200-301 : Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) : Part 13
-
Which Wide Area Network (WAN) switching technology is used by Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)?
- packet switching
- virtual switching
- circuit switching
- cell switching
Explanation:
Cell switching is a WAN switching technology that is used by ATM. ATM is an International Telecommunication Union-Telecommunications (ITU-T) standard for transmission of data, voice, or video traffic using a fixed size frame of 53 bytes, known as cells. Out of these 53 bytes, the initial five bytes are header information and the rest 48 bytes is the payload.Packet switching is incorrect because packet switching is popularly used for data transfer, as data is not delay sensitive and it does not require real time transfer from a sender to a receiver. With packet switching, the data is broken into labeled packets and transmitted using packet-switching networks.
Virtual switching is incorrect because no such WAN switching technology exists.
Circuit switching is incorrect because circuit switching dynamically establishes a virtual connection between a source and destination. The virtual connection cannot be used by other callers unless the circuit is released. Circuit switching is the most common technique used by the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) to make phone calls. A dedicated circuit is temporarily established for the duration of call between caller and receiver. Once the caller or receiver hangs up the phone, the circuit is released and is available for other users.
Objective:
WAN Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Describe WAN access connectivity options -
You are configuring the link between a Cisco 2950 series switch and a Cisco 2611 router. You have physically connected the router’s Ethernet port to the switch using a straight-through cable. The switch has not been configured, except for a hostname. The router’s hostname has also been configured, and the Ethernet port has been enabled. However, you forgot to assign an IP address to the Ethernet port.
You issue the show cdp neighbors command and get the following output:

200-301 Part 13 Q02 121 If you did not configure IP addresses, how is this information being passed between the two devices?
- The devices established a connection using default IP addresses.
- The ip unnumbered command has been issued, which means the interface does not require an IP address to be configured.
- CDP is a Layer 2 protocol and does not require IP addresses to be configured.
- CDP uses its own IP addressing system.
Explanation:
CDP is a Layer 2 protocol and does not require IP addresses to be configured. The structure of the OSI model requires that the upper-layer protocols rely on the lower-layer protocols for operation. Protocols at Layer 3 cannot be operational unless Layers 1 and 2 are operational. Conversely, lower-layer protocols do not rely on upper-layer protocols for their operation. Because CDP operates at Layer 2 of the OSI model, it does not require an IP address to be active, since IP addresses are a function of Layer 3.The ip unnumbered command has not been issued in this scenario. This command can only be used on serial interfaces, not Ethernet interfaces. It allows a serial interface to use an address that is already applied to an Ethernet interface.
Information is not being passed between the devices through default IP addresses. There is no such thing as default IP addresses on Ethernet interfaces for Cisco routers.
Information is not being passed between the devices through CDP’s IP addressing system. CDP does not have its own IP addressing system because it does not use IP addresses for its operation.
Objective:
Infrastructure Management
Sub-Objective:
Use Cisco IOS tools to troubleshoot and resolve problems -
Which of the following is a Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) authentication protocol that supports sending of hashed values instead of sending passwords in clear text?
- LCP
- NCP
- PAP
- CHAP
Explanation:
There are two authentication methods available when implementing a PPP connection: Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) and Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP).Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) uses a one-way hash function based on the Message Digest 5 (MD5) hashing algorithm to hash the password. This hashed value is then sent across the wire. In this situation, the actual password is never sent. No one tapping the wire will be able to reverse the hash to come up with the original password. This is why MD5 is referred to as a one-way function. It cannot be reverse engineered. CHAP uses a three-way handshake process to perform the authentication. Moreover, CHAP periodically repeats the authentication process after link establishment.
When configuring PPP with CHAP authentication, both routers must be configured with a username that will be presented by the other router with a password. Therefore, the username to configure on Router A will be the username of Router B. The password should be the same on both machines. If these settings are not correct, then authentication will fail. The authentication process can be displayed as it happens with the debug PPP authentication command.
