300-835 : Automating Cisco Collaboration Solutions (CLAUTO) : Part 05
-
You issue the show running-config command on a CME router and receive the following partial output:

300-835 Part 05 Q01 016 Examine the output, and use the information you gather to answer the question.
You issue the prefix 911 command on the CME router.
Which of the following will occur when a user dials 411?
- The user will be connected to the 411 service with an outbound prefix of 9.
- The user will be connected to the 411 service directly.
- The user will be connected to the extension 9114 if it exists.
- The user will be connected to an operator.
Explanation:
If you issue the prefix 911 command on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) router, a user who dials 411 will be connected to the extension 9114 if it exists in the system. The prefix command is used to add one or more digits to the front of the dial string before the dial string is forwarded to the destination network. Issuing the prefix 911 command in this scenario will add 911 to the front of the dial string. The last two digits in the destination pattern, 1 and 1, were explicitly matched. By default, CME only forwards digits matched by wildcards in a destination pattern, not digits that are explicitly defined in the destination pattern. Therefore, the dial string 9114 would be forwarded to the public switched telephone network (PSTN).The destination-pattern command is used to match both inbound and outbound dial peers. The sequence of dialed digits that will be matched for a dial peer can contain the digits 0 through 9, the asterisk (*), and the pound sign (#). In addition, you can use a period (.) as a wildcard symbol to refine the dialing pattern or to match multiple dial strings for a single dial peer. The command set in this scenario configures a dial peer on a CME router to explicitly match the pattern 9114. By default, CME only forwards digits matched by wildcards in a destination pattern, not digits that are explicitly defined in the destination pattern. Therefore, the destination-pattern .11 command configures CME to forward only the first of the digits in the destination pattern when a caller dials 411.
-
Which of the following interfaces handles the exchange of availability information between third-party clients and a Cisco Presence deployment?
- AXL/SOAP
- LDAP
- SIP
- XMPP
Explanation:
The Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) interface handles the exchange of availability information between third-party clients and a Cisco Presence deployment. Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) and Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) server together are the primary components of a Cisco Presence deployment.The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) interface does not handle the exchange of availability information between third-party clients and a Cisco Presence deployment. However, a SIP trunk interface does handle the exchange of availability information between UCM and a CUPS server. A UCM SIP trunk interface must point to the CUPS server in order for availability information to be exchanged between the two systems. CUPS is also capable of sending SIP subscribe messages to UCM over the SIP trunk if UCM is configured as a Presence gateway.
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) interface does not handle the exchange of availability information between third-party clients and a Cisco Presence deployment. However, the LDAP interface is used to synchronize user information between UCM and CUPS in order to create a single sign-on (SSO) user experience. For example, a Cisco Unified Personal Communicator user can be authenticated to both the CUPS server and UCM by connecting directly to the CUPS server. LDAP is a directory protocol that is used by other servers, such as CUPS to perform contact lookups. LDAP listens on Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port 389 unencrypted or on port 636 over Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). Third-party XMPP clients can also use LDAP to search the database and add users as contacts.
The Cisco Administrative Extensible Markup Language (AXL)/Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) interface does not handle the exchange of availability information between third-party clients and a Cisco Presence deployment. However, the AXL/SOAP interface is used to handle database synchronization tasks from UCM to the CUPS database. For synchronization to start, the Sync Agent service must be started on the CUPS server.
-
Which of the following reports can be displayed by using the CAR Device Reports menu?
- the current number of billing errors
- the call volume for a given period of time
- malicious call details
- QoS rating information for inbound calls
- Route and Line Group Utilization information
- the top number of users by maximum length of calls
Explanation:
You can display Route and Line Group Utilization information by using the Call Detail Records (CDR) Analysis and Reporting (CAR) Device Reports menu. CAR is a reporting system that can be used to examine a variety of statistics about a Cisco Unified Communications system, including system load and performance.The Route and Line Group Utilization report can be accessed by clicking Device Reports > Route Patterns/ Hunt Pilots in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) CAR graphical user interface (GUI). This report enables a CAR administrator to view Route and Line Group Utilization as a percentage; the report can also be used to determine whether capacity needs to be added to an existing Voice over IP (VoIP) implementation.
You cannot display information about the current number of billing errors by using the CAR Device Reports menu. You can view information about the current number of billing errors by using the System Reports > CDR Error report in the UCM CAR GUI. This report enables a CAR administrator to view the number of errors that occurred when CDR data was loaded into the reporting system.
You cannot display information about call volume for a given period of time by using the CAR Device Reports menu. You can view information about call volume for a given period of time by using the System Reports > Traffic > Summary by Phone Number report in the UCM CAR GUI. This report enables a CAR administrator to choose a range of time and IP phone extension numbers from which to view call volume information, thereby enabling an administrator to view what extensions were in use at a specific time.
You cannot display malicious call details by using the CAR Device Reports menu. You can view malicious call details by using the System Reports > Malicious Call Details report in the UCM CAR GUI. This report enables a CAR administrator to view call information that is tracked by the UCM Malicious Call Identification (MCID) service. An administrator can choose to view MCID information over a period of time.
You cannot display Quality of Service (QoS) rating information for inbound calls by using the CAR Device Reports menu. You can view QoS information for inbound calls by using the System Reports > QoS > Detail report in the UCM CAR GUI. The Detail report enables a CAR administrator to choose a UCM network and a period of time for which to view QoS ratings for both inbound and outbound calls. The Detail report can be used to monitor QoS at a user level.
You cannot display information about the top number of users by maximum length of calls by using the CAR Device Reports menu. You can view information about the top number of users by maximum length of calls by using the User Reports menu. The By Duration report can be accessed by clicking User Reports > Top N in the UCM CAR GUI. This report enables a CAR administrator to view users who have made the longest calls over a given period of time, starting with the user who placed the longest call.
-
You administer a VoIP network in the United States.
You configure two search spaces for your organization. The Local search space contains only the LocalPT partition, which can match only four-digit local dns. The Long Distance search space contains the PSTNPT, which can match patterns up to 12 digits in length.
