200-301 : Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) : Part 16
-
Which is the valid IP address range that can be assigned to hosts on the subnet that includes the address 172.16.4.6/23?
- 172.16.2.1 – 172.16.4.254
- 172.16.3.1 – 172.16.5.254
- 172.16.4.1 – 172.16.5.254
- 172.16.4.1 – 172.16.4.254
Explanation:
172.16.4.1 – 172.16.5.254 is the valid IP address range that can be assigned to hosts on the subnet that includes the address 172.16.4.6/23.To determine the range of addresses that can be assigned in a subnet, you must first determine the network ID and broadcast address of the subnetwork. All addresses that can be assigned to hosts will lie between these two endpoints. The network ID can be obtained by determining the interval between subnet IDs. With a 23-bit mask, the decimal equivalent of the mask will be 255.255.254.0. The interval between subnets can be derived by subtracting the value of the last octet of the mask from 256. In this case that operation would be 256 – 254. Therefore, the interval is 2, and it is applied in the third octet where the subnet mask ends.
The first network ID will always be the classful network you started with (in this case 172.16.0.0). Then each subnetwork ID will fall at 16-bit intervals as follows:
172.16.0.0
172.16.2.0
172.16.4.0
172.16.6.0At 172.16.6.0 we can stop because the address that we are given in the scenario, 172.16.4.6, is in the network with a subnet ID of 172.16.4.0. Therefore, since the broadcast address for this network will be 1 less than the next subnet ID, or 172.16.5.255, the valid range is 172.16.4.1 – 172.16.5.254.
All the other options are incorrect because these are not valid IP address ranges for this scenario.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Apply troubleshooting methodologies to resolve problems -
You are the network administrator for your company and have configured Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) in your network. You recently noticed that when devices send large numbers of CDP neighbor announcements, some devices are crashing. You decide to disable CDP on the router.
Which command should you use to achieve the objective?
- no cdp run
- set cdp disable
- no cdp enable
- no cdp advertise-v2
Explanation:
You should use the no cdp run command to disable CDP on the router. Due to a known vulnerability regarding the handling of CDP by Cisco routers and switches when devices send large numbers of CDP neighbor announcements, some devices can crash or cause abnormal system behavior. To overcome this problem, you can disable CDP for the entire router by using the no cdp run command.You cannot use the set cdp disable command to disable CDP on the router. This command disables CDP on an entire Catalyst switch.
You cannot use the no cdp enable command to disable CDP on the router. This command disables CDP on a specific interface.
You cannot use the no cdp advertise-v2 command to disable CDP on the router. This command disables CDPv2 advertisements.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify Layer 2 protocols -
You are working with an Internet Service Provider (ISP) as network manager. A corporate client approaches you to lease a public IP subnet that can accommodate 250 users. You have assigned him the 192.25.27.0 subnet.
What subnet mask should be assigned to this IP address so that it can accommodate the number of users required by the corporate client?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.252
Explanation:
The 192.25.27.0 subnet should be assigned the subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 to accommodate 250 users. This subnet mask can accommodate a maximum of 254 hosts. The number of hosts that can reside on a subnet can be calculated using the formula 2n – 2 = x, where n is equal to the number of hosts bits in the mask and x is the resulting number of hosts. 2 is subtracted from the results to represent the two address, the network ID and the broadcast address, that cannot be assigned to computers in the subnet. Since the 255.255.255.0 mask leaves 8 bits at the end of the mask, the formula will be 28 – 2, which is 256 – 2, which equals 254.In situations where the same subnet mask must be used for multiple interfaces on a router, the subnet mask that is chosen must provide capacity sufficient for the largest number of hosts on any single interface while also providing the required number of subnets. For example, in the diagram below, the three interfaces on the router R2 have 16, 32 and 58 users respectively on each interface:
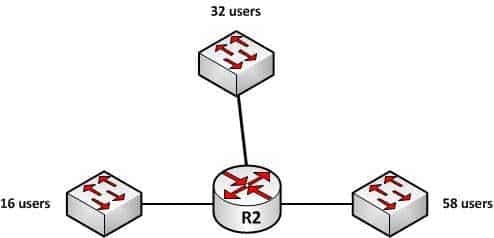
200-301 Part 16 Q03 149 If each interface must have the same subnet mask, the subnet mask would need to be one that yields at least 58 addresses to support the interface with the highest host count and yields at least 3 subnets as well.
