300-835 : Automating Cisco Collaboration Solutions (CLAUTO) : Part 08
-
You are the administrator for your company’s UCM network. Your company is running the UCM 8.6(1).
Examine the exhibit below, and answer the associated question: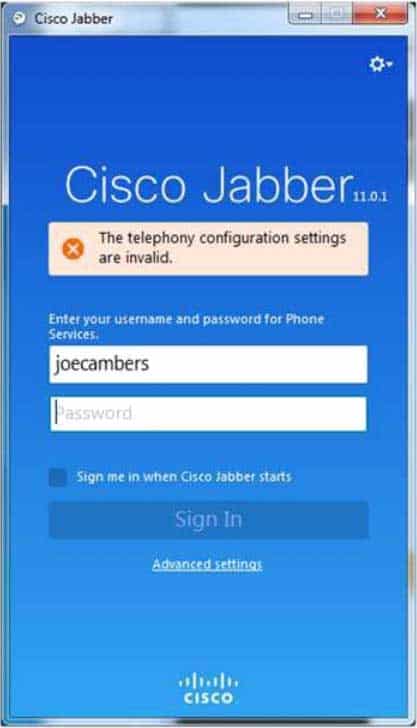
300-835 Part 08 Q01 031 While troubleshooting the error message in this scenario, you decide to reset the Cisco Jabber client. Which of the following could you do? (Select the best answer.)
- Click the gear icon > File > Reset Cisco Jabber.
- Click Advanced settings > Reset Cisco Jabber.
- Click the gear icon > Help > Reset Cisco Jabber.
- Click User Management > Reset Jabber in UCM Administration.
Explanation:
In this scenario, you could click the gear icon > File > Reset Cisco Jabber to reset the Cisco Jabber client, as shown in the following exhibit:
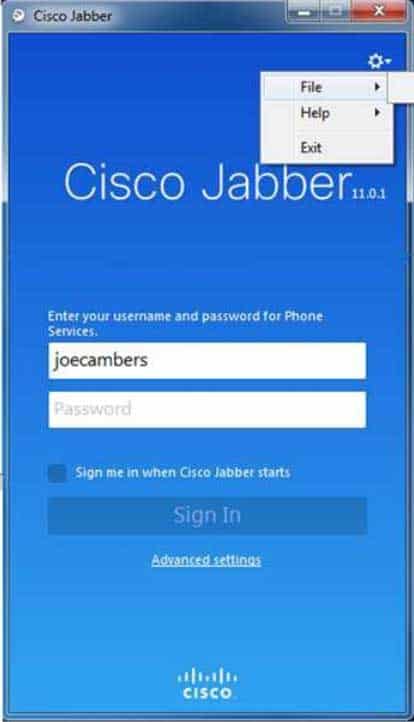
300-835 Part 08 Q01 032 Jabber will prompt you to verify that you want to completely reset the client configuration, as shown in the following exhibit:
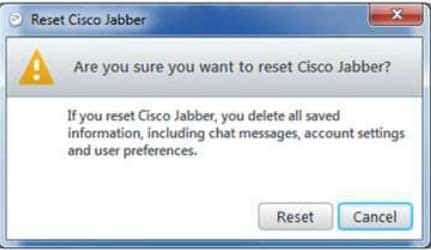
300-835 Part 08 Q01 033 Clicking Reset Cisco Jabber would cause Jabber to delete the current configuration and attempt to replace it with a new one for a different user name. Clicking Cancel returns the user to the login screen.
You would not click User Management > Reset Jabber in Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Administration. The User Management > Reset Jabber option is not available in UCM versions prior to 8.6 (2). This option was introduced with the release of Cisco Jabber for Windows 10.5.
You would not click the gear icon > Help > Reset Cisco Jabber. The gear icon’s Help menu does not contain the Reset Cisco Jabber option, as shown in the following exhibit:
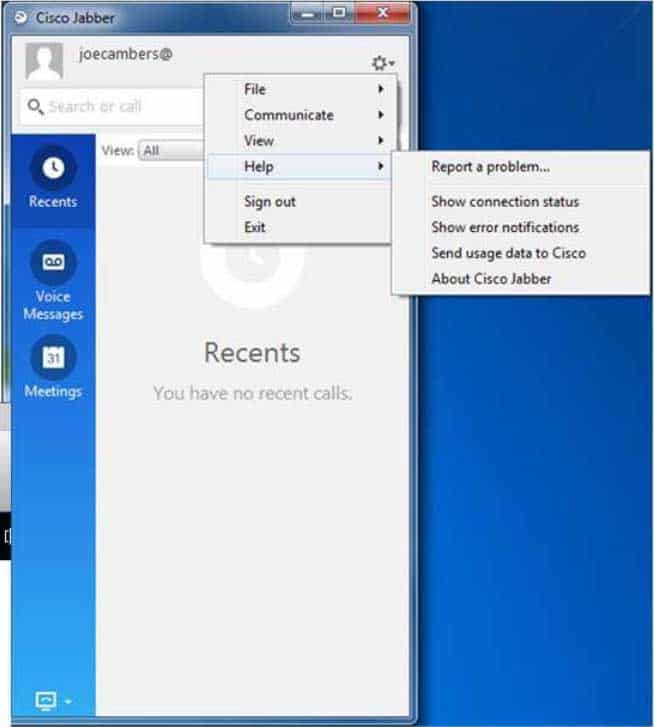
300-835 Part 08 Q01 034 The Report a problem option enables you to send information to Cisco’s developers when a Jabber problem occurs. The Show connection status option enables you to view the status of Jabber’s connections to UCM, Cisco Unity Connection, Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS), desk phone hardware, Microsoft Outlook, and Microsoft Active Directory. The Show error notifications option enables you to view specific details about any errors that have occurred during login or during a session. The Send usage data to Cisco option configures Jabber to send information to Cisco about how Jabber is being used. The About Cisco Jabber option produces a dialog box that contains the version number, build number, and notes about the product.
