300-735 : Automating Cisco Security Solutions (SAUTO) : Part 01
-
You are using ASDM to verify a clientless SSL VPN configuration made by a junior administrator on an ASA. Please click exhibit to answer the following questions.
Exhibit: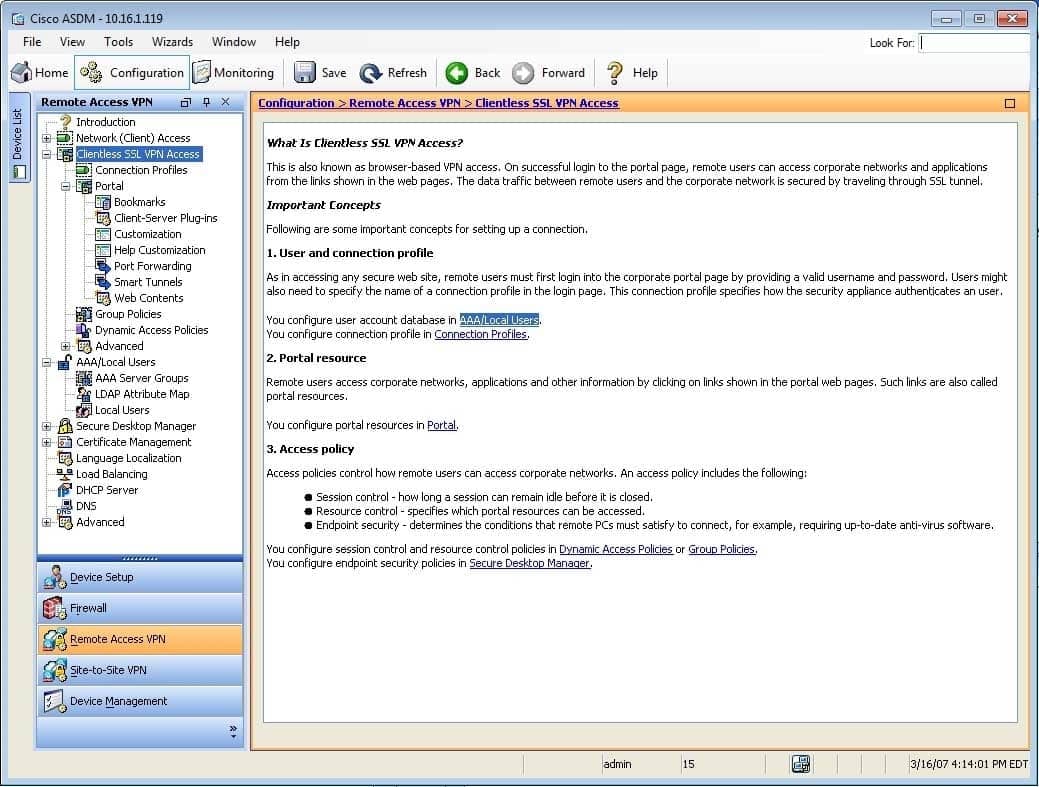
300-735 Part 01 Q01 001 Which of the following user accounts will be able to connect to the ASA by using ASDM? (Select the best answer.)
- only john
- only boson
- only jane
- both john and jane
- both jane and boson
- john, jane, and boson
Explanation:
Both the jane and the boson user accounts will be able to connect to the Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) by using Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM). When you add a user to the local Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) database on an ASA, you can specify security parameters for the user. One security option you can specify is whether the user can establish a management connection to the ASA. This option is configured in the Add or Edit User Account dialog box in ASDM. Under Access Restriction, you can select Full Access (ASDM, SSH, Telnet and Console), CLI login prompt for SSH, Telnet and console (no ASDM access), or No ASDM, SSH, Telnet or Console access. The Full Access (ASDM, SSH, Telnet and Console) option will let the user use ASDM or the command line interface (CLI) to administer the ASA. In this scenario, this option is selected for both the jane and the boson user accounts, as shown in the following exhibits:
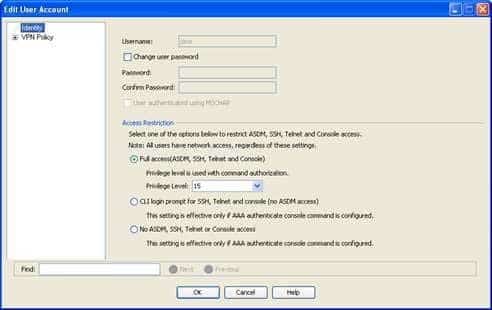
300-735 Part 01 Q01 002 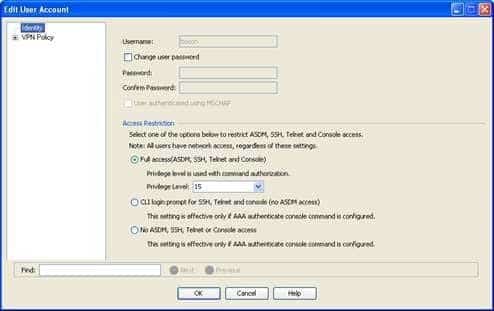
300-735 Part 01 Q01 003 You can access the Add or Edit User Account dialog box in ASDM by clicking Configuration, clicking the Remote Access VPN button, expanding AAA/Local Users, and clicking Local Users. To open the Edit User Account dialog box, you should double click the user account that you want to open.
The john user account is configured with the No ASDM, SSH, Telnet or Console access option. This option will prevent the user from establishing a management connection to the device by using ASDM, SSH, Telnet, or the console. -
You are using ASDM to verify a clientless SSL VPN configuration made by a junior administrator on an ASA. Please click exhibit to answer the following questions.
Which of the following tunneling protocols will the jane user account be able to use when establishing a clientless SSL VPN connection by using the boson tunnel group? (Select the best answer.)