You configure an IP phone that has been assigned the dn 5555 to use the Local search space. You also disable call forwarding on the IP phone.
Upon reviewing call logs, you discover that long distance calls have been made from the IP phone that has been assigned the dn 5555.
Which of the following can cause this problem? (Choose two.)
- A long distance route pattern match exists in the <None> search space.
- A long distance route pattern match exists in the Local search space.
- The Local search space has been assigned as a line search space.
- The Local search space has been assigned as a device search space.
- The Local search space is able to match too many digits.
- The Local search space is able to reach the PSTN.
- The LongDistance search space does not match enough digits.
- The LongDistance search space has been assigned as a line search space.
Explanation:
Long distance calls can be made from the IP phone that has been assigned the directory number (dn) 5555 if a long distance route pattern match exists in the <None> search space. In addition, long distance calls can be made from the IP phone if the Long Distance search space has been assigned as a line search space. A search space is an ordered list of partitions that a device is allowed to search in order to locate patterns that match a dialed number. A partition is a logical grouping of Voice over IP (VoIP) route patterns and dns. A device that is not able to match a dialed number in any of the search spaces that are assigned to the device will generate a busy signal.By default, every VoIP endpoint can match a route pattern or dn that is contained within the <None> search space. The <None> search space contains the <None> partition. The <None> partition initially contains all the dns that are configured in the VoIP network. Therefore, you should move dns from the <None> partition to a custom partition to limit specific pattern matching to specific endpoints. In this scenario, the IP phone at 5555 will be able to call long distance numbers if a pattern that matches long distance numbers is matched in the <None> search space.
There are two types of search spaces that a VoIP device can search: a device search space and a line search space. A device search space is a search space that is assigned to a device itself. The information in a device search space will be searched no matter which line on a device is chosen for the outgoing call. A line search space, on the other hand, is a search space that is assigned to a single line on a device, not to the device itself. The information in a line search space will be searched when the user chooses the line to which the search space is assigned as the outgoing line for the call.
If a device is configured with both a device search space and a line search space, the device will combine the two search spaces together, with the line search space taking precedence. Thus the information contained in the line search space will be searched first. In this scenario, if you assign the Local search space to the IP phone itself and the Long Distance search space to a line on the IP phone, the Long Distance search space will be searched first and a user will be allowed to make long distance calls from the IP phone. Cisco recommends configuring calling search spaces at the device level to prevent users from bypassing calling restrictions by simply placing calls from an alternate phone line.
It is not likely that the Local search space assignment or configuration can cause the problem. In this scenario, the Local search space contains only the LocalPT partition, which in turn can only match patterns that are four digits in length. In order for the Local search space to match a long distance pattern or reach the public switched telephone network (PSTN), the partition would need to be able to match more than four digits. In addition, the Local search space could be assigned as either a device search space or a line search space in this scenario.
It is not likely that the number of digits being matched by the Long Distance search space can cause the problem. In this scenario, the Long Distance search space contains the PSTNPT partition, which can match up to 12 digits. A typical long distance telephone number in the United States contains 11 digits, although you might be required to dial an additional digit at the beginning of the dial string to access the PSTN.
-
Which of the following URLs cannot be used to access Cisco Unified Operating System Administration?
- http://ip-address/admin
- http://ip-address/ccmadmin
- http://ip-address/cmplatform
- http://ip-address/cuadmin
- http://ip-address/cupadmin
Explanation:
You cannot use the Uniform Resource Locator (URL) http://ip-address/admin to access Cisco Unified Operating System Administration. However, you can use http://ip-address/admin, where ip-address is the IP address that has been assigned to the Cisco Unity Express (CUE) network module, to access the CUE browser-based administrative graphical user interface (GUI). CUE is a voice mail messaging system that is typically installed in a Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) router module slot. Both CUE and CME can be administered by using either a command-line interface (CLI) or the browser-based GUI.You can use the URL http://ip-address/cmplatform, where ip-address is the IP address of a Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) server, a Cisco Unity Connection server, or a Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) server, to access Cisco Unified Operating System Administration. Cisco Unified Operating System Administration is a browser-based GUI that can be used to modify operating system and network settings that are common across components of a Cisco Unified Communications network. For example, you can verify Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) settings by using the Unified Operating System Administration GUI.
You can use the URL http://ip-address/ccmadmin, where ip-address is the IP address of a UCM server, to access Cisco Unified Operating System Administration. The URL http://ip-address/ccmadmin launches the UCM administrative GUI. You can then click Navigation > Cisco Unified OS Administration to enter Cisco Unified Operating System Administration.
You can use the URL http://ip-address/cuadmin, where ip-address is the IP address of a Unity Connection server, to access Cisco Unified Operating System Administration. The URL http://ip-address/cuadmin launches the Cisco Unity Connection administrative GUI. You can then click Navigation > Cisco Unified OS Administration to enter Cisco Unified Operating System Administration.
You can use the URL http://ip-address/cupadmin, where ip-address is the IP address of a CUPS server, to access Cisco Unified Operating System Administration. The URL http://ip-address/cupadmin launches the CUPS administrative GUI. You can then click Navigation> Cisco Unified OS Administration to enter Cisco Unified Operating System Administration.
-
Another administrator deletes the IPSec trust store from UCM’s Security > Certificate Management page. Which of the following is most likely to be affected by this change?
- encryption of DRS backups made prior to the change
- encrypted communication between DRS Master Agents and Local Agents
- addition of new backup devices to a DRS schedule
- deletion of old backup devices from a DRS schedule
- access to network storage location configuration
Explanation:
Of the available choices, encrypted communication between Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Disaster Recovery System (DRS) Master Agents and Local Agents is most likely to be affected by this change. Master Agents store component registrations, maintain scheduled tasks, and store backup data on a locally attached device. Local Agents, which are installed and activated by default on each cluster node, are responsible for running backup and restore scripts on the local server. DRS uses Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to both authenticate and encrypt data between a Master Agent and a Local Agent. In addition, DRS uses IP Security (IPSec) for public key infrastructure (PKI) encryption. The deletion of the IPSec trust store from UCM’s security configuration can cause DRS to function improperly.Encryption of DRS backups will not likely be affected by this change. DRS uses the existing cluster security password when performing encryption on a backup. If the cluster security password is modified by using the command-line interface (CLI) or by a fresh UCM installation, you might not be able to decrypt and restore that backup. Workarounds to this issue include remembering the old cluster security password that was used to encrypt the data or immediately performing a fresh backup when the cluster security password changes.
