200-301 : Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) : Part 18
-
You set up several routers in your lab. Two of them are connected back to back using Data Terminal Equipment (DTE)-to-Data Circuit-terminating Equipment (DCE) cable. You need to configure the clock rate.
On which router would you configure the clock rate?
- the DCE
- the DTE
- The clock rate is set by default
- The clock rate cannot be configured
Explanation:
The clock rate is set on the Data Circuit-terminating Equipment (DCE) device. DCE is also known as Data Communications Equipment.DCE terminates a physical WAN connection and provides clocking and synchronization of a connection between two locations and connects to a DTE. The DCE category includes equipment such as CSU/DSUs and modems. If you were connecting a router to a WAN link, the router would be the DTE end and would be connected to a CSU/DSU or a modem. Either of these devices would provide the clocking.
DTE is an end-user device, such as a router or a PC that connects to the WAN via the DCE device.
Other options are incorrect. By default, no clock rate is configured, but can be set on a DCE device by using the clock rate [bps] command.
Objective:
WAN Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Describe WAN access connectivity options -
Which Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) command is used to encrypt passwords on Cisco routers?
- password secure
- service encryption-password
- service password-encryption
- enable password
Explanation:
The service password-encryption command is used to encrypt passwords on Cisco routers. It is used to encrypt all passwords configured on the router, both current and future. This means all passwords in the plain text configuration file will be encrypted. This command is issued in global configuration mode. The syntax of the command is as follows:Router(config)# service password-encryption
This command does not have any parameters.
Once executed any password in the configuration file will appear similar to what is shown below when the running or startup configuration files are viewed:
R1#show run <output omitted> line console 0 password 7 09-4f60C0B1C1B login <output omitted>
The password secure and service encryption-password commands are incorrect because they are not valid Cisco IOS commands.
The enable password command is used to set the privileged EXEC mode password, and does not encrypt the password by default.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic device hardening -
DRAG DROP
Click and drag the command line tools used to troubleshoot the network problems on the left to their associated functions on the right. Not all commands may be used.

200-301 Part 18 Q03 163 Question 
200-301 Part 18 Q03 163 Answer Explanation:
The following commands can be used to troubleshoot network connectivity problems:
– ping 127.0.0.1: This command will attempt to contact the local TCP/IP protocol stack. The 127.0.0.1 address is the reserved loopback IP address, which allows applications to communicate with the local system without using an actual IP address assigned to an interface, such as a workstations Ethernet port. Thus, this command allows you to ping yourself?, and if successful, only verifies that TCP/IP is running locally. It does not confirm that the system can communicate with any other host on the network.
– telnet: Telnet is a network application used to establish a remote terminal connection to a host, such as logging in remotely to a Cisco router or switch via TCP/IP. Since network applications reside on the OSI Application Layer (Layer 7), a successful Telnet connection to a remote has confirms that there is network connectivity through Layer 7.
– arp? a: This command is used to display the local IP address to MAC address mappings on a Windows PC.
– traceroute: This command is used on a Cisco router or switch to verify, or trace, the path that IP packets will take towards a particular destination.
– tracert: This command is used on a Windows PC to verify, or trace, the path that IP packets will take towards a particular destination.
– show ip arp: This command is used to display the local IP address to MAC address mappings on a Cisco router or switch.Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot EIGRP for IPv4 (excluding authentication, filtering, manual summarization, redistribution, stub) -
Which statement correctly identifies a difference between Inter-Switch Link (ISL) and 802.1q?
- 802.1q uses a native VLAN, ISL does not.
- Cisco devices support only ISL.
- ISL uses a 12-bit VLAN number field, and 802.1q does not.
- ISL modifies the original Ethernet frame, while 802.1q encapsulates the original Ethernet frame.
Explanation:
802.1q defines a native virtual LAN (VLAN) on each trunk link, which defaults to VLAN 1. The 802.1q frame tagging method specifies that frames in the native VLAN will not be tagged while transmitting over a trunk link. The switch on the other end of the link identifies a native VLAN frame by the absence of the 802.1q header. ISL does not have the concept of native VLANs, and traffic from all VLANs is encapsulated.While older Cisco devices support both the ISL and 802.1q frame tagging methods, ISL is a deprecated, Cisco-proprietary frame tagging method, and newer Cisco switches only support the 802.1q standard. When switches from multiple vendors are installed in the network, the 802.1q frame tagging method should be used.