Exhibit:
300-735 Part 01 Q02 004 - only clientless SSL VPN
- only SSL VPN client
- only IPSec
- only L2TP/IPSec
- both client and clientless SSL VPN
- both clientless SSL VPN and IPSec
300-735 Part 01 Q02 005 Explanation:
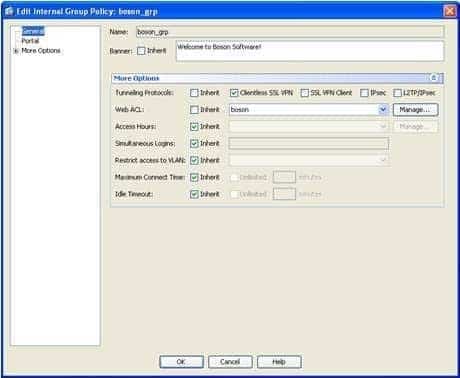
The jane user account will be able to use only the clientless Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) virtual private network (VPN) tunneling protocol when establishing a clientless SSL VPN connection by using the boson tunnel group. You can specify the tunneling protocols that can be used to establish a connection to a tunnel group, which is also known as a connection profile, either in a group policy or within a user account, depending on whether the tunneling protocol configuration should be applied to a group or to a single user.
When you configure a tunneling protocol, you can specify one or more of the following four options: Clientless SSL VPN, SSL VPN Client, IPSec, or L2TP/IPSec.
In this scenario, you can view the tunneling protocols that are configured for the jane user account by accessing her user account information in Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) by clicking Configuration, clicking the Remote Access VPN button, expanding AAA/Local Users, clicking Local Users, and double clicking the jane user account, which will open the Edit User Account dialog box. You should then click VPN Policy, which will display a pane that includes a Tunneling Protocols entry. This entry for the jane user account is configured with the Inherit option, which means that the tunneling protocols that the jane user account can use will be inherited from a group policy that is associated with the jane user account. In this scenario, the jane user account is associated with the boson_grp group policy.
To view the tunneling protocols that are associated with the boson_grp group policy in ASDM, you should click Configuration, click the Remote Access VPN button, expand Clientless SSL VPN Access, select Group Policies, and double click boson_grp, which will open the Edit Internal Group Policy dialog box. The More Options section on the General pane displays the Tunneling Protocols entry. Only the Clientless SSL VPNoption is selected, as shown in the following exhibit: -
You are using ASDM to verify a clientless SSL VPN configuration made by a junior administrator on an ASA. Please click exhibit to answer the following questions.
Exhibit:
300-735 Part 01 Q03 006 Which of the following statements are true regarding clientless SSL VPN connections that are made by using the boson tunnel group? (Select 3 choices.)
- VPN clients will be authenticated using the local AAA database.
- VPN clients will be authenticated using digital certificates.
- The DfltGrpPolicy group policy will be applied to the VPN connections.
- The boson_grp group policy will be applied to the VPN connections.
- No welcome banner will be displayed to VPN clients.
- A welcome banner will be displayed to VPN clients.
Explanation:
Virtual private network (VPN) clients will be authenticated using the local Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) database, the boson_grp group policy will be applied to the VPN connections, and a welcome banner will be displayed to VPN clients. When configuring a tunnel group, which is also known as a connection profile, in Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM), you can specify a number of parameters. For example, you can specify the type of authentication to use and the default group policy to use for VPN connections made by using the tunnel group. This information can be configured or modified on the Add or Edit Clientless SSL VPN Connection Profile dialog box in ASDM. To access this dialog box in ASDM, you should click Configuration, click the Remote Access VPN button, expand Clientless SSL VPN Access, and click Connection Profiles. You should then double click a connection profile, which will open the Edit Clientless SSL VPN Connection Profile dialog box for the selected connection profile. The Edit Clientless SSL VPN Connection Profile dialog box for the boson tunnel group is shown in the following exhibit:

300-735 Part 01 Q03 007 The Authentication section of the Basic screen of the Edit Clientless SSL VPN Connection Profile dialog box indicates that the tunnel group will use the local AAA database for user authentication. Thus any VPN connections made by using this tunnel group will be authenticated against the AAA database.
The Default Group Policy section indicates that the boson_grp group policy will be applied to this connection profile. That is, the settings in the boson_grp group policy will apply to VPN users who connect by using the boson tunnel group.
You can view the details of the boson_grp group policy to determine whether a banner message will be displayed to VPN clients. This information is displayed on the Generalpane of the Add or Edit Internal Group Policy dialog box. To view the details of an existing group policy for clientless SSL VPN users in ASDM, you should click Configuration, expand Clientless SSL VPN Access, and click Group Policies. You can then doubleclick boson_grp, which will open the Edit Internal Group Policy dialog box, which is shown in the following exhibit: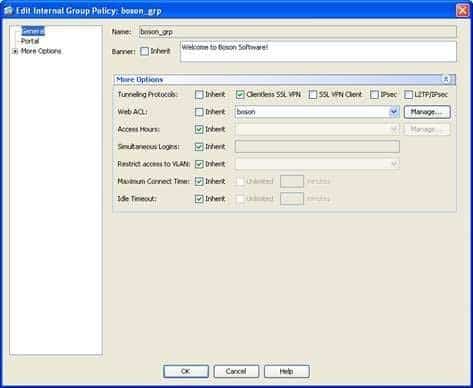
300-735 Part 01 Q03 008 The Banner entry contains a value of Welcome to Boson Software! Because VPN connections made by using the boson tunnel group will use the boson_grp group policy, you can determine that VPN users will be shown a welcome banner in this scenario.
-
You are using ASDM to verify a clientless SSL VPN configuration made by a junior administrator on an ASA. Please click exhibit to answer the following questions.
Exhibit:
300-735 Part 01 Q04 009 Which of the following statements is true regarding VPN connections made by a user who is using the john user account? (Select the best answer.)
- The user will be unable to establish a VPN connection by using the boson tunnel group.
- The user will be able to establish a connection by using any tunnel group.
- The DfltGrpPolicy group policy will be applied to any VPN connection that the user established.
- The user will be able to establish only clientless SSL VPN connections.
Explanation:
The user will be able to establish only clientless Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) virtual private network (VPN) connections. The tunneling protocols that a user can use to establish a VPN connection can be configured in the user profile or in a group policy. To configure the tunneling protocols in a user profile, you should access the VPN Policy pane of the Add or Edit User Account dialog box. To access this pane, you should click Configuration, click the Remote Access VPN button, expand AAA/Local Users, click Local Users, double click john, and then click VPN Policy. The VPN Policy pane of the john user account is shown in the following exhibit:
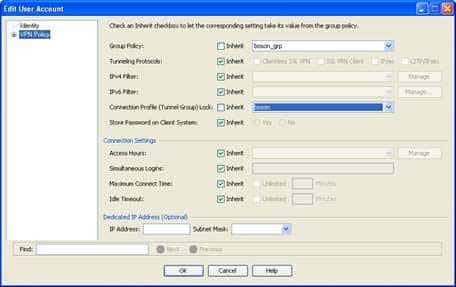
300-735 Part 01 Q04 010 The Tunneling Protocols entry indicates that the john user account is inheriting the tunneling protocol settings from a group policy. The Group Policy entry indicates that the group policy associated with the john user account is boson_grp. Therefore, you must view the details of the boson_grp group policy to determine the tunneling protocols that the john user account can use.
