300-835 : Automating Cisco Collaboration Solutions (CLAUTO) : Part 02
-
Which of the following commands is used to match both inbound and outbound dial peers?
destination-pattern
- port
- session target
- incoming called-number
- answer-address
Explanation:
The destination-pattern command is used to match both inbound and outbound dial peers; a dial peer defines a logical route to a telephony endpoint. The string variable that is used with the destination-pattern command must match the source Automatic Number Identification (ANI) for inbound dial peer matching and must match the destination Dialed Number Identification Service (DNIS) for outbound dial peer matching.A voice gateway router will perform the following evaluations when it must send an outbound call:
1. The router will attempt to match the destination DNIS to a destination-pattern string command on a digit-by-digit basis, comparing the digit string to the destination-pattern as the user dials the digits.
2. If the dial peer is a plain old telephone service (POTS) dial peer, the router will forward the call to the port indicated by the corresponding port-port command.
3. If the dial peer is a Voice over IP (VoIP) dial peer, the router will forward the call to the IP address indicated by the corresponding session target ipv4: ip-address command.
4. If no match is found, the call will be dropped.The dial peer evaluation process will occur for every call leg along the path from the source endpoint to the destination endpoint. A call leg is a logical inbound or outbound connection for a voice gateway. The originating voice gateway and the terminating voice gateway between two telephony endpoints have one call leg in the inbound direction and one call leg in the outbound direction. Therefore, there will be exactly two call legs for each voice gateway.
The port command is not used to match outbound dial peers; it is used by a voice router to match inbound POTS dial peers and to determine where to route outgoing POTS dial peers. The session target command is not used to match outbound dial peers; it is used by a voice router to determine where to route an outgoing VoIP dial peer.
The incoming called-number command and the answer-address command are not used to match outbound dial peers? they are used to match inbound dial peers. A voice router will perform the following evaluations when it receives an inbound call:
1. The router will attempt to match the destination DNIS to an incoming called-number DNIS command.
2. The router will attempt to match the source ANI to an answer-address ANI command.
3. The router will attempt to match the source ANI to a destination-pattern string command.
4. The router will attempt to match the incoming call’s voice port to a port-port command.
5. If no match is found, the router will use the default dial peer.Once a dial peer match is found, the router will immediately route the call without proceeding to the next step. If multiple matches are found for a step, the router will select the longest explicit match. The default dial peer will only be used if no match is found. You cannot configure any of the settings for the default dial peer.
-
View the Exhibit.
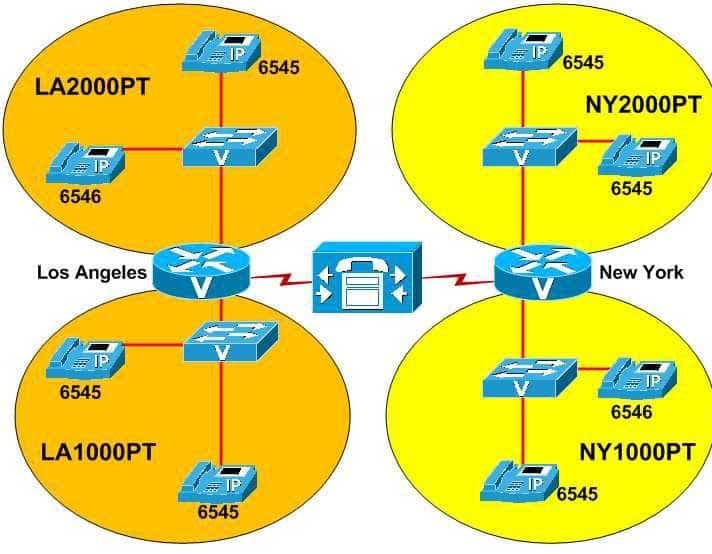
300-835 Part 02 Q02 005 You administer the VoIP network above.
The VoIP network is divided into four partitions. Two of the partitions are in Los Angeles, and two are in New York.
Which of the following are true? (Choose two.)
- The dn 6545 is not shared.
- The dn 6545 is shared within LA1000PT.
- The dn 6545 is shared between LA1000PT and LA2000PT.
- The dn 6546 is not shared.
- The dn 6546 is shared within NY1000PT.
- The dn 6546 is shared between NY1000PT and NY2000PT.
Explanation:
The directory number (dn) 6546 is not shared. However, the dn 6545 is shared within the LA1000PT partition. You can segregate a Voice over IP (VoIP) network into partitions in order to facilitate the use of different route patterns for different subsets of users. For example, if users in the LA1000PT partition should not be allowed to make long distance phone calls, you can restrict long distance phone calls in LA1000PT without affecting the route patterns in the other three partitions.Any dn that is configured in more than one partition will not be shared between the two partitions, because the partitions are treated as individual VoIP networks. Because a dn can be configured in more than one partition, the same dn can present different line identification information depending on its configuration within the given partition. By contrast, a dn that is configured on multiple devices within the same partition is considered to be a shared dn, or a shared line.
