300-835 : Automating Cisco Collaboration Solutions (CLAUTO) : Part 01
-
You want to configure caller ID to display a user name instead of a dn for internal callers.
Which of the following line appearance fields should you modify in UCM?
- Display
- External Phone Number Mask
- Line Text Label
- Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy
Explanation:
You should modify the Display (Internal Caller ID) line appearance field in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) administrative graphical user interface (GUI). Line appearance is the association between a line and a device on a Voice over IP (VoIP) network. Because multiple lines can be associated with a single device, you can configure multiple line appearances for a single IP phone. Line appearance configurations can determine how a line that is associated with an IP phone displays information to an end user.After you create a directory number (dn) in UCM and associate the line to a device, you will be able to edit line appearance options that include display settings, such as internal caller ID, external caller ID, and the user name or dn that is displayed beside a line button on an IP phone. When the Display (Internal Caller ID) field is blank, the dn that is associated with the calling device is shown on the display of the called device. Otherwise, the contents of the Display (Internal Caller ID) field are shown on the display of the called device.
You can configure the Display (Internal Caller ID) field with a name or a description of up to 30 characters in length. If you configure the Display (Internal Caller ID) field, you should also configure the ASCII Display (Internal Caller ID) field with similar information. The contents of the ASCII Display (Internal Caller ID) field are displayed on called devices that do not support Unicode character sets. You cannot use non-ASCII characters in the ASCII Display (Internal Caller ID) field.
You should not modify the Line Text Label field. The contents of the Line Text Label field are displayed beside the associated line button of an IP phone. The field is typically configured with the name of the user that is associated with the line. If the Line Text Label field is not configured, the dn that is associated with the line will be displayed instead. For example, if user John Public has been assigned extension 4000, the dn 4000 will be displayed beside the line button on the main screen of John Public’s IP phone unless you configure the Line Text Label field. If you configure the Line Text Label field with the name John Public, that name will appear beside the line button on the main screen of the IP phone. For shared workstations, you can configure the Line Text Label field with the name of the department or office location that is associated with the IP phone. If you configure the Line Text Label field, you should also configure the ASCII Line Text Label field with similar information. The contents of the ASCII Line Text Label field are displayed on IP phones that do not support Unicode character sets. You cannot use non-ASCII characters in the ASCII Line Text Label field.
You should not modify the External Phone Number Mask field. UCM transmits the contents of the External Phone Number Mask field as caller ID information when an internal user places an outgoing call to an external party. The information in the External Phone Number Mask field can be a string that consists of up to 24 numbers, the international escape character +, and X wildcards that represent the extension number.
The X wildcards should always be at the end of the string. For example, a user that has been assigned extension number 4000 on the internal VoIP network might also be assigned a direct inward dial (DID) number of (555) 5554000. Therefore, you could configure the External Phone Number Mask field with the string 555555XXXX. The number 5555554000 would then be displayed on the caller ID systems of any external parties who are called by the user at extension 4000. If the user at extension 4000 was not assigned a DID number, you could configure the External Phone Number Mask field with your company’s main public switched telephone network (PSTN) number instead.
You should not modify the Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field. The Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field configures the behavior of the message waiting indicator (MWI) lamp and of the MWI line prompt on an IP phone. For example, configuring the Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field to Light and Prompt will configure the IP phone to turn on the MWI lamp that is located on the IP phone’s handset when a new voice mail message arrives. In addition, the IP phone will display a new message prompt beside the associated line button on the IP phone. However, configuring the Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field to Prompt Only will display the new message prompt beside the line button but will not turn on the MWI lamp. You can configure the Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field differently for each line that is associated with the IP phone. For example, if the IP phone is configured with a shared line in addition to a primary line, you could configure the Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field for the shared line to None so that the IP phone never displays MWI information for the shared line.
-
Which of the following is not a service provided by UCM media resources?
- annunciator
- conferencing
- media termination
- MOH
- transcoding
- voice mail
Explanation:
Of the available choices, voice mail is not a service provided by Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) media resources. Voice mail services can be provided to a UCM environment by voice mail products such as Cisco Unity Connection. UCM media resources are available directly from the UCM server on which the services are enabled. In addition, the UCM Media Resource Manager enables UCM to provide those services to other UCM servers in a cluster. When troubleshooting media resource problems, such as conference call failures, it is important to first investigate the UCM media resources configuration.Annunciator, conferencing, media termination, music on hold (MOH), and transcoding are all services that are provided by UCM media resources. The UCM Media Resource Manager is responsible for connecting the media streams that comprise one of these features. In order to perform this function, the Media Resource Manager must interact with a variety of other UCM control components. For example, UCM’s call control features interact with Media Resource Manager to establish conference calls.
-
The user named Joe Cambers is not able to use Cisco Jabber’s IM or Presence functionality.
Which of the following is most likely the reason?
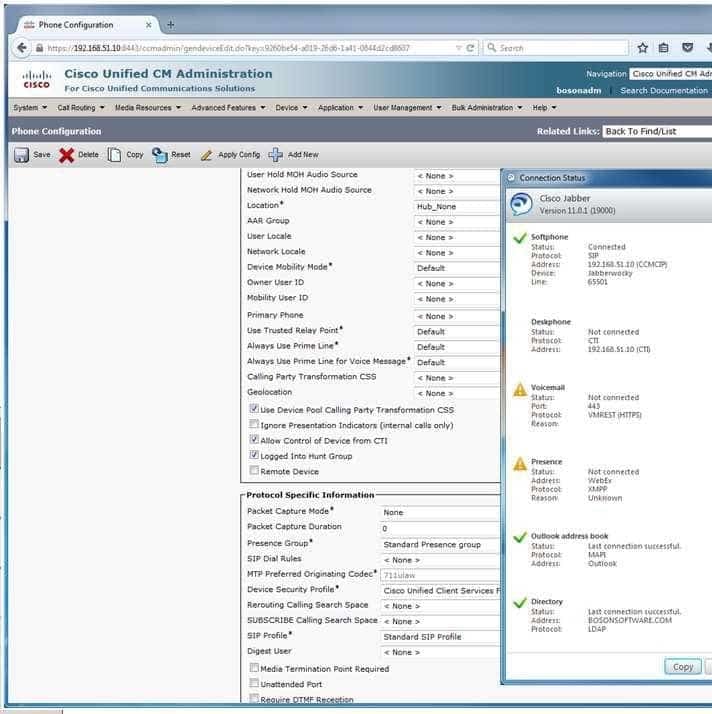
300-835 Part 01 Q03 001 - The softphone has no SIP profile.
