300-835 : Automating Cisco Collaboration Solutions (CLAUTO) : Part 07
-
You are deploying CUPS in order to enable your company’s users to collaborate with each other.
Which of the following are you most likely to deploy as part of your CUPS installation? (Choose two.)
- Cisco UCCX
- Cisco UCCE
- Cisco Quality Management
- Cisco WebEx
- Cisco Jabber
Explanation:
Most likely, you would deploy Cisco WebEx and Cisco Jabber as part of your Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) installation. Cisco WebEx allows web conferencing in real time and can be deployed as an on-premises CUPS component or in the cloud. Cisco Jabber is an application that enables users to instant message (IM) or place audio or video calls without the use of a desk phone. CUPS integrates with an on-premises deployment of Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM).You would not deploy Cisco Unified Contact Center Express (UCCX) or Cisco Unified Contact Center Enterprise (UCCE) as part of your CUPS installation. Each of these products is used to build business-to-customer contact centers. In addition, you would not deploy Cisco Quality Management as part of your CUPS installation. Cisco Quality Management is a set of applications that integrate with Cisco UCCX.
-
Which of the following statements is true?
- The auto-reg-ephone command can automatically create an ephone.
- The auto assign command can automatically create an ephone.
- The auto-reg-ephone command can automatically create an ephone-dn.
- The auto assign command can automatically create an ephone-dn.
Explanation:
The auto-reg-ephone command can automatically create an ephone. When an IP phone registers with a router that is configured with the auto-reg-ephone command, the router will associate the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the IP phone with the first unassigned ephone on the router. If all the ephones on the router are associated with IP phones, the router will create a new ephone, provided that the number of configured ephones does not exceed the value of the max-ephones command. The max-ephones command specifies the maximum number of ephones that you can configure on a router.You can also manually assign an IP phone to an ephone by issuing the mac-address mac-address command in ephone configuration mode, where mac-address is the MAC address of the IP phone you want to assign to the ephone. For example, you can issue the following command set to associate an IP phone with the MAC address 0019:8765:4321 with ephone number 1:
telephony-service
ephone 1
mac-address 0019.8765.4321The auto-reg-ephone command cannot automatically create an ephone-dn. An ephone-dn must be configured before it can be assigned to buttons on ephones.
The auto assign command cannot automatically create an ephone or an ephone-dn. The auto assign command automatically associates button 1 on an ephone with an existing, unused ephone-dn. The ephone-dn is not automatically created? it must already exist. If no ephone-dn is available, the phone will register but none of the phone’s buttons will be associated with ephone-dn extensions.
-
A user presses the messages button on a Cisco IP Phone 7961.
Which of the following will most likely happen?
- The user will receive a prompt from the voice mail system.
- The user will receive directory updates from the administrator.
- The user will receive application notifications from the administrator.
- The user will receive network notifications from the administrator.
- The user will receive system help notifications.
Explanation:
Most likely, the user will receive a prompt from the voice mail system if the user presses the messages button on a Cisco IP Phone 7961. The Cisco IP Phone 7961 series includes a bank of buttons with iconography designed to represent the button’s functions. For example, the messages button is represented by the back of a standard paper envelope. A typical bank of buttons for a Cisco IP Phone 7961 series appears in the following exhibit:

300-835 Part 07 Q03 020 The user will not receive application notifications from the administrator by pressing the messages button. However, a user can launch Cisco Unified Communications IP phone applications by pressing the services button. The services button, which is represented by a globe icon, is used to launch IP phone applications. The applications that are available from the services button are dependent on the Cisco Unified Communications deployment and user privilege levels.
The user will not receive network notifications from the administrator by pressing the messages button. However, the settings button can enable a user to display information about the network to which the IP phone is connected or to configure some network and device settings. The settings button is represented by a selected check box and can be used to view or modify settings specific to the user or IP phone.
The user will not receive directory updates by pressing the messages button. However, a user can display directory information by pressing the directories button. The directories button, which is represented by an open book icon, is used to display lists of missed calls, received calls, placed calls, or local directory contacts. If configured, the directories button can also be used to access a custom Personal Speed Dial directory.
The user will not receive system help by pressing the messages button. However, the help button, which is represented by a question mark (?), is used to provide the end user with information about the specific features of the IP phone. A user can press the help button twice while on a call on an IP phone to view statistical information about the call, such as the codec that is being used by the IP phone, the codec that is being used by the calling phone, and packet error information.
-
Which of the following VLANs can you configure on an FXO port?
- no VLANs
- data VLANs
- native VLANs
- voice VLANs
Explanation:
There are no virtual LANs (VLANs) that you can configure on a foreign exchange office (FXO) port. FXO ports connect a voice gateway to the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or to a private branch exchange (PBX). A voice gateway is a router that is responsible for call processing and routing between the PSTN and a Voice over IP (VoIP) network, including the translation of analog voice signals to digital packets and vice versa.You can configure voice VLANs only on Layer 2 access ports on a Cisco switch. Creating voice VLANs on a switch enables the separation of voice traffic from data traffic on a network. To enable the voice VLAN feature on a Cisco switch, you should issue the switchport voice vlan {vlan-id | dot1p | none | untagged} command in interface configuration mode. The dot1p keyword configures voice traffic to be sent with a default 802.1p priority of 5 and to use VLAN 0 as the VLAN ID.
The switchport voice vlan vlan-id command configures voice traffic to be tagged and sent over a user – specified voice VLAN. Voice traffic will be carried in 802.1Q frames and will be carried on a different VLAN than data traffic. For example, if you issue the switchport voice vlan 2 command, voice traffic will be tagged with 802.1Q information and sent over VLAN 2.
Similar to the switchport voice vlan untagged command, the switchport voice vlan none command configures voice traffic to be untagged and sent over the same VLAN as data traffic, which is the native VLAN. When the none keyword is used, voice traffic does not use 802.1p priority tagging or Class of Service (CoS), and voice traffic is transmitted with data traffic.
The switchport voice vlan untagged command configures voice traffic to be untagged and sent over the native VLAN. However, if data and voice devices are configured to operate on the same VLAN, the voice traffic can experience quality problems, such as jitter or choppiness. Untagged traffic is sent without 802.1Q encapsulation. When the switchport voice vlan untagged command is issued, both voice traffic and data traffic are transmitted over the native VLAN. You do not need to specify a voice VLAN when the switchport voice vlan untagged command is used.
