200-301 : Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) : Part 17
-
You have been asked to examine the following output to identify any security problems with the router. Its configuration is shown:
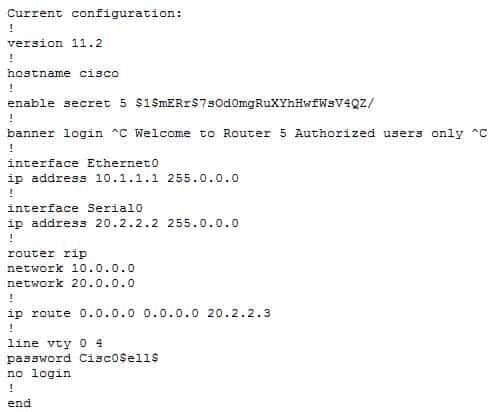
200-301 Part 17 Q01 153 What problems exist? (Choose all that apply.)
- unencrypted privileged mode password
- inappropriate wording in the banner message
- weak password on the VTY line
- Telnet users will not be prompted for a password
Explanation:
The banner logon message should not contain verbiage that includes the word Welcome. This could potentially supply grounds by a hacker that he was “invited” to access the device.Also, although a strong password has been configured on the VTY lines, the presence of the no login command instructs the router to NOT prompt for a password.
The login command should be executed under the VTY configuration so that the router will prompt for the password.
The privileged mode password is encrypted because it is listed as an enable secret password.
The password configured on the VTY lines, Cisc0$ell$, is strong in that it contains numbers, letters, and non-numeric characters and it is at least 8 characters in length.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic device hardening -
As part of a new initiative to tighten the security of your Cisco devices, you have configured the firewall to restrict access to the devices from the outside.
What would be other recommended ways of protecting the integrity of the device configuration files on the devices while ensuring your continued ability to manage the devices remotely? (Choose all that apply.)
- encrypt the configuration files
- use SSH to connect to the devices for management
- prevent the loss of administrator passwords by disabling their encryption
- disable the VTY ports on the devices
- use an encrypted password for VTY access
Explanation:
You should use SSH to connect to the devices for management. You should also require an encrypted password for VTY access. Using Telnet for remote management transmits all information, including the username and passwords, in clear text. Using an encrypted password for VTY access ensures that the password cannot be read either in transit or in the configuration file.Passwords used for access to the console, aux, or VTY connections can be encrypted if desired. When passwords are created with the enable <password> command, the password is saved in clear text. When the enable secret <password> command is used, however the password will be encrypted.
If both types of password are configured for a particular connection type, the system will ignore the enable password and require the enable secret password. For example, if the set of commands shown below were executed, both types of password will be created for console access, but the system will require the password crisco rather than cisco. Also make note that neither of those passwords will required for VTY access. That password is sicso, which is the password configured after accessing the line VTY interface configuration prompt.
Router(config)# enable secret crisco Router(config)# enable password cisco Router(config)# line vty 0 4 Router(config-line)# password sisco
Although it is possible to encrypt the password in the configuration files, it is not possible to encrypt the rest of the files.
You should not disable the encryption of the passwords in the configuration files. Password encryption is a good security measure to take, and sloppy password management should not be a reason to change this practice.
You should not disable the VTY ports on the devices. This would certainly enhance security, but it would prevent you from managing the devices remotely
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic device hardening -
What will be the effect of executing the following command on port F0/1?
switch(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address 00C0.35F0.8301
- The command statically defines the MAC address of 00c0.35F0.8301 as an allowed host on the switch port.
- The command expressly prohibits the MAC address of 00c0.35F0.8301 as an allowed host on the switch port.
- The command configures an inbound access control list on port F0/1 limiting traffic to the IP address of the host.
- The command encrypts all traffic on the port from the MAC address of 00c0.35F0.8301.
Explanation:
The command statically defines the MAC address of 00c0.35F0.8301 as an allowed host on the switch port. By default, an unlimited number of MAC addresses can be learned on a single switch port, whether it is configured as an access port or a trunk port. Switch ports can be secured by defining one or more specific MAC addresses that should be allowed to connect, and violation policies (such as disabling the port) if additional hosts try to gain a connection.The switchport port-security mac-address 00C0.35F0.8301 command statically defines the MAC address of 00c0.35F0.8301 as an allowed host on the switch port.
The switchport port-security mac-address 00C0.35F0.8301 command does not expressly prohibit the MAC address of 00c0.35F0.8301 as an allowed host on the switch port. The port-security command is designed to identify allowed MAC addresses not prohibited addresses.
The switchport port-security mac-address 00C0.35F0.8301 command does not configure an inbound access control list on port F0/1 limiting traffic to the IP address of the host. It will accept traffic to the port, but will only allow a device with that MAC address to be connected to the port.