Link Control protocol (LCP) is defined in Request for Comments (RFCs) 1548 and 1570 and has primary responsibility to establish, configure, authenticate, and test a PPP connection. LCP negotiates the following when setting up a PPP connection:
– Authentication method used (PAP or CHAP), if any
– Compression algorithm used (Stacker or Predictor), if any
– Callback phone number to use, if defined
– Multilink; other physical connections to use, if configuredNetwork Control Protocol (NCP) defines the process for how the two PPP peers negotiate which network layer protocols, such as IP and IPX, will be used across the PPP connection. LCP is responsible for negotiating and maintaining a PPP connection whereas NCP is responsible for negotiating upper-layer protocols that will be carried across the PPP connection.
Password authentication Protocol (PAP) is simpler than CHAP, but less secure. During the authentication phase, PAP goes through a two-way handshake process. In this process, the source sends its user name (or hostname) and password in clear text, to the destination. The destination compares this information with a list of locally stored user names and passwords. If it finds a match, the destination returns an accept message. If it does not find a match, it returns a reject message.
Objective:
WAN Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot PPPoE client-side interfaces using local authentication -
With which type of service is bandwidth and latency the biggest consideration?
- streaming video
- telnet sessions
- FTP transfers
- authentication traffic
Explanation:
Streaming video places the largest demand on both bandwidth and latency. Video traffic is real-time and benefits from dedicated bandwidth with QoS implementation to ensure quality. Moreover, this service can tolerate very little latency.Telnet and FTP sessions are both low bandwidth users and can tolerate a high degree of latency since the data can be reassembled when all pieces arrive, which is not possible when data is coming in real-time, and waiting for retransmissions and reassembly is not feasible.
Authentication traffic is not sensitive to latency and does not require much bandwidth either.
Objective:
WAN Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Describe basic QoS concepts -
How many collision domains are in a LAN with four hubs and two bridges that are connected directly to each other, as shown in the following figure? (Click the Exhibit(s) button.)
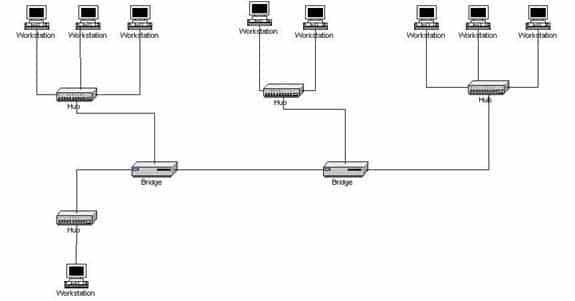
200-301 Part 13 Q05 122 - four
- five
- six
- fourteen
Explanation:
A bridge segments the LAN into separate collision domains. The figure in this scenario has five segments created between these two bridges. Therefore, there will be five collision domains (segments) on the LAN if the two bridges are directly connected as shown in the exhibit. Hubs do not create LAN segments; they act as port aggregators and signal amplifiers.It is also worth noting that with no router in the diagram, the entire network is a single broadcast domain. If a router were present, each of its interfaces could host a different subnet and each of those same interfaces would be a separate broadcast domain.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Describe and verify switching concepts -
With respect to the network shown below, which of the following statements are true when R2 sends a packet to the 192.168.6.0/24 network? (Choose all that apply.)

200-301 Part 13 Q06 123 - If RIPv1 is in use, the path taken will be R2 – R4 – R3
- If both RIPv2 and EIGRP are in use, the EIGRP route will be placed in the routing table
- If EIGRP is in use, the only path taken will be R2 – R4 – R3
- If RIPv2 is in use, the path taken will be R2 – R3
Explanation:
If both RIPv2 and EIGRP are in use, the EIGRP route will be placed in the routing table. If RIPv2 is in use, the path taken will be R2 – R3.EIGRP has a default administrative distance (AD) of 90, while RIPv2 has a default administrative distance (AD) of 120. The route learned by the routing protocol with the lowest AD will be placed in the routing table.