You can configure data VLANs and native VLANs on both trunk ports and access ports on a Cisco switch. To configure a data VLAN or the native VLAN on an access port, you should issue the switchport access vlan vlan-id command, where vlan-id is the ID of the data VLAN or the native VLAN you want to configure. To configure a trunk port with the native VLAN, you should issue the switchport trunk native vlan vlan-id command, where vlan-id is the ID of the native VLAN. In addition, trunk ports are by default configured to allow traffic from all data VLANs that are configured on the switch. You can issue the switchport trunk allowed vlan remove vlan-id list command to specifically remove a list of data VLANs from a trunk port. You can add a specific VLAN to a trunk port by issuing the switchport trunk allowed vlan add vlan-id list command, where vlan-id list is a list of the VLAN IDs you want to add.
-
Which of the following is not a method you can use to update the settings of existing users in Cisco Unity Connection?
- the BAT
- Bulk Edit mode
- editing user templates
- LDAP import
Explanation:
Editing user templates is not a method that you can use to update the settings of existing users in Cisco Unity Connection. If you edit an existing user template, only new user accounts that are created by using that template will be affected by the changes that you make to the template. Any users who have already been created from the template will retain the old template settings.The Bulk Administration Tool (BAT) is a method you can use to update the settings of existing users in Cisco Unity Connection. The BAT enables administrators to import users, update user settings, and delete users by importing comma-separated values (CSV) files. The BAT is also capable of exporting users to CSV files. For example, to modify the voice mail message length limit by using the BAT, you could export the voice mail users to a CSV file, change the message length limit value for each user in the CSV file, and then import the CSV file again.
Bulk Edit mode is a method you can use to update the settings of existing users in Unity Connection. Bulk Edit mode enables an administrator to select a specific subset of Unity Connection users and make identical changes to every user in that subset at once. For example, you can use Bulk Edit mode to modify the message length limit for all existing users who have voice mail. To edit a subset of users in Bulk Edit mode, you should click Users > Users in Unity Connection’s graphical user interface (GUI) and then search for the subset of users you want to edit. When you have found the users you want to edit, select the check boxes beside those users and then click Bulk Edit. You can then modify the settings you want to change and apply the new settings by clicking the Submit button.
A Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) import is a method you can use to update the settings of existing users in Unity Connection. The Cisco Directory Synchronization (DirSync) service enables Unity Connection to synchronize with LDAP directory services, such as Microsoft Active Directory. You must select the Cisco DirSync check box in the Directory Services area of the Unity Connection GUI to enable Unity Connection to synchronize with an LDAP directory. Changes you make to the LDAP directory will be reflected in Unity Connection accounts upon resynchronization of those accounts with the LDAP directory.
-
Which of the following Unity Connection features uses an XML-based service to import new users?
- import by using the BAT
- import from UCM
- synchronize with LDAP
- manual user entry
Explanation:
The Unity Connection import from Unified Communications Manager (UCM) feature uses an Extensible Markup Language (XML)based service to import, or onboard, new users. The Cisco Administrative XML Layer (AXL) Web Service is used to import UCM users into Unity Connection. The service must be enabled on both UCM and Unity Connection in order to import users. In addition, UCM users must be assigned a primary extension in UCM in order to be imported into Unity Connection by AXL.You can enable the AXL Web Service in Unity Connection by clicking the Cisco AXL Web Service check box in Database and Admin Services in the Unity Connection administration graphical user interface (GUI). After you have enabled the service, you should configure the IP address, port number, user name, and password of the UCM AXL Web Service server in the AXL Servers area of the Unity Connection administration GUI. You can then click Users > Import Users to find user accounts on the UCM server and import them into Unity Connection.
The Bulk Administration Tool (BAT) does not use an XML-based service to import new users into Unity Connection. The BAT imports, updates, deletes, or exports users in Unity Connection in comma-separated values (CSV) format, not XML. You can access the BAT by clicking Tools > Bulk Administration Tool in the Unity Connection GUI.
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) does not use an XML-based service to import new users into Unity Connection. The Cisco Directory Synchronization (DirSync) service enables Unity Connection to synchronize existing Unity Connection users with LDAP directory services, such as Microsoft Active Directory. To enable Unity Connection to synchronize with an LDAP directory, you must select the Cisco DirSync check box in the Directory Services area of the Unity Connection GUI. In addition, you can import new users from LDAP by either using the BAT to import a CSV file or by using the Users > Import Users tool to import LDAP information that was previously imported into UCM to Unity Connection. Because Unity Connection stores users locally, a user that is synchronized with Unity Connection from LDAP will continue to be stored locally even if that user is later deleted from the LDAP database.
The Unity Connection manual user entry feature does not use an XML-based service to import new users. Instead, manual user entry enables an administrator to create new users one at a time. You can manually create a new user in Unity Connection by clicking Users > Users > Add New in the Unity Connection administration GUI.
-
Which of the following tasks can be performed by a digital signal processor?
- sampling, but not encoding and compression, of analog audio
- encoding, but not sampling and compression, of analog audio
- sampling and compression, but not encoding, of analog audio
- sampling, encoding, and compression of analog audio
Explanation:
Sampling, encoding, and compression of analog audio can be performed by a digital signal processor (DSP). DSPs execute the steps required to convert an analog voice signal to digital packets, which allow voice data to traverse a Voice over IP (VoIP) network. There are four steps involved in converting analog audio data to digital audio data: sampling, quantization, encoding, and compression.Sampling is the process of capturing an analog voice waveform at a rate of 8,000 times per second. Quantization is the process of assigning a voltage value to each audio sample. Encoding is the process of converting the quantized voltage data into a binary format. Compression is the process of replacing consecutive sets of repeating data with an equivalent mathematical expression that can be used to reconstruct the data pattern.
When analog audio is received by a DSP, the DSP samples and quantizes the analog audio data, encodes the data into binary format, and optionally, compresses it to conserve bandwidth. For example, Cisco Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) with DSP resources are used to process calls between Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) and the public switched telephone network (PSTN).
-
Which of the following is not information that is available by clicking Tools > System Reports > System Overview in Cisco Unified Serviceability? (Choose two.)