The switchport port-security mac-address 00C0.35F0.8301 command does not encrypt all traffic on the port from the MAC address of 00c0.35F0.8301. The port-security command has nothing to do with encryption.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot port security -
What command disables 802.1x authentication on a port and permits traffic without authentication?
- dot1x port-control disable
- dot1x port-control force-unauthorized
- dot1x port-control auto
- dot1x port-control force-authorized
Explanation:
The command dot1x port-control force-authorized is used to disable 802.1x on a port and permit traffic without authentication. Dot1x ports are in one of two states, authorized or unauthorized. Authorized ports permit user traffic to flow through the port. This state usually follows successful authentication. Unauthorized ports only permit authorization traffic to flow through the port.Usually a port begins in the unauthorized state. A user is then allowed to exchange AAA authentication traffic with the port. Once the user has been authenticated successfully, the port is changed to the authorized state and the user is permitted to use the port normally.
Normal use of 802.1x has the port configured with the dot1x port-control auto statement. This places the port in the unauthorized state until successful authentication. After successful authentication, the port is changed to the authorized state.
When 802.1x is initially configured, the default port control of the ports is force-authorized. This forces the port to be in the authorized state without successful authentication. This setting disables the need for authentication and permits all traffic.
The force-unauthorized keyword configures the port as an unauthorized port regardless of authentication traffic. A port configured with this key word would not permit user traffic, not even authentication traffic.
The command dot1x port-control disable is not a valid command due to incorrect syntax.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Describe device security using AAA with TACACS+ and RADIUS -
What will be the output of the show cdp neighbors detail command issued on Router A? (Click the Exhibit(s) button to view the network diagram.)

200-301 Part 17 Q05 154 - Device ID: RTR2511
Entry address(es):
IP address: 178.10.20.1
Platform: cisco 2511, Capabilities: Router
Interface Serial 0
——————————————
Device ID: RTR2611-Edge
Entry address(es):
IP address: 10.10.1.2
Platform: cisco 2611, Capabilities: Router
Interface Ethernet 0 - Device ID: RTR2611
Entry address(es):
IP address: 172.10.20.1
Platform: cisco 2611, Capabilities: Router
Interface Ethernet 0
——————————————–
Device ID: C2924C-123
Entry address(es):
IP address: 10.10.1.3
Platform: cisco WS-C2924, Capabilities: Switch
Interface Ethernet 0 - Device ID: RTR2511
Entry address(es):
IP address: 178.10.20.2
Platform: cisco 2511, Capabilities: Router
Interface Serial 0
——————————————
Device ID: C2924C-123
Entry address(es):
IP address: 10.10.1.3
Platform: cisco WS-C2924, Capabilities: Switch
Interface Ethernet 0 - Device ID: RTR2611
Entry address(es):
IP address: 172.10.20.1
Platform: cisco 2611, Capabilities: Router
Interface Ethernet 0 - Device ID: C2924C-123
Entry address(es):
IP address: 10.10.1.3
Platform: cisco WS-C2924, Capabilities: Switch
Interface Ethernet 0
Explanation:
The following code is the correct partial output of the show cdp neighbors detail command issued on Router A:Device ID: RTR2511
Entry address(es):
IP address: 178.10.20.2
Platform: cisco 2511, Capabilities: Router
Interface Serial 0
——————————————
Device ID: C2924C-123
Entry address(es):
IP address: 10.10.1.3
Platform: cisco WS-C2924, Capabilities: Switch
Interface Ethernet 0The show cdp neighbors detail command displays the Cisco devices directly connected to the router. Therefore, only details of the 2511 router and the Cisco Catalyst 2924 switch will be displayed in the output. The detail keyword in the show cdp neighbor command also displays IP address information for the directly connected devices. The output shows the connected device name, its IP address, its platform, and the local interface through which the device is connected.
All of the other code samples are incorrect, as they include the output of devices that are not connected directly to Router A.
Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a Cisco proprietary protocol used by all Cisco devices to collect information about neighboring devices. CDP operates at Layer 2 of the OSI model. Therefore, it can collect information about neighboring devices that are running different Network layer protocols. It is also useful for collecting information when IP is not functional.
Some variations of this command include:
– The show cdp command, which displays global CDP information, including timer and hold time information.
– The show cdp interface command, which displays information about the interfaces on which CDP is enabled.
– The show cdp neighbors command, which displays detailed information about neighboring devices discovered by the CDP. However, it does not include the IP address of the neighboring device.Objective:
Infrastructure Management
Sub-Objective:
Use Cisco IOS tools to troubleshoot and resolve problems - Device ID: RTR2511
-
Which of the following technologies should be used to prevent a switching loop if a switch is connected to a port configured for PortFast?
