation of your core switches, which are using HSRP. One core switch was left with the default priority; the other was given a lower priority to make it the standby switch. The command show standby brief was executed on one of the switches. Output of the command is shown below:
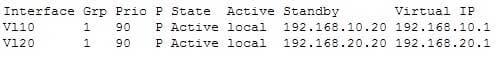
200-301 Part 10 Q09 096 What does this output mean? (Choose all that apply.)
- this switch is using the default priority]
- this switch is the active HSRP switch
- the HSRP devices are up and functioning correctly
- the switch intended to be the active switch has failed and this switch has taken over
- preemption is enabled for the group
Explanation:
The output in the exhibit indicates that this switch is the active HSRP switch, the switch intended to be the active switch has failed, and that preemption is enabled for the group. This is the active switch because Active is the State listed for each interface that is a member of HSRP. The question states that the switch that was intended to be the standby switch was given a priority lower than the default. The default priority is 100, so this is not the switch intended to be the active switch. This information indicates that the switch intended to be the active switch has failed.Preemption is enabled, as indicated by the P following the priority value in line 2. Since preemption is enabled, the switch with the priority of 100 is still down. When that switch is corrected and joins the group again, it will take over as active.
The HSRP group is still providing access for users, but not all devices are functioning properly.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic HSRP -
DRAG DROP
Match the Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) configuration on the switch ports so that a trunk link can be established. (Click and drag the DTP modes on the left and place them with their corresponding port on the right.)
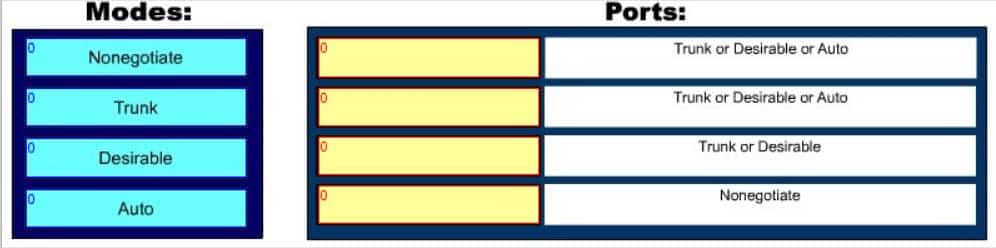
200-301 Part 10 Q10 097 Question 
200-301 Part 10 Q10 097 Answer Explanation:
There are five DTP modes:
– Trunk: Switch will establish trunk if other end port is configured as Trunk/Desirable/Auto.
– Dynamic Desirable: Switch will establish trunk if other end port is configured as Trunk/Desirable/Auto.
– Dynamic Auto: Switch will establish trunk if other end port is configured as Trunk/Desirable.
– Nonegotiate: Other end port should also be configured with Nonegotiate, or should be a device that does not support DTP.
– Access: No trunk establishment.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify Layer 2 protocols -
When executed on a HSRP group member named Router 10, what effect does the following command have?
Router10(config-if)# standby group 1 track serial0 25
- It will cause the router to increase its HSRP priority by 25 if the Serial0 interface on the standby router goes down
- It will cause the router to shut down the Serial0 interface if 25 packets have been dropped
- It will cause the router to notify Router 25 is serial 0 goes down
- It will cause the router to decrement its HSRP priority by 25 if Serial 0 goes down
Explanation:
This command will cause the router to decrement its HSRP priority by 25 if Serial 0 goes down. Interface tracking can be configured in Hot Standby Routing Protocol (HSRP) groups to switch traffic to the standby router if an interface goes down on the active router. This is accomplished by having the active router track its interface. If that interface goes down, the router will decrement its HSRP priority by the value configured in the command. When properly configured, this will cause the standby router to have a higher HSRP priority, allowing it to become the active router and to begin serving traffic. When the standby router in an HSRP group is not taking over the active role when the active router loses its tracked interface, it is usually a misconfigured decrement value, such that the value does not lower the HSRP priority of the active router far enough for the standby to have a superior priority value. The command will not cause the router to increase its HSRP priority by 25 if the Serial0 interface on the standby router goes down. HSRP routers track their own interfaces, not those of another router.
The command will not cause the router to shut down the Serial0 interface if 25 packets have been dropped. It will only do this if the link becomes unavailable.The command will not cause the router to notify Router 25 is serial 0 goes down. The number 25 in the command is the decrement value, not the ID of another router.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic HSRP -
You are a network administrator for your organization. Your organization has two Virtual LANs, named Marketing and Production. All switches in the network have both VLANs configured on them. Switches A, C, F, and G have user machines connected for both VLANs, whereas switches B, D, and E have user machines connected to the Production VLAN only. (Click the Exhibit(s) button to view the network diagram.)