- top five users based on charge
- top five users based on volume
- top five calls based on duration
- top five users based on duration
- top five destinations based on charge
- top five calls based on volume
Explanation:
Neither information about the top five users based on volume nor information about the top five destinations based on volume is available by clicking Tools > System Reports > System Overview in Cisco Unified Serviceability. You can display information about call volume for a given period of time by using the System Reports > Traffic > Summary by Phone Number report in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Call Detail Records (CDR) Analysis and Reporting (CAR) graphical user interface (GUI). This report enables a CAR administrator to choose a range of time and IP phone extension numbers from which to view call volume information, thereby enabling an administrator to view what extensions were in use at a specific time.CAR administrators can choose which automatically or manually generated system reports will appear on the System Overview report by clicking Tools > CDR Analysis and Reporting > System Reports > System Overview in Cisco Unified Serviceability and then selecting the appropriate reports in the System Overview window.
The System Overview report contains all of the following sections:
-Top 5 Users based on Charge: lists the five users whose calls have cost the most over a given period of time
-Top 5 Destinations based on Charge: lists the five called numbers that have cost the most over a given period of time
-Top 5 Calls based on Charge: lists the five calls that have cost the most over a given period of time
-Top 5 Users based on Duration: lists the five users who have spent the most time on calls over a given period of time
-Top 5 Destinations based on Duration: lists the five called numbers on which users have spent the most time over a given period of time
-Top 5 Calls based on Duration: lists the five longest calls over a given period of time
-Traffic Summary Report – Hour of Day: displays the volume of calls for a given hour of the day
-Traffic Summary Report – Day of Week: displays the volume of calls for a given day of the week
-Traffic Summary Report – Day of Month: displays the volume of calls for a given day of the month
-Quality of Service Report – Summary: displays the number of calls that fell within Quality of Service (QoS) parameters over a given period of time
-Gateway Summary Report: displays the call classification, QoS, duration, and number of calls for each voice gateway over a given period of time -
Which of the following issues is most likely to prompt an administrator to verify a user’s primary and proxy SMTP addresses in Cisco Unity Connection? (Select the best answer.)
- Secure messages cannot be played in Outlook.
- Messages are sent to the wrong email account.
- The MWI lamp turns off before a message is read in Outlook.
- No Single Inbox features are working.
Explanation:
An administrator is most likely to verify that the user’s primary or proxy Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) address in Cisco Unity Connection matches the account to which the user wants voice mail messages relayed if messages are sent to the wrong email account. The Single Inbox feature of Cisco Unity Connection enables the synchronization of voice messages between Cisco Unity Connection and Microsoft Exchange Server mailboxes. For example, a voice mail left for a Cisco Unity Connection user can additionally be delivered to that user’s Microsoft Outlook Inbox.An administrator is not likely to verify a user’s primary and proxy SMTP addresses in Cisco Unity Connection if no Single Inbox features are working. However, an administrator might verify that the Cisco Unified Messaging Service is enabled and running in Cisco Unity Connection if no Single Inbox features are working for the group of users that is associated with that Cisco Unified Messaging Service instance. In order for Single Inbox features to be available, the Cisco Unified Messaging Service must be enabled and started.
An administrator is not likely to verify a user’s primary and proxy SMTP addresses in Cisco Unity Connection if the message waiting indicator (MWI) lamp turns off before a message is read in Microsoft Outlook. However, an administrator might verify that the Microsoft Outlook Mark Items as Read When Viewed in the Reading Pane check box is clear in the Outlook Options > Mail > Reading Pane dialog box. If this check box is selected, the MWI lamp will turn off when the user selects the message in Outlook’s reading pane and there are no more new messages in Unity Connection.
An administrator is not likely to verify a user’s primary and proxy SMTP addresses in Cisco Unity Connection if secure messages cannot be played in Outlook. However, an administrator might verify that Cisco Unity Connection ViewMail for Microsoft Outlook is installed on the user’s workstation if secure messages cannot be played in Outlook. When Unity Connection delivers a secure voice mail to Microsoft Exchange, only the introductory text of the email is sent to the user. The audio file containing the message remains on Unity Connection. Cisco Unity Connection ViewMail enables users to listen to the voice mail audio files.
-
Which of the following interfaces enables database synchronization between UCM and a CUPS server? (Select the best answer.)
- AXL/SOAP
- LDAP
- SIP
- XMPP
Explanation:
The Cisco Administrative Extensible Markup Language (AXL)/Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) interface enables database synchronization tasks from Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) to a Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) server database. UCM and CUPS together are the primary components of a Cisco Presence deployment. For synchronization to start, the Sync Agent service must be started on the CUPS server.The Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) interface does not enable database synchronization between UCM and a CUPS server. However, the XMPP interface is used to handle the exchange of availability information between UCM and XMPP clients, such as instant messaging (IM) clients that are developed by third parties.
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) interface does not enable database synchronization between UCM and a CUPS server. However, a SIP trunk interface does handle the exchange of availability information between UCM and a CUPS server. A UCM SIP trunk interface must point to the CUPS server in order for availability information to be exchanged between the two systems. CUPS is also capable of sending SIP subscribe messages to UCM over the SIP trunk if UCM is configured as a Presence gateway.
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) interface does not enable database synchronization between UCM and a CUPS server. However, the LDAP interface is used to synchronize user information between UCM and CUPS in order to create a single signon (SSO) user experience or to search for contacts. For example, a Cisco Unified Personal Communicator user can be authenticated to both the CUPS server and UCM by connecting directly to the CUPS server. LDAP listens on Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port 389 unencrypted or on port 636 over Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). Thirdparty XMPP clients can also use LDAP to search the database and add users as contacts.
-
You issue the following commands on a CME router:
Dial-peer voice 1 pots
Destination-pattern 9911
prefix 9
port 1/0/0Which of the following digits will be forwarded to the PSTN when a caller dials 9911? (Select the best answer.)
- 9
- 911
- 9911
- No digits will be forwarded.
Explanation:
The following command set will forward the digit 9 to the public switched telephone network (PSTN) when a caller dials 9911:Dial-peer voice 1 pots
Destination-pattern 9911
prefix 9
port 1/0/0The dialpeer voice command is used to define how calls are routed to destination endpoints on either the PSTN or a Voice over IP (VoIP) network. To define call routing for the PSTN, you should issue the dialpeer voice command with the pots keyword.
