300-835 : Automating Cisco Collaboration Solutions (CLAUTO) : Part 10
-
Your company has implemented Cisco Unity Connection. A user reports that outside callers are hearing a tone after recording 30 seconds of a voice mail message.
Which of the following is most likely true? (Select the best answer.)
- The user’s Message Settings > Maximum Message Length field is configured to the default value.
- The user’s Message Settings > Maximum Message Length field is configured to 30 seconds.
- The user’s Message Settings > Maximum Message Length field is configured to more than 30 seconds.
- The user’s Message Settings > Maximum Message Length field is configured to less than 30 seconds.
Explanation:
The user’s Message Settings > Maximum Message Length field in the Cisco Unity Connection administrative graphical user interface (GUI) is most likely configured to more than 30 seconds. There are three typical ways to create users in Unity Connection: local manual creation, import from Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM), or synchronization by using Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). When you edit users manually in the GUI, the Message Settings > Maximum Message Length field limits the length of voice mail messages that are left by outside callers. When the Maximum Message Length field is enabled, a caller will hear a tone as a warning that the maximum message length has almost been reached.To modify the Maximum Message Length field value for a single user, you should edit the field on the Message Settings page of the user’s account. You can also modify the setting for a number of users at once by editing the Maximum Message Length field in Bulk Edit Mode. In addition, you can configure the Maximum Message Length field on the Message Settings page of a voice mail user template to apply a nondefault maximum message length to any new user accounts that are based on the template.
It is not likely that the user’s Message Settings > Maximum Message Length field is configured to the default value. By default, the Maximum Message Length field is configured to 300 seconds, or five minutes. If the user’s Message Settings > Maximum Message Length field were configured to the default value, callers would not hear a warning tone until nearly 300 seconds of a message had been recorded.
It is not likely that the user’s Message Settings > Maximum Message Length field is configured to 30 seconds. If the user’s Message Settings > Maximum Message Length field were configured to 30 seconds, callers would not hear a warning tone until nearly 30 seconds of a message had been recorded. In this scenario, callers are hearing a warning tone after 30 seconds of the message has been recorded.
It is not likely that the user’s Message Settings > Maximum Message Length field is configured to less than 30 seconds. If the user’s Message Settings > Maximum Message Length field were configured to less than 30 seconds, callers would hear a warning tone before 30 seconds of a message had been recorded. In this scenario, callers are hearing a warning tone after 30 seconds of the message has been recorded. -
All of your department’s IP phones are connected to a switch that does not support PoE. A DHCP server has been configured for the voice VLAN on the switch. Another administrator power cycles the switch without warning. No calls are in progress.
Which of the following is most likely to occur? (Select the best answer.)
- The IP phones will power down until the switch restarts.
- The IP phones will not be affected by the power cycle.
- The IP phones will disappear from the UCM configuration.
- The IP phones will reset and lose IP configuration information.
Explanation:
Most likely, the IP phones will reset and lose IP configuration information when the administrator power cycles the switch because, in this scenario, the IP addressing information is automatically assigned to each IP phone by a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server. When an IP phone is disconnected from Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM), the phone will automatically reset in an attempt to re-establish communication. Therefore, if an IP phone suddenly resets or is continuously attempting to register with UCM, it is important to first verify the phone’s connectivity to the network switch.IP phones can be manually configured with IP addressing information. In that case, the IP phones would reset. Similarly, the IP phones will not be able to download configuration files from the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server until connectivity to the switch is restored.
The IP phones will not disappear from the UCM configuration. You can verify that an IP phone exists in the UCM by clicking Device > Phone > Find in UCM Administration and searching for the particular IP phone’s Media Access Control (MAC) address. The IP phone will no longer be registered with UCM when it loses connectivity. However, the IP phone’s record in the UCM configuration will remain there.
The IP phones will not power down until the switch restarts, because the switch in this scenario does not support Power over Ethernet (PoE). Therefore, the IP phones in this scenario must be connected to individual power supplies in order to obtain power. In addition to registration problems, IP configuration problems, and TFTP configuration problems, IP phones that are powered directly from a switch by using PoE will not be able to receive power until the switch has restarted.
The IP phones will be affected by the power cycle. In addition to registration problems, IP configuration problems, and TFTP configuration problems, IP phones that are powered directly from a switch by using PoE will not be able to receive power until the switch has restarted. -
Which of the following command sets presents the dial peer commands in the order that they are evaluated by a voice gateway for an inbound dial peer? (Select the best answer.)
- destination-pattern
port
session target - incoming called-number
answer-address
destination-pattern
port - incoming called-number
port
session target
destination-pattern - port
incoming called-number
destination-pattern
answer-address - port
incoming called-number
answer-address
Explanation:
The following command set presents the dial peer commands in the order that they are evaluated by a voice gateway for an inbound dial peer:
incoming called-number
answer-address
destination-pattern
portA dial peer defines a logical route to a telephony endpoint. A voice router will perform the following evaluations when it receives an inbound call:
1. The router will attempt to match the destination Dialed Number Identification Service (DNIS) to an incoming called-number DNIS command.