- RSTP
- BPDU Guard
- Root Guard
- PVST
Explanation:
BPDU Guard prevents switching loops in the case of a switch being connected to a PortFast interface. PortFast is used for ports that connect to host systems, such as workstations and printers, and allows the port to immediately enter a forwarding state. This bypasses the normal 30-second delay that Spanning Tree Protocol would normally use to determine if a switch has been connected to the port. Implementing BPDU Guard will disable the port if a switch is connected and a BPDU is received.Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is incorrect because this is an enhanced Spanning Tree standard that operates on the Data Link layer of the OSI model. RSTP was not designed to protect PortFast ports. PortFast and BPDU Guard are supported by RSTP, but they not required or configured by default.
Root Guard is incorrect because it is used to protect the root bridge placement in the Spanning Tree, not to protect PortFast ports.
Per-VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST) is incorrect because this is an implementation of Spanning Tree (the default protocol for Cisco switches), and was not designed to protect PortFast ports. PortFast and BPDU Guard are supported by RSTP, but are not required, and must be configured manually.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot STP-related optional features -
Which Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) command will you use to view the details of each interface on a router?
- show controllers
- show interfaces ethernet
- show ip interface brief
- show interfaces loopback
Explanation:
The show ip interface brief command is used to view the details of each interface on a router. The output of the command displays the interfaces, the IP addresses configured on each interface, the method, the status, and the protocol.The following is a sample output of this command:
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Ethernet0 10.105.00.5 YES NVRAM up up Ethernet1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down Loopback0 10.105.200.5 YES NVRAM up up Serial0 10.105.100.5 YES NVRAM up up Serial1 10.105.40.5 YES NVRAM up up Serial2 10.105.100.5 YES manual up up Serial3 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
The show controllers command is incorrect. The show controllers command is used to view hardware-related information on router and switch interfaces. It is useful for troubleshooting and diagnosing issues with interfaces. One of the many useful pieces of information yielded by command is the type of cable connected to the interface. When you are using a V.35 cable to connect two serial interfaces directly between two routers, one of the routers must be configured to provide the clocking on the line and it must be the router with the DCE end of the cable. You can determine which router has that end by executing this command, which would display output similar to the following:
R2#show controllers serial 0 HD unit 0, idb = 0xDFE73, driver structure at 0xE52FF Buffer size 1524 HD unit 0, V.35 DCE cable, clockrate 64000
In the above example, the DCE end of the V.35 cable is connected to this router. Therefore, this is the router that must be configured with a clockrate. The output demonstrates that this requirement was already met.
The show interfaces ethernet command is incorrect because this command will display information only for Ethernet interfaces.
The show interfaces loopback command is incorrect because this command will show information regarding loopback interfaces only.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Troubleshoot interface and cable issues (collisions, errors, duplex, speed) -
Which of the following cables would be used to connect a router to a switch?
- v.35
- crossover
- rollover
- straight-through
Explanation:
A straight-through cable would be used. When connecting “unlike” devices, such as a switch to a router, a straight-through cable is used. This is a cable where the wires are in the same sequence at both ends of the cable.NOTE: The one exception to this general rule of connecting unlike devices with a straight-through cable is when a computer NIC is connected to an Ethernet port on a router. In that case, a crossover cable is used.
A v.35 cable is used to connect serial connections between routers. This cable has a male DB-60 connector on the Cisco end and a male Winchester connector on the network end. It comes in two types: DCE and DTE. It is often used to simulate a WAN connection in lab environments. In that case, the DCE end acts as the CSU/DSU and is the end where the clock rate is set. A CSU/DSU (Channel Service Unit/Data Service Unit) is a device that connects the router to the T1 or T3 line.
A crossover cable has two wires reversed and is used to connect “like” devices, such as a switch to a switch. It is also used when a computer NIC is connected to an Ethernet port on a router.
A rollover cable is used to connect to the console port of a router to configure the router. It is also called a console cable.
The diagram below illustrates the correct usage of each of the cable types shown using the following legend:
– SO Ethernet Straight through Cable
– CO Ethernet Crossover Cable
– Serial Serial cable
– RO Rollover cable
200-301 Part 17 Q08 155 
200-301 Part 17 Q08 156 Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Select the appropriate cabling type based on implementation requirements -
Which statements are NOT true regarding Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs)? (Choose two.)
- VLANs define broadcast domains.
- VLANs are logical groups of hosts.
- VLANs are location-dependent.
- VLANs are limited to a single switch.
- VLANs may be subnets of major networks.
Explanation:
VLANs are NOT location-dependent and can span to multiple switches using trunk links. VLANs provide location independence that makes addition, change, and movement of networking devices a simple process. VLANs allow you to group people according to their job function, which also eases the implementation of security policies.A VLAN is a group of networking devices in the same broadcast domain. Each time you create a new VLAN on a switch, a new broadcast domain is created. VLANs are not restricted to any physical boundary in the switched network. VLANs operate as separate subnets, and so for inter-VLAN communication to occur there must be a router in the network or a route feature card in one of the switches. In other words, if a switch is configured with two VLANs, and there are hosts connected to the VLANs, then hosts in one VLAN will be unable to connect to hosts in another VLAN if the switch is not connected to a router.