The destination pattern command is used to match both inbound and outbound dial peers. The sequence of dialed digits that will be matched for a dial peer can contain the digits 0 through 9, the asterisk (*), and the pound sign (#). In addition, you can use a period (.) as a wildcard symbol to refine the dialing pattern or to match multiple dial strings for a single dial peer. The command set in this scenario configures a dial peer on a Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) router to match the destination pattern 9911. By default, CME only forwards digits matched by wildcards in a destination pattern, not digits that are explicitly defined in the destination pattern. In the destination pattern 9911 command, all the destination pattern digits are explicitly defined. Therefore, CME will not forward any of the digits in the destination pattern when a user dials 9911.
The prefix command is used to add one or more digits to the front of the dial string before the dial string is forwarded to the destination network. Issuing the prefix 9 command in this scenario ensures that the digit 9 will be forwarded to the PSTN, even though CME will automatically strip every digit in the destination pattern. Therefore, only the digit 9 will be forwarded to the PSTN when a caller dials 9911.
If the intent of the configuration in this scenario is to forward the emergency service code 911 to the PSTN, the configuration is incomplete. To configure the dial peer to forward the 911 emergency service code to the PSTN without forwarding the internal access code 9, you could do one of the following:
A. Issue the prefix 911 command instead of the prefix 9 command.
B. Issue the forwarddigits 3 command instead of the prefix 9 command.The port command is used to configure a plain old telephone service (POTS) dial peer to send outgoing traffic destined for the PSTN through a specific port on a CME router. In addition, the port command is used to match incoming calls from the PSTN to POTS dial peers. In this scenario, the port 1/0/0 command configures CME to forward outgoing calls made to 9911 through port 1/0/0 to the PSTN.
The forwarddigits command configures a dial peer to forward the rightmost number of digits matched by the destination pattern, even if the digits are explicitly matched. The number of digits forwarded by CME depends on the value configured in the forwarddigits command. For example, if you were to issue the forwarddigits 4 command instead of the prefix 9 command in this scenario, CME would forward the digits 9911 to the PSTN when a caller dials 9911. If you were to issue the forwarddigits 4 command in addition to the prefix 9 command, CME would forward the digits 99911 to the PSTN when a caller dials 9911.
Issuing the forwarddigits implicit command or the no forwarddigits command configures a dial peer to its default behavior of stripping digits that are explicitly matched in the destination pattern. Issuing the forward-digits all command configures a dial peer to forward every digit that matches the destination pattern, even if the digits are explicitly matched.
-
Which of the following Cisco Unified Personal Communicator features require XMPP to communicate with CUPS? (Select 2 choices.)
- availability status
- contact searches
- instant messaging
- media streaming
- softphone mode signaling
- voice mail downloads
Explanation:
Availability status and instant messaging (IM) require Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) to communicate with Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS). XMPP is an open Extensible Markup Language (XML) IM and presence protocol. Cisco Unified Personal Communicator is software that enables a user to connect to several different communication services from a single application. CUPS is server software that integrates network traffic from several different communications services so that it can be transmitted over a Cisco Voice over IP (VoIP) network. CUPS also uses XMPP to communicate with thirdparty IM clients. In addition, CUPS uses Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and SIP for Instant Messaging and Presence Leveraging Extensions (SIMPLE) to integrate with thirdparty clients and applications. SIP is a call signaling protocol that is used by Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) to communicate with collaboration endpoints, such as Unified Personal Communicator and Jabber.Cisco Jabber, which also uses SIP and XMPP, is an application that is intended to integrate CUPS server services, such as user availability, with Microsoft Office. Cisco Jabber is also an IM client, a voice and video call client, and a desktop sharing client.
Unified Personal Communicator uses Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) or LDAP Secure (LDAPS), not XMPP, to perform contact searches on an LDAP directory. LDAP is a directory protocol that is used by other servers, such as CUPS to perform contact lookups. LDAP listens on Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port 389 unencrypted or on port 636 over Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) . In addition, Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM), Cisco Unity Connection, and CUPS can all synchronize user accounts and contacts from an LDAP directory, such as Microsoft Active Directory.
Unified Personal Communicator uses Realtime Transport Protocol (RTP), not XMPP, for media streaming. RTP is used to transport audio or video packets between devices on a VoIP network after a connection has been established. A twoway audio session, such as a telephone conversation, requires two RTP streams: one stream originating from each device. RTP sessions are established on evennumbered User Datagram Protocol (UDP) ports ranging from 16384 through 32767. Once an RTP stream is established on a UDP port, it remains on that port for the duration of the session.
Unified Personal Communicator uses SIP, not XMPP, for softphone mode signaling. SIP is an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)standard call signaling protocol. Although SIP is typically used as a peerto-peer call signaling protocol, it can also operate in client/server mode. A softphone is software that behaves like a phone, enabling a user to have voice conversations over a typical workstation network connection. Softphone mode is an operational mode that Unified Personal Communicator uses to act as a softphone.
Unified Personal Communicator uses Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP), IMAP over SSL, or IMAP over Transport Layer Security (TLS), not XMPP, for voice mail downloads. Unified Personal Communicator uses IMAP over TLS to specifically communicate with Cisco Unity Connection. For other voice mail servers, either IMAP or IMAP over SSL can be used.
-
You assign a UCM user to the Standard CAR Admin Users group in UCM. However, the user reports that CAR cannot be accessed from the Tools menu in Cisco Unified Serviceability.
Which of the following is most likely the cause of the problem? (Select the best answer.)
- The Cisco CAR Web Service is not running.
- The UCM system is generating CDR files too slowly.
- The user does not have the privileges to access CAR.
- The CDR Enabled flag is set to FALSE.
- The disk space where reports are stored is full.
Explanation:
Most likely, the Cisco CAR Web Service is not running if Cisco Call Detail Records (CDR) Analysis and Reporting (CAR) cannot be accessed from the Tools menu in Cisco Unified Serviceability. If the CAR Web Service is not running, CAR will not be available from the Tools menu. To activate the CAR Web Service, click Tools > Service Activation in Cisco Unified Serviceability, select the call processing server from the Servers dropdown menu, and then select the check boxes next to the appropriate CDR services.It is not likely that the CDR Enabled flag is the cause of the problem. The CDR Enabled flag determines whether a given Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) server will generate CDR reports. If the CDR Enabled flag is not set to TRUE on a UCM server, CAR reports will not be generated for that server. In a UCM cluster, the CDR Enabled flag should be set to TRUE on the Publisher server and on all Subscriber servers in the cluster. In addition, you should verify that the Call Diagnostics are enabled and that the Cisco CAR Scheduler service is running on the Publisher server.