To meet a new requirement, Marketing VLAN users must communicate with Production VLAN users and vice versa. What changes would be required for the network in this scenario?
- Disable VTP pruning.
- Convert all switch ports into trunk ports.
- Create an access list with permit statements.
- Install a routing device or enable Layer 3 routing on a switch.
Explanation:
In this scenario, either a Layer 3 device or Layer 3 routing on a switch would be required to implement inter-VLAN routing. Although you could use multiple physical interfaces for the VLAN traffic, using trunk links between the switches and an external router would make more efficient use of the physical interfaces that you have. Only trunk links can carry traffic from multiple VLANs. These data frames must be frame tagged over the trunk link to identify the VLAN that sourced the frame. The receiving switch sees the VLAN ID, and uses this information to forward the frame appropriately. Additionally, the cables used to connect the router to the switches must be a straight-through cable and not a crossover cable. When trunks links do not appear to be operating, it is always a good idea to make sure the port used for the trunk link is set as a trunk link and not as an access link. For example, the output below of the show interface fastethernet 0/15 switchport command indicates that Switch2 will not trunk because the port is set as an access link. This is shown in line 5 of the output:<<output omitted>> Switch2#show Interface fastethernet 0/15 switchport Name: Fa0/15 SwitchportEnabled Administrative Mode: access Operational Mode: access <<output omitted>>
The VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) pruning feature restricts unnecessary broadcast traffic between multiple switches. It does not affect inter-VLAN traffic. Therefore, disabling VTP pruning will not permit inter-VLAN communication between the Marketing and Production VLANs.
Converting all switch ports into trunk ports will permit traffic from multiple VLANs to traverse over these links. However, traffic from one VLAN will be restricted to that VLAN only, and inter-VLAN communication will not be possible.
Access lists can permit or deny packets based on the packets’ source/destination IP address, protocol, or port number. However, access lists can manipulate inter-VLAN traffic only when inter-VLAN traffic is enabled using a Layer 3 device or Layer 3 routing. Therefore, creating access lists will not enable inter-VLAN routing between the Marketing and Production VLANs.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Describe the impact of infrastructure components in an enterprise network -
Which of the following commands will enable a global IPv6 address based on the Modified EUI-64 format interface ID?
- ipv6 address 5000::2222:1/64
- ipv6 address autoconfig
- ipv6 address 2001:db8:2222:7272::72/64 link-local
- ipv6 enable
Explanation:
To configure the interface to create a global IPv6 address based on the Modified EUI-64 format interface ID, you must enable stateless autoconfiguration. In stateless autoconfiguration, the interface will receive the network prefix from the router advertisement (RA) and generate a full IPv6 address by spreading the 48-bit MAC address of the interface across 64 bits to complete the address. This can all be done simply by executing the ipv6 address autoconfig command at the interface configuration prompt. The command ipv6 address 5000::2222:1/64 is used to manually assign a full IPv6 address to the interface without using stateless autoconfiguration or the eui-64 keyword to manually specify the first 64 bits and allow the last 64 bits to be generated from the MAC address of the interface. The command ipv6 address 2001:db8:2222:7272::72/64 link local is used to configure a link-local address manually without allowing the system to generate one from the MAC address, which is the default method.The command ipv6 enable is used to allow the system to generate a link-local address from the MAC address. Because this is the default behavior, the command is not required if any other ipv6 commands have been issued. Regardless of how many manual IPv6 addresses you configure, a link local address is always generated by default.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot IPv6 addressing -
Refer to the following partial output of the show interfaces command:

200-301 Part 10 Q14 098 What are the two troubleshooting steps that you should perform to resolve the problem depicted in the output? (Choose two.)
- Check the cable connections.
- Reset the equipment.
- Check the router configuration.
- Check the router configuration for the shutdown interface command.
Explanation:
You should check the cable connections and reset the equipment to troubleshoot the problem depicted in the output. The Serial 0 is down, line protocol is down message indicates that there is no carrier detect (CD) signal sensed by the router. This problem might be due to incorrect cabling or a possible hardware failure. A complete list of the possible troubleshooting steps that should be performed to resolve this issue include:
– Checking the cable connections.
– Resetting the equipment.
– Checking the CD LED on the CSU/DSU.
– Reporting the issue to the leased-line provider.