The addition or deletion of backup devices to a DRS schedule will not be affected by this change. However, it is important to note that a backup device cannot be deleted from DRS if that backup device is part of an existing backup schedule. In order to remove an existing backup device from a DRS configuration, you must first ensure that the device has been removed from any backup schedules in which it might be configured.
Access to network storage location configuration will not be affected by this change. In order to configure network storage locations, you must have access to a Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) server. In addition to backing up data to devices that are directly connected to a Master Agent, DRS can back up to network storage locations by using SFTP.
-
You administer a Cisco CME router with CUE installed. You issue the show running-config command on the router and receive the following partial output:
ephonedn 51
number 70…
mwi on
!
ephonedn 52
number 71…
mwi offWhich of the following statements are true? (Choose two.)
- When a caller dials 70123, the MWI light for extension 70123 will turn on.
- When a caller dials 70123, the MWI light for extension 123 will turn on.
- When a caller dials 71123, the MWI light for extension 71123 will turn off.
- The MWI lights cannot be turned on manually from an IP phone.
- When a caller leaves a message for extension 123, the MWI light for extension 123 will turn on.
Explanation:
When a caller dials 70123 or when a caller leaves a message for extension 123, the message waiting indicator (MWI) light for extension 123 will turn on. The MWI light appears on a user’s IP phone when a new voice mail message is received in the user’s Cisco Unity Express (CUE) voice mailbox.To configure MWI, you must create two ephone-dns: one ephone-dn to turn the MWI light on when the user receives a message, and one ephone-dn to turn the MWI light off when the user retrieves all of his or her messages. When CUE receives a voice mail message for a user, CUE will send a code to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) router to indicate that the user’s MWI light should be turned on. When the user retrieves the message, CUE will send another code to CME to indicate that the user’s MWI light should be turned off.
The MWI codes can be any number of any length as long as they are not the same as any existing extension numbers. To configure the MWI code that CUE will send to CME, you should issue the number command with the MWI code plus a number of periods equal to the number of digits in the users’ extensions. For example, if you want to create MWI code 70 and your system is configured to use three-digit extensions, you should issue the number 70… command in ephone-dn configuration mode.
Finally, the ephone-dn that is configured with the MWI code must also be configured with the mwi on or the mwi off command, depending on whether the ephone-dn should be responsible for turning the MWI light on or off, respectively. For example, the following command set configures ephone-dn 51 to turn on the MWI light for any three-digit extension that is prefaced by the MWI code 70:
ephone-dn 51
number 70…
mwi onSimilarly, the following command set configures ephone-dn 52 to turn off the MWI light for any threedigit extension that is prefaced by the MWI code 71:
ephone-dn 52
number 71…
mwi offAfter CME receives a dialed string from CUE that contains the MWI code, CME will match the dialed digits to the ephone-dn number pattern, strip off the explicitly matched MWI code, and change the state of the MWI light for the extension that matches the remaining forwarded digits. In this scenario, CUE will send the digit string 70123 to CME when the user at extension 123 receives a voice mail message? CME will then strip off MWI code 70 and turn on the MWI light for extension 123.
The MWI light on an IP phone can be turned on or off manually if a user dials the MWI code plus any extension number, provided that the MWI code can be dialed on an IP phone keypad. For example, if a user dials 70123 from the keypad of an IP phone connected to a CME router that is configured with the command sets shown above, the MWI light will turn on for the IP phone that has been assigned extension 123, even though extension 123 has not received a new voice mail message.
To prevent users from being able to turn the MWI light on or off at will without having to leave or listen to a voice mail message, you can configure the MWI code by using a character from A through D in the digits. The characters ranging from A through D are included in the dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) signaling standard but are not included on typical telephone keypads. For example, the following command set configures ephone-dn 51 to turn on the MWI light for any three-digit extension that is prefaced by the MWI code A7:
ephone-dn 51
number A7…
mwi onThe MWI light for extension 70123 will not turn on when a caller dials 70123. The ephone-dns in this scenario are configured to turn the MWI light on or off for IP phones with three-digit extensions. Extension 70123 is a five-digit extension. Therefore, the MWI light for extension 70123 will not turn on; the MWI light for extension 123 will turn on, even if extension 123 has not received a new voice mail message.
Similarly, the MWI light for extension 71123 will not turn off when a caller dials 71123. The ephone-dns in this scenario are configured to turn the MWI light on or off for IP phones with three-digit extensions. Extension 71123 is a five-digit extension. Therefore, the MWI light for extension 71123 will not turn off? the MWI light for extension 123 will turn off, even if extension 123 contains new voice mail messages.
-
Which of the following is not a Microsoft Exchange storage limit that can be addressed in a Cisco Unity phone conversation?
- Issue Warning
- Prohibit Send
- Prohibit Send and Receive
- Message Aging
Explanation:
Message Aging is not a Microsoft Exchange storage limit. Therefore, a Cisco Unity phone conversation cannot address a Message Aging storage limit. Message Aging is a Cisco Unity option that can be used to move voice mail messages of a given age to the Deleted Items folder, or delete them permanently. This option is disabled by default. However, you can enable this option as a more permanent solution for a user who has a high volume of inbound voice mail messages that are never manually deleted.Cisco Unity integrates voice messaging with email services provided by Microsoft Exchange. In a Cisco Unity and Microsoft Exchange environment, voice messages, email, and fax messages can all be accessed from the same client, such as a PC or a touchtone phone. When a user’s mailbox exceeds Microsoft Exchange storage limit thresholds, Cisco Unity can notify the user by using the phone conversation.