VLANs are logical groups of hosts. A host or user can be located anywhere in the switched network and still belong to the same broadcast domain. If you move a host from one switch to another switch in the same switched network, you can still keep the host in the original VLAN.
VLANs may be subnets of a major network. A subnet is a contained broadcast domain. A broadcast that occurs in one subnet will not be forwarded, by default, to another subnet. Layer 3 devices provide the forwarding function at boundary. Each of these subnets requires a unique network number. To move from one network number to another, you need a Layer 3 device. Each VLAN is a separate broadcast domain and requires a Layer 3 device for inter-VLAN routing.
Securing access to sensitive devices can be achieved in two steps:
– Access lists enforced at the router
– Restricted VLANs configured on the switches
– From a security standpoint, devices can be placed on a private VLAN to prevent sensitive information from being captured by devices on other VLANs. Access lists enforced at the router can be used to prevent unauthorized access to the private VLAN.VLANs provide the following benefits:
– Logical, rather than physical, grouping of devices
– Grouping of devices by function or department
– Enhanced network security
– Decreased size of broadcast domains with the increased number of broadcast domains
– VLAN greatly simplify adding, moving and changing host in the networkVLANs have the following characteristics:
– VLANs logically divide a switch into multiple, independent switches at Layer 2
– A VLAN can span multiple switches
– Trunk links can carry traffic for multiple VLANs between the switches and between the switch and a router
– VLAN create segmented broadcast domains in switched networksObjective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot VLANs (normal/extended range) spanning multiple switches -
You are implementing IP SLA and would like to use it to measure hop-by-hop response time between a Cisco router and any IP device on the network.
Which of the following IP SLA operations would you use for this?
- ICMP path echo operation
- Internet Control Message Protocol Echo Operation
- UDP Jitter Operation for VoIP
- UDP Jitter Operation
Explanation:
The ICMP path echo operation discovers the path using the traceroute command, and then measures response time between the source router and each intermittent hop in the path. IP SLAs allow users to monitor network performance between Cisco routers or from a Cisco router to a remote IP device.The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Operation measures end-to-end response time between a Cisco router and any IP-enabled device. Response time is computed by measuring the time taken between sending an ICMP echo request message to the destination and receiving an ICMP echo reply. It does not measure hop-by-hop response time.
The UDP Jitter Operation for VoIP is an extension to the current jitter operations with specific enhancements for VoIP. The enhancements allow this operation to calculate voice quality scores and simulate the codec’s directly in CLI and the MIB. It does not measure hop-by-hop response time.
The UDP Jitter Operation is designed to measure the delay, delay variance, and packet loss in IP networks by generating active UDP traffic. It does not measure hop-by-hop response time.
Objective:
Infrastructure Management
Sub-Objective:
Troubleshoot network connectivity issues using ICMP echo-based IP SLA -
Which metric does the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol use for optimal path calculation?
- MTU
- Cost
- Delay
- Hop count
Explanation:
OSPF is a link-state routing protocol which uses cost as a metric for optimal path calculation. It is an open standard protocol based on Dijkstra’s Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm. Metrics are used by routing protocols to determine the lowest cost path to a network number, which is considered the optimal or “fastest” path. Cisco’s implementation of OSPF calculates the cost (metric) of a link as inversely proportional to the bandwidth of that interface. Therefore, a higher bandwidth indicates a lower cost, and a more favorable metric.For this to work properly, the bandwidth of the link must be configured to allow OSPF to arrive at the cost of the link. This is done with the bandwidth command executed in interface configuration mode, and is entered in kbps. For example, if the link were 64 kbps, you would enter the following command:
Router(config-if)# bandwidth 64
The metric for any OSPF link defaults to 100,000,000/bandwidth. The bandwidth used in the formula is in bits per second. So, in this example the calculation would be 100,000,000 / 64000 = 1562.5. The cost assigned to the link would be 1562. The cost for a network route is the sum of all individual links in the path to that network.
If multiple paths are assigned equal costs, OSPF will load balance across the multiple paths. By default, it will limit this load balance to a maximum of four equal-cost paths. When this occurs, all four equal-cost paths will be placed in the routing table. There are two approaches to allow or prevent load balancing when multiple equal cost paths are available:
– Use the bandwidth command to make one or more of the paths either less or more desirable.
– Use the ip ospf cost command to change the cost value assigned to one or more of the pathsMaximum Transmission Unit (MTU), bandwidth, delay, load, and reliability form a composite metric used by Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) and Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP). IGRP is a distance vector routing protocol developed by Cisco Systems. Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP) is a Cisco-proprietary hybrid protocol having features of both distance-vector and link-state protocols.
Hop count is a metric used by Routing Information Protocol (RIP). The fewer hops between the routers, the better the path.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast distance vector and link-state routing protocols -
Which commands would be used to enable Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) on a router, and configure the IP addresses 10.2.2.2 and 192.168.1.1 as a part of complete EIGRP configuration? (Choose three.)
- router eigrp 10
- router eigrp
- network 10.2.2.2
- network 10.0.0.0
- network 192.168.1.0
- network 192.168.1.1
Explanation:
The router eigrp 10 command is used to enable EIGRP on a router. The network 10.0.0.0 and network 192.168.1.0 commands are used to activate EIGRP over the interfaces configured with IP addresses 10.2.2.2 and 192.168.1.1. If we were given the subnet mask for the two interfaces, we could include that in the network command as well.The following command sequence is used to configure EIGRP on a router:
router(config) # router eigrp [autonomous-system] router (config-router) # network x.x.x.x [wildcard-mask] router (config-router) # network y.y.y.y [wildcard-mask]
The autonomous-system parameter of the router eigrp command specifies the autonomous system number. To ensure that all the routers in a network can communicate with each other, you should specify the same autonomous system number on all the routers.
The parameters of the network command are:
– x.x.x.x – This is the major (classful) network number connected to the router.
– y.y.y.y – This is the other major (classful) network number connected to the router.If either the AS numbers do not match between two EIGRP routers or one end is not configured with EIGRP, no EIGRP routes will appear in the routing table of either router, because they will not have formed an EIGRP neighbor relationship. In this situation you will be able ping between the routers, but you will not be able to ping LANs attached to the other router.
The router eigrp command is incorrect because you need to specify the autonomous system number after the command to enable EIGRP in a network. The router eigrp 10 command includes the autonomous-system parameter.
The network 192.168.1.1 and network 10.2.2.2 commands are incorrect because the command must be in terms of the network or subnet ID of the network in which the interfaces reside. It is not entered in terms of the address of the interfaces.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot EIGRP for IPv4 (excluding authentication, filtering, manual summarization, redistribution, stub) -
Which Cisco IOS command will display the following partial output?

200-301 Part 17 Q13 157 - show ip
- show ip route
- show ip route summary
- show route summary
Explanation:
The show ip route command will display the output in this scenario. The command is used to display the present status of the routing table. The complete command syntax is:show ip route [[ip-address [mask] [longer-prefixes]] | [protocol [process-id]] | [list access-list-number | access-list-name]]
The following is a sample partial output:
D 168.28.0.0 [140/8] via 10.212.215.122, 0:03:34, serial0/0
The first letter represents the routing protocol through which the route is learned. In this case, the route is learned by EIGRP. The command output also lists codes used for all the routing protocols.
The routing protocol code is followed by the IP address of the remote network.
The first number in the bracket represents the administrative distance of the routing protocol. The number followed by slash within the bracket represents the cost of the route. Different routing protocol uses different methods to calculate the cost of the route. The IP address followed by the keyword via shows the next router to the remote network. The next set of numbers is the time when the route was last updated, which is 0:03:34 in the example. Lastly, it displays the interface through which the network can be reached, which is serial0/0 in the example.
The show ip command is incorrect because it is not a valid Cisco IOS command.
The show ip route summary command is incorrect because this command is used to view the current state of the routing table.
The show route summary command is incorrect because it is not a valid Cisco IOS command.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Interpret the components of routing table -
As part of a new initiative to tighten the security of your Cisco devices, you have configured the firewall to restrict access to the devices from the outside.
What would be other recommended ways of protecting the integrity of the device configuration files on the devices while ensuring your continued ability to manage the devices remotely? (Choose all that apply.)
- encrypt the configuration files
- use SSH to connect to the devices for management
- prevent the loss of administrator passwords by disabling their encryption
- disable the VTY ports on the devices
- use an encrypted password for VTY access
Explanation:
You should use SSH to connect to the devices for management. You should also require an encrypted password for VTY access. Using Telnet for remote management transmits all information, including the username and passwords, in clear text. Using an encrypted password for VTY access ensures that the password cannot be read either in transit or in the configuration file.Passwords used for access to the console, aux, or VTY connections can be encrypted if desired. When passwords are created with the enable <password> command, the password is saved in clear text. When the enable secret <password> command is used, however the password will be encrypted.
If both types of password are configured for a particular connection type, the system will ignore the enable password and require the enable secret password. For example, if the set of commands shown below were executed, both types of password will be created for console access, but the system will require the password crisco rather than cisco. Also make note that neither of those passwords will required for VTY access. That password is sicso, which is the password configured after accessing the line VTY interface configuration prompt.