If you wanted to force R2 to use the RIPv2 route instead of the EIGRP route, this could be accomplished by changing the administrative distance of RIPv2 to a value less than 90, such as 80. The commands that would accomplish this are:
R2(config)# router rip R2(config-router)# distance 80
If either of the versions of RIP is in use, hop count is used to determine the route. The path with the least number of hops is R2 – R3.
If RIPv1 is in use, the path taken would be R2 – R3, not R2 – R4 – R3, because R2 – R3 has a lower hop count.
If EIGRP is in use, the path R2 – R4 – R3 will not be the only path taken. EIGRP load-balances two equal cost paths when they exist, and R2 – R4 – R3 and R2 – R1 – R3 are of equal cost so would both be used.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast distance vector and link-state routing protocols -
You have three EIGRP routers that are connected as shown in the diagram below.

200-301 Part 13 Q07 124 Router A and Router C do not seem to be exchanging information. You execute commands on all three routers, and receive as output the information shown below:

200-301 Part 13 Q07 125 What needs to be done to make Routers A and C start exchanging information?
- Execute the auto-summary command on Router A
- Execute the network 192.168.9.0 command under EIGRP 56 on Router C
- Correct the IP address on the S1 interface of Router C
- Recreate the EIGRP configuration on Router C as EIGRP 55
Explanation:
Router C is not displayed in the neighbor table of Router A, which indicates that Router C and Router A are not forming a neighbor relationship or exchanging information. This is because Router C does not have EIGRP configured for its S1 interface. You can see this is missing from its configuration in the output of the show run command for RouterC. To solve the issue, you should execute the network 192.168.9.0 command under the EIGRP 56 configuration on Router C. Then Router C will start sending hellos on that interface and the two routers will become neighbors.The show ip eigrp neighbors command displays the following information for each EIGRP neighbor. In parentheses is the value of each found in the output of router A for Router B:
IP address (192.168.10.2) Local interface (S1) Retransmit interval (13) Queue count (100)
There is no need to execute the auto-summary command on Router A. It will not affect the establishment of a neighbor relationship between Routers A and C.
There is no need to correct the IP address on the S1 interface of Router C. The address 192.168.9.1 is correctly located in the same subnet as the address on S0 of Router A.
Finally, changing the EIGRP configuration on Router C to EIGRP 55 will not help. Router C will not start sending hellos on its S1 interface until EIGRP is enabled on the S1 interface. Until then, the Routers A and C will not form a neighbor relationship and will not share information.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot EIGRP for IPv4 (excluding authentication, filtering, manual summarization, redistribution, stub) -
You are the network administrator for your company. You recently configured Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) in the network. You want to view output regarding all of the neighboring devices discovered by CDP. This information should include network address, enabled protocols, and hold time.
Which Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) command would allow you to accomplish this task?
- show cdp
- show cdp entry
- show cdp neighbor entries
- show cdp neighbors detail
Explanation:
In this scenario, you should use the show cdp neighbors detail command to view the details of the neighboring devices that were discovered by CDP. CDP is a Layer 2 (data link layer) protocol used to find information about neighboring network devices. The show cdp neighbors detail command is used to view details such as network address, enabled protocols, and hold time. The complete syntax of this command is:show cdp neighbors [type number] [detail]
The command parameters are defined in this way:
type: An optional parameter which specifies the type of interface used to connect to the neighbors for which you require information.
number: An optional parameter used to specify the interface number connected to the neighbors for which you want information.
detail: An optional parameter used to get detailed information about neighboring devices, such as network address, enabled protocols, software version and hold time.The following code is a sample partial output of the show cdp neighbors detail command:
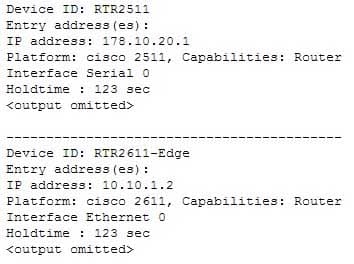
200-301 Part 13 Q08 126 The show cdp command is incorrect because this command is used to view global CDP information such as the timer and hold time.