It is incorrect to state that ISL uses a 12-bit VLAN number field and 802.1q does not. ISL uses a 15-bit VLAN ID field, while 802.1q uses a 12-bit VLAN ID field.
ISL encapsulates the original Ethernet frame, adding a 26-byte header and a 4-byte trailer. 802.1q operates by inserting a 4-byte header inside the original Ethernet frame, then recalculating the checksum (CRC) in the Ethernet trailer.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify Layer 2 protocols -
Examine the following diagram:

200-301 Part 18 Q05 164 While troubleshooting an OSPF routing problem, you need to determine the cost for Router F to reach the 192.168.5.0 24 network via the best route.
What will that cost be?
- 110
- 2
- 3
- 7
Explanation:
The best route to the 192.168.5.0/24 network from the perspective of router F will have an OSPF assigned cost of 2. There are three possible loop-free paths to get from router F to the 192.168.5.0/24 network. The default OSPF costs for a 100 MB link, a T1 link, and a T3 link are 1, 64, and 2, respectively.The three paths and the calculation of their costs are shown:
Router F to Router E to Router A: 1 + 1 = 2
Router F to Router C to Router A: 2 + 1 = 3
Router F to Router B to Router D to Router C to Router A: 64 + 64 + 64 + 1 = 193Each OSPF route calculates the cost of its path to a network, and passes that value on to the next router, which will then add to it the cost to reach that neighbor. For example, the routing table of Router E would look like this for the route to 192.168.5.0/24:
O 192.168.5.0 [110/1] via <output omitted>
Router F would add its own cost to reach Router E to the cost of reaching 192.168.5.0/24, resulting in the following output:
O 192.168.5.0 [110/2] via <output omitted>
110 is the administrative distance of OSPF.
Objective:
Routing FundamentalsSub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot single area and multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4 (excluding authentication, filtering, manual summarization, redistribution, stub, virtual-link, and LSAs) -
DRAG DROP
Click the Exhibits button at the bottom of the page to examine a proposed network diagram. There are four proposed subnets, labeled A, B, C, and D. Subnet A will have 12 users, subnet B will have 300 users, subnet C will have 118 users, and subnet D will have 61 users.

200-301 Part 18 Q06 165 You are designing the IP addressing for this network. You are instructed not to waste IP addresses by making the subnets larger than necessary. Click and drag the correct network ID from the left to the appropriate subnet on the right.

200-301 Part 18 Q06 166 Question 
200-301 Part 18 Q06 166 Answer Explanation:
Subnet A needs to support 12 users. The number of possible addresses in a subnet is determined by the number of host bits or zeros in the mask. The formula is 2n -2, where n is the number of host bits. Therefore, to support 12 users efficiently, the subnet mask requires no more and no less than four host bits. When there are four host bits in the mask there 28 bits in the network portion. That is the case with 192.168.6.0/28.Subnet B needs to support 300 users. To support 300 users without wasting addresses, the mask requires no more and no less than nine host bits. When there nine host bits in the mask, there are 23 bits in the network portion. That is the case with 172.15.0.0/23.
Subnet C needs to support 118 users. To support 118 users without wasting addresses, the mask requires no more and no less than seven host bits. When there seven host bits in the mask, there are 25 bits in the network portion. That is the case with 194.168.6.0/25.
Subnet D needs to support 61 users. To support 61 users without wasting addresses, the mask requires no more and no less than six host bits. When there six host bits in the mask, there are 26 bits in the network portion. That is the case with 193.168.6.0/26.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot IPv4 addressing and subnetting -
Which statements are TRUE regarding Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) addresses? (Choose three.)
- An IPv6 address is divided into eight 16-bit groups.
- A double colon (::) can only be used once in a single IPv6 address.
- IPv6 addresses are 196 bits in length.
- Leading zeros cannot be omitted in an IPv6 address.
- Groups with a value of 0 can be represented with a single 0 in IPv6 address.