The dn 6545 has been configured in all four partitions of the VoIP network. However, dn 6545 has been configured multiple times in only two of the partitions: LA1000PT and NY2000PT. Therefore, dn 6545 has been configured as a shared line in both the LA1000PT partition and the NY2000PT partition of the VoIP network. In Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Administration, you can configure a dn as a shared line by navigating to the device on which you want the shared line to appear and adding the dn for the shared line to that device.
The dn 6546 has been configured in two of the four partitions of the VoIP network. However, dn 6546 has not been configured more than once in the same partition. The dn 6546 is configured on one device in the LA2000PT partition and on one device in the NY1000PT partition. Because it is not configured more than once within the same partition, dn 6546 is not a shared dn.
-
Which of the following Cisco Jabber features are not supported when UCM IM and Presence Service is running in IM-only mode? (Choose two.)
- audio calls
- IM
- Presence
- video calls
- XMPP integration
Explanation:
Neither the audio call feature nor the video call feature of Cisco Jabber is supported when Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) instant message (IM) and Presence Service is running in IM-only mode. The UCM IM and Presence Service enables a company to reduce communications delays in project collaboration by providing real-time, always available communications channels. For example, the IM and Presence Service supports persistent chat rooms, which are chat rooms that remain available even after the last user exits the room, and the ability to review IM history.The UCM IM and Presence Service has two modes of operation: IM-only and Cisco Unified Communications mode. In IM-only mode, Cisco Jabber and third-party Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) clients can connect to and use UCM for IM and Presence services. In Cisco Unified Communications mode, the IM and Presence Service supports IM, Presence, XMPP federation, and audio and video calls. XMPP federation allows Cisco Jabber clients to communicate with clients that are registered to a different Cisco Jabber cluster.
To place an audio or video call from Cisco Jabber, a user will typically click the Contacts button to search the list of contacts. Next, the user should click on the contact to call and press the phone icon. However, IM messaging will be the only available option if UCM is configured in IM-only mode.
-
Which of the following command sets can you issue to associate an IP phone with an ephone? (Choose two.)
- telephony-service auto assign
- telephony-service autoregephone
- ephone 1
mac-address 0019.8765.4321 - ephone-dn 1
mac-address 0019.8765.4321 - ephone 1
ip-address 192.168.12.34 - ephone-dn 1
ip-address 192.168.12.34
Explanation:
You can issue the following command set to associate an IP phone with an ephone:ephone 1
mac-address 0019.8765.4321The ephone 1 command configures ephone number 1. The mac-address 0019.8765.4321 command associates ephone number 1 with the IP phone that has Media Access Control (MAC) address 0019:8765:4321. Alternatively, you can issue the following command set to associate an IP phone with an ephone:
telephony-service
auto-reg-ephoneIssuing the telephony-service command puts the router into telephony-service configuration mode, where you can issue commands that configure telephony settings on the router. Issuing the auto-reg-ephone command configures a router to automatically associate the MAC address of an IP phone with the first unassigned ephone on the router if the IP phone’s MAC address is not already associated with an ephone. If all the ephones on the router are associated with IP phones, the router will create a new ephone, provided that the number of configured ephones does not exceed the value of the max-ephones command. The max-ephones command specifies the maximum number of ephones that you can configure on a router.
The following command set will not associate an IP phone with an ephone, because ephones are associated with MAC addresses, not IP addresses:
ephone 1
ip-address 192.168.12.34The following command sets will not associate an IP phone with an ephone, because ephones are not configured by issuing the ephone-dn command:
ephone-dn 1
ip-address 192.168.12.34ephone-dn 1
mac-address 0019.8765.4321The following command set will not associate an IP phone with an ephone, because the auto assign command associates an ephone button with an existing, unused ephone-dn:
telephony-service
auto assign -
Which of the following are voice messaging products that can be installed on a Cisco UCS? (Choose two.)
- CME
- UCM
- Unity
- CUE
- Unity Connection
Explanation:
Cisco Unity and Cisco Unity Connection are voice messaging products that can be installed on a Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS). A UCS is a virtualized system of Voice over IP (VoIP) platforms that can help lower administrative overhead by consolidating multiple VoIP software platforms into a single hardware platform. In addition to a UCS installation, Unity can be installed on a Microsoft Windows server. Unity Connection can also be installed as a separate appliance. Unity supports a maximum of 15,000 voice mailboxes. Unity Connection supports a maximum of 250 voice messaging ports and 20,000 voice mailboxes. However, Unity Connection also supports two different types of users: users with a mailbox and users without a mailbox. Unity Connection supports voice-enabled features, such as voice navigation and voice dialing; it can also be used to listen to audio translations of email messages and has an automated attendant feature.Cisco Unity Express (CUE) is not a voice messaging product that can be installed on a UCS. CUE is typically installed in a module slot on a Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) router. CUE provides voice mail messaging, automated attendant services, and interactive voice response (IVR) services. CUE can support a maximum of 250 voice mailboxes, depending on the license that is installed.