The show cdp entry command is incorrect because this command is used to view information about a specific neighboring device.
The show cdp neighbor entries command is incorrect because this is not a valid Cisco IOS command.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify Layer 2 protocols -
If a routing table contains multiple routes for the same destination, which were inserted by the following methods, which route will the router use to reach the destination network?
- The route inserted by RIP
- The route inserted by OSPF
- The route inserted by BGP
- The route configured as a static route
Explanation:
A static route will be preferred because it has the lowest administrative distance. Routing protocols are dynamic routing methods. With the default configuration, static routes are preferred over dynamic routes.The default administrative distance for the offered options is:
– RIP 120
– OSPF 110
– eBGP 20
– Static 1When Routing Information Protocol (RIP), Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), and static routing is enabled on a router, the router will prefer the static route.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Interpret the components of routing table -
Which Cisco IOS command is used to view the information about the interfaces on which Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is enabled?
- show cdp interface
- show interfaces
- show cdp
- show cdp interfaces
Explanation:
The show cdp interface command is used to view the information about the interfaces on which Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is enabled.The syntax of the command is as follows:
Router# show cdp interface [type number]
The parameters of the command are as follows:
type: specifies the type of interface for which information is required
number: specifies the number of interfaces for which information is requiredThe output of the show cdp interface command is as follows:
Router#show cdp interface Serial0 is up, line protocol is up, encapsulation is SMDS Sending CDP packets every 100 seconds Holdtime is 300 seconds Serial1 is up, line protocol is up, encapsulation is SMDS Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds Ethernet0 is up, line protocol is up, encapsulation is ARPA Sending CDP packets every 120 seconds Holdtime is 360 seconds
The show interfaces command is incorrect because this command is used to view configured interfaces on the router. The output of this command can be very useful, especially when troubleshooting a connection with no connectivity. Consider the output of the command on the following two routers that are connected with a serial interface:
NewYork#show interfaces s0 Serial0 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is HD64570 Internet Address is 192.168.10.1/24 MTU 1500 bytes,BW 1544 Kbit Reliability 255/255 Encapsulation HDLC, loopback not set Keepalive set (10 sec) LosAngeles#show interfaces s1 Serial0 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is HD64570 Internet Address is 192.168.11.2/24 MTU 1500 bytes,BW 56000 Kbit Reliability 255/255 Encapsulation HDLC, loopback not set Keepalive set (10 sec)
Notice that the following settings are correct:
– The encapsulation matches (HDLC)
– The physical connection is good (indicated by Serial0 is up)Notice, however, that the IP addresses 192.168.10.1 and 192.168.11.2 are NOT in the same subnet when using a 24-bit mask. With a 24-bit mask, the two addresses should agree through the first three octets, and these do not. Problems such as this can be located through inspection of the output produced by the show interfaces command.
The show cdp command is incorrect because this command is used to view the global CDP information.
The show cdp interfaces command is incorrect because this command does not exist in the Cisco command reference. There is a show cdp interface command, which displays CDP activity on a per-interface basis.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify Layer 2 protocols -
Which of the following is NOT a mode of Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP)?
- dynamic auto
- dynamic trunk
- dynamic desirable
- nonegotiate
Explanation:
Dynamic trunk is not a DTP mode. DTP is a Cisco proprietary trunk negotiation protocol and is used to determine if two interfaces on connected devices can become a trunk. There are five modes of DTP:
– Trunk: Puts the interface into permanent trunking mode and negotiates to convert the link into a trunk link. The interface becomes a trunk interface even if the neighboring interface does not agree to the change.
– Access: Puts the interface into permanent nontrunking mode and negotiates to convert the link into a nontrunk link. The interface becomes a nontrunk interface even if the neighboring interface does not agree to the change.