It is not likely that the rate at which the UCM system is generating CDR files is the cause of the problem. By default, every UCM server can generate one CDR file and one Call Management Records (CMR) file every minute for up to one hour. However, the rate at which UCM generates CDR files has nothing to do with whether the service is available from the Tools menu in Cisco Unified Serviceability. In addition, it is not likely that the amount of available disk space where reports are stored is the cause of the problem. The oldest CDR files are deleted on an hourly basis by the CDR Repository Manager’s File Manager process if disk usage reaches a maximum threshold.
The user does have the privileges to access CAR. In this scenario, you have assigned the UCM user to the Standard CAR Admin Users group. By default, any UCM user can be configured as a CAR administrator by adding the user to the Standard CAR Admin Users group in UCM. This includes application users and end users. However, application users cannot access the Individual Bill report even though they might have read and write access to the CAR database.
-
Your company synchronizes Microsoft Active Directory enduser accounts with UCM.
Which of the following tasks cannot be performed by using the UCM administrative GUI? (Select 2 choices.)
- assigning users to groups
- assigning an IP phone to a user
- assigning roles to user groups
- changing user PINs
- creating end-user accounts
- deleting end-user accounts
Explanation:
Because your company synchronizes Microsoft Active Directory end-user accounts with Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM), you cannot create end-user accounts by using the UCM administrative graphical user interface (GUI). In addition, you cannot delete end-user accounts by using the UCM administrative GUI.When UCM is configured to synchronize with a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory, such as OpenLDAP or Microsoft Active Directory, the user ID and all user personal and organizational data that is stored in the LDAP directory, except for passwords, are replicated to the UCM database. It is important to note that the Cisco Directory Synchronization (DirSync) service must be activated before LDAP synchronization can take place.
When LDAP synchronization is configured, UCM configures the synchronized data as readonly data and acknowledges the LDAP directory as the central authority for creating and deleting user accounts. Therefore, UCM prevents administrators from using the UCM GUI to add and delete users. None of the data that was replicated to the UCM database can be modified by using the GUI. However, UCM user data that is not managed by the LDAP directory, such as the user’s password and personal identification number (PIN), can be modified in the UCM administrative GUI.
You can assign roles to user groups in the UCM administrative GUI, even if your company synchronizes Microsoft Active Directory enduser accounts with UCM. UCM roles are configured with privileges that are specific to UCM, such as the ability to log in to the administrative GUI and the ability to modify specific configuration settings. Therefore, an administrator must be able to assign UCM roles to user groups in the UCM administrative GUI so that the end users in those groups can perform tasks in the GUI. However, UCM synchronization with LDAP overrides any role’s privilege to add or delete UCM end users.
You can assign users to groups in the UCM administrative GUI, even if your company synchronizes Microsoft Active Directory enduser accounts with UCM. Because the user groups and user roles that control user privileges in UCM are unique to UCM, administrators must be able to assign those groups and roles to end users by using the UCM administrative GUI.
You can assign an IP phone to a user in the UCM administrative GUI, even if your company synchronizes Microsoft Active Directory enduser accounts with UCM. Because the enduser IP phone assignments are not stored in Active Directory, administrators must be able to assign those devices to end users by using the UCM administrative GUI.
You can change user PINs in the UCM administrative GUI, even if your company synchronizes Microsoft Active Directory enduser accounts with UCM. Because the enduser PIN assignments are not stored in Active Directory, administrators must be able to assign PINs to end users by using the UCM administrative GUI.
-
Which of the following fields is not available in the Cisco Unity Connection VoiceMailUser Template? (Select the best answer.)
- Alias
- Display Name
- Extension
- Alternate Extension
- Employee ID
Explanation:
The Alternate Extension field is not available in the VoiceMailUser Template. The Alternate Extension field is typically used in Cisco Unity Connection Administration to enable a single voice mailbox to serve more than one directory number (dn). For example, up to nine administrator configured alternate extensions, or lines, can be assigned to a single voice mailbox. These alternate extensions can be individual dns from the voice virtual LAN (VLAN) or the numbers of external devices. As a result, it is possible to enable a user to conveniently access Unity Connection from a mobile phone or from another IP phone. Similarly, an Alternate Extension can be used to access a single voice mailbox from multiple line appearances on a single IP phone. However, you can only add alternate extensions by editing a single user’s account or by editing users in Bulk Edit mode.The Alias field and the Extension field are mandatory fields in the VoiceMailUser Template when you manually create a new user with a voice mailbox in Cisco Unity Connection Administration. Cisco Unity Connection can integrate with various phone systems, including Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM). The Alias field holds the key that the Unity Connection database uses to identify a user; therefore, the Alias value must always be unique. The Extension field is used to link a UCM user to a Unity Connection mailbox; therefore, it is important that the Unity Connection user have an extension that matches the extension defined for the corresponding user in UCM. If the extension does not match, some of the Unity Connection integration features will not work correctly. For example, if you changed the extension for a user in UCM and did not make the corresponding change for the user in Unity Connection, the user could receive new voice mail in his or her mailbox but might not receive new voice message notifications to his or her IP phone.
Both the Display Name field and the Employee ID field are available in the VoiceMailUser Template. However, neither the Display Name field nor the Employee ID field is mandatory in the VoiceMailUser Template when you manually create a new user with a voice mailbox in Cisco Unity Connection Administration.
-
Which of the following does not provide access to realtime reporting? (Select the best answer.)
- CAR
- RTMT
- Unified Serviceability
- Unified Reporting
Explanation:
The Cisco Unified Call Detail Records (CDR) Analysis and Reporting Tool (CAR) does not provide access to realtime reporting. CAR generates CDR reports, Quality of Service (QoS) reports, traffic reports, and billing reports from data that is stored in the CDR database. The reports can be automatically generated at scheduled intervals or generated manually. You can access CAR by clicking Tools > CDR Analysis and Reporting in Unified Serviceability if you are a system administrator or by using the Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTPS) address https://ipaddress:8443/car/Logon.jsp, where ipaddress is the IP address of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) server or cluster, if you are a CAR administrator or user.Cisco Unified RealTime Monitoring Tool (RTMT) provides access to realtime reporting. RTMT is a clientside application that enables an administrator to monitor devices on a Cisco Voice over IP (VoIP) network in real time. RTMT uses HTTPS to connect to VoIP devices and gather information, such as device status and performance statistics, in real time. The data that is gathered by RTMT can then be used to pinpoint problems on the VoIP network or to monitor performance thresholds.