CME is not a voice messaging product that can be installed on a UCS. CME is a call processing platform that is based on IOS and contained within a Cisco Integrated Services Router (ISR). CME supports a maximum of 350 IP phones.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) is a call processing platform, not a voice messaging product. However, UCM can be installed in a UCS. UCM supports a maximum of 30,000 IP phones per cluster.
-
Which of the following Cisco Unity Connection services notifies components of changes to the database?
- Connection DB Event Publisher
- Connection CM Database Event Listener
- Connection Message Transfer Agent
- Connection Branch Sync Service
Explanation:
The Connection DB Event Publisher service, which is a Cisco Unity Connection base service, notifies components of changes to the Unity Connection database. Many Cisco Unity Connection services, including base services, can be managed from the Control Center in Cisco Unity Connection Serviceability. However, some status-only services, including Connection DB, Connection Server Role Manager, and Connection Serviceability, cannot be managed from the Control Center and can be deactivated only from a command-line interface (CLI).The Connection Message Transfer Agent does not notify components of changes to the Unity Connection database. The Connection Message Transfer Agent is a critical Unity Connection service that enables voice mail messages to be delivered to the message store. Although Unity Connection will operate without this service, voice mail messages cannot be delivered without it.
The Connection CM Database Event Listener does not notify components of changes to the Unity Connection database. However, the Connection CM Database Event Listener, which is an optional Unity Connection service, is capable of detecting changes in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) database.
The Connection Branch Sync Service does not notify components of changes to the Unity Connection database. The Connection Branch Sync Service, which is an optional Unity Connection service, enables Unity Connection’s Survivable Remote Site Voicemail (SRSV) function.
-
You are troubleshooting voice audio problems on your company’s VoIP network. The network carries both data and VoIP traffic. You have obtained the following measurements:
Jitter: 30 ms
Packet loss: 1 percent
End-to-end delay: 250 msWhich of the following best describes why your company’s network is experiencing voice audio problems?
- The jitter is too high.
- The packet loss is too high.
- The end-to-end delay is too high.
- VoIP traffic should not be carried on the same network as data traffic.
Explanation:
Your company’s network is most likely experiencing voice audio problems because the end-to-end delay is too high. Short delays and low packet loss on a Voice over IP (VoIP) network help protect the rate at which bits flow over the network. Cisco recommends a maximum end-to-end delay of 200 ms. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) considers an end-to-end delay of 150 ms or less to be acceptable for high voice quality. Delay, which is also called latency, can introduce interruptions in conversation flow, causing the speakers at each end of the circuit to interrupt each other. End-to-end delay can be mitigated by implementing Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms.It is not likely that the reason your company’s network is experiencing voice audio problems is because packet loss is too high. Cisco recommends a maximum packet loss of 1 percent for VoIP traffic. Packet loss is often caused when networks become congested and packets are dropped. Dropped packets can cause clips, or breaks, in the audio stream. However, voice traffic is more tolerant of dropped packets than of delayed packets because a small amount of packet loss is not noticeable to the human ear. Some codecs can correct small amounts of packet loss. On networks with limited bandwidth, a low-bit-rate codec can mitigate packet loss. However, the overall quality of the audio will be reduced. Packet loss can also be mitigated by implementing QoS mechanisms.
It is not likely that the reason your company’s network is experiencing voice audio problems is because the jitter is too high. Cisco recommends a maximum jitter of 30 ms for VoIP traffic. Jitter is a variation in delay, which can cause voice traffic to arrive at different times, thereby causing breaks, or choppiness, in the audio stream. Jitter can be mitigated by implementing QoS mechanisms. The effects of VoIP issues like jitter and latency on a network can be analyzed by using data analysis techniques such as Mean Opinion Score (MOS) or RFactor.
It is not likely that the reason your company’s network is experiencing voice audio problems is because VoIP traffic is carried on the same network as data traffic. VoIP traffic can be carried on the same network as data traffic. However, data traffic is usually more tolerant of dropped packets and delay than VoIP traffic. Therefore, VoIP traffic is typically given priority over data traffic.
-
Which of the following is true of both the Cisco Unified Personal Communicator and the Cisco Unified Client Services Framework phone types in UCM?
- Device names must begin with UPC.
- Device names can be no longer than 15 characters.
- Device names can contain uppercase letters only.
- Device names can contain numbers and uppercase letters only.
- Device names have no naming convention.