– Dynamic desirable: Makes the interface actively attempt to convert the link to a trunk link. The interface becomes a trunk interface if the neighboring interface is set to trunk, desirable, or auto mode.
– Dynamic auto: Makes the interface willing to convert the link to a trunk link. The interface becomes a trunk interface if the neighboring interface is set to trunk or desirable mode. This is the default mode for all Ethernet interfaces in Cisco IOS.
– Nonegotiate: Puts the interface into permanent trunking mode but prevents the interface from generating DTP frames. You must configure the neighboring interface manually as a trunk interface to establish a trunk link. Use this mode when connecting to a device that does not support DTP.If one side’s mode of link is in trunk mode, dynamic desirable mode, or dynamic auto mode, and the other side is trunk or dynamic desirable, a trunk will form. Nonegotiate mode enables trunking but disables DTP.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify Layer 2 protocols -
You want to encrypt and transmit data between peer routers with high confidentiality. Which protocol option should you choose?
- Authentication Header (AH) in tunnel mode
- Authentication Header (AH) in transport mode
- Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) in tunnel mode
- Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) in transport mode
Explanation:
You should choose Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) in tunnel mode to encrypt and transmit data between peer routers with high confidentiality. Two protocols can be used to build tunnels and protect data traveling across the tunnel:
– Authentication Header (AH) uses protocol 51.
– ESP uses protocol 50.AH is defined in Request for Comments (RFC) 1826 and 2402. AH does not perform data encryption and therefore, information is passed as clear text. The purpose of AH is to provide data integrity and authentication, and anti-reply service (optional). It ensures that a packet that crosses the tunnel is the same packet that left the peer device and no changes have been made. It uses a keyed hash to accomplish this.
ESP is defined in RFC 2406. ESP can provide data integrity and authentication, but its primary purpose is to encrypt data crossing the tunnel. There are two reasons why ESP is the preferred building block of IPSec tunnels:
– The authentication component of ESP does not include any Layer 3 information. Therefore, this component can work in conjunction with a network using Network Address Translation (NAT).
– On Cisco devices, ESP supports encryption using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Data Encryption Standard (DES), or Triple DES (3DES).Tunnel mode is used between Virtual Private Network (VPN) gateways such as routers, firewalls, and VPN concentrators.
Transport mode is used between end-stations or between an end-station and a VPN gateway.
The options AH in tunnel mode and AH in transport mode are incorrect because AH does not provide encryption.
The option ESP in transport mode is incorrect because transport mode is used between end-stations or between an end-stations and a VPN gateway.
Objective:
WAN Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Describe WAN access connectivity options -
Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding flow control?
- It determines the rate at which the data is transmitted between the sender and receiver.
- It can help avoid network congestion.
- It manages the data transmission between devices.
- It uses a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) to identify and remove corrupted data.
Explanation:
It is NOT true that flow control uses a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) to identify and remove corrupted data. CRC is an error-checking schema that checks and removes corrupted data. It is a calculation that is performed at the source. Flow control uses CRC to identify corrupted data for the purpose of requesting re-transmission, but it does not use CRC to remove the corrupted data from the packet. If corruption is detected, the entire packet will be dropped.Flow control is a function that ensures that a sending device does not overwhelm a receiving device. The following statements are TRUE regarding flow control:
– Flow control controls the amount of data that the sender can send to the receiver.
– Flow control determines the rate at which the data is transmitted between the sender and receiver.
– Flow control of certain types can aid in routing data around network congestionTypes of flow control include windowing, buffering, and congestion avoidance:
– Windowing- a process whereby the sender and receiver agree to increase or decrease the number of packets received before an acknowledgment is required based on network conditions. This packet number is called a window. When conditions are favorable, the window size will be increased. During unfavorable network conditions, it will be decreased.