To access RTMT, you should first ensure that the Cisco RTMT Reporter Servlet and Cisco Serviceability Reporter services are running in the UCM environment. Next, install the RTMT plugin on a workstation by clicking Application > Plugins in the UCM administrative graphical user interface (GUI). After you have installed the plugin, you should launch the RealTime Monitoring Tool application on the workstation, type the appropriate IP address and credential information for accessing the UCM server or cluster, select the Secure Connection check box, and then click OK.
Cisco Unified Serviceability uses RTMT to provide access to realtime reporting. Unified Serviceability is a browserbased troubleshooting tool that uses HTTPS to access information that is provided by other reporting tools, such as RTMT and CAR. In addition, Unified Serviceability provides access to several feature services that can be activated by using the Service Activation window, including database services, CDR services, and security services. You can access Unified Serviceability by clicking Navigation > Cisco Unified Serviceability from within the UCM administrative GUI or by using the HTTPS address https://ip-address:8443/ccmservice/, where ipaddress is the IP address of the UCM server or cluster.Cisco Unified Reporting uses RTMT to provide access to realtime reporting. Similar to Unified Serviceability, Unified Reporting is a browserbased troubleshooting tool that uses HTTPS to access information that is provided by other reporting tools, such as RTMT and CAR. However, Unified Reporting does not provide access to feature activation tools and network service activation tools. You can access Unified Reporting by clicking Navigation > Cisco Unified Reporting from within the UCM administrative GUI or by using the HTTPS address https://ipaddress:8443/cucreports/, where ipaddress is the IP address of the UCM server or cluster. For example, after you have navigated to Cisco Unified Reporting, you could navigate to System Reports > Unified CM Data Summary > Generate Report to monitor system activities.
-
You want to configure caller ID to display a PSTN phone number when the user places an outgoing call.
Which of the following fields should you modify in UCM? (Select the best answer.)
- Display
- External Phone Number Mask
- Line Text Label
- Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy
Explanation:
You should modify the External Phone Number Mask line appearance field in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) administrative graphical user interface (GUI). Line appearance is the association between a line and a device on a Voice over IP (VoIP) network. Because multiple lines can be associated with a single device, you can configure multiple line appearances for a single IP phone. Line appearance configurations can determine how a line that is associated with an IP phone displays information to an end user. After you create a directory number (dn) in UCM and associate the line to a device, you will be able to edit line appearance options that include display settings, such as internal caller ID, external caller ID, and the user name or dn that is displayed beside a line button on an IP phone.UCM transmits the contents of the External Phone Number Mask field as caller ID information when an internal user places an outgoing call to an external party. The information in the External Phone Number Mask field can be a string that consists of up to 24 numbers, the international escape character +, and X wildcards that represent the extension number. The X wildcards should always be at the end of the string. For example, a user that has been assigned extension number 4000 on the internal VoIP network might also be assigned a direct inward dial (DID) number of (555) 5554000. Therefore, you could configure the External Phone Number Mask field with the string 555555XXXX. The number 5555554000 would then be displayed on the caller ID systems of any external parties who are called by the user at extension 4000. If the user at extension 4000 was not assigned a DID number, you could configure the External Phone Number Mask field with your company’s main public switched telephone network (PSTN) number instead.
You should not modify the Line Text Label field. The contents of the Line Text Label field are displayed beside the associated line button of an IP phone. The field is typically configured with the name of the user that is associated with the line. If the Line Text Label field is not configured, the dn that is associated with the line will be displayed instead. For example, if user John Public has been assigned extension 4000, the dn 4000 will be displayed beside the associated line button on the main screen of John Public’s IP phone unless you configure the Line Text Label field. If you configure the Line Text Label field with the name John Public, then that name will appear beside the line button on the main screen of the IP phone. For shared workstations, you can configure the Line Text Label field with the name of the department or office location that is associated with the IP phone. If you configure the Line Text Label field, you should also configure the ASCII Line Text Label field with similar information. The contents of the ASCII Line Text Label field are displayed on IP phones that do not support Unicode character sets. You cannot use non-ASCII characters in the ASCII Line Text Label field.
You should not modify the Display (Internal Caller ID) field. When the Display (Internal Caller ID) field is blank, the dn that is associated with the calling device is shown on the display of the called device. Otherwise, the contents of the Display (Internal Caller ID) field are shown on the display of the called device. You can configure the Display (Internal Caller ID) field with a name or a description of up to 30 characters in length. If you configure the Display (Internal Caller ID) field, you should also configure the ASCII Display (Internal Caller ID) field with similar information. The contents of the ASCII Display (Internal Caller ID) field are displayed on called devices that do not support Unicode character sets. You cannot use nonASCII characters in the ASCII Display (Internal Caller ID) field.
You should not modify the Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field. The Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field configures the behavior of the message waiting indicator (MWI) lamp and of the MWI line prompt on an IP phone. For example, configuring the Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field to Light and Promptwill configure the IP phone to turn on the MWI lamp that is located on the IP phone’s handset when a new voice mail message arrives. In addition, the IP phone will display a new message prompt beside the associated line button on the IP phone. However, configuring the Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field to Prompt Only will display the new message prompt beside the line button but will not turn on the MWI lamp. You can configure the Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field differently for each line that is associated with the IP phone. For example, if the IP phone is configured with a shared line in addition to a primary line, you could configure the Visual Message Waiting Indicator Policy field for the shared line to None so that the IP phone never displays MWI information for the shared line.
-
You are the administrator for your company’s UCM network. Your company is running the UCM 8.6(1).
Examine the exhibit below, and answer the associated question: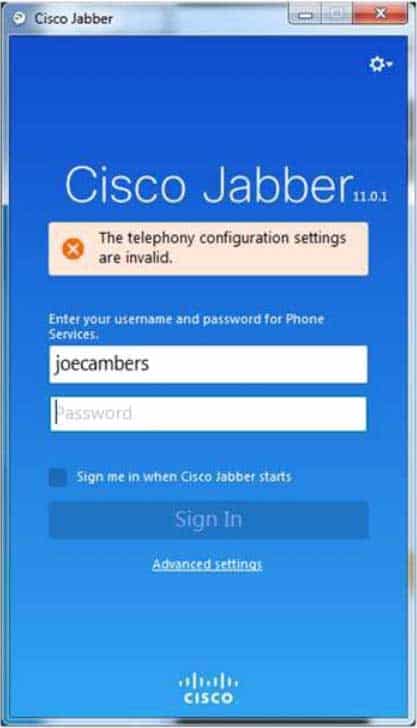
300-835 Part 07 Q18 021 Resetting the Jabber client restores the telephony configuration, but the user is still unable to connect to IM and Presence services.