Router(config)# enable secret crisco Router(config)# enable password cisco Router(config)# line vty 0 4 Router(config-line)# password sisco
Although it is possible to encrypt the password in the configuration files, it is not possible to encrypt the rest of the files.
You should not disable the encryption of the passwords in the configuration files. Password encryption is a good security measure to take, and sloppy password management should not be a reason to change this practice.
You should not disable the VTY ports on the devices. This would certainly enhance security, but it would prevent you from managing the devices remotely
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic device hardening -
You have implemented the following IP SLA configuration, as shown in the following partial output of the show run command:
ip sla 1 dns cow.cisco.com name-server 10.52.128.30 ip sla schedule 1 start-time now
Which of the following statements is true of this configuration?
- It will find the response time to resolve the DNS name cow.cisco.com
- It will find the response time to connect to the DNS server at 10.52.128.30
- It will start in one minute
- It will gather data from one minute
Explanation:
It will find the response time to resolve the DNS name cow.cisco.com. Domain Name System (DNS) response time is computed by calculating the difference between the time taken to send a DNS request and the time a reply is received. The Cisco IOS IP SLAs DNS operation queries for an IP address if the user specifies a hostname, or queries for a hostname if the user specifies an IP address.It will not find the response time to connect to the DNS server at 10.52.128.30. That is the IP address of the DNS server being used for the operation (10.52.128.30). However, it will measure the response time to resolve the DNS name cow.cisco.com.
It will not start in one minute. It will start immediately, as indicated by the start-time now parameter.
It will not gather data for one minute. The numeral 1 in the first line refers to the IP SLA number, and the numeral 1 in the last line refers to the IP SLA number to be scheduled.
Objective:
Infrastructure Management
Sub-Objective:
Troubleshoot network connectivity issues using ICMP echo-based IP SLA -
To minimize routing protocol traffic, you have decided to use static routing in the network displayed in the following diagram. You would like to keep the configuration as simple as possible.

200-301 Part 17 Q16 158 Which command(s) are required for all hosts to communicate with one another and the Internet? (Choose all that apply.)
-
R1(config)#ip route 12.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.1
-
R2(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.2
-
R1(config-if)# ip route 12.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.1
-
R2(config-if)# ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.2
-
R2(config)#ip route 12.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.1 -
R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.5.2
Explanation:
There must be two routes added to make the network functional. From a conceptual standpoint, the network requires the following two routes:
– A static default route on R1 that directs all traffic destined for unknown networks (which would include Internet-bound traffic) to R2
– A static route on R2 to direct traffic destined for 12.168.5.0/24 to R1. Without this route R2 will be unable to route return traffic to the 12.168.5.0/245 network even if the default route in the first bullet point has been added.The commands that would create these routes, respectively, are:
R2(config)#ip route 12.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.1 R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.5.2
Troubleshooting routing problems should always begin with examining the routing table of the routers involved in the path to the destination. If the routes are static, they will also appear in the output of the show run command. One of the characteristics of a static route is that it will remain in the routing table even if routers on the path to the destination network lose their route to the network. If an advertising router loses its route to a destination network, dynamic routes will be removed from the routing tables of the routers that received that advertisement.
Static routes not only reduce routing update traffic in stub networks such as this one, but they also increase security because only the network administrator may change the routing table. On the other hand, the administrator must also stand ready to manually add new routes if current routes become unavailable. Dynamic routing is designed to make these route changes automatically if alternate routes exist.
The commands R1(config-if)# ip route 12.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.1 and R2(config-if)# ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.2 are incorrect because they are executed at an interface prompt, rather than at the global configuration prompt as required.
The command ip route 12.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.1 is the correct command to create a static route to direct traffic destined for 12.168.5.0/24 to R1. However, this command should be executed on R2, not at the R1(config)# prompt.
The command ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.5.2 is the correct command to create a static default route that directs all traffic destined for unknown networks (which would include Internet-bound traffic) to R2. However, this command should be executed on R1 and not at the R2(config)# prompt.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot IPv4 and IPv6 static routing -
-
Router 5 has four interfaces. The networks hosted on each interface are as follows:
Fa0/1 192.168.5.4/29 Fa0/2 192.168.6.0/24 Fa0/3 192.168.7.0/24 S0/0 172.16.5.0/24
You execute the following commands on the router:
Router5(config)# router bgp 20 Router5(config-router)# network 192.168.5.0 Router5(config-router)# network 192.168.6.0 Router5(config-router)# network 192.168.7.0 Router5(config-router)# network 172.16.5.0 Router5(config-router)# neighbor 172.16.5.2 remote-as 50 Router5(config-router)# aggregate-address 192.168.5.0 255.255.252.0
After this command sequence is executed, what routes will be present in the routing table of the router at 172.16.5.2? (Choose all that apply.)