– Buffering- the ability of a network card to store data received but not yet processed in a buffer (memory). This enhances its ability to handle spikes in traffic without dropping any data.
– Congestion avoidance – a process that some routing protocols can perform by adding information in each frame that indicates the existence of congestion on the network, allowing the router to choose a different routing path based on this information.Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast OSI and TCP/IP models -
The partial output displayed in the exhibit is a result of what IOS command? (Click on the Exhibit(s) button.)
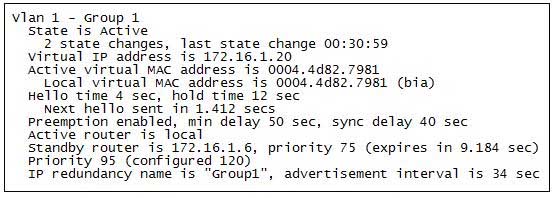
200-301 Part 13 Q14 127 -
switch# show running-config
-
switch# show standby vlan1 active brief
-
switch# show hsrp 1
-
switch# show standby
Explanation:
The command shows standby produces the output displayed in the exhibit. This command displays information about HSRP on all configured interfaces and for all HSRP groups. Important information in the exhibit includes that this router is the active router, the virtual IP address for the HSRP group is 172.16.1.20, the address of the standby router is 172.16.1.6, and the router is configured to preempt.The command show running-config will display the complete configuration of the device, including the configuration of HSRP, but will not display the current status of HSRP on the switch.
The command show standby vlan 1 active brief provides a summary display of all HSRP groups on the switch that are in the active state. This output would provide basic information, not nearly the detail indicated in the exhibit. The following is an example of output for show standby vlan 1 active brief:
Interface Grp Prio P State Active addr Standby addr Group addr
Vlan1 0 120 Active 172.16.1.5 Unknown 172.16.1.20The command show hsrp 1 is not valid due to incorrect syntax.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic HSRP -
-
You are configuring an authenticated connection between two routers named Tacoma and Lansing. The connection on the Lansing end is correctly set up with a password of keypass. You are directing an assistant to configure the name and password on Tacoma.
Which of the following commands would be correct to complete this authenticated connection?
- username Tacoma password keypass
- username Lansing keypass password
- username Tacoma keypass password
- username Lansing password keypass
Explanation:
To complete the configuration, you should run the command username Lansing password keypass. This command creates a user account for the Lansing router with a password of keypass.When creating an authenticated connection between the routers, a user account must be created for the other router. The password configured must match on both ends.
When examining the output produced by the show running-configuration command for two routers, the output should read as below:

200-301 Part 13 Q15 128 The lines that display enable password cisco and enable password cisco1 represent local passwords to enable privileged mode on the local router. These passwords do not have to match. The lines of output that must display matching passwords are username Lansing password keypass and username Tacoma password keypass.
You should not run the command username Tacoma password keypass. The username Tacoma portion of the command will create an account named Tacoma. You need an account for the other router, Lansing.
You should not run the command username Lansing keypass password. The password portion of the command must follow the syntax password [correct_password].
You should not run the command username Tacoma keypass password. The username Tacoma portion of the command will create an account for the wrong router, and the password portion of the command must follow the syntax password [correct_password].
Objective:
WAN Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify PPP and MLPPP on WAN interfaces using local authentication -
Which command is NOT mandatory for inclusion in a plan to implement IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to monitor IP connections and traffic?
- ip sla
- ip sla schedule
- ip sla reset
- icmp-echo
Explanation:
The ip sla reset command is not mandatory for an implementation plan to configure IP SLAs for monitoring IP connections and traffic. This command causes the IP SLA engine to either restart or shutdown. As a result, all IP SLAs operations are stopped, IP SLA configuration information is erased, and IP SLAs are restarted. The IP SLAs configuration information will need to be reloaded to the engine.The following commands are essential to the implementation plan:
ip sla ip sla schedule icmp-echo
The ip sla command allows you to configure IP SLAs operations. When you execute this command in the global configuration mode, it enables the IP SLA configuration mode. In the IP SLA configuration mode, you can configure different IP SLA operations. You can configure up to 2000 operations for a given IP SLA ID number.