- The softphone’s profile does not allow CTI control.
- The SIP trunk to the CUPS server is down.
- The Cisco Unity Connection server either is down or is not installed.
- The Cisco Jabber client is configured to require a nonexistent desk phone.
Explanation:
Most likely, the reason the user named Joe Cambers is not able to use Cisco Jabber’s IM and Presence functionality is because the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) trunk from Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) to the Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) server either is down or is not installed. Cisco Jabber relies on CUPS and the Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) for instant messaging (IM) and Presence functionality. You can display and verify the backend systems to which the Cisco Jabber client is connected by clicking the gear icon and Show Connection Status in the Cisco Jabber home window. Clicking Show Connection Status displays the Connection Status window, which provides the connectivity status of every service to which Jabber is connected or is configured to connect. Services that are preceded by a green check mark have connected successfully. Services that display Not Connected or a caution icon have not connected successfully.The Cisco Unity Connection server either is down or is not installed; however, this is not the reason that the user is not able to use Cisco Jabber’s IM functionality. Cisco Unity Connection is a voice mail platform, not an IM platform.
The softphone has a SIP profile. Based on the value displayed in the SIP Profile field of the UCM Administration page in this scenario, you can determine that the softphone is configured to use the Standard SIP Profile, which is the default UCM SIP profile.
The softphone’s profile does allow Computer Telephony Integration (CTI) control. Based on the value displayed in the Allow Control of Device from CTI field, you can determine that CTI control has been enabled for the softphone. However, disabling this option would not disable Jabber’s IM functionality. CTI enables the Cisco Jabber client to control aspects of a connected hardware phone, or desk phone. However, the Cisco Jabber client does not require a desk phone. Both Jabber and Cisco Unified Personal Communicator communicate with a desk phone by using the CTI Quick Buffer Encoding (CTIQBE) protocol.
-
You are the administrator for your company’s UCM network. Examine the exhibit below, and answer the question:

300-835 Part 01 Q04 002 Which of the following is most likely the reason that Cisco Jabber cannot connect to the user’s desk phone?
- The Cisco Unity Connection server is not running.
- A workstation firewall is preventing Cisco Jabber from connecting to the IP phone.
- The UCM Allow Control of Device from CTI check box cannot be selected for the user’s IP phone.
- UCM is not running.
Explanation:
Of the choices provided, the problem is most likely that a workstation firewall is preventing Cisco Jabber from connecting to the IP phone. Cisco Jabber relies on User Datagram Protocol (UDP) to communicate with an IP phone. If UDP traffic to the IP phone is blocked or denied by a firewall that is installed on the same workstation as Cisco Jabber, the Cisco Jabber client and the IP phone will not be able to communicate.Most likely, the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Allow Control of Device from CTI check box can be selected for the user’s IP phone. To enable a user to control an IP phone by using Cisco Jabber, you should complete the following steps:
1.Click Device > Phone in UCM.
2. Find the IP phone that you want to configure, or add a new IP phone.
3. Edit the Device Information section for the IP phone you want to configure.
4. Select the Allow Control of Device from CTI check box.
5. Associate the IP phone with a directory number (dn), if it is not already.UCM displays the Allow Control of Device from CTI check box only if the model of the IP phone that you add or edit is supported. In this scenario, the Allow Control of Device from CTI check box is available for selection and has already been selected.
Most likely, the UCM server is running. If UCM were not running, you would not be able to access the UCM Administration page that is displayed in this scenario. However, Cisco Unity Connection might not be running, because the Cisco Jabber client is not able to connect to it. Cisco Unity Connection’s state would not prevent Cisco Jabber from communicating with the IP phone.
-
You are the administrator for your company’s UCM network. Examine the exhibit below, and answer the question:
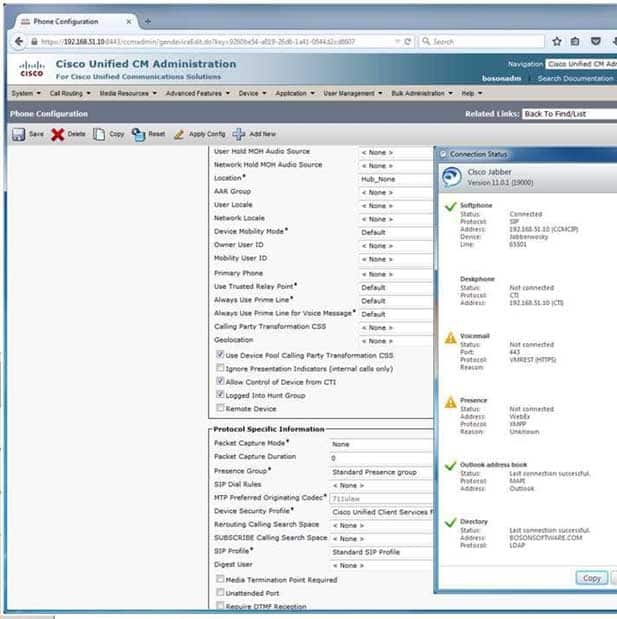
300-835 Part 01 Q05 003 Based on the Cisco Jabber client’s status, which of the following is most likely true?
- The DNS server is down.