To view the details of the boson_grp group policy, you should click Configuration, expand Clientless SSL VPN Access, click Group Policies, and doubleclick boson_grp, which will open the Edit Internal Group Policy dialog box, as shown in the following exhibit: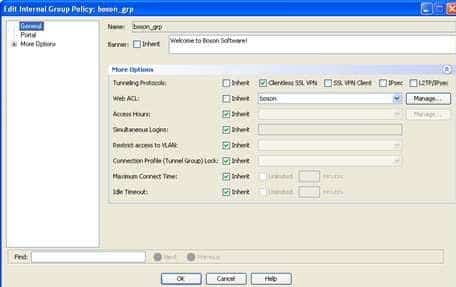
300-735 Part 01 Q04 011 The Tunneling Protocols entry indicates that the group policy allows only clientless SSL VPN connections. Because the john user account inherits this setting, the john user account will be able to establish a VPN connection by using only a clientless SSL VPN connection.
-
You are using ASDM to verify a clientless SSL VPN configuration made by a junior administrator on an ASA. Please click exhibit to answer the following questions.
Exhibit: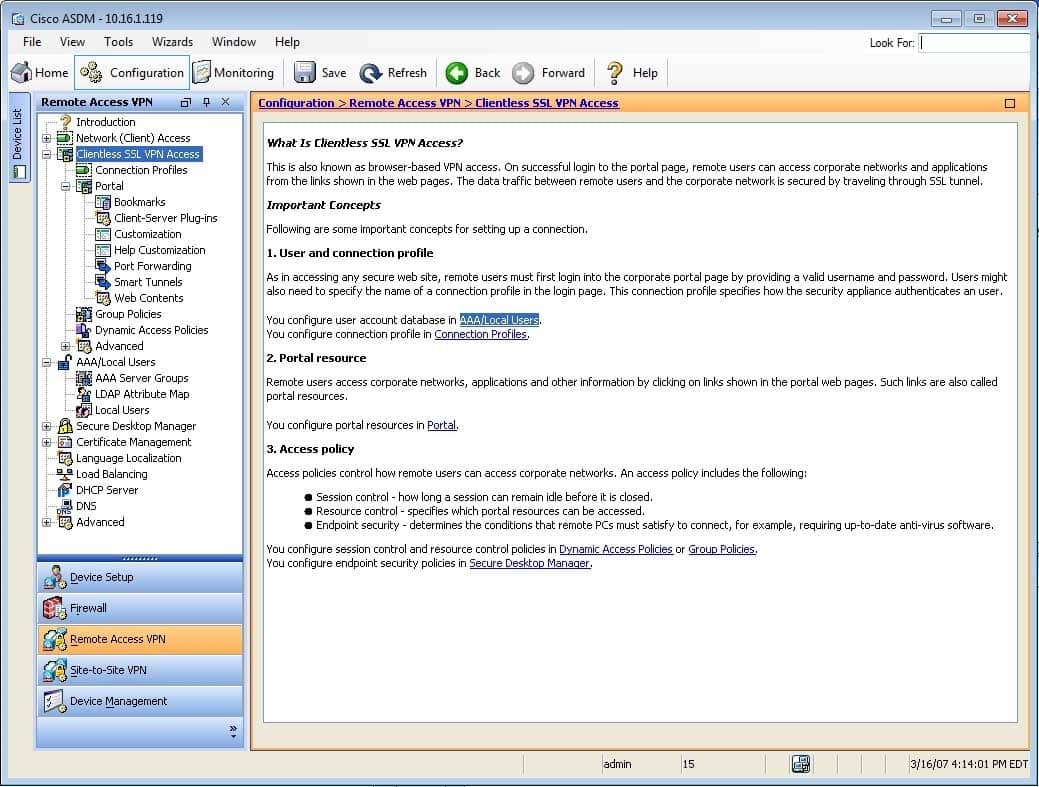
300-735 Part 01 Q05 012 Which of the following connection profiles will use the boson_grp group policy? (Select the best answer.)
- only the boson connection profile
- only the DefaultRAGroup connection profile
- only the DefaultWEBVPNGroup connection profile
- both the boson connection profile and the DefaultWEBVPNGroup connection profile
- both the DefaultRAGroup connection profile and the DefaultWEBVPNGroup
Explanation:
Only the boson connection profile will use the boson_grp group policy. To determine which connection profiles will use the boson_grp group policy, you should access the Connection Profiles pane in Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM). To access this pane, you should click Configuration, click the Remote Access VPN button, expand Clientless SSL VPN Access, and click Connection Profiles, which will open the Connection Profiles configuration pane, as shown in the following exhibit:

300-735 Part 01 Q05 013 This pane displays a summary of the connection profiles that are configured on the Cisco Adaptive Security
Appliance (ASA). In this scenario, there are three connection profiles. There are two default profiles, Default RA Group and Default WEB VPN Group, and one user specified connection profile, boson. To view which group policy is associated with which connection profile, you should double click the connection profiles to open the Edit Clientless SSL VPN Connection Profile dialog box. The default group policy that is associated with a connection profile is displayed on the Basic pane of this dialog box. By viewing this information, you can determine that only the boson connection profile uses the boson_grp group policy. The Basic pane of the boson connection profile is shown in the following exhibit: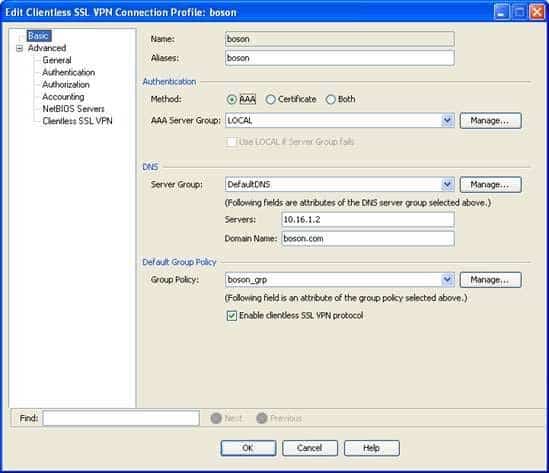
300-735 Part 01 Q05 014 The two default connection profiles use the default group policy, which is DfltGrpPolicy.
-
Which of the following is typically used to manage a Cisco router in-band? (Select the best answer.)
- a VTY port
- a serial port
- a console port
- an auxiliary port
Explanation:
A virtual terminal (VTY) port is typically used to manage a Cisco router in-band. When a Cisco device is operating in its normal state, another device can connect to it by using VTY application protocols such as Telnet or Secure Shell (SSH). The use of VTY lines typically allows multiple administrators or management applications to concurrently access a device from more than one location.
You would not use a console port or an auxiliary (AUX) port to manage a Cisco router in-band. You are most likely to use either an AUX port or a console port to manage a Cisco router out-of-band, such as when the router is in read-only memory (ROM) monitor (ROMmon) mode. The AUX port on a Cisco router is typically capable of supporting most of the features available on a console port. Cisco switches either do not have AUX ports or do not support certain features, such as system recovery, on their AUX ports if they have them.
ROMmon is a management mode that Cisco routers and switches revert to when the system cannot find a software image, the software image is corrupted, or the configuration register has been set to manually enter ROMmon mode. Because ROMmon is an out-of-band management method, it can be used to recover system software images, passwords, or other configuration data even when the router or switch is in a state where it can no longer forward packets.
You would not use a serial port to manage a Cisco router in-band. Serial ports and Ethernet ports are used to directly connect Cisco routers to other network devices. For example, you might use a serial port to directly connect a Cisco router to other data terminal equipment (DTE) or data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE) devices. You would also use a serial port to connect a router to a Channel Service Unit/Data Service Unit (CSU/DSU). -
Which of the following enables the validation of both user and device credentials in a single EAP transaction? (Select the best answer.)
- PEAP
- EAP-FAST
- EAP-FAST with EAP chaining
- EAP-MD5
Explanation:
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP)Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling (FAST) with EAP chaining, which is also sometimes called EAPFAST version 2 (EAPFASTv2), enables the validation of both user and device credentials in a single EAP transaction. EAP chaining enables a Cisco security device to validate authentication credentials for both a user and the user’s device. In order to enable EAP chaining, both the Cisco security device and the supplicant device must support EAP chaining. The Cisco security device will assign a different level of authorization access depending on one of four success and failure possibilities, as shown in the following table:
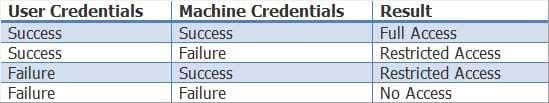
300-735 Part 01 Q07 015 EAPFAST is an authentication protocol that can be used for point-to-point connections and for both wired and wireless links. The EAPFAST authentication process consists of three phases. The first phase, which is optional and is considered phase 0, consists of provisioning a client with a PAC, which is a digital credential that is used for authentication. A PAC can be manually configured on a client, in which case phase 0 is not required. The second phase, which is referred to as phase 1, involves creating a secure tunnel between the client and the server. The final phase, which is referred to as phase 2, involves authenticating the client. If the client is authenticated, the client will be able to access the network.
EAPTransport Layer Security (TLS) is an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard that is defined in Request for Comments (RFC) 5216. It does not support EAP chaining. Protected EAP (PEAP) is an open standard developed by Cisco, Microsoft, and RSA? it does not support EAP chaining.
EAPMessage Digest 5 (MD5) uses an MD5 hash function to provide security and is therefore considered weak when compared to later methods. EAP is an IETF standard that was originally defined in RFC 2284? it does not support EAP chaining. -
Which of the following features protects the control plane by classifying traffic into three separate control plane subinterfaces? (Select the best answer.)
- CoPP
- CPPr
- RBAC
- uRPF
Explanation:
Control Plane Protection (CPPr) protects the control plane by classifying control plane traffic into three separate subinterfaces: the host subinterface, the transit subinterface, and the Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF)exception subinterface. The host subinterface contains control plane IP traffic that is destined for a router interface, including traffic from the following sources and protocols:
– Terminating tunnels
– Secure Shell (SSH)
– Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
– Internal Border Gateway Protocol (iBGP)
– Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)The transit subinterface contains control plane IP traffic that is traversing the router, including the following traffic:
– Nonterminating tunnel traffic
– Traffic that is softwareswitched by the route processorThe CEFexception subinterface contains control plane traffic that is redirected by CEF for process switching, as well as traffic from the following sources and protocols:
– NonIP hosts
– Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
– External BGP (eBGP)
– Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
– Label Distribution Protocol (LDP)
– Layer 2 keepalivesCPPr is used to protect the control plane by filtering and rate limiting traffic in order to prevent excessive CPU and memory consumption. To configure CPPr, you must perform the following steps:
– Create access control lists (ACLs) to identify traffic.
– Create a traffic class.
– Create a traffic policy, and associate the traffic class to the policy
– Apply the policy to the specific control plane subinterface.Control Plane Policing (CoPP) is similar to CPPr, except CoPP does not separate control plane traffic into three subinterfaces. To configure CoPP, you must perform the following steps:
– Create ACLs to identify traffic.
– Create a traffic class.
– Create a traffic policy, and associate the traffic class to the policy.
– Apply the policy to the control plane interface.Both CoPP and CPPr use class maps to filter and ratelimit traffic. However, CPPr separates control plane traffic into three subinterfaces: the host subinterface, the transit subinterface, and the Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF)exception subinterface. For this reason, Cisco recommends that you use CPPr instead of CoPP whenever possible.
RoleBased Access Control (RBAC) does not protect the control plane. RBAC protects the management plane by granting limited access to administrators so that they can perform only the tasks required for their job. For example, you can configure permissions on an administrator’s account so that the administrator can issue only certain commands, which will prevent the administrator from making unauthorized configuration changes or from viewing restricted information.
Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding (uRPF) does not protect the control plane. uRPF protects the data plane by checking the source IP address of a packet to determine whether an inbound packet arrived on the best path back to the source based on routing table information. If the uRPF check passes, the packet is transmitted? if the uRPF check fails, the packet is dropped. -
Which of the following is an outputspreading technique that spammers use to manipulate reputation scores and defeat filters? (Select the best answer.)
- phishing
- snowshoe spam
- waterfalling
- listwashing
Explanation:
Of the available choices, snowshoe spam is an outputspreading technique that spammers use to manipulate reputation scores and defeat filters. Snowshoe spammers establish many false company names and identities, often with unique post office addresses and telephone numbers, so that reputation filters do not perceive the source of the spam as a threat. In addition, the spam output is spread across multiple IP addresses and domain names in order to defeat blacklists.
The Cisco Context Adaptive Scanning Engine (CASE) on a Cisco Email Security Appliance (ESA) is a contextual analysis technology that is intended to detect email threats, such as snowshoe spam, as they are received. CASE checks the reputation of email senders, scans the content of email messages, and analyzes the construction of email messages. As part of this process, CASE submits the email sender to the Cisco SenderBase Network, which contains data on hundreds of thousands of email networks. The sender is assigned a score based on this information. The content of the email messaging is scanned because it could contain language, links, or a call to action that is indicative of a phishing scam.
Phishing is a social engineering technique in which a malicious person uses a seemingly legitimate electronic communication, such as email or a webpage, in an attempt to dupe a user into submitting personal information, such as a Social Security number (SSN), account login information, or financial information. To mitigate the effects of a phishing attack, users should use email clients and web browsers that provide phishing filters. In addition, users should also be wary of any unsolicited email or web content that requests personal information. The CASE on a Cisco ESA appliance is capable of detecting phishing scams.
Listwashing is a spammer technique of cleaning lists of email recipients who complain about spam but without stopping the spam from being sent to other recipients who do not complain. Listwashing is similar to an optout address policy, meaning that email addresses are included in the list without the permission of the email address owner and only removed if the owner complains.
Waterfalling is a spammer technique of cleaning lists of email recipients by sending the lists through multiple email service providers. Spammers with bad lists use this technique to uncover email addresses that bounce or that result in complaints against the spammer. The spammer can then remove those email addresses from the list, which increases the likelihood that spam will be delivered to the remaining recipients. -
You are configuring dynamic PAT on a Cisco ASA 5500 using the CLI. The ASA is running software version 8.3.
Which of the following IP addresses can you configure inline? (Select the best answer.)
- inside global
- outside global
- inside local
- outside local
Explanation:
You can configure an inside global address inline if you are configuring dynamic Port Address Translation (PAT) on a Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) using the command line interface (CLI). A global address is a source or destination IP address as seen from the perspective of a host on the outside network. An inside global address is an IP address that represents an internal host to the outside network? it can be configured inline by using the nat command or defined within a network object.
On a Cisco ASA, a network object is a data structure that is used in place of inline IP information. You might use a network object in place of configuring IP addresses, subnet masks, protocols, and port numbers if you must configure that same information in multiple places. If the information you configure within the object ever changes, you then need only modify the single object instead of locating and modifying each instance of the inline IP information.
An object group is simply a group of network objects. By grouping network objects, you can enable the use of a single application control engine (ACE) to make requests of multiple devices.
Inside global addresses are typically public IP addresses assigned by the administrator of the outside network. Dynamic PAT can translate many inside local IP addresses to a single inside global IP address. In ASA terms, the inside global address is also known as the mapped address, because it is the IP address that you want to map to.
You are more likely to configure an inside local address in a network object or object group, not inline. A local address is a source or destination IP address as seen from the perspective of a host on the inside network. An inside local address is an IP address that represents an internal host to the inside network. Inside local addresses are typically private IP addresses defined by Request for Comments (RFC) 1918. When a NAT router receives a packet from a local host destined for the Internet, the router changes the inside local address to an inside global address and forwards the packet to its destination.
You would not necessarily configure an outside local address in this scenario. An outside local address is an IP address that represents an external host to the inside network. The outside local address is often the same as the outside global address, particularly when inside hosts attempt to access resources on the Internet. However, in some configurations, it is necessary to configure a NAT translation that allows a local address on the internal network to identify an outside host.
You would not configure an outside global address in this scenario. An outside global address is an IP address that represents an external host to the outside network. Outside global addresses are typically public IP addresses assigned to an Internet host by the host’s operator. The outside global address is usually the address registered with the Domain Name System (DNS) server that maps a host’s public IP address to a friendly name, such as www.example.com. -
Your company’s active ASA currently shares its stateful failover link with a regular data interface. Your supervisor asks you to configure a failover key on both the active ASA and the standby ASA.
Which of the following is most likely the reason? (Select the best answer.)
- so that the risk of exposure of VPN configuration information is mitigated
- so that both ASA devices forward traffic for a given group of security contexts
- so that the active ASA can monitor the status of the standby ASA
- so that the stateful failover link cannot use a regular data interface
Explanation:
Most likely, you would configure a failover key on both the active Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) and the standby ASA so that the risk of exposure of virtual private network (VPN) configuration is mitigated. An ASA can share its stateful failover link with a regular data interface only when the unit is operating in single context, routed mode. However, Cisco strongly recommends using a dedicated Ethernet interface or sharing a LAN failover link instead because stateful failover traffic can increase the possibility of congestion and can negatively impact the performance of the shared data interface. In addition, all LAN failover and stateful failover information is transmitted as clear text by default. Therefore, sharing the stateful failover link with a regular data interface can unnecessarily expose VPN configuration information, such as user names, passwords, and preshared keys (PSKs) to malicious users on the shared network segment. You can mitigate this risk by configuring a failover key on both the active unit and the standby unit to protect failover information.
You would not configure a failover key so that the active ASA can monitor the status of the standby ASA. An ASA can be configured to participate in either an active/standby or an active/active failover configuration. In an active/standby configuration, one ASA serves as the active unit and forwards traffic. A second ASA functions as a standby unit, which monitors the status of the active unit. If a failover event is triggered, the standby unit takes on the role of the active unit.
You would not configure a failover key so that both ASA devices forward traffic for a given group of security contexts. An active/active failover configuration enables both ASAs to forward traffic for a select group of security contexts. With active/active failover, two failover groups exist as security contexts on each ASA. When a failover event is triggered, a failover group can become active on a standby unit or the entire standby unit can become the new active unit. Because an active/active failover configuration relies on security contexts, both ASAs must be in multiple context mode before active/active failover can be implemented. The failover configuration for each unit in an active/active failover configuration is managed from within the system context. Unlike user contexts, the system context does not contain any normal data interfaces.
You would not configure a failover key so that the stateful failover link cannot use a regular data interface. Instead, you would configure an ASA to operate in multiple context, routed mode or multiple context, transparent mode. An ASA operating in multiple context, routed mode or multiple context, transparent mode does not support using a regular data interface as the stateful failover link. When an ASA is operating in multiple context mode, the stateful failover link resides in the system context, which does not contain any regular data interfaces. Thus the stateful failover link cannot be a shared data link.
The implementation of the failover process between the active and standby units can be either stateless or stateful. In a stateless failover implementation, the standby unit of a failover pair takes on the IP and Media Access Control (MAC) addresses of the old active unit during a failover event. This mechanism enables network clients to maintain their existing network configurations? however, because no network state information is retained, the clients must reestablish their network connections through the new active unit. By contrast, the active unit in a stateful failover implementation transmits certain types of state information through a stateful failover link to the standby unit. This exchange of state information ensures that the standby unit can preserve the state information for open connections during the failover process. Because the state information is preserved, the impact of a failover event on network hosts with open connections can be mitigated. -
You have configured a BYOD implementation at a branch location, including an extended ACL named DEFAULTACL on the Layer 2 ports of each access switch. BYOD clients are able to obtain IP addresses, but connectivity to other network services seems to be sporadic or nonexistent, depending on the service.
You issue the show ip accesslist command on the switch and receive the following partial output:
Extended IP access list DEFAULTACL10 permit icmp any any
20 permit udp any eq bootpc any eq bootpc
30 permit udp any any eq tftp
40 deny ip any any log
According to Cisco BYOD best practices, which of the following should you perform on the ACL to fix the problem? (Select the best answer.)
- Add a rule to permit DNS traffic before rule 40.
- Add a rule to deny ICMP traffic after rule 40.
- Add a rule to deny TFTP traffic after rule 40.
- Remove rule 40.
Explanation:
According to Cisco best practices, you should add a rule to permit Domain Name System (DNS) traffic before rule 40 in the access control list (ACL) that has been applied to the Layer 2 ports of the access switch. In a Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) environment, 802.1X, Web Authentication (WebAuth), or Media Access Control (MAC) Authentication Bypass (MAB) are used to authenticate and authorize the user and the user’s associated device for network access. Once a wired device authenticates with the Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE), a downloadable ACL (dACL) is typically applied to the appropriate access port on the Layer 2 switch to which the device is attached. Cisco recommends applying a default ACL to the access ports of Layer 2 switches to mitigate situations where a configuration error might prevent a dACL from being applied to the appropriate port during the authorization/authentication process. The default ACL should permit Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP), DNS, Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP), and Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP). In addition, the default ACL should explicitly deny and log all other IP traffic. For example, the following ACL complies with Cisco’s best common practices (BCP) as outlined in the BYOD Design Guide:
switch(config)#ip accesslist extended DEFAULTACL switch(configextnacl)#permit icmp any any
switch(configextnacl)#permit udp any eq bootpc any eq bootps switch(configextnacl)#permit udp any any eq domain switch(configextnacl)#permit udp any any eq tftp switch(configextnacl)#deny ip any any log
You do not need to add any rules after rule 40 in this scenario. In addition, you should not remove rule 40 from the ACL in this scenario. Rule 40 denies and logs all IP traffic that has not already been matched by the preceding rules. Both ICMP traffic and TFTP traffic should be and already are permitted by the ACL. -
You enable logging at the end of the session in Cisco FireSIGHT Management Center.
Which of the following is true? (Select the best answer.)
- The log will contain less information than at the beginning of the session.
- You will not be able to log connections handled by an SSL policy.
- Information will be based on only the first few packets of a connection.
- The log will contain information from throughout the course of a connection.
Explanation/Reference:
In Cisco FireSIGHT Management Center, the log will contain information from throughout the course of a connection if you enable logging at the end of the session, which is also known as endofconnection logging. Endofconnection events are generated when a connection closes, times out, or can no longer be tracked because of memory constraints. Endofconnection events contain significantly more information than beginningofconnection events because they can draw upon data collected throughout the course of a connection. This additional information can be used to create traffic profiles, generate connection summaries, or graphically represent connection data. In addition, the data can be used for detailed analysis or to trigger correlation rules based on session data. Endofconnection events are also required to log encrypted connections that are handled by a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) policy because there is not enough information in the first few packets to indicate that a connection is encrypted.
Beginningofconnection events contain less information than endofconnection events. Cisco FireSIGHT Management Center, which was formerly called Sourcefire Defense Center, can log beginningofconnection events and endofconnection events for various types of network traffic. Although most network traffic will generate both kinds of events, blocked or blacklisted traffic is typically denied without further processing and therefore only generates beginningofconnection events. Beginningofconnection events contain a limited amount of information because they are generated based on the information contained in the first few packets of a connection. -
Which of the following MPF elements can be used to configure Application layer protocol inspection? (Select the best answer.)
- a class map
- a policy map
- a service policy
- a global policy
- an extended access list
- a standard access list
Explanation:
A policy map can be used to configure Application layer protocol inspection. Modular Policy Framework (MPF) is a Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) feature that provides a flexible method of enabling security policies on an interface. This framework consists of three basic components: class maps, policy maps, and service policies. A class map identifies a specific flow of traffic, a policy map determines the action that will be performed on the traffic, and a service policy ties this action to a specific interface. Application inspection is one of the actions that can be applied to traffic with a policy map. Services that embed IP addresses in the packet or utilize dynamically assigned ports for secondary channels require deep packet inspection, which is provided by Application layer protocol inspection. Some traffic, such as File Transfer Protocol (FTP) traffic, might be dropped if inspection for that protocol is not enabled. Application inspection can be configured within the global service policy and within an interface service policy. Service policies can be applied to an individual interface or globally to all interfaces? if traffic matches both an interface policy and a global policy, only the interface policy will be applied to that particular traffic flow.