The icmp-echo command allows you to monitor IP connections and traffic on routers by creating an IP SLA ICMP Echo operation. This operation monitors end-to-end response times between routers.
The ip sla schedule command allows you to schedule the IP SLA operation that has been configured. With this command, you can specify when the operation starts, how long the operation runs, and the how long the operation gathers information. For example, if you execute the ip sla schedule 40 start-time now life forever command, the IP SLA operation with the identification number 40 immediately starts running. This is because the now keyword is specified for the start-time parameter. Using the forever keyword with the life parameter indicates that the operation keeps collecting information indefinitely. Note that you cannot re-configure the IP SLA operation after you have executed the ip sla schedule command.
The information gathered by an IP SLA operation is typically stored in RTTMON-MIB. A Management Information Base (MIB) is a database hosting information required for the management of routers or network devices. The RTTMON-MIB is a Cisco-defined MIB intended for Cisco IOS IP SLAs. RTTMON MIB acts as an interface between the Network Management System (NMS) applications and the Cisco IOS IP SLAs operations.
Objective:
Infrastructure Management
Sub-Objective:
Troubleshoot network connectivity issues using ICMP echo-based IP SLA -
What Cisco Catalyst switch feature can be used to define ports as trusted for DHCP server connections?
- DHCP snooping
- port security
- 802.1x
- private VLANs
Explanation:
DHCP snooping is used to define ports as trusted for DHCP server connections. The purpose of DHCP snooping is to mitigate DHCP spoofing attacks. DHCP spoofing is an attack that can be used to force user traffic through an attacking device. This is accomplished by an attacker responding to DHCP queries from users. Eliminating the response from the correct DHCP server would make this more effective, but if the attacker’s response gets to the client first, the client will accept it.The DHCP response from the attacker will include a different gateway or DNS server address. If they define a different gateway, the user traffic will be forced to travel through a device controlled by the attacker. This will allow the attacker to capture traffic and gain company information. If the attacker changes the DNS server in the response, they can use their own DNS server to force traffic to selected hosts to go to a device they control. Again, this would allow the attacker to capture traffic and gain information.
DHCP snooping can be used to determine what ports are able to send DHCP server packets, such as DHCPOFFER, DHCPACK, and DHCPNAK, from the company DHCP server. DHCP snooping can also cache the MAC address to IP address mapping for clients receiving DHCP addresses from a valid DHCP server.
The three required steps to implement DHCP snooping are:
1. Enable DHCP snooping globally with the ip dhcp snooping command:switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping
2. Enable DHCP snooping for a VLAN with the vlan parameter:
switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping vlan vlan # (for example, ip dhcp snooping 10 12 specifies snooping on VLANs 10 and 12)
3. Define an interface as a trusted DHCP port with the trust parameter:
switch(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping trust
When specifying trusted ports, access ports on edge switches should be configured as untrusted, with the exception of any ports that may have company DHCP severs connected. Only ports where DHCP traffic is expected should be trusted. Most certainly, ports in any area of the network where attacks have been detected should be configured as untrusted.
Some additional parameters that can be used with the ip dhcp snooping command are:
– switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping verify mac-address – this command enables DHCP MAC address verification.
– switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping information option allow-untrusted – this command enables untrusted ports to accept incoming DHCP packets with option 82 information. DHCP option 82 is used to identify the location of a DHCP relay agent operating on a subnet remote to the DHCP server.When DHCP snooping is enabled, no other relay agent-related commands are available. The disabled commands include:
ip dhcp relay information check global configuration ip dhcp relay information policy global configuration ip dhcp relay information trust-all global configuration ip dhcp relay information option global configuration ip dhcp relay information trusted interface configuration
Private VLANs are a method of protecting or isolating different devices on the same port and VLAN. A VLAN can be divided into private VLANs, where some devices are able to access other devices and some are completely isolated from others. This was designed so service providers could keep customers on the same port isolated from each other, even if the customers had the same Layer 3 networks.