If the chosen classful networks were 128.107.4.0/24, the correct mask would be 255.255.255.192. Since the mask is currently 255.255.255.0 (/24), by borrowing 2 bits to /26 or 255.255.255.192, we will get 4 subnets (22 = 4) and each subnet will yield 62 hosts (26 – 2 = 62).
With a subnet mask of 255.255.255.128, the 192.25.27.0 subnet can accommodate only 126 hosts. The mask 255.255.255.128 leaves 7 host bits in the mask and when we plug that into the formula we get 27 – 2, which equals 126.
With a subnet mask of 255.255.255.224, the 192.25.27.0 subnet can accommodate only 30 hosts. The mask 255.255.255.224 leaves 5 host bits in the mask and when we plug that into the formula we get 25 – 2, which equals 30.
With a subnet mask of 255.255.255.252, the IP address 192.25.27.24 can accommodate only two hosts. The mask 255.255.255.252 leaves 2 host bits in the mask and when we plug that into the formula we get 22 – 2, which equals 2.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Apply troubleshooting methodologies to resolve problems -
Which two features do Cisco routers offer to mitigate distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks? (Choose two.)
- Anti-DDoS guard
- Scatter tracing
- Access control lists (ACLs)
- Flow control
- Rate limiting
Explanation:
Cisco routers use access control lists (ACLs) and blackholing features to help mitigate distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. A DoS attack is an attack in which legitimate users are denied access to networks, systems, or resources. One of the most common DoS attacks is the DDoS attack, which is executed by using multiple hosts to flood the network or send requests to a resource. The difference between DoS and DDoS is that in a DoS attack, an attacker uses a single host to send multiple requests, whereas in DDoS attacks, multiple hosts are used to perform the same task.Cisco routers offer the following features to mitigate DDoS attacks:
– ACLs: Filter unwanted traffic, such as traffic that spoofs company addresses or is aimed at Windows control ports. However, an ACL is not effective when network address translation (NAT) is implemented in the network.
– Rate limiting: Minimizes and controls the rate of bandwidth used by incoming traffic.
– Traffic-flow reporting: Creates a baseline for the network that is compared with the network traffic flow, helping you detect any intrusive network or host activity.
– Apart from these features offered by Cisco routers, the following methods can also be used to mitigate DDoS attacks:
– Using a firewall, you can block or permit traffic entering a network.
– The systems vulnerable to attacks can be shifted to another location or a more secure LAN.
– Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), such as Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) and Host Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS), can be implemented to detect intrusive network or host activity such as a DoS attack, and raise alerts when any such activity is detected.Anti-DDoS guard and scatter tracing are incorrect because these features are not offered by Cisco routers to mitigate DDoS attacks.
Flow control is incorrect because flow control is used to prevent the loss of traffic between two devices.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic device hardening -
Which Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) message is sent by a host in the network to test connectivity with another host?
- ICMP redirect message
- ICMP echo-request message
- ICMP time-exceeded message
- ICMP destination-unreachable message
Explanation:
An ICMP echo-request message is sent by a host in the network to test connectivity with another host. An ICMP echo-request message is generated by the ping command. ICMP is a network-layer protocol that uses packets for reporting informational messages. When a host receives an echo-request (a ping), it responds by sending back an echo-reply message.An ICMP redirect message is sent to the source host by the router to make the routing process more efficient.
An ICMP time-exceeded message indicates that the Time-to-Live (TTL) field of the IP packet has reached zero.
An ICMP destination-unreachable message is sent by the router to indicate that the router is unable to send the packet to its intended destination.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot IPv4 addressing and subnetting -
Host A is configured for DHCP, but it is not receiving an IP address when it powers up.
What is the most likely cause? (Click the Exhibit(s) button to view the network diagram.)
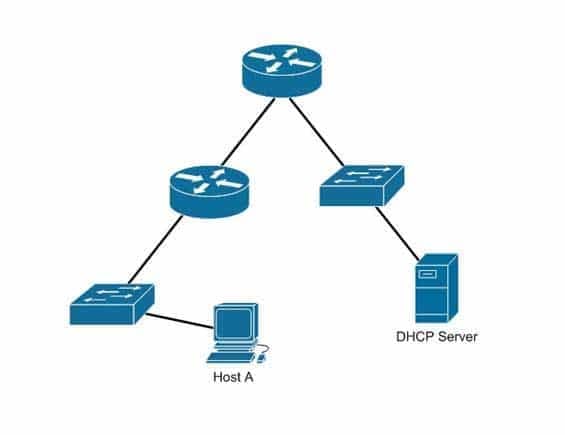
200-301 Part 16 Q06 150 - The DHCP server is on the wrong subnet.