Explanation:
IPv6 addresses are divided into eight 16-bit groups, a double colon (::) can only be used once in an IPv6 address, and groups with a value of 0 can be represented with a single 0 in an IPv6 address.The following statements are also true regarding IPv6 address:
– IPv6 addresses are 128 bits in length.
– Eight 16-bit groups are divided by a colon (:).
– Multiple consecutive groups of 16-bit 0s can be represented with double colon (::) ( only once)
– Double colons (::) represent only 0s.
– Leading zeros can be omitted in an IPv6 address.The option stating that IPv6 addresses are 196 bits in length is incorrect. IPv6 addresses are 128 bits in length.
The option stating that leading zeros cannot be omitted in an IPv6 address is incorrect. Leading zeros can be omitted in an IPv6 address.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast IPv6 address types -
Router-A# show running-configuration s0/0 interface serial0/0 description connected to router A IP address 10.10.10.1 255.0.0.0 encapsulation frame-relay shutdown clock rate 64000
Based on the interface configuration provided, which two statements are TRUE? (Choose two.)
- The router’s serial interface is connected using a DTE cable.
- The router’s serial interface is connected using a DCE cable.
- The router’s serial interface is administratively down.
- The router’s serial interface connects using the point-to-point protocol.
Explanation:
The command output shows that the router’s serial interface is connected to a DCE cable, and the router’s serial 0/0 interface is administratively down. The clock rate is only configured when a DCE cable is connected to the router. Use the clock rate interface configuration command to configure the clock rate for the WAN link on serial interfaces. This command is used to set the interfaces clock rate to match the circuit clock rate.This will only be the case when a router is connected to another router with a back-to-back serial cable. Typically, a CSU/DSU acts as the DCE device and the router acts in a DTE role. The CSU/DSU terminates the digital local loop. In the case of an analog local loop, a modem would terminate the loop.
The command output proves that the router’s serial 0/0 interface is administratively down by the presence of the shutdown statement for the serial 0/0 interface.
The router’s serial interface does NOT connect to the CSU/DSU using a DTE cable. The clock rate statement would not be present when the serial interface is attached to a DTE cable.
The router’s serial interface does NOT connect using the point-to-point protocol. The router is using the frame relay Layer 2 protocol as indicated by the encapsulation frame-relay statement in the output.
DTE and DCE serial cables can also be used to connect routers to each other. When a router connects to a CSU/DSU, it must use a DTE cable to connect. When two routers are connected, the router that supplies the clocking should be connected to the DCE cable. The other router should be connected to the DTE cable. The two cables are then connected to each other.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Select the appropriate cabling type based on implementation requirements -
A new switch is added to the network, and several production VLANs are shut down.
Which of the following is a probable cause for this scenario? (Choose two.)
- The new switch has a lower configuration revision number than existing switches.
- The new switch has a higher configuration revision number than existing switches.
- The new switch is operating in transparent mode.
- The new switch is operating in server mode.
Explanation:
The VLAN database of the new switch will overwrite the VLAN databases of the production switches because it is operating in server mode and has a higher VLAN configuration revision number. The VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) is used to synchronize VLANs between different switches. The VTP configuration revision number is used to determine which VTP switch has the most current version of the VLAN database, and is incremented whenever a VLAN change is made on a VTP server switch. The show vtp status command is used to view the configuration revision number, as shown in this sample output:Switch# show vtp status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 62 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005 Number of existing VLANs : 24 VTP Operating Mode : Server VTP Domain Name : Corporate VTP Pruning Mode : Enabled VTP V2 Mode : Disabled VTP Traps Generation : Disabled MD5 digest : 0x45 0x52 0xB6 0xFD 0x63 0xC8 0x49 0x80
This switch has a configuration revision number of 62, which will be compared to other switches in the same VTP domain. If the production switches have a lower configuration revision number than the new switch, their VLAN databases will be replaced with the VLAN database of the new switch. This could mean that VLANs that formerly existed on those production switches may be deleted. Any switch ports that had been assigned to VLANs that become deleted will be disabled, possibly resulting in catastrophic network failure. All VTP switches in the same VTP domain should have a domain password defined, which will protect against a rogue switch being added to the network and causing VLAN database corruption.
The new switch does not have a lower configuration revision number, since this would cause the new switch to have its VLAN database replaced with the existing production VLANs. This would not cause the problem described in the scenario.