Explanation:
Softphone device names can be no longer than 15 characters for both the Cisco Unified Personal Communicator and the Cisco Unified Client Services Framework phone types in Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM). A softphone is software that behaves like a phone, enabling a user to have voice conversations over a typical workstation network connection. Softphone mode is an operational mode that Unified Personal Communicator uses to act as a softphone. In order to use Unified Personal Communicator as a softphone with UCM, you must add a device to UCM that enables the registration of Unified Personal Communicator in softphone mode.The Cisco Unified Personal Communicator device type naming convention requires that the name begin with the letters UPC and be derived from the UCM user name. The Cisco Unified Client Services Framework device type name has no such naming convention. However, neither the Cisco Unified Personal Communicator device type name nor the Cisco Unified Client Services Framework device type name can exceed 15 characters. In addition, the Cisco Unified Personal Communicator device type cannot contain characters other than uppercase letters and numbers. By contrast, Cisco Unified Client Services Framework device type names can contain uppercase letters, lowercase letters, and numbers.
For example, if you were to configure the user Joe Public with a UCM user name of jpublic, the softphone device name associated with the Cisco Unified Personal Communicator device type would be UPCJPUBLIC. Similarly, the user name of j_public or j.public would have an associated softphone device name of UPCJPUBLIC. If two UCM user names are similar enough to result in identical softphone device names, softphone registration problems can occur in UCM. Therefore, it is important to be aware of the Cisco Unified Personal Communicator naming convention when you are assigning user names and configuring softphone devices.
You can configure a softphone device in UCM by clicking Device > Phone > Add New in the UCM administrative graphical user interface (GUI) and selecting either Cisco Unified Personal Communicator or Cisco Unified Client Services Framework from the Phone Type dropdown field. You must configure the Phone Type field with Cisco Unified Personal Communicator if the user is using Unified Personal Communicator version 7.0. You must configure the Phone Type field with Cisco Unified Client Services Framework if the user is using Unified Personal Communicator version 8.0 or later.
-
Users are reporting garbled voice mail message recordings left by callers from the PSTN.
Which of the following actions should you perform first?
- Confirm that the connection to the caller is clear.
- Obtain a sniffer capture at the closest point to Unity Connection.
- Use network analysis tools to check for latency and packet loss.
- Modify the target decibels configured in AGC.
Explanation:
When troubleshooting garbled voice mail message recordings left by callers from the public switched telephone network (PSTN), you should first confirm that the connection to the caller is clear. For example, a voice mail message could become garbled if a mobile phone caller is traveling through an area with a weak or intermittent signal. If this is the case, there is nothing you can do to solve the issue. You can confirm that the connection is clear by asking the mobile caller to place another call to the voice mail system or by placing calls to the voice mail system from other mobile phones.If voice mail messages are still garbled when the connection is clear, you should next use network analysis tools to check for latency and packet loss. Network analysis tools enable you to determine whether the network itself is causing the garbled audio stream. For example, mismatched packet size configurations among voice devices on the network could cause packet loss or delay that might affect the quality of voice mail recordings.
As a final troubleshooting step, you should obtain a sniffer capture at the closest point of the recording to Cisco Unity Connection. This will help you determine whether the audio stream is being garbled before or after Unity Connection records it. If the stream is not garbled before Unity Connection records it, there might be a problem with Unity Connection itself.
You do not need to modify the target decibels configured in Automatic Gain Control (AGC). AGC is a Unity Connection feature that enables Unity Connection to automatically adjust the audio volume of calls. You can disable or adjust AGC settings if users report that the audio volume of voice mail recordings is always too loud or always too quiet. However, the AGC feature does not typically produce garbled recordings.
-
None of your company’s Cisco Jabber clients are able to automatically retrieve configurations from your company’s UCM 8.6 deployment.
Which of the following is most likely the reason?
- A service profile has not been configured in UCM.
- The _cisco-uds SRV record has not been configured in DNS.
- Automatic configuration is not selected in Jabber’s Advanced settings.
- The users have not been configured with the IM and Presence Service.
- UCM releases earlier than 9 do not support automatic configuration.
Explanation:
Of the available choices, the most likely reason that your company’s Cisco Jabber clients are not able to automatically retrieve configurations is that Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) releases earlier than 9 do not support the automatic configuration of Cisco Jabber clients by using service profiles. Cisco Jabber’s Advanced settings dialog box features an Automatic option that allows Cisco Jabber to automatically configure itself as long as all of the following are true:-UCM is operating at release 9 or later.
-A correct _cisco-uds Service (SRV) record has been configured on the Domain Name System (DNS) server.
-Automatic is selected in Advanced settings.
-An instant message (IM) and Presence Service profile has been configured in UCM.
-The IM and Presence Service profile has been correctly applied to end users in UCM User Management.There is not enough information in the scenario to determine whether a service profile has not been configured, whether the DNS record is missing, whether automatic configuration is not selected, or whether the users have not been configured with the IM and Presence Service. Even if that information were provided, the UCM deployment in this scenario is running release 8.6, which does not support the automatic configuration of Cisco Jabber clients.