2. The router will attempt to match the source Automatic Number Identification (ANI) to an answer-address ANI command.
3. The router will attempt to match the source ANI to a destination-pattern string command.
4. The router will attempt to match the incoming call’s voice port to a port port command.
5. If no match is found, the router will use the default dial peer.Once a dial peer match is found, the router will immediately route the call without proceeding to the next step. If multiple matches are found for a step, the router will select the longest explicit match. The default dial peer will only be used if no match is found. You cannot configure any of the settings for the default dial peer.
The dial peer evaluation process will occur for every call leg along the path from the source endpoint to the destination endpoint. A call leg is a logical inbound or outbound connection for a voice gateway. The originating voice gateway and the terminating voice gateway between two telephony endpoints have one call leg in the inbound direction and one call leg in the outbound direction. Therefore, there will be exactly two call legs for each voice gateway.
The session target command is not evaluated by a voice gateway router for an incoming dial peer; it is used by a voice gateway router to determine where to route an outgoing Voice over IP (VoIP) dial peer. A voice router will perform the following evaluations when it must send an outbound call:
1. The router will attempt to match the destination DNIS to a destination-pattern string command.
2. If the dial peer is a POTS dial peer, the router will forward the call to the port indicated by the corresponding port port command.
3. If the dial peer is a VoIP dial peer, the router will forward the call to the IP address indicated by the corresponding session target ipv4: ip-address command.
4. If no match is found, the call will be dropped.The destination-pattern command is used for both inbound and outbound dial peer matching. However, the string variable must match the source ANI for inbound dial peer matching and must match the destination DNIS for outbound dial peer matching. The port-command is used for inbound POTS dial peer matching and to determine where to route an outgoing POTS dial peer.
- destination-pattern
-
With which of the following control components do UCM media resources interact when UCM needs to locate resources to establish transcoding? (Select the best answer.)
- call control
- media control
- MTP control
- MOH control
Explanation:
Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) media resources interact with UCM’s media control component in order to locate resources to establish transcoding, or to establish a media termination point (MTP). The UCM media control component is responsible for managing the creation and teardown of media streams for a given endpoint. The UCM Media Resource Manager is responsible for connecting the media streams that comprise conferencing features, among others. When troubleshooting media resource problems, such as conference call failures, it is important to first investigate the UCM media resources configuration. UCM media resources are available directly from the UCM server on which the services are enabled. In addition, the UCM Media Resource Manager enables UCM to provide those services to other UCM servers in a cluster.
UCM media resources do not interact with UCM’s call control component when UCM needs to locate resources to establish transcoding. However, UCM media resources do interact with UCM’s call control component when locating resources to establish a conference call or music on hold (MOH).UCM media resources do not interact with UCM’s MTP control component when UCM needs to locate resources to establish transcoding. UCM media resources interact with UCM’s MTP control component in order to reserve transcoders within a UCM cluster.
UCM media resources do not interact with UCM’s MOH control component when UCM needs to locate resources to establish transcoding. UCM media resources interact with UCM’s call control component in order to locate resources to establish an MOH session. Because the MOH control enables UCM to redirect a caller to an audio server, UCM media resources also interface with the MOH control when establishing such a session.
-
Which of the following are considered to be presence entities by the Presence feature of UCM? (Select 2 choices.)
- a dn
- an application user
- an end user
- an IP phone
- a SIP trunk
Explanation:
A directory number (dn) and a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) trunk are considered to be presence entities, or presentities, in the Presence feature of Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM). Presence entities can be monitored in real time by the UCM Presence feature, which enables a user or a device known as a watcher to monitor the registration status of a dn or a SIP trunk. In addition, Presence enables watchers to view whether an IP phone that is associated with a specific dn is onhook or offhook. A SIP trunk can be both a presence entity and a watcher.
Presence enables a watcher to monitor dns in real time by displaying a status icon beside dns that appear in speeddial lists or directory lists, such as the Missed Calls list, on an IP phone. The icon can represent one of the following three states:Unknown – The registration status of the device that is associated with the dn cannot be determined.
Onhook – The device that is associated with the dn is registered and currently in the onhook state.
Offhook – The device that is associated with the dn is registered and currently in the offhook state.Presence can send and receive presence requests and responses only on Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) lines, SIP lines, and SIP trunks. If Presence requests or responses are sent to a Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) trunk or to an H.323 trunk, those requests are rejected by UCM.
Application users, end users, and IP phones are considered to be watchers, not presence entities, in the Presence feature of UCM. Because a dn or line that is associated with an IP phone can be monitored by the Presence feature, only the IP phone itself is considered to be a watcher. The dn or line that is associated with an IP phone is a presence entity.