Microsoft Exchange has three different storage limit thresholds that can be configured system-wide or on a per-user basis. When a user’s mailbox size exceeds a configured threshold, Microsoft Exchange and Cisco Unity carry out different actions depending on the storage limit that applies.
When the Issue Warning threshold is exceeded, both Cisco Unity and Microsoft Exchange will send a notification to the user that the mailbox has exceeded the threshold. The warning gives users an opportunity to delete or archive old messages before stricter mailbox size enforcement measures are activated. When the Prohibit Send threshold is exceeded, neither Cisco Unity nor Microsoft Exchange will allow the user to send messages. When the Prohibit Send and Receive threshold is exceeded, neither Microsoft Exchange nor Cisco Unity will allow the user to send or receive messages. In addition, Cisco Unity will forward any messages that cannot be delivered to its Unaddressed Messages distribution list. Messages that are forwarded to the Unaddressed Messages distribution list will not be delivered to the intended recipients.
-
You administer a UCM network of 500 IP phones
You need to add 50 new IP phones to your company’s UCM network before the end of the workday. Which of the following does Cisco recommend you do? (Select the best answer.)
- Add a second UCM server to the cluster.
- Add the phones by using the BAT.
- Enable auto-registration in UCM.
- Provision the IP phones manually in UCM.
Explanation:
Cisco recommends that you enable auto-registration in Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) to add fewer than 100 new IP phones to a UCM network. There are three ways to add IP phones to a UCM database: by configuring auto-registration, by using the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT), and by manually provisioning the IP phones in the UCM administrative graphical user interface (GUI). Both auto-registration and the BAT provide a means of adding many phones to the database simultaneously. However, Cisco does not recommend using the BAT if you need to add fewer than 100 IP phones.Auto-registration enables UCM to automatically add new IP phones to the UCM database as the IP phones are connected to the network. When a new IP phone is connected to the network, UCM will automatically assign an unused directory number (dn) to the IP phone from a pool of available dn numbers.
Auto-registration is a security risk because rogue devices can be connected to the network and registered with UCM by using auto-registration. In addition, you could accidentally register a valid IP phone with a dn from the wrong dn pool if you leave auto-registration enabled after you have completed an auto-registration process. Therefore, Cisco recommends that you enable auto-registration only for short periods of time, such as when you need to add fewer than 100 IP phones to the network. In this scenario, you want to add 50 new IP phones to your company’s UCM network before the end of the workday. Because of the time limitation and the small number of IP phones, enabling auto-registration would require the least amount of administrative effort.
You do not need to provision the IP phones manually in UCM. Although you can manually add an IP phone to a UCM database, adding 50 new IP phones by using manual provisioning would require more administrative effort than by using auto-registration or the BAT. When you are manually provisioning an IP phone in UCM, you must fill in the MAC Address field, the Device Pool field, the Phone Button Template field, and the Device Security Profile field. In this scenario, you want to add 50 new IP phones to your company’s UCM network before the end of the workday. Because of the time limitation and the number of IP phones, enabling auto-registration would require the least amount of administrative effort. Therefore, you should not manually provision the IP phones. You do not need to add a second UCM server to the cluster. UCM supports a maximum of 7,500 devices as a standalone server and a maximum of 30,000 IP phones per UCM cluster. In this scenario, you administer a network of 500 IP phones. In addition, you are adding only 50 new IP phones, which brings the total number of IP phones to 550.
You do not need to add the phones by using the BAT. The BAT enables a UCM administrator to add or modify multiple IP phones at once. However, Cisco recommends that you use the BAT to add 100 or more new IP phones to a UCM network. In this scenario, using the BAT would require more administrative effort than using auto-registration because the BAT requires you to provide Media Access Control (MAC) addresses for the IP phones that are being added. Auto-registration does not require you to provide MAC addresses.
-
You are upgrading the firmware on all Cisco IP Phone 7961s that are connected to your company’s network.
Which of the following upgrade methods is most likely to require high bandwidth?
- individual IP phone upgrades
- load server download
- peer firmware sharing
- traditional TFTP server download
Explanation:
Of the available choices, the traditional Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server download method of IP phone firmware upgrade is most likely to require high bandwidth. When using the traditional TFTP server download method, each IP phone independently downloads the new image from the TFTP server in an “every man for himself” style strategy. When firmware images were small, this strategy was acceptable even when the IP phones were on a network at a separate location from Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM). Over time, IP phone firmware sizes have increased, which could cause slow upgrades over WAN links. In addition, the traditional TFTP download method could create high CPU usage on the UCM TFTP server.You can also update the firmware on an individual IP phone by using the traditional TFTP method. First, you should make a note of the existing Phone Load Name value for the phone model that you want to upgrade by navigating to Device > Device Settings > Device Defaults in UCM Administrator. This is important because installing the new firmware image will automatically overwrite the value of the Phone Load Name field in Device > Device Settings > Device Defaults. You should then upload the new firmware to UCM by navigating to Software Upgrades > Install/Upgrade.
After you upload the new firmware, specify the name of the new firmware in the Phone Load Name field for the specific IP phone you want to upgrade by using UCM Administration’s Device > Phone menu. Next, navigate to Device > Device Settings > Device Defaults and replace the new value of the Phone Load Name field with its original value. This will prevent other IP phones from downloading the new firmware after you restart the TFTP service.
Finally, you should restart the TFTP service in Cisco Unified Serviceability. After the service restarts, the IP phone you edited in UCM Administration should download the new firmware, upgrade the firmware, and restart. Other IP phones might restart as well. However, those IP phones will not be upgraded.