-
How many Subscriber servers can be added to a UCM cluster?
- one
- two
- six
- eight
Explanation:
A Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) cluster can support up to eight Subscriber servers. Subscriber servers typically handle call routing, dial tone, receiving digits, and the streaming of on-hold music in a UCM cluster. In medium to large environments, the Subscriber servers perform most of the work in connecting and maintaining calls so that the performance of the Publisher server is not hindered. A UCM cluster is an environment that contains a Publisher server and up to eight Subscriber servers. Each server in the UCM cluster has a unique configuration.The Publisher server in a UCM cluster has two roles. It holds the master writable copy of the IBM Informix database for the cluster, and it acts as a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server for IP phone configuration downloads. The Publisher server is the only server that contains a writable copy of the IBM Informix database that stores directory numbers (dns), calling permissions, route plans, and other information. The Publisher server replicates the data that is stored in the master database to the Subscriber servers, all of which then store their own read-only copies of the database.
A Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) server cluster can support up to six servers. CUPS is server software that centralizes network traffic from several different communications services so that it can all be transmitted over the same Cisco Voice over IP (VoIP) network. CUPS uses industry-standard Jabber XCP for communication between different instant messaging (IM) clients; Extensible Message and Presence Protocol (XMPP) is the protocol that establishes the IM sessions. In addition, Jabber XCP facilitates other features such as file and application sharing and video conferencing.
-
You administer a UCM network of 500 IP phones.
Your supervisor asks you to add 101 new IP phones to the network before the end of the workday.
Which of the following does Cisco recommend you do?
- Add a second UCM server to the cluster.
- Add the phones by using the BAT.
- Enable auto-registration in UCM.
- Provision the IP phones manually in UCM.
Explanation:
Cisco recommends that you use the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT) to add more than 100 new IP phones to a Unified Communications Manager (UCM) network. There are three ways to add IP phones to a UCM database: by configuring auto-registration, by using the BAT, and by manually provisioning the IP phones in the UCM administrative graphical user interface (GUI). Both auto-registration and the BAT provide a means of adding many phones to the database simultaneously. However, Cisco does not recommend using the auto-registration method of adding IP phones if you need to add 101 or more IP phones.You do not need to provision the IP phones manually in UCM. Although you can manually add an IP phone to a UCM database, adding 101 new IP phones by using manual provisioning would require more administrative effort than by using auto-registration or the BAT. When you are manually provisioning an IP phone in UCM, you must fill in the MAC Address field, the Device Pool field, the Phone Button Template field, and the Device Security Profile field. In this scenario, your supervisor has asked you to add 101 IP phones to the network before the end of the workday. Therefore, you should not manually provision the IP phones.
You do not need to enable auto-registration in UCM. Auto-registration enables UCM to automatically add new IP phones to the UCM database. When a new IP phone is connected to the network, UCM will automatically assign an unused directory number (dn) to the IP phone from a pool of available dn numbers. However, auto-registration is a security risk because rogue devices can be connected to the network and registered with UCM by using auto-registration. In addition, you could accidentally register a valid IP phone with a dn from the wrong dn pool if you leave auto-registration enabled after you have completed an auto-registration process. Therefore, Cisco recommends that you enable auto-registration only for short periods of time, such as when you need to add fewer than 100 IP phones to the network.
You do not need to add a second UCM server to the cluster. UCM supports a maximum of 7,500 devices as a standalone server and a maximum of 30,000 IP phones per UCM cluster. In this scenario, you administer a network of 500 IP phones. In addition, you are adding only 101 new IP phones, which brings the total number of IP phones to 601.
-
Which of the following statements about UCM default phone button templates is not true?
- You cannot modify the button assignments within them.
- You can copy them and rename the copies to customize them.
- You cannot delete them.
- You can rename them, but doing so will automatically unassign them.
Explanation:
You cannot rename Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) default phone button templates. However, you can rename custom phone button templates. Renaming an in-use custom phone button template will not break the relationship between that template and its assigned phones. Each phone that has been assigned to that custom template will use that template under its new name.A phone button template is a UCM feature that enables the application of a configuration for many phones within an organization without configuring each phone individually. Cisco IP phones have standard, or default, phone button templates that can be applied to configure phones with default button settings. The standard phone button template that can be applied to a given IP phone depends on the model of the IP phone.
You cannot modify the button assignments within default phone button templates. However, you can copy default phone button templates and rename the copies to customize them. It is possible to reassign the buttons on an IP phone to functions that differ from the standard phone button template that was originally applied to the phone. Although you cannot modify the buttons on a default phone button template, you can copy the default template and rename the copy, which enables you to base a custom phone button template on a default template.
You cannot delete default phone button templates, even if the default template is not assigned to a phone. You can delete custom phone button templates as long as the custom template is not assigned to any phones and is not the only template for the given model of IP phone.
-
Which of the following issues is most likely to prompt an administrator to verify that the Cisco Unified Messaging Service is enabled and running in Cisco Unity Connection?
- Secure messages cannot be played in Outlook.
- Messages are sent to the wrong email account.
- The MWI lamp turns off before a message is read in Outlook.
- No Single Inbox features are working.
Explanation:
An administrator is most likely to verify that the Cisco Unified Messaging Service is enabled and running in Cisco Unity Connection if no Single Inbox features are working for the group of users that is associated with that Cisco Unified Messaging Service instance. The Single Inbox feature of Cisco Unity Connection enables the synchronization of voice messages between Cisco Unity Connection and Microsoft Exchange Server mailboxes. For example, a voice mail left for a Cisco Unity Connection user can additionally be delivered to that user’s Microsoft Outlook Inbox. In order for these features to be available, the Cisco Unified Messaging Service must be enabled and started.An administrator is not likely to verify that the Cisco Unified Messaging Service is enabled and running in Cisco Unity Connection if messages are sent to the wrong email account. However, an administrator might verify that the user’s primary or proxy Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) address in Unity Connection matches the account to which the user wants voice mail messages relayed.
An administrator is not likely to verify that the Cisco Unified Messaging Service is enabled and running in Cisco Unity Connection if the message waiting indicator (MWI) lamp turns off before a message is read in Microsoft Outlook. However, an administrator might verify that the Microsoft Outlook Mark Items as Read When Viewed in the Reading Pane check box is clear in the Outlook Options > Mail > Reading Pane dialog box. If this check box is selected, the MWI lamp will turn off when the user selects the message in Outlook’s reading pane and there are no more new messages in Unity Connection.
An administrator is not likely to verify that the Cisco Unified Messaging Service is enabled and running in Cisco Unity Connection if secure messages cannot be played in Outlook. However, an administrator might verify that Cisco Unity Connection ViewMail for Microsoft Outlook is installed on the user’s workstation if secure messages cannot be played in Outlook. When Unity Connection delivers a secure voice mail to Microsoft Exchange, only the introductory text of the email is sent to the user. The audio file containing the message remains on Unity Connection. Cisco Unity Connection ViewMail enables users to listen to the voice mail audio files.
-
Which of the following can you display by clicking System Reports > CDR Error in the UCM 8.0 CAR GUI?
- the current number of billing errors
- the call volume for a given period of time
- malicious call details
- QoS rating information for inbound calls
- Route and Line Group Utilization information
- the top number of users by maximum length of calls
Explanation:
You can view information about the current number of billing errors by using the System Reports > CDR Error report in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Call Detail Records (CDR) Analysis and Reporting (CAR) graphical user interface (GUI). This report enables a CAR administrator to view the number of errors that occurred when CDR data was loaded into the reporting system.You can view information about the call volume for a given period of time by using the System Reports > Traffic > Summary by Phone Number report in the UCM CAR GUI. This report enables a CAR administrator to choose a range of time and IP phone extension numbers from which to view call volume information, thereby enabling an administrator to view what extensions were in use at a specific time.
You can view malicious call details by using the System Reports > Malicious Call Details report in the UCM CAR GUI. This report enables a CAR administrator to view call information that is tracked by the UCM Malicious Call Identification (MCID) service. An administrator can choose to view MCID information over a period of time.
You can view Quality of Service (QoS) rating information for inbound calls by using the System Reports > QoS > Detail report in the UCM CAR GUI. The Detail report enables a CAR administrator to choose a UCM network and a period of time for which to view QoS ratings for both inbound and outbound calls. The Detail report can be used to monitor QoS at a user level.
You can display the Route and Line Group Utilization report by using Device Reports > Route Patterns/Hunt Pilots in the UCM CAR GUI. This report enables a CAR administrator to view Route and Line Group Utilization as a percentage; the report can also be used to determine whether capacity needs to be added to an existing Voice over IP (VoIP) implementation.
You can view information about the top number of users by maximum length of calls by using the User Reports menu. The By Duration report can be accessed by clicking User Reports > Top N in the UCM CAR GUI. This report enables a CAR administrator to view users who have made the longest calls over a given period of time, starting with the user who placed the longest call.
-
For which of the following would you not typically use the Cisco Unity Connection Alternate Extension field?
- for Unity Connection call-in convenience from a mobile phone
- to load balance callers between voice mailboxes
- to handle multiple line appearances on a single IP phone
- for Unity Connection call-in convenience from another IP phone
- to filter multiple lines to a single voice mailbox
Explanation:
You would not use the Cisco Unity Connection Alternate Extension field to load balance callers between voice mailboxes. To load balance calls to Unity Connection, you would first need to ensure that Unity Connection is integrated with Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) by using the Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP). In UCM Administration, you should then change the distribution algorithm to Longest Idle Time on the Call Routing > Route/Hunt > Line Group page for the line group that answers calls on both the publisher server and the subscriber server.In Unity Connection Administration, you should then assign the first half of the answering ports, starting with the lowest-numbered port, to the publisher server. The last half of the answering ports can then be assigned to the subscriber server. You should then assign half the dial-out ports to the publisher server. The remainder of the dial-out ports should be assigned to the subscriber server.
Alternatively, in UCM Administration, you could use the Top Down distribution algorithm for the line group that contains ports that answer calls on each server in a Unity Connection cluster. In Unity Connection Administration, assign the first half of the answering ports to the subscriber server. Assign the remainder of the answering ports to the publisher server. This configuration ensures that the subscriber server will answer the majority of the calls when the Top Down distribution algorithm is used. Next, assign the first half of the dial-out ports to the publisher server so that the publisher server handles the majority of the message waiting indictors (MWIs) and notifications. Assign the second half to the subscriber server.
The Alternate Extension field is typically used to enable a single voice mailbox to serve more than one directory number (dn), or line. For example, up to nine administrator configured alternate extensions can be assigned to a single voice mailbox. These alternate extensions can be individual dns from the voice virtual LAN (VLAN) or the numbers of external devices. As a result, it is possible to enable a user to conveniently access Unity Connection from a mobile phone or from another IP phone. Similarly, an Alternate Extension can be used to access a single voice mailbox from multiple line appearances on a single IP phone.
-
Which of the following is not a benefit of integrating LDAP with UCM?
- LDAP users are automatically provisioned in UCM.
- LDAP users can be authenticated to UCM by using LDAP passwords.
- UCM applications can perform LDAP user lookups.
- LDAP passwords can be synchronized with UCM application users.
Explanation:
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) passwords cannot be synchronized with Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) application users. LDAP synchronization with UCM does not apply to application users. For example, users of the Cisco Unified Personal Communicator application are manually provisioned by using the UCM graphical user interface (GUI) and cannot be created or managed automatically through the corporate directory like UCM users can be.LDAP users being automatically provisioned in UCM is a benefit of integrating LDAP with UCM. When UCM is configured to synchronize with an LDAP directory, such as OpenLDAP or Microsoft Active Directory, the user ID and all user personal and organizational data that is stored in the LDAP directory, except for passwords, are replicated to the UCM database. It is important to note that the Cisco Directory Synchronization (DirSync) service must be activated before LDAP synchronization can take place.
When LDAP synchronization is configured, UCM configures the synchronized data as read-only data and acknowledges the LDAP directory as the central authority for creating and deleting user accounts. Therefore, UCM prevents administrators from using the UCM GUI to add and delete users. None of the data that was replicated to the UCM database can be modified by using the GUI. However, UCM user data that is not managed by the LDAP directory, such as the user’s password and personal identification number (PIN), can be modified in the UCM administrative GUI.
The ability for Cisco UCM applications, such as Unified Personal Communicator, to perform LDAP user lookups is a benefit of integrating LDAP with UCM. When LDAP directory lookups are enabled, not only can a Unified Personal Communicator client search for and view information in the LDAP directory, but the client can also add contacts from the LDAP directory to contact lists. Administrators can configure a limitless number of LDAP custom filters in UCM Administration to filter the results of LDAP searches.
LDAP users being authenticated to UCM by using LDAP passwords, which is also known as single sign-on (SSO), is a benefit of integrating LDAP with UCM. Although user personal and organizational data is not synchronized with the LDAP directory and can be modified separately from the LDAP directory, you can change the user password only by using the LDAP directory’s change-password tool. When a user attempts to authenticate with UCM, the user’s credentials are passed to the LDAP directory authentication service. If the credentials are correct, the user is authenticated and permitted to log in to the UCM GUI.
-
All of your department’s IP phones are connected to the same Cisco Catalyst switch. The switch acts as a DHCP server for the voice VLAN. Another administrator power cycles the switch without warning. No calls are in progress.
Which of the following is most likely to occur?
- The IP phones will reset.
- The IP phones will disconnect but retain IP configuration information.
- The IP phones will disappear from the UCM configuration.
- The IP phones will not be affected by the power cycle.
Explanation:
Most likely, the IP phones will all reset when the administrator power cycles the switch. When an IP phone is disconnected from Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM), the phone will automatically reset in an attempt to reestablish communication. Therefore, if an IP phone suddenly resets or is continuously attempting to register with UCM, it is important to first verify the phone’s connectivity to the network switch.The IP phones will disconnect but will not retain IP information. In this scenario, the IP phones receive their IP configurations from the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server that is running on the Cisco Catalyst switch that has been power cycled. When the IP phones reset, they will lose IP configuration information that was obtained from the DHCP server. Similarly, the IP phones will not be able to download configuration files from the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server until connectivity to the switch is restored.