- 192.168.5.4/29
- 172.16.5.0/24
- 192.168.6.0/24
- 192.168.7.0/24
- none of these will be present
- only network addresses beginning with 192 will be present
Explanation:
Despite the inclusion of the command aggregate-address 192.168.5.0 255.255.252.0, all subnets of the aggregate route will also be placed in the routing updates because of the omission of the summary-only keyword. Therefore, 192.168.5.4/29, 172.16.5.0/16, 192.168.6.0/24 and 192.168.7.0/24 will be present.Had the following command been executed, the subnet addresses would not appear in the routing table of the router at 172.16.5.2:
Router5(config-router)# aggregate-address 192.168.5.0 255.255.252.0 summary-only
Therefore, both the aggregate address and all of the 192.168.0.0 subnets will be in the routing table.
The 172.16.5.0/24 network will be in the routing table of the router at 172.160.5.1 because it is directly connected.
Objective:
WAN Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify single-homed branch connectivity using eBGP IPv4 (limited to peering and route advertisement using Network command only) -
DRAG DROP
Click and drag the command(s) used to configure passwords on a Cisco router to their appropriate purposes. (Not all options will be used.)
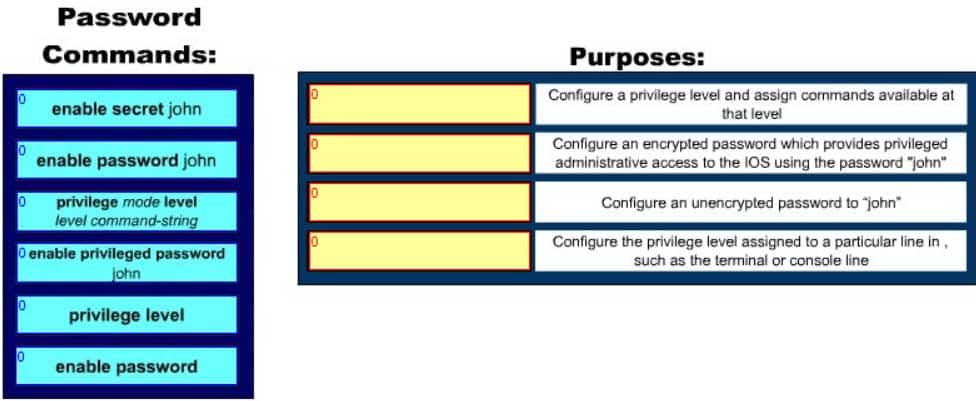
200-301 Part 17 Q18 160 Question 
200-301 Part 17 Q18 160 Answer Explanation:
Following are the commands along with their descriptions:
enable secret john: The enable secret command is used to configure an encrypted password, which provides privileged administrative access to the IOS using the password “John”. It is always advisable to configure an enable secret password. If an enable secret password is not configured and a console TTY password is configured, then a remote user can gain privileged administrative access from a remote VTY session which poses a risk to the network security.
enable password john: The enable password command is used to configure an unencrypted password.To set a user mode password, which is one that you are prompted for when you connect to the router rather than when you try to execute the enable command, enter the line at which you want it effective (either line console 0, line aux 0, or line vty 0 4) and then password <password>. An example of setting the user mode password for both the console and the telnet connections are shown below:
Router(config)#Line console 0 Router(config-line)#login Router(config-line)#password cisco Router(config)#Line vty 0 4 Router(config-line)#login Router(config-line)#password cisco
Also be aware that as executed above the password will not be encrypted without the execution of the service password-encryption command prior to creating the passwords.
privilege level: This command is used to configure the privilege level assigned to a particular line in, such as the terminal or console line
privilege mode level level command-string: This command would be used to configure a particular privilege level and assign commands available at that level.The other options offered are not valid commands.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic device hardening -
You are troubleshooting a problem with two routers configured in a HSRP group. You intended to configure the routers so that Router A and Router B would each track their respective Fa0/1 interfaces and decrement their priorities for several VLAN groups if the tracked interface went down. However, you find that Router A is not taking over as the active device for the HSRP group on VLAN 101 when the Fa0/1 interface on Router B fails.
Which command would NOT be useful for discovering the problem?
- show running-configuration
- show vlans
- show standby brief
- show standby
Explanation:
The show vlans command would NOT be useful for discovering the problem. When troubleshooting a problem with Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP), the show vlans command will yield no useful information. The output of the command is shown below, demonstrating that there is no HSRP information provided.
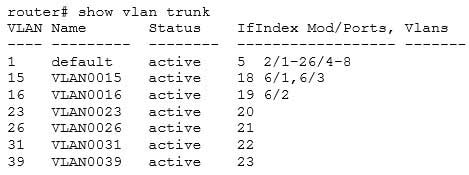
200-301 Part 17 Q19 161 All three of the remaining commands will be useful in discovering information. Each is shown below with an example of its application to troubleshooting.