In contrast to the traditional TFTP server method, the load server download method enables the administrator of the LAN on which the IP phone operates to provide his or her own local TFTP server for firmware upgrades instead of relying on a remotely located default UCM TFTP server. This means that IP phones on remote networks will be able to download firmware updates in approximately the same amount of time it would take for an IP phone that is local to UCM. In addition, the TFTP load can be balanced among multiple TFTP servers at multiple sites. One disadvantage to the load server download method is that the local administrator is responsible for copying the firmware update to the TFTP server. Therefore, the TFTP upload and server configuration is subject to human error.
Peer firmware sharing is a method of updating the firmware on Cisco IP phones. When peer firmware sharing is implemented, only one Cisco IP phone at a location is responsible for downloading the new firmware. The firmware is then distributed to the other IP phones on the LAN in a parent-child hierarchy. The downloading phone distributes the firmware to its children. Those children then distribute the firmware to their children, and so on. No one parent in the hierarchy can have more than two children. Some disadvantages to the peer firmware sharing method are that the hierarchies are limited to their own subnets and are specific to phone model. In addition, peer firmware sharing must be enabled on each IP phone.
-
Which of the following are not Cisco Unity Connection features that you can modify in the Phone section of a user template? (Choose two.)
- the CoS
- the partition
- the search scope
- the voice mail password
- the web application password
Explanation:
You cannot modify the voice mail password in the Phone section of a Cisco Unity Connection user template. In addition, you cannot modify the web application password in the Phone section of a Cisco Unity Connection template. Unity Connection user templates enable administrators to apply a range of settings to new users automatically. Template, where you specify the template to apply to a given user, is one of four required fields when creating new Cisco Unity Connection users. The other required fields are Alias, User type, and Extension.Cisco Unity Connection users have two passwords: the voice mail system password that is issued by using the telephone user interface (TUI) and the web application password that is issued by using Cisco Unity Connection’s web-based graphical user interface (GUI). The voice mail password is a personal identification number (PIN) that enables a user to access his or her voice mailbox in Cisco Unity Connection. The web application password is an alphanumeric password that enables a user to access and modify specific Cisco Unified Communications settings by using a browser.
To access the Voice Mail Password Settings section of a user template, you should click Templates > User Templates in Cisco Unity Connection, then select Voice Mail from the Choose Password dropdown menu. To access the Web Application Password Settings section of a user template, you should click Templates > User Templates in Cisco Unity Connection, then select Web Application from the Choose Password drop-down menu.
You can modify Class of Service (CoS) features in the Phone section of a Cisco Unity Connection user template. CoS settings enable an administrator to apply a specific set of privileges to Cisco Unity Connection users. In addition, you can modify partition features and search space features in the Phone section of a Cisco Unity Connection user template. A partition is a logical grouping of Voice over IP (VoIP) route patterns and directory numbers (dns). A search space is an ordered list of partitions that a device is allowed to search for patterns that match a dialed number.
-
Which of the following dial peer commands will not match dial strings 3331, 3332, and 3333?
- destination-pattern .T
- destination-pattern 33T
- destination-pattern ….
- destination-pattern 333.
- destination-pattern 333(123)
- destination-pattern 3+[123]
- destination-pattern 333[^49]
Explanation:
The dial peer command destination-pattern 333(123) will not match dial strings 3331, 3332, and 3333. The destination-pattern command is used to match both inbound and outbound dial peers; a dial peer defines a logical route to a telephony endpoint. The sequence of dialed digits that will be matched for a dial peer can contain the digits 0 through 9, the asterisk (*), and the pound sign (#). In addition, you can use the following symbols to refine the dialing pattern or to match multiple dial strings for a single dial peer:
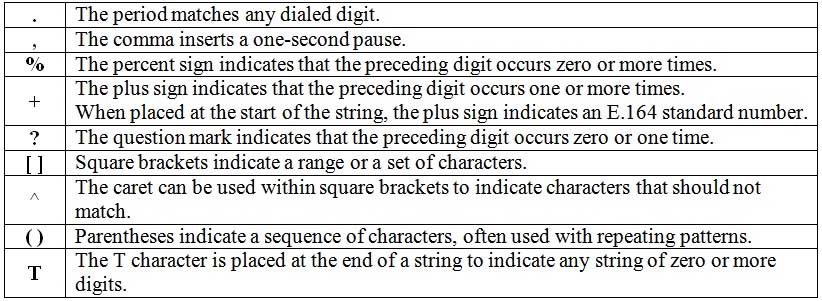
300-835 Part 05 Q12 017 Parentheses are used to indicate a specific sequence of characters. Therefore, the dial peer command destination-pattern 333(123) will match only the dial string 333123. Parentheses are often used with the %, +, and ? characters to indicate a repeating pattern. For example, the destination-pattern 333(123)% command matches 333, 333123, 333123123, 333123123123, and so on.
The following dial peer commands will match dial strings 3331, 3332, and 3333:
-destination-pattern .T
-destination-pattern 33T
-destination-pattern ….
-destination-pattern 333.
-destination-pattern 3+[123]
-destination-pattern 333[^49]The dial peer command destination-pattern .T is used to indicate any string of up to 32 digits. The T character is used at the end of a string to instruct the router to wait for the complete dial string to be entered before matching a call to a dial peer. Cisco recommends that you use the destination-pattern .T command rather than the destination-pattern T command because the destination-pattern .T command requires that the caller dial a digit. By default, a dial peer with the destination-pattern T command will be matched if an outbound caller takes the phone off-hook for 10 seconds.
The dial peer command destination-pattern 33T matches any dial string of up to 32 digits that begins with 33. Not only will the dial peer command destination-pattern 33T match 3331, 3332, and 3333, it will also match 334567 and 3331234, among others. However, if a dial string matches multiple dial peers, the longest explicit match is chosen. For example, if one dial peer contains the destination-pattern 333T command and another dial peer contains the destination-pattern 3334T command, a call from a caller dialing 3334000 would match the second dial peer.
The dial peer command destination-pattern …. matches any four-digit dial string. The period is used as a wildcard character that matches any digit. Therefore, the destination-pattern …. command matches dial strings 3331, 3332, 3333, 0000, 1257, and 6538, among many others.