- Routers do not forward broadcast traffic.
- The DHCP server is misconfigured.
- Port security is enabled on the switch.
Explanation:
Host A is not receiving a DHCP configuration because its initial DHCP Discover frame is a broadcast, and routers do not forward broadcast frames by default.A DHCP client sends out a DHCP Discover packet when booting up, enveloped within an Ethernet broadcast frame. The broadcast frame will be flooded by switches, but filtered by routers. There must either be a DHCP server on the local subnet or a DHCP Relay Agent, which will forward the request from the local subnet to the DHCP server.
The DHCP server is not on the wrong subnet. A DHCP server can be centrally located and configured to support multiple remote subnets, as long as those subnets have DHCP Relay Agents configured to forward the DHCP Discover requests.
No information is provided on the DHCP server configuration. The router is the most obvious cause of the problem, so this option is incorrect.
Port security can be configured to restrict hosts based on the MAC address, but the scenario does not provide information on any port security configurations. The router is the most obvious cause of the problem as shown in the network exhibit.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify DHCP on a router (excluding static reservations) -
Which command is used on a Catalyst 2950 series switch to enable basic port security on the interface?
- set port-security
- switchport port-security
- set port-security enable
- switchport port-security enable
Explanation:
The switchport port-security command is an interface configuration command used on a Catalyst 2950 series switch to enable basic port security on the interface. The syntax of the command is as follows:switch(config-if)#switchport port-security
Switchport security can be used to:
– Limit the computers that are allowed to connect to the LAN (by specifying the MAC addresses allowed on the port)
– Limit the number of MAC address allowed to be accessing a port
– Set the action the port will take when a violation of the security rule occursThe set port-security, set port-security enable, and switchport port-security enable commands are incorrect because these are not valid Cisco IOS commands.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot port security -
Which VLAN can NOT be filtered through the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) Pruning feature of Cisco switches?
- VLAN 1
- VLAN 10
- VLAN 100
- VLAN 1000
Explanation:
VLAN 1 traffic cannot be pruned. Cisco recommends that VLAN 1 be used for management of VLANs.VTP pruning is a Cisco VTP feature that allows switches to dynamically delete or add VLANs to a trunk for traffic transmission. It creates an efficient switching network by optimal use of available trunk bandwidth.
The options 10, 100, and 1000 are incorrect because these VLAN numbers can be pruned. By default, VLANs 2 to 1000 are eligible for pruning.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot VLANs (normal/extended range) spanning multiple switches -
DRAG DROP
Click and drag the network devices from the left to their appropriate descriptions on the right.
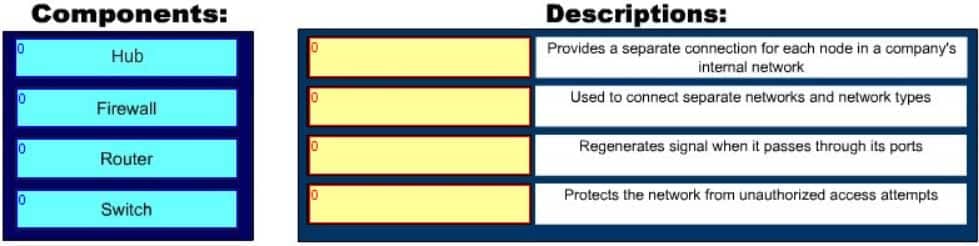
200-301 Part 16 Q09 151 Question 
200-301 Part 16 Q09 151 Answer Explanation:
The following are some of the network devices and their corresponding functions:
– Hub: Regenerates a signal when it passes through its ports. Hubs provide a common connection point for network devices. Hubs are generally used for LAN connectivity and works at Layer 1 of the OSI model.
– Firewall: Protects the network from unauthorized access attempts. It is typically placed between the Internet and a private network, but can also be placed between two private networks.
– Router: Provides a means for connecting LAN and WAN segments together. A router separates broadcast domains while connecting different logical and physical networks.
– Switch: Provides a separate collision domain for each node in a company’s internal network. Switches work at Layer 2 in the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model and perform their function by observing the source and destination MAC addresses of packets. Because of this method of operation, it can provide dedicated bandwidth to each connected node. Advantages of switches over hubs include the ability to filter frames based on MAC addresses and to allow simultaneous frame transmissions. The diagram below illustrates the ability of a switch to provide a separate collision domain to each device, as compared to the hub, which cannot.