Which of the following steps are you most likely to perform next to obtain more information about possible problems? (Select the best answer.)
- Click the gear icon > File > Reset Cisco Jabber.
- Click Advanced settings > Reset Cisco Jabber.
- Click the gear icon > Help > Report a problem.
- Click the gear icon > Help > Show error notifications.
Explanation:
Most likely, you would click the gear icon > Help > Show error notifications next to obtain more information about possible problems. The Show error notifications option opens a Jabber window that displays error codes and associated messages. When connectivity to Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) and Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) servers is established, Jabber will report any errors it encounters in communications in the Show error notifications window. For example, a CJ:1000:101 error indicates that Jabber’s integration with Microsoft Office has become corrupt and that you might need to reinstall the Jabber client.You would not click the gear icon > Help > Report a problem option. The Report a problem option enables you to send information to Cisco’s developers when a Jabber problem occurs. However, in this scenario, you have not yet determined that the problem is one you cannot solve on your own.
You would not click the gear icon > File > Reset Cisco Jabber option. In this scenario, you have already reset Cisco Jabber to establish connectivity to the servers. In addition, you would not click Advanced Settings > Reset Cisco Jabber, because this is an invalid menu path.
-
You are the administrator for your company’s UCM network. Your company is running the UCM 8.6(1).
Examine the exhibit below, and answer the associated question: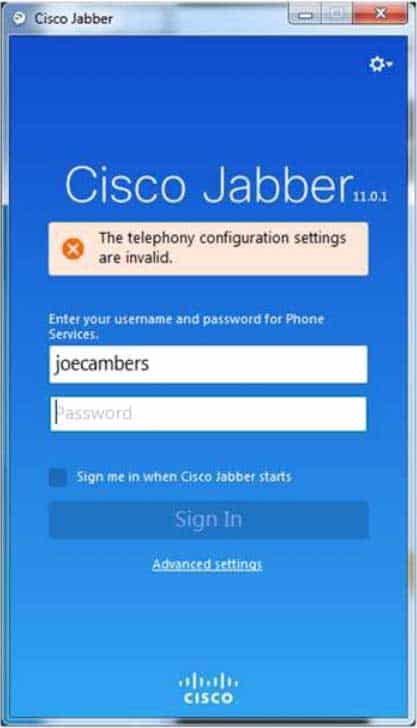
300-835 Part 07 Q19 022 You have verified that the softphone named Jabberwocky has been created and associated with the correct end user in UCM Administration.
Which of the following is least likely to have caused the Cisco Jabber error message? (Select the best answer.)
- The TFTP server is down.
- The IM and Presence server is down.
- Servers have not been configured by using host names.
- Cisco Jabber requires a fully qualified user name.
Explanation:
Although Cisco Jabber does require a fully qualified user name, such as [email protected], to register with Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) and to configure a new Jabber user for the first time, typing an incorrectly formatted user name in an unconfigured or manually configured Cisco Jabber client will produce the following error message:

300-835 Part 07 Q19 023 After Cisco Jabber has been correctly configured and registered with UCM for the first time, it is possible to log in to Jabber with only a shortened form of the user name in the user name field, as shown in the following exhibit:

300-835 Part 07 Q19 024 However, if you mistype the user name or type a different, valid user name into the login field, Jabber will prompt you to verify that you want to completely reset the client configuration, as shown in the following exhibit:
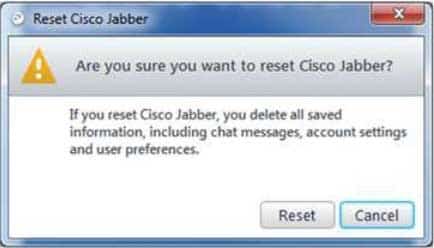
300-835 Part 07 Q19 025 Clicking Reset would cause Jabber to delete the current configuration and attempt to replace it with a new one for a different user name. Clicking Cancel returns the user to the login screen.
If Jabber had not been previously configured for a given user, Jabber would produce the following if provided with a short invalid user name:
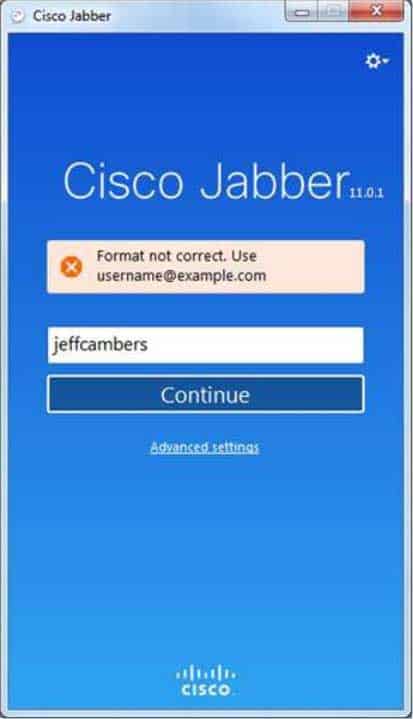
300-835 Part 07 Q19 026 Cisco Jabber uses Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) to connect to UCM in softphone mode. SIP is an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)standard call signaling protocol. Although SIP is typically used as a peer-to-peer call signaling protocol, it can also operate in client/server mode. A softphone is software that behaves like a phone, enabling a user to participate in voice sessions over a typical workstation network connection.
The Cisco Jabber client can be configured automatically by the UCM server or manually by clicking Advanced Settings from the login screen. Regardless of the configuration method, the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server and the Cisco Unified Communications Manager IP Phone (CCMCIP) server must be reachable by the client on which Jabber is installed. If the TFTP server is not available or is misconfigured, the Jabber client will not be able to download configuration files. If the CCMCIP server is not available or is misconfigured, Jabber cannot participate in instant messaging (IM) and Presence.
Cisco does not recommend configuring endpoints, whether they are desk phones or softphones like Cisco Jabber, by using host names. Configuring the Jabber client with server information by using host names instead of IP addresses could cause the error message in this scenario. When using host names or fully qualified domain names (FQDNs), the Domain Name System (DNS) server or local hosts file must be present and working. In addition, the Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) server or IM and Presence server must be up and working. Otherwise, the user might receive a Cannot communicate with the server error message when attempting to log in, even if the login servers are correctly configured.