The dial peer command destination-pattern 333. matches any four-digit dial string that begins with 333. Not only will the destination-pattern 333. command match 3331, 3332, and 3333, it will also match 3330, 3334, 3335, 3336, and so on.
The dial peer command destination-pattern 3+[123] matches any dial string that contains one or more 3s and ends with a 1, 2, or 3. The plus sign indicates that the preceding digit can occur one or more times. The square brackets are used to indicate that the pattern should match any of the bracketed digits for that digit position. Therefore, not only does the destination-pattern 3+[123] command match the dial strings 3331, 3332, and 3333, it also matches the dial strings 31, 32, 33, 331, 332, 333, 333331, 3333332, and 33333333333, among many others.
The dial peer command destination-pattern 333[^49] matches any dial string that starts with 333 and ends with a digit that is not 4 through 9. The caret symbol (^) can be used within square brackets to indicate characters that should not match. The dash can be used between two digits within brackets to indicate a range of characters. Therefore, the destination-pattern 333[^49] command matches the dial strings 3330, 3331, 3332, 3333, and 333*, but the command does not match the dial strings 3334, 3335, 3336, 3337, 3338, and 3339.
-
Which of the following protocols does Cisco Unified Personal Communicator use to connect to UCM in softphone mode?
- CCMCIP
- HTTPS
- IMAP
- IMAP over SSL
- IMAP over TLS
- SIP
- XMPP
Explanation:
Cisco Unified Personal Communicator uses Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) to connect to Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) in softphone mode. SIP is a call signaling protocol that is used by UCM to communicate with collaboration endpoints, such as Unified Personal Communicator and Cisco Jabber. Unified Personal Communicator is software that enables a user to connect to several different communication services from a single application. For example, you can use Unified Personal Communicator to place phone calls, download voice mails, and instant message (IM) another user.SIP is an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)standard call signaling protocol. Although SIP is typically used as a peer-to-peer call signaling protocol, it can also operate in client/server mode. A softphone is software that behaves like a phone, enabling a user to have voice conversations over a typical workstation network connection. Softphone mode is an operational mode that Unified Personal Communicator uses to act as a softphone.
Unified Personal Communicator does not use Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) to connect to UCM in softphone mode. XMPP is an open Extensible Markup Language (XML) IM and presence protocol. Unified Personal Communicator uses XMPP to establish IM sessions with Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS). CUPS is server software that centralizes network traffic from several different communications services so that it can all be transmitted over the same Cisco Voice over IP (VoIP) network. CUPS also uses XMPP to communicate with IM clients? it uses SIP and SIP for Instant Messaging and Presence Leveraging Extensions (SIMPLE) to integrate with third-party clients and applications.
Cisco Jabber, which also uses SIP and XMPP, is an application that is intended to integrate CUPS server services, such as user availability, with Microsoft Office. Cisco Jabber is also an IM client, a voice and video call client, and a desktop sharing client.
Unified Personal Communicator does not use Cisco Unified Communications Manager IP Phone (CCMCIP) service to connect to UCM in softphone mode. CCMCIP is used in desk phone mode. The difference between softphone mode and desk phone mode is that Unified Personal Communicator uses a physical IP phone as a proxy for voice conversations in desk phone mode. In softphone mode, Unified Personal Communicator handles the voice conversations itself.
Unified Personal Communicator does not use Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTPS) to connect to UCM in softphone mode. Unified Personal Communicator uses HTTPS to establish encrypted connections to a conferencing server. In addition, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) can be used to connect to a conferencing server without encryption.
Unified Personal Communicator does not use Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP), IMAP over Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), or IMAP over Transport Layer Security (TLS) to connect to UCM in softphone mode. Unified Personal Communicator uses IMAP to communicate with a voice mail server. IMAP over SSL is used to encrypt communications between Unified Personal Communicator and the voice mail server. IMAP over TLS is used to encrypt voice mail transmissions specifically between Unified Personal Communicator and Cisco Unity Connection.
-
With which of the following control components do UCM media resources interact when UCM needs to locate resources to establish a conference call?
- call control
- media control
- MTP control
- MOH control
Explanation:
Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) media resources interact with UCM’s call control component when UCM needs to locate resources to establish a conference call. The UCM Media Resource Manager is responsible for connecting the media streams that comprise conferencing features, among others. When troubleshooting media resource problems, such as conference call failures, it is important to first investigate the UCM media resources configuration. UCM media resources are available directly from the UCM server on which the services are enabled. In addition, the UCM Media Resource Manager enables UCM to provide those services to other UCM servers in a cluster.UCM media resources do not interact with UCM’s media control component when UCM needs to locate resources to establish a conference call. UCM media resources interact with UCM’s media control component in order to locate resources to establish a media termination point (MTP) or to transcode compression types. The UCM media control component is responsible for managing the creation and teardown of media streams for a given endpoint.
UCM media resources do not interact with UCM’s MTP control component when UCM needs to locate resources to establish a conference call. UCM media resources interact with UCM’s MTP control component in order to reserve transcoders within a UCM cluster.
UCM media resources do not interact with UCM’s music on hold (MOH) control component when UCM needs to locate resources to establish a conference call. UCM media resources interact with UCM’s call control component in order to locate resources to establish an MOH session. Because the MOH control enables UCM to redirect a caller to an audio server, UCM media resources also interface with the MOH control when establishing such a session.
-
You want to manually create a new user with a voice mailbox in Cisco Unity Connection Administration. The user already exists in UCM.
Which of the following fields are mandatory when you complete the VoiceMailUserTemplate? (Choose two.)