A class map cannot be used to configure Application layer protocol inspection. Class maps identify traffic by matching a variable characteristic that you specify, such as traffic going to a unique IP address or traffic using a specific port. Generally, each class map can contain only a single match statement, and a packet can match only a single class map within the policy map of a particular feature type. For example, if a packet matched a class map for FTP inspection and a class map for traffic policing, the ASA would apply both policy map actions to the packet. However, if a packet matched a class map for FTP inspection and a second, different class map that included FTP inspection, the ASA would apply only the actions of the first matching policy map. Class maps are assigned to a policy map, which defines the action or actions to be performed on the traffic.
A service policy cannot be used to configure Application layer protocol inspection. Service policies tie the policy map to the interface and can be applied to an individual interface or globally to all interfaces? if traffic matches both an interface policy and a global policy, only the interface policy will be applied to that particular traffic flow. Service policies can be configured by using Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) or by command line interface (CLI) configuration. Neither an extended access list nor a standard access list can be used to configure Application layer protocol inspection. Access control lists (ACLs) can be used to filter traffic based on a set of configured rules. You can create either standard or extended ACLs. Whereas standard ACLs can be used to filter based only on source IP addresses, extended ACLs can be used to filter based on source and destination IP addresses, protocols, and ports. A class map can match traffic to an extended ACL that is specified as a parameter to the accesslist keyword in a match statement. -
To which of the following are you most likely to connect to manage a Cisco router in ROMmon mode? (Select 2 choices.)
- an auxiliary port
- a console port
- a serial port
- an Ethernet port
- a VTY port
Explanation:
Of the available choices, you are most likely to use either an auxiliary (AUX) port or a console port to manage a Cisco router in readonly memory (ROM) monitor (ROMmon) mode. ROMmon is a management mode that Cisco routers and switches revert to when the system cannot find a software image, the software image is corrupted, or the configuration register has been set to manually enter ROMmon mode. Because ROMmon is an outofband management method, it can be used to recover system software images, passwords, or other configuration data even when the router or switch is in a state where it can no longer forward packets. On a Cisco router, you could use either the console port or the AUX port for outofband access if the router is in ROMmon mode. The AUX port on a Cisco router is typically capable of supporting most of the features available on a console port. Cisco switches either do not have AUX ports or do not support certain features, such as system recovery, on their AUX ports if they have them.
You are not likely to use a serial port, an Ethernet port, or a virtual terminal (VTY) port to manage a Cisco router in ROMmon mode. Serial ports and Ethernet ports are used to directly connect Cisco routers to other network devices. However, you cannot access ROMmon mode by using any of these ports. Management applications and administrators who want to manage a Cisco device when it is operating in its normal state could connect to the device by using VTY application protocols such as telnet or Secure Shell (SSH). -
RADIUS and TACACS+ have which of the following in common? (Select the best answer.)
- They communicate by using the same transport protocol.
- They are AAA protocols.
- They are Ciscoproprietary protocols.
- They encrypt the entire packet.
Explanation:
Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus (TACACS+) and Remote Authentication DialIn User Service (RADIUS) are both Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) protocols. However, there are some important differences between TACACS+ and RADIUS.
TACACS+ encrypts the entire body of a packet and provides router command authorization capabilities.
TACACS+ is a Ciscoproprietary protocol that uses Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) for transport during AAA operations. TACACS+ provides more security and flexibility than other authentication protocols, such as RADIUS, which is an open standard protocol commonly used as an alternative to TACACS+. Because TACACS+ can be used to encrypt the entire body of a packet, users who intercept the encrypted packet cannot view the user name or contents of the packet. In addition, TACACS+ provides flexibility by separating the authentication, authorization, and accounting functions of AAA. This enables granular control of access to resources. For example, TACACS+ gives administrators control over access to configuration commands? users can be permitted or denied access to specific configuration commands. Because of this flexibility, TACACS+ is used with Cisco Secure Access Control Server (ACS), which is a software tool that is used to manage user authorization for router access.
RADIUS was developed as an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard protocol. Like TACACS+, RADIUS is a protocol used with AAA operations. However, RADIUS uses User Datagram Protocol (UDP) for packet delivery and is less secure and less flexible than TACACS+. RADIUS encrypts only the password of a packet? the rest of the packet would be viewable if the packet were intercepted by a malicious user. With RADIUS, the authentication and authorization functions of AAA are combined into a single function, which limits the flexibility that administrators have when configuring these functions. Furthermore, RADIUS does not provide router command authorization capabilities. -
Which of the following is most likely to protect the availability component of the CIA triad? (Select the best answer.)
- data encryption B. an IPS
- a virus scanner
- a VPN
Explanation:
Of the available choices, an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) is most likely to protect the availability component of the confidentiality, integrity, availability (CIA) triad. The availability component of the CIA triad ensures the protection of systems against unplanned downtime as a result of security breaches. For example, a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is a security threat that attacks availability. An IPS can help protect availability by ensuring that attacks and threats are detected and intercepted before they have a chance to cause harm.
Data encryption and a virtual private network (VPN) protect confidentiality, not availability. The confidentiality component of the CIA triad ensures that transmitted data cannot be read by an unauthorized party if the data is intercepted before it reaches its destination. IP Security (IPSec), which is a security protocol often used in VPNs, can use either Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) or Data Encryption Standard (DES) to provide the confidentiality component of the CIA triad. Depending on the amount of confidentiality desired, IPSec can use AES or DES with Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) in either transport mode or tunnel mode. In transport mode, ESP uses AES or DES to encrypt only the original payload data and the resultant ESP trailer, leaving the original IP header unencrypted. The following diagram illustrates the components of an ESP packet in transport mode:
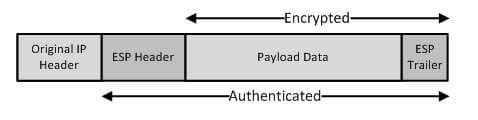
300-735 Part 01 Q17 016 A virus scanner protects integrity, not availability. The integrity component of the CIA triad ensures that unauthorized parties have not modified data as it was transmitted over the network. Data integrity can also be provided by using algorithms such as Message Digest 5 (MD5) or Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) to produce checksums on each end of a connection. If the data generates the same checksum value on each end of the connection, the data was not modified in transit.