Example A: show running-configuration
Router B is not taking over as the active device for VLAN 101’s HSRP group when the Fa0/1 interface on Router A fails. Below is a partial output of show run for both routers with the output focused on the section concerning VLAN 101’s configuration on each.
The above output displays the source of the problem. Router A has a decrement value of 5 configured for Fa0/1, as shown on the last line of the output after the specification of Fastethernet 0/1. This means that when its Fa0/1 interface goes down, Router A will subtract 5 from its priority for the VLAN 101 group, lowering it to 175. This is still higher than the priority of Router B, which is 170. Therefore, the solution is to change the decrement value for Router A to at least 11. When the interface goes down, Router A’s priority will be decremented to 169, allowing Router B to take the role as active for the HSRP group in VLAN 101.
Example B: show standby brief
Router C is not taking over as the active device for VLAN 102’s HSRP group when the Fa0/1 interface on Router D fails. Below is a partial output of show standby brief for both routers C and D, with the output focused on the section concerning VLAN 102’s configuration on each.
Router C Interface Grp Prio P State Active addr Standby addr Group addr Fa0/1 102 200 Active local 10.10.10.253 10.10.10.251 Router D Interface Grp Prio P State Active addr Standby addr Group addr Fa0/1 102 200 P Active local 10.10.10.253 10.10.10.251
The absence of a P in the P (preempt) column in the output for Router C shows that it is not set to preempt. If not configured to preempt, it will never take over for Router D, regardless of its priority with respect to Router D.
Example C: show standby
Router F is supposed to be the active router for VLAN 103’s HSRP group. Occasionally both routers are shut down for maintenance over the weekend. After the routers are rebooted, Router F is not taking over as the active device for VLAN 103’s HSRP group. Below is a partial output of the show standby command for both routers, with the output focused on the section concerning VLAN 103’s configuration on each

200-301 Part 17 Q19 162 The output shows that Router F is not assuming the active role because of the priority and decrement values configured on the routers. When both routers go down, Router E will decrement its priority (200) by 10, as shown in last two lines of its output, leaving the priority at 190. Router F will decrement its priority (190) by 50 as shown in last two lines of its output, leaving the priority at 140. Therefore, to ensure that Router F maintains its role as active even after the dual shutdowns, the priority of Router F should be increased to at least 241. When both routers decrement their priorities after shutdown, Router F will then have a priority of 191, which will be higher than the priority value of Router E.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic HSRP -
Which of the following are characteristics of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)? (Choose three.)
- Administrative distance of OSPF is 90
- Administrative distance of OSPF is 110
- OSPF uses the Dijkstra algorithm to calculate the SPF tree
- OSPF uses the Diffusing Update algorithm (DUAL) algorithm to calculate the SPF tree
- OSPF uses 224.0.0.5 as multicast address for ALLDRouters
- OSPF uses 224.0.0.6 as multicast address for ALLDRouters
Explanation:
The following are characteristics of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol:
– The default administrative distance is 110.
– It uses 224.0.0.6 as the multicast address for ALLDRouters.
– It uses the Dijkstra algorithm to calculate the Shortest Path First (SPF) tree.
– It uses Internet Protocol (IP) protocol 89.
– OSPF supports Non-Broadcast Multi-Access (NBMA) networks such as Frame Relay, X.25, and Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM). The default hello interval for NBMA networks is 30 seconds.
– OSPF supports point-to-point and point-to-multipoint connections.
– It also supports authentication.
– OSPF uses 224.0.0.5 as the multicast address for ALLSPFRouters.
– It uses link-state updates and SPF calculations that provides fast convergence.
– OSPF is recommended for large networks due to good scalability.
– It uses cost as the default metric.
– There is no maximum hop count as with distance vector routing protocols. The number of hops to a network can be unlimited.The option stating that AD of OSPF is 90 is incorrect because 90 is the default administrative distance for an internal Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) route.
The option stating that OSPF uses the Diffusing Update algorithm (DUAL) algorithm to calculate the SPF tree is incorrect. The DUAL algorithm is used by EIGRP to calculate the SPF tree.
Keep the following in mind when comparing OSPF and EIGRP:
– EIGRP is vendor specific; OSPF is not
– EIGRP has an AD of 90; OSPF has an AD of 110
– OSPF elects a DR on each multi-access network; EIGRP does not
– OSPF uses cost as its metric, and EIGRP uses bandwidth as its metricThe option stating that OSPF uses 224.0.0.5 as multicast address for ALLDRouters is incorrect because OSPF uses 224.0.0.6 as multicast address for ALLDRouters, and 224.0.0.5 as multicast address for ALLSPFRouters.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot single area and multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4 (excluding authentication, filtering, manual summarization, redistribution, stub, virtual-link, and LSAs)