– Replacing the faulty equipment. The router configuration is not a possible issue in this scenario because both serial 0 and line protocol are down, indicating a problem in the physical layer. Configuration issues, such as an incorrect IP address, would be indicated in the second section of the output (line protocol is up/down). The second section, regardless of whether it says up or down is meaningless when the first section indicates a problem.You should not check the router configuration for the shutdown interface command. When an interface has been manually shut down with this command, it will be indicated in the output as Serial 0 is administratively down, line protocol is down.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Troubleshoot interface and cable issues (collisions, errors, duplex, speed) -
How is the designated router (DR) determined by OSPF on a multi-access network segment?
- The lowest interface priority, then the highest RID
- The highest interface priority, then the highest RID
- The lowest interface priority, then the highest OSPF process ID
- The highest interface priority, then the highest OSPF process ID
Explanation:
OSPF routers elect a designated router (DR) and backup designated router (BDR) on multi-access network segments in order to minimize the amount of update traffic sent between OSPF neighbors. All routers on multi-access network segment form adjacencies with the DR and BDR, but not with each other. Network events are communicated to the DR, and the DR distributes the event to the rest of the network. The DR is determined by the router with the highest interface priority number. If the priority numbers tie (which will be the case if they are left to the default of 1), then the router with the highest router ID (RID) becomes the DR. The default priority number is 1, and can be configured as high as 255.In many cases, it is desirable to intervene in this process and select the router you want to be the DR. If that is the case and the selected router is not becoming the DR for whatever reason, the following options are available to ensure that the selected router wins the election:
– Change the priority value of the router to a value higher than the other routers
– Set the priority value of the other routers to 0
– Create a loopback address on the selected router with an IP address higher than the IP addresses used on the other routersChanging the priority to 0 makes the router ineligible to become the DR or BDR. The ip ospf priority # command is used to manually configure a priority on a specific interface.
It is also worth noting that a single OSPF area can have more than one DR. The election is NOT performed per area, but per network segment. So if you had six OSPF routers in area 0 with three in one IP subnet and three in another, there would be two elections, one for each segment.
The lowest interface priority does not determine the DR.
The OSPF process ID has no effect on DR elections.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot single area and multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4 (excluding authentication, filtering, manual summarization, redistribution, stub, virtual-link, and LSAs) -
Which statement is TRUE of the CSMA/CD Ethernet media access method?
- It requires centralized monitoring and control.
- It is ideal for a switched network environment.
- It uses a back-off algorithm to calculate a random time value.
- Each station is allotted a time slot in which they can transmit data.
Explanation:
The Carrier Sense Multiple Access – Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) Ethernet Media Access Control (MAC) method uses a back-off algorithm to calculate random times to transmit packets across a channel. When two stations start transmitting at same time, their signals will collide. The CSMA/CD method detects the collision and causes both stations to hold the retransmission for an amount of time determined by the back-off algorithm. This is done in an effort to ensure that the retransmitted frames do not collide. CSMA/CD does not require centralized monitoring and control nor does it assign time slots to stations. Moreover, the CSMA/CD method is designed to work in non-switched environment. It is an alternative to a token-passing topology, in which each station waits in turn to receive a token that allows it to transmit data. With CSMA/CD, each station is capable of making the decision regarding when to transmit the data.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Describe and verify switching concepts -
A device has an address of 192.168.144.21 and a mask of 255.255.255.240.
What will be the broadcast address for the subnet to which this device is attached?
- 192.168.144.23
- 192.168.144.28
- 192.168.144.31
- 192.168.144.32
Explanation:
The broadcast address for the subnet to which this device is attached will be 192.168.144.31.To determine the broadcast address of a network where a specific address resides, you must first determine the network ID of the subnetwork where the address resides. The network ID can be obtained by determining the interval between subnet IDs. With a 28-bit mask, the decimal equivalent of the mask will be 255.255.255.240. The interval between subnets can be derived by subtracting the value of the last octet of the mask from 256. In this case, that operation would be 256 – 240. Therefore, the interval is 16.The first network ID will always be the classful network you started with (in this case 192.168.144.0). Then each subnetwork ID in this network will fall at 16-bit intervals as follows:192.168.144.0
192.168.144.16
192.168.144.32
192.168.144.48At 192.168.144.48 we can stop, because the address that we are given as a guide is in the network with a subnet ID of 192.168.144.16. Therefore, since the broadcast address for this network will be 1 less than the next subnet ID (192.168.144.32), the broadcast address for the subnet to which this device is attached is 192.168.144.31.