- The UCM server is not configured to use DNS.
- The UCM server’s host name is CCMCIP.
- Joe Cambers’ user name is Jabberwocky.
Explanation:
Most likely, the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) server is not configured to use Domain Name System (DNS) name resolution. Based on the Cisco Jabber client’s status, you can determine that the Jabber client is connected to UCM by using the IP address of 192.168.51.10. In addition, The Cisco UCM Administration page has been loaded in a web browser by using the IP address of 192.168.51.10.Although UCM can be deployed with a DNS configuration, Cisco recommends that administrators who are deploying UCM in a high availability environment not rely on DNS to connect endpoints to UCM, because doing so could create a single point of failure. Even if DNS is required for systems management purposes, Cisco recommends not using host names to configure endpoints, gateways, and UCM servers.
When Cisco Jabber cannot connect to a server by using either DNS or an IP address, the Cannot communicate with the server message will appear on the Cisco Jabber client’s login screen. The same message will appear if the server to which Cisco Jabber is configured to connect is down. In this scenario, the Cisco Jabber client has successfully connected to the UCM device at 192.168.51.10.
Joe Cambers’ user name is not Jabberwocky. In this scenario, the user’s login information has not been provided. Jabberwocky is the name of the Cisco Jabber client endpoint in UCM. In addition, there is not enough information to determine whether a DNS server is down, because the Cisco Jabber client is not relying on DNS to connect to the UCM server. If the Cisco Jabber user logged in with a fully qualified domain name (FQDN), you could surmise that the DNS server is still functional because Cisco Jabber was able to resolve the login credential. However, you do not know what credentials Joe Cambers used to log in.
The UCM server’s host name is not CCMCIP. The Cisco Unified Communications Manager IP Phone (CCMCIP) service is a UCM service that enables UCM to associate devices with end users.
-
You are the administrator for your company’s UCM network. Examine the exhibit below, and answer the question:
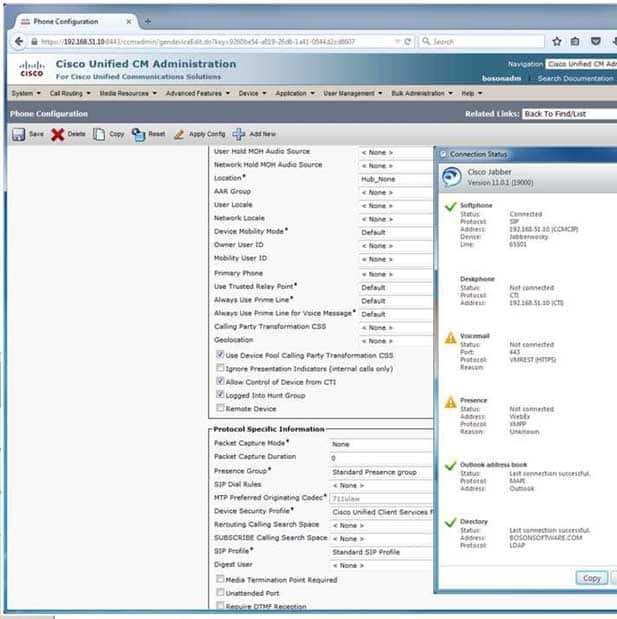
300-835 Part 01 Q06 004 Which of the following fields should you configure to enable calls from this Cisco Jabber client to be rerouted through the PSTN if bandwidth is lacking?
- AAR Group
- Location
- Rerouting Calling Search Space
- SUBSCRIBE Calling Search Space
- Use Trusted Relay Point
Explanation:
You should configure the AAR Group field to enable calls from this Cisco Jabber client to be rerouted through the public switched telephone network (PSTN) if bandwidth is lacking. Automated Alternate Routing (AAR) Group configurations enable calls to be rerouted to specified destinations when Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) blocks a call because bandwidth is lacking. AAR Group profiles are configured by navigating to Call Routing > AAR Group in UCM Administration. After you have configured a profile, you can assign it to an endpoint by selecting the profile from the AAR Group dropdown field on the Device > Phone configuration page for the given endpoint.You should not configure the Location field. The Location field is used to configure call admission control (CAC). CAC is used to limit bandwidth available for audio and video calls between locations, thereby regulating the quality of those calls. The location of Hub_None, which is used in this scenario, indicates that UCM is not monitoring the bandwidth that this particular endpoint is using. Locations can be configured by navigating to System > Location in UCM Administration. After locations have been configured, you can apply the configuration to an endpoint by selecting it from the Location dropdown field on the Device > Phone configuration page for the given endpoint.
You should configure neither the Rerouting Calling Search Space field nor the SUBSCRIBE Calling Search Space field. A search space is an ordered list of partitions that a device is allowed to search for patterns that match a given string, such as a dialed number. The Rerouting Calling Search Space field determines the route to a refer to target. The target is specified in a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Refer message. The SUBSCRIBE Calling Search Space field, on the other hand, is used to route Presence subscribe requests from an endpoint.
You should not configure the Use Trusted Relay Point field. A Trusted Relay Point (TRP) is a transcoder or media termination point (MTP) device that UCM considers to be the closest to a given endpoint if multiple resources are required for the endpoint. When this option is configured to the Default setting, the endpoint uses a common device configuration to determine the TRP setting. If this option is configured to Off, UCM will not attempt to use a TRP for the endpoint regardless of the common device configuration. If this option is configured to On, UCM will attempt to use a TRP for the endpoint regardless of the common device configuration.
-
Your company uses Cisco Unity Connection for voice messaging.
The MWI light on a user’s IP phone is not turning on, even though the user has new voice mail messages.
The user’s extension number is 555.
You want to dial the MWI on number for extension 555 to test the MWI light on the IP phone, but you do not know the MWI on number.
Which of the following should you do?
- Issue the show ephone dn 555 command in CME.
- Click Telephony Integration > Port in the Cisco Unity Connection administrative GUI.