-
Which of the following is a Cisco Unity Connection feature that you can modify in the Location section of the User Templates Basics page? (Select the best answer.)
- CoS
- partition
- search space
- time zone
Explanation:
Of the available choices, only the Cisco Unity Connection time zone feature can be modified in the Location section of the User Templates Basics page. If your company’s Cisco Unity Connection implementation must support users in different time zones, you can create a unique user template for each time zone. You can also adjust the system default language in this section of a user template.You can modify the Class of Service (CoS) settings, the partition, and the search space in the Phone section of the Cisco Unity Connection User Templates Basics page.
CoS settings enable an administrator to apply a specific set of privileges to Cisco Unity Connection users. A partition is a logical grouping of Voice over IP (VoIP) route patterns and directory numbers (dns). A search space is an ordered list of partitions that a device is allowed to search for patterns that match a dialed number.
-
You want to view information about called numbers that have cost the most over a given period of time in Cisco Unified Serviceability’s System Overview report.
Which of the following sections of the report should you examine? (Select the best answer.)
- Top 5 Users based on Charge
- Top 5 Destinations based on Charge
- Top 5 Calls based on Charge
- Traffic Summary Report -Hour of Day
- Gateway Summary Report
Explanation:
To view information about called numbers that have cost the most over a given period of time, you should examine the Top 5 Destinations based on Charge section of the System Overview report in Cisco Unified Serviceability. Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Call Detail Records (CDR) Analysis and Reporting (CAR) administrators can display the System Overview report by clicking Tools > System Reports > System Overviewin Cisco Unified Serviceability.The System Overview report contains all of the following sections:
– Top 5 Users based on Charge: lists the five users whose calls have cost the most over a given period of time
– Top 5 Destinations based on Charge: lists the five called numbers that have cost the most over a given period of time
– Top 5 Calls based on Charge: lists the five calls that have cost the most over a given period of time
– Top 5 Users based on Duration: lists the five users who have spent the most time on calls over a given period of time
– Top 5 Destinations based on Duration: lists the five called numbers on which users have spent the most time over a given period of time
– Top 5 Calls based on Duration: lists the five longest calls over a given period of time
– Traffic Summary Report -Hour of Day: displays the volume of calls for a given hour- of the day
– Traffic Summary Report -Day of Week: displays the volume of calls for a given day of the week
– Traffic Summary Report -Day of Month: displays the volume of calls for a given day of the month
– Quality of Service Report -Summary: displays the number of calls that fell within Quality of Service (QoS) parameters over a given period of time
– Gateway Summary Report: displays the call classification, QoS, duration, and number of calls for each voice gateway over a given period of time -
Which of the following will not be supported? (Select the best answer.)
- Cisco Jabber
- Cisco WebEx Social
- Microsoft Office Communicator desk phone control
- thirdparty XMPP clients
Explanation:
Of the available choices, Microsoft Office Communicator desk phone control will not be supported by Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) IM and Presence Service in instant message (IM)only mode. The UCM IM and Presence Service enables a company to reduce communications delays in project collaboration by providing realtime, always available communications channels. For example, the IM and Presence Service supports persistent chat rooms, which are chat rooms that remain available even after the last user exits the room, and the ability to review IM history.
The UCM IM and Presence Service has three modes of operation: IMonly mode, Cisco Unified Communications mode, and Microsoft Office Communicator and Microsoft Lync interoperability mode. In Microsoft Office Communicator and Microsoft Lync interoperability mode, UCM IM and Presence Service enables users of Microsoft Office Communicator or Microsoft Lync to control Cisco IP phones.
In IMonly mode, Cisco Jabber and third party Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) clients can connect to and use UCM for IM and Presence services. In Cisco Unified Communications mode, the IM and Presence Service supports IM, Presence, XMPP federation, and audio and video calls. XMPP federation allows Cisco Jabber clients to communicate with clients that are registered to a different Cisco Jabber cluster.
Neither the audio call feature nor the video call feature of Cisco Jabber is supported when UCM IM and Presence Service is running in IMonly mode. To place an audio or video call from Cisco Jabber, a user will typically click the Contacts button to search the list of contacts. Next, the user should click on the contact to call and press the phone icon. However, IM messaging will be the only available option if UCM is configured in IMonly mode. -
Which of the following can you display by clicking System Reports > Traffic > Summary by Phone Number in the UCM 8.0 CAR GUI? (Select the best answer.)
- the current number of billing errors
- the call volume for a given period of time
- the QoS rating information for inbound calls
- the top number of users by maximum length of calls
Explanation:
You can display information about call volume for a given period of time by using the System Reports > Traffic > Summary by Phone Number report in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Call Detail Records (CDR) Analysis and Reporting (CAR) graphical user interface (GUI). This report enables a CAR administrator to choose a range of time and IP phone extension numbers from which to view call volume information, thereby enabling an administrator to view what extensions were in use at a specific time.You can view information about the top number of users by maximum length of calls by using the User Reports menu. The By Duration report can be accessed by clicking User Reports > Top N in the UCM CAR GUI. This report enables a CAR administrator to view users who have made the longest calls over a given period of time, starting with the user who placed the longest call.