- Alias
- Display Name
- Extension
- Alternate Extension
- Employee ID
Explanation:
The Alias field and the Extension field are mandatory fields in the VoiceMailUserTemplate when you manually create a new user with a voice mailbox in Cisco Unity Connection Administration. Cisco Unity Connection can integrate with various phone systems, including Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM). The Alias field holds the key that the Unity Connection database uses to identify a user; therefore, the Alias value must always be unique. The Extension field is used to link a UCM user to a Unity Connection mailbox; therefore, it is important that the Unity Connection user have an extension that matches the extension defined for the corresponding user in UCM. If the extension does not match, some of the Unity Connection integration features will not work correctly. For example, if you changed the extension for a user in UCM and did not make the corresponding change for the user in Unity Connection, the user could receive new voice mail in his or her mailbox but might not receive new voice message notifications on his or her IP phone.The Alternate Extension field is not mandatory in the VoiceMailUserTemplate when you manually create a new user with a voice mailbox in Cisco Unity Connection Administration, because the Alternate Extension field is not available in the VoiceMailUserTemplate. The Alternate Extension field is typically used in Cisco Unity Connection Administration to enable a single voice mailbox to serve more than one directory number (dn). For example, up to nine administrator-configured alternate extensions, or lines, can be assigned to a single voice mailbox. These alternate extensions can be individual dns from the voice virtual LAN (VLAN) or the numbers of external devices. As a result, it is possible to enable a user to conveniently access Unity Connection from a mobile phone or from another IP phone. Similarly, an Alternate Extension can be used to access a single voice mailbox from multiple line appearances on a single IP phone. However, you can only add alternate extensions by editing a single user’s account or by editing users in Bulk Edit mode.
Neither the DisplayName field nor the Employee ID field is mandatory in the VoiceMailUserTemplate when you manually create a new user with a voice mailbox in Cisco Unity Connection Administration.
-
Which of the following is a function of the BAT?
- using a CSV file to update users
- generating Cisco Unity Connection reports
- synchronizing with LDAP
- using an XML-based service to import new users
Explanation:
Using a comma-separated values (CSV) file to update users is a function of the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT). The BAT enables administrators to import, or onboard, users and modify user settings by importing CSV files. For example, to use the BAT to modify the voice mail message length limit in Cisco Unity Connection, you could export the voice mail users to a CSV file, change the message length limit value for each user in the CSV file, and then import the CSV file again. You can access the BAT by clicking Tools > Bulk Administration Tool in the Unity Connection graphical user interface (GUI).Generating Cisco Unity Connection reports is a function of the Connection Reports Data Harvester service, not the BAT. Cisco Unity Connection reports can be accessed in Cisco Unified Serviceability, which enables an administrator to view reports and manage Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) features. Cisco Unified Serviceability is a browser-based troubleshooting tool that uses Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTPS) to access information that is provided by other reporting tools, such as Cisco Unified Real-Time Monitoring Tool (RTMT) and Call Detail Records (CDR) Analysis and Reporting (CAR) tool. The Connection Reports Data Harvester service allows data to be collected from log files and entered into the Cisco Unified Serviceability Reports Archive, which holds information from which reports can be generated. You can verify that the Connection Reports Data Harvester service is running by clicking Navigation > Cisco Unified Serviceability from within the UCM GUI and then clicking Service Management from the Tools menu. The Connection Reports Data Harvester service can be found under Optional Services. If the service is deactivated, you can click Activate to turn it on.
Using an Extensible Markup Language (XML)based service to import new users is a function of the ability to import from UCM into Unity Connection, not a function of the BAT. The Cisco Administrative XML Layer (AXL) Web Service is used to import UCM users into Unity Connection. The service must be enabled on both UCM and Unity Connection in order to import users. In addition, UCM users must be assigned a primary extension in UCM in order to be imported into Unity Connection by AXL.
Synchronizing existing Unity Connection users with Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory services, such as Microsoft Active Directory, is a function of the Cisco Directory Synchronization (DirSync) service, not the BAT. To enable Unity Connection to synchronize with an LDAP directory, you must select the Cisco DirSync check box in the Directory Services area of the Unity Connection GUI. In addition, you can import new users from LDAP either by using the BAT to import a CSV file or by using the Users > Import Users tool to import into Unity Connection LDAP information that was previously imported into UCM. Because Unity Connection stores users locally, a user that is synchronized with Unity Connection from LDAP will continue to be stored locally even if that user is later deleted from the LDAP database.
-
You are troubleshooting voice audio problems on your company’s VoIP network. The network carries both data and VoIP traffic. You have obtained the following measurements:
-Jitter: 50 ms
-Packet loss: 1 percent
-End-to-end delay: 150 msWhich of the following best describes why your company’s network is experiencing voice audio problems?
- The jitter is too high.
- The packet loss is too high.
- The end-to-end delay is too high.
- VoIP traffic should not be carried on the same network as data traffic.
Explanation:
Your company’s network is most likely experiencing voice audio problems because the jitter is too high. Short delays and low packet loss on a Voice over IP (VoIP) network help protect the rate at which bits flow over the network. Cisco recommends a maximum jitter of 30 ms for VoIP traffic. Jitter is a variation in delay, which can cause voice traffic to arrive at different times, thereby causing breaks, or choppiness, in the audio stream. Jitter can be mitigated by implementing Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms. The effects of VoIP issues like jitter and latency on a network can be analyzed by using data analysis techniques such as Mean Opinion Score (MOS) or R-Factor.It is not likely that the reason your company’s network is experiencing voice audio problems is because packet loss is too high. Cisco recommends a maximum packet loss of 1 percent for VoIP traffic. Packet loss is often caused when networks become congested and packets are dropped. Dropped packets can cause clips, or breaks, in the audio stream. However, voice traffic is more tolerant of dropped packets than of delayed packets because a small amount of packet loss is not noticeable to the human ear. Some codecs can correct small amounts of packet loss. On networks with limited bandwidth, a low-bitrate codec can mitigate packet loss. However, the overall quality of the audio will be reduced. Packet loss can also be mitigated by implementing QoS mechanisms.
It is not likely that the reason your company’s network is experiencing voice audio problems is because end-to-end delay is too high. Cisco recommends a maximum end-to-end delay of 200 ms. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) considers an end-to-end delay of 150 ms or less to be acceptable for high voice quality. Delay, which is also called latency, can introduce interruptions in conversation flow, causing the speakers at each end of the circuit to interrupt each other. End-to-end delay can be mitigated by implementing QoS mechanisms.