- Click Telephony Integration > Port Group in the Cisco Unity Connection administrative GUI.
- Press the **#** keypad sequence on the IP phone.
- Press settings > Device Configuration > MWI on the IP phone.
Explanation:
You should click Telephony Integration > Port Group in the Cisco Unity Connection administrative graphical user interface (GUI) to obtain the message waiting indicator (MWI) on extension number. The MWI light on an IP phone can be used to inform users when new voice mail messages have arrived. In this scenario, the MWI light on the IP phone that is associated with extension number 555 should turn on when new, unheard voice mail messages are available; it should turn off after the user has listened to the new voice mail messages.To configure MWI, you must create two extension numbers: one number to turn the MWI light on when the user receives a message, and one number to turn the MWI light off when the user retrieves all of the new voice mail messages. When the voice mail server receives a voice mail message for a user, the server will send a code to Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) to indicate that the user’s MWI light should be turned on. When the user retrieves the message, the voice mail server will send another code to UCM to indicate that the user’s MWI light should be turned off. The MWI codes can be any number of any length as long as they are not the same as any existing extension numbers. To configure or view the MWI code that Unity Connection will send to UCM, you should click Telephony Integration > Port Group in the Unity Connection administrative GUI and then view or edit the MWI numbers in Port Group Basics.
If you configure the MWI on number and the MWI off number with an extension number that can be dialed from a typical telephone keypad, you can test the MWI light by dialing the MWI on number from the IP phone you want to test. For example, you can turn on the MWI light for extension 555 by dialing the MWI on number from the phone assigned to extension 555. Similarly, you can turn off the MWI light for extension 555 by dialing the MWI off number from the IP phone that is associated with extension 555.
You can prevent users from manually turning the MWI light on or off by configuring the MWI numbers with characters that cannot be dialed from a typical telephone keypad. For example, if you were to configure the MWI on extension number as AAA1 and the MWI off extension number as AAA0, Unity Connection and UCM could dial the MWI extensions but an individual who is using a typical IP phone could not.
You should not click Telephony Integration > Port in the Cisco Unity Connection administrative GUI. Although you can use the Telephony Integration > Port page in Cisco Unity Connection to enable a port to send MWI requests, you cannot create and enable MWI extension numbers from the Telephony Integration > Port page.
You should not issue the show ephone dn 555 command in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME). Although you can configure MWI on and MWI off extension numbers in CME and Cisco Unity Express (CUE), the show ephone dn 555command displays information about the association between an ephone-dn and an ephone. To configure an MWI extension number in CME, you should create an ephone-dn that represents the MWI extension number that you want and issue either the mwi on-command or the mwi off command in ephone-dn configuration mode, depending on the action that you want to occur when the ephone-dn is dialed.
You should not press the **#** keypad sequence on the IP phone. The phone will reset when you press the **#** keypad sequence at the Settings menu of an IP phone. You can access the Settings menu by pressing the settings button on the phone’s keypad. An IP phone reset will reinitialize the phone, which means that the phone will reboot, contact the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server to obtain network configuration information, and then download its configuration file from the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server. You can also reset an IP phone in IOS by issuing the reset command in ephone configuration mode. You can reset all IP phones on a network by issuing the reset all command in telephony services configuration mode.
You should not press settings > Device Configuration > MWI on the IP phone. The Settings > Device Configuration menu enables the user or administrator to view information about the IP phone’s connection to UCM. In addition, the Settings > Device Configuration menu displays information about the phone’s locale settings, which default to English unless a locale installer has been pushed to the IP phone from UCM. However, there are no MWI settings in the Settings > Device Configuration > MWI menu of an IP phone.
-
You want to configure an alerting name that will be displayed on a caller’s IP phone when the recipient’s IP phone is ringing.
Which of the following fields in UCM Administration should you edit?
- the Alerting Name field on the dn configuration page
- the Alerting Name field on the phone configuration page
- the Alerting Name field on the end user configuration page
- the Alerting Name field on the server configuration page
Explanation:
You should edit the Alerting Name field on the directory number (dn) configuration page in Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Administration if you want to configure an alerting name that will be displayed on a caller’s IP phone when the recipient’s IP phone is ringing. For example, if you want the name JOE to be displayed when a user calls Joe’s extension, you would configure an alerting name of JOE on the dn configuration page for Joe’s extension. The dn configuration page also contains a variety of other configuration options, such as the route partition to which the dn belongs and the maximum number of calls.You should not edit the Alerting Name field on the phone configuration page, because that field does not exist on that page. The UCM Administration phone configuration page enables you to configure settings specific to a given IP phone. To identify the IP phone that you are configuring, you should enter the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the IP phone in the MAC Address field on the phone configuration page. You can also configure softkey templates and the common device configuration that you want to apply to the IP phone on this page.
You should not edit the Alerting Name field on the end user configuration page, because that field does not exist on that page. The UCM Administration end user configuration page enables you to configure settings specific to a given user. For example, you can configure a user ID, password, and personal identification number (PIN) on the end user configuration page.
You should not edit the Alerting Name field on the server configuration page, because that field does not exist on that page. The UCM Administration server configuration page enables you to configure settings such as the host name or IP address of the server, the IP version 6 (IPv6) name of the server, and a description of the server.
-
An administrator has configured Cisco Unity Connection Port Monitor in order to monitor connections. Soon after, users begin reporting performance problems with Cisco Unity Connection.
Which of the following is most like the cause?
- Port Monitor is not the correct tool for Cisco Unity Connection.
- The administrator selected an incorrect node.
- The Display Status field is not Idle.
- The polling rate is too low.