You can view information about the current number of billing errors by using the System Reports > CDR Error report in the UCM CAR GUI. This report enables a CAR administrator to view the number of errors that occurred when CDR data was loaded into the reporting system.
You can view Quality of Service (QoS) rating information for inbound calls by using the System Reports > QoS > Detail report in the UCM CAR GUI. The Detail report enables a CAR administrator to choose a UCM network and a period of time for which to view QoS ratings for both inbound and outbound calls. The Detail report can be used to monitor QoS at a user level. -
You are configuring an IM and Presence deployment. You have configured the CUPS servers, enabled the appropriate UCM services, and created the appropriate service profile. You want to add a group of new users with the IM and Presence feature enabled.
Which of the following are you most likely to do next? (Select the best answer.)
- Click User Management > End User in the enduser configuration window.
- Click Bulk Administration > Users > Insert Users in the BAT.
- Click Bulk Administration > Users > Update Users in the BAT.
- Click User Management > User/Phone Add > Feature Group Templates.
Explanation:
Of the available choices, you would most likely click Bulk Administration > Users > Insert Users in the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT)? that option is used to simultaneously add multiple new users to Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM). Before you can configure UCM users with instant message (IM) and Presence, you must configure Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) servers and ensure that the Cisco Call Manager service and the Cisco Administrative Extensible Markup Language (AXL) Web Service are enabled and running. If you want to use Cisco Unified Personal Communicator in softphone mode, you should also ensure that Cisco Trivial File Transfer Protocol (Cisco TFTP) is enabled. To use Cisco Unified Personal Communicator in desk phone control mode, you must enable and start Cisco CTIManager. After the services are configured, you must create an IM and Presence Service profile and assign users to that profile.
The Update Users option enables you to use the BAT to simultaneously update multiple existing users at once. In this scenario, you want to simultaneously enable IM and Presence services for multiple users. However, you would not use this option to add a group of new users with the IM and Presence feature enabled.
You would not click User Management > End User, because that option is used to edit a single existing user. You would most likely click User Management > End User in the UCM Administration enduser configuration window if you are configuring and testing an IM and Presence server for a single existing end-user account. You can manually configure end users in UCM by clicking User Management > End User in the UCM administrative graphical user interface (GUI). You can also verify whether an existing user account is active by navigating to the End User page.
You would not click User Management > User/Phone Add > Feature Group Templates, because that option is used to create feature groups that can be assigned to users, not to create or update users themselves. Feature groups can be used to restrict users to a given UCM feature set. By creating a feature group template, you can assign users a common set of restrictions instead of having to configure each new user’s entire feature set manually. -
DRAG DROP
Select the voice gateway trunk interfaces on the left, and drag them to the appropriate columns on the right. All interfaces will be used. Not all boxes will be filled.

300-835 Part 10 Q11 042 Question 
300-835 Part 10 Q11 042 Answer Explanation:
Ear and mouth (E&M), foreign exchange office (FXO), and foreign exchange station (FXS) interfaces are all analog interfaces. Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) Primary Rate Interface (PRI) and channel-associated signaling (CAS) T1 interfaces are digital interfaces.An E&M interface is used to interconnect private branch exchanges (PBXs) or telephone switches. Because an E&M interface is typically used as a trunk interface for a PBX, it does not supply ring voltage. In addition, an E&M interface uses its own signaling for voice transmission and call control.
An FXO interface is typically used to connect an analog device to the public switched telephone network (PSTN). In addition, if a PBX is configured with an FXS port, the FXO interface on an analog device can terminate an analog trunk from a PBX. FXO interfaces are commonly found on standard telephones, fax machines, and analog modems. Thus devices that have FXO interfaces typically connect to the PSTN by using plain old telephone service (POTS) lines.
An analog trunk from the central office typically originates from an FXS interface on a phone switch. The switch provides dial tone, ring voltage, and line voltage for the customer site. Because the FXS interface on the phone switch provides power, it cannot be connected to another FXS interface; instead, the FXS interface must be connected to a device with an FXO interface, such as an analog telephone or a legacy voice mail system. Cisco Analog Voice Gateways, such as the VG202 and the VG204, come with FXS ports that enable you to connect FXO devices, such as corded analog telephones or cordless analog telephone bases, to Cisco Unified Communications Manager. The VG202 supports up to a maximum of two analog devices. The VG204 supports up to a maximum of four analog devices.
A PRI T1 circuit uses time division multiplexing (TDM) to allocate up to 24 time slots, or channels, that can be used to transmit voice, video, and data traffic. Time slots 1 through 23 can be used to send data, such as analog voice? time slot 24 is used for signaling. Each of the 24 channels provides 64 Kbps of bandwidth for a total data bandwidth of 1.536 Mbps. One framing bit is added to each 192bit frame for an additional 8 Kbps, bringing the total line bandwidth to 1.544 Mbps. PRI T1 circuits can transmit proprietary PBX signaling messages by using ISDN signaling.
A T1 circuit is a digital trunk that uses TDM to allocate up to 24 time slots for voice channels. CAS uses a portion of each channel to send signaling information to the central office (CO). By contrast, common-channel signaling (CCS) devotes an entire channel to signaling information. Although this allocation provides one less channel for voice, it ensures that the entire bandwidth of each voice channel can be used for transmissions. -
You have enabled SIP Early Offers.
Which of the following is most likely the reason? (Select the best answer.)
- A service provider requires it.
- Analog audio must be compressed in the stream.
- Codec conversion is required.
- H.323 trunks are in use.
Explanation:
Of the available choices, you are most likely to enable Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Early Offers if a public switched telephone network (PSTN) service provider requires it. By default, Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) uses SIP Delayed Offers. UCM uses the SIP Offer/Answer model to establish SIP sessions. SIP Offers, which are messages sent in the Session Description Protocol (SDP) fields of a SIP message, contain information about the streams, codecs, IP addresses, and ports supported by the device. The remote device receives the SIP Offer and sends a SIP Answer in the SDP fields of its response. SIP Early Offers are sent by the session initiator in the SIP Invite, before the session is established. SIP Delayed Offers are sent by the session initiator after the receiver sends its capabilities.
Delivering SIP Early Offers over SIP trunks is a function of Media Termination Points (MTPs). There are two ways to enable Early Offers on SIP trunks in Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM): select the MTP Required check box on the SIP trunk or select the Early Offer support for voice and video calls (insert MTP if needed) check box on the SIP profile that is connected to the SIP trunk. If MTP is required, all outbound calls will use MTP, as will calls operating on the same codec. If MTP is enabled as needed, it is inserted if the trunk is incapable of sending complete information about its media capabilities in the SIP Invite message.
Converting digital audio from one codec to another is a function of a transcoder. Transcoders enable communication between devices that support dissimilar audio codecs. For example, a transcoder can translate a G.729encoded packet to a G.711encoded packet and vice versa. Transcoders translate the data stream in real time between two devices so that no audio delay is experienced by either endpoint.
Sampling, encoding, and compression of analog audio is a function of a digital signal processor (DSP). DSPs execute the steps required to convert an analog voice signal to digital packets, which allow voice data to traverse a Voice over IP (VoIP) network. There are four steps involved in converting analog audio data to digital audio data: sampling, quantization, encoding, and compression.
Providing connectivity for SIP devices and H.323 devices is a function of a UCM’s SIP trunks and H.323 trunks, respectively, not of MTPs. UCM supports both SIP trunks and H.323 trunks. -
You administer a Cisco VoIP network of 1,500 users. The Unity Connection Phone Menu is configured to the default settings for all users.
You want to configure the touchtone menu system so that experienced users hear a shorter set of instructions than inexperienced users hear.
Which of the following actions would you most likely perform? (Select the best answer.)- Set each experienced user’s Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field to Brief.
- Set each inexperienced user’s Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field to Full.
- Create an experienced user template, and set the Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field to Brief.
- Create an inexperienced user template, and set the Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field to Full.
- Use Bulk Edit Mode to set the experienced users’ Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field to Brief.
- Use Bulk Edit Mode to set the inexperienced users’ Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field to Full.
Explanation:
You would most likely use Bulk Edit Mode in the Cisco Unity Connection browser based graphical user interface (GUI) to set the experienced users’ Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field to Brief. By default, the Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field is configured as Full, meaning that the user will hear a full-length set of touchtone menu instructions after dialing into the voice mail system. If a user’s Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field is configured as Brief, the user will hear a shortened version of the touchtone menu instructions.
The Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field in the Unity Connection Phone Menu can be configured in three ways: on an individual user account basis, on the basis of a user account template, or from Bulk Edit Mode. Modifying user accounts on an individual basis requires that an administrator open the user’s account, edit the fields in the account, and then save the account before opening the next user account. This process can create significant administrative overhead if you have a large number of users. In addition, modifying user templates affects only new user accounts that are created from those templates; the changes do not affect existing user accounts. Until user templates and Classes of Service (CoS) have been configured, user accounts cannot be added to Unity Connection by using the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT).
Modifying the Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field simultaneously for multiple user accounts is the most efficient method of configuring the touchtone menu for experienced user accounts. Therefore, using Bulk Edit Mode to set the experienced users’ Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field to Brief is most likely the action you would perform.
It is not likely that you would use Bulk Edit Mode to set the inexperienced users’ Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field to Full, because Full is the default setting. In this scenario, all users’ Phone Menu settings are configured to the defaults.
It is not likely that you would configure the Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field from either an experienced user template or an inexperienced user template. Although you could configure a user template to automatically set the Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field to Brief, the template would affect only new user accounts that are based off that template. Existing accounts would not be changed by the template.
Although you could set each experienced user’s Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field to Brief, doing so would create more administrative overhead than using Bulk Edit Mode. Therefore, it is not likely that you would configure user accounts individually to complete the task in this scenario. In addition, you would not need to set each inexperienced user’s Touchtone Conversation Menu Style field to Full, because Full is the default setting. In this scenario, all users’ Phone Menu settings are configured to the defaults. -
A user informs you that CAR queries are failing consistently for recent dates. However, older dates are still accessible.
Which of the following is most likely the problem? (Select the best answer.)
- The Cisco CAR Web Service is not running.
- The UCM system is generating CDR files too slowly.
- The user does not have the privileges to log on to CAR.
- The CDR Enabled flag is set to FALSE.
- The disk space where reports are stored is full.
Explanation:
Of the choices provided, the problem is mostly likely that the CDR Enabled flag is set to FALSE if Cisco Call Detail Records (CDR) Analysis and Reporting (CAR) queries are failing consistently for recent dates but older dates are still accessible. If the CDR Enabled flag is not set to TRUE on a Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) server, CAR reports will not be generated for that server. In a UCM cluster, the CDR Enabled flag should be set to TRUE on the Publisher server and on all Subscriber servers in the cluster. If the CDR Enabled flag is already set to TRUE, you should verify that only the Publisher server has the Cisco CDR Insert service activated. In addition, you should verify that the Call Diagnostics are enabled and that the Cisco CAR Scheduler service is running on the Publisher server.
It is likely that the Cisco CAR Web Service is running if older dates are still accessible, even though CAR queries are failing consistently for recent dates. CAR is typically accessed by using the Tools menu in Cisco Unified Serviceability. If the CAR Web Service were not running, CAR would not be available from the Tools menu. Thus the user would have no way of knowing whether recent queries were failing or whether older dates were still accessible. To activate the CAR Web Service, click Tools > Service Activation in Cisco Unified Serviceability, select the call processing server from the Servers dropdown menu, and then select the check boxes next to the appropriate CDR services.
It is not likely that the UCM system is generating CDR files too slowly. By default, every UCM server can generate one CDR file and one Call Management Records (CMR) file every minute for up to one hour. In addition, it is not likely that the disk space where reports are stored is full. The oldest CDR files are deleted on an hourly basis by the CDR Repository Manager’s File Manager process if disk usage reaches a maximum threshold. Therefore, if the disk were full, older dates would be affected by the issue, not recent ones.
It is not likely that the user does not have the privileges to log on to CAR, because the user can see the results of older queries. By default, any UCM user can be configured as a CAR administrator by adding the user to the Standard CAR Admin Users group in UCM. This includes application users and end users.
However, application users cannot access the Individual Bill report even though they might have read and write access to the CAR database. -
Which of the following Cisco voice products do not use Cisco Unified Operating System Administration? (Select 2 choices.)
- CME
- CUPS
- UCM
- Unity Connection
- CUE
Explanation:
Neither Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) nor Cisco Unity Express (CUE) uses Cisco Unified Operating System Administration. CME is a call processing platform that is based on IOS and contained within a Cisco Integrated Services Router (ISR). CUE is a voice mail messaging system that is typically installed in a CME router module slot. You can configure CME and CUE by using a command line interface (CLI) or a browser based graphical user interface (GUI). The GUI must be configured in the CLIb efore it can be used to administer the CME router. The CME GUI can be used to configure IP phone settings, to configure voice mail settings, to configure backup and restore settings, and to view reports.Cisco Unified Operating System Administration is a browser based GUI that can be accessed by using the Navigation menu of the Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) administrative GUI, the Navigation menu of the Cisco Unity Connection administrative GUI, or the Navigation menu of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) administrative GUI. Unlike the CME GUI, the Unified Operating System Administration GUI is not used to modify IP phone settings, to configure voice mail settings, or to view reports.
Unified Operating System Administration can be used to modify operating system and network settings that are common across components of a Cisco Unified Communications network. For example, you can verify Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) settings by using the Unified Operating System Administration GUI. -
Which of the following clients is most likely to use CTIQBE for signaling? (Select the best answer.)
- a Cisco IP phone communicating with CUPS
- a thirdparty IP phone communicating with CUPS
- a Cisco IP phone communicating with UCM
- a thirdparty IP phone communicating with UCM
Explanation:
Of the available choices, a Cisco IP phone communicating with Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) is likely to use Computer Telephony Integration Quick Buffer Encoding (CTIQBE) for signaling. The Cisco Computer Telephony Integration (CTI) feature is a development system that enables programmers to create applications that can connect to and communicate with a Cisco Unified Communications system. By using CTI, programmers can create server software and desktop applications that interface directly with Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM), CUPS, and other Cisco Voice over IP (VoIP) products.UCM can use Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) on Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port 5060 or User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port 5060 for call signaling with a Cisco IP phone or a third party IP phone. In addition, UCM can use Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) for call signaling with Cisco IP phones. The signaling conversation between UCM and an IP phone controls many of the IP phone’s functions, such as call initiation, call termination, and call waiting notification. UCM can have multiple, simultaneous signaling conversations with IP phones using different protocols. For example, UCM can use SIP to communicate with one IP phone and use SCCP to communicate with another IP phone on the same network. SCCP uses TCP port 2000.
SIP is an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)standard call signaling protocol. Although SIP is typically used as a peertopeer call signaling protocol, it can also operate in client/server mode. A softphone is software that behaves like a phone, enabling a user to have voice conversations over a typical workstation network connection. Softphone mode is an operational mode that Unified Personal Communicator uses to act as a softphone.
SCCP is a Cisco-proprietary, client/server call signaling protocol. SCCP must be used with a Cisco call processing platform, such as UCM, because SCCP is proprietary to Cisco. The firmware on Cisco IP phones is configured to use SCCP by default. SCCP must be used on Cisco IP phones to enable the phones to use Cisco’s full VoIP feature set. SIP is supported on Cisco IP phones with a firmware replacement. -
A user has asked you to configure an IP phone PIN so that the user can circumvent afterhours call blocking restrictions.
Which of the following PINs will the CME router not accept? (Select 2 choices.)
- 123
- 4312
- 5670192
- 12943560112
- 34872345
Explanation:
The Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) router will not accept a personal identification number (PIN) of 123, because that PIN is too short. In addition, the CME router will not accept a PIN of 12943560112, because that PIN is too long. CME administrations can issue the pin number command in ephone configuration mode to configure a specific IP phone with a PIN. The number parameter accepts a numeric string with a length in the range from four digits through eight digits. Therefore, you cannot configure a PIN of less than four digits nor can you configure a PIN of more than eight digits.
When an ephone is configured with a PIN, that PIN can be used to circumvent any afterhours calling restrictions that have been placed on the ephone. Afterhours calling restrictions are typically used to prevent certain types of calls from taking place during a specifically defined time period. For example, you could configure a calling restriction that prevents calls to long distance numbers from the time your company closes for the day until the time it reopens for the next business day. -
Which of the following search spaces is used by every VoIP endpoint by default? (Select the best answer.)
- a custom device search space
- a custom line search space
- the <None> search space
- both a custom device search space and a custom line search space
Explanation:
The <None> search space is used by every Voice over IP (VoIP) endpoint by default. A search space is an ordered list of partitions that a device is allowed to search in order to locate patterns that match a dialed number. A partition is a logical grouping of VoIP route patterns and directory numbers (dns). A device that is not able to match a dialed number in any of the search spaces that are assigned to the device will generate a busy signal. However, every VoIP endpoint can match a route pattern or dn that is contained within the <None> search space.
The <None> search space contains the <None> partition. The <None> partition initially contains all the dns that are configured in the VoIP network. Therefore, you should move route patterns and dns from the <None> partition to a custom partition to limit specific pattern matching to specific endpoints. Cisco recommends that you not leave dns in the <None> partition, because doing so could enable users to dial numbers that you intend to restrict.
Custom device search spaces and custom line search spaces are not used by every VoIP endpoint by default, because custom search spaces must be created by an administrator before they can be assigned. By default, only the <None> search space initially exists in Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM). A device search space is a search space that is assigned to a device itself. The information in a device search space will be searched no matter which line on a device is chosen for the outgoing call. A line search space, on the other hand, is a search space that is assigned to a single line on a device, not to the device itself. The information in a line search space will be searched when the user chooses the line to which the search space is assigned as the outgoing line for the call.
If a device is configured with both a device search space and a line search space, the device will combine the two search spaces together, with the line search space taking precedence. Thus the information that is contained in the line search space will be searched first. For example, if you assign a search space named Local to the IP phone itself and a search space named Long Distance to a line on the IP phone, the Long Distance search space will be searched first and a user will be allowed to make long distance calls from the IP phone. Cisco recommends configuring calling search spaces at the device level to prevent users from bypassing calling restrictions by simply placing calls from an alternate phone line. -
Which of the following tools can be used to export data from both Cisco Unity and Cisco Unity Connection? (Select the best answer.)
- the BAT
- COBRAS
- Cisco Unity to Connection Migration Export Tool
- DiRT for Unity
- DiRT for Connection
Explanation:
Of the choices provided, only the Cisco Object Backup and Restore Application Suite (COBRAS) can be used to export data from both Cisco Unity and Cisco Unity Connection. COBRAS is a suite of applications that can be used to import and export data for Unity or Unity Connection. In addition, you can import a Unity export from COBRAS into Unity Connection. For example, you can use COBRAS Export for Unity to extract information from Unity 4.0(5) and later and then use COBRAS Import for Connection to import the Unity data into Unity Connection 7.0 or later.
Cisco Unity is a voice mail server that runs on Microsoft Windows? it can integrate with Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM), Microsoft Exchange Server, and Lotus Domino. Cisco Unity supports a subscriber based model instead of a user based model, meaning that Unity subscribers are stored in a database that is separate from Unity, such as UCM, Microsoft Exchange Server, or Lotus Domino.
Cisco Unity Connection, on the other hand, is a voice mail server that runs on Linux? it can use Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) to retrieve email and collaboration information from Microsoft Exchange Server and Lotus Domino. Unity Connection supports a userbased model, meaning that users can be imported to Unity Connection from UCM, Microsoft Exchange Server, or Lotus Domino. Unity Connection stores its own users.
You cannot use the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT) to export data from both Cisco Unity and Cisco Unity Connection. Instead, you can use the BAT to export data from Unity Connection into commaseparated values (CSV) format. In addition, the BAT enables administrators to import users, update user settings, and delete users by importing CSV files.
You cannot use Disaster Recovery Tools (DiRT) for Connection to export data from both Cisco Unity and Cisco Unity Connection. In addition, you cannot use DiRT for Unity to export data from both Cisco Unity and Cisco Unity Connection. DiRT is a set of two applications: Disaster Recover Backup and Disaster Recover Restore. Furthermore, there are two different versions of DiRT. You can use DiRT for Connection to back up and restore data in only Unity Connection. You can use DiRT for Unity to back up and restore data in only Unity.
You cannot use the Cisco Unity to Connection Migration Export Tool to export data from both Cisco Unity and Cisco Unity Connection. Instead, you can use the Cisco Unity to Connection Migration Export Tool to export data from Unity into CSV format. You can then use the BAT to import the CSV file into Unity Connection. -
You issue the show running-config command on a CME router and receive the following partial output:
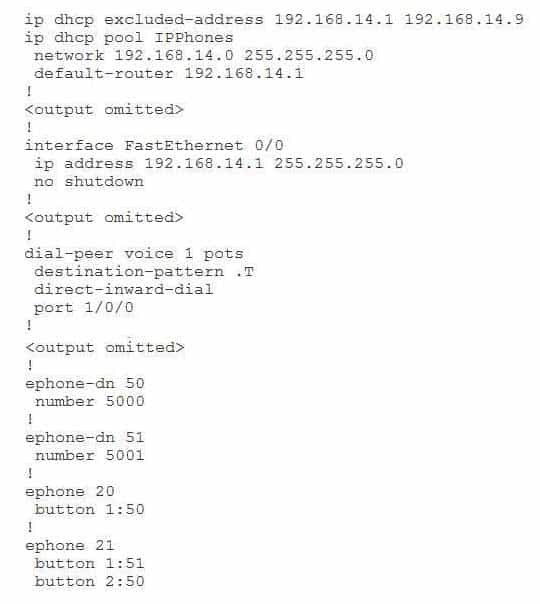
300-835 Part 10 Q20 043 Examine the output, and use the information you gather to answer the question.
Which of the following statements is true? (Select the best answer.)- There will be no delay after the phone number is dialed.
- IP phones will not be able to download their configurations.
- IP phones will require manual IP address configuration.
- No dialed digit can be matched.
Explanation:
IP phones will not be able to download their configurations from a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server, because the option 150 ip ip address command is missing from the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) configuration in the output above. To automatically assign a TFTP server to IP phones, you should issue the option 150 ip ipaddress command, where ipaddress is the address of the TFTP server. A TFTP server is required so that IP phones can download their startup configuration files. In this scenario, the option 150 ip 192.168.14.1 command would configure the DHCP server on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) router to assign the TFTP server address of 192.168.14.1 to IP phones that are configured by using DHCP.There will be a delay after the called number is dialed, and up to 32 digits will be matched by the destination pattern. The dial peer command destination pattern .T is used to indicate any string of up to 32 digits. The T character is used at the end of a string to instruct the router to wait for the complete dial string to be entered before matching a call to a dial peer. Cisco recommends that you use the destination pattern .T command rather than the destination pattern T command because the destination pattern .T command requires that the caller dial a digit.
IP phones will not require manual IP address configuration. The ip address 192.168.14.1 255.255.255.0 command configures the FastEthernet 0/0 interface on the CME router with the IP address 192.168.14.1. In addition, the ip dhcp excluded address 192.168.14.1 192.168.14.9 command prevents the CME router from assigning the IP address 192.168.14.1 to an IP phone.