It is not likely that the reason your company’s network is experiencing voice audio problems is because VoIP traffic is carried on the same network as data traffic. VoIP traffic can be carried on the same network as data traffic. However, data traffic is usually more tolerant of dropped packets and delay than VoIP traffic. Therefore, VoIP traffic is typically given priority over data traffic.
-
You want an IP phone to use a line prompt instead of an MWI lamp to display information about a new message.
Which of the following line appearance fields should you modify in UCM?
- Display
- External Phone Number Mask
- Line Text Label
- Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy
Explanation:
You should modify the Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) administrative graphical user interface (GUI). The Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field configures the behavior of the message waiting indicator (MWI) lamp and of the MWI line prompt on an IP phone. For example, configuring the Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field to Light and Prompt will configure the IP phone to turn on the MWI lamp that is located on the IP phone’s handset when a new voice mail message arrives. In addition, the IP phone will display a new message prompt beside the associated line button on the IP phone. However, configuring the Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field to Prompt Only will display the new message prompt beside the line button but will not turn on the MWI lamp. You can configure the Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field differently for each line that is associated with the IP phone. For example, if the IP phone is configured with a shared line in addition to a primary line, you could configure the Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field for the shared line to None so that the IP phone never displays MWI information for the shared line.You should not modify the Line Text Label line appearance field. The contents of the Line Text Label field are displayed beside the associated line button of an IP phone. The field is typically configured with the name of the user that is associated with the line. If the Line Text Label field is not configured, the directory number (dn) that is associated with the line will be displayed instead. For example, if user John Public has been assigned extension 4000, the dn 4000 will be displayed beside the associated line button on the main screen of John Public’s IP phone unless you configure the Line Text Label field. If you configure the Line Text Label field with the name John Public, then that name will appear beside the line button on the main screen of the IP phone.
You should not modify the Display (Internal Caller ID) field. When the Display (Internal Caller ID) field is blank, the dn that is associated with the calling device is shown on the display of the called device. Otherwise, the contents of the Display (Internal Caller ID) field are shown on the display of the called device. You can configure the Display (Internal Caller ID) field with a name or a description of up to 30 characters in length. If you configure the Display (Internal Caller ID) field, you should also configure the ASCII Display (Internal Caller ID) field with similar information. The contents of the ASCII Display (Internal Caller ID) field are displayed on called devices that do not support Unicode character sets. You cannot use nonASCII characters in the ASCII Display (Internal Caller ID) field.
You should not modify the External Phone Number Mask field. UCM transmits the contents of the External Phone Number Mask field as caller ID information when an internal user places an outgoing call to an external party. The information in the External Phone Number Mask field can be a string that consists of up to 24 numbers, the international escape character +, and X wildcards that represent the extension number. The X wildcards should always be at the end of the string. For example, a user that has been assigned extension number 4000 on the internal Voice over IP (VoIP) network might also be assigned a direct inward dial (DID) number of (555) 5554000. Therefore, you could configure the External Phone Number Maskfield with the string 555555XXXX. The number 5555554000 would then be displayed on the caller ID systems of any external parties who are called by the user at extension 4000. If the user at extension 4000 was not assigned a DID number, you could configure the External Phone Number Mask field with your company’s main public switched telephone network (PSTN) number instead.
-
Three UCM users are connected on a conference call by using Cisco IP phones. The switch port to which one of the users is connected fails.
Which of the following will occur?
- The other two users will remain on the call.
- The other two users will also be disconnected.
- All three users will remain active on the call.
- The disconnected user will be processed by another server in the cluster.
Explanation:
The other two users will remain on the call if the switch port to which one of the users is connected fails because Cisco IP phones are supported by the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) call preservation feature. The call preservation feature enables some Voice over IP (VoIP) devices to continue active sessions even if UCM fails or communication between UCM and the device is interrupted.When a UCM server fails, other UCM servers and supported devices in a cluster can detect the failure. UCM is then able to ensure that active calls remain active until either the users hang up or media stops streaming between the devices. Similarly, if UCM does not fail but loses connectivity to a device that is involved in an active call, both UCM servers and connected devices will detect the failure. The active call will remain active until the users end the call or media stops streaming between the devices.
When a supported device other than UCM fails, that device will no longer stream media. Thus the device is no longer able to participate in its active call. However, UCM will detect this failure and any other devices that might have been active on the same call will remain connected and active.
-
With which of the following can users manage IP phone settings? (Choose two.)
- a CME router console session
- the CME browser-based GUI
- Telnet
- the telephone keypad
Explanation:
Users can manage IP phone settings either by using the telephone keypad or by logging on to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) browser-based graphical user interface (GUI). In order for a phone user to log on to the GUI, a systems administrator must create a phone user account for that user and associate that account with a device. The phone user can then access the GUI by using the Uniform Resource Locator (URL) http://ipaddress/ccme.html, where ip-address is the IP address of the CME router. To create a phone user account in the CME GUI, you should click Configure > Phones in the GUI.You can also create phone user accounts by using the command-line interface (CLI) on the CME router. To create a phone user by using the CLI, issue the username user-name password password command in ephone configuration mode, where username is the user name you want to assign to the user and password is the password that you want to assign to the user. You should issue the username user-name password password command only in ephone configuration mode of the device that you want to assign to the user you are creating. For example, if you want user John to be able to manage the device settings of ephone 5 by using the CME GUI, you should issue the following commands on the CME router:
ephone 5
username john password b0s0nThe ephone 5 command places the router into ephone configuration mode for ephone 5. The username john password b0s0n command creates a new user name of john for ephone 5 and assigns that user name the password b0s0n.
A phone user cannot typically manage phone settings by using a CME router console session or Telnet. Although you could provide users with access to the CME CLI via either a console session or a Telnet session, users do not need access to the CLI to manage end-user phone settings. In addition, providing phone users with administrative access to the CLI is a security risk.