-
Which of the following ISAKMP states indicates that the IKE peers have negotiated security parameters and exchanged keys using aggressive mode during phase 1 of the IKE process? (Select the best answer.)
- AG_INIT_EXCH
- MM_KEY_EXCH
- MM_SA_SETUP
- QM_IDLE
Explanation:
The AG_INIT_EXCH Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) state indicates that the Internet Key Exchange (IKE) peers have negotiated security parameters and exchanged keys using aggressive mode during phase 1 of the IKE process. Aggressive mode uses only three transactions to perform the same IKE security negotiations that main mode performs in six transactions.
The QM_IDLE state does not indicate that the IKE peers have negotiated security parameters and exchanged keys using aggressive mode during phase 1 of the IKE process. The QM_IDLE state indicates that an IKE security association (SA) has been authenticated. You can issue the show crypto isakmp sa command from privileged EXEC mode to determine the status of current IKE SAs on the router. You can specify the active or standby keywords to limit the type of SA displayed in the output. Standby SAs are present when fault tolerance is configured? however, they are inactive until a failover occurs. The status of an IKE SA is reflected in the state field of the command output as shown below:dst src state connid slot status 10.1.2.3 10.1.2.4 QM_IDLE 2 0 STDBY 10.3.2.1 10.3.2.4 QM_IDLE 1 0 ACTIVE
The QM_IDLE state indicates that IKE phase 1 negotiations have successfully completed and that an IKE SA has been authenticated and is available for use. IKE SAs are used during the quick mode of the IKE process, which is also referred to as IKE phase 2, to facilitate the creation of IP Security (IPSec) SAs. IPSec SA status is not displayed by the show crypto isakmp sa command? you can issue the show crypto ipsec sa command to determine the status of the IPSec SAs created during phase 2 negotiations.
The MM_SA_SETUP state does not indicate that the IKE peers have negotiated security parameters and exchanged keys using aggressive mode during phase 1 of the IKE process. The MM_SA_SETUP state indicates that the IKE peers are using main mode for phase 1 negotiations and that they have successfully negotiated security parameters. IKE has two modes for phase 1 security negotiation: main mode and aggressive mode. Main mode uses six transactions for IKE peers to negotiate security parameters, generate a shared secret, and authenticate. Aggressive mode performs the same actions in three consolidated transactions.
Similarly, the MM_KEY_EXCH state indicates that the IKE peers are using main mode for phase 1 negotiations? it does not indicate that the IKE peers have negotiated security parameters and exchanged keys using aggressive mode during phase 1 of the IKE process. The MM_KEY_EXCH state indicates that the IKE peers have exchanged keys and have generated a shared secret. IKE peers use the DiffieHellman (DH) algorithm to exchange public keys and to generate a shared secret. The shared secret and public keys are used during the authentication process, which is the final part of phase 1 main mode. -
You have been asked to enable the Cisco IOS Resilient Configuration feature on a Cisco router. You issue the following commands on the router:
Router#configure terminal Router(config)#secure boot-image
Which of the following commands are you most likely to issue next to complete the configuration? (Select the best answer.)
- reload
- confreg 0x2102
- secure boot-config
- secure boot-config restore
Explanation:
Most likely, you will next issue the secure boot-config command if you are enabling the Cisco IOS Resilient Configuration feature on a Cisco router. The Resilient Configuration feature is designed to protect system and configuration files from tampering and accidental deletion. You can issue the following block of commands to enable the Resilient Configuration feature:Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#secure boot-image
Router(config)#secure boot-config
When the feature is enabled, the primary system image file and associated running configuration are securely archived in local persistent storage? you cannot select a remote storage location. The secure boot-image command enables the image resilience component of the Resilient Configuration feature and effectively hides the system image from the directory structure. This means that the system image will no longer be displayed when the dir command is issued from the command prompt of an EXEC shell? you can issue the show secure bootset command to verify that the system image has been archived. In addition, because the system image file is not copied to a secure location, extra storage is not required to secure it. By contrast, the secure bootconfig command creates a hidden copy of the running configuration file. The secured versions of the system image and running configuration are referred to as the primary bootset.
Once the system image and running configuration have been secured, the router will track version mismatches and produce a console message if the system image or running configuration have mismatched versions. Once the Resilient Configuration feature is enabled, it can only be disabled from the console.
You would not issue the confreg 0x2102 command. The confreg 0x2102 command configures the router to load an IOS image from flash memory. This is the factory default setting on a Cisco router. You would not issue the secure boot-config restore command. You would issue the secure boot-config restore filename command, where filename is the filesystem and file name under which you want to save the restored file, only if you were attempting to recover the hidden running configuration. The secure boot-config command should be issued from global configuration mode.
You would not issue the reload command. The reload command reloads the startup configuration into the running configuration. Issuing the reload command is not required to enable the Cisco IOS Resilient Configuration feature. -
Which of the following threats has a dedicated FirePOWER preprocessor engine? (Select the best answer.)
- Back Orifice
- distributed port scan
- port sweep
- SYN flood
Explanation:
Of the choices provided, only Back Orifice is a threat that has a dedicated FirePOWER preprocessor engine. A FirePOWER Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) has several predefined preprocessor engines that can be used in network policies to detect specific threats? the preprocessors focus on detecting Back Orifice attacks, detecting port scan attacks, preventing ratebased attacks, and detecting sensitive data.
Back Orifice and its variants exploit a vulnerability in Microsoft Windows hosts to gain complete administrative control of the host. Back Orifice traffic can be identified by the presence of a specific token, known as a magic cookie, in the first eight bytes of a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packet.
The ratebased prevention preprocessor detects traffic abnormalities, including SYN flood attacks, based on the frequency of certain types of traffic. The following traffic patterns can trigger ratebased attack prevention:– Traffic containing excessive incomplete Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) connections
– Traffic containing excessive complete TCP connections
– Excessive rule matches for a particular IP address or range of IP addresses
– Excessive rule matches for one particular rule regardless of IP addressDistributed port scan traffic and port sweep traffic can be detected by the portscan detection preprocessor. Port scanning traffic can be an indicator that an attacker is conducting network reconnaissance prior to an attack. Although legitimate port scanning traffic can periodically exist on a network, the portscan detection preprocessor can distinguish between legitimate scanning and potentially malicious traffic based on the activity patterns found in the analysis of port scanning traffic.