Explanation:
Most likely, the polling rate is too low if users are reporting performance problems after an administrator has configured Cisco Unity Connection Port Monitor. The Cisco Unity Connection Port Monitor is a Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Real-Time Monitoring Tool (RTMT) option that can be used to monitor activity on each Cisco Unity Connection port in real time. The polling rate determines how many seconds elapse before Port Monitor gathers and updates data. If the polling rate is too low, Port Monitor can drag down performance of a Cisco Unity Connection system.Port Monitor is the correct tool for Cisco Unity Connection. You can access Port Monitor by using UCM RTMT, navigating to Unity Connection, and clicking Port Monitor.
Although the administrator might have selected an incorrect node, the selection of an incorrect node is not as likely to cause a performance problem as configuring a low polling rate. You can choose the node you want to monitor from the Node dropdown box in the Port Monitor window.
Although it is possible that the Display Status field would display a value other than Idle, this is not likely the cause of a performance problem. The Port Monitor Window’s Display Status field is used to display the action that is currently being performed in a conversation. The Idle value indicates that the given port is not currently handling a call.
-
You are editing the user account named jpublic in the Cisco Unity Connection administrative GUI. Which of the following cannot be modified from the Message Settings page?
- the maximum voice mail message length
- the voice mail message greeting
- voice mail message editing
- the voice mail message language
- the voice mail message urgency
Explanation:
You cannot modify a user’s voice mail message greeting from the Message Settings page when editing a user account in the Cisco Unity Connection administrative graphical user interface (GUI). There are three typical ways to create users in Unity Connection: local manual creation, import from Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM), or synchronization by using Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). When manually editing users in the GUI, you can modify settings that are related to a user’s voice mail greeting by modifying the options on the Greeting page. For example, you can use the Callers Hear field on the Greeting page to determine whether callers who reach the user’s voice mail hear the system default greeting, the user’s personal greeting, or nothing. If you want to modify the Callers Hear field value for a single user, you should edit the field on the Greeting page of the user’s account. You can also modify the setting for a number of users at once by editing the Callers Hear field in Bulk Edit Mode. In addition, you can configure the Callers Hear field on the Greeting page of a voice mail user template.You can modify the maximum voice mail message length that can be recorded by an outside caller in a user’s voice mailbox from the Message Settings page. By default, the Maximum Message Length field is configured to 300 seconds. If you want to modify the Maximum Message Length field value for a single user, you should edit the field on the Message Settings page of the user’s account. You can also modify the setting for a number of users at once by editing the Maximum Message Length field in Bulk Edit Mode. In addition, you can configure the Maximum Message Length field on the Message Settings page of a voice mail user template to apply a nondefault maximum message length to any new user accounts that are based on the template.
You can modify whether a caller can edit voice mail messages from the Message Settings page. By default, the Callers Can Edit Messages check box is configured to allow callers to listen to, append to, rerecord, or delete their messages in a user’s voice mailbox. If you want to modify the Callers Can Edit Messages check box for a single user, you should edit the check box on the Message Settings page of the user’s account. You can also modify the setting for a number of users at once by editing the Callers Can Edit Messages check box in Bulk Edit Mode. In addition, you can configure the Callers Can Edit Messages check box on the Message Settings page of a voice mail user template to apply a nondefault setting to any new user accounts that are based on the template.
You can modify the language that callers hear from the Message Settings page. By default, the Language That Callers Hear field is configured to use the system default language. Modifying this field changes only the language of system prompts, not the language of user-recorded greetings. If you want to modify the Language That Callers Hear field for a single user, you should edit the field on the Message Settings page of the user’s account. You can also modify the setting for a number of users at once by editing the Language That Callers Hear field in Bulk Edit Mode. In addition, you can configure the Language That Callers Hear field on the Message Settings page of a voice mail user template to apply a nondefault setting to any new user accounts that are based on the template.
You can modify the default urgency level of voice mail messages from the Message Settings page. The Message Urgency field can be configured to mark all voice mails as urgent, to mark all voice mails as normal, or to prompt callers to mark a message as urgent. If you want to modify the Message Urgency field for a single user, you should edit the field on the Message Settings page of the user’s account. You can also modify the setting for a number of users at once by editing the Message Urgency field in Bulk Edit Mode. In addition, you can configure the Message Urgency field on the Message Settings page of a voice mail user template to apply a nondefault setting to any new user accounts that are based on the template.
-
You want to verify that an IP phone has downloaded a configuration file from a TFTP server.
Which of the following would you most likely do on the IP phone?
- Press settings > Network Configuration, and verify the TFTP server’s IP address.
- Press settings > Network Configuration, and verify the DHCP server’s IP address.
- Press settings > Network Configuration, and verify that DHCP is enabled.
- Press settings > Network Configuration, and verify the VLAN ID.
- Press settings > Status > Status Messages.
- Press settings > Status > Network Statistics.
Explanation:
You would most likely press settings > Status > Status Messages on the IP phone to verify that an IP phone has downloaded a configuration file from a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server. A TFTP server is required so that IP phones can download their startup configuration files. If an IP phone has successfully downloaded a configuration file from a TFTP server, you will see output in Status Messages indicating the time of the download and the name of the configuration file. A Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)-enabled phone configuration file typically consists of the letters SEP and the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the IP phone. Therefore, an IP phone with the MAC address 0012:3456:789A will attempt to download a configuration file named SEP00123456789A.cnf.xml from the TFTP server. If the IP phone does not successfully download the file, you might see one of the following messages in the Status Messages output:-CFG file not found, which indicates that the TFTP server is reachable but that the configuration file was not found on the TFTP server
-CFG TFTP Size Error, which indicates that the TFTP server is reachable and the configuration file is available but that the configuration file is too large for the IP phone
-TFTP access error, which indicates that the IP phone can connect to the TFTP server but that the configuration file directory does not exist
-TFTP Error, which indicates that the TFTP server generated an unknown error
-TFTP timeout, which indicates that the TFTP server did not respond to the download requestYou would not press settings > Network Configuration on the IP phone and verify the virtual LAN (VLAN) ID. Although you could verify that the IP phone is able to contact a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server by ensuring that the DHCP server and the IP phone are operating on the same VLAN, the ability to communicate with a DHCP server alone is not an indicator that the IP phone has successfully downloaded a configuration file from the TFTP server.
You would not press settings > Network Configuration on the IP phone and verify the TFTP server’s IP address to verify that an IP phone has downloaded a configuration file from a TFTP server. Although you could verify that the TFTP server’s IP address is correct by viewing the information in the settings > Network Configuration > TFTP Server 1field, a valid TFTP server IP address alone is not an indicator that the IP phone has successfully downloaded a configuration file from the TFTP server.
You would not press settings > Network Configuration on the IP phone and verify that DHCP is enabled to verify that an IP phone has downloaded a configuration file from a TFTP server. Although the IP phone can receive a TFTP server IP address from a DHCP server, the configuration of a TFTP server IP address alone is not an indicator that the IP phone has successfully downloaded a configuration file from the TFTP server.
You would not press settings > Network Configuration on the IP phone and verify the DHCP server’s IP address to verify that an IP phone has downloaded a configuration file from a TFTP server. Although the IP phone can receive a TFTP server IP address from a DHCP server, and the IP phone must be able to communicate with the DHCP server so that the IP phone can receive network information from the DHCP server, verifying the DHCP server IP address alone is not an indicator that the IP phone has successfully downloaded a configuration file from the TFTP server.
You would not press settings > Status > Network Statistics on the IP phone to verify that an IP phone has downloaded a configuration file from a TFTP server. The settings > Status > Network Statistics display provides statistics about packets that have been transmitted to and from the IP phone. In addition, you can see whether the IP phone is bound to a DHCP server. However, none of the information in the Network Statistics output indicates that the IP phone has successfully downloaded a configuration file from the TFTP server.
-
Another administrator modifies the UCM cluster security password by using the CLI.
Which of the following is most likely to be affected by this change?
- encryption of DRS backups that were made prior to the change
- encrypted communication between DRS Master Agents and Local Agents
- the addition of new backup devices to a DRS schedule
- the deletion of old backup devices from a DRS schedule
- access to network storage location configuration
Explanation:
Of the available choices, encryption of Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Disaster Recovery System (DRS) backups that were made prior to the password change will most likely be affected if another administrator modifies the cluster security password by using the command-line interface (CLI). DRS, which is a cluster-level backup system for UCM, uses the existing cluster security password when performing encryption on a backup. If the cluster security password is modified by using the CLI or by a fresh UCM installation, you might not be able to decrypt and restore that backup. Workarounds to this issue include remembering the old cluster security password that was used to encrypt the data or immediately performing a fresh backup when the cluster security password changes.Encrypted communications between DRS Master Agents and Local Agents are not likely to be affected by this change. Master Agents store component registrations, maintain scheduled tasks, and store backup data on a locally attached device. Local Agents, which are installed and activated by default on each cluster node, are responsible for running backup and restore scripts on the local server. DRS uses Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to both authenticate and encrypt data between a Master Agent and a Local Agent. In addition, DRS uses IP Security (IPSec) for public key infrastructure (PKI) encryption.
The addition or deletion of backup devices to a DRS schedule will not be affected by the password change. However, it is important to note that a backup device cannot be deleted from DRS if that backup device is part of an existing backup schedule. In order to remove an existing backup device from a DRS configuration, you must first ensure that the device has been removed from any backup schedules in which it might be configured.
Access to network storage location configuration will not be affected by the password change. In order to configure network storage locations, you must have access to a Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) server. In addition to backing up data to devices that are directly connected to a Master Agent, DRS can back up to network storage locations by using SFTP.
-
Which of the following processes can a transcoder perform?
- conversion of analog audio to digital audio
- conversion of digital audio to analog audio
- conversion of digital audio from one codec to another
- sampling, encoding, and compression of analog audio
Explanation:
A transcoder can convert digital audio from one codec to another. Transcoders enable communication between devices that support dissimilar audio codecs. For example, a transcoder can translate a G.729-encoded packet to a G.711encoded packet and vice versa. Transcoders translate the data stream in real time between two devices so that no audio delay is experienced by either endpoint.A digital signal processor (DSP), not a transcoder, can convert analog audio to digital audio and convert digital audio to analog audio. When analog audio is received by a DSP, the DSP samples and quantizes the analog audio data, encodes the data into binary format, and optionally, compresses it to conserve bandwidth. For example, Cisco Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) with DSP resources are used to process calls between Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) and the public switched telephone network (PSTN).
-
You are manually provisioning an IP phone by using UCM Administration. You want to replace the conference call button on the user’s IP phone with a speed dial button.
Which of the following fields should you update?
- Device Pool
- Phone Security Profile
- MAC Address
- Phone Button Template
Explanation:
You should update the Phone Button Template field to ensure that the IP phone you are provisioning by using Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Administration replaces the conference call button with a speed dial button. Phone button templates are used to add or arrange IP phone buttons for a given device or group of devices. You can create or edit phone button templates by clicking Device > Device Settings > Phone Button Template in UCM. When you are manually provisioning an IP phone in UCM Administration, you must fill in the MAC Address field, the Device Pool field, the Phone Button Template field, and the Phone Security Profile field.You do not need to update the Device Pool field to ensure that the IP phone you are provisioning provides the user with a Mobility option. Although required when manually provisioning an IP phone in UCM Administration, the Device Pool field specifies a given set of characteristics that are to be applied to IP phones within the pool, such as region, date and time groups, softkey templates, and more. However, Device Pool does not configure an IP phone with a Mobility button.
You do not need to update the Phone Security Profile field to ensure that the IP phone you are provisioning provides the user with a Mobility option. The Phone Security Profile field is used to create or modify the security configuration of devices to which the profile is applied. For example, you can assign a profile that supports UCM authentication or encryption to a device that supports those features.
You do not need to update the MAC Address field to ensure that the IP phone you are provisioning provides the user with a Mobility option. The MAC Address field contains the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the device that you are provisioning. The MAC address is a hardware address that is assigned by the device manufacturer.
-
Which of the following cannot be watched by the Presence feature of UCM?
- an MGCP trunk
- an SCCP line
- a SIP line
- a SIP trunk
Explanation:
A Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) trunk cannot be watched by the Presence feature of Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM). Presence enables an IP phone user to monitor other directory numbers (dns) in real time by displaying a status icon beside dns that appear in speed-dial lists or directory lists, such as the Missed Calls list, on an IP phone. The icon can represent one of the following three states:-Unknown – The registration status of the device that is associated with the directory dn cannot be determined.
-On-hook – The device that is associated with the dn is registered and currently in the on-hook state.
-Off-hook – The device that is associated with the dn is registered and currently in the off-hook state.Devices that can send Presence requests for information about dns are called watchers. Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) or dns that can be monitored by Presence are known as presence entities, or presentities. Presence can send and receive presence requests and responses only on Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) lines, SIP lines, and SIP trunks. If Presence requests or responses are sent to an MGCP trunk or to an H.323 trunk, those requests are rejected by UCM.
-
A caller from the PSTN attempts to connect to an extension that does not exist on your company’s VoIP network.
Which of the following settings in the Call Forward and Pickup Settings section of the UCM Administration Directory Number Configuration page would direct such callers to voice mail?
- Forward All
- Forward Busy External
- Forward Busy Internal
- Forward No Answer External
- Forward No Answer Internal
- Forward Unregistered External
Explanation:
Of the available choices, the Forward Unregistered External setting in the Call Forward and Pickup Settings section of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Administration Directory Number Configuration page would direct a caller from the public switched telephone network (PSTN) to voice mail if that caller attempted to connect to an extension that does not exist on your company’s Voice over IP (VoIP) network. The Directory Number Configuration page enables a UCM administrator to configure several settings related to directory numbers (dns), including the following: call forwarding, call pickup, call waiting, line display text, ring settings, and voice mailboxes. In contrast to the Forward Unregistered External setting, the Forward Unregistered Internal setting would forward internal callers to a specific voice mailbox if the internal caller dialed a nonexistent dn.The Forward All setting forwards all callers, internal or external, to a specific voice mailbox. This is the same behavior as the CFwdAll softkey that appears on a Cisco IP phone. However, an administrator can configure this behavior for a user by accessing the Directory Number Configuration page if the user for some reason does not have access to the CFwdAll softkey.
The Forward Busy External setting forwards any calls from the PSTN that arrive while the given dn is already in use. Similarly, the Forward Busy Internal setting forwards any internal calls that arrive while the given dn is already in use.
The Forward No Answer External setting forwards any calls from the PSTN that go unanswered by the user. Similarly, the Forward No Answer Internal setting forwards any internal calls that go unanswered by the user.
-
You are configuring and testing an IM and Presence deployment for a single existing end-user account. You have configured the CUPS servers, enabled the appropriate UCM services, and created the appropriate service profile.
Which of the following are you most likely to do next?
- Click User Management > End User in the end-user configuration window.
- Click Bulk Administration > Users > Insert Users in the BAT.
- Click Bulk Administration > Users > Update Users in the BAT.
- Click User Management > User/Phone Add > Feature Group Templates.
Explanation:
Of the available choices, you would most likely click User Management > End User in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Administration end-user configuration window if you are configuring and testing an instant message (IM) and Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) server for a single existing end-user account. You can manually configure end users in UCM by clicking User Management > End User in the UCM administrative graphical user interface (GUI). You can also verify whether an existing user account is active by navigating to the End User page. Because you are configuring IM and Presence for a single existing user, a manual configuration of that user would use the least amount of administrative effort.Before you can configure UCM users with IM and Presence, you must configure CUPS servers and ensure that the Cisco Call Manager service and the Cisco Administrative Extensible Markup Language (AXL) Web Service are enabled and running. If you want to use Cisco Unified Personal Communicator in softphone mode, you should also ensure that Cisco Trivial File Transfer Protocol (Cisco TFTP) is enabled. To use Cisco Unified Personal Communicator in desk phone control mode, you must enable and start Cisco CTI Manager. After the services are configured, you must create an IM and Presence Service profile and assign users to that profile.
You would not click Bulk Administration > Users > Insert Users in the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT), because that option is used to simultaneously add multiple new users to UCM. Similarly, you would not click Bulk Administration > Users > Update Users in the BAT, because you want to edit a single existing user. The Update Users option enables you to use the BAT to simultaneously update multiple existing users at once.
You would not click User Management > User/Phone Add > Feature Group Templates, because that option is used to create feature groups that can be assigned to users, not to create or update users themselves. Feature groups can be used to restrict users to a given UCM feature set. By creating a feature group template, you can assign users a common set of restrictions instead of having to configure each new user’s entire feature set manually.
-
You are integrating an existing Cisco UCM system with a new CUPS server. You will be using Cisco Unified Personal Communicator in both its softphone mode and its desk phone control mode. You navigate to Cisco Unified Serviceability > Tools > Service Activation and ensure that TFTP and the Cisco AXL Web Service are both enabled.
Which of the following services must also be enabled on the UCM system to complete the integration?
- Cisco CTIManager
- Cisco DirSync
- Cisco Extension Mobility
- Cisco Messaging Interface
Explanation:
The Cisco CTI Manager server must also be enabled to integrate an existing Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) system with a Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) server and to use Cisco Unified Personal Communicator in both its softphone mode and its desk phone control mode. The Cisco Computer Telephony Integration (CTI) feature is a development system that enables programmers to create applications that can connect to and communicate with a Cisco Unified Communications system. By using CTI, programmers can create server software and desktop applications that interface directly with UCM, CUPS, and other Cisco Voice over IP (VoIP) products. In order to use Cisco Unified Personal Communicator in desk phone control mode, the Cisco CTI Manager service must be enabled and started on UCM. Unified Personal Communicator communicates with the desk phone by using the CTI Quick Buffer Encoding (CTIQBE) protocol.Cisco Call Manager, Cisco Trivial File Transfer Protocol (Cisco TFTP), and Cisco Administrative Extensible Markup Language (AXL) Web Service must also be enabled and started in order to integrate CUPS and UCM in the configuration described in this scenario. The Cisco TFTP service is required to enable Cisco Unified Personal Communicator to operate in softphone mode. The Cisco AXL Web Service is required to enable the synchronization of data between CUPS and UCM. Finally, the Call Manager service, which is also called the Cisco Unified Communications Service, is required for UCM to use software call processing, signaling, and control.
The Cisco Directory Synchronization (DirSync) service is not required to integrate CUPS with UCM. The Cisco DirSync service enables an administrator to keep the UCM database synchronized with external directories, such as Microsoft Active Directory.
The Cisco Extension Mobility service is not required to integrate CUPS with UCM. Extension Mobility enables a user to log in to an IP phone that is capable of extension mobility service and to use that IP phone with the same features and settings as the user’s typical desk phone.
The Cisco Messaging Interface service is not required to integrate CUPS with UCM. Messaging Interface enables the connection of Simplified Message Desk Interface (SMDI) voice mail systems to UCM. The SMDI protocol defines how voice mail systems interact with telephone systems.
-
Which of the following commands should you issue to set the maximum number of extensions that you can configure on a CME router? (Choose two.)
- ephone
- ephone-dn
- max-dn
- max-ephones
- telephony-service
- dnwebedit
Explanation:
You should issue the telephony-service command and the max-dn command to set the maximum number of directory numbers (dns), or extensions, that you can configure on a Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) router. Issuing the telephony-service command puts the router into telephony-service configuration mode, where you can issue commands that configure telephony settings on the router, such as the max-dn and max-ephones commands.A CME router requires three values in order to configure basic telephony service: an IP address, a max-dn value, and a max-ephones value. The maximum value of the max-dn parameter varies based on the router model, the IOS version, and the amount of memory. If you do not issue the max-dn command, you will not be able to configure any ephone-dns on the router.
You should issue the dn-webedit command to enable the addition of ephone-dns by using the browser-based graphical user interface (GUI). By default, you cannot add an extension to CME by using the browser-based GUI. The dn-webedit command should be issued in telephony-service configuration mode.
You should issue the max-ephones command to set the maximum number of phones, not the maximum number of extensions, that you can configure on a router. Like the max-dn command, the max-ephones command must be issued in telephony-service configuration mode. The maximum value of the max-ephones parameter varies based on the router model and the IOS version. If you do not issue the max-ephones command, you will not be able to configure any ephones on the router.
You cannot issue the ephone-dn command to set the maximum number of extensions that you can configure on a router. The ephone-dn command configures an ephone-dn. The syntax of the ephone-dn command is ephone-dn dn-tag [dual-line | octo-line]. Issuing the ephone-dn command puts the router into ephone-dn configuration mode. To set the extension number for an ephone-dn, you should issue the number command in ephone-dn configuration mode.
You cannot issue the ephone command to set the maximum number of extensions that you can configure on a router. The ephone command configures an ephone. The syntax of the ephone command is ephone phonetag. Issuing the ephone command puts the router into ephone configuration mode. To associate a physical IP phone with an ephone, you should issue the ma-caddress mac-address command in ephone configuration mode, where mac-address is the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the IP phone.
-
Which of the following terms describes LFI?
- a QoS model
- a queuing method
- a link efficiency mechanism
- a resource reservation method
- a congestion avoidance mechanism
Explanation:
Link fragmentation and interleaving (LFI) is a link efficiency mechanism. Without LFI, small packets, such as voice packets, can become stuck behind large packets as the large packets are transmitted through an interface, thereby causing delay and jitter. LFI breaks up large data packets into small pieces and then interleaves the small packets among the fragments of the large packet. Another link efficiency mechanism used by Voice over IP (VoIP) is Compressed Real-time Transport Protocol (cRTP), which compresses the Layer 3 and Layer 4 headers of voice packets to a fraction of their original size.LFI is a Quality of Service (QoS) feature, not a QoS model. QoS enables a network to treat a specific type of traffic with a different priority than other types of traffic. For example, QoS can ensure that voice traffic gets higher priority on a network than data traffic. QoS models include the best-effort model, the Integrated Services (IntServ) model, and the Differentiated Services (DiffServ) model. Each QoS model handles packet flows in a different manner. For example, IntServ requires that applications reserve their end-to-end bandwidth requirements, and DiffServ prioritizes packets by traffic class. Because of some inherent shortcomings in the IntServ model, Cisco recommends using DiffServ when delivering voice traffic.
LFI is not a resource reservation method. When IntServ is used, bandwidth resources must be reserved for each traffic flow. These resources are reserved from the source to the destination by Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP).
LFI is not a queuing method. Queuing methods deal with congestion management. Each queuing method handles network congestion in a different manner. Queuing methods employed by Cisco routers include first-in-first-out (FIFO) queuing, priority queuing (PQ), custom queuing (CQ), round robin (RR), weighted RR (WRR), weighted fair queuing (WFQ), class-based WFQ (CBWFQ), and low latency queuing (LLQ). By default, Cisco devices use FIFO queuing for interfaces faster than 2.048 Mbps and use WFQ for serial interfaces at 2.048 Mbps or lower.
LFI is not a congestion avoidance mechanism. Congestion avoidance mechanisms mitigate tail drop, which occurs when a router drops new packets because its queues are too full to accept them. Congestion avoidance mechanisms employed by Cisco routers include random early detection (RED), weighted RED (WRED), and class-based WRED (CBWRED).