Port security is a method of only permitting specified MAC addresses access to a switch port. This can be used to define what computer or device can be connected to a port, but not to limit which ports can have DHCP servers connected to them.
802.1x is a method of determining authentication before permitting access to a switch port. This is useful in restricting who can connect to the switch, but it cannot control which ports are permitted to have a DHCP server attached to it.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Describe common access layer threat mitigation techniques -
You execute the ping command from a host, but the router does not have a path to its destination.
Which of the following ICMP message types will a client receive from the router?
- ICMP redirect
- ICMP time exceeded
- ICMP destination unreachable
- ICMP echo-reply
Explanation:
When a router receives a ping packet and has no route to the destination in its routing table, it will respond to the client with an ICMP destination-unreachable message. Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a Layer 3 protocol used to test the connectivity between hosts in a network. There are six types of unreachable destination message:
1. Network unreachable
2. Host unreachable
3. Protocol unreachable
4. Port unreachable
5. Fragmentation needed and Don’t Fragment (DF) bit set
6. Source route failedAn ICMP redirect message would not be received. This type of response is received when the router is configured to direct clients to a different router for better routing.
An ICMP time-exceeded message would not be received. This type of response occurs when the router successfully sent the packet but did not receive an answer within the allotted time; in other words, the time-to-live of the ICMP packet has been exceeded.
An ICMP echo-reply message would not be received. This would be the response received if the destination received the ping command and responded successfully.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Troubleshoot basic Layer 3 end-to-end connectivity issues -
Examine the partial output from two adjacent routers:

200-301 Part 13 Q19 129 Which of the following statements describes why the two routers are NOT forming an OSPF neighbor adjacency?
- The process IDs do not match
- The router IDs are misconfigured
- The distance is misconfigured
- The reference bandwidth does not match
Explanation:
The output shows that the router IDs for RTR78 and RTR79 are the same value, which should not be the case. One of the two routers has been misconfigured with the other router’s ID. This will prevent an OSPF neighbor adjacency from forming.Other issues can that can prevent an adjacency are:
– Mismatched OSPF area number
– Mismatched OSPF area type
– Mismatched subnet and subnet mask
– Mismatched OSPF HELLO and dead timer valuesThe process IDs do not have to match. It does not matter whether they match or do not match because the process ID is only locally significant on the device.
The administrative distance is not misconfigured in the output. Both routers are using the default OSPF administrative distance of 110.
If the reference bandwidths do not match, it will affect the calculation of the path cost, but it will not prevent an adjacency from forming.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot single area and multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4 (excluding authentication, filtering, manual summarization, redistribution, stub, virtual-link, and LSAs) -
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)?
- Is a Cisco-proprietary routing protocol
- Has a default administrative distance of 110
- Supports authentication
- Uses cost as the default metric
Explanation:
OSPF is not a Cisco-proprietary routing protocol. It is an industry standard protocol supported by a wide range of vendors. The following are characteristics of OSPF:
– Uses Internet Protocol (IP) protocol 89.
– Has a default administrative distance of 110.
– Is an industry standard protocol (non Cisco-proprietary).
– Supports Non-Broadcast Multi-Access (NBMA) networks such as frame relay, X.25, and Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM). The default hello interval for NBMA networks is 30 seconds.
– Supports point-to-point and point-to-multipoint connections.
– Supports authentication.
– Uses 224.0.0.6 as multicast address for ALLDRouters.
– Uses 224.0.0.5 as multicast address for ALLSPFRouters.
– Uses link-state updates and SPF calculation that provides fast convergence.
– Recommended for large networks due to good scalability.
– Uses cost as the default metric.Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast interior and exterior routing protocols