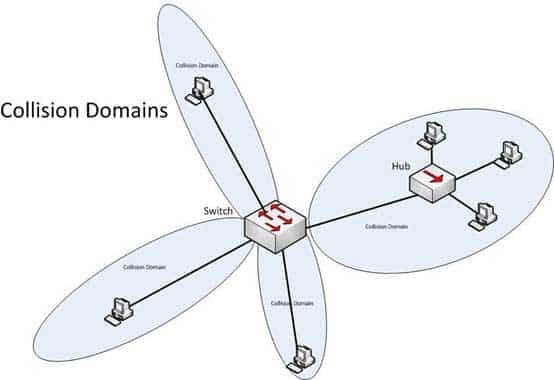
200-301 Part 16 Q09 152 Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Describe the impact of infrastructure components in an enterprise network -
Which of the following TCP port numbers is used by Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)?
- 23
- 21
- 53
- 80
- 57
- 25
Explanation:
TCP port 25 is assigned to SMTP. SMTP is a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)/ Internet Protocol (IP) protocol used to send and receive e-mail messages.Important TCP port number assignments are as follows:
– TCP port 23 is used by Telnet to allow remote logins.
– TCP port 21 is assigned to File Transfer Protocol (FTP) for FTP control. FTP also uses port 20 to transmit FTP data.
– TCP and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port 53 is assigned to Domain Name Service (DNS), which is used to convert hostnames into Internet Protocol (IP) addresses.
– TCP port 80 is used by Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), which is the base for transferring Web pages over the Internet.
– TCP port 57 is assigned to Mail Transfer Protocol (MTP).
– TCP port 22 is used by Secure Shell (SSH).
– UDP ports 67 and 68 are used by Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
– UDP port 69 is used by Trivial FTP (TFTP).
– TCP port 110 is used by Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3).
– UDP port 161 is used by Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
– TCP port 443 is used by Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).TCP port numbers help to direct data to the appropriate application, service, or application window. TCP port numbers ensure that data is displayed in the correct browser window when accessing Web data from multiple sources, and ensures it is directed to the proper application or service when received.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot IPv4 and IPv6 access list for traffic filtering -
Which Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) command is used to encrypt passwords on Cisco routers?
- password secure
- service encryption-password
- service password-encryption
- enable password
Explanation:
The service password-encryption command is used to encrypt passwords on Cisco routers. It is used to encrypt all passwords configured on the router, both current and future. This means all passwords in the plain text configuration file will be encrypted. This command is issued in global configuration mode. The syntax of the command is as follows:Router(config)# service password-encryption
This command does not have any parameters.
Once executed any password in the configuration file will appear similar to what is shown below when the running or startup configuration files are viewed:
R1#show run <output omitted> line console 0 password 7 09-4f60C0B1C1B login <output omitted>
The password secure and service encryption-password commands are incorrect because they are not valid Cisco IOS commands.
The enable password command is used to set the privileged EXEC mode password, and does not encrypt the password by default.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic device hardening -
A new security policy has been adopted by your company. One of its requirements is that only one host is permitted to attach dynamically to each switch port. The security settings on all of the ports have been altered from the default settings.
You execute the following command on all switch ports of Switch A:
SwitchA(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 1
After executing the command, you discover that users in the Sales department are still successfully plugging a hub into a port and then plugging two or three laptops into the hub.
What did you do wrong?
- The command should be executed at the global prompt.
- The command should be executed as switchport port-security maximum 0.
- You also need to execute the switchport port-security violation shutdown command at the global prompt.
- You also need to execute the switchport port-security violation shutdown command on each switch port.
Explanation:
When configuring switch port security to enforce the policy described in the scenario, two commands are required. One command specifies how many addresses are allowed per switch port and the other tells the switch what to do when a violation occurs. Configuring the first without the second is like creating a rule without enforcing the rule. Both commands must be executed on each switch port, as shown in the following example:switchA(config)# interface fa0/22 switchA(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 1 switchA(config-if)# switchport port-security violation shutdown
By default, ports are configured to shut down on a violation, but the scenario states the default settings have been altered.
The switchport port-security violation command can be set to shutdown, restrict, or protect. The shutdown option shuts down the port if there is a security violation, but does not send an SNMP trap logging the violation. The restrict option drops all packets from insecure hosts at the port-security process level and increments the security-violation count, and can send an SNMP trap. The protect option drops all the packets from the insecure hosts at the port-security process level, but does not increment the security-violation count or send an SNMP trap.
You should not execute either the switchport port-security violation command or the switchport port-security maximum command at the global prompt. Both commands must be executed on each switch port.
You should not execute the command switchport port-security maximum 0. This would tell the switch to not allow any addresses at all per switch port.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot port security -
Which service is denoted by TCP/UDP port number 53?
- Domain Name Service (DNS)
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- Telnet
- HTTP
Explanation:
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port number 53 is assigned to Domain Name Service (DNS), which is used to convert hostnames into Internet Protocol (IP) addresses.Some common TCP and UDP port number assignments are as follows:
– port 25: Assigned to Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), a TCP protocol used to send and receive e-mail messages.
– port 23: Assigned to Telnet to allow remote logins and command execution.
– port 21: Assigned to File Transfer Protocol (FTP). It is used to control FTP transmissions. Port number 20 is also used by FTP for FTP data.
– port 80: Assigned to Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), which is the base for transferring Web pages over the Internet.Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot IPv4 and IPv6 access list for traffic filtering -
Which of the following is NOT true of APIC-EM?
- It supports greenfield but not brownfield deployments
- It provides a single point for network automation
- It saves time and cost
- It is open and programmable
Explanation:
Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module (APIC_EM) is an SDN controller platform that supports both greenfield implementations, which use no previous code and design from the ground up, and brownfield implementations, which incorporate existing code.APIC-EM does provide a single point for network automation. This automation leads to both time and cost savings.
APIC-EM uses an open and programmable approach to devices, policies, and analytics.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Verify ACLs using the APIC-EM Path Trace ACL analysis tool -
Which two statements represent physical security guidelines that should be followed during Cisco security deployment? (Choose two.)
- Potential security breaches should be evaluated.
- Network equipment should be accessed remotely with Secure Socket Layer (SSL) instead of Telnet.
- Images should be managed using File Transfer Protocol (FTP) and Secure FTP (SFTP) instead of Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP).
- Simple Network Management Protocol version 3 (SNMPv3) should be used for security and privacy features.
- The potential impact of stolen network resources and equipment should be assessed.
Explanation:
Potential security breaches should be evaluated and the potential impact of stolen network resources and equipment should be assessed when designing the physical security architecture during Cisco security deployment.Physical security is considered during security implementation to increase the strength of the complete security design. It helps to protect and limit access to network resources and physical network equipment. The following physical security guidelines should be followed during Cisco security deployment:
– Potential security breaches should be evaluated.
– The impact of stolen network resources and equipment should be accessed.
– Physical access control such as locks and alarms should be used.
– To secure traffic flowing on networks outside the user control, a control mechanism such as cryptography should be used.All the other options are incorrect because they do not represent physical security guidelines. They deal more with the transmission of information and the performance and security implications of that transmission rather than the protection of physical devices.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic device hardening -
You are configuring a Cisco router.
Which command would you use to convey a message regarding the remote access security policy of your organization to a user logging into the router?
- hostname
- banner motd
- description
- boot system
- terminal monitor
Explanation:
The banner motd command is used to specify a message of the day (MOTD) banner to users logging into the router. This is a global configuration mode command and is generally used to communicate routers identification information, display any warning specific to the router, or display a remote access security policy, such as “Unauthorized access to the router is prohibited.” The syntax for this command is as follows:banner motd [d message d]
d is the delimiter character. It can be any character of the administrator’s choice, with the limitation that the delimiter character cannot be used in the message text.
The hostname command is a global configuration command to assign the router a name for identification. The command syntax is hostname [name].
The description command is an interface configuration mode command that sets a description for that interface.
The boot system command is used to specify the path to the primary IOS file. It is a global configuration command.
The terminal monitor command is used to direct debug and system error message to the monitor when connected to a router using telnet. When you are connected to a router using telnet and you issue the debug command, by default the output can only have been seen through a console session with that router. Executing the terminal monitor command directs that output to the terminal session where it can be viewed.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic device hardening -
What switch security configuration requires AAA to be configured on the switch?
- VACL
- 802.1x
- Private VLAN
- port security
Explanation:
802.1x requires AAA to be configured on the switch. 802.1x uses AAA authentication to control access to the port.The overall steps required to configure a switch for 802.1x are:
– Enable AAA on the switch.
– Define the external RADIUS server(s) and the key to be used for encryption.
– Define the authentication method.
– Enable 802.1x on the switch.
– Configure each switch port that will use 802.1x.