The new switch is not operating in transparent VTP mode because a switch operating in transparent VTP mode will never synchronize its VLAN database with other switches.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot VLANs (normal/extended range) spanning multiple switches -
The execution of the show interfaces command yields the following as a part of its output:
Ethernet 0/0 is up, line protocol is down
Which of the following can be determined from this output?
- the link is not functional due to a Data Link layer issue
- the link is fully functional
- the link is not functional due to a Physical layer issue
- the link is not functional due to both a Physical layer and a Data Link layer issue
Explanation:
The command output excerpt indicates that the link is not functional due to a Data Link layer (or “line protocol”) issue, while the Physical layer (Layer 1) is operational. The first (left) column indicates the Physical layer state of the interface, while the second (right) column indicates the Data Link layer state of the interface.The link is not fully functional. Were it fully functional, the command output would be:
Ethernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
The link is not suffering a Physical layer issue or a combination of Physical layer and Layer 2 (Data Link) layer issues. Were either the case, the output would be:
Ethernet 0/0 is down, line protocol is down
Note: if a Physical layer issue exists, there will also be a Data Link issue, since the Data Link layer depends on the Physical layer to provide connectivity.
Objective:
LAN Switching FundamentalsSub-Objective:
Troubleshoot interface and cable issues (collisions, errors, duplex, speed) -
You have a Telnet session established with a switch from a router. You would like to maintain that connection while you return to the session with the router, and then easily return to the switch session after connecting to the router.
What command should you use?
- <Ctrl-Shift-6>x
- resume
- suspend
- <Ctrl-Alt-6>shift
Explanation:
After typing the Ctrl-Shift-6 sequence, you can tap the x key and return to the previous session, which in this case was the session with the router. Below is the full sequence of commands described in this item:Router1#telnet 192.168.3.3 Tying 192.168.3.3..Open User Access Verification Password: Switch2><Ctrl-Shift-6>x Router1#
When you desired to return to the session with the switch, you would use the resume command as shown below:
Router1#resume Switch>
Neither the suspend nor the <Ctrl-Alt-6>shift commands are valid commands.
Objective:
Infrastructure Management
Sub-Objective:
Perform device maintenance -
Which of the following situations could cause a switch to enter initial configuration mode upon booting?
- Corrupt or missing image file in flash memory
- Corrupt or missing configuration file in NVRAM memory
- Corrupt or missing configuration file in flash memory
- Corrupt or missing configuration file in ROM memory
Explanation:
A missing or corrupt file in the switch’s Non Volatile Random Access Memory (NVRAM) can cause the switch to enter initial configuration mode upon booting. When a Cisco switch boots up and finds no configuration file in NVRAM, it goes into initial configuration mode and prompts the user to enter basic configuration information to make the switch operational. The initial configuration mode of a switch is similar to the initial configuration mode of a router, but the configuration parameters are different.A corrupt or missing image or configuration file in flash or ROM memory would not cause a switch to enter initial configuration mode upon booting. The IOS image file is stored in flash, and if it is corrupt or missing, the switch goes in to ROMMON mode, in which a limited version of the IOS image from ROM is loaded into RAM.
Objective:
Infrastructure Management
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify initial device configuration -
Which command(s) will enable you to configure only serial interface 0 on a Cisco router?
-
router>interface serial 0
-
router#interface serial 0
-
router(config)#interface serial 0 -
router(config-if)#interface serial 0
Explanation:
You can use either the router(config)# interface serial 0 command or the router(config-if)# interface serial 0 command to configure serial interface 0 on the router. To perform configuration changes on a single interface, you must either enter interface configuration mode for that interface, or simply execute the command to enter configuration mode for another interface while still at the configuration prompt for the previous interface.Router configuration mode (as indicated by the prompt router(config)#) allows global configuration of the router. This mode, also referred to as the global configuration mode, must be entered as a precursor to entering the interface configuration mode for a specific interface. The sequence of commands and prompts to arrive at this mode would be:
Router> enable (enters privileged mode) Router# config t (enters global configuration mode, t is short for terminal) Router(config)# interface serial 0 (enters interface configuration mode for the serial 0 interface) Router(config-if)#
At this point, any commands executed would be configuration changes limited to the serial 0 interface. For example, to place an address on the interface, enable the interface, and save the configuration, the command series and prompts would be:
Router> enable Router# config t Router(config)# interface serial 0 Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 (addresses the interface) Router(config-if)# no shutdown (enables or "turns on" the interface) Router(config-if)# exit (exits global configuration mode) Router(config)# exit (exits privileged mode) Router# copy running-config startup config (copies the changes to the configuration file on the router)
Alternately, you could enter interface configuration mode for one interface while still in configuration mode for another interface, as shown below. After entering the interface serial 1 command, you will be editing serial 1 instead of serial 0.
Router(config)# interface serial 0 Router(config)# Router(config)# interface serial 1
You should not use the command router> interface serial 0. User EXEC mode, as indicated by the prompt router>, provides limited access to a router and is the initial mode you see after authenticating to the router. The subcommand interface serial 0 is not functional before you proceed to global configuration mode and interface configuration mode for a specific interface.
You should not use the command router# interface serial 0. Privileged mode (as indicated by the prompt router#) must be traversed to get to global configuration mode before you can execute the subcommand interface serial 0. This subcommand is not functional while you are still in privileged mode.
Objective:
Infrastructure Management
Sub-Objective:
Use Cisco IOS tools to troubleshoot and resolve problems -
-
Which Cisco IOS command will enable a switch to copy the configuration from NVRAM to its RAM?
- copy tftp flash
- copy running-config flash
- copy startup-config flash
- copy startup-config running-config
- copy running-config startup config
Explanation:
The copy startup-config running-config command enables a switch (or a router) to copy configuration from NVRAM to its RAM. The configuration file located in NVRAM is referred to as the startup configuration, and a configuration currently loaded and running in RAM is referred to as the running configuration.The copy running-config startup-config command is incorrect because it will save your running configuration in RAM to the non-volatile NVRAM, which is the reverse of the scenario’s requirement. This would be the required command to run if you have edited the running configuration and would like to save the changes so that they are effective the next time you restart the switch.
The copy tftp flash command does not enable a switch to copy the configuration from NVRAM to its RAM. This command is used to restore backup IOS images stored on a TFTP server to the target switch (or router).
The copy running-config flash command does not enable a switch to copy the configuration from NVRAM to its RAM. This command is used to save the running configuration in RAM to the switch’s flash memory.
The copy startup-config flash command does not enable a switch to copy the configuration from NVRAM to its RAM. This command is used to save the startup configuration in NVRAM to the switch’s flash memory.
Objective:
Infrastructure Management
Sub-Objective:
Perform device maintenance -
DRAG DROP
Click and drag the show commands on the left to their appropriate description on the right.

200-301 Part 18 Q15 167 Question 
200-301 Part 18 Q15 167 Answer Explanation:
The show commands and their appropriate descriptions are as follows:
– show interfaces: Used to view configured interfaces on the router.
– show running-config: Used to view the currently running configuration.
– show startup-config: Used to view the stored configuration in router’s NVRAM.
– show version: Used to view configuration of system hardware, software version, and boot images.
The following commands are also used to view the information on the router:
– show controllers: Used to view interface card controllers.
– show flash: Used to view contents of flash memory.
– show process cpu: Used to view active processes on the router.
– show debugging: Used to view which type of debugging is enabled on the router.Objective:
Infrastructure Management
Sub-Objective:
Perform device maintenance -
A switch that you manage has three VLANs configured. Its MAC address table is shown below:
Vlan Mac address Type Ports <output omitted> 1 000f.e544.c2b3 dynamic Fa0/10 1 000d.4589.00b8 dynamic Fa0/5 1 00bd.000b.005bb dynamic Fa0/8 11 0001.0d44.bbdb dynamic Fa0/12 55 0014.0bd4.0054 dynamic Fa0/15 66 00bb.224b.0ac5 dynamic Fa0/1
You execute the following command on the switch:
Switch# show int trunk Port mode Encapsulation Status Native VLAN Fa0/10 on 802.1q trunking 1 Fa0/5 on 802.1q trunking 1 Fa0/8 on 802.1q trunking 1
Considering only the ports listed in the output, if a frame enters the switch untagged with a destination address of 0002.254b.0015, which ports will receive the frame? (Choose all that apply.)