-
You issue the show running-config command on a CME router and receive the following partial output:
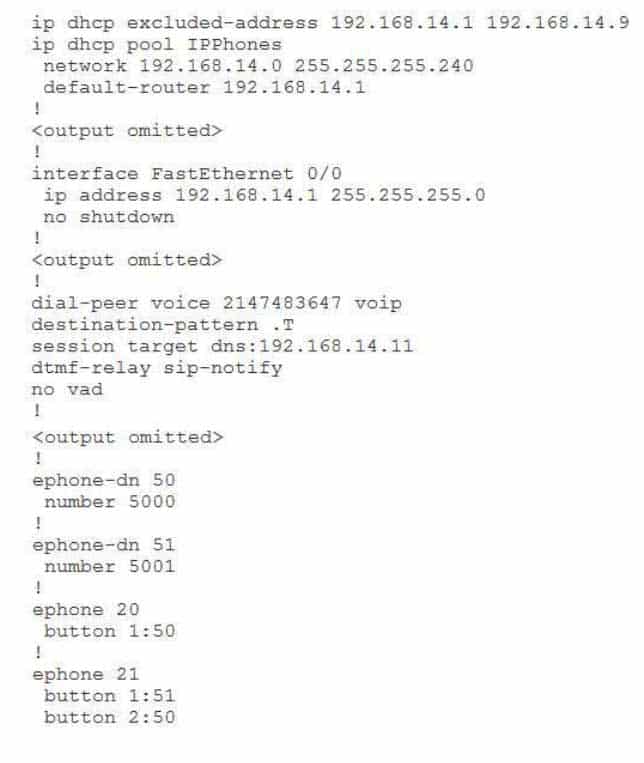
300-835 Part 08 Q02 035 Examine the output, and use the information you gather to answer the question.
Which of the following statements about the dial peer configuration is true? (Select the best answer.)
- The dial peer number is invalid.
- The destination pattern is invalid.
- The wrong keyword has been used to define the session target.
- The session target is the same as the default router.
Explanation:
The wrong keyword has been used to define the session target. Dial peer session targets can be specified by IP address or by host name. To specify a session target by IP address, you should configure the session target ipv4:ipaddress command, where ip address is the IP address of the router to which an outbound call matching the dial peer should be forwarded. To specify a session target by host name, you should configure the session target dns: hostname command, where hostname is the alphanumeric host name that is mapped to an IP address by a Domain Name System (DNS) server. The dns keyword also supports some wildcard options.A voice gateway router will perform the following evaluations when it must send an outbound call:
1. The router will attempt to match the destination Dialed Number Identification Service (DNIS) to a destinationpattern string command on a digitbydigit basis, comparing the digit string to the destination pattern as the user dials the digits.
2. If the dial peer is a plain old telephone service (POTS) dial peer, the router will forward the call to the port indicated by the corresponding portport command.
3. If the dial peer is a Voice over IP (VoIP) dial peer, the router will forward the call to the IP address indicated by the corresponding session target ipv4: ipaddress command.
4. If no match is found, the call will be dropped.The dial peer number is not invalid. A VoIP dial peer can be configured with any number in the range from 1 through 2145483647.
The destination pattern is not invalid. The dial peer command destination-pattern .T is used to indicate any string of up to 32 digits. The T character is used at the end of a string to instruct the router to wait for the complete dial string to be entered before matching a call to a dial peer.
The session target is not the same as the default router in this configuration. The default router is defined by the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) defaultrouter 192.168.14.1 command. The session target is misconfigured and is therefore unlikely to map a host name of 192.168.14.11 to the default router’s IP address of 192.168.14.1.
-
You issue the show running-config command on a CME router and receive the following partial output:

300-835 Part 08 Q03 036 Examine the output, and use the information you gather to answer the question.
Based on the configuration, which of the following codecs should be displayed in the call statistics when a user presses the ? key twice on an IP phone? (Select the best answer.)
- G.711 alaw
- G.711 µlaw
- G.726
- G.729
- iLBC
Explanation:
Given the configuration commands in this scenario, the G.729 codec should be displayed in the call statistics when a user presses the question mark (?) key twice on the IP phone. The G.729 codec is a high-complexity compressed codec that consumes bandwidth at a rate of 8 Kbps. Cisco IOS uses the G.729 codec by default unless you specify a codec by issuing the codec command in dial peer configuration mode. For example, the codec g729br8 command configures a dial peer to use the G.729 Annex B codec, which adds Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)standard voice activity detection (VAD) and comfort noise generation features to the G.729 codec.There are two ways that you can verify the codec that is being used on a call from a Cisco IP phone: by pressing the ? key twice while a call is in progress and by pressing settings> Status > Call Statistics after a call has been disconnected. Both methods of accessing call statistics display the same information, including the codec being used by the caller, the codec being used by the receiver, the size of voice packets being transmitted, the size of voice packets being received, the average amount of jitter on the call, the maximum amount of jitter on the call, and the number of packets that were discarded by the receiver.
Neither the G.711 a-law codec nor the G.711 µ-law (mulaw) codec will be used by the dial peer. The G.711 codec is an uncompressed, 64Kbps audio codec common to all Voice over IP (VoIP) devices. Two variations of G.711 encoding exist: µlaw and a-law. Only the United States, Canada, and Japan use the G.711 µlaw codec to encode audio data; the rest of the world uses G.711 a-law. To configure a dial peer to use the G.711 a-law codec, you should issue the codec g711alaw command in dial peer configuration mode. To configure a dial peer to use the G.711 µlaw codec, you should issue the codec g711ulaw command in dial peer configuration mode.
The G.726 codec will not be used by the dial peer. The G.726 codec is a medium complexity compression codec. To configure a dial peer to use the G.726 codec at a bit rate of 32 Kbps, you should issue the codec g726r32 command in dial peer configuration mode.
The Internet Low Bitrate Codec (iLBC) will not be used by the dial peer. The iLBC codec is a nonproprietary, high- complexity compression codec that consumes bandwidth at a rate of up to 15.2 Kbps. To configure a dial peer to use the iLBC codec, you should issue the codec ilbc command in dial peer configuration mode.
-
You issue the show running-config command on a CME router and receive the following partial output:
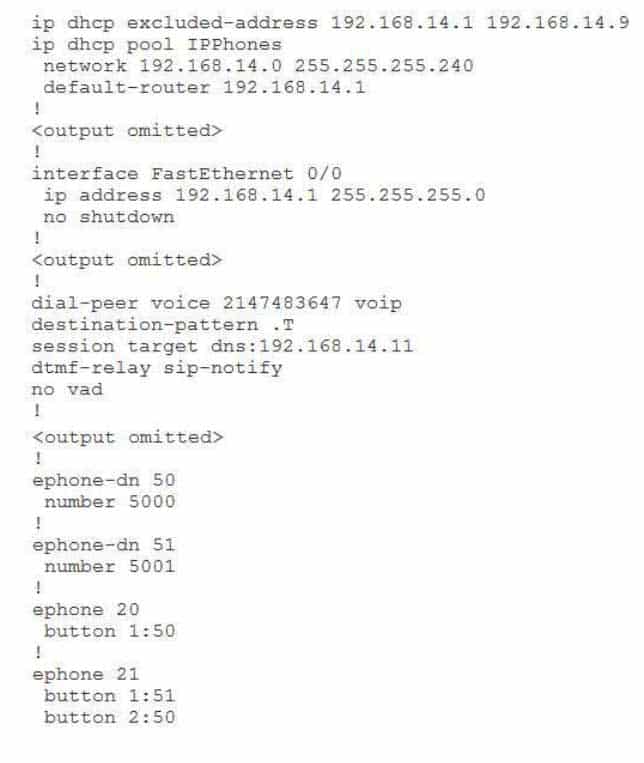
300-835 Part 08 Q04 037 Examine the output, and use the information you gather to answer the question.
How long can the user pause between digits before CME will attempt to dial? (Select the best answer.)
- two seconds
- four seconds
- six seconds
- eight seconds
- 10 seconds
Explanation:
The user can pause up to 10 seconds between digits dialed before Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) will attempt to dial because no other interdigit delay has been configured on the router. The dial peer command destination-pattern .T is used to indicate any string of up to 32 digits. The T character is used at the end of a string to instruct the router to wait for the complete dial string to be entered before matching a call to a dial peer. By default, CME will wait up to 10 seconds for the user to dial a digit after a key has been pressed.You can change the CME interdigit delay value for IP phones connected to CME by issuing the timeouts interdigit seconds command in telephony-service configuration mode, where seconds is the number of seconds CME should wait between key presses before attempting to route the call. The seconds value can be in the range from two through 10. The interdigit delay value for CME plain old telephone service (POTS) phones can be configured in voice port configuration mode.
-
You issue the show running-config command on a CME router and receive the following partial output
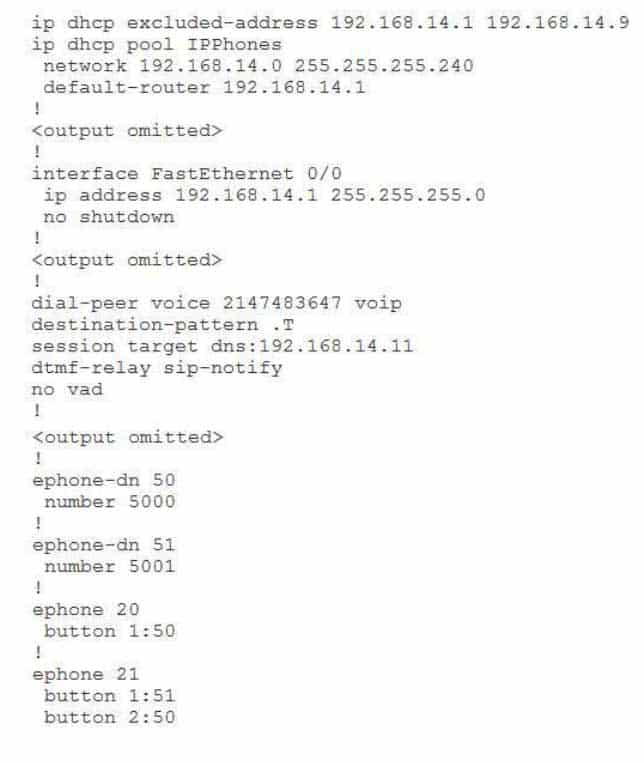
300-835 Part 08 Q05 038 Examine the output, and use the information you gather to answer the question.
How many IP phones will be able to automatically obtain an IP address? (Select the best answer.)
- zero
- one
- five
- 14
- 254
Explanation:
Only five IP phones will be able to automatically obtain an IP address because nine IP addresses in the network range have been excluded from being leased by Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) in this configuration. The syntax of the ip dhcp excluded address command is ip dhcp excluded address low-address [highaddress], where low address and highaddress specify the lower and upper boundaries of the excluded address range, respectively. In this configuration, the assignable host address range from 192.168.14.1 through 192.168.14.9 has been excluded from being automatically assigned by DHCP.
Furthermore, the network command in this configuration limits the entire range of the Voice over IP (VoIP) network to a total of 14 assignable addresses. The network command is used to specify which IP address range should be assigned to clients and which subnet should receive the addresses. The syntax of the network command is network address [mask | /prefix], where address is the network address, mask is the subnet mask, and prefix is the prefix length in Classless InterDomain Routing (CIDR) notation.
In this configuration, the subnet mask of 255.255.255.240 creates a 16address subnet of the Class C 192.168.14.0 network. The first address and the last address of that subnet are the network address and the broadcast address, respectively. Therefore, only the address range from 192.168.14.1 through 192.168.14.14 is assignable to hosts. Because the range from 192.168.14.1 through 192.168.14.9 is excluded from DHCP, only the range from 192.168.14.10 through 192.168.14.14 can be automatically assigned to IP phones.
-
A caller presses an IP phone softkey labeled QRT. The caller is logged in to the IP phone. The recipient is not logged in to an IP phone.
Which of the following will not be sent to an administrator? (Select the best answer.)
- the time stamp
- the category
- the reason
- the source user name
- the destination user name
- the source IP address
- the destination IP address
Explanation:
Of the available choices, the destination user name will not be sent to an administrator if the caller who is logged in to the IP phone presses the soft key labeled QRT and the recipient is not logged in to an IP phone. The Cisco Quality Report Tool (QRT) can be configured as an extended function to enable users to send QRT information to Cisco Unified Communications administrators directly from the user’s IP phone. The report can then be displayed from the Tools menu within Cisco Unified Serviceability. However, if the user is not logged in to the IP phone at the time the data is sent, the user name will be null.The QRT tool collects a variety of available source device information, destination device information, Real-time Information Server (RIS) information, Cisco CallManager service and CTIManager service information, CallManager database information, and enduser information when a user presses the QRT softkey. An administrator can then analyze that information to troubleshoot quality issues or other issues that occurred during a given call.
The source user name will be sent to the administrator because, in this scenario, the caller is logged in to the IP phone. If the caller is logged in to the source IP phone, the source user name will be sent to the administrator. However, if the caller is not logged in to the source IP phone, the source user name will be null.
Enduser information, such as the time stamp, the category, and the reason, will be sent to the administrator. In addition, the source IP address and the destination IP address will be sent to the administrator.
-
Which of the following does Cisco recommend as the maximum amount of packet loss on a VoIP network? (Select the best answer.)
- 1 percent
- 3 percent
- 20 percent
- 50 percent
Explanation:
Cisco recommends a maximum packet loss of 1 percent for Voice over IP (VoIP) traffic. Packet loss is often caused when networks become congested and packets are dropped. Dropped packets can cause clips, or breaks, in the audio stream. However, voice traffic is more tolerant of dropped packets than of delayed packets because a small amount of packet loss is not noticeable to the human ear. Some codecs can correct small amounts of packet loss. On networks with limited bandwidth, a lowbitrate codec can mitigate packet loss. However, the overall quality of the audio will be reduced. Packet loss can also be mitigated by implementing Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms.Short delays and low packet loss on a VoIP network help protect the rate at which bits flow over the network. In addition to the packet loss recommendations, Cisco recommends a maximum jitter of 30 ms for VoIP traffic. Jitter is a variation in delay, which can cause voice traffic to arrive at different times, thereby causing breaks, or choppiness, in the audio stream. Jitter can be mitigated by implementing QoS mechanisms.
Cisco also recommends a maximum endtoend delay of 200 ms. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) considers an endtoend delay of 150 ms or less to be acceptable for high voice quality. Delay, which is also called latency, can introduce interruptions in conversation flow, causing the speakers at each end of the circuit to interrupt each other. Endtoend delay can be mitigated by implementing QoS mechanisms.
-
Which of the following are functions that are provided by either an ITSP or the PSTN? (Select 3 choices.)
- QoS
- call setup and teardown
- audio signal compression
- call supervision
- call routing
Explanation:
Call setup and teardown, call supervision, and call routing are all functions that are provided by Internet telephony service providers (ITSPs) and the public switched telephone network (PSTN). ITSPs enable customers to use Voice over IP (VoIP) to make phone calls over the Internet. Call setup involves the series of events between a phone going offhook and establishing a connection; these events include dialtone signals and ring signals. Call supervision involves the change in the state of a line or trunk port, such as line seizure, answer, or disconnect. Call routing involves selecting the path on which a call is transported from a source endpoint to a destination endpoint. On a VoIP network, voice gateways are responsible for call routing.Quality of Service (QoS) and audio signal compression are functions that are often provided by ITSP but are not typically provided by the PSTN. QoS is a VoIP technique that ensures call quality and integrity by mitigating delay and dropped packets, which can interrupt the flow of a VoIP call. Typical QoS techniques include buffer management and the use of multiple transmission queues to separate types of multimedia packets. Because voice traffic is sent in real time, quality is critical. Audio signal compression replaces consecutive repeating audio signals with code that instructs an endpoint to play one specific signal a given number of times. The bandwidth consumed by a call is reduced when compression is used.
-
You are the administrator for a small VoIP network connected to an ITSP in the United States. Your supervisor informs you that he is hearing a fast busy signal when he picks up the handset of his IP phone. You have verified that no other users are experiencing this problem.
In which of the following fault domains should you begin troubleshooting? (Select the best answer.)
- the IP phone
- the cable connecting the IP phone to the switch
- the network switch that is connected to the IP phone
- the voice network’s router
Explanation:
Because only one user is experiencing the problem, you should begin troubleshooting the IP phone fault domain. Fast busy signals can be caused by a codec mismatch between an IP phone and a Cisco voice gateway. You can determine what codec your supervisor’s phone is using by pressing settings > Status > Call Statistics on the IP phone keypad. The default audio codec on a Cisco voice gateway is the G.729 codec, which is a high-complexity compressed codec that consumes bandwidth at a rate of 8 Kbps.You would not begin the troubleshooting process by examining the cable connecting the IP phone to the switch. You might check the cable connecting the IP phone to the switch or the switch port to which the cable is connected if the IP phone were a Power over Ethernet (PoE) device that was not receiving power from the switch or if Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) reported that the device is of an unknown type. You might also check the network cable and switch port if the device were powered by a power supply but unable to register and download a configuration.
It is not likely that you would begin troubleshooting the network switch or the voice network’s router in this scenario, because only one user is affected by the problem. You might begin troubleshooting the problem at the network switch if an entire department within an organization were reporting a problem. You might begin troubleshooting at the voice router if more than one department or the entire organization were experiencing a problem.
-
An administrator wants to know whether a Cisco IP Phone 7961’s IP address was obtained from a DHCP server.
Which of the following can the administrator do? (Select 2 choices.)
- press settings > Network Configuration on the IP phone
- press services > DHCP Client on the IP phone
- press settings > Status on the IP phone
- press messages > Status on the IP phone
- press directories > Network on the IP phone
- press help > Network Configuration on the IP phone
Explanation:
An administrator who wants to know whether a Cisco IP Phone 7961’s IP address was obtained from a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server can either press settings > Network Configuration on the IP phone or press settings > Status on the IP phone. The settings > Network Configuration page on the IP phone typically contains the IP address of the DHCP server. The settings > Status page on the IP phone typically displays whether the IP phone is bound to a DHCP server.The Cisco IP Phone 7961 series includes a bank of buttons with iconography designed to represent the button’s functions. For example, the settings button is represented by a selected check box and can be used to view or modify settings specific to the user or IP phone. A typical bank of buttons for a Cisco IP Phone 7961 series appears in the following exhibit:

300-835 Part 08 Q10 039 The administrator could not press messages > Status on the IP phone, because that option does not exist. The messages button, which is represented by the back of a standard paper envelope, is used to log in to the voice mail system.
The administrator could not press services > DHCP Client on the IP phone, because that option does not exist. However, a user can launch Cisco Unified Communications IP phone applications by pressing the services button. The services button, which is represented by a globe icon, is used to launch IP phone applications. The applications that are available from the services button are dependent on the Cisco Unified Communications deployment and user privilege levels.
The administrator could not press directories > Network on the IP phone, because that option does not exist. However, a user can display directory information by pressing the directories button. The directories button, which is represented by an open book icon, is used to display lists of missed calls, received calls, placed calls, or local directory contacts. If configured, the directories button can also be used to access a custom Personal Speed Dial directory.
The administrator could not press help > Network Configuration on the IP phone, because that option does not exist. However, the help button, which is represented by a question mark (?), is used to provide the end user with information about the specific features of the IP phone. A user can press the help button twice while on a call on an IP phone to view statistical information about the call, such as the codec that is being used by the IP phone, the codec that is being used by the calling phone, and packet error information.
-
Which of the following is not true of both CUPS persistent chat rooms and CUPS ad-hoc chat rooms? (Select the best answer.)
- Neither room can be created or managed by users.
- Users cannot invite other users to a persistent room.
- The presence status of users cannot be viewed in an ad-hoc room.
- Both rooms are deleted when the last user logs out.
- Ad-hoc chat rooms allow the recording of transcripts.
Explanation:
Both Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) adhoc chat rooms and persistent chat rooms can be created or managed by users. There are two types of CUPS chat rooms: adhoc and persistent. Adhoc chat rooms are temporary. Persistent chat rooms, on the other hand, are always available in CUPS, even after all users have logged out. Support for persistent chat rooms must be specifically enabled when configuring CUPS.Persistent chat rooms, not adhoc chat rooms, enable the recording of transcripts of the discussions that occur within the room. Persistent chat rooms therefore enable users to collaborate on and store information about longterm collaborative projects by using CUPS instant messaging (IM) and Presence. CUPS maintains no records or transcripts related to the adhoc chat room.
Both adhoc chat rooms and persistent chat rooms allow users to invite other users to the room. In addition, users can view the presence status of other users in a CUPS chat room regardless of the type of chat room. However, only an adhoc chat room is deleted when the last user logs out.
-
Which of the following UCM services enables the use of Cisco Unified Personal Communicator in desk phone control mode when integrating a CUPS server with UCM? (Select the best answer.)
- Cisco AXL Web Service
- Cisco CallManager
- Cisco CTIManager
- Cisco TFTP
Explanation:
The Cisco CTIManager service enables the use of Cisco Unified Personal Communicator in desk phone control mode when integrating a Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) server with Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM). The Cisco Computer Telephony Integration (CTI) feature is a development system that enables programmers to create applications that can connect to and communicate with a Cisco Unified Communications system. The CTIManager service is required in order to use Cisco Unified Personal Communicator in desk phone control mode. Unified Personal Communicator communicates with the desk phone by using the CTI Quick Buffer Encoding (CTIQBE) protocol.The Cisco Trivial File Transfer Protocol (Cisco TFTP) service does not enable the use of Cisco Unified Personal Communicator in desk phone control mode. However, the Cisco TFTP service enables the use of Cisco Unified Personal Communicator in softphone mode when integrating a CUPS server with UCM. The Cisco TFTP service is also used by UCM to update physical IP phone firmware.
The Cisco CallManager service does not enable the use of Cisco Unified Personal Communicator in desk phone control mode. However, the Cisco CallManager service, which is also called the Cisco Unified Communications Service, is required for UCM to use software call processing, signaling, and control.
Cisco Administrative Extensible Markup Language (AXL) Web Service does not enable the use of Cisco Unified Personal Communicator in desk phone control mode. However, the Cisco AXL Web Service is required to enable the synchronization of data between CUPS and UCM.
-
You are deploying Cisco Jabber in a UCM 10.0 environment with full integration. You have already configured all of the following:
1. A _cisco-uds Service DNS SRV record for UCM on the DNS server
2. An IM and Presence Service Profile in UCM Service Profiles
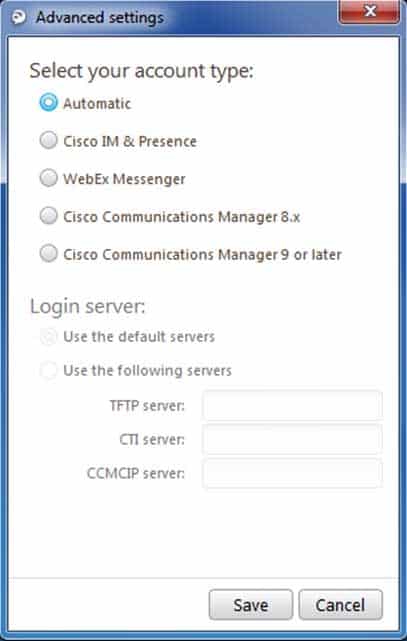
3. End users with the IM and Presence Service Profile in UCM User ManagementYou click the Advanced settings link in Cisco Jabber.
Which of the following radio buttons should most likely be selected for the Select your account type group in order to complete the Cisco Jabber configuration? (Select the best answer.)
- Automatic
- Cisco IM & Presence
- WebEx Messenger
- Cisco Communications Manager 8.x
- Cisco Communications Manager 9 or later
Explanation:
Most likely, the Automatic radio button should be selected for the Select your account type group in Cisco Jabber’s Advanced settings dialog box because, in this scenario, you have correctly configured all the requirements for enabling the automatic configuration of Cisco Jabber clients from Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM). Cisco Jabber’s Advanced settings dialog box features an Automatic option that allows Cisco Jabber to automatically configure itself as long as all of the following are true:1. UCM is operating at release 9 or later.
2. A correct _cisco-uds Service (SRV) record has been configured on the Domain Name System (DNS) server.
3. Automatic is selected in Advanced settings.
4. An instant message (IM) and Presence Service profile has been configured in UCM.
5. The IM and Presence Service Profile has been correctly applied to end users in UCM User Management.The following exhibit displays the Cisco Jabber Advanced settings dialog box with the Automatic radio button selected:
300-835 Part 08 Q13 040 You would not select the Cisco Communications Manager 9 or later radio button unless you were configuring Cisco Jabber so that it could not be automatically configured by UCM. You might select the Cisco Communications Manager 9 or later radio button if you had not configured the _cisco-uds SRV record on the DNS server. Cisco Jabber relies on that SRV record to automatically connect to the appropriate UCM 9.0 or later services.
You would not select the Cisco Communications Manager 8.x radio button, because you have deployed UCM 10.0. In addition, you would not select either the Cisco IM & Presence radio button or the WebEx Messenger radio button, because those options do not allow Cisco Jabber to fully integrate with UCM.
-
Which of the following can managers display by clicking Device Reports > Gateway in the CAR GUI? (Select the best answer.)
- the Gateway Detail report
- the Gateway Summary report
- the Gateway Utilization report
- none of the gateway reports
Explanation:
Only administrators can display reports by clicking Device Reports > Gateway in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Call Detail Records (CDR) Analysis and Reporting (CAR) graphical user interface (GUI)? managers cannot display reports by using this path. CAR provides three privilege levels for reporting: administrators, managers, and individual users. However, only administrators are permitted to view Gateway device reports.The Gateway Detail report can be used to examine issues with a specific gateway. The Gateway Summary report can be used to examine a summary of every call that was transmitted through the gateways. Therefore, the Gateway Summary report can be used to monitor traffic and Quality of Service (QoS). The Gateway Utilization report can be used to determine whether a given gateway or gateways are over utilized. Therefore, you can use the Gateway Utilization report to determine whether new gateways need to be added to the network.
-
Which of the following Unity Connection features cannot be modified from a user account’s Phone Menu screen? (Select the best answer.)
- touchtone conversation style
- touchtone conversation live reply
- touchtone conversation menu style
- touchtone conversation speed
- touchtone conversation volume
- message locator sort order
Explanation:
You cannot modify the Cisco Unity Connection touchtone conversation live reply feature from a user account’s Phone Menu screen in the Unity Connection graphical user interface (GUI). Live reply is a Unity Connection Class of Service (CoS) feature that enables voice mail users to reply to a voice mail message by pressing a key on the IP phone keypad or by using the Unity Connection voice recognition feature. CoS feature settings can be modified only from the CoS screen, by using Bulk Edit Mode, or by using the Phone section of a Unity Connection user template. You can implement multiple CoS configurations in a single Unity Connection environment. Therefore, you can modify an individual CoS configuration or use Bulk Edit Mode to edit multiple CoS configurations. Until user templates and CoS have been configured, user accounts cannot be added to Unity Connection by using the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT).The touchtone conversation style feature can be modified from a user account’s Phone Menu screen in the Unity Connection GUI. A touchtone conversation is a series of voice prompts that users can answer by pressing keys on the IP phone keypad. The Touchtone Conversation dropdown field in the Touchtone Conversation Style area of the Phone Menu enables an administrator to choose from a list of available conversation styles. By default, the Touchtone Conversation dropdown field is set to Classic Conversation. The Touchtone Conversation field can be configured by editing individual user accounts, editing user templates, or editing user accounts in Bulk Edit Mode.
The touchtone conversation menu style feature can be modified from a user account’s Phone Menu screen in the Unity Connection GUI. The Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field determines whether a user will hear a full set of instructions or a brief set of instructions after dialing into the voice mail system. Cisco recommends configuring the touchtone conversation style to Full for inexperienced users and Brief for experienced users. By default, the Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field is configured to Fullfor all users. The Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field can be configured by editing individual user accounts, editing user templates, or editing user accounts in Bulk Edit Mode.
The touchtone conversation speed feature can be modified from a user account’s Phone Menu screen in the Unity Connection GUI. The Conversation Speed field determines the rate at which the touchtone conversation is played back to the user; it can be configured as Slow, Normal, Fast, or Fastest. The Conversation Speed field can be configured by editing individual user accounts, editing user templates, or editing user accounts in Bulk Edit Mode.
The touchtone conversation volume feature can be modified from a user account’s Phone Menu screen in the Unity Connection GUI. The Conversation Volume field determines the decibel rate at which the touchtone conversation is played back to the user; it can be configured as Low, Medium, or High. The Conversation Volume field can be configured by editing individual user accounts, editing user templates, or editing user accounts in Bulk Edit Mode.
The message locator sort order feature can be modified from a user account’s Phone Menu screen in the Unity Connection GUI. The Message Locator Sort Order field determines the order that voice mail messages are listed in when a voice mail user uses Message Locator to search for voice mail messages from other users. In order to use the Message Locator feature, you must select the Enable check box of the Finding Messages with Message Locator area of the Phone Menu. The Message Locator Sort Order drop-down field can be configured as Last In, First Out or First In, Last Out. The Message Locator Sort Order field can be configured by editing individual user accounts, editing user templates, or editing user accounts in Bulk Edit Mode.
-
Which of the following is a Cisco voice messaging product that is typically installed in a router module slot? (Select the best answer.)
- CME
- UCM
- Unity
- CUE
- Unity Connection
Explanation:
Cisco Unity Express (CUE) is a voice messaging product that is typically installed in a router module slot on a Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) router. CUE provides voice mail messaging, automated attendant services, and interactive voice response (IVR) services. CUE can support a maximum of 250 voice mailboxes, depending on the license that is installed. Both CUE and CME can be administered by using either a command line interface (CLI) or the browser based graphical user interface (GUI).CME is not a voice messaging product that is typically installed in a router module slot. CME is a call processing platform that is based on IOS and is contained within a Cisco Integrated Services Router (ISR). CME supports a maximum of 350 IP phones.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) is not a voice messaging product that is typically installed in a router module slot. UCM is a call processing platform that can be installed on Cisco Media Convergence Servers, on a Cisco Unified Computing System, or on one of a specific list of third party server platforms. UCM supports a maximum of 30,000 IP phones per cluster. UCM and its components can be administered by using Cisco Unified Operating System Administration. You can use the URL http://ipaddress/ccmadmin, where ip address is the IP address of a UCM server, to access Cisco Unified Operating System Administration.
Cisco Unity Connection is not a voice messaging product that is typically installed in a router module slot. Unity Connection is a voice messaging product that is typically installed as an appliance. Unity Connection supports a maximum of 250 voice messaging ports and 20,000 voice mailboxes. Unity Connection supports voice enabled features, such as voice navigation and voice dialing; it can also be used to listen to audio translations of email messages.
Cisco Unity is not a voice messaging product that is typically installed in a router module slot. Unity is typically installed on Windows servers. Unity supports a maximum of 15,000 voice mailboxes.
-
Which of the following is not available from the Service Statistics Report in Cisco Unified Serviceability? (Select the best answer.)
- the number of registered phones per server
- the number of aborted TFTP requests
- the number of TFTP requests
- the number of open CTI lines
Explanation:
The number of registered phones per server is available from the Cisco Unified Serviceability Device Statistics Report, not the Service Statistics Report. You can access the Device Statistics Report by navigating to Tools > Serviceability Reports Archive in Cisco Unified Serviceability. The Cisco Unified Serviceability Reports Archive contains all of the following types of statistical reports:-Device Statistics Report
-Server Statistics Report
-Service Statistics Report
-Call Activities Report
-Alert Summary Report
-Performance Protection ReportEach report type contains statistical information, including charts, about the given activity. The number of aborted Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) requests, the number of TFTP requests, and the number of open Computer Telephony Integration (CTI) lines are all available from the Service Statistics Report. In addition, the number of open CTI devices is available from the Service Statistics Report.
-
Which of the following statements are true? (Select 2 choices.)
- A reset is faster than a restart.
- A reset restores the IP phone to the factory default settings.
- You can reset an IP phone by pressing ##*## on the phone’s keypad.
- You can restart an IP phone by pressing ##*## on the phone’s keypad.
- An IP phone reset contacts the TFTP server.
- An IP phone restart contacts the TFTP server.
Explanation:
Both an IP phone reset and an IP phone restart will contact the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server to check for and download phone configuration updates. A Cisco IP phone can be reset by issuing the reset command in ephone configuration mode on a Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) router or by pressing the **#** key sequence at the Settings menu of an IP phone. You can access the Settings menu of an IP phone by pressing the settings button on the phone’s keypad.A Cisco IP phone can be restarted by issuing the restart command in ephone configuration mode on a CME router. When you restart an IP phone, the phone will unregister and reregister with the Cisco call processing platform in addition to contacting the TFTP server. In the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) graphical user interface (GUI), you can restart a phone by clicking Device > Phone > Restart.
You must reset a phone after performing the following tasks:
-Updating the phone’s firmware
-Modifying the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) scope
-Changing the IP address of the TFTP server
-Changing Uniform Resource Locators (URLs)
-Changing the date and time settings
-Changing the language displayed on the phone
-Changing the call progress tones for the phone
-Changing the voice mail access numberYou can either reset or restart a phone after performing the following tasks:
-Adding or deleting a phone button
-Associating a button with a new ephone-dn
-Modifying an extension on an ephone-dn
-Modifying speed-dial numbers on an ephone
-Enabling call parkBoth the reset command on a CME router and the **#** key sequence on an IP phone perform a hard reset of the phone, similar to powering down the device and powering it back up again. In the UCM GUI, you can reset a phone by clicking Device > Phone > Reset. When you reset the IP phone, the phone contacts the DHCP server to obtain IP configuration information, including the IP address of the TFTP server. The phone then contacts the TFTP server and downloads the most recent phone configuration information. The phone will also unregister and reregister with the Cisco call platform.
A reset is not faster than a restart. A restart is a soft reboot of the phone, which causes the phone to boot much quicker than a reset. When you restart an IP phone, the phone does not contact the DHCP server to obtain new IP configuration information. However, it does contact the TFTP server to download the most recent phone configuration information.
A reset does not restore the IP phone to the factory default settings. When an IP phone is restored to the factory default settings, any configuration changes that might be stored on the IP phone itself are lost. The method you use to restore a Cisco IP phone to factory default settings varies by phone model.
You can neither reset nor restart an IP phone by pressing ##*## on the phone’s keypad. The proper keypad sequence for resetting an IP phone is **#**. There is no similar keypad sequence for restarting an IP phone.
-
Your company uses DRS to back up UCM data on a tape drive. You want to add a network directory as a DRS backup device.
Which of the following is required to complete your task? (Select the best answer.)
- IPSec
- SFTP
- SSL
- a cluster security password
Explanation:
Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) is required in order to add a network directory as a Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Disaster Recovery System (DRS) backup device. DRS is a Cisco application that can be used to back up data from UCM, Cisco Unity Connection, and Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) server. SFTP is a file transport protocol that uses the secure transport protocol Secure Shell (SSH) to perform operations on remote file systems. Because SFTP is protected by a secure transport protocol, the transmission of data over an SFTP link is encrypted. DRS supports only tape devices and SFTP network directories as backup devices.It is important to note that a backup device cannot be deleted from DRS if that backup device is part of an existing backup schedule. In order to remove an existing backup device from a DRS configuration, you must first ensure that the device has been removed from any backup schedules in which it might be configured.
Although DRS requires the cluster security password to encrypt backup data for storage, SFTP is specifically required to add a network directory. DRS uses the existing cluster security password when performing encryption on a backup. If the cluster security password is modified by using the command line interface (CLI) or by a fresh UCM installation, you might not be able to decrypt and restore that backup. Workarounds to this issue include remembering the old cluster security password that was used to encrypt the data or immediately performing a fresh backup when the cluster security password changes.
Although DRS requires Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) for authentication and encryption between Master Agents and Local Agents, SFTP is specifically required to add a network directory. Although DRS requires IP Security (IPSec) for public key infrastructure (PKI) encryption, IPSec is not required to add a network directory as a DRS backup device. Master Agents store component registrations, maintain scheduled tasks, and store backup data on a locally attached device. Local Agents, which are installed and activated by default on each cluster node, are responsible for running backup and restore scripts on the local server. The deletion of the IPSec trust store from UCM’s security configuration can cause DRS to function improperly.
-
Which of the following is not a function of Cisco Unified Attendant Console Business Edition? (Select the best answer.)
- determining user availability by using presence status
- promoting voice calls to video conference calls
- reverting transferred calls back to the operator if the call is unanswered
- support for conferencing a single third party into an existing call
Explanation:
Promoting voice calls to video conference calls is not a function of Cisco Unified Attendant Console Business Edition. Cisco Unified Attendant Console is a software application that enables human operators to streamline the process of routing incoming calls across a Cisco IP phone network. There are several versions of Cisco Unified Attendant Console, including Compact Edition, Business Edition, Department Edition, Enterprise Edition, and Premium Edition.
Some features of Cisco Unified Attendant Console are common to all versions. Others require a specific version in order to use the feature set. For example, in Cisco Unified Attendant Console Enterprise Edition, it is possible to configure the Night Service feature, which enables the definition of operator working hours. If incoming calls arrive outside of the operator’s working hours, those calls can be automatically redirected to an answering service or a voice mail system.
Determining user availability by using presence status is a function of Cisco Unified Attendant Console Business Edition. Operators can determine the presence of a given contact by selecting the contact from the corporate directory and then pressing the F2 key on the keyboard. The IP phone user’s presence and line status are indicated by various phone icons.
Reverting transferred calls back to the operator if the call is unanswered is a function of Cisco Unified Attendant Console Business Edition. Cisco Unified Attendant Console will return a call to the application’s Call Progress area if the call is not answered by the user at the destination. From there it will move to Active Calls, at which point the operator can right click on the call and choose from one of several options for handling the call.
Support for conferencing a single third party into an existing call is a function of Cisco Unified Attendant Console Business Edition. You can add a third party to an existing call by clicking the party’s extension in the application and then clicking Start Conference. If the third party you attempt to add does not want to participate in the conference or does not answer, the call automatically reverts back to the original two participants.