The IP phones will not disappear from the UCM configuration. You can verify that an IP phone exists in the UCM by clicking Device > Phone > Find in UCM Administration and searching for the particular IP phone’s Media Access Control (MAC) address. The IP phone will no longer be registered with UCM when it loses connectivity. However, the IP phone’s record in the UCM configuration will remain there.
The IP phones will be affected by the power cycle. In addition to registration problems, IP configuration problems, and TFTP configuration problems, IP phones that are powered directly from the Cisco Catalyst switches by using Power over Ethernet (PoE) will not be able to receive power until the switch has restarted.
-
Which of the following is not a function of MTPs?
- addressing DTMF transport mismatches
- converting between IPv4 and IPv6 RTP streams
- converting digital audio from one codec to another
- delivering SIP Early Offers over SIP trunks
Explanation:
Converting digital audio from one codec to another is a function of a transcoder, not of Media Termination Points (MTPs). Transcoders enable communication between devices that support dissimilar audio codecs. For example, a transcoder can translate a G.729-encoded packet to a G.711encoded packet and vice versa. Transcoders translate the data stream in real time between two devices so that no audio delay is experienced by either endpoint.In Cisco Unified Communications systems, MTPs are used to deliver Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Early Offers over SIP trunks. There are two ways to enable Early Offers on SIP trunks in Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM): select the MTP Required-check box on the SIP trunk or select the Early Offer support for voice and video calls (insert MTP if needed) check box on the SIP profile that is connected to the SIP trunk. If MTP is required, all outbound calls will use MTP, as will calls operating on the same codec. If MTP is enabled as needed, it is inserted if the trunk is incapable of sending complete information about its media capabilities in the SIP Invite message.
In addition to SIP Early Offers, MTPs are used to address dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) transport mismatches, to convert between IP version 4 (IPv4) and IPv6 for voice Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) streams, to act as Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) agents, and to act as a Trusted Relay Point (TRP).
-
Your supervisor provides you with a file named users.csv and asks you to add the user accounts from that file to Cisco Unity Connection.
Which of the following tools will you most likely use to accomplish your task?
- AXL Web Service
- BAT
- DirSync
- manual entry
Explanation:
You will most likely use the Cisco Bulk Administration Tool (BAT) to import, or onboard, Cisco Unity Connection users from a file named users.csv. You can access the BAT by clicking Tools > Bulk Administration Tool in the Unity Connection graphical user interface (GUI).To import users from a comma-separated values (CSV) file, you should first click the Create radio button in the Select Operation area of the BAT. You can also choose Update, Delete, or Export operations from this area, depending on the operation you want the BAT to perform. The Update operation modifies existing user accounts based on the information in the CSV file. The Delete operation deletes existing user accounts based on the information in the CSV file. The Export operation outputs existing user accounts to a CSV file in CSV format.
After you have selected an operation, you should select a type of user to create from the Select Object Type area of the BAT. There are four user types you can create by using the BAT: Users, Users with Mailbox, System Contacts, and Users from LDAP Directory.
In the Override CSV Fields When Creating User Accounts area of the BAT, you can choose either to override CSV-imported fields with default fields from a Unity Connection user template or to allow the direct import of the information from all the fields that are contained within the CSV file you want to import.
After you have configured all the information above, you should click the Browse button in the Select File area to choose the CSV file you want to import. You should also configure a separate CSV file name in the Failed Objects Filename field; the created file stores records that fail during the import process. The file name you configure in the Failed Objects Filename field should be descriptive and different from the name of the file you want to import. For example, if the name of the file you want to import is users.csv, you could name the failed objects file userserr.csv, or something similar. To help troubleshoot CSV import errors, you should review the information in the failed objects file after you have attempted an import. You can review the failed objects file by clicking the Download the Failed Objects File link on the BAT import summary screen.
When you are ready to import the CSV file, click the Submit button to start the import process. Once the import process is complete, the BAT will display the import summary screen.
You cannot use the Cisco Administrative XML Layer (AXL) Web Service to import Unity Connection users from a file named users.csv. The Cisco AXL Web Service is used to import Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) users into Unity Connection. The service must be enabled on both UCM and Unity Connection in order to import users. In addition, UCM users must be assigned a primary extension in UCM in order to be imported into Unity Connection by AXL.
You cannot use the Cisco Directory Synchronization (DirSync) service to import Unity Connection users from a file named users.csv. The DirSync service enables Unity Connection to synchronize with Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory services, such as Microsoft Active Directory. To enable synchronization between Unity Connection and an LDAP directory, you must select the Cisco DirSync check box in the Directory Services area of the Unity Connection GUI. Because Unity Connection stores users locally, a user that is synchronized with Unity Connection from LDAP will continue to be stored locally even if that user is later deleted from the LDAP database.
You would not use manual entry to import Unity Connection users from a file named users.csv. Although you can manually create new users in Unity Connection, manually parsing and populating the new user information from the CSV would be time-consuming and prone to human error.