- All ports
- Ports 5, 8, and 11
- All unaccounted-for access ports
- All ports in the same VLAN except the port on which it arrived
- All 802.1q trunk links
Explanation:
When a switch receives a frame, the first thing it will do is determine if the frame’s MAC address is already in its MAC table. If it is not, as in this scenario, it will send the frame out on all access ports in the same VLAN and any 802.1q trunks with the exception of the port on which it arrived. Since the frame is untagged it will be in VLAN 1 by default.In the MAC table shown in the output, there is no listing for the MAC address 0002.254b.0015. This indicates that the destination is not directly connected to this switch. Therefore, the switch will send the frame to all trunk links, which in this case would be ports 10, 5, and 8, and all access links in VLAN 1 with the exception of the one on which it arrived, which was not identified in the scenario.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Describe and verify switching concepts -
Which device will always have all of its ports in the same collision domain?
- Hub
- Bridge
- Switch
- Router
Explanation:
Open Systems Interconnect (OSI) Layer 1 devices, such as hubs and repeaters, do not create multiple collision domains. All of their ports remain in the same collision domain as well as the same broadcast domain.A collision domain is a domain where two or more devices in the domain could cause a collision by sending frames at the same time. Each switch port is a separate collision domain. Replacing a hub with a switch effectively eliminates collisions for devices connected to the switch ports.
Bridges and switches create multiple collision domains and can reduce collisions within a broadcast domain, as each port constitutes a separate collision domain. However, if the network is not segmented with Virtual LANs (VLANs), all ports remain in the same broadcast domain. The main difference between a bridge and a switch is that the latter has a higher port capacity and better performance. VLANs segment the network into smaller broadcast domains using a Layer 2 device such as switch.
Routers segment the network into multiple broadcast domains. Routers are Layer 3 devices, and thus they interconnect different Layer 3 IP networks. Every interface/subinterface on a router has a unique IP network/subnet address that corresponds to a broadcast domain. Thus, every interface on a router defines a broadcast domain.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Describe and verify switching concepts -
A switch is powered up, and the system LED is amber.
Which of the following describes this situation?
- The switch is malfunctioning.
- Utilization level is high.
- The switch is performing normally.
- There is a security violation on a switch port.
Explanation:
The system LED indicates the overall health of the switch. The LED should turn solid green after a successful Power On Self Test (POST). An amber system LED indicates that there is a system-wide failure in the switch.High utilization will not cause the system LED to turn amber.
An amber system LED indicates a general switch malfunction. It does not indicate that the switch is performing normally.
Port security violations will not cause the system LED to be amber. The system LED is used to identify the overall health of the switch.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Troubleshoot interface and cable issues (collisions, errors, duplex, speed) -
Which of the following commands will configure a router to use DNS for hostname resolution?
- ip dns primary
- ip domain lookup
- ip dns server
- ip name-server
Explanation:
The ip domain lookup command configures the device to use DNS for hostname resolution. It must be accompanied by a command that specifies the location of the DNS server, which is done with the ip name-server command.The ip dns-primary command is used to configure the device as the primary DNS name server for a domain (zone) and as the start of authority (SOA) record source, which designates the start of a zone.
The ip dns server command is used to make the device a DNS server.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Describe DNS lookup operation -
Which Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) command is used to view information about the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) address pool?
- show ip dhcp server statistics
- show ip dhcp pool
- show dhcp pool
- show ip dhcp server pool
Explanation:
The show ip dhcp pool command is used to view information about the DHCP address pool. The following code is a sample output of this command:
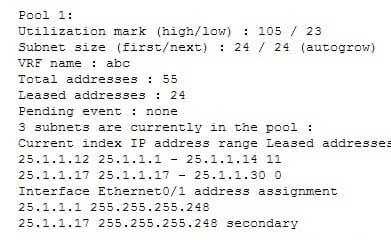
200-301 Part 18 Q20 168 The show ip dhcp server statistics command is incorrect because this command is used to view the statistics of the DHCP server.
The show dhcp pool command and show ip dhcp server pool commands are both incorrect because these are not valid Cisco IOS commands.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Troubleshoot client- and router-based DHCP connectivity issues