-
You are the administrator for your company’s UCM network. Your company is running the UCM 8.6(1).
Examine the exhibit below, and answer the associated question: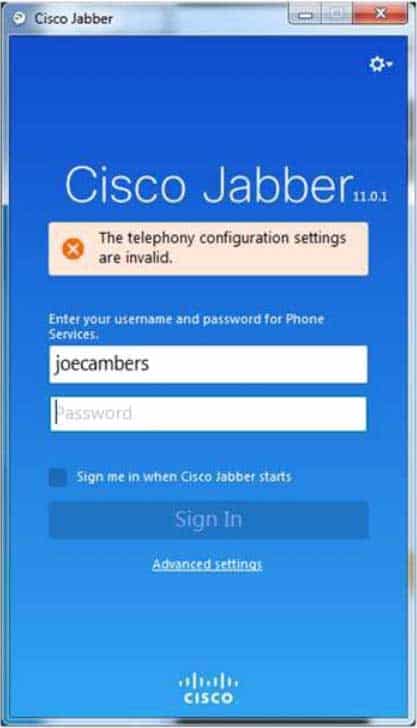
300-835 Part 07 Q20 027 Which of the following is not a step you might take to troubleshoot the error in this scenario? (Select the best answer.)
- Click Advanced settings on the Cisco Jabber login page.
- Click User Management > End User in UCM Administration.
- Click User Management > User Settings > Service Profile in UCM Administration.
- Click Application > CUPC/Cisco Jabber in CUPS Administration.
Explanation:
Because your company is using Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) 8.6(1), you would not click User Management > User Settings > Service Profile in UCM Administration to troubleshoot the error in this scenario. Service profile data is not editable under the User Management menu in UCM 8.6(1), as shown in the following exhibit:
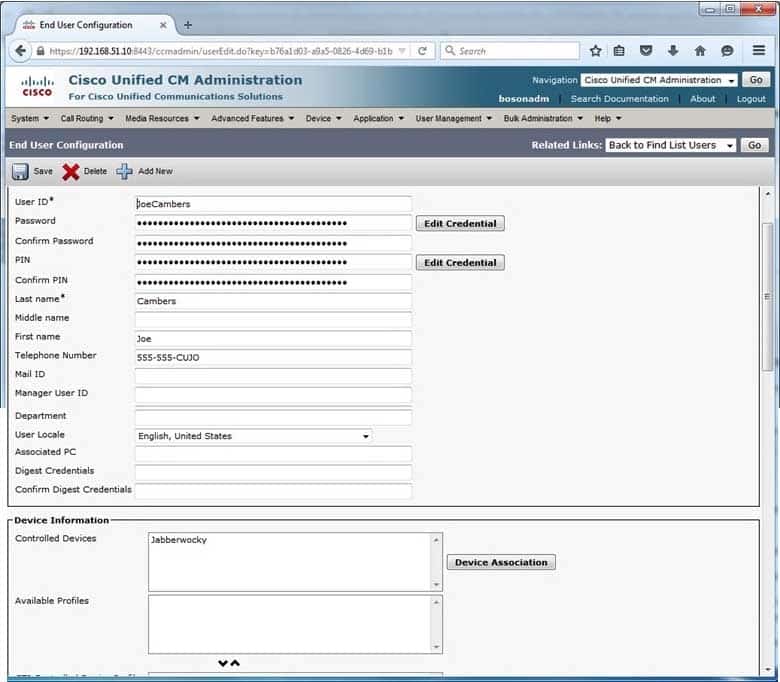
300-835 Part 07 Q20 028 To troubleshoot the service profile associated with the Jabber client in the version of UCM that is deployed in this scenario, you would need to click Application> CUPC/Cisco Jabber in the Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) Administration interface.
You might click User Management> End User to troubleshoot error in this scenario. Clicking End User provides a list of the users configured in UCM. By clicking on a given user’s name, you can view and edit the devices that are associated with the user. For example, in the exhibit below, the user named Joe Camber is associated with a capable of controlling the device named Jabberwocky:
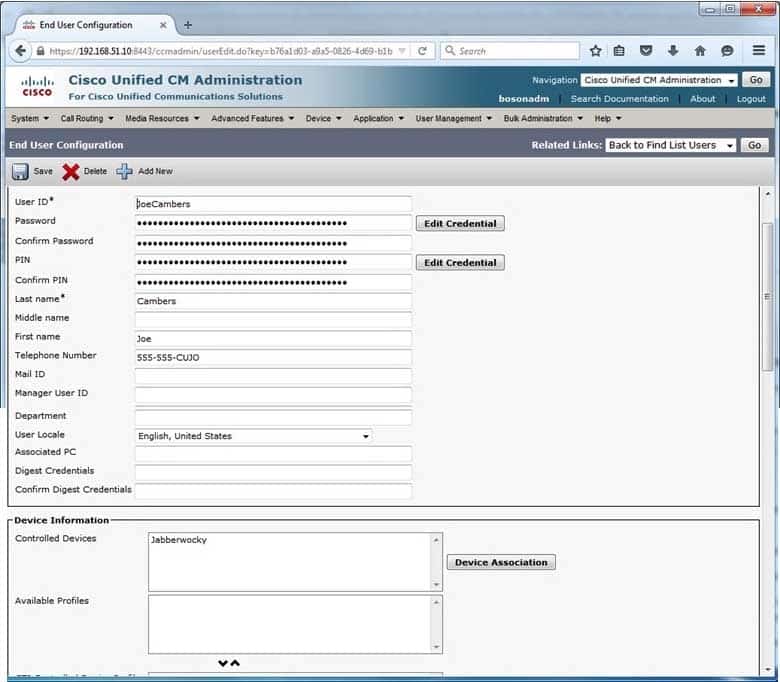
300-835 Part 07 Q20 029 You might click Advanced settings on the Cisco Jabber login screen to troubleshoot the error in this scenario. The Advanced settings link opens the Advanced settings dialog box, where Cisco Jabber can be set to automatic or manual configuration. In the exhibit below, Cisco Jabber is configured to connect to Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP), Cisco Computer Telephony Integration (CTI), and Cisco Unified Communications Manager IP Phone (CCMCIP) services on the UCM server that has been assigned the IP address of 192.168.51.10:
