300-410 : Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) : Part 09
-
Which of the following translation scenarios is NOT supported by stateless NAT64?
- translation from IPv6 Internet to an IPv4 network
- translation from IPv4 Internet to an IPv6 network
- translation from IPv6 network to an IPv4 network
- translation from IPv4 network to an IPv6 network
Explanation:
Translation from IPv6 Internet addresses to an IPv4 network is not supported by the stateless version of NAT64. There are two versions of NAT 64: stateful and stateless. Stateful NAT64 creates or modifies bindings or session state while performing translation, while stateless NAT64 does not create or modify bindings or session state while performing translation/Translation from IPv4 Internet to an IPv6 network is supported by both NAT64 methods, although the stateful version requires static 6 to 4 mappings.
Translation from an IPv6 network to an IPv4 network is supported by both methods, stateful and stateless.
Translation from an IPv4 network to an IPv6 network is supported by both methods, although the stateful version requires static 6-to-4 mappings.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Describe IPv6 NAT -
Examine the following partial output of the show run command.
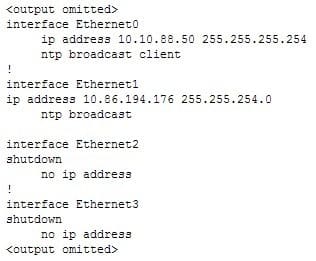
300-410 Part 09 Q02 104 Which of the following statements is true?
- NTP broadcasts will be sent on E0
- NTP broadcasts will be received on E0
- NTP broadcasts will be received on E1
- NTP broadcasts will be sent on E2
Explanation:
NTP broadcasts will be received on E0. This information is indicated by the presence of the command ntp broadcast client under that interface:interface Ethernet0
ip address 10.10.88.50 255.255.255.254
ntp broadcast client
!The ntp broadcast client command configures a device to listen to NTP broadcast messages.at that interface. NTP broadcasts will be received, not sent, on E0.
NTP broadcasts will be sent, not received, on E1, because the ntp broadcast command was applied to the Ethernet1 interface:
interface Ethernet1
ip address 10.86.194.176 255.255.254.0
ntp broadcastThe required command to receive broadcasts, ntp broadcast client, is present under the E0 interface, not the E1 interface.
NTP broadcasts will not be sent on E2. There are no ntp commands under that interface.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify Network Time Protocol (NTP) -
The following configuration is present on a router R1:

300-410 Part 09 Q03 105 Which part of the configuration provides many-to-one access for all devices on the defined segments to share a single IP address upon exiting the external interface?
- ip nat inside
- ip nat outside
- ip nat inside source list 7 serial0 overload
- access-list 7 permit 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.31
access-list 7 permit 10.10.20.0 0.0.0.31
Explanation:
The command ip nat inside source list 7 serial0 overload specifies the following:
- The translation should occur in the interface specified as inside.
- It should only be done for inside IP addresses that are specified in access list number 7.
- The IP address that inside addresses should be translated to belongs to the Serial0 interface.
- The translated IP address should be shared by all, as indicated by the overload keyword.The command ip nat inside identifies the inside interface. In this case, it indicates the one on which translation will take place.The command ip nat outside identifies the outside interface, which can be configured for translation. However, it has not been configured for translation in this scenario.The commands below define the inside IP addresses that are allowed to be translated:access-list 7 permit 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.31
access-list 7 permit 10.10.20.0 0.0.0.31Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify IPv4 Network Address Translation (NAT)
-
You have configured DHCP on a router and configured it to assign IP addresses in the range of 192.168.1.10 through 192.168.1.150. You just discovered that one of your print servers is using the address 192.168.1.100 and you cannot change it.
What command can you use on the router to solve this problem?
-
Router(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address -
Router(config)# access-list
-
Router(dhcp-config)# ip dhcp excluded-address
-
Router(config)# dhcp exclude-address
-
Router(config)# service dhcp excluded-address
Explanation:
The ip dhcp excluded-address command will allow you to specify an address or group of addresses in a pool that the DHCP server will not assign. This is typically used when a host has a permanent address assigned that would conflict with addresses that the DHCP server would hand out. The proper syntax for this command is as follows:Router(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address low-address [high-address]
The other options use improper syntax or are executed at an incorrect prompt. The ip dhcp excluded-address command should be executed at global configuration mode.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify IPv4 and IPv6 DHCP -
-
Yesterday one of your associates made some change to the syslog configuration on the router R69. Today, while working on the router you received this syslog message:000019: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by vty2 (10.34.195.36)Based on this output, which of the following commands did the associate execute?
-
service sequence-numbers
- service timestamps log
- service timestamps log datetime msec
- logging console 4
Explanation:
The associate must have executed the service sequence-numbers command during his changes. This command instructs the syslog system to add a sequence number to each message, which can help to organize a timeline when messages are sent to a syslog server from various sources.The associate could not have executed the service timestamps log command. This command enables time stamps on log messages, showing the time since the system was rebooted. If this had been done, a time stamp similar to the following would have been added to the message:
*Mar 1 18:46:11: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by vty2 (10.34.195.36)
The associate could not have executed the service timestamps log datetime msec command. This command enables time stamps on log messages, showing the time since the system was rebooted in milliseconds. If this had been done, a time stamp similar to the following would have been added to the message:
*Mar 1 18:46:11:058 %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by vty2 (10.34.195.36)
The associate could not have executed the logging console 4 command. This command instructs the syslog system to only display messages of levels 4, 3, 2 and 1 in severity. Since the message displayed is a level 5 message, this command could not have been executed.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify logging -
-
Which of the following translation mechanisms has the following characteristics?
Translates 1 to 1
Translates IPv6 to IPv6
Translates only the prefix
Is deployed at the network edge- NAT64
- NAT44
- NPTv6
- NPTv4
Explanation:
Network Prefix Translation (NPTv6) is a stateless method of translating the prefix of a received IPv6 address to another prefix without changing the host portion of the IPv6 address. Its mappings are 1 to 1, and it translates only the prefix of the address.NAT64 translates from IPv6 to IPv4 and vice versa. It does not translate from IPv6 to IPv6.
NAT44 translates from IPv4 to IPv4. It does not translate from IPv6 to IPv6.
There is IPv4 version of Network Prefix Translation, called NPTv4. IT does not translate from IPv6 to IPv6.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Describe IPv6 NAT -
You have applied the following configuration to Router71, as indicated in the following partial output of the show run command:

300-410 Part 09 Q07 106 Which of the following statements is true of this configuration?
- This is a GLBP configuration
- 171.16.6.100 is the IP address of the HSRP group
- The numeral 1 is the number of the HSRP group
- This router will be prevented from taking back over as active router when it recovers from a loss of its Serial0 interface
Explanation:
One is the number of the HSRP group. Hot Standby Routing Protocol (HSRP) can be used to provide default gateway redundancy for computers sharing the same gateway. At least two routers are gathered into a routing group, which in this case is numbered 1. One of the routers will answer ARP requests for the standby IP address (in this case 171.16.6.100), which is the address the computers will have configured as their default gateway. That router is called the active router. If that router goes down, then the other router will start answering ARP requests for the standby IP address.This is not a Gateway Load Balancing Protocol configuration. That is an alternative to HSRP which allows both routers to be used while still providing backup to one another. That configuration would be different in that it uses GLBP groups rather than standby groups, among other differences.
This router will be not prevented from taking back over as active router when it recovers from an outage of its Serial 0 interface. The presence of the command standby 1 preempt indicates that the router can take back over or preempt the other router when it recovers from an outage of its Serial 0 interface. The command standby 1 track Serial0 tells the router to track the up/down state of its Serial 0 interface. If it goes down, it knows to decrement its HSRP priority by 10 (the decrement value). This will drop its HSRP priority to 95. We do not see the priority of the other router in the group, but if for example its priority is 100, this configuration would allow it to take over as active router.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify tracking objects -
You have been asked to troubleshoot the NTP configuration of a router named R70. After executing the show run command, you receive the following partial output of the command that shows the configuration relevant to NTP:

300-410 Part 09 Q08 107 Based on this output, which of the following statements is true?
- the time zone is set to 8 hours less than Pacific Standard time
- the router will listen for NTP broadcasts on interface E0/0
- the router will send NTP broadcasts on interface E0/0
- the router will periodically update its software clock
Explanation:
The router will send NTP broadcast on its E0/0 interface. The command ntp broadcast, when executed under an interface, instructs the router to send NTP broadcast packets on the interface. Any devices on the network that are set with the ntp broadcast client command on any interface will be listening for these NTP broadcasts. While the clients will not respond in any way, they will use the information in the NTP broadcast packets to synchronize their clocks with the information.The time zone is not set to 8 hours less than Pacific Standard Time. The value -8 in the command clock timezone PST -8 is the amount of hours offset from UTC time, not from the time zone stated in the command.
The router will not listen for NTP broadcasts on the interface E0/0. The ntp broadcast command, when executed under an interface, instructs the router to send NTP broadcast packets on the interface. To set the interface to listen and use NTP broadcasts, you would execute the ntp broadcast client command on the interface.
The router will not periodically update its software clock. The command ntp update-calendar configures the system to update its hardware clock from the software clock at periodic intervals.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify Network Time Protocol (NTP) -
Some of the technicians in your organization use the secure web interface to make some of the configurations changes on the router R68. Today it was reported that a technician could not make a connection to the secure web server. You execute a show run command on R68 and receive the following output:

300-410 Part 09 Q09 108 What must the technician do to make the connection to the secure web interface?
- specify port 443 in the command
- specify port 1025 in the command
- disable the HTTP server first
- enable the secure server
Explanation:
The partial output of the show run command indicates that the port number of the HTTPS interface has been changed to 1025. This is indicted by the presence of this command in the configuration:ip http secure-port 1025
That is not the default port configuration of 443. Therefore, anyone wishing to connect to the secure server will need to reference the new port number in the command. If you change the HTTPS port number, clients attempting to connect to the HTTPS server must specify the port number in the URL, in this format:
https://device:port_number
In this syntax, port_number is the HTTPS port number.
It will not help for the technician to reference port 443 in the command, because that is no longer the port number of the secure server. It is now 1025.
It is not required to disable the HTTP server to use the HTTPS server, although it is a best practice to do so.
There is no need to enable the secure server. We can see it has been enabled by the presence of this command in the configuration:
ip http secure-server
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify device management -
You just received the following system message.*Mar 1 18:46:11:553 %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by vty2 (10.34.195.36)
(Switch-2)
With this message in mind, which of the following commands were executed on the device? (Choose all that apply.)
- logging console level notifications
- logging console level 4
- service timestamps log datetime msec
- service timestamps log datetime
Explanation:
The two commands that must have been executed to produce output in that format are logging console level notifications and service timestamps log datetime msec.The logging console level notifications command species that all messages at level 5 (notifications and above) will be sent to the console. This is not entered by the number of the message type, but the name of the message type.
The service timestamps log datetime msec command specifies that a timestamp up to the millisecond should be included in all messages that include the time.
While the logging console level command can be used with a level number on some devices, notifications are level 5, not 4.
The service timestamps log datetime command specifies that a timestamp should be included in all messages, but it will not include the millisecond. Better logging functionality can be achieved by using the msec keyword to help organize tightly spaced events.
The logging history command can specify the proper level of messages to reduce unnecessary messages.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify logging -
Which of the following statements is NOT true of NPTv6?
- is transport agnostic
- translates the entire IPv6 address to another IPv6 address
- is check sum neutral
- translates only the IPv6 prefix
Explanation:
Network Prefix Translation (NPTv6) is a stateless method of translating the prefix of a received IPv6 address to another prefix without changing the host portion of the IPv6 address. Some of its characteristics are:
It supports both transports that perform checksums on the IP header and those that do not.
It provides a 1 to 1 relationship between the inside and outside prefixes.
It translates only the prefix, and not the entire address.Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Describe IPv6 NAT -
You are configuring NAT64 to allow communication between a host running IPv6 and a server running IPv4. The router R1 sits between the host and the server. The router’s Fa0/2/7 interface is connected to the IPv6 host, and the Fa0/2/6 interface is connected to the IPv4 server.The IPv6 host has an IPv6 address of 2001::a00:1/128 and the IPv4 server is at 10.0.0.1. Below is the relevant configuration on R1:
When the IPv4 server responds to the IPv6 host, what IPv6 address will be in the source address in the packet?
- 2001::a001
- 2001::A00:B
- 3001::a00:1
- 2001::A00:A
Explanation:
NAT64 is a solution when IPv6 hosts need to communicate with IPv4-only servers. When the translation occur on the router the IPv4 address 10.0.0.1 will converted to hex as a00:1 and will be attached to the end of the stateful prefix of 3001::/96 that was configured on the router interface connected to the IPv4 server. The result will be 3001::a00:1.The address will not be 2001::a001. The prefix that will be attached to the hex version of 10.0.0.1 will not be that of the interface fa0/2/7 but will be the prefix that was configured on that interface for nat64 translation which is 3301::/96.
The address will not be 2001::a00:b. That is the IPv6 address on the interface connected to the IPv6 host, but that address is not used for IPv4 to IPv6 communication. A translated address will be generated by converting the IPv4 address of the IPv4 host to hex and attaching it to the IPv6 prefix configured on the interface connected to the IPv4 server.
The address will not be 2001::A00:A. That is the IPv6 address of the IPv6 host. That was statically mapped to 10.0.0.10 in the configuration and as such will be the IPv4 address used by the IPv6 host on the IPv4 side of the router.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Describe IPv6 NAT -
Your network team is assessing options available to translate IPv6 address to IPv4 addresses. You have focused your attention on the variants of NAT64. One of your requirements is the conservation of IPv4 addresses.
Which of the following versions of NAT 64 helps to conserve IPv4 addresses?
- stateless
- manual
- static
- stateful
Explanation:
One of the characteristics of stateful NAT64 is that it conserves IPv4 addresses. NAT64 is a version of network address translation that translates IPv6 address to IPv4 and vice versa. It has two variants, stateless and stateful. The following table describes some of the major differences between the two:
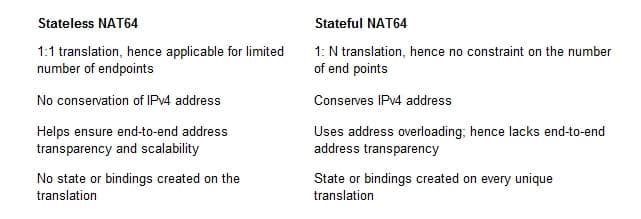
300-410 Part 09 Q13 109 NAT64 has neither the variant static nor the variant manual.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Describe IPv6 NAT -
The network team is reviewing its options with regard to network address translation. Now that the network has been completely changed over to IPv6, you need a mechanism to translate from the private IPv6 addresses inside your network to public IPv6 addresses. You would like for these mappings to be one-to-one.
Which of the following performs this function?
- stateful NAT64
- NPT6
- NAT44
- stateless NAT 64
Explanation:
NPT6 is a version of NAT that translates private IPv6 addresses to public or global IPv6 addresses. It is a stateless mechanism and requires a one-to-one mapping of private to global IPv6 addresses.Neither version of NAT64 translates from private IPv6 addresses to public or global IPv6 addresses. Both stateful and stateless NAT64 translate from IPv4 to IPv6.
NAT44 does translate private IPv6 addresses to public or global IPv6 addresses, but it is stateful in operation. It does not perform one-to-one mappings.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Describe IPv6 NAT -
Your network team is assessing options available to translate IPv6 address to IPv4 addresses.
In which of the following scenarios is stateless NAT64 NOT supported as a solution?
- translating from an IPv4 network to an IPv6 network
- translating from an IPv6 network to an IPv4 network
- translating from the IPv6 Internet to an IPv4 network
- translating from an IPv6 network to the IPv4 Internet
Explanation:
Stateless NAT64 does not support translating from the IPv6 Internet to an IPv4 network. NAT64 is a version of network address translation that translates IPv6 address to IPv4 and vice versa. It has two variants, stateless and stateful. In stateless translation, mappings are created using an algorithm, but those mappings are not maintained while translation is being performed. Stateful NAT64 both creates and maintains mappings during translation.Due to the fact it does not maintain mappings, stateless NAT64 supports all of the options given except translating from the IPv6 Internet to an IPv4 network.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Describe IPv6 NAT -
You are implementing IP SLA and would like to use it to measure hop-by-hop response time between a Cisco router and any IP device on the network.
Which of the following IP SLA operations would you use for this?
- ICMP path echo operation
- Internet Control Message Protocol Echo Operation
- UDP Jitter Operation for VoIP
- UDP Jitter Operation
Explanation:
The ICMP path echo operation discovers the path using the traceroute command, and then measures response time between the source router and each intermittent hop in the path. IP SLAs allow users to monitor network performance between Cisco routers or from either a Cisco router to a remote IP device.The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Operation measures end-to-end response time between a Cisco router and any IP-enabled device. Response time is computed by measuring the time taken between sending an ICMP echo request message to the destination and receiving an ICMP echo reply. It does not measure hop-by-hop response time.
The UDP Jitter Operation for VoIP is an extension to the current jitter operations with specific enhancements for VoIP. The enhancements allow this operation to calculate voice quality scores and simulate the codec’s directly in CLI and the MIB. It does not measure hop-by-hop response time.
The UDP Jitter Operation is designed to measure the delay, delay variance, and packet loss in IP networks by generating active UDP traffic. It does not measure hop-by-hop response time.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Describe SLA architecture -
You have implemented the following IP SLA configuration, as shown in the following partial output of the show run command:ip sla 1
dns cow.cisco.com name-server 10.52.128.30
ip sla schedule 1 start-time now
Which of the following statements is true of this configuration?
- it will find the response time to resolve the DNS name cow.cisco.com
- it will find the response time to connect to the DNS server at 10.52.128.30
- it will start in one minute
- it will gather data from one minute
Explanation:
It will find the response time to resolve the DNS name cow.cisco.com. Domain Name System (DNS) response time is computed by calculating the difference between the time taken to send a DNS request and the time a reply is received. The Cisco IOS IP SLAs DNS operation queries for an IP address if the user specifies a hostname, or queries for a hostname if the user specifies an IP address.It will not find the response time to connect to the DNS server at 10.52.128.30. That is the IP address of the DNS server being used for the operation (10.52.128.30). However, it will measure the response time to resolve the DNS name cow.cisco.com.
It will not start in one minute. It will start immediately, as indicated by the start-time now parameter.
It will not gather data for one minute. The numeral 1 in the first line refers to the IP SLA number, and the numeral 1 in the last line refers to the IP SLA number to be scheduled.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify IP SLA -
A TFTP server, a DNS server, and a TACACS server are residing in the 192.168.5.0/24 subnet. Their IP addresses are 192.168.5.2, 192.168.5.3, and 192.168.5.4, respectively.You would like to configure the routers to forward UDP broadcasts to these servers.
Which of the following commands or sets of commands would configure this to occur using the LEAST number of commands?
- ip helper-address 192.168.5.2 69
ip helper-address 192.168.5.3 53
ip helper-address 192.168.5.4 49 - ip helper-address 192.168.5.2
ip helper-address 192.168.5.3
ip helper-address 192.168.5.4 - ip helper-address 192.168.50 69 53 49
- ip helper-address 192.168.5.255
Explanation:
The only command required is ip helper-address 192.168.5.255. This command is a directed broadcast to the subnet on which the servers reside which will cause all servers to receive the broadcast. Each server will process only the packets aimed at the port on which they are listening.It not necessary to specify any port numbers because the ip helper-address command will forward to the following ports by default:
NTP – port 37
TACACs – port 49
DNS – port 53
BootP – port 67
TFTP – port 69
NetBIOS Name server – port 137
NetBIOS Datagram server – port 138While the following command set would work, it does not contain the least number of commands:
ip helper-address 192.168.5.2 69
ip helper-address 192.168.5.3 53
ip helper-address 192.168.5.4 49It is not required to specify each server and its respective port number.
The following command set would also have the desired results, because port numbers are not required for the default services:
ip helper-address 192.168.5.2
ip helper-address 192.168.5.3
ip helper-address 192.168.5.4However, this is not the least number of commands you can execute to achieve the solution.
The command ip helper-address 192.168.50 69 53 49 would not work because it is addressed to the network number of the subnet to which the servers are connected. To send to them all requires a directed broadcast.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify IPv4 and IPv6 DHCP - ip helper-address 192.168.5.2 69
-
You are configuring Netflow and you are explaining its operation to your assistant. He wants to know what constitutes a flow.
Which of the following items are NOT used to distinguish one flow from another?
- source IP address
- destination IP address
- source port number
- Layer 2 protocol type
Explanation:
Layer 2 protocol type is not used to distinguish one flow from another. A flow in Netflow refers to an individual communication session between two devices. A flow is defined by the combination of the following seven key fields:- Source IP address
- Destination IP address
- Source port number
- Destination port number
- Layer 3 protocol type
- Type of service (ToS)
- Input logical interfaceObjective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify Cisco NetFlow
-
Examine the output of the show ip flow export command:

300-410 Part 09 Q20 110 Which statement is true regarding the results?
- 15 export packets were dropped because there was insufficient memory to create the export packet
- 3 export packets were dropped because CEF was unable to switch or forward the packet to the process level
- 61 packets were dropped because the send queue was full
- 8 flows were exported
Explanation:
Sixty-one packets were dropped because the send queue was full. The last line in the output, 61 export packets were dropped due to output drops, will result when the send queue is full.Fifteen packets were not dropped because there was insufficient memory to create the export packet. Drops that occurred from insufficient memory are indicated with the line 3 flows failed due to lack of export packet, and there were only three of them.
Three export packets were not dropped because CEF was unable to switch or forward the packet to the process level. Drops that occurred because CEF was unable to switch or forward the packet, are indicated with the line 15 export packets were dropped due to no fib, and there were fifteen of them.
Eleven flows were sent, not eight. The eleven flows were sent in eight datagrams.
Objective:
Infrastructure Services
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify Cisco NetFlow