– Optionally allow multiple hosts on the switch port.Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Describe device security using AAA with TACACS+ and RADIUS -
Which two features do Cisco routers offer to mitigate distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks? (Choose two.)
- Anti-DDoS guard
- Scatter tracing
- Access control lists (ACLs)
- Flow control
- Rate limiting
Explanation:
Cisco routers use access control lists (ACLs) and blackholing features to help mitigate distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. A DoS attack is an attack in which legitimate users are denied access to networks, systems, or resources. One of the most common DoS attacks is the DDoS attack, which is executed by using multiple hosts to flood the network or send requests to a resource. The difference between DoS and DDoS is that in a DoS attack, an attacker uses a single host to send multiple requests, whereas in DDoS attacks, multiple hosts are used to perform the same task.Cisco routers offer the following features to mitigate DDoS attacks:
– ACLs: Filter unwanted traffic, such as traffic that spoofs company addresses or is aimed at Windows control ports. However, an ACL is not effective when network address translation (NAT) is implemented in the network.
– Rate limiting: Minimizes and controls the rate of bandwidth used by incoming traffic.
– Traffic-flow reporting: Creates a baseline for the network that is compared with the network traffic flow, helping you detect any intrusive network or host activity.
– Apart from these features offered by Cisco routers, the following methods can also be used to mitigate DDoS attacks:
– Using a firewall, you can block or permit traffic entering a network.
– The systems vulnerable to attacks can be shifted to another location or a more secure LAN.
– Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), such as Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) and Host Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS), can be implemented to detect intrusive network or host activity such as a DoS attack, and raise alerts when any such activity is detected.Anti-DDoS guard and scatter tracing are incorrect because these features are not offered by Cisco routers to mitigate DDoS attacks.
Flow control is incorrect because flow control is used to prevent the loss of traffic between two devices.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic device hardening -
Which statement is TRUE regarding the switchport protected interface configuration command and its effects?
- The command is used to configure private VLAN edge ports.
- The command enables the highest level switch port security.
- All the traffic through protected port should go via a Layer 2 device such as switch.
- A protected port can directly communicate with any other port on the same switch.
Explanation:
The switchport protected interface configuration command is used to configure private VLAN edge ports on a Cisco Catalyst 2950 switch. A VLAN edge port is another name given to a protected port. Protected ports do not forward any traffic to other protected ports on the same switch. All traffic passing between protected ports on the same switch must be routed through a Layer 3 device. Protected ports have no restrictions on forwarding to non-protected ports, and they forward as usual to all ports on other switchesFollowing are the steps to configure a switch port as a protected port:
1. configure terminal
2. interface interface-id
3. switchport protected
4. endUse the show interfaces switchport command to verify that the protected port is enabled.
It is incorrect to state that the command enables the highest level of switch port security. It places no additional restrictions on the port other than preventing it from directly forwarding from one protected port to another.
It is incorrect to state that all traffic through protected port should go via a Layer 2 device such as a switch. Traffic through the protected port should go via a Layer 3 device, such as a router.
It is incorrect to state that a protected port can directly communicate with any other port on the same switch. A protected port cannot directly communicate with another protected port on the same switch.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot port security -
Which Cisco IOS interface configuration command is used to configure the private VLAN edge ports on a Cisco Catalyst 2950 switch?
- switchport protected
- switchport port-security
- switchport port-vlan-edge
- switchport port-security violation
Explanation:
The switchport protected interface configuration command is used to configure protected ports (private VLAN edge ports) on a Cisco Catalyst 2950 switch. A protected port cannot directly communicate with any other protected port on the same switch. It is used in cases where an application requires that no traffic be directly passed from port to port on the same switch. All traffic through the protected port must be transmitted via a Layer 3 device, such as a router.The switchport port-security command enables basic switch port security. With this command, you can define a group of source MAC addresses (called an address table) that are allowed to access the port. The switch will not forward any packets to the port with source addresses that do not match this group. This is one method a network administrator can use to prevent unauthorized access to the LAN by only allowing company-known MAC addresses. Controlling which MAC addresses can access a port has the following advantages:
– It can ensure full bandwidth on the port if the table is limited to a single source address.
– It can make the port more secure by preventing access from unknown MAC addresses. It can also be used to prevent access on unused ports to prevent unauthorized hosts from accessing the LAN.The switchport port-security violation command further defines actions a switch can take on the interface in the event of a security violation by following the command with a choice from the {shutdown | restrict | protect} options.
The switchport port-vlan-edge command is incorrect because this is not a valid Cisco command.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot port security