All the other options are incorrect because none of these will be the broadcast address for the subnet to which this device is attached.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Apply troubleshooting methodologies to resolve problems -
DRAG DROP
Click and drag the OSI layer, on the left, to the commands at which they test functionality. If a command can test more than one layer, choose the highest layer for which it can test. (It may be necessary to use an OSI layer multiple times.)
200-301 Part 10 Q18 099 Question 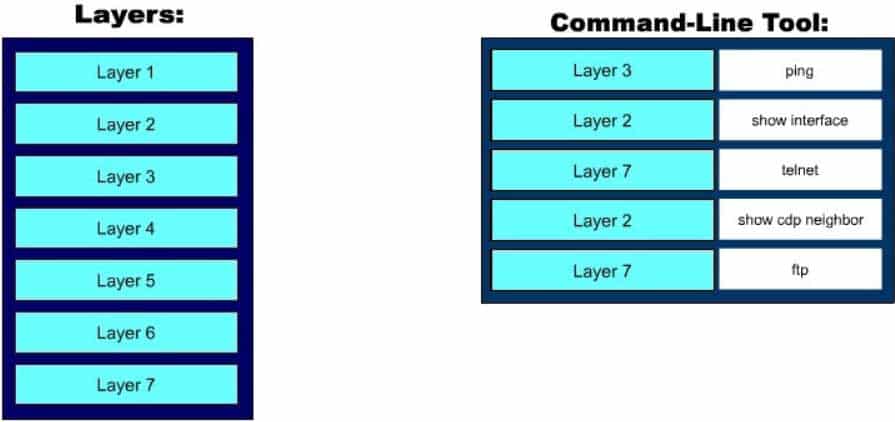
200-301 Part 10 Q18 099 Answer Explanation:
Telnet operates at the application layer, which is Layer 7 of the OSI model. File transfer Protocol (FTP) is a generic command that is also used by some high-end Cisco routers but in a different format. FTP also operates at Layer 7. The ping command operates at the network layer, which is Layer 3 of OSI reference model. Therefore, it is used to test the connectivity up to Layer 3. The show interface command will display the status of line protocol. If it displays the message interface up, line protocol up it means that Layer 2 is functioning correctly. The show cdp neighbor command also operates at Layer 2, which is the data link layer.
Objective:
Infrastructure Management
Sub-Objective:
Perform device maintenance -
Which is the shortest possible notation of the following Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) address?
2001:0DB8:0000:0001:0000:0000:0000:F00D
- 2001:DB8::1::F00D
- 2001:DB8:0:1::F00D
- 2001:DB8:0:1:0:0:0:F00D
- 2001:0DB8:0:1::F00D
Explanation:
The shortest possible notation of the IPv6 address 2001:0DB8:0000:0001:0000:0000:0000:F00D is 2001:DB8:0:1::F00D. The address is shortened according to the following rules:
– Remove leading zeros.
– Remove the consecutive fields of zeros with double colon (::).
– The double colon (::) can be used only once. The option 2001:DB8::1::F00D is incorrect because the double colon (::) can be used only once in the process of shortening an IPv6 address. The option 2001:DB8:0:1:0:0:0:F00D is incorrect because 2001:DB8:0:1:0:0:0:F00D can be further shortened to 2001:DB8:0:1::F00D.The option 2001:0DB8:0:1::F00D is incorrect because 2001:0DB8:0:1::F00D can be further shortened to 2001:DB8:0:1::F00D.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast IPv6 address types -
You have connected two routers in a lab using a Data Terminal Equipment (DTE)-to-Data Circuit-terminating Equipment (DCE) cable.
Which command must be issued on the DCE end for the connection to function?
- bandwidth
- no clock rate
- clock rate
- no bandwidth
Explanation:
You should issue the clock rate command on the DCE end for the connection to function. The clock rate is set on the Data Circuit-terminating Equipment (DCE) device. DCE is also known as Data Communications Equipment. The DCE terminates a physical WAN connection, provides clocking and synchronization of a connection between two locations, and connects to a DTE. The DCE category includes equipment such as CSU/DSUs, NT1s, and modems. In the real world, the clock rate is provided by the CSU/DSU end at the telcom provider. In a lab, you must instruct the DCE end to provide a clock rate. The DTE is an end user device, such as a router or a PC, which connects to the WAN via the DCE device.You would not issue the bandwidth command. This command is used to inform the router of the bandwidth of the connection for purposes of calculating best routes to locations where multiple routes exist. It is not necessary for the link described to function.
You should not issue the no clock rate command. This command is used to remove any previous settings implemented with the clock rate command.
You would not issue the no bandwidth command. This command is used to remove any previous settings implemented with the bandwidth command
Objective:
WAN Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Describe WAN access connectivity options